APPS
Twitter’s political ads ban is a distraction from the real problem with platforms

Sometimes it feels as if Internet platforms are turning everything upside down, from politics to publishing, culture to commerce, and of course swapping truth for lies.
This week’s bizarro reversal was the vista of Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey, a tech CEO famed for being entirely behind the moral curve of understanding what his product is platforming (i.e. nazis), providing an impromptu ‘tweet storm’ in political speech ethics.
Actually he was schooling Facebook’s Mark Zuckerberg — another techbro renowned for his special disconnect with the real world, despite running a massive free propaganda empire with vast power to influence other people’s lives — in taking a stand for the good of democracy and society.
So not exactly a full reverse then.
In short, Twitter has said it will no longer accept political ads, period.
Whereas Facebook recently announced it will no longer fact-check political ads. Aka: Lies are fine, so long as you’re paying Facebook to spread them.
You could argue there’s a certain surface clarity to Facebook’s position — i.e. it sums to ‘when it comes to politics we just won’t have any ethics’. Presumably with the hoped for sequitur being ‘so you can’t accuse us of bias’.
Though that’s actually a non sequitur; by not applying any ethical standards around political campaigns Facebook is providing succour to those with the least ethics and the basest standards. So its position does actually favor the ‘truth-lite’, to put it politely. (You can decide which political side that might advantage.)
Twitter’s position also has surface clarity: A total ban! Political and issue ads both into the delete bin. But as my colleague Devin Coldewey quickly pointed out it’s likely to get rather more fuzzy around the edges as the company comes to defining exactly what is (and isn’t) a ‘political ad’ — and what its few “exceptions” might be.
Indeed, Twitter’s definitions are already raising eyebrows. For example it has apparently decided climate change is a ‘political issue’ — and will therefore be banning ads about science. While, presumably, remaining open to taking money from big oil to promote their climate-polluting brands… So yeah, messy.
There will clearly be attempts to stress test and circumvent the lines Twitter is setting. The policy may sound simple but it involves all sorts of judgements that expose the company’s political calculations and leave it open to charges of bias and/or moral failure.
Still, setting rules is — or should be — the easy and adult thing to do when it comes to content standards; enforcement is the real sweating toil for these platforms.
Which is also, presumably, why Facebook has decided to experiment with not having any rules around political ads — in the (forlorn) hope of avoiding being forced into the role of political speech policeman.
If that’s the strategy it’s already looking spectacularly dumb and self-defeating. The company has just set itself up for an ongoing PR nightmare where it is indeed forced to police intentionally policy-provoking ads from its own back-foot — having put itself in the position of ‘wilfully corrupt cop’. Slow hand claps all round.
Albeit, it can at least console itself it’s monetizing its own ethics bypass.
Twitter’s opposing policy on political ads also isn’t immune from criticism, as we’ve noted.
Indeed, it’s already facing accusations that a total ban is biased against new candidates who start with a lower public profile. Even if the energy of that argument would be better spent advocating for wide-ranging reform of campaign financing, including hard limits on election spending. If you really want to reboot politics by levelling the playing field between candidates that’s how to do it.
Also essential: Regulations capable of enforcing controls on dark money to protect democracies from being bought and cooked from the inside via the invisible seeding of propaganda that misappropriates the reach and data of Internet platforms to pass off lies as populist truth, cloaking them in the shape-shifting blur of microtargeted hyperconnectivity.
Sketchy interests buying cheap influence from data-rich billionaires, free from accountability or democratic scrutiny, is our new warped ‘normal’. But it shouldn’t be.
There’s another issue being papered over here, too. Twitter banning political ads is really a distracting detail when you consider that it’s not a major platform for running political ads anyway.
During the 2018 US midterms the category generated less than $3M for the company.
And, secondly, anything posted organically as a tweet to Twitter can act as a political call to arms.
It’s these outrageous ‘organic’ tweets where the real political action is on Twitter’s platform. (Hi Trump.)
Including inauthentically ‘organic’ tweets which aren’t a person’s genuinely held opinion but a planted (and often paid for) fake. Call it ‘going native’ advertising; faux tweets intended to pass off lies as truth, inflated and amplified by bot armies (fake accounts) operating in plain sight (often gaming Twitter’s trending topics) as a parallel ‘unofficial’ advertising infrastructure whose mission is to generate attention-grabbing pantomimes of public opinion to try and sway the real thing.
In short: Propaganda.
Who needs to pay to run a political ad on Twitter when you can get a bot network to do the boosterism for you?
Let’s not forget Dorsey is also the tech CEO famed for not applying his platform’s rules of conduct to the tweets of certain high profile politicians. (Er, Trump again, basically.)
So by saying Twitter is banning political ads yet continuing to apply a double standard to world leaders’ tweets — most obviously by allowing the US president to bully, abuse and threaten at will in order to further his populist rightwing political agenda — the company is trying to have its cake and eat it.
More recently Twitter has evolved its policy slightly, saying it will apply some limits on the reach of rule-breaking world leader tweets. But it continues to run two sets of rules.
To Dorsey’s credit he does foreground this tension in his tweet storm — where he writes [emphasis ours]:
Internet political ads present entirely new challenges to civic discourse: machine learning-based optimization of messaging and micro-targeting, unchecked misleading information, and deep fakes. All at increasing velocity, sophistication, and overwhelming scale.
These challenges will affect ALL internet communication, not just political ads. Best to focus our efforts on the root problems, without the additional burden and complexity taking money brings. Trying to fix both means fixing neither well, and harms our credibility.
This is good stuff from Dorsey. Surprisingly good, given his and Twitter’s long years of free speech fundamentalism — when the company gained a reputation for being wilfully blind and deaf to the fact that for free expression to flourish online it needs a protective shield of civic limits. Otherwise ‘freedom to amplify any awful thing’ becomes a speech chiller that disproportionately harms minorities.
Aka freedom of speech is not the same as freedom of reach, as Dorsey now notes.
Even with Twitter making some disappointing choices in how it defines political issues, for the purposes of this ad ban, the contrast with Facebook and Zuckerberg — still twisting and spinning in the same hot air; trying to justify incoherent platform policies that sell out democracy for a binary ideology which his own company can’t even stick to — looks stark.
The timing of Dorsey’s tweet-storm, during Facebook’s earnings call, was clearly intended to make that point.
“Zuckerberg wants us to believe that one must be for or against free speech with no nuance, complexity or cultural specificity, despite running a company that’s drowning in complexity,” writes cultural historian, Siva Vaidhyanathan, confronting Facebook’s moral vacuousness in a recent Guardian article responding to another Zuckerberg ‘manifesto’ on free speech. “He wants our discussions to be as abstract and idealistic as possible. He wants us not to look too closely at Facebook itself.”
Facebook’s position on speech does only stand up in the abstract. Just as its ad-targeting business can only run free of moral outrage in unregulated obscurity, where the baked in biases — algorithmic and user generated — are safely hidden from view so people can’t joins the dots on how they’re being damaged.
We shouldn’t be surprised at how quickly the scandal-prone company is now being called on its ideological BS. We have a savvier political class as a result of the platform-scale disinformation and global data scandals of the past few years. People who have have seen and experienced what Facebook’s policies translate to in real world practice. Like compromised elections and community violence.
With lawmakers like these turning their attention on platform giants there is a genuine possibility of meaningful regulation coming down the pipe for the antisocial media business.
Not least because Facebook’s self regulation has always been another piece of crisis PR, designed to preempt and steer off the real thing. It’s a cynical attempt to maintain its profitable grip on our attention. The company has never been committed to making the kind of systemic change necessary to fix its toxic speech issues.
The problem is, ultimately, toxicity and division drives engagement, captures attention and makes Facebook a lot of money.
Twitter can claim a little distance from that business model not only because it’s considerably less successful than Facebook at generating money by monopolizing attention, but also because it provides greater leeway for its users to build and follow their own interest networks, free from algorithmic interference (though it does do algorithms too).
It has also been on a self-proclaimed reform path for some time. Most recently saying it wants to be responsible for promoting “conversational health on its platform. No one would say it’s there yet but perhaps we’re finally getting to see some action. Even if banning political ads is mostly a quick PR win for Twitter.
The really hard work continues, though. Namely rooting out bot armies before their malicious propaganda can pollute the public sphere. Twitter hasn’t said it’s close to being able to fix that.
Facebook is also still failing to stem the tide of ‘organic’ politicized fake content on its platform. Fakes that profit at our democratic expense by spreading hate and lies.
For this type of content Facebook offers no searchable archive (as it now does for paid ads which it defines as political) — thereby providing ongoing cover for dark money to do its manipulative hack-job on democracy by free-posting via groups and pages.
Plus, even where Facebook claims to be transparently raising the curtain on paid political influence it’s abjectly failing to do so. Its political ads API is still being blasted by research academics as not fit for purpose. Even as the company policy cranks up pressure on external fact-checkers by giving politicians the green light to run ads that lie.
It has also been accused of applying a biased standard when it comes to weeding out “coordinated inauthentic behavior”, as Facebook euphemistically calls the networks of fake accounts set up to amplify and juice reach — when the propaganda in question is coming from within the US and leans toward the political right.
Facebook denies this, claiming for example that a network of pages on its platform reported to be exclusively boosting content from US conservative news site, The Daily Wire, are “real pages run by real people in the U.S., and they don’t violate our policies“. (It didn’t offer us any detail on how it reached that conclusion.)
A company spokesperson also said: “We’re working on more transparency so that in the future people have more information about Pages like these on Facebook.”
So it’s still promising ‘more transparency’ — rather than actually being transparent. And it remains the sole judge interpreting and applying policies that aren’t at all legally binding; so sham regulation then.
Moreover, while Facebook has at times issued bans on toxic content from certain domestic hate speech preachers’, such as banning some of InfoWars’ Alex Jones’ pages, it’s failed to stop the self-same hate respawning via new pages. Or indeed the same hateful individuals maintaining other accounts on different Facebook-owned social properties. Inconsistency of policy enforcement is Facebook’s DNA.
Set against all that Dorsey’s decision to take a stance against political ads looks positively statesmanlike.
It is also, at a fundamental level, obviously just the right thing to do. Buying a greater share of attention than you’ve earned politically is regressive because it favors those with the deepest pockets. Though of course Twitter’s stance won’t fix the rest of a broken system where money continues to pour in and pollute politics.
We also don’t know the fine-grained detail of how Twitter’s algorithms amplify political speech when it’s packaged in organic tweet form. So whether its algorithmic levers are more likely to be triggered into boosting political tweets that inflame and incite, or those that inform and seek to unite.
As I say, the whole of Twitter’s platform can sum to political advertising. And the company does apply algorithms to surface or suppress tweets based on its proprietary (and commercial) determination of ‘engagement quality’. So its entire business is involved in shaping how visible (or otherwise) tweeted speech is.
That very obviously includes plenty of political speech. Not for nothing is Twitter Trump’s platform of choice.
Nothing about its ban on political ads changes all that. So, as ever, where social media self-regulation is concerned, what we are being given is — at best — just fiddling around the edges.
A cynical eye might say Twitter’s ban is intended to distract attention from more structural problems baked into these attention-harvesting Internet platforms.
The toxic political discourse problem that democracies and societies around the world are being forced to grapple with is as a consequence of how Internet platforms distribute content and shape public discussion. So what’s really key is how these companies use our information to program what we each get to see.
The fact that we’re talking about Twitter’s political ad ban risks distracting from the “root problems” Dorsey referenced in passing. (Though he would probably offer a different definition of their cause. In the tweet storm he just talks about “working hard to stop people from gaming our systems to spread misleading info”.)
Facebook’s public diagnosis of the same problem is always extremely basic and blame-shifting. It just says some humans are bad, ergo some bad stuff will be platformed by Facebook — reflecting the issue back at humanity.
Here’s an alternative take: The core issue underpinning all these problems around how Internet platforms spread toxic propaganda is the underlying fact of taking people’s data in order to manipulate our attention.
This business of microtargeting — or behavioral advertising, as it’s also called — turns everyone into a target for some piece of propaganda or other.
It’s a practice that sucks regardless of whether it’s being done to you by Donald Trump or by Disney. Because it’s asymmetrical. It’s disproportionate. It’s exploitative. And it’s inherently anti-democratic.
It also incentivizes a pervasive, industrial-scale stockpiling of personal data that’s naturally hostile to privacy, terrible for security and gobbles huge amounts of energy and computing resource. So it sucks from an environmental perspective too.
And it does it all for the very basest of purposes. This is platforms selling you out so others can sell you stuff. Be it soap or political opinions.
Zuckerberg’s label of choice for this process — “relevant ads” — is just the slick lie told by a billionaire to grease the pipes that suck out the data required to sell our attention down the river.
Microtargeting is both awful for the individual (meaning creepy ads; loss of privacy; risk of bias and data misuse) and terrible for society for all the same reasons — as well as grave, society-level risks, such as election interference and the undermining of hard-won democratic institutions by hostile forces.
Individual privacy is a common good, akin to public health. Inoculation — against disease or indeed disinformation — helps protect the whole of us from damaging contagion.
To be clear, microtargeting is also not only something that happens when platforms are paid money to target ads. Platforms are doing this all the time; applying a weaponizing layer to customize everything they handle.
It’s how they distribute and program the masses of information users freely upload, creating maximally engaging order out of the daily human chaos they’ve tasked themselves with turning into a compelling and personalized narrative — without paying a massive army of human editors to do the job.
Facebook’s News Feed relies on the same data-driven principles as behavioral ads do to grab and hold attention. As does Twitter’s ‘Top Tweets’ algorithmically ranked view.
This is programmed attention-manipulation at vast scale, repackaged as a ‘social’ service. One which uses what the platforms learn by spying on Internet users as divisive glue to bind our individual attention, even if it means setting some of us against each another.
That’s why you can publish a Facebook post that mentions a particular political issue and — literally within seconds — attract a violently expressed opposing view from a Facebook ‘friend’ you haven’t spoken to in years. The platform can deliver that content ‘gut punch’ because it has a god-like view of everyone via the prism of their data. Data that powers its algorithms to plug content into “relevant” eyeballs, ranked by highest potential for engagement sparks to fly.
It goes without saying that if a real friendship group contained such a game-playing stalker — who had bugged everyone’s phones to snoop and keep tabs on them, and used what they learnt to play friends off against each other — no one would imagine it bringing the group closer together. Yet that’s how Facebook treats its captive eyeballs.
That awkward silence you could hear as certain hard-hitting questions struck Zuckerberg during his most recent turn in the House might just be the penny dropping.
It finally feels as if lawmakers are getting close to an understanding of the real “root problem” embedded in these content-for-data sociotechnical platforms.
Platforms that invite us to gaze into them in order that they can get intimate with us forever — using what they learn from spying to pry further and exploit faster.
So while banning political ads sounds nice it’s just a distraction. What we really need to shatter the black mirror platforms are holding against society, in which they get to view us from all angles while preventing us from seeing what they’re doing, is to bring down a comprehensive privacy screen. No targeting against personal data.
Let them show us content and ads, sure. They can target this stuff contextually based on a few generic pieces of information. They can even ask us to specify if we’d like to see ads about housing today or consumer packaged goods? We can negotiate the rules. Everything else — what we do on or off the platform, who we talk to, what we look at, where we go, what we say — must remain strictly off limits.
APPS
Best ASO Tips To Boost Your App Search In 2022

You need your application to be really effective in the overpopulated application market. Then, at that point, you will have to drive downloads to endure. So when it’s all said and done, you must account for yourself. Get your application the consideration it merits.
The uplifting news, however, is that customers love to download applications – last year, we downloaded in excess of 200 billion applications around the world, and that figure is set to increment to 258 billion every year by 2022 as cell phone reception increments.
Assuming you need to be seen and have your application downloaded by however many clients as could reasonably be expected, then, at that point, you should begin by taking a gander at the application store.
Underneath, we’ve assembled probably the best application store improvement methods to assist you with creating more downloads in 2021 and then some…
Start with Your Application Name
The odds are you as of now have an extraordinary name for your application, yet an appropriately advanced application is about significantly more than marking.
Assuming you need to amplify transparency and guarantee you’re showing up when clients look for applications like yours, you ought to remember the primary keywords for your application name or title, comparable to how you’d make a title label while improving a site page.
You could begin with your application name so it tends to be plainly recognized, thus it appears on the home screen of gadgets.
Then, at that point, you can add a scramble or vertical bar prior to adding a few pertinent watchwords to your speciality, or even put your application name in quotes as we did with FORE Business Golf Networking.
Urge Users to Leave Reviews
You could ask for reviews by clients through the means of your site, or through an in-application notice toward the finish of their meeting, yet make sure to restrict the number of pop-ups you execute with the goal that you don’t disturb or disappoint your clients, as this could urge them to erase your application.
We’d support all application engineers and entrepreneurs to react to criticism on their applications, as this can further develop client relations and resolve issues in an open arena.
Zero in on Your Application Depiction
Your application depiction is your principle assemblage of text your landing page content, in a manner of speaking. Utilize a site like KeywordTool.io to discover information on your picked catchphrases to expand your openness. As portrayals are shortened, ensure you remember the main data for the initial three lines of your depiction, and afterwards add things like social confirmation, emoticon, and suggestions to take action to build commitment and downloads.
Incorporate Appealings Screen Captures
Pictures and recordings won’t help your application rank, yet they will expand changes and assist clients with working out whether it’s an application they truly need.
There’s a little guide in empowering clients toward downloading your application if in any case, they’re not going to interface with it, or download and leave a negative survey when they understand it wasn’t what was promoted.
Assuming you need to ‘tart up’ your item page, then, at that point, you can add marking and extra text and data and designs to your recordings and screen capture, yet they ought not to diminish your item.
Pay for App Store or Play Store
As we have SEO and pay-per-click, you need to work one next to the other (one is a gradual methodology with long haul benefits – the other is a speedy success yet requires an endless spending plan), application store promotions can be utilized to get the message out with regards to your new programming and assist you with positioning at the highest point of query items pages – in front of your opposition and enormous names in the application world.
Keep in mind, you’ll need to focus on the right crowd and art an advertisement that will assist you with changing over and that since you’re paying for situations, that doesn’t mean clients will download or cooperate with your application.
Wrapping Up!
You can employ a group of App Store Optimization Services suppliers to benefit a scope of application store improvement administrations, including watchword advancement, resource enhancement, and restriction to guarantee your application is seen by individuals that matter.
We have long periods of involvement in creating and showcasing applications and have assisted different customers with expanding their downloads by infiltrating rewarding and regularly undiscovered business sectors.
Author:
Prachi Gupta likes to write information about Digital Marketing Trends that can help audience to grow their business.
APPS
WhatsApp will finally let users encrypt their chat backups in the cloud
WhatsApp said on Friday it will give its two billion users the option to encrypt their chat backups to the cloud, taking a significant step to put a lid on one of the tricky ways private communication between individuals on the app can be compromised.
The Facebook-owned service has end-to-end encrypted chats between users for more than a decade. But users have had no option but to store their chat backup to their cloud — iCloud on iPhones and Google Drive on Android — in an unencrypted format.
Tapping these unencrypted WhatsApp chat backups on Google and Apple servers is one of the widely known ways law enforcement agencies across the globe have for years been able to access WhatsApp chats of suspect individuals.
Now WhatsApp says it is patching this weak link in the system.
“WhatsApp is the first global messaging service at this scale to offer end-to-end encrypted messaging and backups, and getting there was a really hard technical challenge that required an entirely new framework for key storage and cloud storage across operating systems,” said Facebook’s chief executive Mark Zuckerberg in a post announcing the new feature.
Store your own encryption keys
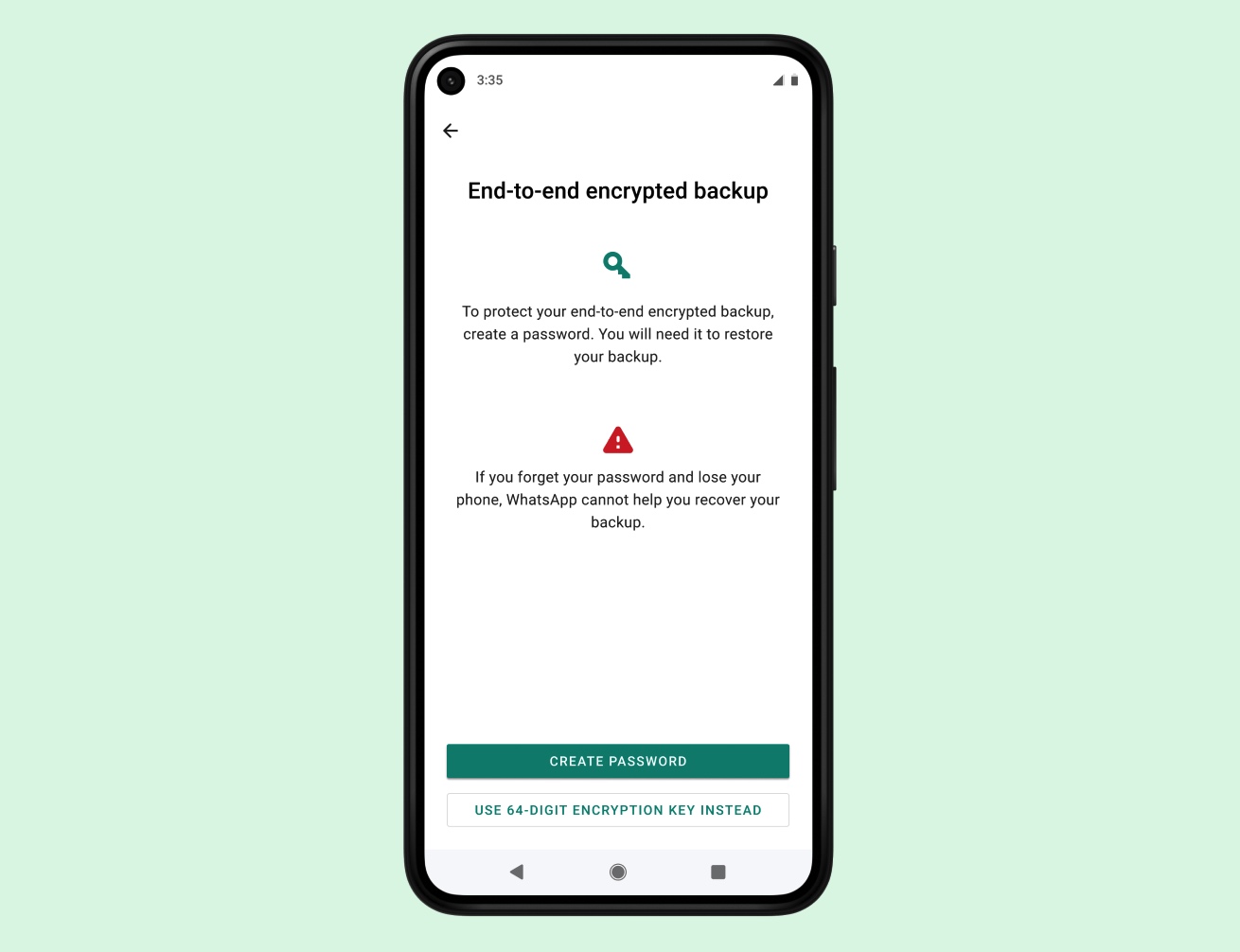
The company said it has devised a system to enable WhatsApp users on Android and iOS to lock their chat backups with encryption keys. WhatsApp says it will offer users two ways to encrypt their cloud backups, and the feature is optional.
In the “coming weeks,” users on WhatsApp will see an option to generate a 64-digit encryption key to lock their chat backups in the cloud. Users can store the encryption key offline or in a password manager of their choice, or they can create a password that backs up their encryption key in a cloud-based “backup key vault” that WhatsApp has developed. The cloud-stored encryption key can’t be used without the user’s password, which isn’t known by WhatsApp.
Image Credits: WhatsApp/supplied
“We know that some will prefer the 64-digit encryption key whereas others want something they can easily remember, so we will be including both options. Once a user sets their backup password, it is not known to us. They can reset it on their original device if they forget it,” WhatsApp said.
“For the 64-digit key, we will notify users multiple times when they sign up for end-to-end encrypted backups that if they lose their 64-digit key, we will not be able to restore their backup and that they should write it down. Before the setup is complete, we’ll ask users to affirm that they’ve saved their password or 64-digit encryption key.”
A WhatsApp spokesperson told TechCrunch that once an encrypted backup is created, previous copies of the backup will be deleted. “This will happen automatically and there is no action that a user will need to take,” the spokesperson added.
Potential regulatory pushback?
The move to introduce this added layer of privacy is significant and one that could have far-reaching implications.
End-to-end encryption remains a thorny topic of discussion as governments continue to lobby for backdoors. Apple was reportedly pressured to not add encryption to iCloud Backups after the FBI complained, and while Google has offered users the ability to encrypt their data stored in Google Drive, the company allegedly didn’t tell governments before it rolled out the feature.
When asked by TechCrunch whether WhatsApp, or its parent firm Facebook, had consulted with government bodies — or if it had received their support — during the development process of this feature, the company declined to discuss any such conversations.
“People’s messages are deeply personal and as we live more of our lives online, we believe companies should enhance the security they provide their users. By releasing this feature, we are providing our users with the option to add this additional layer of security for their backups if they’d like to, and we’re excited to give our users a meaningful advancement in the safety of their personal messages,” the company told TechCrunch.
WhatsApp also confirmed that it will be rolling out this optional feature in every market where its app is operational. It’s not uncommon for companies to withhold privacy features for legal and regulatory reasons. Apple’s upcoming encrypted browsing feature, for instance, won’t be made available to users in certain authoritarian regimes, such as China, Belarus, Egypt, Kazakhstan, Saudi Arabia, Turkmenistan, Uganda and the Philippines.
At any rate, Friday’s announcement comes days after ProPublica reported that private end-to-end encrypted conversations between two users can be read by human contractors when messages are reported by users.
“Making backups fully encrypted is really hard and it’s particularly hard to make it reliable and simple enough for people to use. No other messaging service at this scale has done this and provided this level of security for people’s messages,” Uzma Barlaskar, product lead for privacy at WhatsApp, told TechCrunch.
“We’ve been working on this problem for many years, and to build this, we had to develop an entirely new framework for key storage and cloud storage that can be used across the world’s largest operating systems and that took time.”
APPS
Dispo launches a test to gauge user interest in selling their photos as NFTs

Dispo, the photo-sharing app that emulates disposable cameras, started rolling out a test yesterday that will record user interest in selling photos as NFTs. Some users will now see a sell button on their photos, and when they tap it, they can sign up to be notified when the ability to sell Dispo photos launches.
CEO and co-founder Daniel Liss told TechCrunch that Dispo is still deciding how it will incorporate NFT sales into the app, which is why the platform is piloting a test with its users. Dispo doesn’t know yet what blockchain it would use, if it would partner with an NFT marketplace or what cut of sales Dispo would take.
“I think it’s safe to say from the test that there will be an experience native to the Dispo app,” Liss said. “There are a number of ways it could look — there could be a native experience within Dispo that then connects through an API to another platform, and in turn, they’re our partner, but to the community, it would look native to the Dispo app.”
Image Credits: Dispo
This marks a new direction for the social media app, which seeks to redefine the photo-sharing experience by only letting users see the photos they took at 9 AM the next morning. From Dispo’s perspective, this gimmick helps users share more authentically, since you take one photo and then you’re done — the app isn’t conducive to taking dozens of selfies and posting the “best” image of yourself. But though it only launched in December 2019, Dispo has already faced both buzzy hype and devastating controversy.
Until about a year ago, the app was called David’s Disposables, named after co-founder and YouTuber David Dobrik. The app was downloaded over a million times in the first week after its release and hit No. 1 on the App Store charts. In March 2021, the app dropped its waitlist and relaunched with social network features, but just weeks later, Insider reported sexual assault allegations against a member of Vlog Squad, Dobrik’s YouTube prank ensemble. In response, Spark Capital severed ties with the company, leading to Dobrik’s departure. Other investors like Seven Seven Six and Unshackled Ventures, which contributed to the company’s $20 million Series A round, announced that they would donate any profits from their investments in Dispo to organizations working with survivors of sexual assault.
Liss told TechCrunch in June, when the company confirmed its Series A, that Dobrik’s role with the company was as a marketing partner — Liss has been CEO since the beginning. In light of the controversy, Liss said the app focused on improving the product itself and took a step back from promotion.
According to data from the app analytics firm SensorTower, Dispo has reached an estimated 4.7 million global installs to date since launch. Though the app saw the most downloads in January 2020, when it was installed over 1 million times, the app’s next best month came in March 2021, when it removed its waitlist — that month, about 616,000 people downloaded Dispo. Between March and the end of August, the app was downloaded around 1.4 million times, which is up 118% year over year compared to the same time frame in 2020 — but it should be expected that this year’s numbers would be higher, since last year, the app’s membership was exclusive.

Image Credits: Dispo
Now, with the announcement that Dispo is pursuing NFTs, Liss hopes that his company won’t just change how people post photos, but what the relationship will be between platforms and the content that users create.
“Why NFTs? The most powerful memories of our lives have value. And they have economic value, because we created them, and the past of social media fails to recognize that,” Liss told TechCrunch. “As a result, the only way that a creator with a big following is compensated is by selling directly to a brand, as opposed to profiting from the content itself.”
Adding NFT sales to the app offers Dispo a way to profit from a cut of user sales, but it stands to question how adding NFT sales could impact the community-focused feel of Dispo.
“I think there is tremendous curiosity and interest,” Liss said. “But these problems and questions are why we need more data.”
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Limits News Links In California Over Proposed ‘Link Tax’ Law
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 12, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Unplugs “Notes on Search” Experiment
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days ago5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails














