SEO
How to Create a Content Plan in 5 Easy Steps
Content planning is the process of deciding what you’ll publish and when. Its main role is to prioritize content creation based on a marketing and content strategy.
If you regularly create content (as you probably should), you need proper content planning to prioritize the creation based on what makes the most sense for your business at a given time. That’s because the resources required to realize content ideas that you come up with or are thrown at you usually far exceed the resources you have.
In this guide to content planning, we’ll go through five steps.
Do you want to create a content plan for your social media accounts, newsletter, YouTube channel, or your own website? You can do that for all of them—but you should do so separately. That’s because each channel has its own objectives, and there are many ways to achieve them.
Some channels also don’t necessarily require their own content plans. For example, it is enough for most businesses to schedule social media posts a few days ahead of time in a tool like MeetEdgar, and there’s rarely a need for high-effort plans.
Generally speaking, the more resources you invest into creating the content, the more you should invest into efforts to plan it properly. This will naturally have the biggest payoff for long-form articles, blog posts, landing pages, and videos.
For this reason, we’ll mainly focus on content planning for websites here. That’s what most people are looking to learn anyway. Let’s dig into it.
Having a sizeable list of topics you’ll like to cover someday is essential to content planning. How else will you be able to prioritize what’s best to work on at a given time? We want the list to minimize the opportunity cost of not covering highly valuable pieces of content that you’re not aware of.
This is when keyword research comes into play. It’s the process of understanding the language your target customers use when searching for your products, services, and content. It then involves analyzing, comparing, and prioritizing the best keyword opportunities for your website.
Keyword research is the best method to find out which topics are popular with your audience. It also allows you to later prioritize the list based on provided metrics (more on that later).
For example, we can brainstorm a few seed keywords that characterize the niches we’re in. Then plug the keywords into a keyword research tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. Here’s what you’ll be looking at:

See the check marks on the left of each keyword? That means the keyword is part of a list that you created. It’s an easy way to keep all relevant keywords in one place. Here’s what expanding on a “coffee” keyword list looks like:

The process of discovering and selecting relevant keywords will take hours, but it’s well worth it. After you’re done, export your keyword list to Excel or Google Sheets because you’ll have to add your own input besides all the Ahrefs-provided metrics. Here’s an example from a subsection of our own list of topics:

Not everything revolves around getting search traffic that converts into customers, though. Of course, that’s the most common SEO goal. But you can write about topics with no or little search demand that can be highly valuable for SEO too. I’m talking about link baits: content designed to attract backlinks that can pass their link equity to your other pages.
You can find what type of content gets the most backlinks in your niche by looking up any website in the Best by links report in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. What works the best in our case is unique data studies:

This is where you let your creativity shine. You can even plan content pieces that you want to go viral as part of a PR campaign. Those naturally have their SEO benefits in the form of links and mentions too.
Now, you may be thinking that I’m too focused on SEO. Yes—but that’s because search engines are usually the best, constant source of traffic.
But there are cases where it makes sense to publish content without any SEO goal in mind. Think about important announcements or product updates, for example. We have a separate section on our blog for these, and they’re as important as any other part of the blog:

When you’re done with keyword research, you’ll find that 2 out of 3 metrics we’ll be talking about here are already available to you in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer: Traffic Potential (TP) and Keyword Difficulty (KD). The last metric you need to fill in manually is something we call “business potential.”
Let’s look at each one of them.
Traffic Potential (TP)
Just targeting a keyword with high search volume isn’t enough. You need to look at the overall TP because one piece of content can rank for thousands of different keywords.
For example, the keyword “how to make cold brew coffee” has a search volume of 29K in the U.S. But its TP is estimated to be 93K, and the main keyword responsible for most of that traffic is “cold brew”:

Looking at the box above, you may have already guessed how we calculate the TP metric. It’s the sum of organic traffic that the #1 ranking page for your target keyword receives from all the keywords that it ranks for.
Consider it a search volume on steroids.
Keyword Difficulty (KD)
This metric is an estimate of how difficult it is to rank for a given keyword on a scale from 0 to 100 based on the strength of link profiles of the top-ranking pages. The lower the score, the easier it is to rank at the top for the keyword.
If you were to target the “cold brew” keyword from above, you’d likely need quite a lot of backlinks to have a chance of ranking in the top 10 search results:

Business potential (BP)
To attract the right audience that drives conversions, you need to focus on writing content that highlights your product as a solution. To quantify the degree to which you can pitch your own products, we came up with this BP metric. Here’s how we work with it at Ahrefs:

Now comes the most important part of content planning: prioritization. Unless you’re in a narrow niche, you’ll likely have hundreds, if not thousands, of content ideas if you follow our process.
Generally speaking, the best keywords (topics) to target are those with high traffic, high business potential, and low keyword difficulty. In reality, you’ll almost never find such opportunities, so you’ll have to make compromises.
The easiest compromises are made on the KD metric. This is because, in the long term, you’ll likely want to cover pretty much every topic with solid TP and BP.
Also, the sooner you tackle high-KD topics, the more time you have to accumulate the links you need organically. That’s because the content can rank for long-tail keywords, you point more internal links to it over time, or you get eyeballs on it through content distribution.
As for TP and BP, we can often see an inverse proportionality for these two metrics. Usually, the more search demand there is for a given non-branded topic, the further away those searchers are from making a purchase.
The distance from making a purchase is portrayed in this customer journey illustration:

Someone searching for a high-TP topic like “what are backlinks” isn’t likely ready to become our customer yet. But that person may later search for something like “link building tools,” which has lower TP but much higher BP.
The best solution for this lies in a balance between everything. If you plan your content according to your customers’ journeys, you’ll have a nice mix in the end. We give the highest priority to BP. So if that and all other things are equal, we then select topics based on lower KD and higher TP.
A good approach may also be to focus on one topic at a time, such as the “link building” example from above. We have 42 articles on this topic on our blog as of now, and many of them drive a good amount of search traffic:

This is relevant to creating topic clusters, also known as content hubs, which are sometimes used as an effective SEO tactic:

Now that you’ve picked topics to focus on first, it’s time to put them into a content calendar. It’s a system that organizes, manages, and schedules content production to give you an overview of everything that will be published in a specific time frame. Here’s a sneak peek of our own content calendar:

It’s created in Notion, with each card in the calendar structured like this:

I recommend planning content one to three months ahead. If you’re just starting out with everything, don’t sweat it if you can’t meet your initial plans and deadlines. It takes time to get used to estimates of content production based on your resources (writers, SEOs, designers, etc.).
Here’s one thing to point out. Choosing quality over quantity is usually the right decision, so don’t rush it at all costs. Creating great content takes a lot of time, so adjust accordingly.
Recommended reading: How to Create a Content Calendar That Works for You
Final thoughts
Content planning isn’t rocket science and is something you should do at all costs if you’re serious about content marketing. Your prioritization criteria will likely evolve over time; you’ll add more keywords, topics, etc. Content plans aren’t one and done.
As you publish more and more content, you’ll inevitably have to take into account updating older content as well. You’ll get to the point where doing so will give you a higher return than creating new pieces of content.
At Ahrefs, we’re exactly at that stage. And as you can see, 20% of our articles published this year so far (29 out of 144) are republished posts:

Got any questions? Ping me on Twitter.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
SEO
Google Confirms Links Are Not That Important

Google’s Gary Illyes confirmed at a recent search marketing conference that Google needs very few links, adding to the growing body of evidence that publishers need to focus on other factors. Gary tweeted confirmation that he indeed say those words.
Background Of Links For Ranking
Links were discovered in the late 1990’s to be a good signal for search engines to use for validating how authoritative a website is and then Google discovered soon after that anchor text could be used to provide semantic signals about what a webpage was about.
One of the most important research papers was Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment by Jon M. Kleinberg, published around 1998 (link to research paper at the end of the article). The main discovery of this research paper is that there is too many web pages and there was no objective way to filter search results for quality in order to rank web pages for a subjective idea of relevance.
The author of the research paper discovered that links could be used as an objective filter for authoritativeness.
Kleinberg wrote:
“To provide effective search methods under these conditions, one needs a way to filter, from among a huge collection of relevant pages, a small set of the most “authoritative” or ‘definitive’ ones.”
This is the most influential research paper on links because it kick-started more research on ways to use links beyond as an authority metric but as a subjective metric for relevance.
Objective is something factual. Subjective is something that’s closer to an opinion. The founders of Google discovered how to use the subjective opinions of the Internet as a relevance metric for what to rank in the search results.
What Larry Page and Sergey Brin discovered and shared in their research paper (The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine – link at end of this article) was that it was possible to harness the power of anchor text to determine the subjective opinion of relevance from actual humans. It was essentially crowdsourcing the opinions of millions of website expressed through the link structure between each webpage.
What Did Gary Illyes Say About Links In 2024?
At a recent search conference in Bulgaria, Google’s Gary Illyes made a comment about how Google doesn’t really need that many links and how Google has made links less important.
Patrick Stox tweeted about what he heard at the search conference:
” ‘We need very few links to rank pages… Over the years we’ve made links less important.’ @methode #serpconf2024″
Google’s Gary Illyes tweeted a confirmation of that statement:
“I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that”
Why Links Matter Less
The initial state of anchor text when Google first used links for ranking purposes was absolutely non-spammy, which is why it was so useful. Hyperlinks were primarily used as a way to send traffic from one website to another website.
But by 2004 or 2005 Google was using statistical analysis to detect manipulated links, then around 2004 “powered-by” links in website footers stopped passing anchor text value, and by 2006 links close to the words “advertising” stopped passing link value, links from directories stopped passing ranking value and by 2012 Google deployed a massive link algorithm called Penguin that destroyed the rankings of likely millions of websites, many of which were using guest posting.
The link signal eventually became so bad that Google decided in 2019 to selectively use nofollow links for ranking purposes. Google’s Gary Illyes confirmed that the change to nofollow was made because of the link signal.
Google Explicitly Confirms That Links Matter Less
In 2023 Google’s Gary Illyes shared at a PubCon Austin that links were not even in the top 3 of ranking factors. Then in March 2024, coinciding with the March 2024 Core Algorithm Update, Google updated their spam policies documentation to downplay the importance of links for ranking purposes.
The documentation previously said:
“Google uses links as an important factor in determining the relevancy of web pages.”
The update to the documentation that mentioned links was updated to remove the word important.
Links are not just listed as just another factor:
“Google uses links as a factor in determining the relevancy of web pages.”
At the beginning of April Google’s John Mueller advised that there are more useful SEO activities to engage on than links.
Mueller explained:
“There are more important things for websites nowadays, and over-focusing on links will often result in you wasting your time doing things that don’t make your website better overall”
Finally, Gary Illyes explicitly said that Google needs very few links to rank webpages and confirmed it.
I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (so official, trust me) (@methode) April 19, 2024
Why Google Doesn’t Need Links
The reason why Google doesn’t need many links is likely because of the extent of AI and natural language undertanding that Google uses in their algorithms. Google must be highly confident in its algorithm to be able to explicitly say that they don’t need it.
Way back when Google implemented the nofollow into the algorithm there were many link builders who sold comment spam links who continued to lie that comment spam still worked. As someone who started link building at the very beginning of modern SEO (I was the moderator of the link building forum at the #1 SEO forum of that time), I can say with confidence that links have stopped playing much of a role in rankings beginning several years ago, which is why I stopped about five or six years ago.
Read the research papers
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment – Jon M. Kleinberg (PDF)
The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine
Featured Image by Shutterstock/RYO Alexandre
SEO
How to Become an SEO Lead (10 Tips That Advanced My Career)

A few years ago, I was an SEO Lead managing enterprise clients’ SEO campaigns. It’s a senior role and takes a lot of work to get there. So how can you do it, too?
In this article, I’ll share ten tips to help you climb the next rung in the SEO career ladder.
Helping new hires in the SEO team is important if you want to become an SEO Lead. It gives you the experience to develop your leadership skills, and you can also share your knowledge and help others learn and grow.
It demonstrates you can explain things well, provide helpful feedback, and improve the team’s standard of work. It shows you care about the team’s success, which is essential for leaders. Bosses look for someone who can do their work well and help everyone improve.
Here are some practical examples of things I did early in my career to help mentor junior members of the team that you can try as well:
- Hold “lunch and learn” sessions on topics related to SEO and share case studies of work you have done
- Create process documents for the junior members of the team to show them how to complete specific tasks related to your work
- Compile lists of your favorite tools and resources for junior members of the team
- Create onboarding documents for interns joining the company
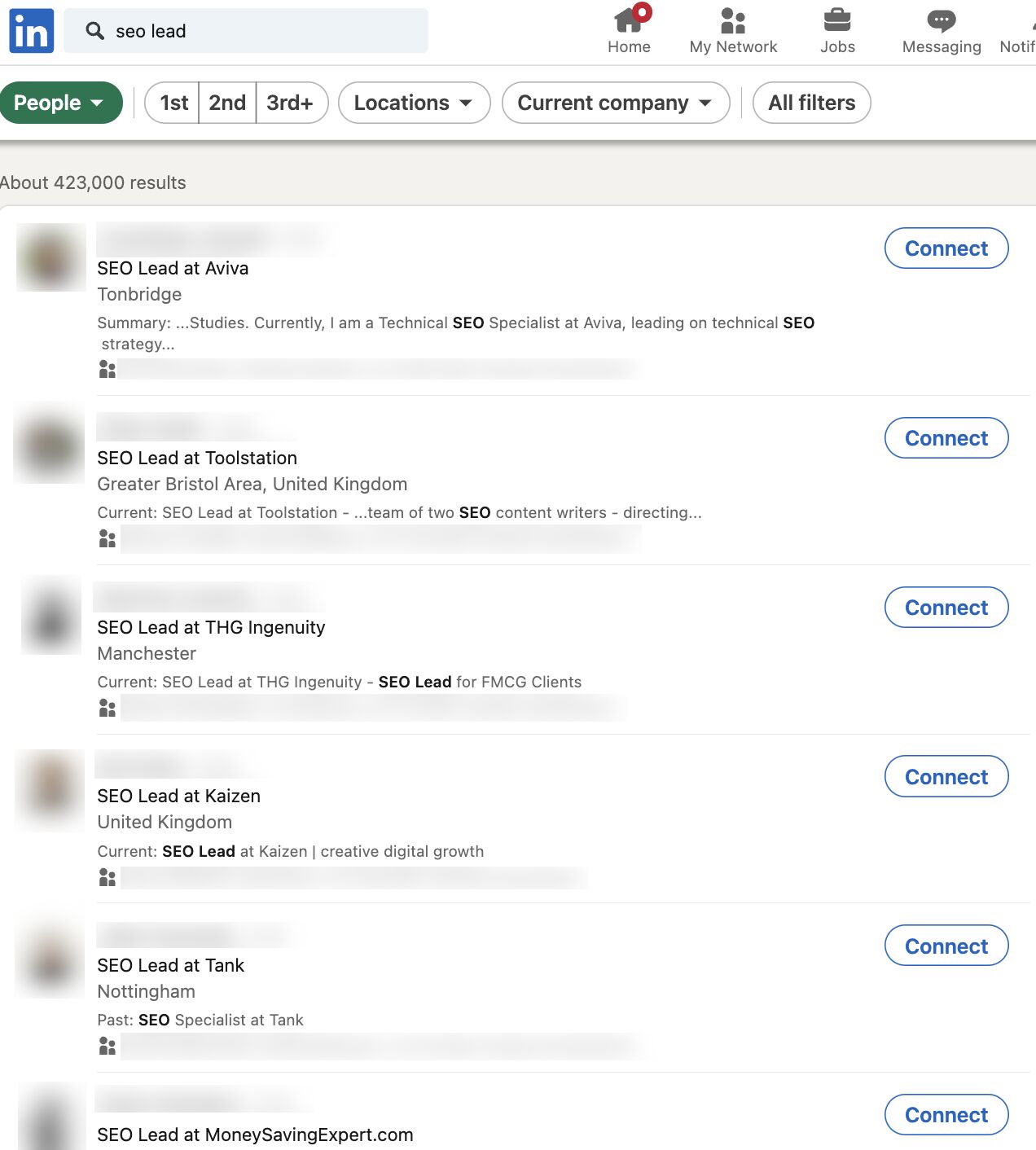
Wouldn’t it be great if you could look at every single SEO Lead’s resume? Well, you already can. You can infer ~70% of any SEO’s resume by spying on their LinkedIn and social media channels.
Type “SEO Lead” into LinkedIn and see what you get.
Tip
Look for common career patterns of the SEOs you admire in the industry.
I used this method to understand how my favorite SEOs and people at my company navigated their way from a junior role to a senior role.
For example, when the Head of SEO at the time Kirsty Hulse, joined my team, I added her on LinkedIn and realized that if I wanted to follow in her footsteps, I’d need to start by getting the role of SEO Manager to stand any possible chance of leading SEO campaigns like she was.
The progression in my company was from SEO Executive to Senior SEO Executive (Junior roles in London, UK), but as an outsider coming into the company, Kirsty showed me that it was possible to jump straight to SEO Manager given the right circumstances.
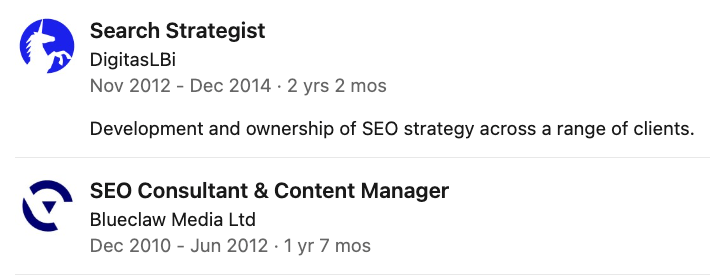

Using Kirsty’s and other SEOs’ profiles, I decided that the next step in my career needed to be SEO Manager, and at some point, I needed to get some experience with a bigger media agency so I could work my way up to leading an SEO campaign with bigger brands.
Sadly, you can’t just rock up to a monthly meeting and start leading a big brand SEO campaign. You’ll need to prove yourself to your line manager first. So how can you do this?
Here’s what I’d suggest you do:
- Create a strong track record with smaller companies.
- Obsessively share your wins with your company, so that senior management will already know you can deliver.
- At your performance review, tell your line manager that you want to work on bigger campaigns and take on more responsibility.
If there’s no hope of working with a big brand at your current job, you might need to consider looking for a new job where there is a recognizable brand. This was what I realized I needed to do if I wanted to get more experience.
Tip
Get recruiters on LinkedIn to give you the inside scoop on which brands or agencies are hiring. Ask them if you have any skill gaps on your resume that could prevent you from getting a job with these companies.
Being critical of your skill gaps can be hard to do. I found the best way to identify them early in my career was to ask other people—specifically recruiters. They had knowledge of the industry and were usually fairly honest as to what I needed to improve.
From this, I realized I lacked experience working with other teams—like PR, social, and development teams. As a junior SEO, your mind is focused 99% on doing SEO, but when you become more senior, your integration with other teams is important to your success.
For this reason, I’d suggest that aspiring SEO Leads should have a good working knowledge of how other teams outside of SEO operate. If you take the time to do this, it will pay dividends later in your career:
- If there are other teams in your company, ask if you can do some onboarding training with them.
- Get to know other team leads within your company and learn how they work.
- Take training courses to learn the fundamentals of other disciplines that complement SEO, such as Python, SQL, or content creation.
Sometimes, employers use skill gaps to pay you less, so it’s crucial to get the skills you need early on…

Examples of other skill gaps I’ve noticed include:
Tip
If you think you have a lot of skill gaps, then you can brush up your skills with our SEO academy. Once you’ve completed that, you can fast-track your knowledge by taking a course like Tom Critchlow’s SEO MBA, or you can try to develop these skills through your job.
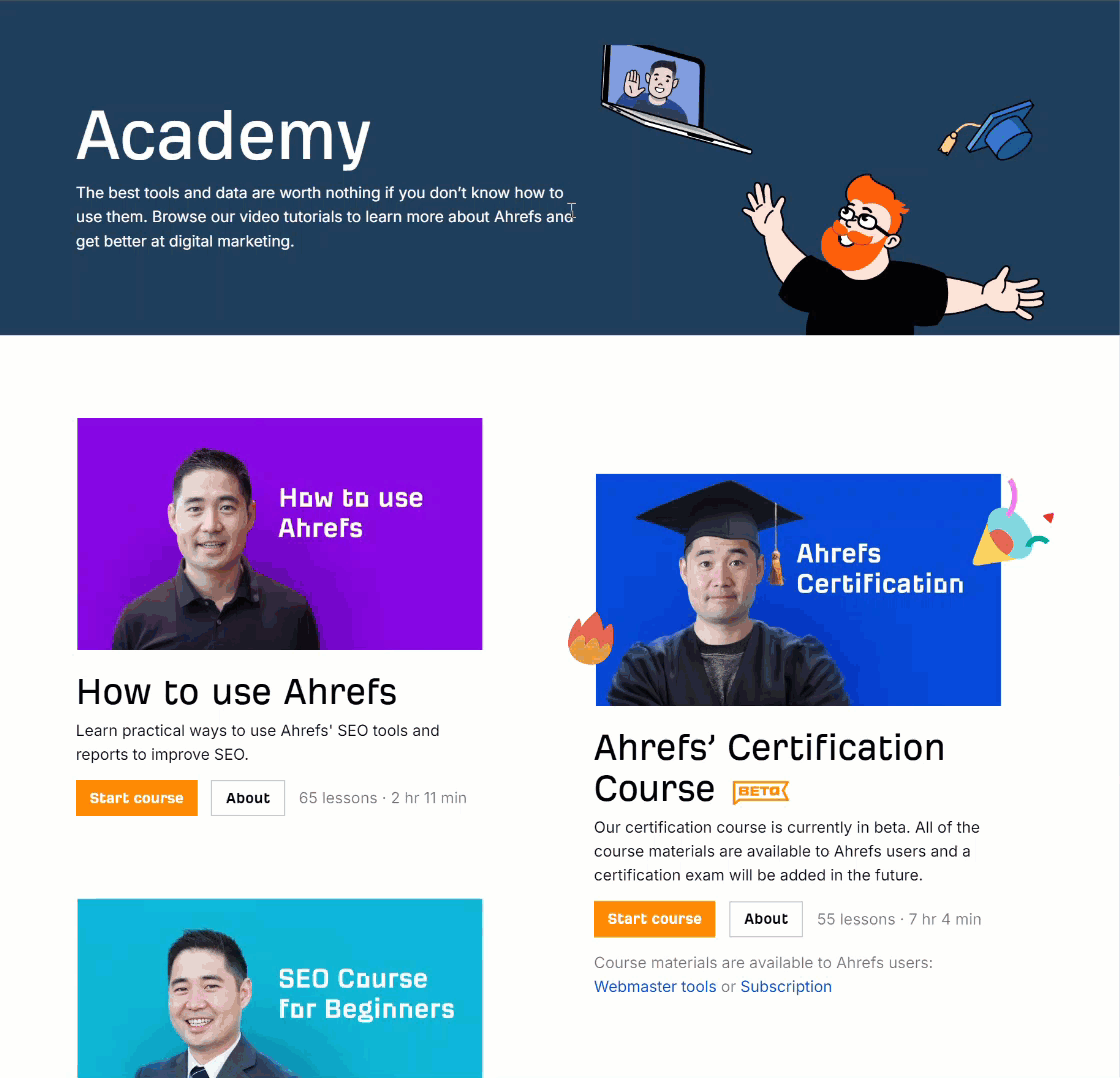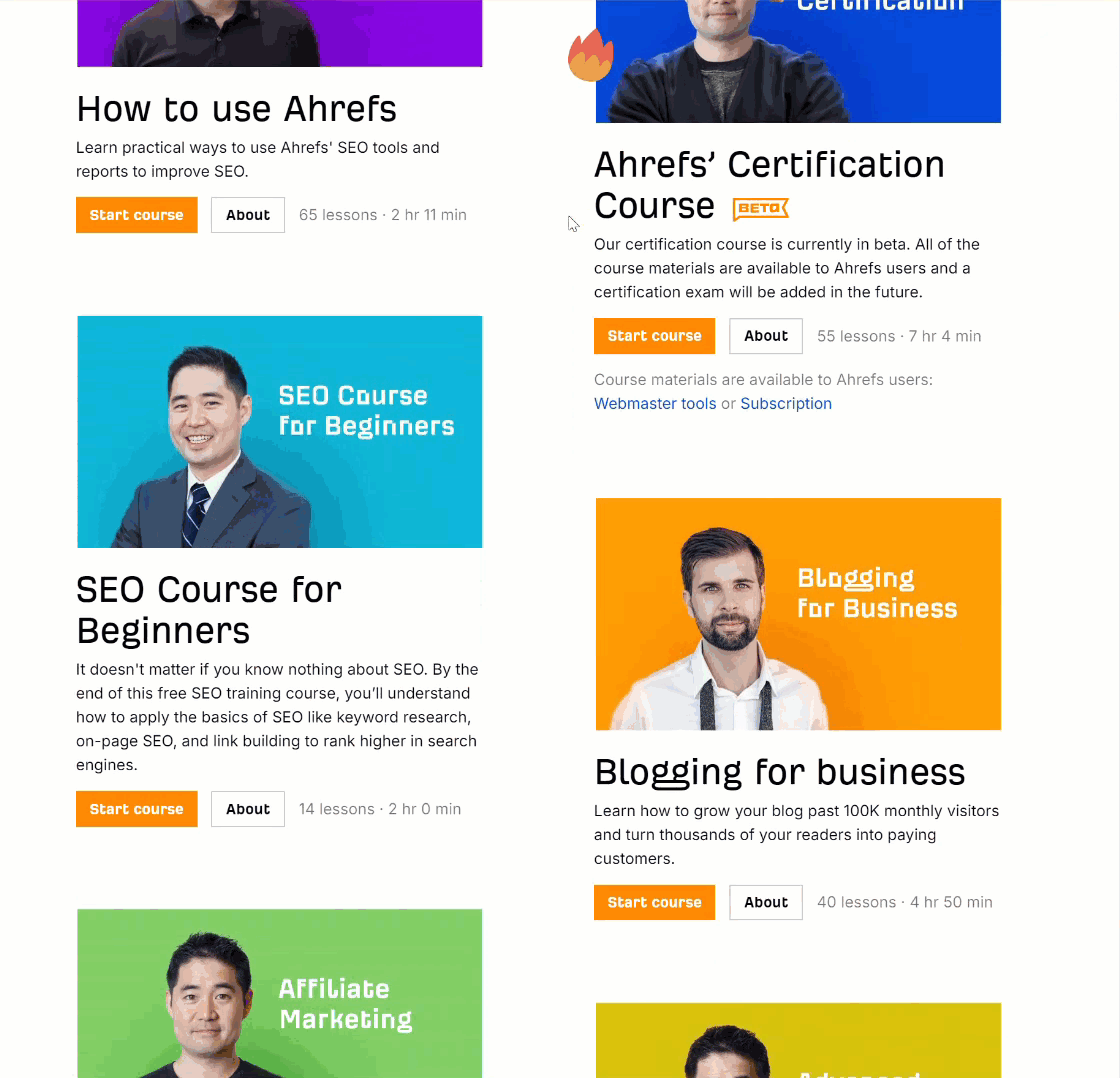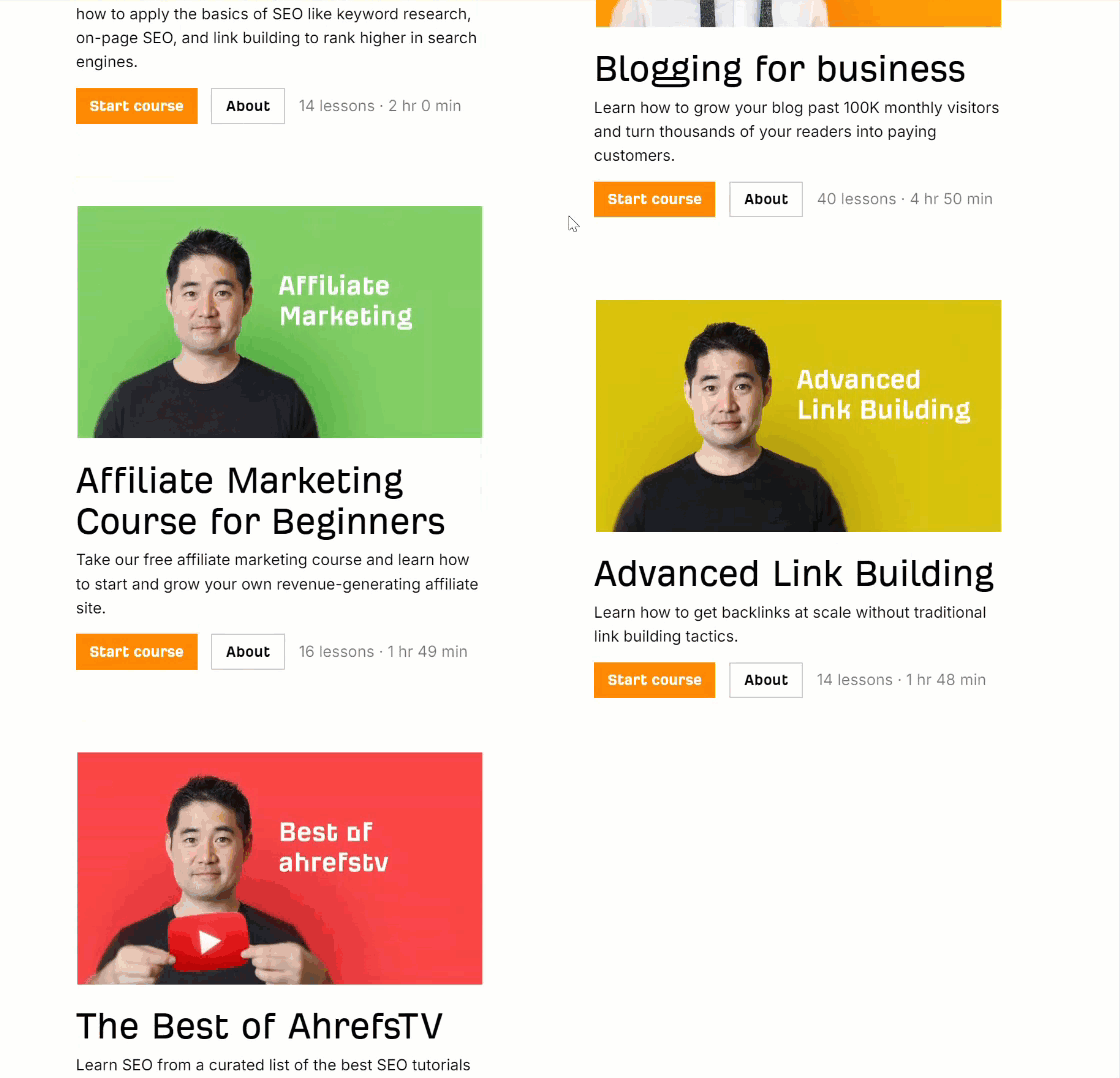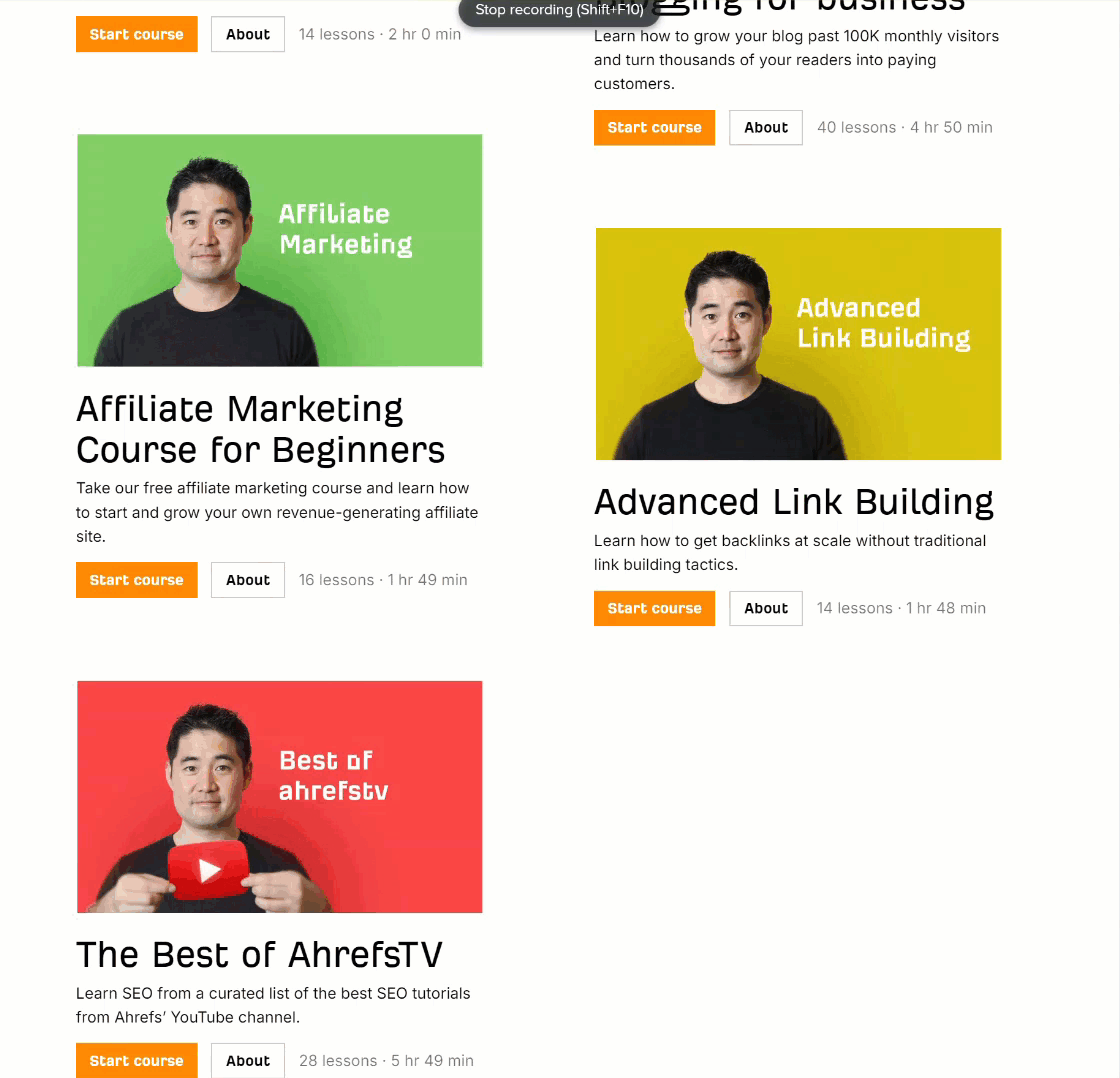

As a junior in any company, it can be hard to get your voice heard amongst the senior crowd. Ten years ago, I shared my wins with the team in a weekly group email in the office.
Here’s what you should be sharing:
- Praise from 3rd parties, e.g. “the client said they are impressed with the work this month.”
- Successful performance insights, e.g “following our SEO change, the client has seen X% more conversions this month.”
- Examples of the work you led, e.g. if your leadership and decision-making led to good results, then you need to share it.
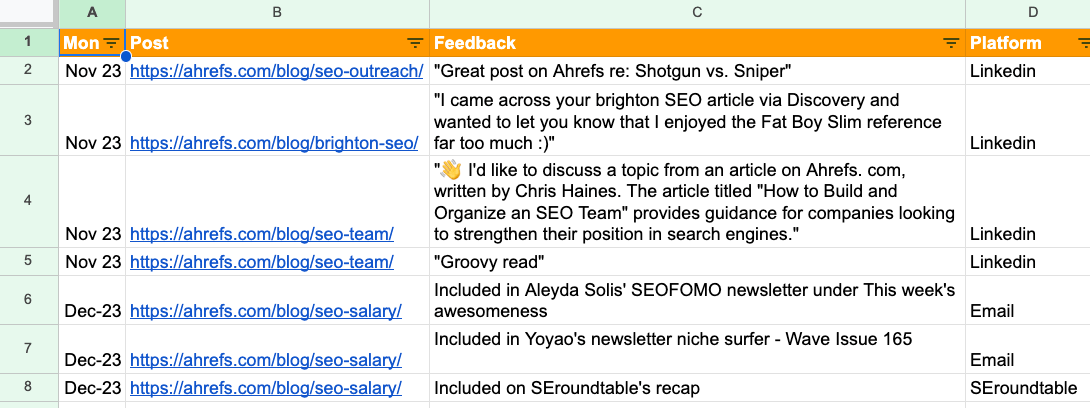
At Ahrefs I keep a “wins” document. It’s just a simple spreadsheet that lists feedback on the blog posts I’ve written, the links I’ve earned and what newsletters my post was included in. It’s useful to have a document like this so you have a record of your achievements.

Sidenote.
Junior SEOs sometimes talk about the things “we” achieved as a team rather than what they achieved at the interview stage. If you want the SEO Lead role, remember to talk about what you achieved. While there’s no “I” in team, you also need to advocate for yourself.
One of my first big wins as an SEO was getting a link from an outreach campaign on Buzzfeed. When I went to Brighton SEO later that year and saw Matthew Howells-Barby sharing how he got a Buzzfeed link, I realized that this was not something everyone had done.
So when I did manage to become an SEO Lead, and my team won a prize in Publicis Groupe for our SEO performance, I made sure everyone knew about the work we did. I even wrote a case study on the work for Publicis Groupe’s intranet.
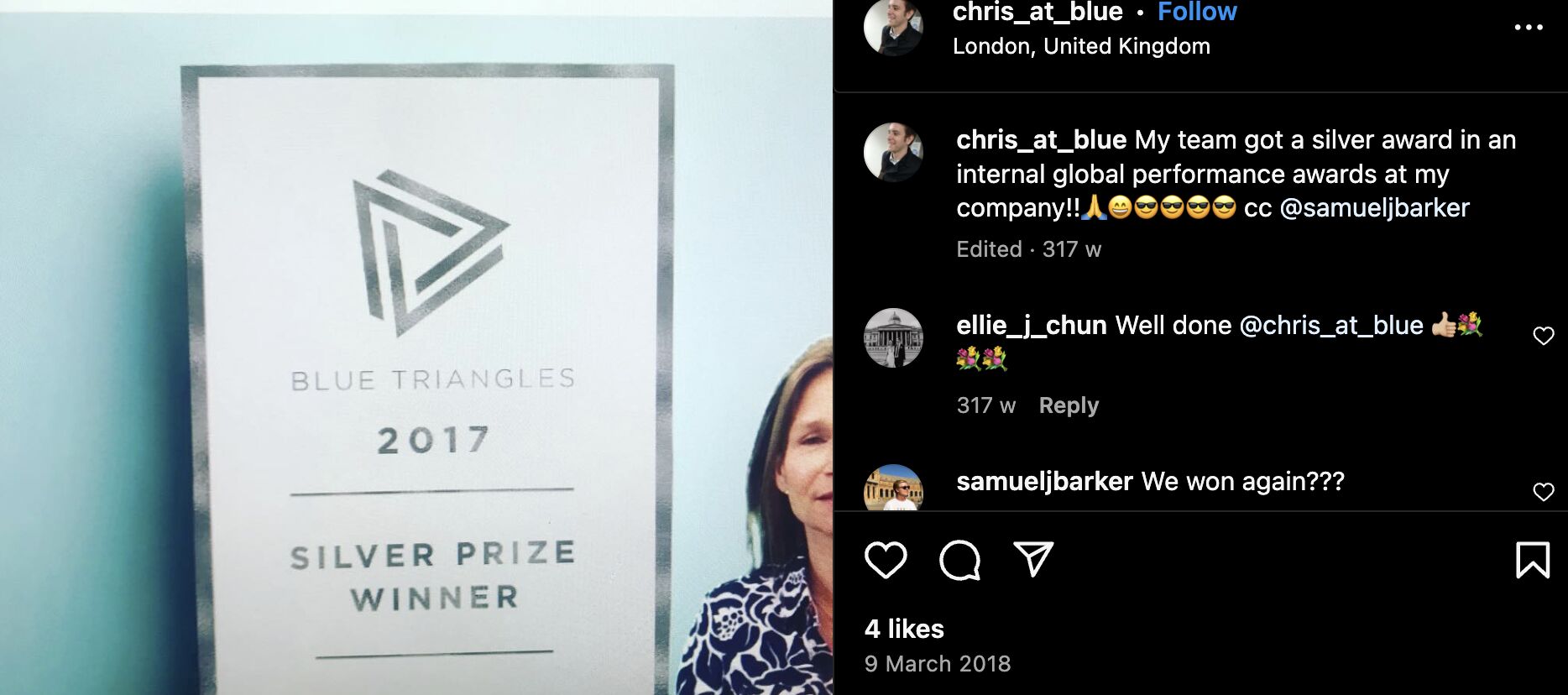

I’ve worked with some incredibly talented people, many of whom have helped me in my career.
I owe my big break to Tim Cripps, Laura Scott, and Kevin Mclaren. Without their support and encouragement, I wouldn’t be where I am today. Even before that, David Schulhof, Jodie Wheeler, and Carl Brooks let me mastermind some bonkers content campaigns that were lucky enough to succeed:

I wasn’t even an SEO Lead at that point, but they gave me the reins and trusted me.
So, how can you find your tribe?
- Speak to recruiters – they might hold the ticket to your next dream job. I spoke to many recruiters early in my career, but only two recruiters delivered for me—they were Natasha Woodford, and Amalia Gouta. Natasha helped me get a job that filled my skill gap, and Amalia helped me get my first SEO Lead role.
- Go to events and SEO conferences, and talk to speakers to build connections outside of your company.
- Use LinkedIn and other social media to interact with other companies or individuals that resonate with you.
Many senior SEO professionals spend most of their online lives on X and LinkedIn. If you’re not using them, you’re missing out on juicy opportunities.


Sharing your expertise on these platforms is one of the easiest ways to increase your chances of getting a senior SEO role. Because, believe it or not, sometimes a job offer can be just a DM away.
Here’s some specific ideas of what you can share:
- Share your thoughts on a trending topic – like the latest Google algorithm update.
- Share what you learned during the course of a campaign.
- Ask the community for their thoughts on a certain topic.
I’ve recently started posting on LinkedIn and am impressed by the reach you can get by posting infrequently on these topics.
Here’s an example of one of my posts where I asked the community for help researching an article I was writing:
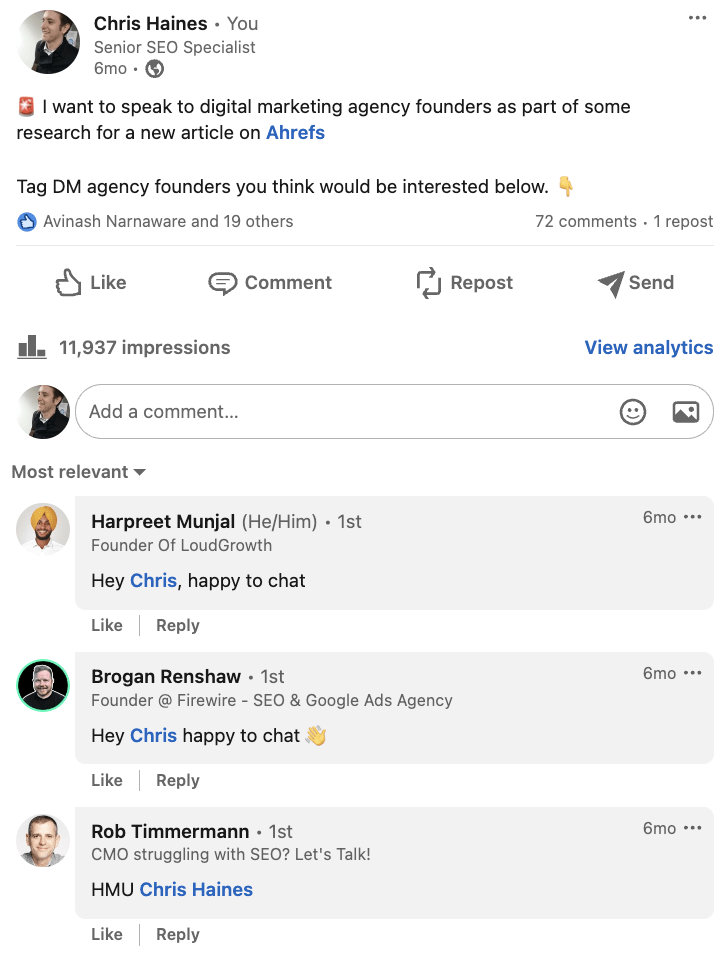

And here is the content performance across the last year from posting these updates.
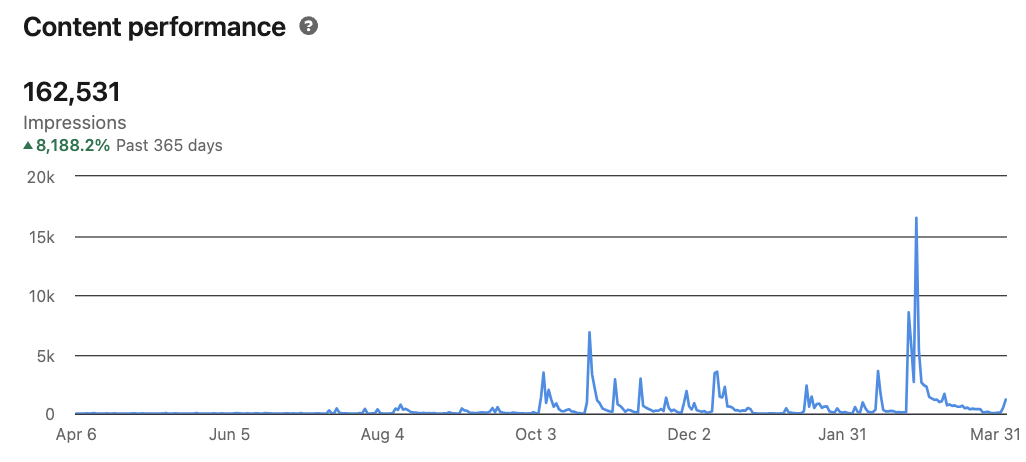

I’m clearly not a LinkedIn expert—far from it! But as you can see, with just a few months of posting, you can start to make these platforms work for you.
Godard Abel, co-founder of G2, talked on a podcast about conscious leadership. This struck a chord with me recently as I realized that I had practiced some of the principles of conscious leadership—unconsciously.
You can start practicing conscious leadership by asking yourself if your actions are above or below the line. Here are a few examples of above and below-the-line thinking:
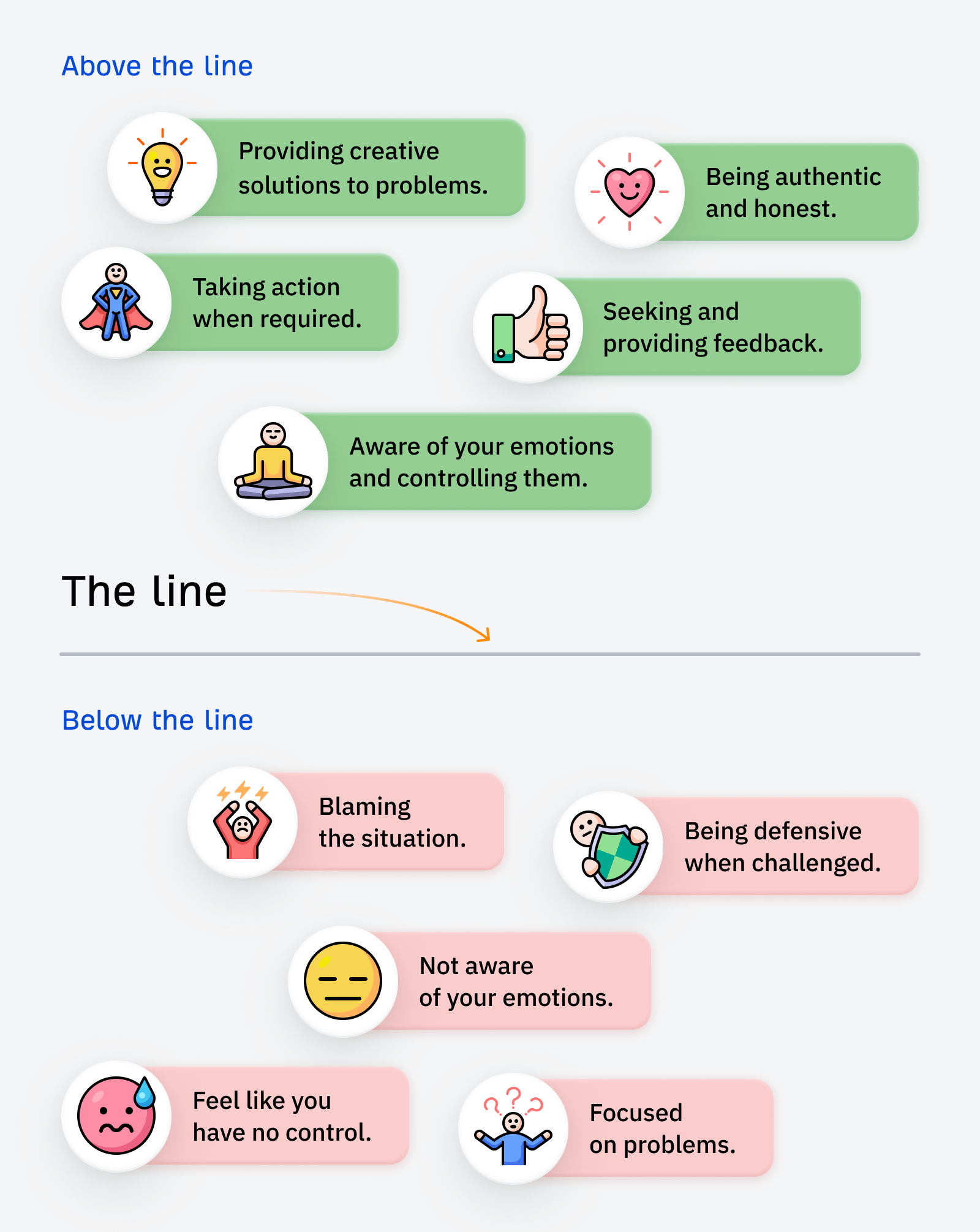

If you want a senior SEO role, I’d suggest shifting your mindset to above-the-line thinking.
In the world of SEO, it’s easy to blame all your search engine woes on Google. We’ve all been there. But a lot of the time, simple changes to your website can make a huge difference—it just takes a bit of effort to find them and make the changes.
SEO is not an exact science. Some stakeholders naturally get nervous if they sense you aren’t sure about what you’re saying. If you don’t get their support early on then you fall at the first hurdle.


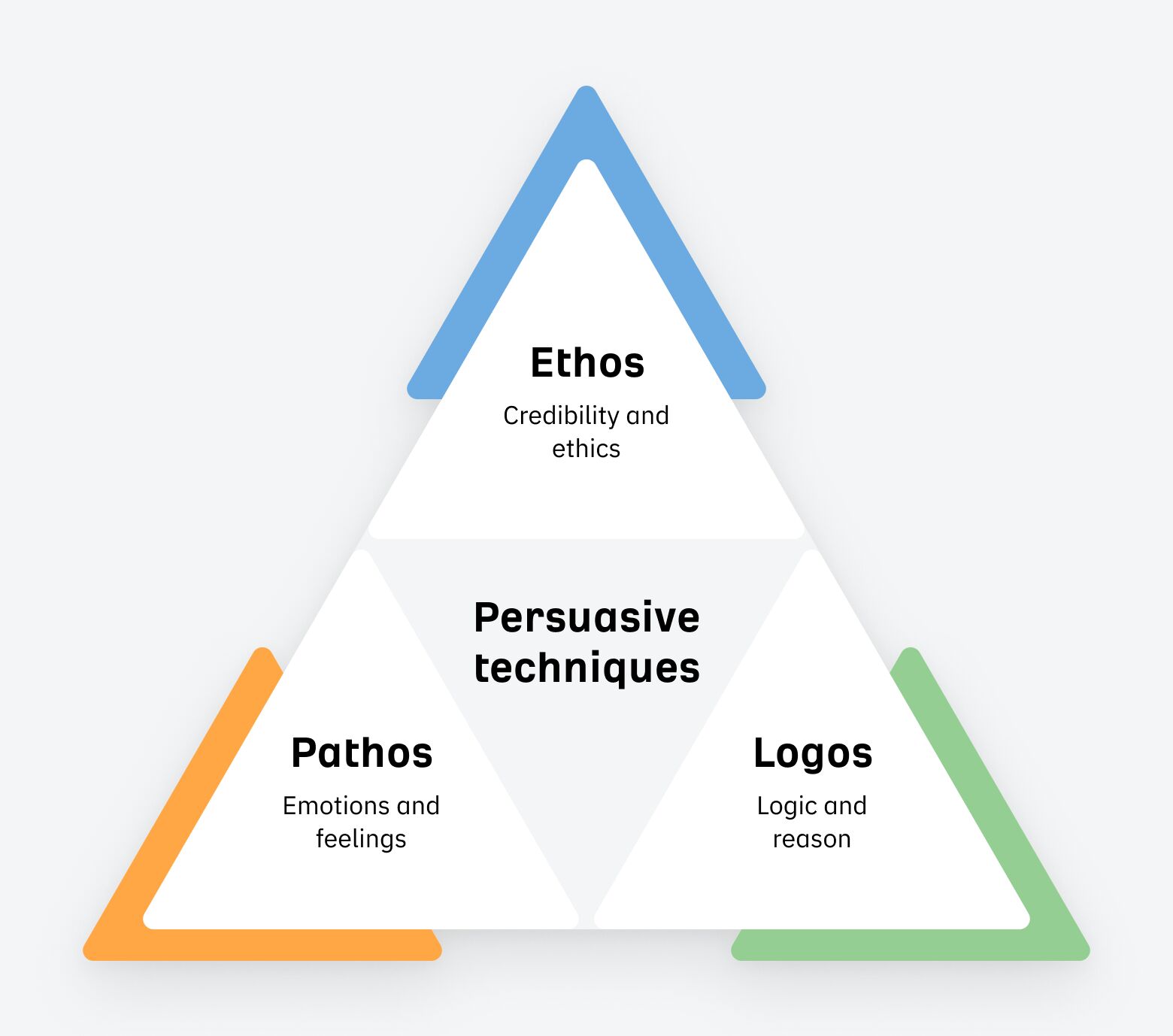
To become more persuasive, try incorporating Aristotle’s three persuasive techniques into your conversations.
- Pathos: use logical reasoning, facts, and data to present water-tight arguments.
- Ethos: establish your credibility and ethics through results.
- Logos: make your reports tell a story.

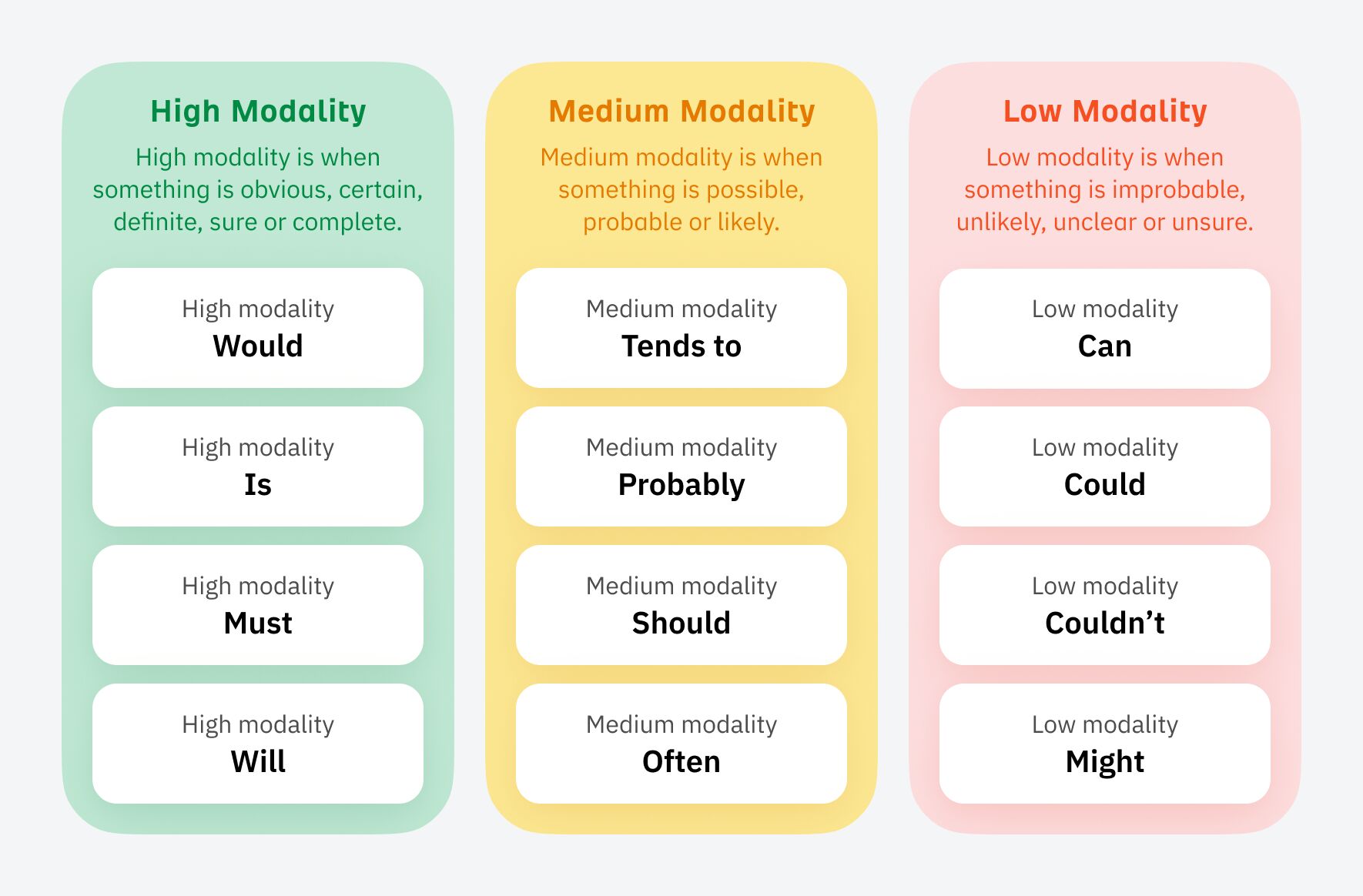
Then sprinkle in language that has a high level of modality:

Some people will be able to do this naturally without even realizing it, but for others, it can be an uphill struggle. It wasn’t easy for me, and I had to learn to adapt the way I talked to stakeholders early on.
The strongest way I found was to appeal to emotions and back up with data from a platform like Ahrefs. Highlight what competitors have done in terms of SEO and the results they’ve earned from doing it.
Sidenote.
You don’t have to follow this tip to the letter, but being aware of these concepts means you’ll start to present more confident and persuasive arguments for justifying your SEO strategies.
When I started in SEO, I had zero connections. Getting a job felt like an impossible challenge.
Once I’d got my first SEO Lead job, it felt stupidly easy to get another one—just through connections I’d made along the way in my SEO journey.
I once got stuck on a delayed train with a senior member of staff, and he told me he was really into Google Local Guides, and he was on a certain high level. He said it took him a few years to get there.
Local Guides is part of Google Maps that allows you submit reviews and other user generated content
When he showed me the app, I realized that you could easily game the levels by uploading lots of photos.
In a “hold my beer” moment, I mass downloaded a bunch of photos, uploaded them to Local Guides and equaled his Local Guide level on the train in about half an hour. He was seething.
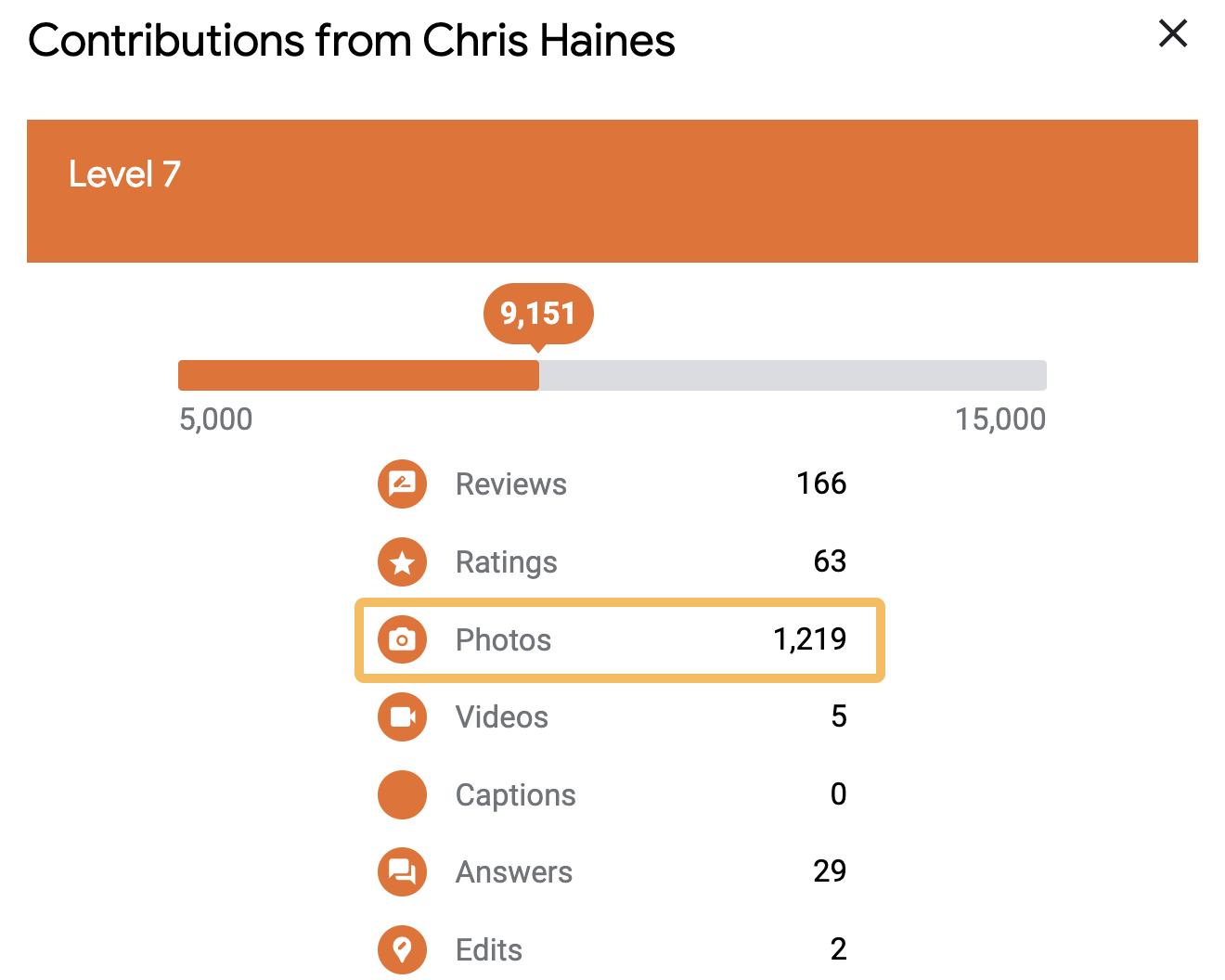

One of the photos I uploaded was a half-eaten Subway. It still amazes me that 50,974 people have seen this photo:
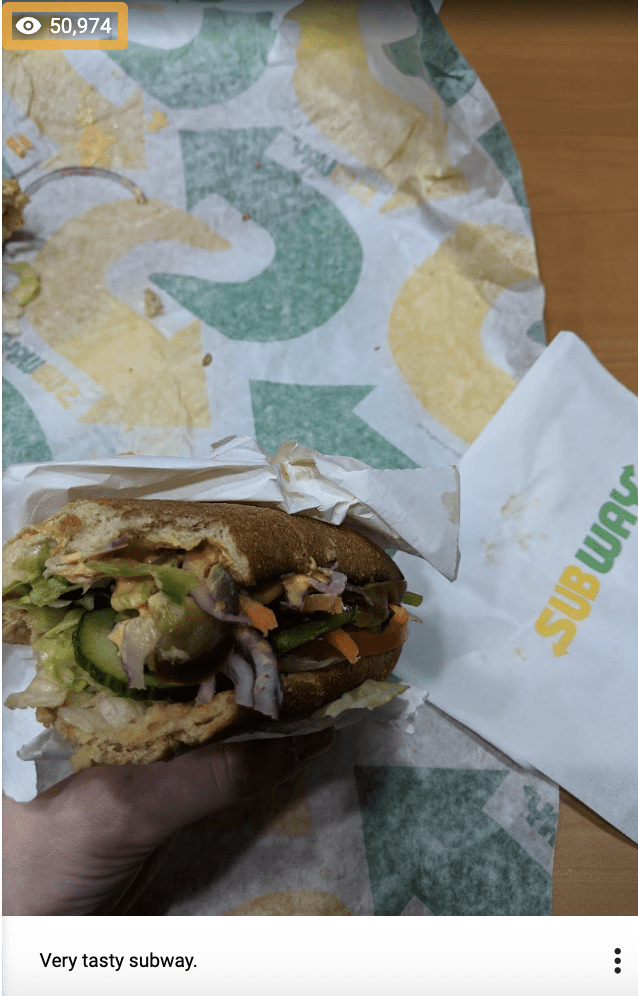
This wasn’t exactly SEO, but the ability to find this ‘hack’ so quickly impressed him, and we struck up a friendship.
The next month that person moved to another company, and then another few months later, he offered me an SEO Lead job.
Tip
Build connections with everyone you can—you never know who you might need to call on next.
Final thoughts
The road to becoming an SEO Lead seems straightforward enough when you start out, but it can quickly become long and winding.
But now armed with my tips, and a bucket load of determination, you should be able to navigate your way to an SEO Lead role much quicker than you think.
Lastly, if you want any more guidance, you can always ping me on LinkedIn. 🙂
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoWill Google Buy HubSpot? | Content Marketing Institute
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 16, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Clarifies Vacation Rental Structured Data
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoStreamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoHow to Collect & Use Customer Data the Right (& Ethical) Way
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO













You must be logged in to post a comment Login