SEO
25 Best SEO-Friendly Alternatives To WordPress Websites

There’s a reason why WordPress is so popular: it’s relatively easy to use, offers a lot of functionality, and gives you many customization options. And it can be great for SEO, too.
If you know what you’re doing, you can use it for structuring, managing, and publishing content in a way that generates traffic.
It’s a sort of a one-stop shop for blogging, content management, ecommerce, and website building. And maybe best of all – it’s free.
But, running your own WordPress site isn’t without its drawbacks.
For one thing, you’re responsible for your own updates, security, and backups. Click the wrong box in the settings section, and you could be vulnerable to hackers.
And you will be dealing with frequent updates because it relies so heavily on plugins to provide the functionality you want.
It can also be problematic for web developers. If you have a high degree of skill in creating websites, you may find WordPress’ templated approach restricting.
On the other end of the spectrum, you may struggle without drag and drop functionality if you don’t know how to code.
Finally, WordPress is a jack-of-all-trades type of platform. It does many things well but is not exceptional in any area. This means you may want more functionality in an area that’s important to you.
In this piece, we’ll look at 25 SEO-friendly WordPress alternatives separated by primary functionality and give you a quick rundown of each, so you can make the best choice for your needs.
Ready to get started?
Web Design Platforms
1. Wix
If you’re looking for an easy, all-in-one, fully customizable platform that doesn’t require third-party sites and plugins, look no further than Wix.
This option houses everything you need within the Wix platform, from hosting to handling structured data. Their step-by-step guide helps beginners create a beautiful website without any prior experience.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available for all plans.
- Free custom domain available with paid plans.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No option to retain full control of your site as you can with WordPress.
- No access to source code.
2. Squarespace
This all-in-one option allows you to easily create a website on Squarespace’s fully hosted platform. You do not need prior experience to use this intuitive site builder.
Squarespace hosts all its features in-house, meaning you can’t install third-party extensions or use custom coding.
It’s a great solution for hobbyists and small businesses to build a professional site themselves, although it can be an expensive solution if all you’re doing is running a basic website.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution (including video).
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available for all plans.
- Free custom domain available with an annual subscription.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No option to retain full control of your site as you can with WordPress.
- No custom coding.
- No access to source code.
- No third-party extensions.
3. Weebly
If you’re looking for simple and affordable, Weebly might be up your alley.
This site builder takes an all-in-one approach to make website creation accessible for everyone, not just programmers and web developers.
Weebly is revered for being user and SEO-friendly, but if you’re on the free plan, your website will be limited to only five pages.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available.
- Inexpensive premium plans are as low as $6.00 per month.
- Free custom domain available with premium plans.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No option to retain full control of your site as you can with WordPress.
- No access to source code.
- The free version restricts you to a maximum of five pages.
4. Google Sites
Google’s webpage and wiki creation tool, Google Sites is a free and easy way to build a website.
Because it was developed by the search engine giant, it integrates smoothly with all other Google products, including Gmail, YouTube, and Fitbit.
It is free to build, host, and maintain with a Google account, with no web hosting fees.
However, if you want to link your site with Google Apps, it costs $50 per user per year.
Key Features:
- Creator has full control over page access and permissions.
- Tools can be accessed anywhere.
- It can be used as a basic project management program.
- Plenty of web development and deployment options.
- Real-time editing.
- Uses website speed optimization tools to minimize loading times.
Pros:
- Fast to get started and easy to use.
- Free to use.
- Integrated with other Google products.
Cons:
- Limited functionality compared to other website builders.
- It may not work with non-Google apps.
- Limited customization options.
- No SEO tools and you can’t edit metadata.
- It cannot integrate Facebook pixels.
5. Jekyll
Jekyll was designed to be a lightweight alternative to other website creation platforms, including only necessary components so you can run your website without database access or other additional software.
It’s an open-source platform that allows you to quickly create and launch a website.
Key Features:
- No programming involved.
- SEO is built-in.
- GitHub manages redirects.
- Easy setup of custom domains.
Pros:
- No server maintenance.
- Very fast.
- Secure.
- Free hosting.
- Free SSL certificate.
- Works with GitHub as CMS.
Cons:
- It can’t create contact forms.
- No dynamic content options.
- Posts cannot be scheduled.
- Does not include image manipulation functionality.
6. Hugo
Billing itself as “the world’s fastest framework for building websites,” Hugo is an open-source platform for creating static sites.
It can generate most webpages in under one millisecond, with new pages built every time you create or update content.
Its goal is to provide an optimal viewing experience for users and authors.
Key Features:
- Can build most websites in seconds.
- Cross-platform with easy installation.
- Allows you to host your site anywhere.
- Customizable URLs.
- “Minutes to Read” and “WordCount” functionality.
- Integrated Google Analytics and Disqus comment support.
Pros:
- It easily integrates with Google Calendar and other apps.
- Easy to use with responsive customer service.
- Multilingual capabilities built-in.
- Extendable as needed.
Cons:
- It can’t create one-off tasks.
- It can be confusing upon initial use, particularly in templating syntax.
- No plugins are available.
- Limited text formatting features.
7. Webflow
Webflow is a responsive tool for web design that lets you create websites without the required coding knowledge.
It includes a visual designer, which lets you see the changes you’re making in real-time and includes significant versatility.
You can create nearly any website you need, including ecommerce, blogs, and business sites.
Key Features:
- More than 100 templates to choose from.
- Design is prioritized, with animation, interaction, and parallax scrolling options.
- Offers automatically generated sitemaps and customizable 301 redirects.
- Multiple payment options for ecommerce sites and automatic tax calculation.
Pros:
- Affordable, with plans ranging from free to $235 for top-tier ecommerce plans.
- Free starter plan.
- Numerous learning and help resources.
- Good range of templates.
- Good security.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Integration with social media can be frustrating.
- Advanced capabilities aren’t built-in and require integration.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
8. Joomla
Like WordPress, Joomla is an open-source content management system (CMS).
Joomla is free, but you have to pay for your web hosting.
Joomla’s appeal is its broad range of functionality that allows you to run any type of website – blogs, ecommerce, portfolios, informational websites, and more.
The downside to Joomla is that it isn’t ideal for beginners, so it’s best if you have some experience.
Key Features:
- Almost 6,000 extensions are available.
- Traditional content editing (no drag-and-drop visual editor).
- Optimized for mobile (depending on the template).
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- Free, open-source software.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Access to source code.
Cons:
- No free subdomains or custom domains are available.
- No customer support.
- Requires a PHP-enable server to run.
- Fewer templates and extensions than WordPress.
9. Drupal
Like WordPress and Joomla, Drupal is a CMS platform. The software is free, although you’ll have web hosting fees.
Drupal is one of the most technical and powerful CMS options on the market, but it requires more skills to tap into Drupal’s full potential.
This site-building option is best suited for advanced users.
Key Features:
- Content Management System (CMS).
- Over 47,000 modules are available.
- Traditional content editing (no drag-and-drop visual editor).
- Optimized for mobile (depending on the theme you choose).
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- Free, open-source software.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Access to source code.
- Strong security and data encryption.
Cons:
- No free subdomains.
- No customer support.
- Requires a PHP-enabled server to run.
10. DataLife Engine
DataLife Engine, often referred to as DLE, is a multifunctional CMS. Primarily designed for mass media websites and blogs, it allows you to manage news, articles, and users.
Flexible and customizable, it can be used to create websites that can handle high levels of visitors with minimal load on your servers.
DLE emphasizes SEO and security, which has led to its adoption by more than 100,000 organizations.
Key Features:
- Content Management System (CMS).
- Designed for multiple users.
- SEO-focused.
- Tracks statistics.
- Automatically filters words in comments.
- It supports an unlimited number of categories.
- Low server load.
- Allows plugins.
Pros:
- Stores data using MySQL.
- Excellent user experience
- Websites load quickly, even on low-end servers.
- Excellent for publishing news and blog posts.
Cons:
- No free version licenses vary from $79 for basic to $199 for unlimited.
- English users are a secondary focus.
- A limited number of plugins and themes.
- The lowest license doesn’t include customer support.
11. Sitefinity
Progress’ Sitefinity is a CMS and digital experience platform that allows you to create multi-channel marketing experiences.
Sitefinity allows you to create, store, manage, and publish content on your website. It lets you operate across departments, units, locations, and brands from one platform.
Key Features:
- Manage multiple sites from one location.
- Sync assets across pages and sites.
- It makes personalization simpler.
- Integrated analytics and optimization.
- Four versions include basic, marketing-focused, PaaS, and ecommerce.
- Multilingual capabilities.
Pros:
- Low-cost license compared to other CMS.
- No setup fee.
- Minimal coding is required for integration.
- Flexible deployment time shortens time to market.
- Options for marketing automation.
Cons:
- Free trial, but no free version.
- Setup and administration can be challenging.
- No mobile interface.
12. Hubspot CMS
Hubspot is one of the biggest names in marketing software, so it should be no surprise that they also have a CMS tool.
Combining website creation with a customer relationship management (CRM) tool lets you cover the entire buying journey from one place.
And because it was built for cross-departmental use, it doesn’t require extensive development knowledge.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based.
- Includes SEO recommendations.
- Includes numerous themes and responsive templates.
- Fully integrated CRM.
- Drag-and-drop webpage editor.
- Built-in security.
Pros:
- Adaptive A/B testing helps you identify the best page layout.
- All-in-one publishing tools.
- Built-in SEO tools.
- Supports smart content with personalized rules.
- Mobile pages supported with Google AMP.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Does not support ecommerce.
- No automatic backup and recovery.
13. Contentful
Contentful is a backend-only CMS. Intended to allow users to create content at scale, it integrates various tools, giving you the freedom to publish across channels.
A cloud-native platform, it has a clean interface and was designed to be API-first, which provides serious flexibility.
Features:
- RESTful API gives you full control over assets, translations, and versions.
- Customizable interface and framework that works across third-party component providers.
- It provides regional autonomy, so pieces in multiple languages and time zones can be published globally.
- Content modeling allows you to structure content by channel.
- Single sign-on and secure access.
Pros:
- Focus on integration simplifies the technology stack.
- User-friendly with a clean interface.
- Free version for up to five users.
- Good scalability.
Cons:
- Expensive for an upgraded version ($489/month).
- Poor internal search tools.
- Modeling content can be tricky.
14. Adobe Experience Manager
Combining the functionality of a CMS with a digital asset management (DAM) platform, Adobe Experience Manager is intended to be an all-in-one platform for building websites, managing marketing content, and overseeing media libraries.
It offers cloud integration and plays well with other programs, including its own flagship creative suite.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive marketing platform.
- End-to-end digital document solution.
- Enterprise-level security.
- Analytics included.
- Intelligent search.
- Scalable to your needs.
Pros:
- Streamlines workflows by keeping everything on one platform.
- Authoring and publishing can be handled by individual marketers.
- Easy authorization of workflow.
- Can handle massive content loads.
- Can manage multiple sites at once.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Requires different sign-ins to access different areas.
- Doesn’t integrate well with external DAMs.
- Not ideal for communities and forums.
Ecommerce Platforms
15. BigCommerce
If you’re looking for scalability in an SEO-friendly WordPress alternative, BigCommerce might be the right option for you.
It features strong SEO support and smooth multi-channel integration, and there are no platform fees or commissions.
However, customer reviews weren’t overly favorable regarding setup, and this ecommerce-targeted platform isn’t the best for small businesses or stores with tight margins.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- High level of customization options.
- Over 100 themes to choose from (including some free).
- No platform commission fees.
- Free subdomain available.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No free version is available.
- No access to source code.
- Pricing is based on revenue, which isn’t great if you have tight margins.
16. Shopify
One of the most popular ecommerce platforms on the market, Shopify, is designed to help you sell products.
That gives this option a major edge in the post-COVID digital shopping era, especially if your Shopify site is optimized for SEO.
Although Shopify can handle blogging and other niches, it isn’t the best solution for anything outside of ecommerce needs.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No free version is available.
- No access to source code.
- Platform commission fees.
17. Magento
Magento is an ecommerce-based platform with more bells and whistles than Shopify.
And while it offers a ton of business features especially suited to large-scale enterprises, it’s not the easiest platform to use.
Magento specializes in ecommerce and not much else. If you want a website that capitalizes on different features, your investment in Magento probably isn’t worth your time.
Key Features:
- Option to pay for Magento Commerce for a full hosting platform or download the free, open-source software to install on your own web server.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one ecommerce platform or open-source ecommerce software package.
- Free version available.
- Designed for large-scale ecommerce.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available (mainly for setup and testing purposes).
- Customer support (paid version only).
- Access to source code with the downloadable version.
Cons:
- No blog module, although you can add it as an extension.
- Not optimized for web projects or website purposes outside of ecommerce.
- The steep learning curve for inexperienced users.
- A large investment for small-scale ecommerce.
18. Prestashop
Prestashop is a freemium open-source ecommerce platform that allows you to set up stores on your host or via the cloud.
Available in 65 languages, it offers a powerful interface that is responsive to mobile users.
Prestashop has a variety of add-on features and provides a reliable online shopping solution.
Key Features:
- Customizable to your needs, including themes and features.
- Includes backend tools like payments, shipping and data.
- Community of translators for multilanguage digital stores.
- Secure payment modules.
- Scalable.
- Includes demographic assistance.
Pros:
- Free version available.
- Open source, so you can customize your site to your needs.
- 5,000+ themes, modules, and services are available with the premium plan.
- Excellent user experience.
Cons:
- Limited scalability.
- No support team.
- Initial setup requires some programming knowledge.
19. OpenCart
A PHP-based ecommerce solution, OpenCart is free to use. Flexible and customizable, it comes with access to a dedicated community to help you troubleshoot.
Because it’s open source, there are extensive add-ons and modules for just about anything.
Features:
- The administrator dashboard gives you information at a glance.
- User management allows you to assign permissions and separate access.
- Allows you to run multiple stores from one dashboard.
- Customizable variables let you include options for sizes, colors, or anything else.
Pros:
- The platform is completely free, as are many add-ons.
- Extensive metrics and reports provided.
- Works with your current payment gateway.
- Comes with dedicated technical support.
- Flexible.
Cons:
- Often creates duplicate pages, which can cause SEO problems.
- Not all extensions, modules, plug-ins, and add-ons work well together.
- Checkout can be slow, particularly if you have numerous plug-ins.
- Can be difficult to import a list of inventory.
- Requires some degree of technical ability for optimal use.
Blogging Platforms
20. Medium
Rather than joining the others on this list as a site builder or web software, Medium stands alone as a publishing platform with its own community and user base.
This is a great solution if you’re a blogger looking for an inexpensive way to publish content.
But remember that you don’t have customization options, meaning you can’t brand your own website.
If you need a unique website with design control, Medium isn’t going to suit your requirements.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Limited social media tools.
Pros:
- A community site for blogs.
- Free version available.
- Medium Partner Program to earn revenue.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No extensions.
- No ecommerce stores.
- No premade designs or themes.
- No free subdomains.
- No third-party extensions.
- No access to source code.
21. Ghost
This platform is a WordPress contender for blogging, but Ghost’s capabilities are limited for anything more.
Ghost is a simple and straightforward platform to suit your needs if you’re in the right niche.
But if you know your website might grow, remember that Ghost isn’t designed to scale a blog up into a business website or complex project.
Key Features:
- Option to subscribe through Ghost’s hosting platform or download the free open source software to install on your own web server.
- Basic drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available through integrations with other tools.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store (subscription only).
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available with the paid version.
- Customer support.
- Access to source code.
Cons:
- Not compatible with all third-party web hosts.
- Highly specialized with limited capabilities beyond blogging.
- Not built to scale up into a business site or complex website.
22. Tumblr
Tumblr is a unique blend of social media and microblogging.
Like a traditional social media platform, it allows you to post status updates and share images, as well as re-blog posts your audience may find relevant.
Customizable to your needs, it has a unique tagging system that helps you accurately target an audience and build a community.
Key Features:
- Features strong social media functionality.
- Customizable.
- Google Analytics Integration.
- Unlimited storage.
- Ad-free blog themes.
- Free SSL certification.
Pros:
- Free to use; no upgrades are required to access all features.
- Free web hosting.
- User-friendly and easy to set up.
- No storage limits.
- Can post audio, video, images, gifs, and more.
Cons:
- Daily posting limit (250/day).
- Files must be under 10 MB.
- No plugins.
- Safety and security leave something to be desired.
- Unsuited to long-form content.
23. Bluehost
After Typepad stopped accepting new signups in 2020, EIG began directing people to Bluehost for their web hosting needs.
Bluehost supports over 80 open-source projects beyond WordPress, including Drupal, Joomla, and phpBB. It’s currently used by more than 2 million websites.
Key Features:
- Domain names can be purchased through Bluehost.
- Versatile hosting options let you choose what works best for you.
- Dedicated servers and virtual private servers are available.
- A variety of plans are available based on your needs.
- Comes with customer service chat options.
Pros:
- The first term is inexpensive.
- Lots of storage and unlimited bandwidth.
- Good uptime.
- Free SSL certificates.
Cons:
- Extra features come with added costs, which can get pricey.
- High renewal rates.
- Speed could be better.
- All servers are U.S.-based.
24. Blogger
If you’re going to name your company “Blogger,” you better be good at blog hosting; it shouldn’t be surprising that Blogger delivers.
Acquired by Google in 2003, Blogger is more than just one of the oldest blogging platforms; it’s also a CMS.
Free to use, it lets you publish everything in your own personal space, whether it’s a business blog or a series of posts about your favorite Harry Potter characters.
Your site can be hosted at yourname.blogspot.com or your own domain.
Features:
- Clear analytics.
- Included layout/themes.
- Monetization options, including Google Adsense integration.
- Uses Google security.
- Unlimited storage.
Pros:
- Free to use.
- Extremely user-friendly.
- Free SSL security.
- Good uptime.
Cons:
- You don’t own your website.
- Fewer options and control over design.
- Limited support.
- Hard to port to a different platform.
Community Management
25. vBulletin
If your site’s primary purpose is to create a community and host forums and message boards, vBulletin may be the right choice for you.
Easily installed on any web hosting service or run from vBulletin’s cloud, its primary focus is on community websites, though it does include tools for content discovery and site management.
It comes with various templates, graphics, and styles, so you can customize your forum to your brand.
Key Features:
- Built-in SEO and security.
- Includes a chat app.
- Easy to get started.
- Built-in applications.
- Optimized for mobile users.
- Blogging functionality.
- Fully customizable.
Pros:
- Frequent patches and bug fixes.
- Customer support.
- Easy to install and get started.
- Designed to host forums.
- Includes templates.
Cons:
- No free option.
- Limited features compared to some other platforms.
- Requires some tech skills to take full advantage of the functionality.
- It can’t customize code for the cloud-based version.
Which One Is Right For You?
Including WordPress, you have 26 options for building your website.
So, how do you know which one is right for you? It comes down to your needs and what you want your website to accomplish.
If you’re looking to create a website that is ecommerce-first, you’d be well served to pick from one of the options listed in that section.
On the other hand, if you’re primarily interested in blogging, you’ll want a platform that focuses on that.
And if you want one that does everything, well, there are a few on the list.
Hopefully, by reading this, you’ve gained a little insight into which platform will work best for you.
More Resources:
Featured Image: GaudiLab/Shutterstock
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
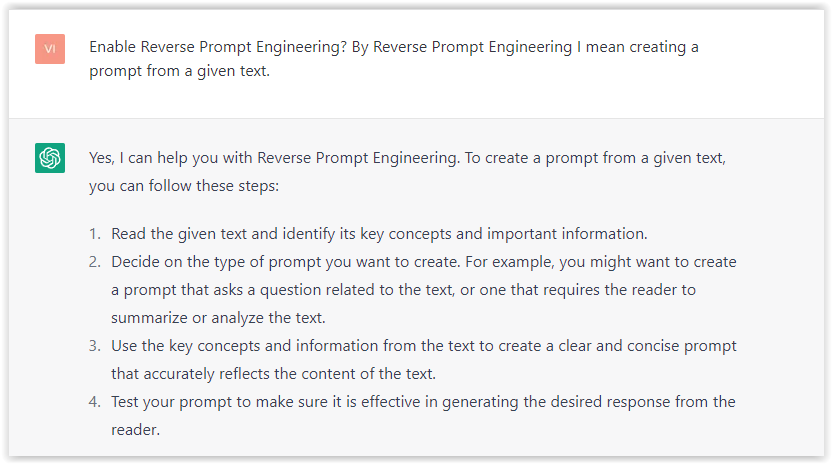
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
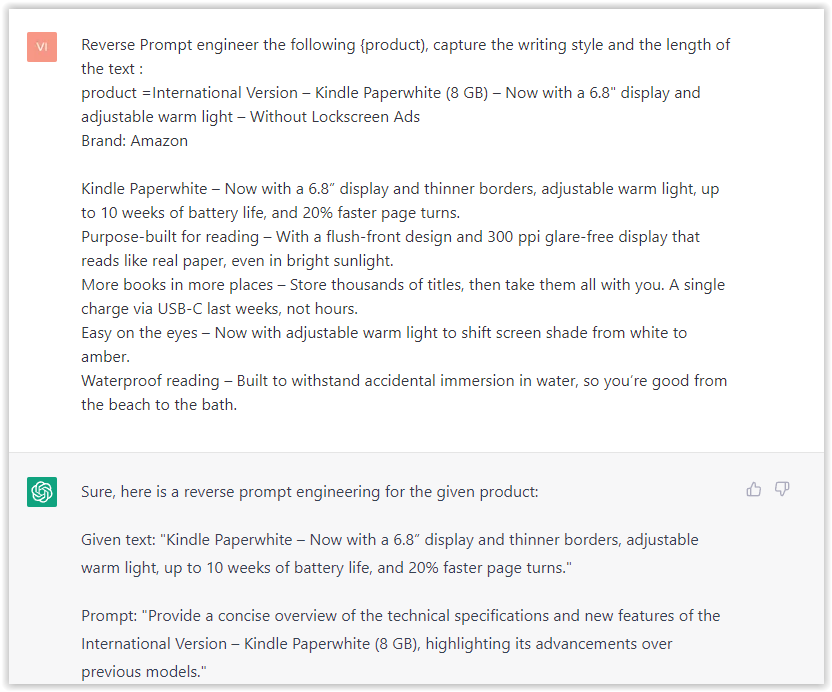 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress













You must be logged in to post a comment Login