SEO
8 Experiments To Improve Organic Traffic

Imagine the results you could achieve if you knew the Google search algorithm.
Just think of the organic traffic you could drive to your site if you knew exactly what Google was taking into account when generating search engine results, the precise amount each factor plays on rankings, and precisely what it would take to get to the top.
But of course, Google would never let you see behind the curtain. Not only could a bad actor use this information for nefarious purposes, but it would take all the fun out of search engine optimization.
So instead, every time there’s a new algorithm update, it’s up to us to figure out what exactly has changed and how to best leverage this to our advantage.
And because we in the search engine optimization world are a community, we tend to figure these things out collectively.
And because there are no (or very few, anyway) absolute answers, a lot of optimization comes down to best practices, theories, and outright guesswork.
Luckily, there’s a great way to determine if these theories are based on reality or just sheer conjecture. Of course, we’re talking about experimentation.
(Insert mad scientist laugh here.)
Before you get carried away and rush to put on your safety goggles and lab coats, relax. No bubbling beakers full of mystery liquids are involved, and your risk of accidentally creating a monster is very low.
(I would say zero, but I’ve seen the “Terminator” series, and it never explicitly says that a search engine optimizer didn’t create Skynet, so let’s play it safe.)
All your SEO experiments can be done from your desk chair’s comfort (and safety).
But before we dive into those, let’s first talk about how to test your SEO.
Steps For A Successful SEO Experiment
Thankfully, we don’t have to develop an entirely new framework for devising, conducting, and measuring our SEO tests – we can repurpose the scientific method you’re probably already familiar with.
Been a while since high school chemistry? Don’t worry; these five steps are sure to sound familiar:
- Make an observation. (E.g., my site is not on the first page of Google search results.)
- Ask a question and form a hypothesis. Is my meta description optimized for ranking? If I write better meta descriptions, it will improve my ranking.
- Gather data. Upon changing these descriptions, track the change in ranking position and site visits.
- Analyze the data. Create tables, graphs, and diagrams to help you understand the link between what was changed and changing results.
- Draw conclusions. Does the evidence support your prediction? Why or why not? Was site traffic increased due to your new meta descriptions, or did you also receive national news coverage during your testing period?)
You’ll want to do what marketers call A/B testing for accurate results. This means creating two versions of the same page, with only one difference, so you can see which gets the better response.
Before you start, keep one thing in mind: Incremental changes are essential. If you go wild and change all of these at once, you’ll have no idea which one(s) is making a difference.
Play it slowly and be patient. Test one, then wait for the results before moving on to the next. This will give you an obvious idea of what you need to do moving forward to ensure you’re always claiming front-page real estate.
With that out of the way, here’s a look at eight different things you can test to improve the ranking of your site:
1. SEO Title
Have you ever written what you thought was an amazing page title, only for Google to rewrite it in search results? That usually happens when the search engine doesn’t feel like your title was a good reflection of the page’s content.
But you can change this anytime you like.
And even if Google does replace the one you created, Google’s John Mueller confirmed the original title is still used for ranking purposes. This means even if you’re getting your SEO titles changed, it’s still a good idea to try to optimize them.
Here are a few things you can test to see if they generate results:
- Include your target keyword.
- Change their length (shorter is not always better).
- Experiment with brand name positioning or remove it altogether.
- Get click-baity (e.g., Do you want to lose 20 lbs. fast?).
- Add published date to demonstrate information relevancy.
- Get creative (people love what’s new and whimsical).
2. SEO Meta Description
Now, wait just a minute – you’re probably saying right now – Search Engine Journal has been clear that Google hasn’t used meta description in its rankings since sometime between 1999 and 2004.
Put down your pitchforks. Just because they aren’t a direct factor in SERPs doesn’t mean meta descriptions aren’t an essential SEO element.
For example, they can help improve your click-through rate, compel searchers, generate brand exposure, and help differentiate you from the competition. And all of these impact user behavior, which is a signal that Google factors in.
There have been entire articles written about creating awesome meta descriptions. But for our purposes, here are a few things you can A/B test to see if you can improve your organic traffic:
- Try different lengths. Traditional SEO wisdom suggests character count between 156-165 – see what works for you.
- Add keywords.
- Change your tone. Generally speaking, your style should match your brand’s voice, but for a specific page, maybe this isn’t the case.
- Get specific – are you getting a lot of visits from one long-tail keyword? Add that to your meta description.
3. Internal Anchor Text
You may know anchor text as the visible, clickable (usually blue) text in a hyperlink like this.
Not only is this useful for giving additional context to users, but Google has confirmed: Anchor text helps it better understand a page’s content, allowing it to rank those pages for relevant searches.
For example, in the paragraph above, “Google has confirmed” is the anchor text attached to the target link, which directs to a link proving that confirmation.
There are several types of anchor text you can use, including those with exact or partial-match keywords, branded (Search Engine Journal), images, generic (“click here”), and naked links (https://www.searchenginejournal.com).
To experiment with the impact, internal anchor text can have on your organic traffic. You can try things like:
- Changing their length (though shorter is often better).
- Adding keywords, particularly low-density keywords.
- Increasing specificity.
- Changing them to be more target link-specific.
4. Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of structured data used by Google and other search engines.
Following guidelines established by Schema.org, it is essentially a lingua franca for search engines. It’s an established standard that uses a unique vocabulary to help search engines more clearly understand your content.
It’s used to create rich snippets for adding information about events, recipes, people, videos, reviews, and products, among other things. These, in turn, make your link appear more prominent in SERPs.
And while schema is not directly factored into your ranking score, like SEO title, it can improve your click-through rate and impact your user behavior scores.
Experiment with adding schema markup to your pages and see if it improves your results.
5. Images
A picture is worth a thousand words – everyone knows that. This is because humans are visual creatures. And web designers and SEO professionals have recognized the importance of including images on webpages for a long time.
And it’s not just because they add visual interest and grab attention; they can also improve your search ranking.
Original (not stock), high-quality images optimized for SEO can reap the rewards.
Here are some things you can try with your images to improve your traffic:
- Add images. You should add images to every page. No one wants to read a wall of text.
- Choose a different file name. You want to immediately make it clear to Google what your image is depicting. Try adding your keywords.
- Change your formatting. There is no one-size-fits-all for digital images. You may want to change your file type depending on your image needs. JPEGs are good for larger photos. PNG files preserve background transparency.
- Compress files when possible. In general, smaller files are always better.
- Ensure responsiveness. With mobile search being such an essential factor in modern SEO, you want to ensure your images always look great on phones and desktops.
- Add alt text if the image can’t be displayed for some reason.
6. Headers
Your headlines and subheads give your page structure. This makes it easier for humans to browse and for search engines to understand what each section is about.
Google’s John Mueller was very clear about this, emphasizing the presence of any headings, not just H1s, sends a strong signal about the page’s content. It would be best if you took special care with all your H tags, from H1 down to H6. This is because they also serve as an accessibility aid and navigational tool in addition to their structural benefits.
Once upon a time, your headers were a massive factor in your ranking. But then, like always, people abused them, and Google started cracking down on keyword stuffing, overuse, and other dirty heading tricks.
That said, while they are far from the only factor Google takes into account, there is no question they are essential.
Here are a few things you can play with to try and improve your SEO results:
- Add more headings (except H1s). Improve the structure and clarity of your content by adding more subheads.
- Try using them to break up blocks of text. No one likes massive text blocks. H2s, H3s, etc., are the perfect solution.
- Add keywords. Like nearly everything else we’ve discussed, you should experiment with the use of keywords in your headings.
- Optimize for featured snippets. Grab attention and draw new traffic by claiming those special boxes on search results. Write your headers to land these.
- Get creative. Try making your headings and subheads more interesting.
7. Word Count
You already know content is the essential thing in any SEO strategy. But you may not have thought much about how the number of words you use can impact your ranking and traffic.
While you shouldn’t expect word count to push you over the top and take you from page six to the top result, it can help define your site as relevant and valuable to a search query – and draw in readers.
What do we mean by this? Again, it’s not a direct ranking factor, according to John Mueller.
With that said, longer-form copy tends to rank higher. This is because using more words provides Google with more information on what your page is about.
And if these longer pieces are well-written (like the one you’re reading in the author’s ever-so-humble opinion), they’ll help establish you as an authority on the topic.
And experimentation is easy. Take one of your existing articles or blog posts and duplicate it. On the second one, expound at greater length upon your topic.
Please note, we’re not talking about using your word count tricks from college (e.g., “at a later date” instead of just “later”). Instead, you should expand on ideas and topics, add examples and cite additional sources.
Then, see which one performs better on search engines. Chances are, it will be the longer one.
Read this piece for more on using word count for SEO optimization.
8. URL
Some SEO experts will swear URLs with keywords perform better than generic ones. Is this the case?
Well, yes and no.
On the one hand, Google has confirmed when it performs its initial crawl of a site, keywords in URLs help it understand what the site is about.
However, as this is only factored in when a new site is crawled, its role in an ongoing SEO strategy is minimal.
But again, this doesn’t mean you can’t use them to your advantage. Clear URLs create a better user experience and can be used as naked anchor tags much more accessible than one with 75 random numbers and letters tacked on at the end.
Experiment with your URLs. Take some of your old, non-descriptive links and add keywords to them. Shorten long URLs.
If you’re worried about losing links from the old page, add a 301-redirect pointing to the new one.
Don’t Be Afraid To Try Something New
Search engine optimization is a constantly shifting landscape. Changing trends can change how people interact with your website.
As algorithms change and new technologies emerge, your strategy needs to evolve.
There has never been, and probably never will be, “set it and forget it” search engine optimization. It will always require forward-thinkers and people willing to experiment to find new ways to get their websites to the top of the rankings.
Who says you can’t be one of them? Someone had to be the first to figure out that keyword stuffing helped rankings, and someone else had to figure out when it stopped working.
If you’re willing to experiment and try new things, you may find the next brilliant new strategy. Just don’t forget to share it with us.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Tatyana Vyc/Shutterstock
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
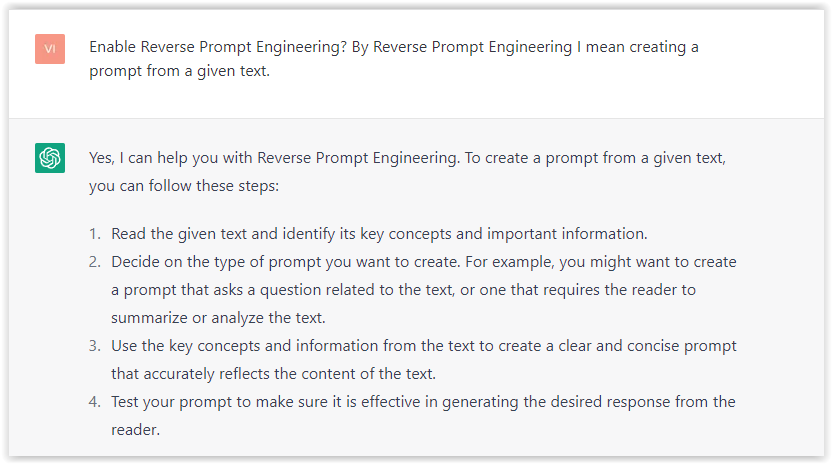
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
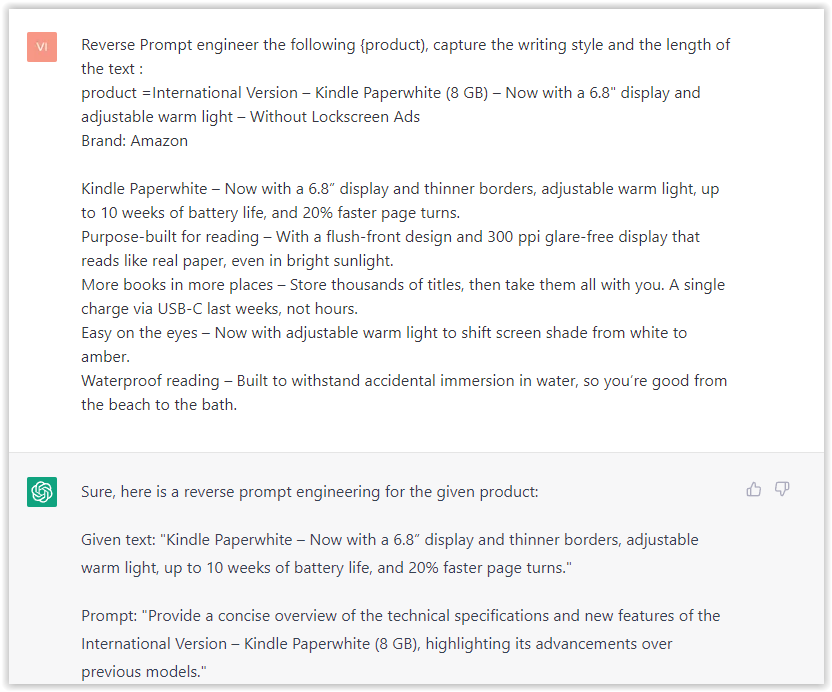
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News















You must be logged in to post a comment Login