SEO
Everything You Need To Know

Google has just released Bard, its answer to ChatGPT, and users are getting to know it to see how it compares to OpenAI’s artificial intelligence-powered chatbot.
The name ‘Bard’ is purely marketing-driven, as there are no algorithms named Bard, but we do know that the chatbot is powered by LaMDA.
Here is everything we know about Bard so far and some interesting research that may offer an idea of the kind of algorithms that may power Bard.
What Is Google Bard?
Bard is an experimental Google chatbot that is powered by the LaMDA large language model.
It’s a generative AI that accepts prompts and performs text-based tasks like providing answers and summaries and creating various forms of content.
Bard also assists in exploring topics by summarizing information found on the internet and providing links for exploring websites with more information.
Why Did Google Release Bard?
Google released Bard after the wildly successful launch of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, which created the perception that Google was falling behind technologically.
ChatGPT was perceived as a revolutionary technology with the potential to disrupt the search industry and shift the balance of power away from Google search and the lucrative search advertising business.
On December 21, 2022, three weeks after the launch of ChatGPT, the New York Times reported that Google had declared a “code red” to quickly define its response to the threat posed to its business model.
Forty-seven days after the code red strategy adjustment, Google announced the launch of Bard on February 6, 2023.
What Was The Issue With Google Bard?
The announcement of Bard was a stunning failure because the demo that was meant to showcase Google’s chatbot AI contained a factual error.
The inaccuracy of Google’s AI turned what was meant to be a triumphant return to form into a humbling pie in the face.
Google’s shares subsequently lost a hundred billion dollars in market value in a single day, reflecting a loss of confidence in Google’s ability to navigate the looming era of AI.
How Does Google Bard Work?
Bard is powered by a “lightweight” version of LaMDA.
LaMDA is a large language model that is trained on datasets consisting of public dialogue and web data.
There are two important factors related to the training described in the associated research paper, which you can download as a PDF here: LaMDA: Language Models for Dialog Applications (read the abstract here).
- A. Safety: The model achieves a level of safety by tuning it with data that was annotated by crowd workers.
- B. Groundedness: LaMDA grounds itself factually with external knowledge sources (through information retrieval, which is search).
The LaMDA research paper states:
“…factual grounding, involves enabling the model to consult external knowledge sources, such as an information retrieval system, a language translator, and a calculator.
We quantify factuality using a groundedness metric, and we find that our approach enables the model to generate responses grounded in known sources, rather than responses that merely sound plausible.”
Google used three metrics to evaluate the LaMDA outputs:
- Sensibleness: A measurement of whether an answer makes sense or not.
- Specificity: Measures if the answer is the opposite of generic/vague or contextually specific.
- Interestingness: This metric measures if LaMDA’s answers are insightful or inspire curiosity.
All three metrics were judged by crowdsourced raters, and that data was fed back into the machine to keep improving it.
The LaMDA research paper concludes by stating that crowdsourced reviews and the system’s ability to fact-check with a search engine were useful techniques.
Google’s researchers wrote:
“We find that crowd-annotated data is an effective tool for driving significant additional gains.
We also find that calling external APIs (such as an information retrieval system) offers a path towards significantly improving groundedness, which we define as the extent to which a generated response contains claims that can be referenced and checked against a known source.”
How Is Google Planning To Use Bard In Search?
The future of Bard is currently envisioned as a feature in search.
Google’s announcement in February was insufficiently specific on how Bard would be implemented.
The key details were buried in a single paragraph close to the end of the blog announcement of Bard, where it was described as an AI feature in search.
That lack of clarity fueled the perception that Bard would be integrated into search, which was never the case.
Google’s February 2023 announcement of Bard states that Google will at some point integrate AI features into search:
“Soon, you’ll see AI-powered features in Search that distill complex information and multiple perspectives into easy-to-digest formats, so you can quickly understand the big picture and learn more from the web: whether that’s seeking out additional perspectives, like blogs from people who play both piano and guitar, or going deeper on a related topic, like steps to get started as a beginner.
These new AI features will begin rolling out on Google Search soon.”
It’s clear that Bard is not search. Rather, it is intended to be a feature in search and not a replacement for search.
What Is A Search Feature?
A feature is something like Google’s Knowledge Panel, which provides knowledge information about notable people, places, and things.
Google’s “How Search Works” webpage about features explains:
“Google’s search features ensure that you get the right information at the right time in the format that’s most useful to your query.
Sometimes it’s a webpage, and sometimes it’s real-world information like a map or inventory at a local store.”
In an internal meeting at Google (reported by CNBC), employees questioned the use of Bard in search.
One employee pointed out that large language models like ChatGPT and Bard are not fact-based sources of information.
The Google employee asked:
“Why do we think the big first application should be search, which at its heart is about finding true information?”
Jack Krawczyk, the product lead for Google Bard, answered:
“I just want to be very clear: Bard is not search.”
At the same internal event, Google’s Vice President of Engineering for Search, Elizabeth Reid, reiterated that Bard is not search.
She said:
“Bard is really separate from search…”
What we can confidently conclude is that Bard is not a new iteration of Google search. It is a feature.
Bard Is An Interactive Method For Exploring Topics
Google’s announcement of Bard was fairly explicit that Bard is not search. This means that, while search surfaces links to answers, Bard helps users investigate knowledge.
The announcement explains:
“When people think of Google, they often think of turning to us for quick factual answers, like ‘how many keys does a piano have?’
But increasingly, people are turning to Google for deeper insights and understanding – like, ‘is the piano or guitar easier to learn, and how much practice does each need?’
Learning about a topic like this can take a lot of effort to figure out what you really need to know, and people often want to explore a diverse range of opinions or perspectives.”
It may be helpful to think of Bard as an interactive method for accessing knowledge about topics.
Bard Samples Web Information
The problem with large language models is that they mimic answers, which can lead to factual errors.
The researchers who created LaMDA state that approaches like increasing the size of the model can help it gain more factual information.
But they noted that this approach fails in areas where facts are constantly changing during the course of time, which researchers refer to as the “temporal generalization problem.”
Freshness in the sense of timely information cannot be trained with a static language model.
The solution that LaMDA pursued was to query information retrieval systems. An information retrieval system is a search engine, so LaMDA checks search results.
This feature from LaMDA appears to be a feature of Bard.
The Google Bard announcement explains:
“Bard seeks to combine the breadth of the world’s knowledge with the power, intelligence, and creativity of our large language models.
It draws on information from the web to provide fresh, high-quality responses.”
LaMDA and (possibly by extension) Bard achieve this with what is called the toolset (TS).
The toolset is explained in the LaMDA researcher paper:
“We create a toolset (TS) that includes an information retrieval system, a calculator, and a translator.
TS takes a single string as input and outputs a list of one or more strings. Each tool in TS expects a string and returns a list of strings.
For example, the calculator takes “135+7721”, and outputs a list containing [“7856”]. Similarly, the translator can take “hello in French” and output [‘Bonjour’].
Finally, the information retrieval system can take ‘How old is Rafael Nadal?’, and output [‘Rafael Nadal / Age / 35’].
The information retrieval system is also capable of returning snippets of content from the open web, with their corresponding URLs.
The TS tries an input string on all of its tools, and produces a final output list of strings by concatenating the output lists from every tool in the following order: calculator, translator, and information retrieval system.
A tool will return an empty list of results if it can’t parse the input (e.g., the calculator cannot parse ‘How old is Rafael Nadal?’), and therefore does not contribute to the final output list.”
Here’s a Bard response with a snippet from the open web:
 Screenshot of a Google Bard Chat, March 2023
Screenshot of a Google Bard Chat, March 2023Conversational Question-Answering Systems
There are no research papers that mention the name “Bard.”
However, there is quite a bit of recent research related to AI, including by scientists associated with LaMDA, that may have an impact on Bard.
The following doesn’t claim that Google is using these algorithms. We can’t say for certain that any of these technologies are used in Bard.
The value in knowing about these research papers is in knowing what is possible.
The following are algorithms relevant to AI-based question-answering systems.
One of the authors of LaMDA worked on a project that’s about creating training data for a conversational information retrieval system.
You can download the 2022 research paper as a PDF here: Dialog Inpainting: Turning Documents into Dialogs (and read the abstract here).
The problem with training a system like Bard is that question-and-answer datasets (like datasets comprised of questions and answers found on Reddit) are limited to how people on Reddit behave.
It doesn’t encompass how people outside of that environment behave and the kinds of questions they would ask, and what the correct answers to those questions would be.
The researchers explored creating a system read webpages, then used a “dialog inpainter” to predict what questions would be answered by any given passage within what the machine was reading.
A passage in a trustworthy Wikipedia webpage that says, “The sky is blue,” could be turned into the question, “What color is the sky?”
The researchers created their own dataset of questions and answers using Wikipedia and other webpages. They called the datasets WikiDialog and WebDialog.
- WikiDialog is a set of questions and answers derived from Wikipedia data.
- WebDialog is a dataset derived from webpage dialog on the internet.
These new datasets are 1,000 times larger than existing datasets. The importance of that is it gives conversational language models an opportunity to learn more.
The researchers reported that this new dataset helped to improve conversational question-answering systems by over 40%.
The research paper describes the success of this approach:
“Importantly, we find that our inpainted datasets are powerful sources of training data for ConvQA systems…
When used to pre-train standard retriever and reranker architectures, they advance state-of-the-art across three different ConvQA retrieval benchmarks (QRECC, OR-QUAC, TREC-CAST), delivering up to 40% relative gains on standard evaluation metrics…
Remarkably, we find that just pre-training on WikiDialog enables strong zero-shot retrieval performance—up to 95% of a finetuned retriever’s performance—without using any in-domain ConvQA data. “
Is it possible that Google Bard was trained using the WikiDialog and WebDialog datasets?
It’s difficult to imagine a scenario where Google would pass on training a conversational AI on a dataset that is over 1,000 times larger.
But we don’t know for certain because Google doesn’t often comment on its underlying technologies in detail, except on rare occasions like for Bard or LaMDA.
Large Language Models That Link To Sources
Google recently published an interesting research paper about a way to make large language models cite the sources for their information. The initial version of the paper was published in December 2022, and the second version was updated in February 2023.
This technology is referred to as experimental as of December 2022.
You can download the PDF of the paper here: Attributed Question Answering: Evaluation and Modeling for Attributed Large Language Models (read the Google abstract here).
The research paper states the intent of the technology:
“Large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive results while requiring little or no direct supervision.
Further, there is mounting evidence that LLMs may have potential in information-seeking scenarios.
We believe the ability of an LLM to attribute the text that it generates is likely to be crucial in this setting.
We formulate and study Attributed QA as a key first step in the development of attributed LLMs.
We propose a reproducible evaluation framework for the task and benchmark a broad set of architectures.
We take human annotations as a gold standard and show that a correlated automatic metric is suitable for development.
Our experimental work gives concrete answers to two key questions (How to measure attribution?, and How well do current state-of-the-art methods perform on attribution?), and give some hints as to how to address a third (How to build LLMs with attribution?).”
This kind of large language model can train a system that can answer with supporting documentation that, theoretically, assures that the response is based on something.
The research paper explains:
“To explore these questions, we propose Attributed Question Answering (QA). In our formulation, the input to the model/system is a question, and the output is an (answer, attribution) pair where answer is an answer string, and attribution is a pointer into a fixed corpus, e.g., of paragraphs.
The returned attribution should give supporting evidence for the answer.”
This technology is specifically for question-answering tasks.
The goal is to create better answers – something that Google would understandably want for Bard.
- Attribution allows users and developers to assess the “trustworthiness and nuance” of the answers.
- Attribution allows developers to quickly review the quality of the answers since the sources are provided.
One interesting note is a new technology called AutoAIS that strongly correlates with human raters.
In other words, this technology can automate the work of human raters and scale the process of rating the answers given by a large language model (like Bard).
The researchers share:
“We consider human rating to be the gold standard for system evaluation, but find that AutoAIS correlates well with human judgment at the system level, offering promise as a development metric where human rating is infeasible, or even as a noisy training signal. “
This technology is experimental; it’s probably not in use. But it does show one of the directions that Google is exploring for producing trustworthy answers.
Research Paper On Editing Responses For Factuality
Lastly, there’s a remarkable technology developed at Cornell University (also dating from the end of 2022) that explores a different way to source attribution for what a large language model outputs and can even edit an answer to correct itself.
Cornell University (like Stanford University) licenses technology related to search and other areas, earning millions of dollars per year.
It’s good to keep up with university research because it shows what is possible and what is cutting-edge.
You can download a PDF of the paper here: RARR: Researching and Revising What Language Models Say, Using Language Models (and read the abstract here).
The abstract explains the technology:
“Language models (LMs) now excel at many tasks such as few-shot learning, question answering, reasoning, and dialog.
However, they sometimes generate unsupported or misleading content.
A user cannot easily determine whether their outputs are trustworthy or not, because most LMs do not have any built-in mechanism for attribution to external evidence.
To enable attribution while still preserving all the powerful advantages of recent generation models, we propose RARR (Retrofit Attribution using Research and Revision), a system that 1) automatically finds attribution for the output of any text generation model and 2) post-edits the output to fix unsupported content while preserving the original output as much as possible.
…we find that RARR significantly improves attribution while otherwise preserving the original input to a much greater degree than previously explored edit models.
Furthermore, the implementation of RARR requires only a handful of training examples, a large language model, and standard web search.”
How Do I Get Access To Google Bard?
Google is currently accepting new users to test Bard, which is currently labeled as experimental. Google is rolling out access for Bard here.
 Screenshot from bard.google.com, March 2023
Screenshot from bard.google.com, March 2023Google is on the record saying that Bard is not search, which should reassure those who feel anxiety about the dawn of AI.
We are at a turning point that is unlike any we’ve seen in, perhaps, a decade.
Understanding Bard is helpful to anyone who publishes on the web or practices SEO because it’s helpful to know the limits of what is possible and the future of what can be achieved.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Whyredphotographor/Shutterstock
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
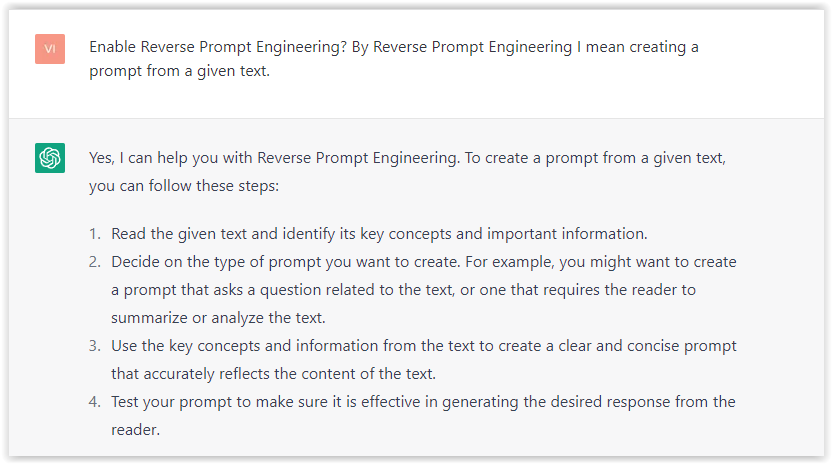
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
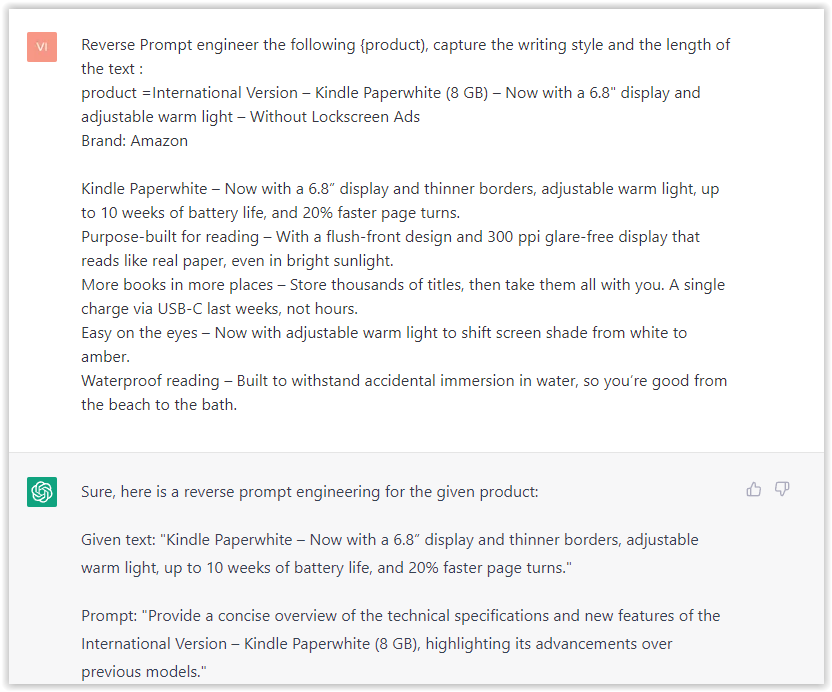
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress















