The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Google Explains Rendering and Impact on SEO

Google’s Martin Splitt participated in a Duda Webinar about web page rendering and how it impacts SEO. Rendering is what happens when a browser requests a web page, it’s a key part of Core Web Vitals scores. Understanding this helps take some of the mystery out of Core Web Vitals.
Web Page Rendering
Web page rendering is what happens between the browser and the web page, the process of building a web page. An efficient rendering process results in high Core Web Vitals scores.
Less efficient rendering can impact sales, advertising earnings and even web page crawling to a certain extent.
Google’s Martin Splitt was asked to define what rendering is.
Screenshot of Martin Splitt Explaining Rendering

Martin responded with an analogy between cooking a meal from a recipe and making a web page.
HTML means HyperText Markup Language. It’s a format for creating documents that can be accessed with a browser through the rendering process.
Martin Splitt explained rendering:
“If you think about HTML as a recipe, and you have all the ingredients in there:
You have a bunch of text
You have a bunch of images
You have a bunch of stuff
But you don’t really have it in the recipe. The recipe is a piece of paper with all these instructions on how to make a thing.”
The first part of Martin’s explanation is that HTML is like a recipe, the instructions. The text and images are the things used to create the finished meal, which is the web page.
Martin continued the analogy by comparing web page resources with the actual physical ingredients:
“Now, the resources of a website are the ingredients, such as the CSS, the JavaScript files as well as the images, the videos, all that stuff that you load to actually make the page look the way that it looks afterwards.
And the website that you know and use in your browser you see in your browser, that’s the final dish.”
Screenshot of Jason Barnard

Rendering is Like the Process of Cooking
Martin next compared rendering to the actual process of taking the ingredients (resources like images, CSS, etc.) and doing the cooking.
He continued:
“And rendering is pretty much the cooking or the preparation process of that.”
Googlebot Crawling and Rendering
Next Martin explains what rendering is for Googlebot.
Martin explained Googlebot and rendering:
“So crawling fundamentally just goes into a big book of recipes and just takes out a page with a recipe and puts that into our realm, our reach, like basically we are standing here at a kitchen table …and we wait for the cooking to begin and crawling will basically just hand us a recipe.
And then rendering is the process where, rendering goes, Aha! Interesting! Crawler over there, can you get me these ten ingredients?
And the crawler will be conveniently, yes, I got you these ten ingredients that you need.
Thank you very much!
And then we start cooking.
That’s what rendering is.”
Related: How (& Why) Search Engines Render Pages
Parsing the HTML for Web Page Assembly
The next part introduces a programming word, parse. Parsing is just taking all the parts of the HTML document (JavaScript, CSS, HTML elements) and following the directions for creating the web page.
Martin continued his discussion of rendering:
“So rendering parses the HTML.
HTML fundamentally, when it comes from crawling, is just a bunch of text, conveniently formatted but …Text!
In order to make that into a visual representation, which is the website really, we need to render it, which means we need to fetch all the resources, we need to fundamentally understand what the text tells us to be like:
There’s a header here, okay.
Then there’s an image there and next to the image there’s a bunch of text and then under the image there’s another heading, it’s a smaller heading, it’s a lower level heading …and then there’s a video and then below that video there’s some more text and in this text there’s three links going to here, here and here.
And all this assembly process, this understanding what it is and then this assembling it into a visual representation that you can interact with in your browser window, that is rendering.”
The Role of JavaScript in Rendering
Some JavaScript is critical for rendering (creating) the web page. Quite a bit of JavaScript, like the scripts associated with a contact form, aren’t really necessary in the initial creation of an interactive web page that a site visitor can scroll, read, and click a navigation menu.
In order to speed up the web page rendering (and improve Core Web Vitals) some non-critical JavaScript can be delayed or excluded altogether if not necessary for the web page.
There are some JavaScript that is important to making the page visible and interactive and some that is not important yet or at all.
Martin explained:
“And as part of rendering, at the very first stage, we execute the JavaScript because JavaScript happens to be basically a recipe within the recipe.
So JavaScript can be like, now go chop those onions!
So now you have the onions as a raw ingredient but you don’t put the onions as a whole into your dish, you cut them up.
And that’s what the JavaScript is needed for, right?
…The JavaScript execution is just a part of rendering.”
Screenshot of Bartosz Goralewicz
 Related: Rendering SEO Manifesto: Why We Need to Go Beyond JavaScript SEO
Related: Rendering SEO Manifesto: Why We Need to Go Beyond JavaScript SEO
The Layout Tree
Martin next begins talking about the Layout Tree. He’s making a reference to the Document Object Model, which is an arrangement of all of the parts of the web page in a hierarchical representation.
The different “bits and pieces” of a web page are like the leaves of a tree. In HTML those leaves on what Martin calls the Layout Tree, are called, nodes.
Martin explains the Layout Tree:
“But then when the JavaScript execution has finished or if there was no JavaScript execution that is fine, too.
But what then happens is we are assembling, like we are figuring out these bits and pieces and how we need to like assemble them on the page and that leads to something called, Layout Tree.
And the Layout Tree tells us how big things are, where on the page things are.
If they are visible or if they are not visible, if one thing is behind another thing.
This information is important for us as well, just as much as executing the JavaScript because the JavaScript might change, delete or add content that wasn’t in the initial HTML as it has been delivered by the server.
So that’s rendering in a nutshell.
From we have some HTML to we have potentially a bunch of pixels on the screen. That’s rendering.”
Costly Rendering Can Impact User Experience
Martin next introduces the useful insight about the impact of JavaScript on energy consumption. He uses the word “expensive” to describe the how costly in time and energy some JavaScript can be.
He mentions how JavaScript has been compared to carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas and how that impacts users and ultimately the bottom line of publishers and ecommerce stores.
Martin Splitt Explains Expensive Rendering
 Martin explains the impact of expensive rendering:
Martin explains the impact of expensive rendering:
“Google Search has the exact same struggle as a real-world user in this case.
Because, for a real-world user, even if you are on a modern phone and a really fast and fantastic and expensive phone as well, more execution also always, always, means more power consumption.
That’s just the thing. And …there have been people who called JavaScript the CO2 of the Internet and I don’t think that’s completely wrong.
…The more expensive you make it the worse it is for us as an experience.
Google Search doesn’t really care. We just have to invest in the resources that we need and we do a lot of optimizations to make sure that we are wasting as few energy and time as possible.
But obviously, if you are optimizing that, a nice and really nice side effect is that your users will probably also be happier because they need less battery, their old phone will still work fine with what you put out there and they will be able to consume your web content and maybe not your competitors because your competitors don’t care and actually produce something that is less convenient to use on their phones.
So this is not something where you would pit Google versus user experience.
This is kind of like the same problem or the same challenge and we are all facing it, including Google Search.”
Screenshot of Google’s Martin Splitt

Insights into Importance of Rendering
Core Web Vitals can be somewhat abstract and mysterious, especially when techies talk about Document Object Models, DOM trees and rendering.
Martin Splitt’s analogies helped take some of that mystery out of one important part of understanding Core Web Vitals scores, which is rendering.
Another benefit of his discussion is creating awareness about the concept of expensive rendering and how that might impact site visitors whose phones might be older and have trouble rendering the page. And it’s not just older phones but newer phones might have an issue downloading a web page if it’s been on for days and the RAM is spread thin across multiple open browser windows.
Lastly, he demystified the concept of rendering. That helps move the conversation forward on improving web page speed and Core Web Vitals performance because there are few things like technical jargon to slow down or stop progress on understanding something important.
Citations
Original Duda Webinar Page for Essential Rendering
Watch Martin Splitt explain rendering from about the 15:36 minute mark
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
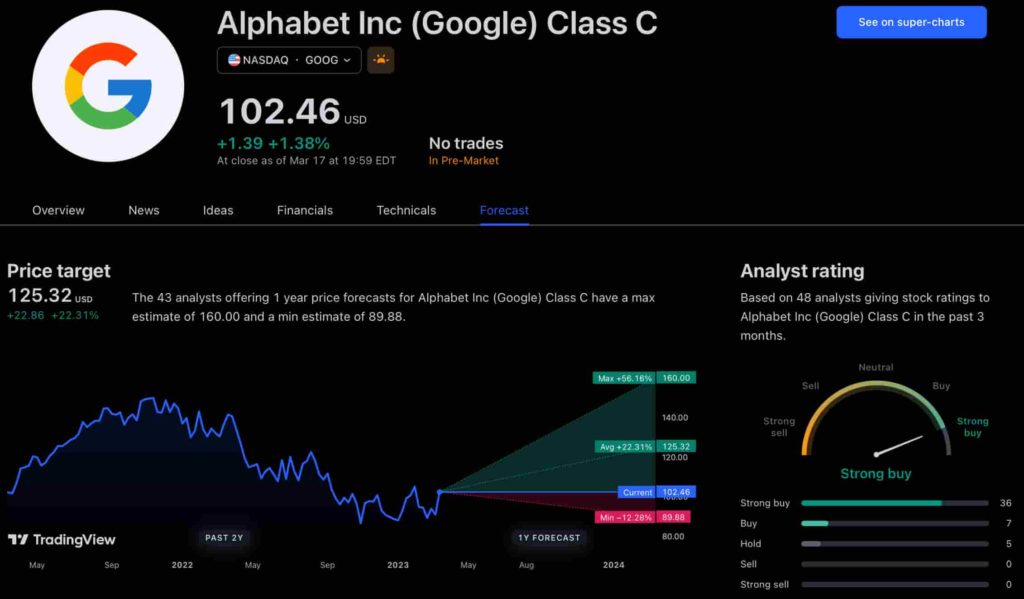
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Limits News Links In California Over Proposed ‘Link Tax’ Law
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 12, 2024
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Unplugs “Notes on Search” Experiment
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoCritical Display Error in Brand Safety Metrics On Twitter/X Corrected















You must be logged in to post a comment Login