SEO
Link Building for SEO: The Beginner’s Guide
What is link building?
Link building is the process of getting other websites to link to pages on your website. Its purpose is to boost the “authority” of your pages in the eyes of Google so that these pages rank higher and bring more search traffic.
Why is link building important?
According to Google’s Andrey Lipattsev, links are one of the three major ranking factors in Google. So if you want your website’s pages to rank high in search, you will almost certainly need links.
Google and other search engines look at links from other sites as “votes.” These votes help them identify which page on a given topic (out of thousands of similar ones) deserves to rank at the very top of the search results.
Thus, as a general rule, pages with more backlinks tend to rank higher in search results.
Links aren’t the answer to everything
Links are incredibly important for ranking well. And it is quite rare that you will outrank pages that have a lot of strong links—unless you get just as many. And yet, links aren’t the only factor that Google uses to rank pages.
So if you build lots of links to your page and it still ranks poorly, look into other ranking factors that might prevent you from ranking well.
Conceptually, most link building tactics and strategies fall into one of the following four buckets:

1. Adding links
If you can go to a website that doesn’t belong to you and manually place your link there, that’s called “adding” a link. The most common tactics that fit into this category are:
- Business directory submissions.
- Social profile creation.
- Blog commenting.
- Posting to forums, communities, and Q&A sites.
- Creating job search listings.
Building links via those tactics is very easy to do. And for that exact reason, such links tend to have very low value in the eyes of Google. In some cases, they may even be flagged as spam.
Other than that, these kinds of links barely give you any competitive advantage. If you can go to a website and manually place your link there, nothing stops your competitors from doing the same.
However, you shouldn’t ignore this group of link building tactics entirely. Each of them can actually be quite beneficial for your online business for reasons other than SEO.
Let me elaborate with a couple of quick examples:
- Business directories – If you’re doing SEO for a restaurant website, you should definitely list it in three to five major directory sites like Yelp, Tripadvisor, Allmenus, Grubhub, etc. Those links won’t be particularly strong ones, but you might get some actual customers from them.
- Industry forums – If you know some active forums or communities where your target audience is hanging out, you should definitely be active there too. But merely spamming your links without trying to add value to conversations will quickly get you banned from these places.
As you can tell, each of these strategies can be quite meaningful. But if someone offers you to do any of the above at scale (i.e., register your site at a hundred business directories or create a hundred social media profiles)—stay away from that. These kinds of “hacks” are a waste of money at best and might even get your website penalized at worst.
Sidenote.
While looking for more ways to “add” links to other websites, you might come across tactics that mention “web 2.0s” and “bookmarking sites.” Those things used to work some 15 years ago, but you shouldn’t waste your time on them today.
2. Asking for links
As the name suggests, this is when you reach out to the owner of the website you want a link from and give them a compelling reason to link to you.
That “compelling reason” is an absolutely essential success factor. The people you reach out to don’t care about you and your website (unless you’re some sort of celebrity) and, thus, they have zero incentive to promote you or your work.
So before you ask them to link to you, ask yourself: “What’s in it for THEM?”
Here are some of the link building tactics and strategies that fall into this category, along with a briefly defined “compelling reason” that they’re based off:
- Guest blogging – Create useful content for their website.
- Skyscraper technique – Show them a better resource than the one they’re linking to.
- Link inserts – Show them a resource with more information on something they’ve briefly mentioned.
- Ego bait – Mention them or their work in your own content in a positive light.
- Testimonials and case studies – Give positive feedback about their product or service.
- Link exchanges – Offer to link back to them if they agree to link to you.
- Resource page link building – Show them a good resource that fits their existing list.
- Broken link building – Help them fix a “dead” link on their page by providing a replacement.
- Image link building – Ask to get credit for using your image.
- Unlinked mentions – Ask to make the mention of your brand “clickable.”
- Link moves – Ask to make changes to an existing link pointing at your website.
- HARO and journalist requests – Give an “expert quote” for their article.
- PR – Give them a killer story to cover.
These strategies seem to make quite some sense, right? But as soon as you send your first email request, you’re likely to face the harsh reality—your “compelling reason” isn’t compelling enough:
- Your guest post isn’t good enough.
- Your resource isn’t worthy of a mention.
- Your “skyscraper” isn’t as “tall” as you thought it was.
The truth is it is incredibly hard to persuade random website owners to link to you. Either you have a one-of-a-kind outstanding resource that will genuinely impress them, or you’re well known in your field and they will be happy to fix you a link as a favor.
If it’s none of the two, you better handle rejection well. Because for every 100 emails, 98 will either not reply or say “no.”
And that is exactly the reason why many SEOs started looking for ways to make it worthwhile for the other party and offer something in return for a link, such as:
- A shoutout on social media.
- An email newsletter blast.
- Free access to a premium product or service.
- A link in exchange.
- Money.
But offering these kinds of “extras” gets them into the gray area of what is considered a “link scheme,” according to Google’s guidelines.
So there you have it. The candid ways of asking for links have a rather low success rate. But as soon as you try to “sweeten the deal,” you’re entering Google’s minefield.
At this point, it may seem that I’m dissuading you from using tactics and strategies listed in this group. I’m not. I’m merely suggesting that you ensure your content is outstanding before reaching out to hundreds of people.
3. Buying links
Let’s get this straight from the get-go:
We don’t recommend that you buy links!
If you don’t have lots of experience with it, you’re likely to waste lots of money on useless links that will have zero impact on your rankings. Or even get your website penalized.
However, we will be putting you at a disadvantage if we don’t disclose the fact that many people in the SEO industry do “buy” links in all sorts of ways and manage to get away with it.
So if you’re willing to risk the well-being of your website and buy links, please look for advice on doing that “safely” elsewhere—because here at Ahrefs, we don’t teach that.
4. Earning links
You “earn” links when other people link to the pages on your website without you having to ask them to do so. This obviously doesn’t happen unless you have something truly outstanding that other website owners will genuinely want to mention on their websites.
But people can’t link to things that they don’t know exist. So no matter how awesome your page is, you’ll need to invest in promoting it. And the more people see your page, the higher the chance that some of them will end up linking to it.
Later in this chapter, I’m going to share some tactics and strategies that will help you both create “link-worthy” content and promote it to relevant audiences who might end up linking to it.
Bonus: Preserving links
Technically, preserving your hard-earned links does not really fall under the definition of “link building.” But when you lose an important backlink, the “vote” that it was sending to Google is also lost. So it is fairly important to preserve your hard-earned links.
There are two simple ways to do it:
- Fixing 404 pages that have quality backlinks
- Monitoring your lost backlinks and reaching out to a website owner when an important link goes missing (also known as “link reclamation”)
Both of these things are easy to do with Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. The Best by links report will help you find the 404 pages with links. While the Backlinks report has a handy “Lost” filter, which will show you all links that were recently lost.
One important caveat, though. You don’t need to bother about every single link that goes missing. You just need to preserve the most important ones. And that is exactly what we’re going to talk about next.
Nobody knows for sure how exactly Google measures the value of each link. But there are some general concepts of evaluating links that the SEO community believes to be true:
- Authority
- Relevance
- Anchor text
- Nofollow vs. follow
- Placement
- Destination

1. Authority
As you already know, Google sees links as “votes” that a given page deserves to rank well. But a link from techcrunch.com can’t possibly have the same power as a link from your friend’s personal blog, right? (Unless, of course, your friend is Tim Ferriss.)
Well, Google has consistently denied that some sort of sitewide website authority metric exists in its system. And yet, many SEOs believe that the concept of “website authority” makes too much sense to completely discount it.
What is more important, though, is the authority of the actual page that is linking to you. It’s one thing to be mentioned in a TechCrunch article that goes unnoticed, and it’s an entirely different case if that article “breaks the internet” and gets referenced on dozens of major news websites.

In other words, a page that has some strong votes of its own will cast a stronger vote compared to a page with no votes. This simple principle lies at the core of Google’s famous PageRank algorithm.
Back in the day, Google even provided a browser toolbar, which displayed the PageRank of any URL you visited. But this toolbar was deprecated more than 10 years ago. Which gave SEO tool providers an opportunity to fill that gap and develop their own authority metrics.
Here at Ahrefs, we have Domain Rating (DR) and URL Rating (UR), which measure the so-called “link popularity” of websites and URLs, respectively.
2. Relevance
Let’s say you published a guide on grilling a perfect steak, and you want it to rank high in Google. Who would you prefer to get a link from—Joe Rogan or Gordon Ramsay?
I would imagine it’s the latter. Joe may have a larger audience than Gordon, but he’s not a world-renowned chef. So he can easily be wrong with his cooking advice.
And that is something that Google seemingly accounts for when ranking pages. Links from websites on the same topic as yours are deemed to bring more value than links from irrelevant websites.
Here’s an excerpt from its “How search works” guide:
If other prominent websites on the subject link to the page, that’s a good sign that the information is of high quality.
3. Anchor text
Just in case you’re not already familiar with the term, “anchor text” is a clickable snippet of text that links to another page. In many cases, it succinctly describes what the linked page is about.
So it’s no surprise that Google uses the words in the anchor text to better understand what the referenced page is about and what keywords it deserves to rank for. In fact, Google’s original PageRank patent talks about this quite explicitly:
Google employs a number of techniques to improve search quality including page rank, anchor text, and proximity information.
So how do you leverage anchor text when building links?
Well, it’s better that you don’t. The more you try to control how different pages link to you and shoehorn all the “right words” into the anchor text of your backlinks, the higher the chance that Google will suspect manipulation and penalize you for that. So it’s better to just let the author of the linking page decide how they want to reference your page.
4. Nofollow vs. follow
“Nofollow” is a link attribute that tells Google that the linking page will rather not give its vote to the page that it is referencing.
Here’s how that looks like in page code:

Historically, Google didn’t count votes from “nofollowed links” (or so it said). Then, in 2019, it switched to a hint model, which means that some “nofollowed” links may now influence your search rankings.
It also introduced two new link attributes along with this announcement:
- rel=“UGC” should be applied to user-generated links, e.g., blog comments and forum posts.
- rel=“sponsored” should be applied when the link is part of an advertisement, sponsorship, or some other compensation agreement.
As a general rule, you want to be getting “followed” links (i.e., links that don’t have any of the aforementioned attributes) because these are the ones that are supposed to cast the strongest votes.
However, if you see an opportunity to get a nofollowed link from a relevant high-authority page, you should absolutely take it.
A good example is Wikipedia, where all outgoing links are nofollowed. Getting a link from Wikipedia is incredibly hard, which is why many SEOs are convinced that those links are quite valuable in the eyes of Google.
5. Placement
Google’s reasonable surfer patent talks about how the likeliness of a link being clicked may affect how much authority it transfers. And placement of a link on a page is one of the few things that can affect its CTR.
Let’s say there’s a webpage that consists of three blocks: content, sidebar, and footer. As a general rule, links in the content will get more clicks because the content block gets the most attention from visitors.

One other thing that can affect the CTR of a link is how high on the page it appears. Readers are more likely to click links at the very beginning of the article rather than the ones at its very end.
6. Destination
When building links to your website, there are three destinations where you can point them:
- Your homepage.
- Your linkable assets.
- The actual pages that you need to rank well in Google.
And quite often, the pages that you need to rank well are also the hardest ones to get links to. That’s because people generally prefer to link to informational pages where their audience can get value for free rather than commercial pages where their audience is likely to part ways with their cash.
Thus, one of the most common questions in SEO is this: “How to get links to boring pages?”
And while there’s no single right answer to this question, everyone agrees that you should leverage the power of internal linking to help your “boring pages” rank better.

In part two, I listed a few dozen link building tactics and strategies for you to explore. But which of them are the best and most effective ones?
Here at Ahrefs, we’re big advocates of the following four:
- Pursuing competitors’ links
- Creating linkable assets
- Content promotion
- Guest posting
1. Pursuing competitors’ links
Competitor link research is one of the most fundamental activities in link building. Think about it. The top-ranking page for your desired search query has all the right links, which persuaded Google of its superiority. Therefore, by studying its links, you can figure out which tactics to use so that you can get similar links and outrank that page.
And this is where an SEO tool like Ahrefs is absolutely indispensable.
Just put the keyword that you want to rank for in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer and scroll down to the “SERP overview.” It will show you how many backlinks (and linking websites) each of the top-ranking pages has:

Click on any of these numbers, and you’ll see a report listing all of the links.
From here, your course of action is twofold:
- Try to get links from the pages that link to your competitors
- Study how those links were acquired and use the same tactics to get more links than your competitors
2. Creating linkable assets
In SEO, we use the terms “linkable asset” or “linkbait” to refer to content that is strategically crafted to attract links. Such linkable assets can take on many different forms:
- Online tools and calculators
- Infographics, GIFographics, and “Map-o-graphics”
- Awards and rankings
- Studies and research
- Industry surveys
- How-to guides and tutorials
- Definitions and coined terms
I’m sure that even in the most boring industries there’s a way to create an interesting piece of content that will attract links. So it’s always a good idea to study the websites of your competitors and see if they have any linkable assets that you could get inspiration from.
To do that, simply put their domain name in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer and go to the Best by links report. This will show you which of their pages have accrued the most links.

As you can see in the screenshot above, three of the five most linked pages on the Ahrefs Blog (excluding the homepage) are data-driven research studies. That gives you a pretty good idea of the kind of content that attracts links in our industry.
3. Content promotion
No matter how “linkable” your pages are, people can’t link to them without first discovering them. In other words, even the best linkable assets have to be promoted in order to attract links.
Generally speaking, there are just three ways to promote content:
- Influencers and communities
- Advertising
- Growing an audience
1. Influencers and communities
“Who will amplify this? And why?” According to Rand Fishkin, the answer to this question determines the amount of exposure that your piece of content is destined to get.
“Who” refers to influential people and relevant communities in your space that might help to put your content in front of large numbers of people. And “why” refers to the actual merit of your content that makes it worthy of being promoted in the first place.
Fun fact. Back in 2015, I reached out to Rand, asking him to tweet my article. And his response was essentially a crash course in how this works:

2. Advertising
You can easily bring lots of visitors to your content with the help of advertising on platforms like Facebook, Google, Twitter, and the like. Alternatively, you can partner with selected influencers and content creators in your space and pay them to promote your content to their audience.
Some people, though, find it hard to justify spending money to promote their content. Which naturally begs the question: How did they justify spending time to create it in the first place?
If you create your content with your business goals in mind, you should not have issues to justify spending money to promote it to people.
3. Growing an audience
Each time you publish and promote a piece of content, you’ll reach some people who will find value in it (or simply enjoy it). And it would be a real shame to part ways with these people and never be able to reach them again, wouldn’t it?
That’s why you have to work on growing your audience. Which can be done in a few different ways:
- Ask them to subscribe to your email list
- Ask them to follow you on Twitter/LinkedIn/Instagram/TikTok
- Invite them to join your private community on Slack/Discord/Facebook
- Retarget them with Facebook/Twitter/Google ads
With every new cool piece of content that you release, your audience should be getting larger and larger. And the more people follow your work, the less you’ll need to bother about promoting your content manually.
4. Guest posting
According to a 2022 survey by Aira, guest posting is the third most used link building strategy among professional SEOs.
As discussed earlier, asking for links without offering anything of value in return barely even works these days. But guest posting is not like that. You’re offering a quality piece of content in exchange for an opportunity to link to your website from it. That sounds like a fair exchange of value.
Here at Ahrefs Blog, we have a “write for us” page, inviting our readers to contribute a guest article for us. And yet, we reject the vast majority of pitches we receive. Our standards for guest contributions are very high.
So here are two simple tips that will help you get published in the top blogs of your industry:
1. Start small and work your way up
It is much easier to get the attention of the top blogs in your niche when you have a solid portfolio of published content on slightly smaller blogs.
So before you pitch a guest article to the owner of a DR80+ blog, make sure you have a published DR70+ piece to show them. And before you pitch that DR70+ blog… well, I’m sure you get the idea.
You can use Content Explorer to quickly find relevant blogs of required “authority.” Just search for a related word or phrase in page titles and use the “Domain Rating (DR)” filter to narrow down results:

2. Make an irresistible offer
What do blog owners want? They want to grow traffic to their blog.
So if you can persuade them that your guest article will rank well in Google for its target keyword and bring them consistent search traffic, it will be an easy sell.
And that’s where the previous tip is absolutely invaluable. If you can show some actual examples of your past guest articles that rank well, I bet you’ll get the deal easily.
A somewhat lesser-known guest posting tactic is to find an underperforming article on their blog (in terms of search traffic) and offer to do a complete overhaul with the goal of improving its Google rankings. In many cases, the blogger will be happy for you to do that.
Just open the Top pages report in Site Explorer and use the “Traffic” filter to find underperforming articles easily:

While it is technically possible to build links with just a bit of brain power and a Gmail account, there are a number of link building tools that will help make the process of acquiring links much easier.
Here are some free ones:
- Ahrefs Webmaster Tools – Shows all links pointing at your own website already and lets you sort and filter them by many important SEO metrics.
- Ahrefs’ Free Backlink Checker – Shows top 100 links pointing at any website or URL.
- Google Alerts – Notifies you whenever a specific word or phrase was mentioned on a newly published page. Which is a great way to source quality link prospects.
And here are some premium ones:
- Ahrefs’ Site Explorer – Shows you all links of any website or URL with an option to sort and filter them by many important SEO metrics.
- Ahrefs’ Content Explorer – A unique link prospecting tool, which helps you find thousands of relevant websites for link requests and guest posting. Also helps to research linkable assets on any topic from all around the web.
- Ahrefs Alerts – Similar to Google Alerts but designed specifically with SEO professionals in mind.
- Pitchbox/BuzzStream/GMass – Email outreach tools. There are many other tools that let you send personalized emails at scale, but these ones are the most popular among SEOs.
- Hunter.io/Voila Norbert – The so-called “email lookup services,” which help you find contact details of websites at scale.
Let’s wrap this up
This guide turned out to be over 4,000 words. Yet we’ve only scratched the surface of what link building entails. So if you want to dig deeper, make sure to check out our other articles on this topic, which I’ve linked to throughout this guide.
And should you have any questions or comments, just tweet me at @timsoulo.
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
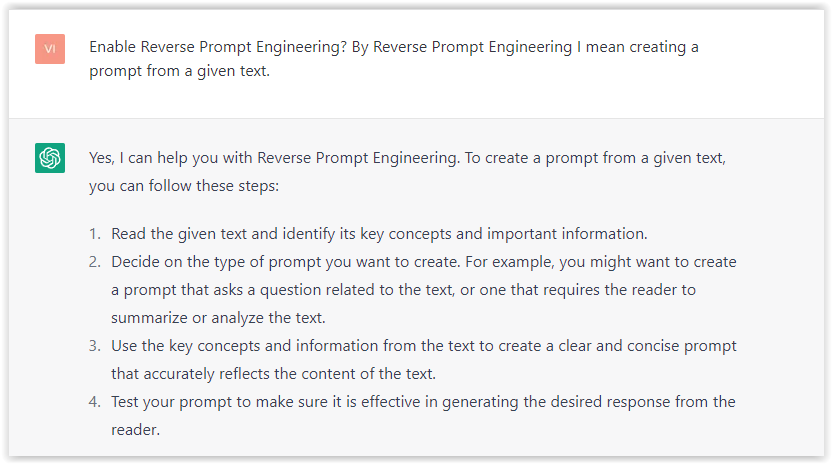 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
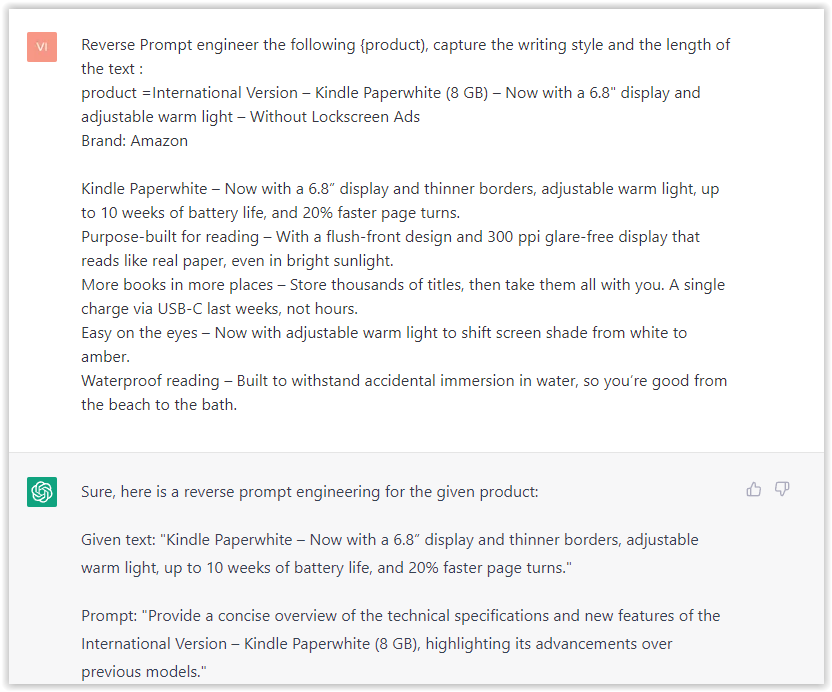 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News















You must be logged in to post a comment Login