PPC
Ultimate Guide to Dominating Black Friday PPC in 2023

Black Friday is a special day for PPC. Normally, we’re able to launch new campaigns and carefully mold them into perfection so we can reap the rewards for months, if not years to come.
Black Friday in Google Ads is different. You have a very short time to make the absolute most out of what you do. The wrong ad, bid, or settings can ruin your results.
No matter your strategy, the tips below will help you maximize your potential. We’ll be covering exactly what you need to do to adjust your bids and budgets, ad text and extensions, display and remarketing ads, keyword strategy, Shopping campaigns, and more.
Quick note: Whenever I refer to Black Friday, I’m actually talking about the entire Black Friday weekend. Some advertisers treat Black Friday differently from the rest of the weekend, while others see it as a five-day sale, starting on Thanksgiving and ending with Cyber Monday.
Table of contents
How to prepare your Google Ads campaigns for Black Friday
In order to prepare for Black Friday, it’s essential to understand what promotions you’ll be running. It’s taking it back to ecommerce 101, but defining what promotions you’ll run will make a lot of sense as I go through the rest of the tips.
So first of all, find out:
- What will your offers be?
- Will you have enough stock?
If you don’t have a large stock, consider being less aggressive in your bidding or just pushing the product via Shopping or Search – whatever works best for you.
If you’re not sure you’ll have enough stock for a specific promotion, make sure you have a backup offer ready for your more generic keywords.
🎁 Get more holiday marketing tips here!
Review last year’s performance
I’ve written extensively about getting more success with PPC during seasonal swings, so I won’t dig too much into looking at historic performance.
The gist is that it’s crucial not to pretend this year is a single event. Despite the changing landscape in PPC, there are several areas that you can learn from based on historic performance. Some of these are:
- What did you learn from the ads you ran? Did any generic messaging perform better than others?
- Did ads that described the product benefits/features do better than the ads with price, shipping, and other specific info?
- What bid did it take you to get into the first position?
- Did any keywords or product categories turn out to be hard to advertise in?
- How did the sections of your account that didn’t have a promotion do?
- How big of an increase in spend did you experience? (Note, if you were capped out by your budget, then this is an important step for you to review)
- Was your Display Remarketing a bust or did it succeed on the day itself?
- What happened in the days after Black Friday and Cyber Monday? How much do you need to lower your bids in the immediate days after the promotion to avoid losing money?
And so on. Learn from what happened last year and you’ll be able to get more out of this year.
Define your rules of engagement
Before we get into the nitty-gritty I want to touch on one more non-PPC matter.
Chances are you’re not the boss. And even if you’re the boss, then this section will be healthy for you to prepare in advance.
Consider the following scenario: You’re expecting to spend $5,000 on Black Friday and aiming for an 800% ROAS.
However, Black Friday comes along and by 1 p.m. you’ve spent the entire $5,000 and have a ROAS of 1,100%. What do you do?
All the PPC managers yell: INCREASE THE BUDGET. But how much? What can the business afford? How much stock is left? And what if the ROAS was 700%? Should you still increase the budget? If you don’t have any stock left, do you have a backup promotion ready?
Having your rules of engagement set for the day can be incredibly powerful. You might think you’ll deal with that dream scenario if it happens, but what if on that same day your site starts loading slowly because of the high traffic AND your boss needs to pick up his sick daughter from school?
All of a sudden, you can’t get an answer until it’s too late.
Rules of engagement have the potential to save you a huge headache and give you a better opportunity to get the most out of the sale weekend.
Budget and bidding tips for Black Friday PPC
Bidding is one of the trickiest areas to work with. Not necessarily on Black Friday itself, but afterward. If you run any type of automated bidding, you’ll have to run bids manually for at least 1-2 weeks after Black Friday due to the influx of data.
I haven’t personally found a bidding system where I can tell the system to ignore data generated in a specific time frame when it runs its algorithms. This poses an issue, as you’ll convert much better on Black Friday than in the weeks after. Depending on your industry, this might be a big issue.
To solve this, I typically do the following:
Download your bids the week before Black Friday
If you’re running automated bidding in Google, then remove the bids and look in Google Ads interface to see what the bids are. There are a few issues you should watch for, though.
Depending on the day and time you download your bids, you might get a different bid than the one that’s running the rest of the time. Especially with Google’s own ROAS and CPA bidding, automation changes dynamically based on day of the week and time of day (amongst other factors).
Therefore, there is a chance you might not get the actual bid you should reinstate after Black Friday, but it’s the best chance you have. It’s much better to reinstate a previous bid that might be 20-30% off than continue running the bids you had for the Black Friday weekend.
Increase your budget, significantly
It goes without saying that you have to increase your budget quite a bit on Black Friday.
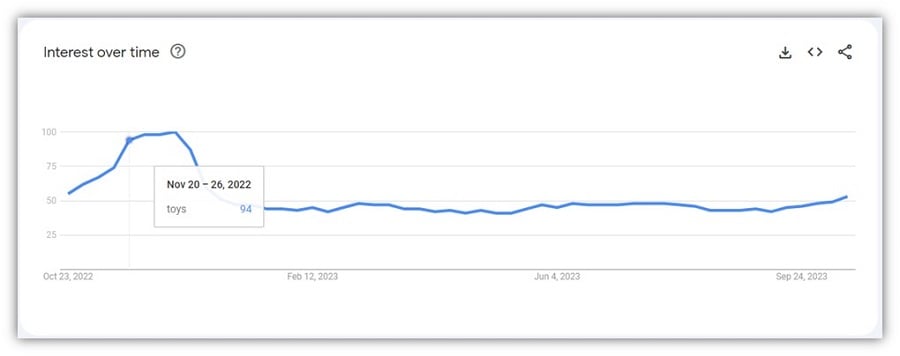
For example, searches for smartphone deals go up 10X.
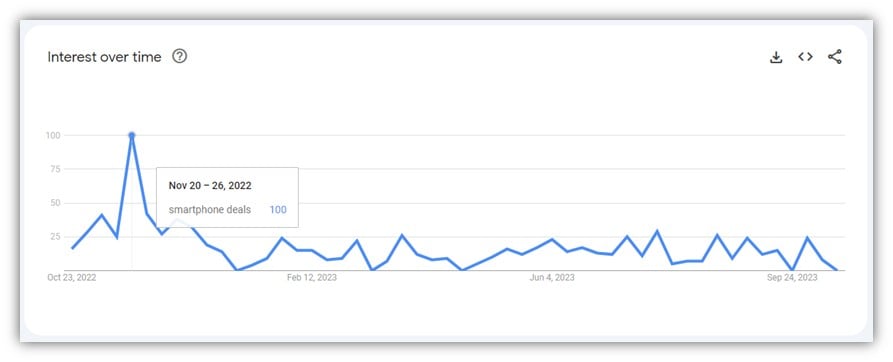
While searches for toys increased by 50%:
Ad writing tips for Black Friday
Writing ads for Black Friday is similar to writing ads for promotions throughout the year. Make sure they are relevant to the sale and use an adequate amount of ad space so users are aware of the promotion you’re running.
There are some specific factors you need to take into account for Black Friday, though.
I’ve split up the tactics in Mandatory and Recommended. If you’re new or this is your first Black Friday you can choose to just follow the mandatory tactics. But if you’ve been around the block, make sure you invest the extra time to do the additional Recommended tactics.
Mandatory for all:
- Set up a Promotion asset
- Add Black Friday references in your ads
Recommended for intermediates:
- Consider changing your sitelinks to specific products that will be in high demand.
- Consider adding Inventory References
How to set up Google Ads promotion assets
The promotion asset should be an essential part of your ad writing strategy moving forward. Your ads for Black Friday are no exception.
Promotion assets look like this:
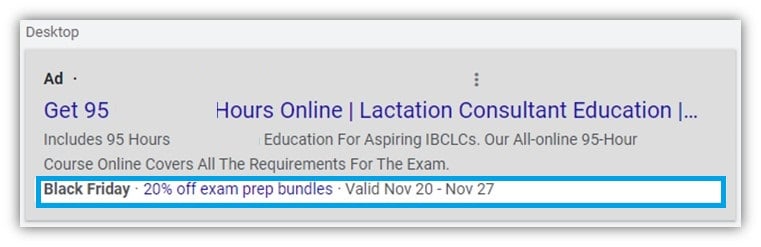
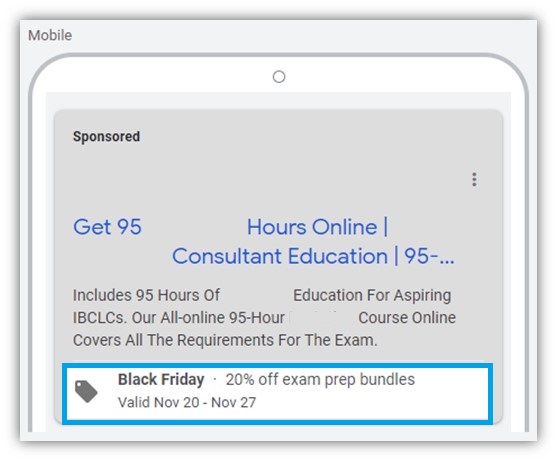
The extra line of ad text can really help set your ads apart from your competitors. The fact that it highlights a Black Friday sale is just the icing on the cake.
On top of this, you should also set your promotion to only run in a specific time frame. For Black Friday, this might be from Friday to Sunday.
This will give your ad additional space and add a sense of urgency to your offer.
Just remember, all ad assets aren’t necessarily guaranteed to show. It’s not enough to solely rely on the promotion asset to highlight your promotions.
Add Black Friday references in your ads
One of the oldest best practices is to make sure your ads are relevant, and one of the best ways to do that is to reference current events like Black Friday.
You can keep it simple, for example:
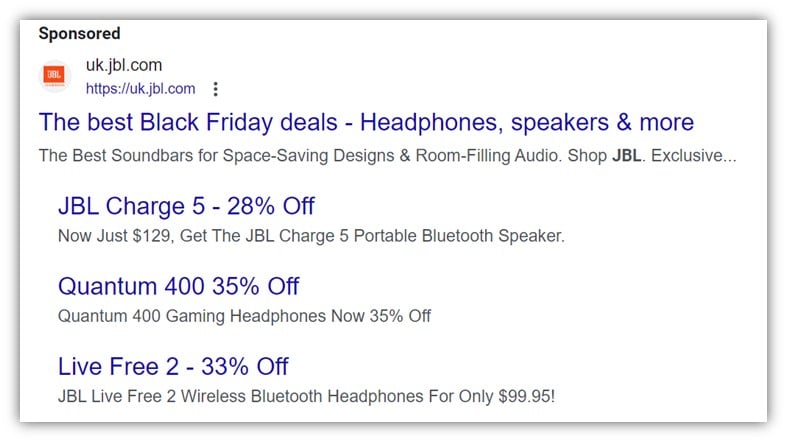
If you want the biggest impact for the least amount of effort, you can just change the second headline in all your ads to text referencing your Black Friday offer. This can be done super quick in the Google Ads interface.
For a higher CTR, better conversion rate, and ROI, I do recommend spending the time to write more specific ad copy for your most important products and categories.
Remember, Black Friday is a high-volume day. Any time you invest in writing better ads will pay off more than any other time of the year (with the exception of the Christmas season) – even if the ads only run for that day.
Change your sitelinks to specific, high-demand products [recommended]
Sitelinks are usually not the biggest focus area when writing ads. Most advertisers just take a minute or so to put in a couple of random sitelinks.
On Black Friday, it might be worthwhile to add a bit of extra finesse to your sitelinks. One idea is to include the specific products you run promotions for in your sitelinks.
So, let’s say you are running a campaign for Bluetooth speakers. Normally, you might have sitelinks like these:
- Most popular BT speakers
- Newest BT speakers
- BT speakers on sale
- All BT speakers
On Black Friday, consider adding sitelinks that are more specific to the offers you’re running:
- Soundlink: 33% Off Now
- 20% Off All Bose
- 25% Off Bose Headphones
- All Black Friday Sales
The reason why I advise going a bit broader than normal is because during Black Friday you are more likely to convince consumers to buy something they weren’t really out to get.
Many of us will just start searching for various products to see what deals are out there. Just because someone specifically searches for Bluetooth speakers it doesn’t mean they can’t be interested in headphones or other types of speakers if there is a good deal to be had.
Add inventory references [recommended]
Let’s say you create a killer promotion for Bose speakers. It’s right in the middle of being a sought-after product, at the right price with an exceptional promotion.
You start selling it and you can see that it’ll sell out by noon. Boom!
But you could have taken advantage of this in your ads. By indicating how many products are left, you can create even more scarcity.
Just make sure you have backup promotions for when you run out of a specific product.
Tag your current ads with the label “evergreen”
Running PPC for clients always makes you think of ways to do things more efficiently. Especially in eCommerce, as there are times of the year when the workload increases significantly.
Black Friday is that day.
Before you start your Black Friday ads, you should take all the ads in the ad groups where you will be adding the Black Friday promotion and add the label Evergreen.
That way you can easily pause the ads and reactivate them again when the sale is over.
The same way, you should label all your Black Friday ads with BF. You should probably add the year to your label as well. So for 2023, you’d add the tag BF-2023. That way you don’t accidentally activate last year’s ads next year.
Write your ads at least a week in advance
You know those annoying emails you get from Google Ads about your paused ads being disapproved?
There’s a reason behind the madness, and it’s for days like Black Friday.
When you prepare your ads in advance (and upload to your Google Ads account) you’ll make sure that they get approved, or disapproved, well in advance of you actually needing them to run.
It’s a common mistake to write, or upload, your ads the same day that you need them. You’ll lose valuable time.
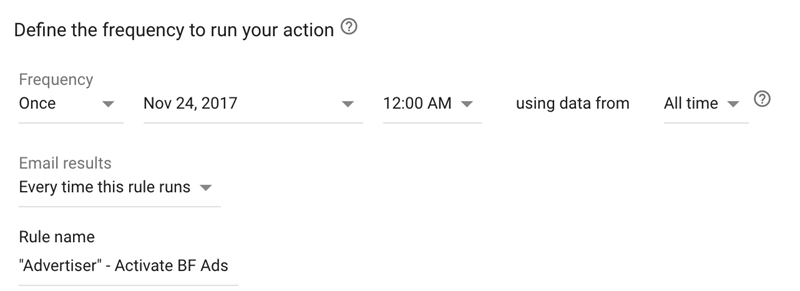
Use an automatic rule to pause and activate ads
The exact way you should build the rule is like this:
Just in case, I recommend checking the ads in your account and live in the search results. Even though I’m a big fan of automation, I’ve seen these things go wrong for the stupidest reasons.
While it’s not fun, you can normally live with ads not being live for half a day or even a couple of days, but on Black Friday you can’t afford to lose out on one hour of downtime.
How to maximize your Black Friday Google Shopping returns
Shopping campaigns are tricky when it comes to Black Friday. You have a lot less control than your regular Search campaigns, but Shopping campaigns still account for more than 50% of the revenue in most e-commerce Google Ads accounts, so you need to get this part right.
Create a new Shopping campaign
There are a couple of angles you can take with Google Shopping campaigns on Black Friday, but my go-to approach is the following:
- Create a new Shopping campaign for your most important products
- Use a “SPAG” structure (single product ad groups)
- Start it at least one week in advance, preferably two weeks
Depending on how many products you have, it can be super easy for individual products to slip through the cracks in your Shopping campaign.
By creating a new campaign, you’ll be able to keep an eye on the specific products you’re expecting will perform very well on Black Friday.
Just remember that if you’re using a tactic like segmenting your Shopping campaigns based on search query, then you should continue this with this campaign. You can quickly get in trouble with your ROI if you change that strategy for your key products all of a sudden.
Add storewide promotions to your new Shopping campaign
Okay. So you have a promotion that runs storewide with 20%. I get it.
It still doesn’t mean that all your products are equally important. If you look at your orders from the last 60 days, you must have a list of 10, 20, 50 products that vastly outsell the rest of your products.
Add these to the new Shopping campaign.
How to prepare your Shopping feed for Black Friday
This is where you need to make a decision. Do you run with a promotion that requires a coupon code (as listed above), or do you lower pricing in your feed and see it reflected in the ads?
Often, this decision will be made for you either by the strategy you take as a business (coupon or no coupon) or by the restraints of your platform.
If you run with the coupon code, then it’s crucial that you set up Promotions in the Merchant Center. Otherwise, your price in your Google Shopping ads will not reflect the actual lower price and it will undoubtedly decrease your CTR.
Lowered prices need to be reflected in your feed
It’s crucial that your feed contains the same price as on your website for each individual product. For two reasons:
- If your price isn’t lower in your feed, then your ads will show your original price, which will severely cripple your success on a day like Black Friday.
- There is a strong likelihood that Google will catch the price discrepancy and disapprove your product.
Again, from the time you catch this to the time the product gets approved by Google might take 4-6 hours. This is time that you can’t afford to lose. And that’s if you catch it at all!
I recommend regenerating/updating your feed and sending it to the Merchant Center right after you update the prices on your website. This might be midnight or it might be the day before. The second the prices on your website are updated, you should update your feed.
This is especially important as products go out of stock throughout the day.
Update your feed more frequently on Black Friday
Usually, you set your shopping feed to update every 24 hours. Typically at night.
On Black Friday I highly recommend you update it more frequently. Especially as products go out of stock or as you change your promotions.
Black Friday tips for remarketing
Most ecommerce stores run Dynamic Remarketing, but on Black Friday sending generic messages will not break through the digital noise.
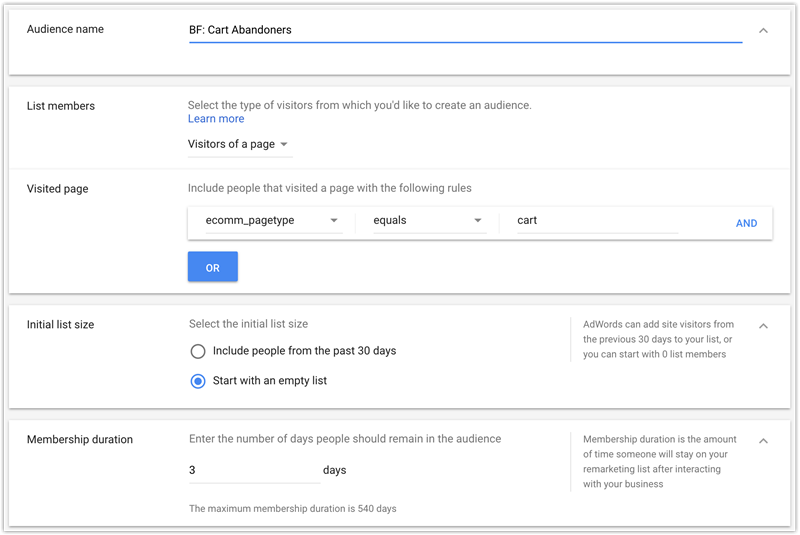
I advise creating a new audience list solely for Black Friday. This means you’ll create a brand new audience the day before Black Friday that doesn’t include previous visitors:
This way you can set a more aggressive bid for the people who’ve visited your site on Black Friday and another bid for the people who visited your site before Black Friday.
Bonus tip: decrease remarketing bids after Black Friday
Lower your remarketing efforts in the days after Black Friday. Most users will have bought what they needed, or they simply weren’t interested in the first place.
Consider static image ads for your remarketing
I would highly recommend some sort of static images in your remarketing mix on Black Friday. Your regular dynamic display remarketing ads most likely look something like this:
Again, usually, this works great. But on Black Friday you’ll want something that pushes through the noise and delivers a message that adequately reflects the scarcity of the day.
Having some banners designed in the most popular sizes can be an easy win, and it shouldn’t cost you much if you use a site like Upwork to find a designer. If your store has an in-house designer, then spending some time on the designs in exchange for a pizza is well-worth the results you’ll most likely get.
The only thing I will add, which will complicate things, is to try to segment your retargeting when you do this. Meaning if a user visits the speaker section, then you’ll show a Black Friday display ad that contains your speaker promotion, etc.
You can try a general, generic banner, but it’ll be more effective if you put in the extra effort and create better-targeted ads.
Again, if your store is beyond a certain size this might prove impossible to do in practice. When you work at scale, you have to somehow limit your efficiency with hands-on tactics for the sake of getting out to as many people as possible.
Black Friday PPC keyword strategy tips
Your keywords should more or less stay the same for Black Friday.
I would highly recommend adding or reactivating keywords that have previously been paused for products you’re running promotions for. On Black Friday, most of your keyword portfolio will convert better than it will the rest of the year, which means you can afford to re-enable those keywords you paused due to low performance.
The exact opposite is also true. With keywords increasing three to four times in search volume, you want to consider pausing parts of your Google Ads account that you are not running promotions for.
Here’s an example of a search term that increased significantly when comparing to the same day a week before Black Friday:
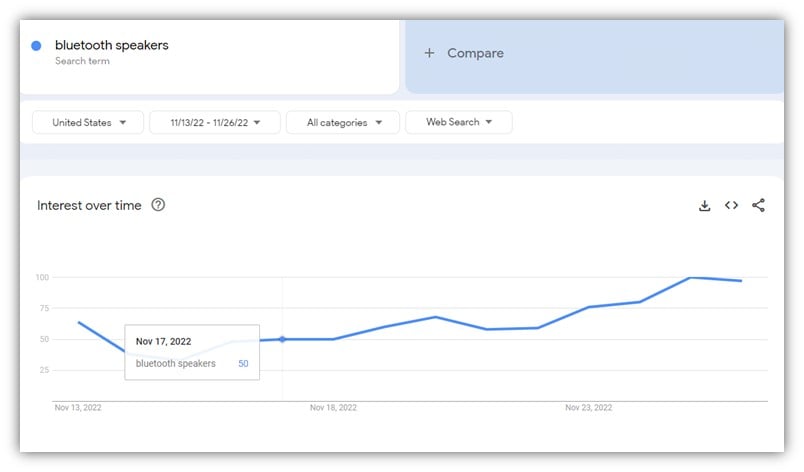
With the added volume and the fact that your competitors will run promotions, which consumers are likely chasing, then your standard pricing will most likely not do anything to incite them to buy from you instead.
Advertise for “black friday + my keyword”
Yes, definitely.
You’ll already show up when someone searches for your keyword, so you might as well control the search by adding black friday to some of your keywords.
However, it will not make or break your success. In big markets, though, you want to be able to control it better. Let’s say that you’re selling Bose speakers, and you show up fine for searches on the keyword bose speakers, but you’re in position six for bose speakers black friday deal.
This search term might convert much higher than your regular keywords, so if your market is big enough it’s an excellent tactic to add black friday to your keywords.
Don’t advertise for the keyword “black friday“
It’s too broad for you to target effectively.
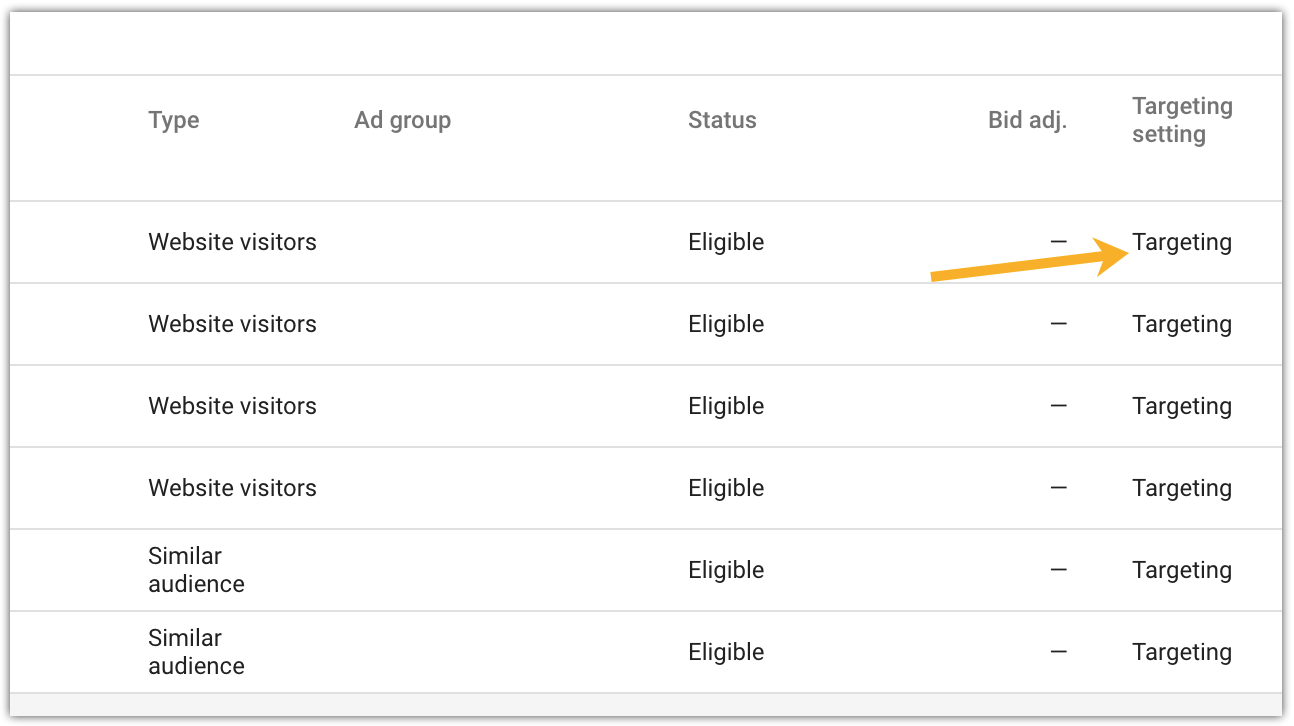
The exception is to create a campaign only targeting your remarketing lists that target the word Black Friday. Find your largest list. Say, anyone who’s visited your site in the last 6 months. Anyone who’s bought from you, well, ever. Add all of them to a remarketing list for search ads campaign with the Targeting targeting setting:
By doing this, you’ll show an ad to anyone who has ever visited your site and searches for Black Friday deals.
Since they’ve already visited your site once before, or possibly even bought from you, we can assume that they have some interest in the products you’re offering, despite them not showing any intent outright. (Remember–brand affinity dramatically increases CTR and conversion rates.)
Black Friday scenarios to be prepared for
Scenario #1: Low average position on key products
Make sure you review the early stats when it comes to your average position on Black Friday. If you’re coming in low for some of your key products, consider increasing your bids.
Throughout the day you can decrease or increase as you normally would based on ROAS, but you need to make sure your keywords have a fighting chance in a proper position.
Your position should preferably be in the 2-3 average position range. This will depend a lot on your ROAS, but the higher position your get, the more ad extensions and CTR you’ll get–which all results in more sales.
Scenario #2: No sales of key products
You need to be ruthless about admitting to yourself if you’ve been beat. It might not even be related to your Google Ads efforts.
Does your competitor run a better offer than you?
If so, then you might want to mimic their promotion or cut your losses. It’s incredibly difficult to beat a competitor that’s severely beating you on price under normal conditions.
On Black Friday with zombie-like consumers chasing deals like that kid on the Walking Dead, it’s almost impossible.
If you’re not getting anything out of your Black Friday efforts in some of your campaigns, consider solely focusing on remarketing. That way you’ll only show your ads to people who’ve visited your site before. With this strategy, you’ll bank on the fact that these consumers know who you are, which has been proven to impact your conversions significantly.
Scenario #3: Budget maxed out
You should routinely check in on your budget. Make sure that you’re not maxed out, or about to max out. If you are maxed out, consider adding more budget based on your rules of engagement that you’ve established.
What to do after Black Friday?
Make sure you do the following in your PPC account once the Black Friday madness is over:
- Reinstate your old bids
- Pause Black Friday ads
- Re-enable your evergreen ads
- Do an after-action report
- Have a beer and enjoy sending out all those orders!
When you review your performance in the days after Black Friday, make sure you don’t take these days into account. For many advertisers, the days after Black Friday can be a time to lose a lot of money.
Wow, Black Friday PPC is… a lot…
If this was more than you could handle, I don’t blame you. It was a bit of a brain dump.
I created a checklist version of this article that you can print out or save for later. Get your simplified Black Friday checklist here.
I’ve also summarized the most actionable Black Friday PPC tips below:
For Bids
- Download your bids a week in advance, so you can reinstate them after Black Friday
- Increase your budget, significantly
For Ads:
- Set up the promotion extension
- Add Black Friday references to your ads
- Consider changing sitelinks
- Consider adding inventory references
For Shopping
- Add a new campaign with your most important products (or the products you run promotions for)
- Use Merchant Center promotions, OR include sale_price in your feed
- Upload your updated prices in your feed around midnight
Remarketing
- Focus your bids around your most recent visitors
- Decrease your bids significantly in the days after Black Friday, or exclude Black Friday
Keywords
- Add previously paused keywords that cover products that are on sale
- Increase bids for low-position keywords that cover products that are on sale
Whatever you do, it’s crucial that you set yourself up for success on Black Friday. Take the time and acknowledge that you can’t just be in maintenance mode.
Get out of your comfort zone and start making some changes in your account.
Want more Black Friday tips? Find out how to drive results from your Black Friday Facebook ads!
PPC
Critical Display Error in Brand Safety Metrics On Twitter/X Corrected

In a recent public statement on Twitter, Linda Yaccarino, CEO of X, highlighted a critical error in the display of the company’s Brand Safety Rate which was provided by DoubleVerify, a third-party company known for verifying brand safety metrics.
The error, identified in the graphical display of the Brand Safety Rate on X’s dashboard, persisted for nearly five months, from October 24, 2023, to March 14, 2024. During this period, the dashboard erroneously displayed a significantly lower Brand Safety Rate, which sharply contrasted with X’s actual rate. According to the statement, the true Brand Safety Rate for X has consistently exceeded 99.99% since October 2023, a figure that surpasses global benchmarks for brand safety across all campaigns, as per DoubleVerify’s global industry data.
Brand Safety Rate refers to a metric used to measure the extent to which a brand’s advertising efforts appear in environments that are deemed safe and appropriate, aligning with the brand’s values and standards. This rate is crucial for ensuring that ads do not appear alongside content that could harm the brand’s reputation.
DoubleVerify has accepted full responsibility for this oversight, acknowledging the display of incorrect and misleading safety rates on X’s dashboard. They have assured that they have communicated the error to the affected advertisers and have corrected the display to accurately reflect the current and retroactive Brand Safety data for X.
Yaccarino assured advertisers on social media platform, that immediate actions are being taken to rectify this issue in collaboration with DoubleVerify to ensure that all clients receive accurate and reliable information. She also mentioned that the X team, along with DoubleVerify support, will reach out to advertisers who may have made business decisions based on the erroneous data.
This situation underscores the critical importance of accurate data representation in digital marketing and the potential consequences of data inaccuracies on business decisions. It serves as a cautionary tale for all involved in paid social advertising and emphasizes the need for continuous vigilance and rigorous verification processes to maintain the integrity of marketing metrics.
Of course this follows a number of issues where paid social advertising platforms have shared incorrect data with advertisers leading to concerns about measurement accuracy and transparency.
Here are a few notable examples:
Facebook Video Metrics Issue: In 2016, Facebook admitted to overestimating average viewing time for video ads on its platform for two years. This error reportedly inflated the average viewing times by 60-80%, which could have misled advertisers about the performance of their video ads on the platform.
Twitter Ad Billing Error: In 2016, Twitter disclosed a bug in its Android app that led to overcharging advertisers over a month-long period. The bug affected campaigns using the feature that charges advertisers for the first engagement with a campaign each day but instead charged them for engagements that occurred afterwards as well.
These incidents highlight the importance of accuracy in digital advertising metrics and underscore the need for ongoing vigilance by both advertisers and platforms to ensure data integrity and transparency. Such errors can have significant financial implications and can affect strategic decisions made by advertisers and we can’t always trust the data shared with us by platforms 100%.
PPC
14 Ways to Use AI in Marketing that Actually Work

Does your head spin when someone mentions artificial intelligence? It’s understandable. LinkedIn and Twitter (fine…X) are rife with newly minted AI experts and tech bros sharing their latest 27-step process for gaming algorithms and automating entire marketing programs.
That’s not useful for most ground-level marketers.
What can help? Knowing which everyday marketing challenges the technology can solve for us right now is a great start. So, I reached out to several marketers I admire to see how they’re using AI in marketing.
The response was outstanding. They shared specific, tactical examples, plus the prompts and AI tools they use—everything you need to repeat their processes.
Contents
💡 Download this handy, free Guide to AI in Marketing for more tips and strategies.
14 ways the pros use AI in Marketing
Interestingly, no one said they were using AI to spin up entire ready-to-publish articles. But they are using AI tools to get out of writing ruts, analyze data, inform strategy, and automate marketing flows. The use cases were way more diverse than I imagined.
1. Pull insights from past campaigns for future strategy
Knowing which ad or blog post generated the most leads is easy. It’s harder to learn why they worked so you can double down on their success. Curt Woodward, Director of Content at ZoomInfo, devised a genius way to get Jasper, a generative AI copywriting tool, to help him figure it out.
Curt started by ranking a list of ZoomInfo’s content titles by a “power score” comprised of three weighted KPIs. Here’s a mockup of that list with fake data he uses for demonstration purposes.

Next, he fed the list to Jasper, along with a prompt asking the AI to identify commonalities that would inform future content campaign choices.
His prompts looked like this:
“Act as a marketing analyst. I am going to give you a list of content titles with corresponding numbers, which represent a value score we use to determine top content. Higher scores are better.”
“Compare the content titles to find common themes, keywords, ideas, and approaches among the top-scoring titles. Suggest ways to replicate successful content packages.”
“Jasper, as a tool, often asks for more information about what you want the output of your prompt to look like,” Curt explained. “In this case, I gave it instructions about format, use of the memo, etc.”
Here’s the follow-up prompt Curt gave Jasper:
“I want to come away with a memo that summarizes our best themes, formats, and concepts for our future marketing content campaigns. Give us ideas and frameworks to use going forward.”


Based on the data and prompts Curt gave it, Jasper created a list of recommendations with detailed ideas for future content.
Curt qualified the fairly obvious results from this example by pointing out that it was fictitious data. He said you get a more insightful analysis when you feed it accurate information. Next up, he plans to get Jasper to proactively rank and sort the content assets by the power score, which will make the process even faster.
But for now, Curt suggests trying this tactic with other marketing copy. “You can easily adapt this for any measurable marketing asset. Ad and landing page copy comes to mind. Just rank them by whatever KPIs are important, and ask the AI to find themes you can use in future campaigns.”
📚 Free guide >> 135 of the Best Words & Phrases for Marketing With Emotion
2. Complete competitive analyses
Completing a competitive analysis is a core function for just about every marketer. The hard part is synthesizing competitive product features and brand positioning for multiple competitors.
Celia Quillian is an MBA and product marketing leader who’s also an influential voice in the artificial intelligence space through her channel @smartworkai on TikTok and Instagram. She uses ChatGPT Plus (the paid version) to quickly curate competitive intel.
“ChatGPT Plus’ web browsing feature is fabulous for competitive analysis,” she said. “In my prompts, I provide the links to competitor websites, asking that it only source from these sites for its competitive intel, and have it craft a table comparing the features of different market competitors.”
The free version of ChatGPT can’t surf the web. I tried a quick version of the request on perplexity AI using three HR software competitors.
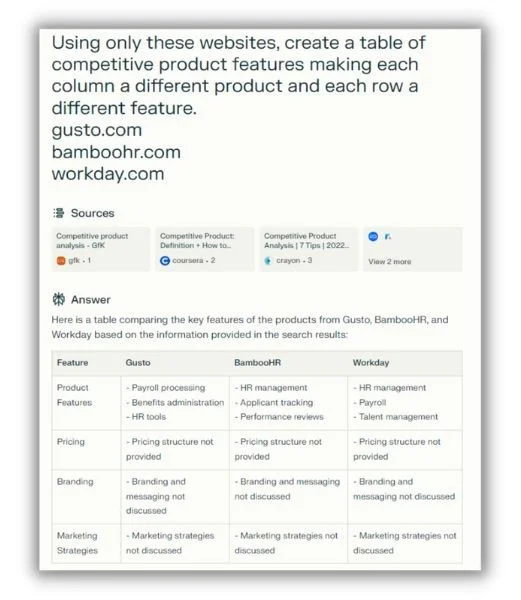

Obviously, this would need some additional prompts to make it useful. But Celia said AI is really good at that. “Generative AI models like GP-4 have lengthy ‘context windows,’ meaning I can continually ask follow-up questions,” she said. “My combined prompts and answers only build on each other, helping me to learn, brainstorm, and find answers more efficiently.”
For context, Celia said ChatGPT Plus can “remember” the context of about 100 pages of written text.
3. Roleplay for customer sentiment
AI can’t replace humans, but it can pretend to be one. Celia said that’s a valuable feature of the technology. “ChatGPT is great at playing pretend, so when it comes to thinking of how I might solve a problem for a customer, I can ask ChatGPT to roleplay as my ideal customer persona.”
I gave this a try with the free version of ChatGPT. I fed the AI a description of a backpacking tent that focused on its weight, then entered this prompt:
“Pretend you’re the target customer for a company that sells outdoor camping gear. You’re very concerned about the durability and weight of the next backpacking tent you buy. How would you feel about this product description.”
Here’s what I got back.
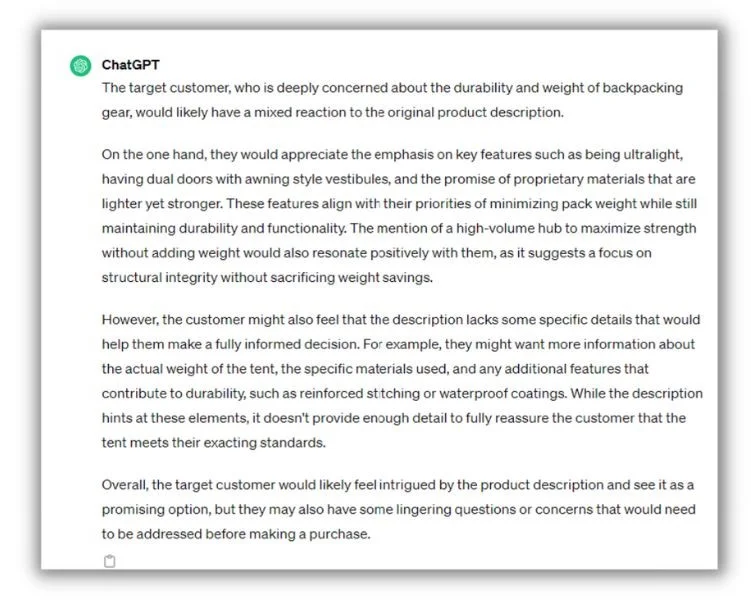

This was a simple example, but ChatGPT spotted the durability gap and suggested we add more specificity. Not bad.
“It’s never as good as talking with a real customer,” Celia added. “But it can make for a great stand-in when I’m in the early phases of research and ideation.”
4. Produce internal project management assets
One of the best applications of AI is to automate repetitive marketing tasks. That’s a common way Alaura Weaver, Content Marketing & Community Leader at Writer, uses it.
“I use Writer to spin up internal project management assets instantly—stuff like writing briefs, editing checklists, and creating content promotion plans,” she said. “That way, I don’t have to start from scratch with routine tasks.”
Alaura detailed how she creates briefs since that’s a common task for many marketing team leaders and those who work with freelancers.
“I built a custom ‘brief generator’ app in our no-code Writer App Studio,” she explained. “All I have to do is give a working title, indicate what audience the piece is for, and paste or upload source material (like an executive LinkedIn post, research article, or dev documentation). The app generates content briefs that align with our business goals and content strategy (which I baked into the prompt that powers the generator).”
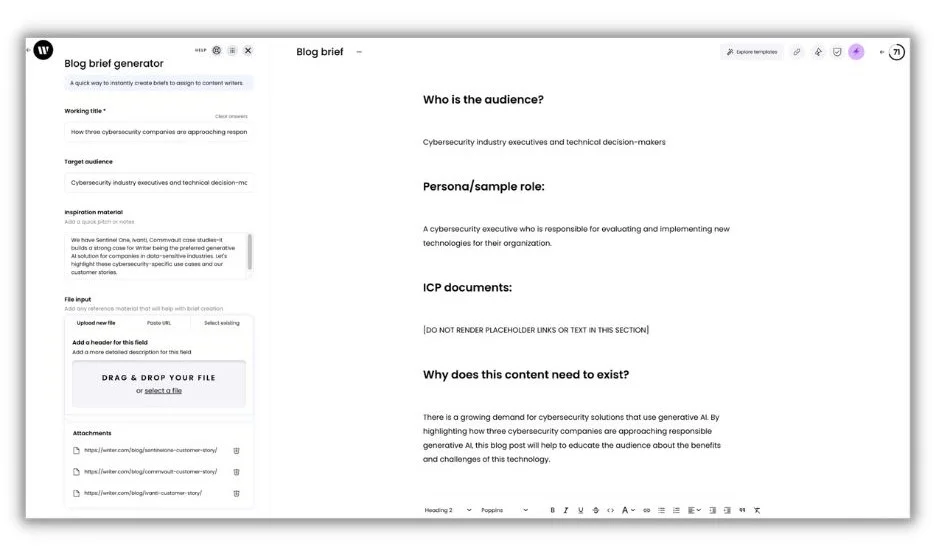

Alaura said that using AI this way speeds up the entire editorial process, freeing up bandwidth for high-level tasks.
“The output follows a consistent format, so I can easily plug it into docs without much editing,” she said. “It means that my writers have what they need to get started on assignments a lot faster, and it means I have more time to focus on fun, creative, strategic work like producing our Humans of AI podcast.”
5. Find thinking models for thought leadership content
The best thought leadership content has a unique, personal, and interesting point of view. It’s not the typical wheelhouse for robotic writing.
But Anjana Vasan, a Senior Copywriter and Content Strategist at Block Club, found an unexpected way to improve thought leadership content with AI. She asks ChatGPT for thinking models or academic concepts related to her topic.
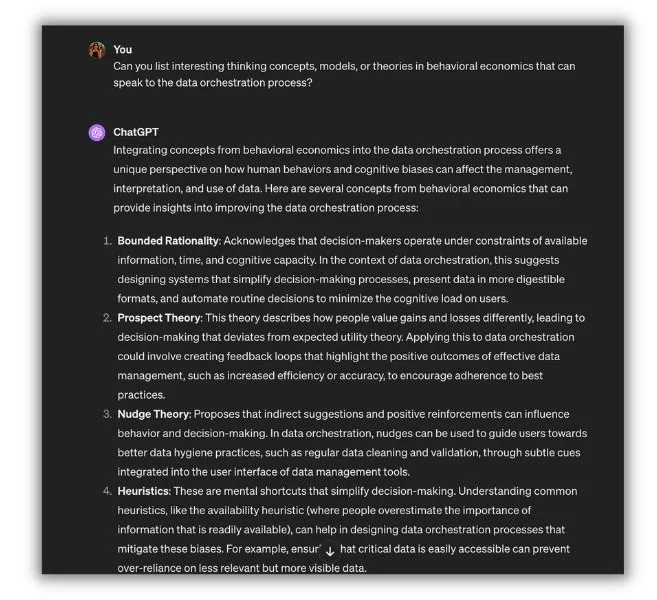

“Using AI this way, I can develop a unique point of view or think of an interesting metaphor and connect the dots to the topic or the person I’m writing for,” Anjana said. “All while still keeping their experience and expertise in mind.”
The great thing about this tactic is that it works with just about any AI writing assistant or even generative search platforms like Perplexity AI.
6. Analyze data for SEO audits
Anjana showed us another way AI can help analyze large blocks of data—this time for SEO audits.
Here, she asked ChatGPT to review a spreadsheet of content links.
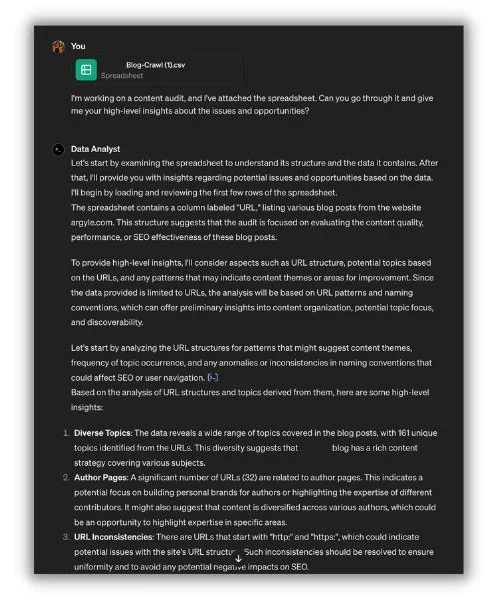

“Usually, I dig in further with additional questions or prompts to draw the insights I’m looking for,” she said. “Or I ask ChatGPT to organize the data so I don’t spend my time on administrative tasks.”
Here are some of the follow-up prompts Anjana uses:
- “Based on the available data, can you identify the top 10 pieces of content?”
- “Have you noticed any themes or overarching topic categories in all the content?”
- “Can you edit the spreadsheet to include only the URL, date of publication, title, meta description, and word count and remove the other columns?”
She warned that this tactic only works with the right information and that any AI output should be double-checked.
“The results are only as good as the quality of your data, so ensure you include the right types of information in your file,” she said “And remember to validate the information since you may not always get the right insights if you rely completely on ChatGPT.”
7. Link ideas while you write automatically
If you have folders full of half-complete ideas and clever copy that are hard to find when you need them, Anna Burgess Yang feels your pain. “I publish a lot of work online and have thousands of notes from articles I’ve read, podcasts I’ve listened to, and even my own writing. In the past, I’ve relied on tags or categorization in note-taking apps to connect topics or ideas.”
Anna is a prolific freelance content marketer and a self-described workflow automation geek. She uses an AI tool called Reflect to surface related notes based on the text she’s writing. So, mid-draft, Anna will see categorized suggestions from her network of documents.


Our human brains are wonderful, but they’re not always great at quickly recalling a specific point buried amongst thousands of others. AI is ideally suited for the job. “This has become an invaluable part of my note-taking since AI can pull ideas together that I may have overlooked or not considered,” Anna said.
8. Repurpose long-form content for social media posts
Social media marketing is one of the best channels for brand awareness and lead generation. But it’s also a never-ending grind that requires a constant flow of content ideas to stay relevant.
Anna came through with another AI tip: a way to pull social media posts from the content she previously produced. “I’ve already done the hard work by crafting long-form content. Why not use AI to speed up the process of creating social posts?”
Anna uses a content summarization feature in the generative AI platform Writer to do this.
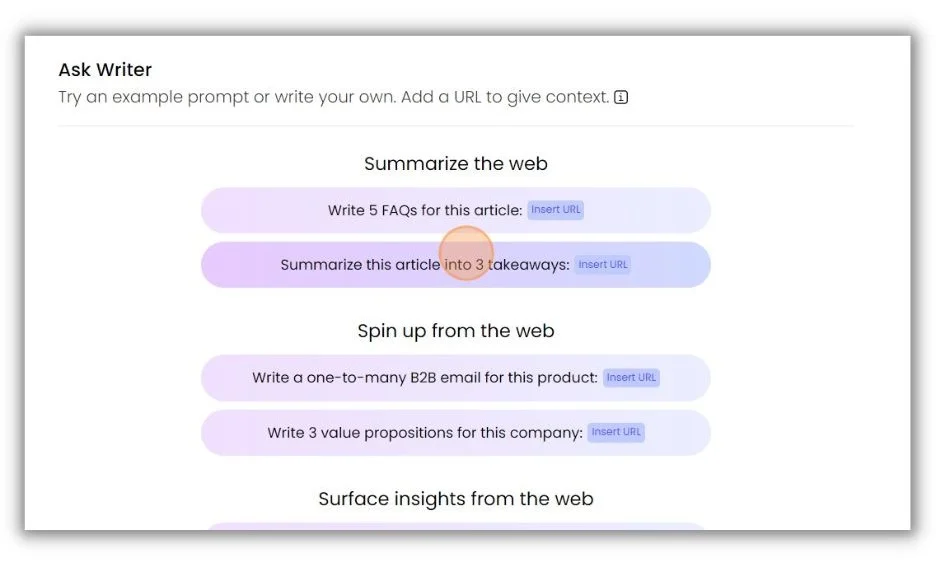

After dropping in the URL of her source article, Writer comes back with a brief synopsis of three key takeaways.


Next, she pastes the takeaways into Trello, the tool she uses for content planning. Those snippets inspire social posts when she’s ready to write them.
Why not just ask AI to write the posts? “You can try and use AI to write social posts for you, but I’ve found that it never sounds like me,” Anna said. “I’d rather use key takeaways as a launching pad and write my own social posts.”
👍 Get copy-and-paste social media posts you can customize >> Social Media Calendar Template
9. Create customized SMS and email marketing campaigns
Customer journeys are like choose-your-own-adventure stories with dozens or hundreds of potential flows. Personalizing those journeys requires a lot of manual work.
Angela Rollins, an ecommerce-focused content marketer and strategist, suggested a tool called Attentive AI as a solution. “Instead of manually creating all the different flows a brand normally would and layering on segments, Attentive AI basically personalizes SMS and email messages at scale based on all the data a brand has on its customers,” Angela explained.
This screenshot from Attentive AI’s website shows the campaign creation workflow.
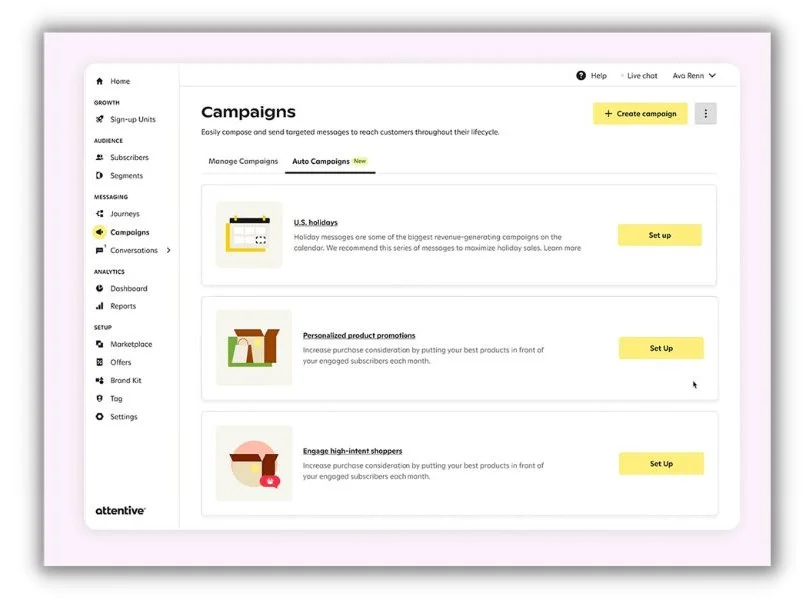

The tool continually learns from the highest-performing marketing interactions to create multi-channel campaigns. It can also build refined segments from your pool of subscribers and dial in the best time to send messages for the highest rate of response.
By using AI, you can “send each person the right message at the right time depending on where they’re at in their relationship with the brand,” Angela said.
10. Prepare an interview question list
Here’s an exciting use of AI’s ability to riff off an existing text. Angela gives the AI assistant Claude outlines and asks it to fill out question lists for subject matter expert interviews.
Here’s an anonymized version of a conversation Angela recently had with Claude.
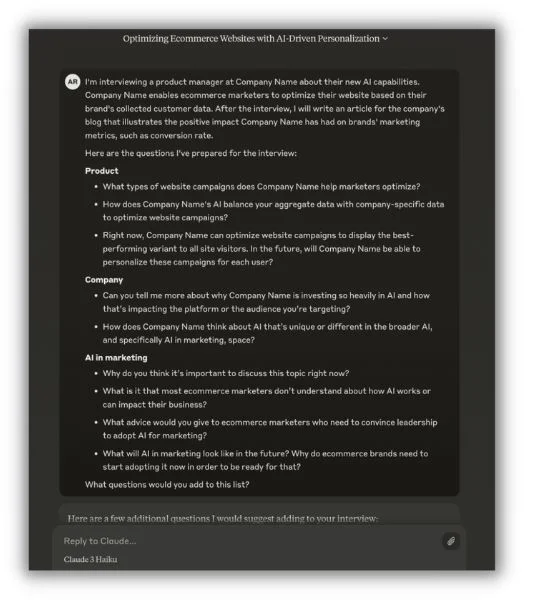

Claude replied with some pretty insightful new questions to add to the list. It even categorized them like Angela did in the original structure.
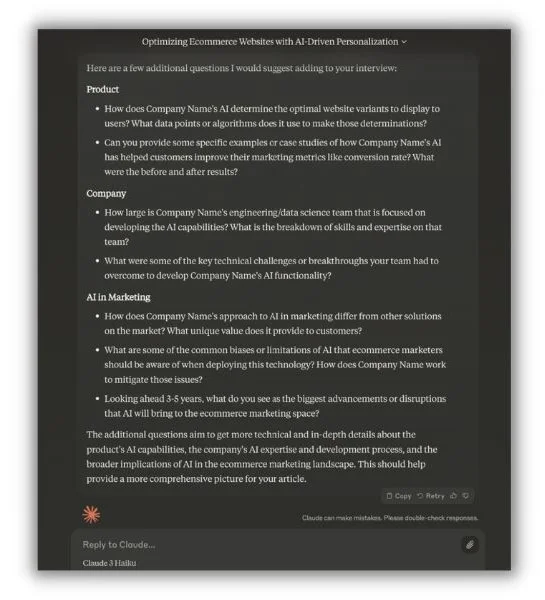

Once the interview is over, Angela goes back to Claude to help pull out the most interesting bits. “It’s so helpful to just plug large amounts of content into Claude and ask it to summarize for me. That helps me find specific answers from a long interview.”
11. Improve design elements in email headers
Marketers who aren’t necessarily graphic designers are often called on to produce visuals for the assets they manage. When Ceillie Clark-Keene, Head of Marketing & Communications at Building Ventures, finds herself in this position, she turns to AI.
“I’m not a designer, but I do put together the occasional email header,” she said. “I’ve started experimenting with the AI features in Canva and Designs.ai to improve design elements or generate graphics.”
I gave it a try on Canva. I had trouble creating a new newsletter design (I found plenty of pre-made templates), but with a few clicks, I got a handful of post designs that were properly sized for Instagram.
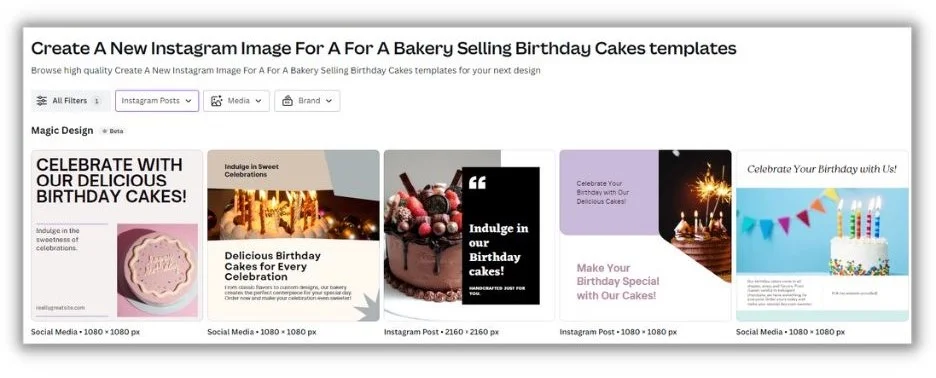

“These tools help me create better graphics for those times when outsourcing a professional isn’t in the budget or timeline,” Ceillie said.
A word of caution is warranted. Review AI image generators closely. They can sometimes go off the rails and create less-than-ideal visuals.
12. Build article outlines quickly
I’ve written hundreds of articles, and without fail, creating the initial structure is the hardest step. Once you have the logic and framework down, it’s just a matter of filling in the blank spots.
Will Ruzvidzo is a seasoned B2B SaaS content marketer who’s worked with global brands for over 10 years. Will explained how he uses Writer to overcome outlining obstacles.
He starts by entering a straightforward headline. “With just a few clicks, I can generate a well-structured outline for my blog post, complete with relevant subheadings, key points, and supporting examples.”
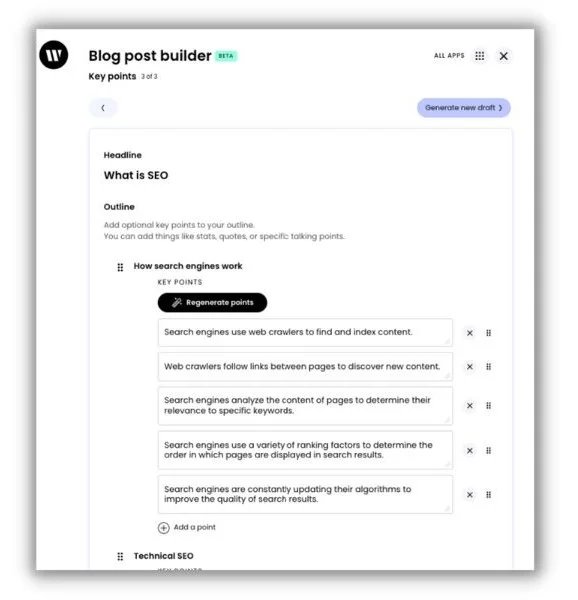

With the “bones” in place, Will customizes the outline to “add my own voice, insights, and creativity into the blog post.” Writer also gives Will AI-powered copy suggestions as he writes.
He said the time saved lets him focus on crafting captivating introductions and compelling arguments—the types of things that make human-written content stand out.
13. Write craftier subheadings
Subheadings are among the most important aspects of a blog page. They help readers skim and search engines crawl articles more effectively. That’s why Hsing Tseng, a freelance content writer, editor, and strategist, uses ChatGPT as a sounding board when she writes subheadings.
“AI tools can brainstorm much faster and more imaginatively (sometimes) than I have the creative bandwidth to do,” she said.
Here’s an example prompt Hsing shared.
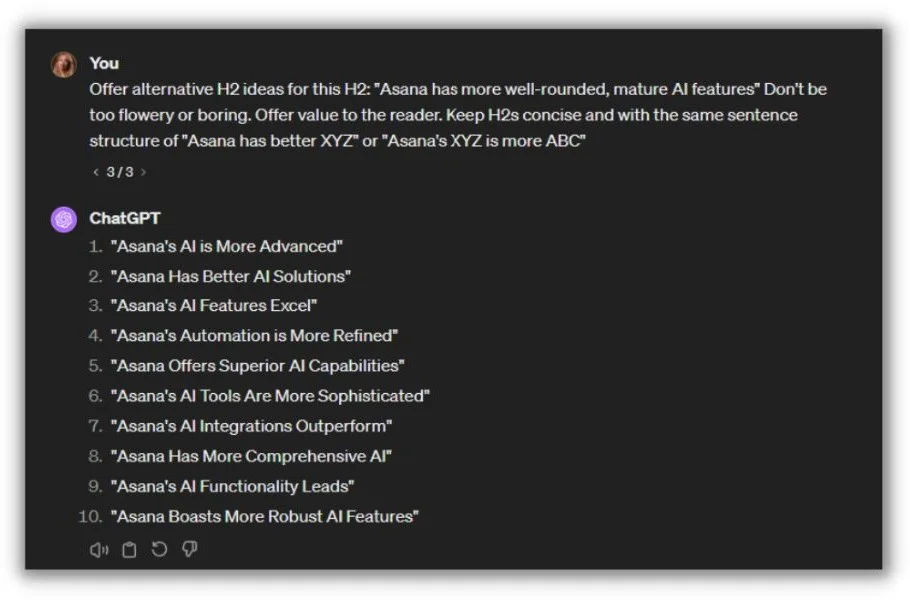

Notice how she adds tone and structure instructions to the prompt, like “don’t be too flowery” and “keep H2s concise.” Hsing said the more specific you can be, the better your output will be.
It’s not just about banging out better section titles, though. The AI suggestions Hsing gets incite new directions for a post she hadn’t considered yet. “I’m able to explore a broader range of angles, picking and choosing wording that might align better with the framing of my article,” she noted.
14. Scale product descriptions and ad copy
A single ecommerce website can have hundreds of products, each needing a concise description and advertising copy.
Gordon Donnelly, a multi-discipline marketer and SEO expert, said that’s one of his favorite use cases for AI. “I have a couple of affiliate/dropshipping sites, and ChatGPT is great for creating product descriptions and ads.”
Here’s an example of how Gordon prompts ChatGPT to zhuzh up a bland product description.


The key, said Gordon, is that you need to coach your AI tool with the right prompts to get it to say something interesting and useful. As he previously wrote, when prompting an AI tool, you should:
- Be specific
- Provide all the relevant information
- Follow up
The future of AI in marketing
We’re just scratching the surface of what AI can do for marketers. Current trends seem to be headed towards more automation, more complex customer-facing AI tools, and analytics that predict as well as review.
Celia also sees a comeuppance on the horizon for marketers trying to game the system with AI.
“There’s an ethical issue behind passing off AI-generated writing as your own, which is unfortunately becoming more popular a pastime as people chase a quick buck or a shortcut,” she said. “If you were to ask ChatGPT to generate the content of a blog post packed with SEO keywords, it would certainly be possible. But you risk not only false information making it in, but ethically not flagging the content as AI generated is by most considered plagiarism.”
Does that really matter to less-ethical marketers who only care about driving traffic? Celia said it should, in light of the recent volatility of Google SERPs.
“Well, it might end up doing more harm than good for your site’s SEO,” Celia warned. “Google recently announced updates to its algorithm that will make it more vigilant at removing low-quality content like much of what AI produces without human refinement. So, if ethics aren’t as much of a concern for you, a drop in your site’s rankings might be!”
PPC
A History of Google AdWords and Google Ads: Revolutionizing Digital Advertising & Marketing Since 2000

What started in 2000 as Google AdWords with just 350 advertisers has burgeoned into a comprehensive digital advertising platform, indispensable to digital marketing strategies worldwide. Now re-branded as Google Ads, it stands as a colossus, shaping the way businesses reach their target audience online.
If you’re your looking for a guide on how to use Google Adwords to advertise your business you might enjoy our Ultimate Guide to PPC.
The Conceptual Foundation of Google Ads
Before Google Adwords was launched, the online advertising landscape was vastly different. Traditional models dominated, and the concept of pay-per-click (PPC) advertising was still in its infancy. Google Ads introduced a game-changing model that allowed advertisers to pay only when a user clicked on their ad, offering a more performance-driven approach than ever before. This innovation not only maximized the efficiency of advertising budgets but also laid the groundwork for a more interactive and targeted advertising ecosystem.
But Google Adwords was not technically the first pay per click advertising platform. There was another PPC paid search platform known as Overture which launched before Adwords.
The Early Days of Online PPC Search Advertising
Before Google AdWords became synonymous with search advertising, there was Overture. Founded in 1998 as GoTo.com, Overture was the pioneer of the pay-per-click (PPC) advertising model. In February of that year, Jeffrey Brewer of Goto.com presented a pay per click search engine proof-of-concept to the TED conference in California.
This model was revolutionary, allowing advertisers to bid for placement in search results based on specific keywords, with the cost determined by the bid amount. This approach enabled advertisers to directly connect with potential customers actively searching for related information, products, or services online.
When Google introduced AdWords in 2000, the digital advertising landscape was ripe for innovation. Google’s entry with AdWords brought a new player into the field, initially offering a cost-per-impression model before shifting to Overture’s PPC model in 2002. This shift was a clear acknowledgment of the effectiveness of PPC advertising in connecting businesses with their target audiences in a measurable and cost-effective way.
Mutual Influence and Evolution
Overture felt Google’s approach was too similar to their’s and ended up filing a patent infringement lawsuit against Google, claiming that Google’s AdWords service violated its patents on PPC and bidding systems. The lawsuit was settled in 2004, with Google agreeing to issue 2.7 million shares to Yahoo (which had acquired Overture in 2003) in exchange for a perpetual license to the patents in question. This legal battle underscored the high stakes in the online advertising arena and the importance of intellectual property.
For the broader industry the relationship between Overture and Google AdWords is a classic example of competitive innovation, where the presence of each spurred the other to evolve and improve.
Google’s innovation wasn’t just in adopting the PPC model but also in enhancing it with a focus on ad relevance and targeting. Google introduced the Quality Score, a metric that determined ad placement not just on the bid amount but also on the relevance of the ad to the search query. This move forced Overture to refine its own algorithms and offerings to stay competitive, emphasizing the importance of ad quality and relevance.
Both companies played crucial roles in expanding and enriching the digital advertising ecosystem. Overture’s model laid the groundwork for keyword-based advertising, while Google AdWords introduced innovations that improved ad relevance and efficiency. These advancements helped attract more advertisers to online platforms, increasing the diversity and quality of ads presented to users.
The competition and innovations brought forth by Overture and Google laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in digital advertising. It influenced the development of advertising platforms on social media and other online channels, highlighting the importance of targeted advertising, relevance, and the user experience.

Early Challenges and Evolution of Google Adwords
The journey was not without its hurdles. As internet usage surged and Google’s popularity soared, the platform faced significant technical and scaling challenges. This period also saw the expansion of Adwords beyond search to include display advertising, marking the beginning of the Google Display Network.
Its rise to prominence in digital advertising can be attributed to several key factors:
1. Integration with Google Search
- Vast Reach: Google’s dominance as a search engine provided a vast audience for AdWords ads, offering advertisers unparalleled access to potential customers.
- Intent-Based Targeting: Ads on Google are shown based on user search queries, meaning that AdWords could deliver highly targeted advertising based on real-time intent, a significant advantage over traditional advertising mediums.
2. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Model
- Cost-Effectiveness: AdWords popularized the PPC model, where advertisers only pay when a user clicks on their ad. This efficiency made it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes, ensuring budget spend was tied directly to tangible results.
- Accessibility to Small Businesses: The PPC model leveled the playing field, allowing small businesses to compete with larger companies for ad space, as long as their ads were relevant and of high quality.
3. Continuous Innovation
- Quality Score and Ad Rank: Google introduced the Quality Score, a metric that assesses the relevance and quality of ads and their landing pages. This innovation ensured users saw more relevant ads, improving the user experience and increasing the likelihood of ad clicks, benefitting both advertisers and users. Ad Rank built on quality score and improved the quality of adverts for search users.
- Advanced Targeting Options: Over time, Google introduced sophisticated targeting options, including location targeting, demographic targeting, and later, remarketing. These features allowed advertisers to refine their audience with precision, improving the effectiveness of their campaigns.
4. Comprehensive Analytics and Tools
- Google Analytics Integration: AdWords’ seamless integration with Google Analytics provided advertisers with detailed insights into their ad performance and website traffic, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Robust Toolset: Tools like AdWords Editor and later, Google Ads Manager, allowed advertisers to manage and optimize their campaigns efficiently, saving time and enhancing campaign performance.
5. Expanding Beyond Search
- Google Display Network: AdWords expanded beyond search ads to include the Google Display Network, offering visual ads across millions of websites. This expansion allowed advertisers to reach users across different stages of the buying cycle, not just when they were searching for specific terms.
- YouTube and Mobile Advertising: The acquisition of YouTube and the growth of mobile advertising opened new channels for AdWords advertisers, tapping into video and the increasing use of smartphones for internet access.
6. A User-Centric Approach
- Enhancing User Experience: Google has consistently prioritized the user experience, refining its algorithms to display the most relevant ads and penalizing low-quality content. This focus on user satisfaction has kept users engaged and trusting in the Google ecosystem, indirectly benefiting advertisers by maintaining a high user base.
7. Global Reach and Local Relevance
- Language and Localization: AdWords supported multiple languages and localized advertising, making it a powerful tool for businesses targeting global markets or aiming for hyper-local advertising.

Key points in history and Milestones for Google Adwords
1. Launch and PPC Model Introduction (2000-2002)
- 2000: Google AdWords launches with a cost-per-thousand (CPM) impressions model.
- 2002: The introduction of the pay-per-click (PPC) model, significantly altering the online advertising landscape. This shift made advertising more accessible to businesses of all sizes, offering a more performance-oriented advertising solution.
2. Quality Score and Ad Rank Introduction (2005-2006)
- 2005: Google introduces the Quality Score, a critical component that would determine the cost and placement of ads based on relevance, landing page quality, and click-through rate (CTR).
- 2006: The Ad Rank formula, which decides the position of an ad on the search results page, now includes Quality Score along with the bid amount. This emphasized the importance of relevant, high-quality ads.
3. Expansion Beyond Search (2005-2008)
- 2005: Launch of the Google Display Network (GDN), allowing advertisers to place ads on a wide network of websites beyond Google’s search results.
- 2006: Introduction of local search ads, enabling businesses to target ads based on the geographical location of users.
- 2007: Acquisition of DoubleClick, enhancing ad serving and providing advertisers with sophisticated tools for managing display ads.
- 2008: Google introduces AdWords for Video, later integrated into YouTube, allowing for video-based advertising.
4. Mobile Advertising and Enhanced Campaigns (2010-2013)
- 2010: With the rise of smartphones, Google focuses on mobile advertising, introducing features that allow advertisers to target mobile device users.
- 2013: The launch of Enhanced Campaigns, making it easier for advertisers to target users across devices with the right ad type, size, and message based on user context, time of day, and device type.
5. Introduction of Machine Learning and Automation (2015-Present)
- 2015: Google starts incorporating machine learning into AdWords to improve ad targeting and bidding.
- 2016: Introduction of Smart Bidding, using machine learning to optimize bids for conversions.
- 2017: Launch of Google Ads Data Hub, offering advanced analysis and reporting features.
6. Rebranding to Google Ads (2018)
- 2018: Google AdWords is rebranded as Google Ads. This change reflects the platform’s growth beyond search to encompass a variety of advertising formats across Google’s vast array of services, including the Display Network, YouTube, and Google Maps.
7. Introduction of New Advertising Solutions and Platforms (2019-Present)
- 2019 and beyond: Continuous introduction of new ad types and formats, such as Discovery Ads and Gallery Ads, aimed at providing more engaging and visually appealing advertising options. Expansion of automation and AI-driven tools to optimize campaign performance.
These milestones highlight Google Ads’ evolution from a simple text-based advertising system to a comprehensive digital advertising platform. By continually integrating new technologies and adapting to changes in user behavior and advertiser needs, Google Ads has maintained its position as a leading platform in the digital advertising space.
Impact on Digital Marketing and Economy
Google Ads has undeniably shaped modern digital marketing strategies, enabling businesses to reach their audience with unprecedented precision and efficiency. Its impact extends beyond marketing, contributing significantly to economic growth by providing businesses of all sizes with accessible and effective advertising tools.
Challenges and Controversies
However, the platform has not been without its challenges and controversies, particularly concerning privacy and regulatory issues. Balancing advertising effectiveness with user privacy remains an ongoing challenge for Google Ads.
The Future of Google Ads
Looking ahead, Google Ads is expected to continue its trajectory of innovation, with automation, personalization, and integration with emerging digital platforms at the forefront. Its role in the digital marketing ecosystem remains as vital as ever, adapting to the changing needs of businesses and consumers alike.
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoHow 6 SEO Experts Are Navigating Google Update Chaos
-
 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoBing Search Testing Removing Cache Link From Search Results
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago60 Remote Work Stats to Know in 2024
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago10 WordPress Influencers to Follow in 2024 – WordPress.com News
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago8 Best WordPress Migration Services (Compared)
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoFeeling Stuck: What to Do When You Don’t Know What to Do
-

 SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
SEARCHENGINES4 days agoMore Google March 2024 Core Update Ranking Volatility
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Explains How It Chooses Canonical Webpages