SEO
What Is A Sitemap? Do I Need One?

Sitemap. While this is a term you may be familiar with, what does it mean?
Do you need one? Where do you find one? How do you make one?
These are valid questions; for some, there might be more than one answer.
Today, we will take a deep dive into the sitemap world, so that you can walk away with the necessary answers and confidence around the topic!
What Is A Sitemap?
Let’s start here.
Defining a sitemap is essential for several reasons, and we are going to go through the two main types that apply to technical SEO: XML and HTML sitemaps.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a file that provides a website’s essential pages, videos, and other important files for Google to discover when crawling the site.
Not only are these listed in the file, but the sitemap can also provide details for Google to know – for instance, when the page was last updated, and if the content is available in other languages.
As I mentioned, you can also provide details about content types like videos, photos, and news-related content, specifically in your XML sitemap.
According to the Google Developers Sitemaps section, the following can be included for specific types of content in your sitemap:
- A sitemap video entry can specify the video running time, rating, and age-appropriateness rating.
- A sitemap image entry can include the location of the images included on a page.
- A sitemap news entry can include the article title and publication date.
Next, we will talk about what an HTML sitemap is and the differences between the two.
HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap is more targeted for users on your site than for Google.
This is a page that exists on your site and has links to the pages on your website – and in some cases, includes a little context into what those pages are.
Google mentions that you should try to establish a consistent and clear hierarchy on the HTML sitemap as, although not its purpose, it can help with indexation.
You can think of an HTML sitemap as a directory that users can leverage to navigate your site and find what they need.
An HTML sitemap should not be an attempt to replace the important pages in your site’s navigation.
XML Sitemaps Vs. HTML Sitemaps
So, what are the key differences between these two types of sitemaps? Let’s review.
XML
- The intent is for Google and other bots.
- There is no hierarchy.
- Used primarily for indexing.
- You can submit via Google Webmaster Tools.
HTML
- The intent is for users.
- A hierarchy should be used.
- No place to submit in Google Webmaster Tools.
Do You Need A Sitemap?
If you are wondering if you need a sitemap, that depends!
First, let’s discuss the XML sitemap. There are a few questions you can ask to determine if you need an XML sitemap:
- How big is your site? Is it large enough that Google may miss newly updated content when it is crawling?
- Is your site relatively new? If so, it may not have a ton of external links on the Internet that point to it to help Google discover it. Even if your site isn’t new, and you don’t have external links, your answer to this question should be yes.
- Is your site content heavy? Do you have many photos, videos, news content, etc.?
- Does your site need a better architecture that results in pages not being well linked to each other? This can also be the case with archived and orphan pages you want to be indexed.
If you answered yes to any of the questions above, then yes, it is best practice to have an XML sitemap.
Even if you answered no to all of the above, I would recommend an XML sitemap for a few reasons; If your site grows, expands its scope, and other situations may arise, having a sitemap will be beneficial!
Next, let’s review whether it makes sense for you to have an HTML sitemap. Depending on where you look, you will find that answer to be yes or no.
HTML sitemaps are known to be an older concept, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t have one.
The XML sitemap has the information needed for Google to crawl, index, and learn other important information about these pages. However, an XML sitemap does not show hierarchy like an HTML sitemap.
Google will crawl the links on your site, and including an HTML sitemap could allow Google to understand your site’s architecture and relationships better.
This is even more useful for sites that have an incredibly large number of pages.
So, is having an HTML sitemap critical? No, it is not.
It is also not a cure-all for a poorly architected and nested website. While it isn’t a critical element of success, it has shown benefits that make having one a best practice.
To close this topic out, I recommend you have an XML and HTML sitemap because let’s be honest, why not, when the pros outweigh the cons very clearly?
Now you may be wondering how to create these two assets and what to do with them – so, let’s jump into some ways you can create these files and where to put them on the site.
How To Create An XML Sitemap
First, we will go over how you can generate sitemaps from scratch, and then we will get into some great tools that can do it for you.
XML sitemaps have specific criteria in order to be rendered valid.
Below are a few specific requirements for XML sitemaps:
- Begin with a <urlset> tag and end with that tag closing </urlset>.
- Include the protocol you are using within the <urlset> tag.
- Each URL entry must have a <url> tag as a parent XML tag.
- Include a <loc> child entry for each <url> parent tag.
- Each sitemap can only contain up to 50,000 URLs and 50MB.
- Must be UTF-encoded.
XML Sitemap Best Practices
Now, let’s look at some key best practices when it comes to creating XML sitemaps:
- Only URLs you want to be indexed should appear in your sitemap. This means no redirected URLs, non-canonical URLs, or pages marked as no-index.
- Do not use session Ids.
- Only include the primary if you have two versions (mobile and desktop) of your site.
- Include media assets like videos, photos, and news items.
- Use hreflang to show Google that there are alternative language versions of your website.
- Google documentation notes it leverages <lastmod>, but only if it’s consistent and verifiable. If you can’t keep this accurate, don’t use it.
- Google ignores the <priority> and <changefreq> tags at this time, according to John Mueller on this Search Off the Record podcast.
- Google will not crawl your URLs in the order they are listed, nor does it guarantee indexation.
- Your sitemap should be updated regularly – automatically, or manually – or Google may not trust it.
Now, if you felt lost reading those beginning requirements, that is okay, because there are tools to help you achieve your desired outcomes! We will go over some later in this article.
Check out the refined version below:
 Screenshot from lowes.com, January 2023
Screenshot from lowes.com, January 2023How To Create An HTML Sitemap
When putting together an HTML sitemap, remember its purpose is to serve a user on the site and help Google understand the hierarchy of your website.
You do not want to no index this page from Google; keep it crawlable!
You will want to ensure you don’t just throw thousands of links on an HTML sitemap page with no sense of organization, as this won’t help anyone – bots included.
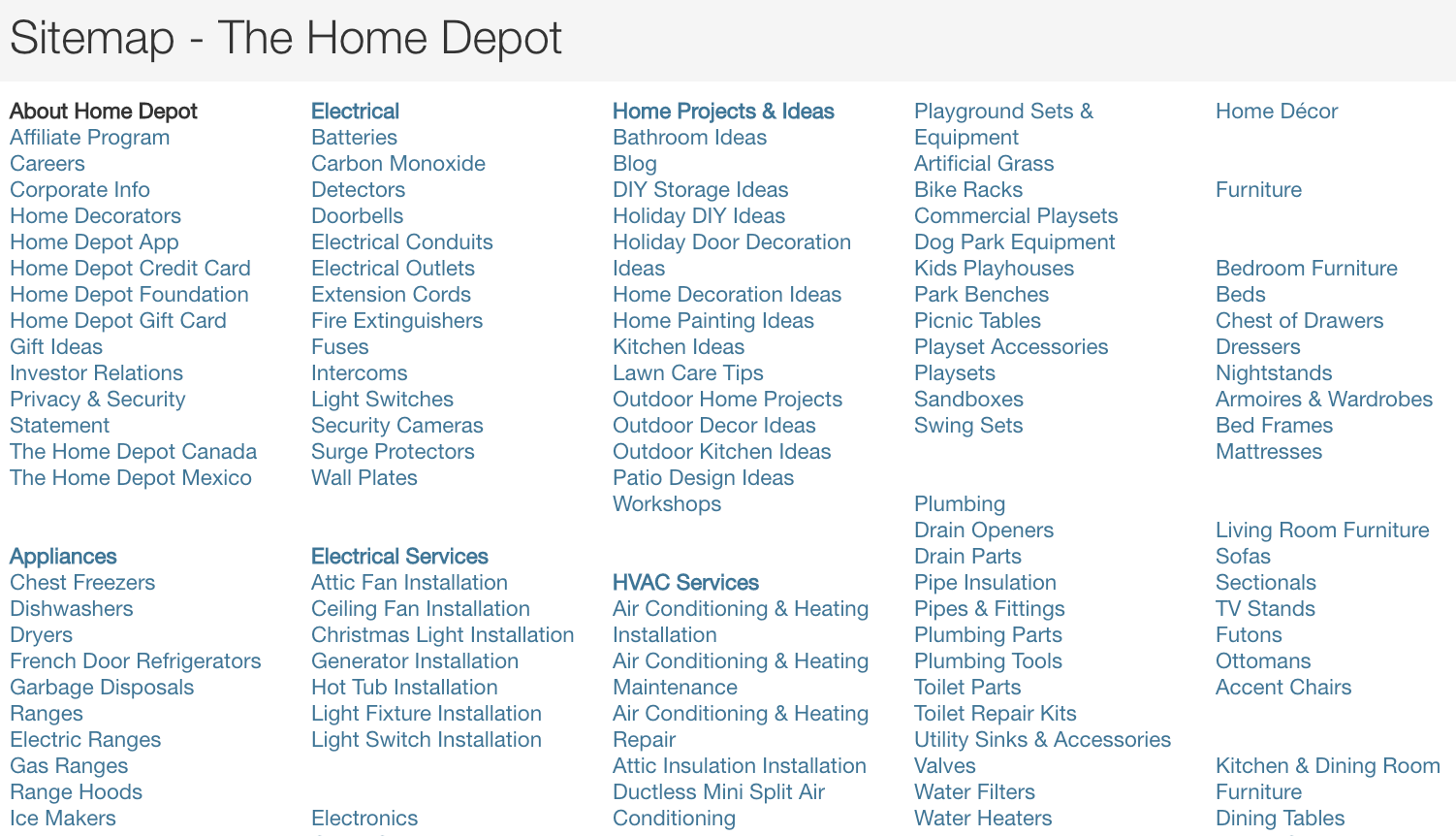 Screenshot from Home Depot, January 2023
Screenshot from Home Depot, January 2023HTML Sitemap Best Practices
Let’s go over a few quick best practices when it comes to HTML sitemaps:
- Arrange the page’s structure to align with your website’s structure. You will want to make sure that the hierarchy is easily understood.
- The HTML sitemap should be located somewhere the user can easily find it. You will often see it in the footer links of a website.
- Use anchor text that is valuable to the user.
Need a little help getting started? No worries – there are plenty of tools to help you.
Sitemap Generator Tools
There are a number of tools to help you generate different types of sitemaps. Let’s go over a few now.
XML Sitemap Generator Tools
- Screaming Frog – This tool is a great option for generating a sitemap, especially if you want to generate one after crawling your URLs. Screaming Frog is free if you have under 1,000 URLs, but you would have to buy a license if you have more.
- XML-Sitemaps.com – This web-based application allows you to enter your website URL and it generates an XML file for you. This is a free tool for up to 500 URLs.
Depending on which CMS you are leveraging, there are also thousands of XML sitemap generator plug-ins, but be cautious as even the best generator tools have their limitations, so make sure to double-check the output.
Here are a few popular XML sitemap plugins for WordPress:
HTML Sitemap Generator Tools
- com: this is a free online tool where you can scan your website URL or upload a document to generate an HTML sitemap. As we discussed earlier, there may be better approaches than a generator if your site is poorly architected.
- Crawler: Like Eli mentions, if you have a large site and are already using a crawler like OnCrawl, DeepCrawl, Screaming Frog, or SiteBulb, you can leverage the output from a crawl to help generate your HTML sitemap.
Like XML sitemaps, there are also a variety of CMS plugins for creating HTML sitemaps. Here are a few for WordPress:
In Conclusion
Sitemaps have existed in the SEO world for some time as a method for helping search engines discover and crawl websites.
And, while having a sitemap isn’t always necessary for every site, it certainly doesn’t hurt – and can be especially useful for both new and large sites.
When you are determining your next steps for creating a sitemap for your website – whether XML or HTML – I hope you can leverage this guide to decide which path makes the most sense for your site’s needs.
More resources:
Featured Image: Sammby/Shutterstock
SEO
Google Confirms Links Are Not That Important

Google’s Gary Illyes confirmed at a recent search marketing conference that Google needs very few links, adding to the growing body of evidence that publishers need to focus on other factors. Gary tweeted confirmation that he indeed say those words.
Background Of Links For Ranking
Links were discovered in the late 1990’s to be a good signal for search engines to use for validating how authoritative a website is and then Google discovered soon after that anchor text could be used to provide semantic signals about what a webpage was about.
One of the most important research papers was Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment by Jon M. Kleinberg, published around 1998 (link to research paper at the end of the article). The main discovery of this research paper is that there is too many web pages and there was no objective way to filter search results for quality in order to rank web pages for a subjective idea of relevance.
The author of the research paper discovered that links could be used as an objective filter for authoritativeness.
Kleinberg wrote:
“To provide effective search methods under these conditions, one needs a way to filter, from among a huge collection of relevant pages, a small set of the most “authoritative” or ‘definitive’ ones.”
This is the most influential research paper on links because it kick-started more research on ways to use links beyond as an authority metric but as a subjective metric for relevance.
Objective is something factual. Subjective is something that’s closer to an opinion. The founders of Google discovered how to use the subjective opinions of the Internet as a relevance metric for what to rank in the search results.
What Larry Page and Sergey Brin discovered and shared in their research paper (The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine – link at end of this article) was that it was possible to harness the power of anchor text to determine the subjective opinion of relevance from actual humans. It was essentially crowdsourcing the opinions of millions of website expressed through the link structure between each webpage.
What Did Gary Illyes Say About Links In 2024?
At a recent search conference in Bulgaria, Google’s Gary Illyes made a comment about how Google doesn’t really need that many links and how Google has made links less important.
Patrick Stox tweeted about what he heard at the search conference:
” ‘We need very few links to rank pages… Over the years we’ve made links less important.’ @methode #serpconf2024″
Google’s Gary Illyes tweeted a confirmation of that statement:
“I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that”
Why Links Matter Less
The initial state of anchor text when Google first used links for ranking purposes was absolutely non-spammy, which is why it was so useful. Hyperlinks were primarily used as a way to send traffic from one website to another website.
But by 2004 or 2005 Google was using statistical analysis to detect manipulated links, then around 2004 “powered-by” links in website footers stopped passing anchor text value, and by 2006 links close to the words “advertising” stopped passing link value, links from directories stopped passing ranking value and by 2012 Google deployed a massive link algorithm called Penguin that destroyed the rankings of likely millions of websites, many of which were using guest posting.
The link signal eventually became so bad that Google decided in 2019 to selectively use nofollow links for ranking purposes. Google’s Gary Illyes confirmed that the change to nofollow was made because of the link signal.
Google Explicitly Confirms That Links Matter Less
In 2023 Google’s Gary Illyes shared at a PubCon Austin that links were not even in the top 3 of ranking factors. Then in March 2024, coinciding with the March 2024 Core Algorithm Update, Google updated their spam policies documentation to downplay the importance of links for ranking purposes.
The documentation previously said:
“Google uses links as an important factor in determining the relevancy of web pages.”
The update to the documentation that mentioned links was updated to remove the word important.
Links are not just listed as just another factor:
“Google uses links as a factor in determining the relevancy of web pages.”
At the beginning of April Google’s John Mueller advised that there are more useful SEO activities to engage on than links.
Mueller explained:
“There are more important things for websites nowadays, and over-focusing on links will often result in you wasting your time doing things that don’t make your website better overall”
Finally, Gary Illyes explicitly said that Google needs very few links to rank webpages and confirmed it.
I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (so official, trust me) (@methode) April 19, 2024
Why Google Doesn’t Need Links
The reason why Google doesn’t need many links is likely because of the extent of AI and natural language undertanding that Google uses in their algorithms. Google must be highly confident in its algorithm to be able to explicitly say that they don’t need it.
Way back when Google implemented the nofollow into the algorithm there were many link builders who sold comment spam links who continued to lie that comment spam still worked. As someone who started link building at the very beginning of modern SEO (I was the moderator of the link building forum at the #1 SEO forum of that time), I can say with confidence that links have stopped playing much of a role in rankings beginning several years ago, which is why I stopped about five or six years ago.
Read the research papers
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment – Jon M. Kleinberg (PDF)
The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine
Featured Image by Shutterstock/RYO Alexandre
SEO
How to Become an SEO Lead (10 Tips That Advanced My Career)

A few years ago, I was an SEO Lead managing enterprise clients’ SEO campaigns. It’s a senior role and takes a lot of work to get there. So how can you do it, too?
In this article, I’ll share ten tips to help you climb the next rung in the SEO career ladder.
Helping new hires in the SEO team is important if you want to become an SEO Lead. It gives you the experience to develop your leadership skills, and you can also share your knowledge and help others learn and grow.
It demonstrates you can explain things well, provide helpful feedback, and improve the team’s standard of work. It shows you care about the team’s success, which is essential for leaders. Bosses look for someone who can do their work well and help everyone improve.
Here are some practical examples of things I did early in my career to help mentor junior members of the team that you can try as well:
- Hold “lunch and learn” sessions on topics related to SEO and share case studies of work you have done
- Create process documents for the junior members of the team to show them how to complete specific tasks related to your work
- Compile lists of your favorite tools and resources for junior members of the team
- Create onboarding documents for interns joining the company
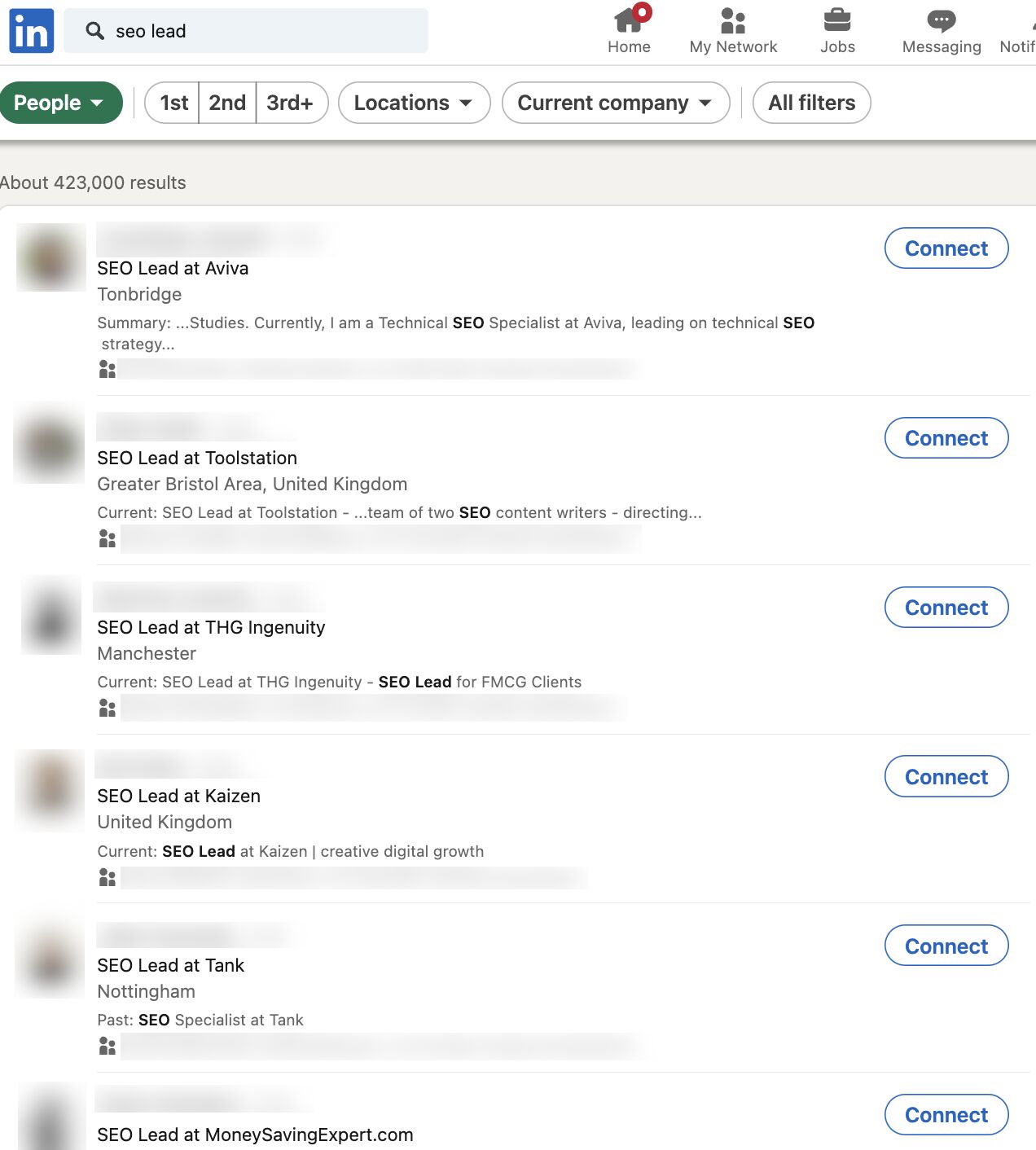
Wouldn’t it be great if you could look at every single SEO Lead’s resume? Well, you already can. You can infer ~70% of any SEO’s resume by spying on their LinkedIn and social media channels.
Type “SEO Lead” into LinkedIn and see what you get.
Tip
Look for common career patterns of the SEOs you admire in the industry.
I used this method to understand how my favorite SEOs and people at my company navigated their way from a junior role to a senior role.
For example, when the Head of SEO at the time Kirsty Hulse, joined my team, I added her on LinkedIn and realized that if I wanted to follow in her footsteps, I’d need to start by getting the role of SEO Manager to stand any possible chance of leading SEO campaigns like she was.
The progression in my company was from SEO Executive to Senior SEO Executive (Junior roles in London, UK), but as an outsider coming into the company, Kirsty showed me that it was possible to jump straight to SEO Manager given the right circumstances.
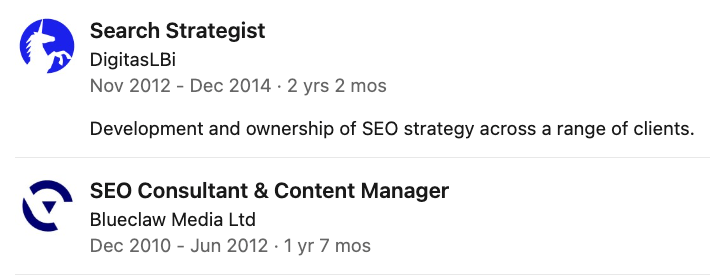

Using Kirsty’s and other SEOs’ profiles, I decided that the next step in my career needed to be SEO Manager, and at some point, I needed to get some experience with a bigger media agency so I could work my way up to leading an SEO campaign with bigger brands.
Sadly, you can’t just rock up to a monthly meeting and start leading a big brand SEO campaign. You’ll need to prove yourself to your line manager first. So how can you do this?
Here’s what I’d suggest you do:
- Create a strong track record with smaller companies.
- Obsessively share your wins with your company, so that senior management will already know you can deliver.
- At your performance review, tell your line manager that you want to work on bigger campaigns and take on more responsibility.
If there’s no hope of working with a big brand at your current job, you might need to consider looking for a new job where there is a recognizable brand. This was what I realized I needed to do if I wanted to get more experience.
Tip
Get recruiters on LinkedIn to give you the inside scoop on which brands or agencies are hiring. Ask them if you have any skill gaps on your resume that could prevent you from getting a job with these companies.
Being critical of your skill gaps can be hard to do. I found the best way to identify them early in my career was to ask other people—specifically recruiters. They had knowledge of the industry and were usually fairly honest as to what I needed to improve.
From this, I realized I lacked experience working with other teams—like PR, social, and development teams. As a junior SEO, your mind is focused 99% on doing SEO, but when you become more senior, your integration with other teams is important to your success.
For this reason, I’d suggest that aspiring SEO Leads should have a good working knowledge of how other teams outside of SEO operate. If you take the time to do this, it will pay dividends later in your career:
- If there are other teams in your company, ask if you can do some onboarding training with them.
- Get to know other team leads within your company and learn how they work.
- Take training courses to learn the fundamentals of other disciplines that complement SEO, such as Python, SQL, or content creation.
Sometimes, employers use skill gaps to pay you less, so it’s crucial to get the skills you need early on…

Examples of other skill gaps I’ve noticed include:
Tip
If you think you have a lot of skill gaps, then you can brush up your skills with our SEO academy. Once you’ve completed that, you can fast-track your knowledge by taking a course like Tom Critchlow’s SEO MBA, or you can try to develop these skills through your job.

As a junior in any company, it can be hard to get your voice heard amongst the senior crowd. Ten years ago, I shared my wins with the team in a weekly group email in the office.
Here’s what you should be sharing:
- Praise from 3rd parties, e.g. “the client said they are impressed with the work this month.”
- Successful performance insights, e.g “following our SEO change, the client has seen X% more conversions this month.”
- Examples of the work you led, e.g. if your leadership and decision-making led to good results, then you need to share it.
At Ahrefs I keep a “wins” document. It’s just a simple spreadsheet that lists feedback on the blog posts I’ve written, the links I’ve earned and what newsletters my post was included in. It’s useful to have a document like this so you have a record of your achievements.
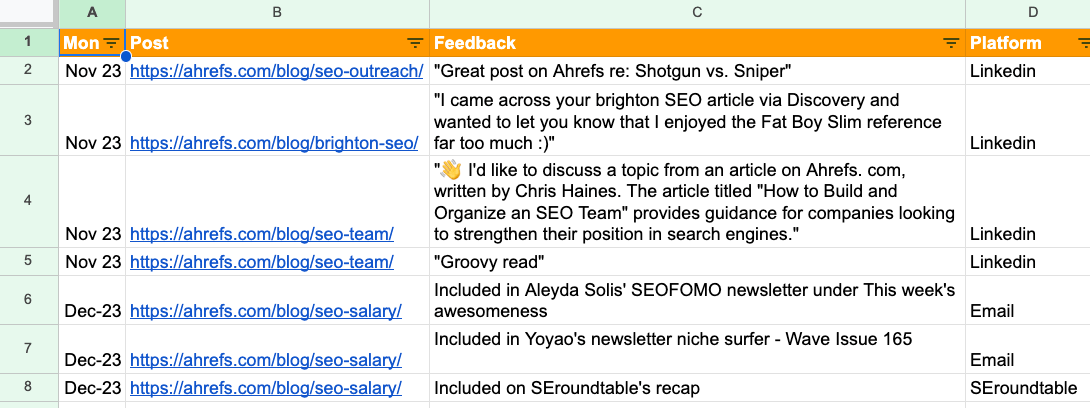

Sidenote.
Junior SEOs sometimes talk about the things “we” achieved as a team rather than what they achieved at the interview stage. If you want the SEO Lead role, remember to talk about what you achieved. While there’s no “I” in team, you also need to advocate for yourself.
One of my first big wins as an SEO was getting a link from an outreach campaign on Buzzfeed. When I went to Brighton SEO later that year and saw Matthew Howells-Barby sharing how he got a Buzzfeed link, I realized that this was not something everyone had done.
So when I did manage to become an SEO Lead, and my team won a prize in Publicis Groupe for our SEO performance, I made sure everyone knew about the work we did. I even wrote a case study on the work for Publicis Groupe’s intranet.
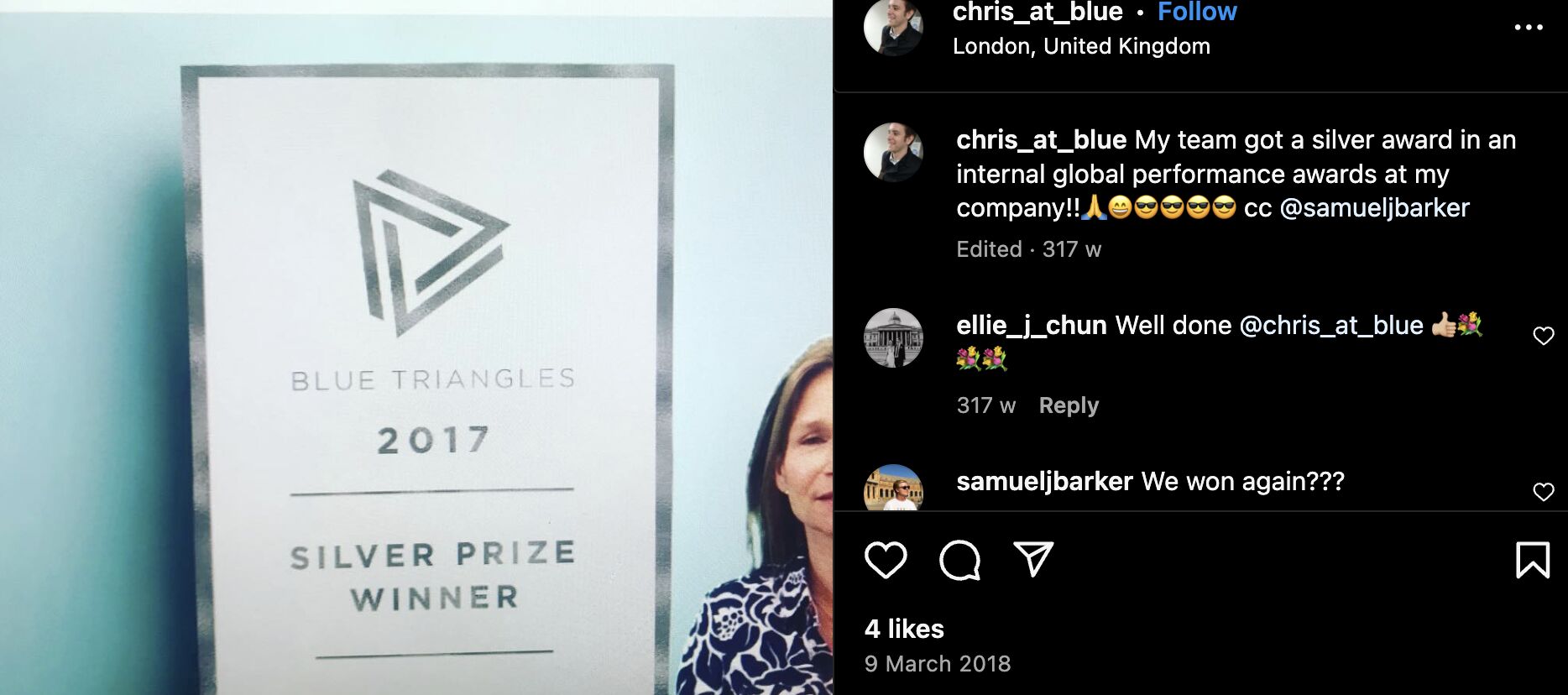

I’ve worked with some incredibly talented people, many of whom have helped me in my career.
I owe my big break to Tim Cripps, Laura Scott, and Kevin Mclaren. Without their support and encouragement, I wouldn’t be where I am today. Even before that, David Schulhof, Jodie Wheeler, and Carl Brooks let me mastermind some bonkers content campaigns that were lucky enough to succeed:

I wasn’t even an SEO Lead at that point, but they gave me the reins and trusted me.
So, how can you find your tribe?
- Speak to recruiters – they might hold the ticket to your next dream job. I spoke to many recruiters early in my career, but only two recruiters delivered for me—they were Natasha Woodford, and Amalia Gouta. Natasha helped me get a job that filled my skill gap, and Amalia helped me get my first SEO Lead role.
- Go to events and SEO conferences, and talk to speakers to build connections outside of your company.
- Use LinkedIn and other social media to interact with other companies or individuals that resonate with you.
Many senior SEO professionals spend most of their online lives on X and LinkedIn. If you’re not using them, you’re missing out on juicy opportunities.


Sharing your expertise on these platforms is one of the easiest ways to increase your chances of getting a senior SEO role. Because, believe it or not, sometimes a job offer can be just a DM away.
Here’s some specific ideas of what you can share:
- Share your thoughts on a trending topic – like the latest Google algorithm update.
- Share what you learned during the course of a campaign.
- Ask the community for their thoughts on a certain topic.
I’ve recently started posting on LinkedIn and am impressed by the reach you can get by posting infrequently on these topics.
Here’s an example of one of my posts where I asked the community for help researching an article I was writing:
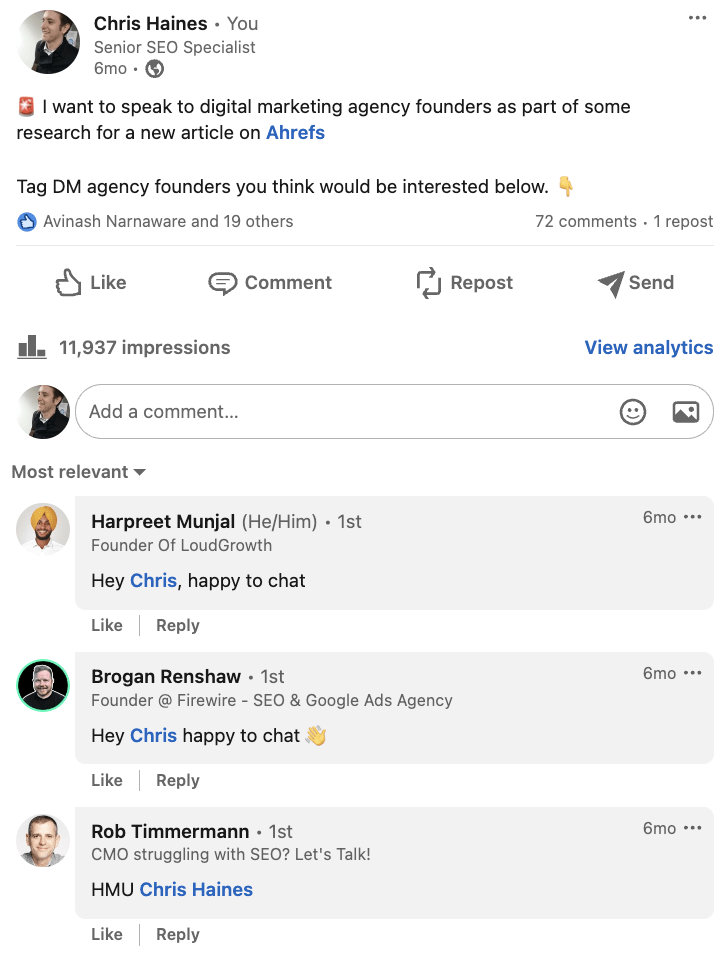

And here is the content performance across the last year from posting these updates.
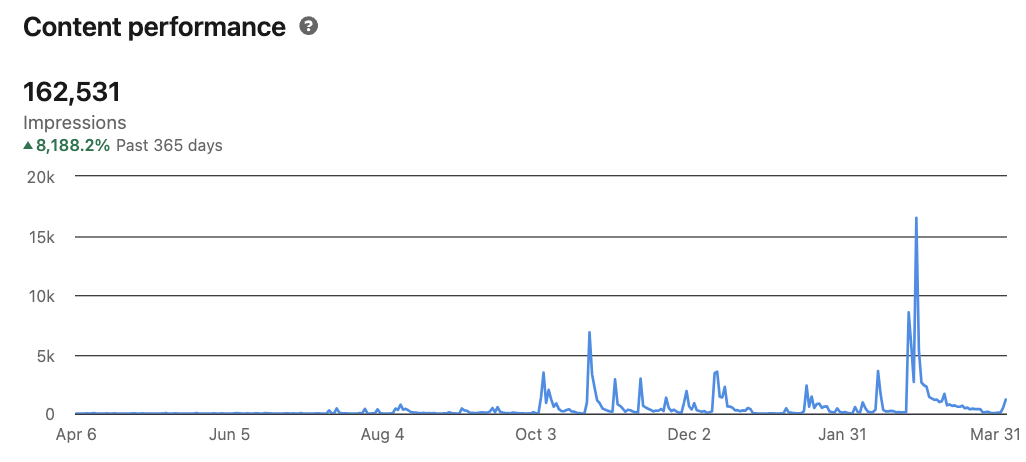

I’m clearly not a LinkedIn expert—far from it! But as you can see, with just a few months of posting, you can start to make these platforms work for you.
Godard Abel, co-founder of G2, talked on a podcast about conscious leadership. This struck a chord with me recently as I realized that I had practiced some of the principles of conscious leadership—unconsciously.
You can start practicing conscious leadership by asking yourself if your actions are above or below the line. Here are a few examples of above and below-the-line thinking:
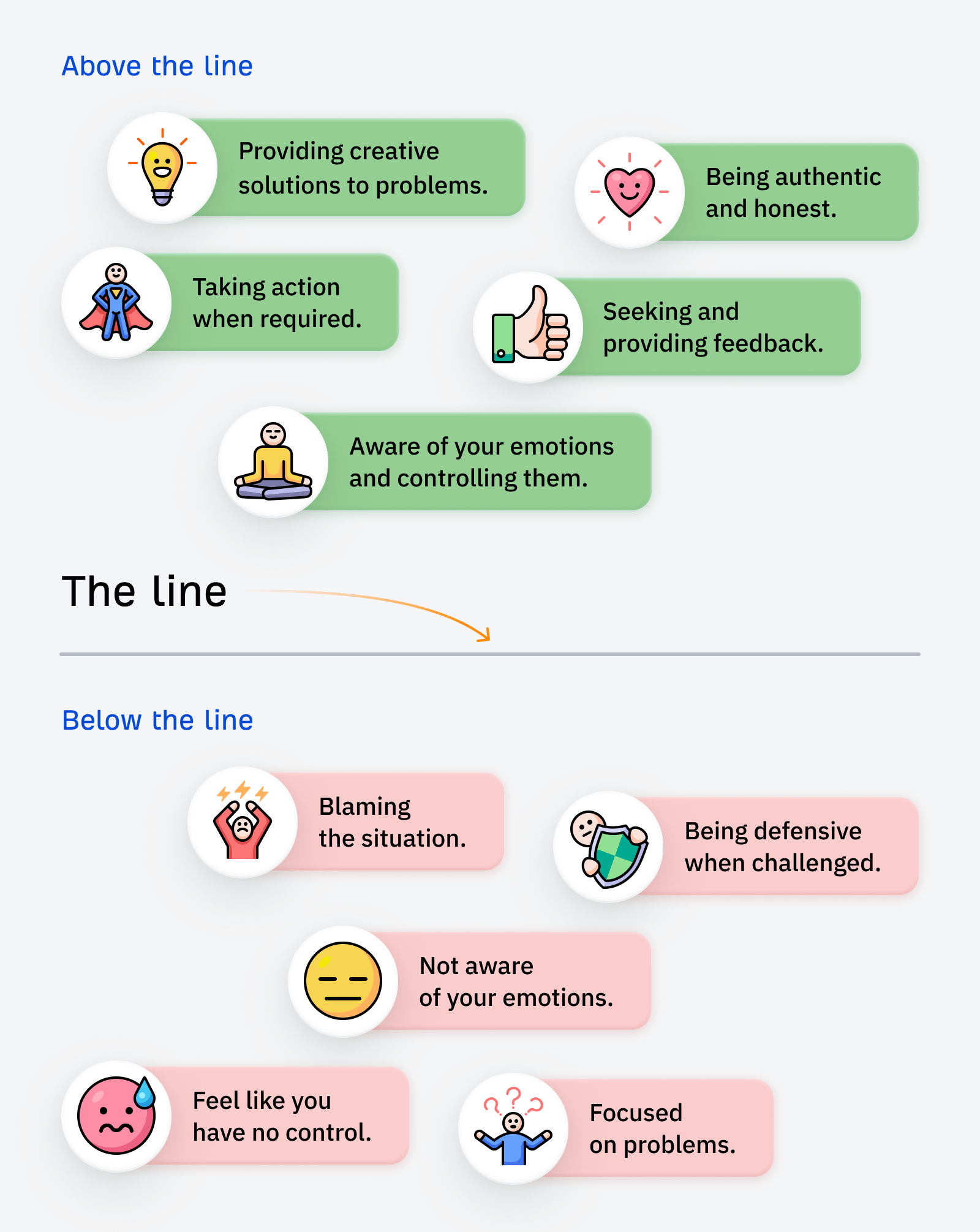

If you want a senior SEO role, I’d suggest shifting your mindset to above-the-line thinking.
In the world of SEO, it’s easy to blame all your search engine woes on Google. We’ve all been there. But a lot of the time, simple changes to your website can make a huge difference—it just takes a bit of effort to find them and make the changes.
SEO is not an exact science. Some stakeholders naturally get nervous if they sense you aren’t sure about what you’re saying. If you don’t get their support early on then you fall at the first hurdle.


To become more persuasive, try incorporating Aristotle’s three persuasive techniques into your conversations.
- Pathos: use logical reasoning, facts, and data to present water-tight arguments.
- Ethos: establish your credibility and ethics through results.
- Logos: make your reports tell a story.
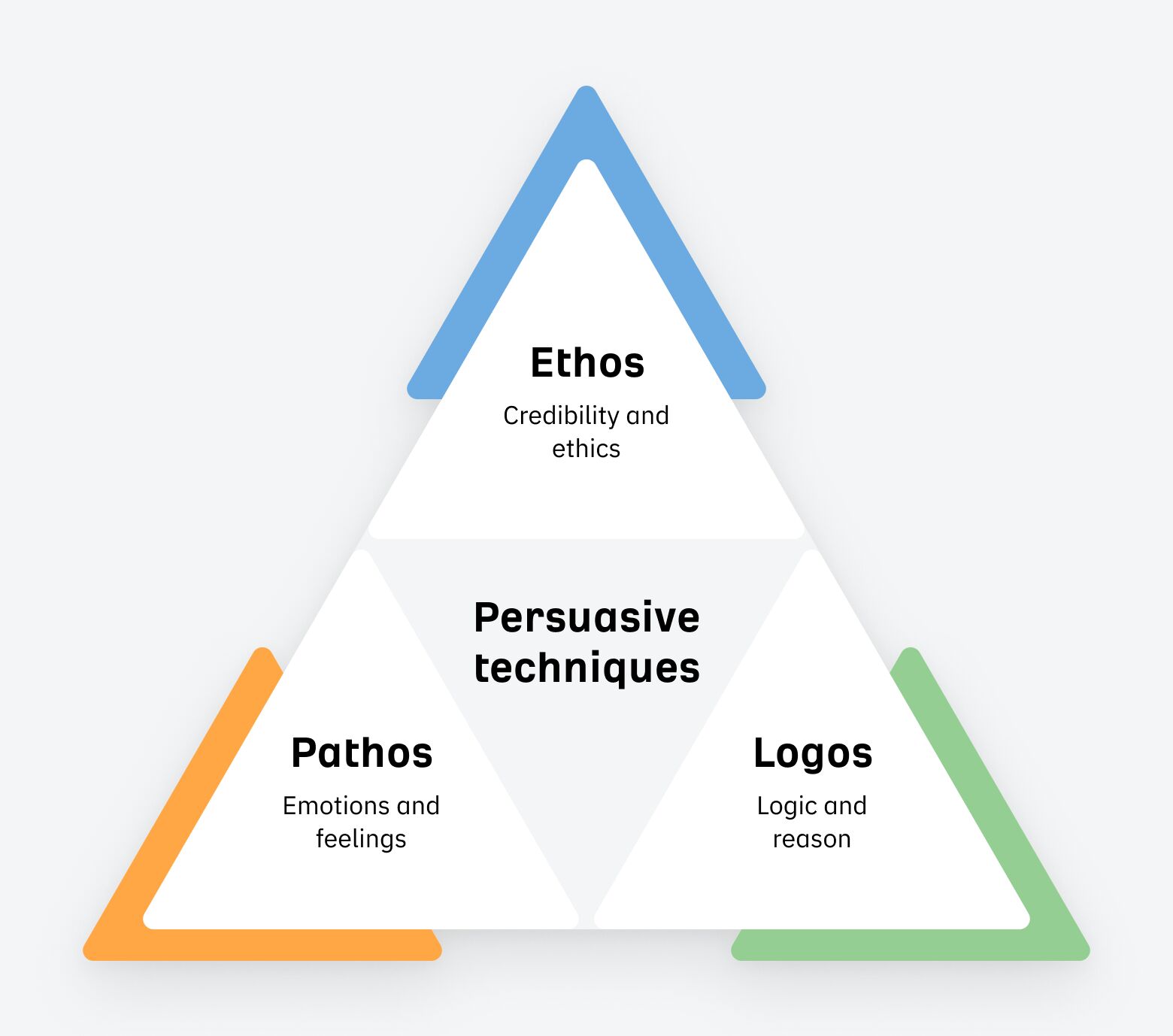

Then sprinkle in language that has a high level of modality:
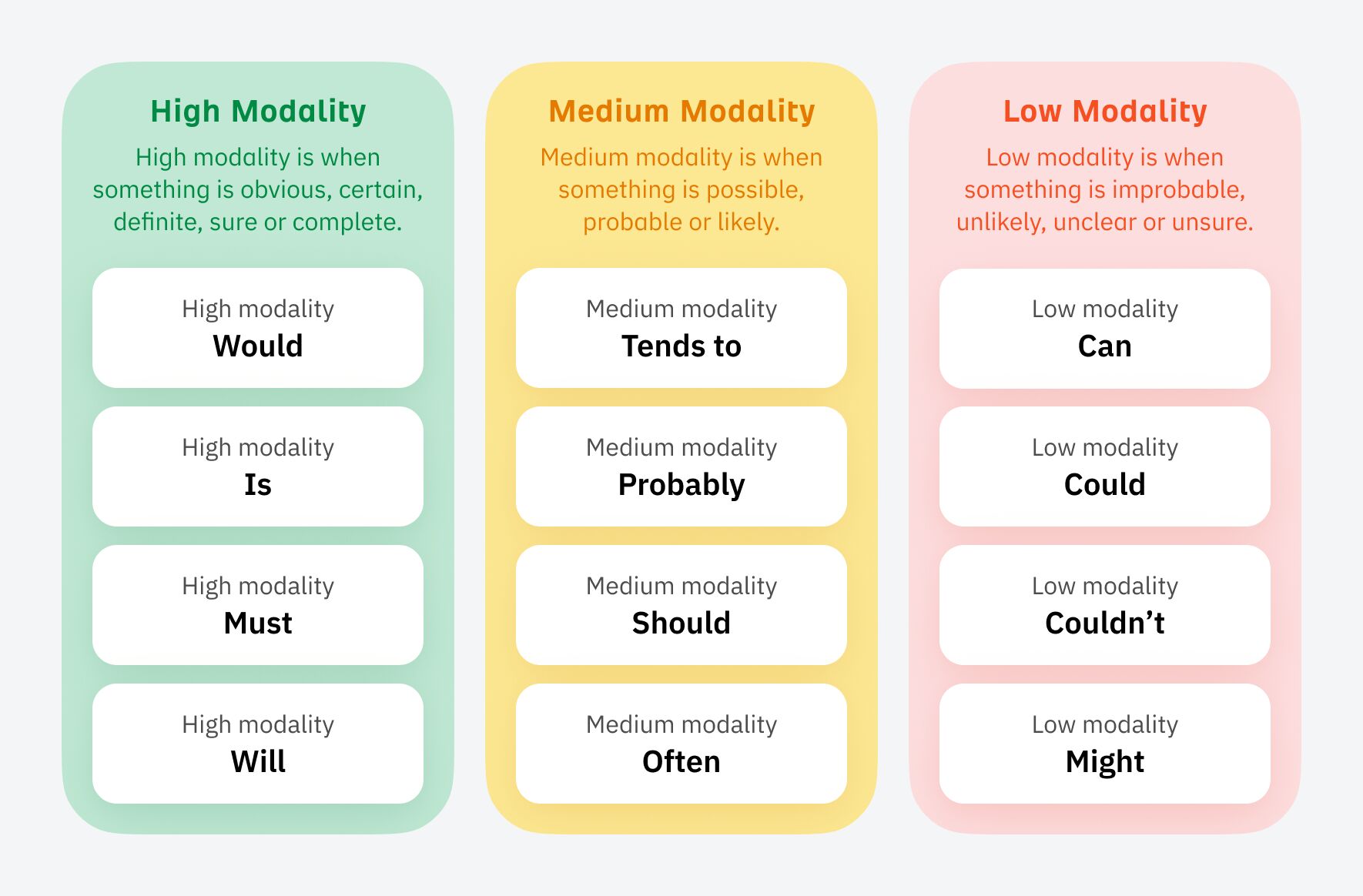

Some people will be able to do this naturally without even realizing it, but for others, it can be an uphill struggle. It wasn’t easy for me, and I had to learn to adapt the way I talked to stakeholders early on.
The strongest way I found was to appeal to emotions and back up with data from a platform like Ahrefs. Highlight what competitors have done in terms of SEO and the results they’ve earned from doing it.
Sidenote.
You don’t have to follow this tip to the letter, but being aware of these concepts means you’ll start to present more confident and persuasive arguments for justifying your SEO strategies.
When I started in SEO, I had zero connections. Getting a job felt like an impossible challenge.
Once I’d got my first SEO Lead job, it felt stupidly easy to get another one—just through connections I’d made along the way in my SEO journey.
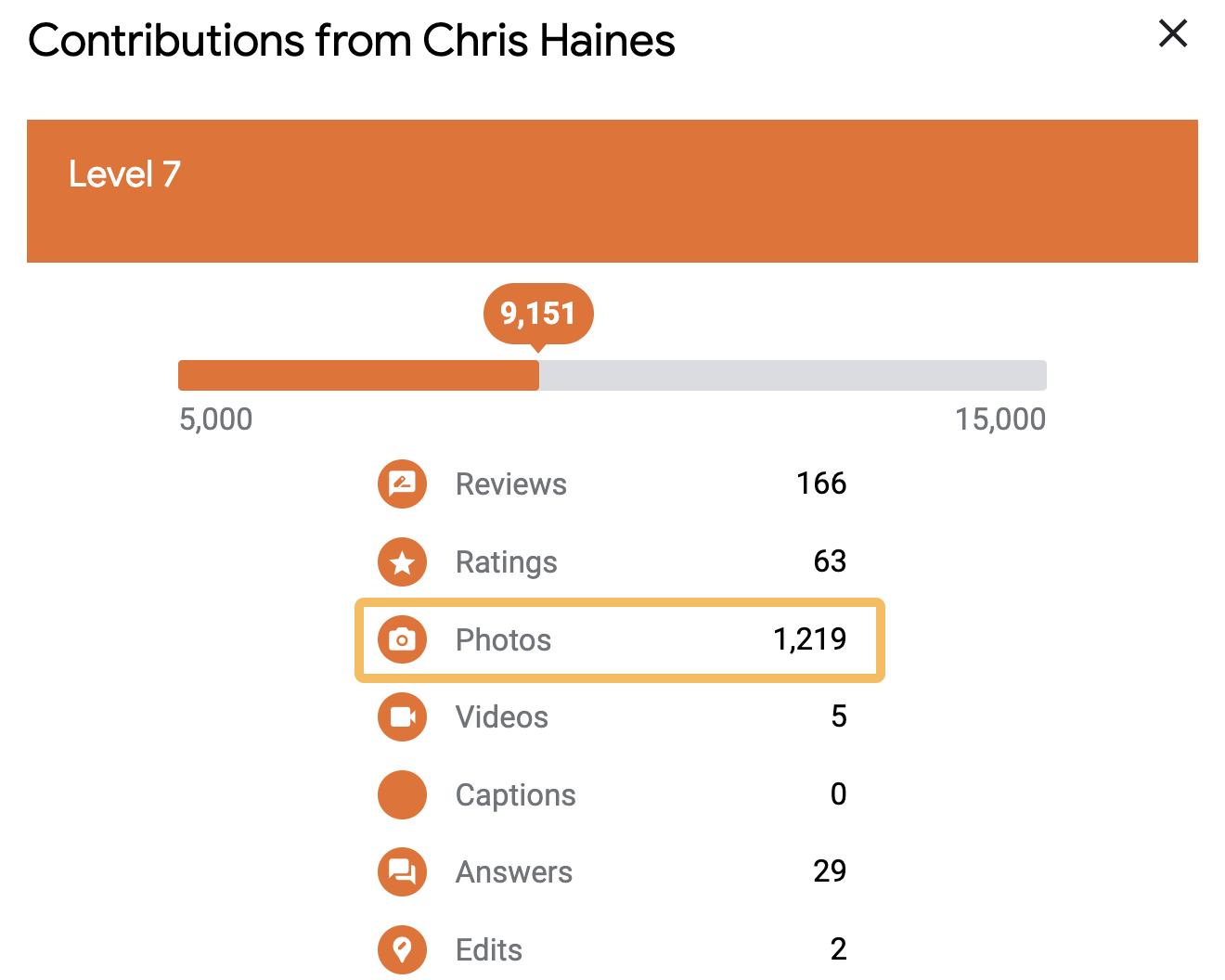
I once got stuck on a delayed train with a senior member of staff, and he told me he was really into Google Local Guides, and he was on a certain high level. He said it took him a few years to get there.
Local Guides is part of Google Maps that allows you submit reviews and other user generated content
When he showed me the app, I realized that you could easily game the levels by uploading lots of photos.
In a “hold my beer” moment, I mass downloaded a bunch of photos, uploaded them to Local Guides and equaled his Local Guide level on the train in about half an hour. He was seething.

One of the photos I uploaded was a half-eaten Subway. It still amazes me that 50,974 people have seen this photo:
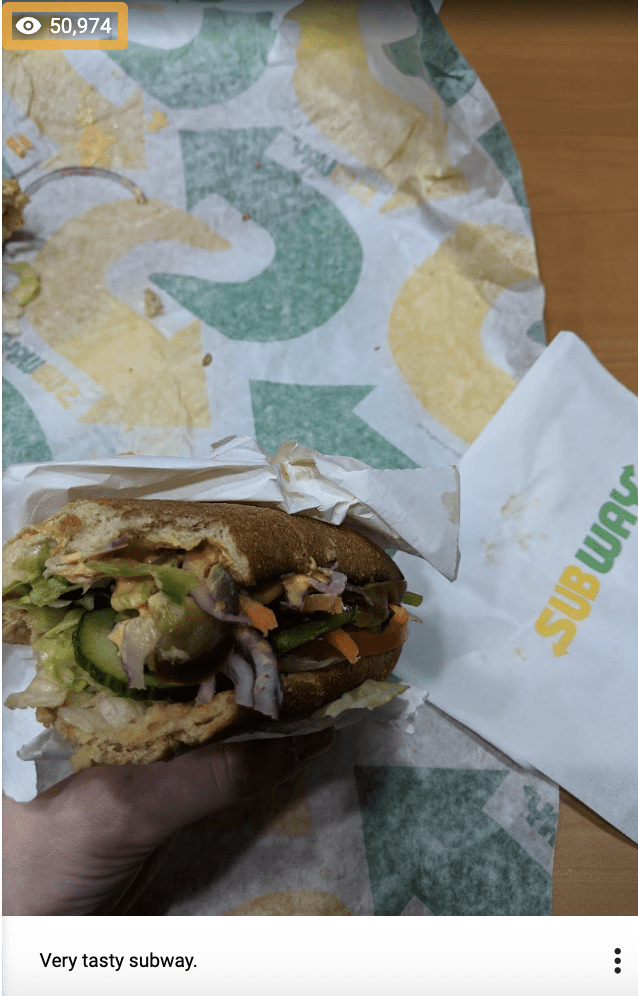
This wasn’t exactly SEO, but the ability to find this ‘hack’ so quickly impressed him, and we struck up a friendship.
The next month that person moved to another company, and then another few months later, he offered me an SEO Lead job.
Tip
Build connections with everyone you can—you never know who you might need to call on next.
Final thoughts
The road to becoming an SEO Lead seems straightforward enough when you start out, but it can quickly become long and winding.
But now armed with my tips, and a bucket load of determination, you should be able to navigate your way to an SEO Lead role much quicker than you think.
Lastly, if you want any more guidance, you can always ping me on LinkedIn. 🙂
SEO
7 Content Marketing Conferences to Attend in 2024

I spend most of my days sitting in front of a screen, buried in a Google Doc. (You probably do too.)
And while I enjoy deep work, a few times a year I get the urge to leave my desk and go socialize with other human beings—ideally on my employer’s dime 😉
Conferences are a great excuse to hang out with other content marketers, talk shop, learn some new tricks, and pretend that we’re all really excited about generative AI.
Without further ado, here are the biggest and best content marketing conferences happening throughout the rest of 2024.
Dates: May 5–7
Prices: from $795
Website: https://cex.events/
Location: Cleveland, OH
Speakers: B.J. Novak, Ann Handley, Alexis Grant, Justin Welsh, Mike King
CEX is designed with content entrepreneurs in mind (“contenpreneurs”? Did I just coin an awesome new word?)—people that care as much about the business of content as they do the craft.
In addition to veteran content marketers like Ann Handley and Joe Pulizi waxing lyrical about modern content strategy, you’ll find people like Justin Welsh and Alexis Grant exploring the practicalities of quitting your job and becoming a full-time content creator.
Here’s a trailer for last year’s event:
Sessions include titles like:
- Unlocking the Power of Book Publishing: From Content to Revenue
- Quitting A $200k Corporate Job to Become A Solo Content Entrepreneur
- Why You Should Prioritize Long-Form Content
(And yes—Ryan from The Office is giving the keynote.)
Dates: Jun 3–4
Location: Seattle, WA
Speakers: Wil Reyolds, Bernard Huang, Britney Muller, Lily Ray
Prices: from $1,699
Website: https://moz.com/mozcon
Software company Moz is best known in the SEO industry, but its conference is popular with marketers of all stripes. Amidst a lineup of 25 speakers there are plenty of content marketers speaking, like Andy Crestodina, Ross Simmonds, and Chima Mmeje.
Check out this teaser from last year’s event:
This year’s talks include topics like:
- Trust and Quality in the New Era of Content Discovery
- The Power of Emotion: How To Create Content That (Actually) Converts
- “E” for Engaging: Why The Future of SEO Content Needs To Be Engaging
Dates: Sep 18–20
Location: Boston, MA
Speakers: TBC
Prices: from $1,199
Website: https://www.inbound.com/
Hosted by content marketing OG HubSpot, INBOUND offers hundreds of talks, deep dives, fireside chats, and meetups on topics ranging from brand strategy to AI.
Here’s the recap video:
I’ve attended my fair share of INBOUNDs over the years (and even had a beer with co-founder Dharmesh Shah), and always enjoy the sheer choice of events on offer.
Keynotes are a highlight, and this year’s headline speaker has a tough act to follow: Barack Obama closed out the conference last year.
Dates: Oct 22–23
Location: San Diego, CA
Speakers: TBC
Prices: from $1,199
Website: https://www.contentmarketingworld.com/
Arguably the content marketing conference, Content Marketing World has been pumping out content talks and inspiration for fourteen years solid.
Here’s last year’s recap:
The 2024 agenda is in the works, but last year’s conference explored every conceivable aspect of content marketing, from B2C brand building through to the quirks of content for government organizations, with session titles like:
- Government Masterclass: A Content Marketing Strategy to Build Public Trust
- A Beloved Brand: Evolving Zillow’s Creative Content Strategy
- Evidence-Based SEO Strategies: Busting “SEO Best Practices” and Other Marketing Myths
Dates: Oct 24–25
Location: Singapore
Speakers: Andy Chadwick, Nik Ranger, Charlotte Ang, Marcus Ho, Victor Karpenko, Amanda King, James Norquay, Sam Oh, Patrick Stox, Tim Soulo (and me!)
Prices: TBC
Website: https://ahrefs.com/events/evolve2024-singapore
That’s right—Ahrefs is hosting a conference! Join 500 digital marketers for a 2-day gathering in Singapore.
We have 20 top speakers from around the world, expert-led workshops on everything from technical SEO to content strategy, and tons of opportunities to rub shoulders with content pros, big brands, and the entire Ahrefs crew.
I visited Singapore for the first time last year and it is really worth the trip—I recommend visiting the Supertree Grove, eating at the hawker markets in Chinatown, and hitting the beach at Sentosa.
If you need persuading, here’s SEO pro JH Scherck on the Ahrefs podcast making the case for conference travel:
And to top things off, here’s a quick walkthrough of the conference venue:
Dates: Oct 27–30
Location: Portland, OR
Speakers: Relly Annett-Baker, Fawn Damitio, Scott Abel, Jennifer Lee
Prices: from $1,850
Website: https://lavacon.org/
LavaCon is a content conference with a very technical focus, with over 70 sessions dedicated to helping companies solve “content-related business problems, increase revenue, and decrease production costs”.
In practice, that means speakers from NIKE, Google, Meta, Cisco, and Verizon, and topics like:
- Operationalizing Generative AI,
- Taxonomies in the Age of AI: Are they still Relevant?, and
- Out of Many, One: Building a Semantic Layer to Tear Down Silos
Here’s the recap video for last year’s conference:
Dates: Nov 8
Location: London
Speakers: Nick Parker, Tasmin Lofthouse, Dan Nelken, Taja Myer
Prices: from £454.80
Website: https://www.copywritingconference.com/
CopyCon is a single-day conference in London, hosted by ProCopywriters (a membership community for copywriters—I was a member once, many years ago).
Intended for copywriters, creatives, and content strategists, the agenda focuses heavily on the qualitative aspects of content that often go overlooked—creative processes, tone of voice, and creating emotional connections through copy.
It’s a few years old, but this teaser video shares a sense of the topics on offer:
This year’s talks include sessions like:
- The Mind-Blowing Magic of Tone of Voice,
- The Power of AI Tools as a Content Designer, and the beautifully titled
- Your Inner Critic is a Ding-Dong.
(Because yes, your inner critic really is a ding-dong.)
Final thoughts
These are all content-specific conferences, but there are a ton of content-adjacent events happening throughout the year. Honourable mentions go to DigiMarCon UK 2024 (Aug 29–30, London, UK), Web Summit (Nov 11–14, Lisbon, Portugal), and B2B Forum (Nov 12–14, Boston, MA).
I’ve focused this list solely on in-person events, but there are also online-only conferences available, like ContentTECH Summit (May 15–16).
Heading to a content conference that I haven’t covered? Share your recommendation with me on LinkedIn or X.
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days ago4 New Google Ads Performance Max Updates: What You Need to Know
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 16, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Clarifies Vacation Rental Structured Data
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoWill Google Buy HubSpot? | Content Marketing Institute
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoStreamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoHow to Collect & Use Customer Data the Right (& Ethical) Way
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login