SEO
8 White Hat SEO Techniques To Double Your Search Traffic
Stuck in a cycle of optimizations that don’t move the needle?
This post reveals white hat techniques that can potentially double, triple, or even 10x your traffic from organic search.
The Google system for ranking websites incorporates a series of algorithms designed to give the “best” results.
These algorithms take into consideration many factors, including the words in a query, relevance, page usability, source expertise, geo-location, and settings.
Furthermore, the weighting of these factors is dependent on the nature of a query.
For current topics, freshness carries a lot of weight.
For a dictionary type definition, the page trust and authority play a larger role.
To ensure the algorithms are functioning as intended, Google employs an army of Quality Raters.
They follow strict guidelines developed by Google to ensure the algorithm output matches the standards established for Page Quality and Needs Met. These guidelines are a must-read for anyone serious about building a top-performing website.
According to Google, their search algorithm looks at five key factors in determining which results appear at the top of their search results:
- Meaning of your query.
- Relevance of webpages.
- Quality of content.
- Usability of webpages.
- Context and settings.
By addressing these five factors, you will be putting yourself in a position to outperform the competition. Here are some specific tips on how to do it:
1. Mobile First
I first began promoting a “mobile-first” approach to SEO back in March of 2015, after dubbing Google’s pending mobile update “mobilegeddon.”
The name caught on, but on April 21, 2015, the update didn’t create as big an upheaval as expected at the time.
It did, however, put everyone on notice, that mobile was here and no longer “the future.” Those who did not heed the warning to go mobile later paid the price.
Today, Google is all-in on mobile.
If you aren’t certain as to whether your website meets the criteria for being mobile-friendly, log in to your Search Console account and view the Mobile Usability Report.
Google will report mobile issues there, so you can take the appropriate actions to come into compliance.
2. Claim Your Business Listing
Google Business Profile, formerly known as Google My Business, is a free business listing.
Business Profiles show up in Google Search, Google Maps, and Google Shopping. If your business has a physical location or travels to customers, you can create a Business Profile on Google.
Top 5 Google Business Profile Benefits
- It’s FREE advertising – cheaper than paid search and faster than SEO.
- Google Maps/3-Pack favors geographically relevant businesses.
- An optimized profile makes a good first impression.
- A good star rating builds trust and provides social proof.
- The ability to check profile performance & gain insights.
As Google continues to improve its ability to deliver hyper-local results, it is critically important to have complete and accurate data in one’s Google Business Profile.
This continues to be an easy win, as many businesses have yet to even claim their listing.
3. Improve Your Page Experience
Google’s page experience is defined by a set of signals which are designed to measure how users react to a webpage. This measurement goes beyond basic information value.
It utilizes Core Web Vitals, a set of metrics that measure page loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability, as well as mobile-friendliness, HTTPS, and intrusive interstitial guidelines.
How Does Page Experience Affect Rankings?
In cases where several pages may satisfy the search criteria for relevance, page experience carries more weight.
A page that delivers sought-after information still trumps a page with less relevance, but a better page experience.
In short, page experience can be the SERP tiebreaker.
4. Focus On User Experience (UX)
Google has always encouraged webmasters to make their primary focus one of providing a good user experience.
As the algorithm gets “smarter,” websites that do so are positioned to benefit the most. A good user experience goes much deeper than writing clean code.
According to this study from the Oxford Journal, “The goal of UX design in business is to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty through the utility, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction with a product.”
For our purposes, your website is the product. The objective is to first determine a user’s intent, then develop a methodology for smooth navigation – a methodology that evokes a positive emotion and leads to an overall good experience.
Incorporating UX best practices is easy. The web is filled with templates and advice.
What separates the pros from the amateurs is A/B testing.
Each one of us has our own biases that will influence how a webpage is constructed.
By running a series of experiments, you will be able to quantify what is working, and what isn’t, and continue testing until you get it right.
5. Do Your Keyword Research
That’s right – keyword research is still important.
With Google providing less keyword data, third parties like Ahrefs and Semrush have developed their own keyword tools to fill the void.
However, the way that one goes about performing and using the results from keyword research has changed, thanks to RankBrain and BERT.
At its core, RankBrain is machine learning. This allows Google to put things in context rather than rely solely on strings of metadata. Google now understands language nuances like stemming, synonyms, and answers.
BERT is an acronym for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers.
The primary goal is to deliver better search results for longer and more conversational searches where prepositions like “for” and “to” affect the context of a query.
At the time of launch in October 2019, Google projected that BERT would impact 10% of all searches in the United States.
The new generation of keyword tools takes this into consideration by generating relevant data like Parent Topics, Keyword Groups, and Search Intent.
Armed with this information, users can develop contextually relevant content.
6. Have A Well-Rounded Content Marketing Plan
According to the Content Marketing Institute, 51% of all respondents report that it’s more difficult to capture the audience’s attention today than it was just a year ago.
Since content is one of the top Google ranking factors, it’s important to get it right. Once again, this presents a huge opportunity for those willing to invest the time to make that happen.
Everyone talks about creating “great content,” but what does that even mean?
It really comes down to having useful content, finding the right audience, and then reaching that audience.
This doesn’t have to be a difficult exercise. It boils down to having empathy with your prospects and customers. Ann Handley created the following formula to sum it up:
Useful x Enjoyable x Inspired = Innovative Content
Great content comes in many different forms. A well-rounded content marketing plan will include a combination of the following:
- Blogs.
- Data-driven visuals (Original Research).
- Images.
- Infographics.
- SlideShare presentations.
- Videos.
7. Pay Attention To On-Page Optimization
Did you know that Google publishes its own Search Engine Optimization Starter Guide? You do now.
Despite its name, this guide is a great resource for everyone looking to maximize their chances of appearing in Google search results.
The guide covers key on-page basics, including the best practices for optimizing:
- Page Titles.
- Headers.
- Meta Descriptions.
- Image Alt-text.
- Structured Markup.
- Page URLs.
- Internal Linking.
Additional resources for improving on-page optimization:
8. Link Building Supercharges All Other Efforts
The day may come when links are less important to rankings, but that day hasn’t arrived yet. The key is to get the right kinds of links.
Links that have relevance to your site. Links that require a human editorial review. The kinds of links that are earned.
My favorite approach to earning relevant links is to build a resource center. A resource center can work on just about any kind of website. In addition to attracting links, a good resource center helps to build trust and authority.
Learn about this approach and more by downloading Link Building for SEO: A Complete Guide.
The Bottom Line
Organic search is a game of inches. There is no single best way to dominate the SERPs. But it doesn’t need to be overwhelming.
If you just focus on the eight areas presented above, you can double, triple, or even 10x your traffic.
More Resources:
Featured Image: goodbishop/Shutterstock
!function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s)
{if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function(){n.callMethod?
n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments)};
if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version=’2.0′;
n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0;
t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0];
s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)}(window,document,’script’,
‘https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js’);
if( typeof sopp !== “undefined” && sopp === ‘yes’ ){
fbq(‘dataProcessingOptions’, [‘LDU’], 1, 1000);
}else{
fbq(‘dataProcessingOptions’, []);
}
fbq(‘init’, ‘1321385257908563’);
fbq(‘track’, ‘PageView’);
fbq(‘trackSingle’, ‘1321385257908563’, ‘ViewContent’, {
content_name: ‘white-hat-seo-techniques’,
content_category: ‘seo seo-strategy ‘
});
SEO
2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making

WordPress security scanner WPScan’s 2024 WordPress vulnerability report calls attention to WordPress vulnerability trends and suggests the kinds of things website publishers (and SEOs) should be looking out for.
Some of the key findings from the report were that just over 20% of vulnerabilities were rated as high or critical level threats, with medium severity threats, at 67% of reported vulnerabilities, making up the majority. Many regard medium level vulnerabilities as if they are low-level threats and that’s a mistake because they’re not low level and should be regarded as deserving attention.
The WPScan report advised:
“While severity doesn’t translate directly to the risk of exploitation, it’s an important guideline for website owners to make an educated decision about when to disable or update the extension.”
WordPress Vulnerability Severity Distribution
Critical level vulnerabilities, the highest level of threat, represented only 2.38% of vulnerabilities, which is essentially good news for WordPress publishers. Yet as mentioned earlier, when combined with the percentages of high level threats (17.68%) the number or concerning vulnerabilities rises to almost 20%.
Here are the percentages by severity ratings:
- Critical 2.38%
- Low 12.83%
- High 17.68%
- Medium 67.12%
Authenticated Versus Unauthenticated
Authenticated vulnerabilities are those that require an attacker to first attain user credentials and their accompanying permission levels in order to exploit a particular vulnerability. Exploits that require subscriber-level authentication are the most exploitable of the authenticated exploits and those that require administrator level access present the least risk (although not always a low risk for a variety of reasons).
Unauthenticated attacks are generally the easiest to exploit because anyone can launch an attack without having to first acquire a user credential.
The WPScan vulnerability report found that about 22% of reported vulnerabilities required subscriber level or no authentication at all, representing the most exploitable vulnerabilities. On the other end of the scale of the exploitability are vulnerabilities requiring admin permission levels representing a total of 30.71% of reported vulnerabilities.
Permission Levels Required For Exploits
Vulnerabilities requiring administrator level credentials represented the highest percentage of exploits, followed by Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) with 24.74% of vulnerabilities. This is interesting because CSRF is an attack that uses social engineering to get a victim to click a link from which the user’s permission levels are acquired. This is a mistake that WordPress publishers should be aware of because all it takes is for an admin level user to follow a link which then enables the hacker to assume admin level privileges to the WordPress website.
The following is the percentages of exploits ordered by roles necessary to launch an attack.
Ascending Order Of User Roles For Vulnerabilities
- Author 2.19%
- Subscriber 10.4%
- Unauthenticated 12.35%
- Contributor 19.62%
- CSRF 24.74%
- Admin 30.71%
Most Common Vulnerability Types Requiring Minimal Authentication
Broken Access Control in the context of WordPress refers to a security failure that can allow an attacker without necessary permission credentials to gain access to higher credential permissions.
In the section of the report that looks at the occurrences and vulnerabilities underlying unauthenticated or subscriber level vulnerabilities reported (Occurrence vs Vulnerability on Unauthenticated or Subscriber+ reports), WPScan breaks down the percentages for each vulnerability type that is most common for exploits that are the easiest to launch (because they require minimal to no user credential authentication).
The WPScan threat report noted that Broken Access Control represents a whopping 84.99% followed by SQL injection (20.64%).
The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) defines Broken Access Control as:
“Access control, sometimes called authorization, is how a web application grants access to content and functions to some users and not others. These checks are performed after authentication, and govern what ‘authorized’ users are allowed to do.
Access control sounds like a simple problem but is insidiously difficult to implement correctly. A web application’s access control model is closely tied to the content and functions that the site provides. In addition, the users may fall into a number of groups or roles with different abilities or privileges.”
SQL injection, at 20.64% represents the second most prevalent type of vulnerability, which WPScan referred to as both “high severity and risk” in the context of vulnerabilities requiring minimal authentication levels because attackers can access and/or tamper with the database which is the heart of every WordPress website.
These are the percentages:
- Broken Access Control 84.99%
- SQL Injection 20.64%
- Cross-Site Scripting 9.4%
- Unauthenticated Arbitrary File Upload 5.28%
- Sensitive Data Disclosure 4.59%
- Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) 3.67%
- Remote Code Execution 2.52%
- Other 14.45%
Vulnerabilities In The WordPress Core Itself
The overwhelming majority of vulnerability issues were reported in third-party plugins and themes. However, there were in 2023 a total of 13 vulnerabilities reported in the WordPress core itself. Out of the thirteen vulnerabilities only one of them was rated as a high severity threat, which is the second highest level, with Critical being the highest level vulnerability threat, a rating scoring system maintained by the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
The WordPress core platform itself is held to the highest standards and benefits from a worldwide community that is vigilant in discovering and patching vulnerabilities.
Website Security Should Be Considered As Technical SEO
Site audits don’t normally cover website security but in my opinion every responsible audit should at least talk about security headers. As I’ve been saying for years, website security quickly becomes an SEO issue once a website’s ranking start disappearing from the search engine results pages (SERPs) due to being compromised by a vulnerability. That’s why it’s critical to be proactive about website security.
According to the WPScan report, the main point of entry for hacked websites were leaked credentials and weak passwords. Ensuring strong password standards plus two-factor authentication is an important part of every website’s security stance.
Using security headers is another way to help protect against Cross-Site Scripting and other kinds of vulnerabilities.
Lastly, a WordPress firewall and website hardening are also useful proactive approaches to website security. I once added a forum to a brand new website I created and it was immediately under attack within minutes. Believe it or not, virtually every website worldwide is under attack 24 hours a day by bots scanning for vulnerabilities.
Read the WPScan Report:
WPScan 2024 Website Threat Report
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Ljupco Smokovski
SEO
An In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO

Over the years, search engines have encouraged businesses to improve mobile experience on their websites. More than 60% of web traffic comes from mobile, and in some cases based on the industry, mobile traffic can reach up to 90%.
Since Google has completed its switch to mobile-first indexing, the question is no longer “if” your website should be optimized for mobile, but how well it is adapted to meet these criteria. A new challenge has emerged for SEO professionals with the introduction of Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which replaced First Input Delay (FID) starting March, 12 2024.
Thus, understanding mobile SEO’s latest advancements, especially with the shift to INP, is crucial. This guide offers practical steps to optimize your site effectively for today’s mobile-focused SEO requirements.
What Is Mobile SEO And Why Is It Important?
The goal of mobile SEO is to optimize your website to attain better visibility in search engine results specifically tailored for mobile devices.
This form of SEO not only aims to boost search engine rankings, but also prioritizes enhancing mobile user experience through both content and technology.
While, in many ways, mobile SEO and traditional SEO share similar practices, additional steps related to site rendering and content are required to meet the needs of mobile users and the speed requirements of mobile devices.
Does this need to be a priority for your website? How urgent is it?
Consider this: 58% of the world’s web traffic comes from mobile devices.
If you aren’t focused on mobile users, there is a good chance you’re missing out on a tremendous amount of traffic.
Mobile-First Indexing
Additionally, as of 2023, Google has switched its crawlers to a mobile-first indexing priority.
This means that the mobile experience of your site is critical to maintaining efficient indexing, which is the step before ranking algorithms come into play.
Read more: Where We Are Today With Google’s Mobile-First Index
How Much Of Your Traffic Is From Mobile?
How much traffic potential you have with mobile users can depend on various factors, including your industry (B2B sites might attract primarily desktop users, for example) and the search intent your content addresses (users might prefer desktop for larger purchases, for example).
Regardless of where your industry and the search intent of your users might be, the future will demand that you optimize your site experience for mobile devices.
How can you assess your current mix of mobile vs. desktop users?
An easy way to see what percentage of your users is on mobile is to go into Google Analytics 4.
- Click Reports in the left column.
- Click on the Insights icon on the right side of the screen.
- Scroll down to Suggested Questions and click on it.
- Click on Technology.
- Click on Top Device model by Users.
- Then click on Top Device category by Users under Related Results.
- The breakdown of Top Device category will match the date range selected at the top of GA4.
You can also set up a report in Looker Studio.
- Add your site to the Data source.
- Add Device category to the Dimension field.
- Add 30-day active users to the Metric field.
- Click on Chart to select the view that works best for you.
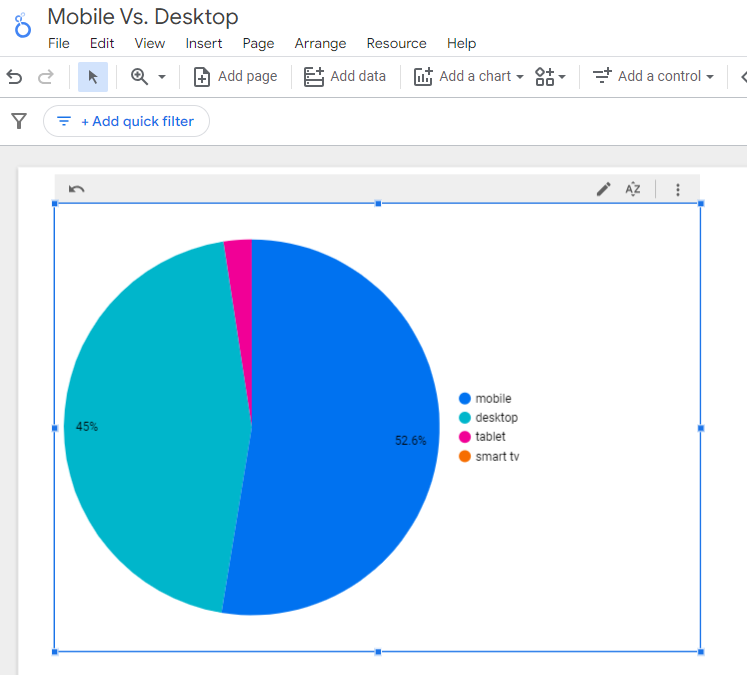 Screenshot from Looker Studio, March 2024
Screenshot from Looker Studio, March 2024You can add more Dimensions to really dig into the data to see which pages attract which type of users, what the mobile-to-desktop mix is by country, which search engines send the most mobile users, and so much more.
Read more: Why Mobile And Desktop Rankings Are Different
How To Check If Your Site Is Mobile-Friendly
Now that you know how to build a report on mobile and desktop usage, you need to figure out if your site is optimized for mobile traffic.
While Google removed the mobile-friendly testing tool from Google Search Console in December 2023, there are still a number of useful tools for evaluating your site for mobile users.
Bing still has a mobile-friendly testing tool that will tell you the following:
- Viewport is configured correctly.
- Page content fits device width.
- Text on the page is readable.
- Links and tap targets are sufficiently large and touch-friendly.
- Any other issues detected.
Google’s Lighthouse Chrome extension provides you with an evaluation of your site’s performance across several factors, including load times, accessibility, and SEO.
To use, install the Lighthouse Chrome extension.
- Go to your website in your browser.
- Click on the orange lighthouse icon in your browser’s address bar.
- Click Generate Report.
- A new tab will open and display your scores once the evaluation is complete.
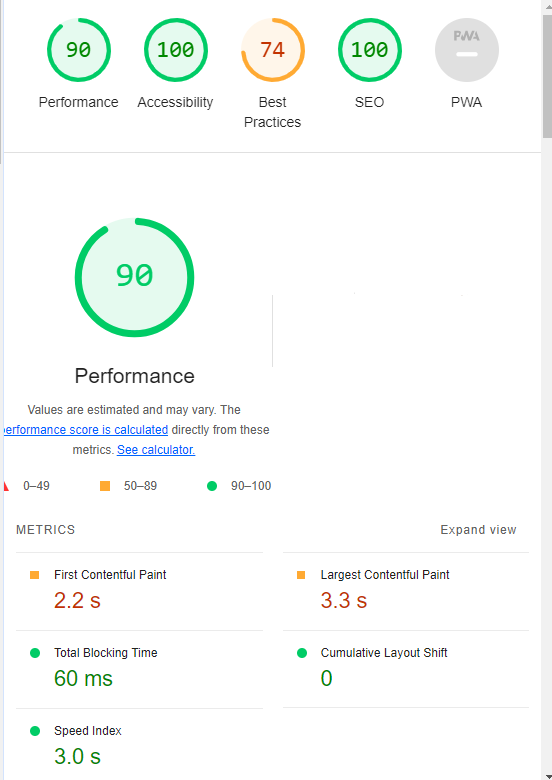 Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024
Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024You can also use the Lighthouse report in Developer Tools in Chrome.
- Simply click on the three dots next to the address bar.
- Select “More Tools.”
- Select Developer Tools.
- Click on the Lighthouse tab.
- Choose “Mobile” and click the “Analyze page load” button.
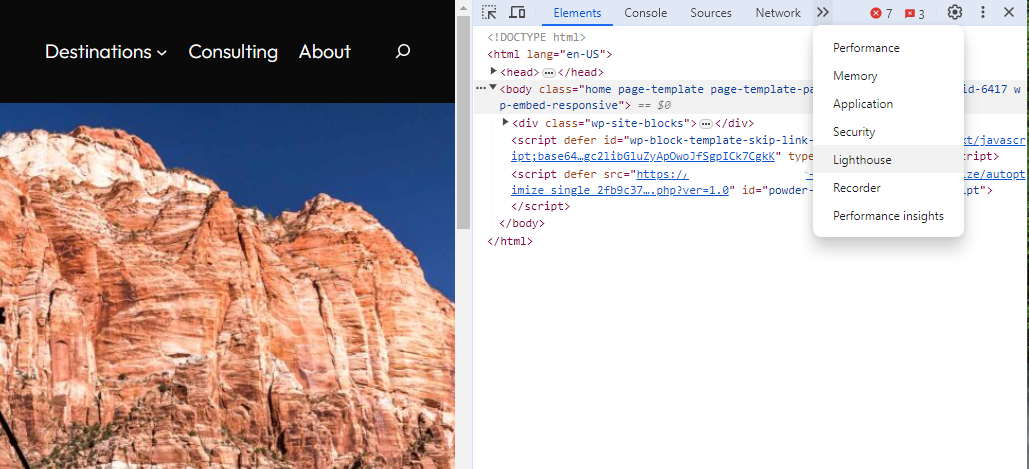 Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024
Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024Another option that Google offers is the PageSpeed Insights (PSI) tool. Simply add your URL into the field and click Analyze.
PSI will integrate any Core Web Vitals scores into the resulting view so you can see what your users are experiencing when they come to your site.
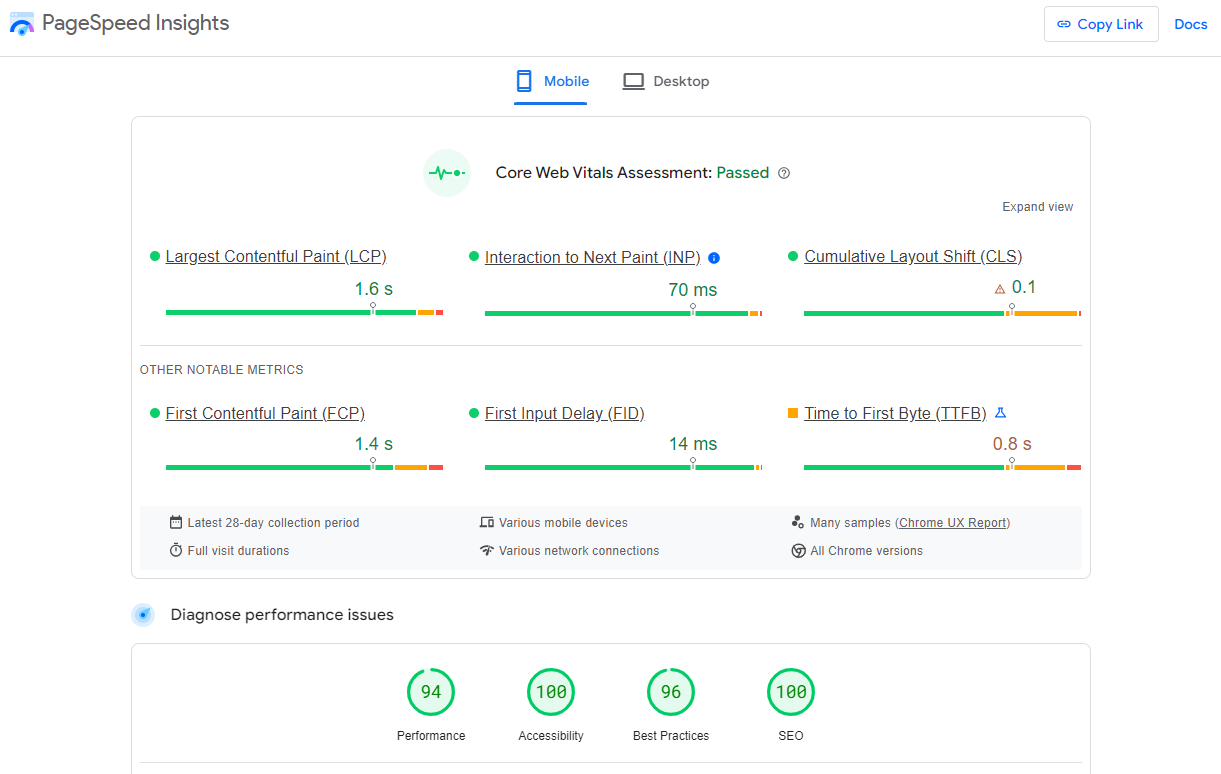 Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, March 2024
Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, March 2024Other tools, like WebPageTest.org, will graphically display the processes and load times for everything it takes to display your webpages.
With this information, you can see which processes block the loading of your pages, which ones take the longest to load, and how this affects your overall page load times.
You can also emulate the mobile experience by using Developer Tools in Chrome, which allows you to switch back and forth between a desktop and mobile experience.
 Screenshot from Google Chrome Developer Tools, March 2024
Screenshot from Google Chrome Developer Tools, March 2024Lastly, use your own mobile device to load and navigate your website:
- Does it take forever to load?
- Are you able to navigate your site to find the most important information?
- Is it easy to add something to cart?
- Can you read the text?
Read more: Google PageSpeed Insights Reports: A Technical Guide
How To Optimize Your Site Mobile-First
With all these tools, keep an eye on the Performance and Accessibility scores, as these directly affect mobile users.
Expand each section within the PageSpeed Insights report to see what elements are affecting your score.
These sections can give your developers their marching orders for optimizing the mobile experience.
While mobile speeds for cellular networks have steadily improved around the world (the average speed in the U.S. has jumped to 27.06 Mbps from 11.14 Mbps in just eight years), speed and usability for mobile users are at a premium.
Read more: Top 7 SEO Benefits Of Responsive Web Design
Best Practices For Mobile Optimization
Unlike traditional SEO, which can focus heavily on ensuring that you are using the language of your users as it relates to the intersection of your products/services and their needs, optimizing for mobile SEO can seem very technical SEO-heavy.
While you still need to be focused on matching your content with the needs of the user, mobile search optimization will require the aid of your developers and designers to be fully effective.
Below are several key factors in mobile SEO to keep in mind as you’re optimizing your site.
Site Rendering
How your site responds to different devices is one of the most important elements in mobile SEO.
The two most common approaches to this are responsive design and dynamic serving.
Responsive design is the most common of the two options.
Using your site’s cascading style sheets (CSS) and flexible layouts, as well as responsive content delivery networks (CDN) and modern image file types, responsive design allows your site to adjust to a variety of screen sizes, orientations, and resolutions.
With the responsive design, elements on the page adjust in size and location based on the size of the screen.
You can simply resize the window of your desktop browser and see how this works.
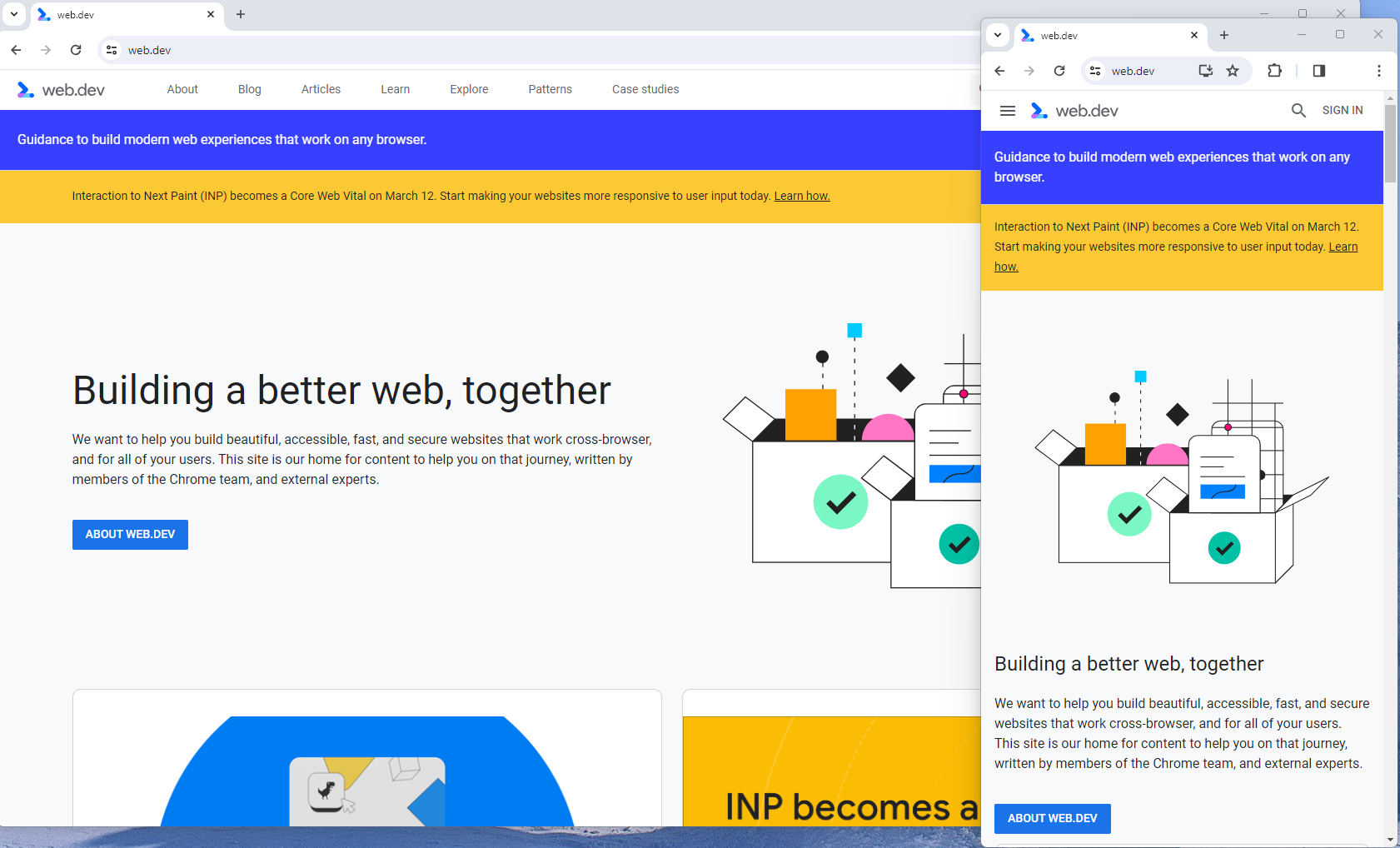 Screenshot from web.dev, March 2024
Screenshot from web.dev, March 2024This is the approach that Google recommends.
Adaptive design, also known as dynamic serving, consists of multiple fixed layouts that are dynamically served to the user based on their device.
Sites can have a separate layout for desktop, smartphone, and tablet users. Each design can be modified to remove functionality that may not make sense for certain device types.
This is a less efficient approach, but it does give sites more control over what each device sees.
While these will not be covered here, two other options:
- Progressive Web Apps (PWA), which can seamlessly integrate into a mobile app.
- Separate mobile site/URL (which is no longer recommended).
Read more: An Introduction To Rendering For SEO
Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
Google has introduced Interaction to Next Paint (INP) as a more comprehensive measure of user experience, succeeding First Input Delay. While FID measures the time from when a user first interacts with your page (e.g., clicking a link, tapping a button) to the time when the browser is actually able to begin processing event handlers in response to that interaction. INP, on the other hand, broadens the scope by measuring the responsiveness of a website throughout the entire lifespan of a page, not just first interaction.
Note that actions such as hovering and scrolling do not influence INP, however, keyboard-driven scrolling or navigational actions are considered keystrokes that may activate events measured by INP but not scrolling which is happeing due to interaction.
Scrolling may indirectly affect INP, for example in scenarios where users scroll through content, and additional content is lazy-loaded from the API. While the act of scrolling itself isn’t included in the INP calculation, the processing, necessary for loading additional content, can create contention on the main thread, thereby increasing interaction latency and adversely affecting the INP score.
What qualifies as an optimal INP score?
- An INP under 200ms indicates good responsiveness.
- Between 200ms and 500ms needs improvement.
- Over 500ms means page has poor responsiveness.
and these are common issues causing poor INP scores:
- Long JavaScript Tasks: Heavy JavaScript execution can block the main thread, delaying the browser’s ability to respond to user interactions. Thus break long JS tasks into smaller chunks by using scheduler API.
- Large DOM (HTML) Size: A large DOM ( starting from 1500 elements) can severely impact a website’s interactive performance. Every additional DOM element increases the work required to render pages and respond to user interactions.
- Inefficient Event Callbacks: Event handlers that execute lengthy or complex operations can significantly affect INP scores. Poorly optimized callbacks attached to user interactions, like clicks, keypress or taps, can block the main thread, delaying the browser’s ability to render visual feedback promptly. For example when handlers perform heavy computations or initiate synchronous network requests such on clicks.
and you can troubleshoot INP issues using free and paid tools.
As a good starting point I would recommend to check your INP scores by geos via treo.sh which will give you a great high level insights where you struggle with most.
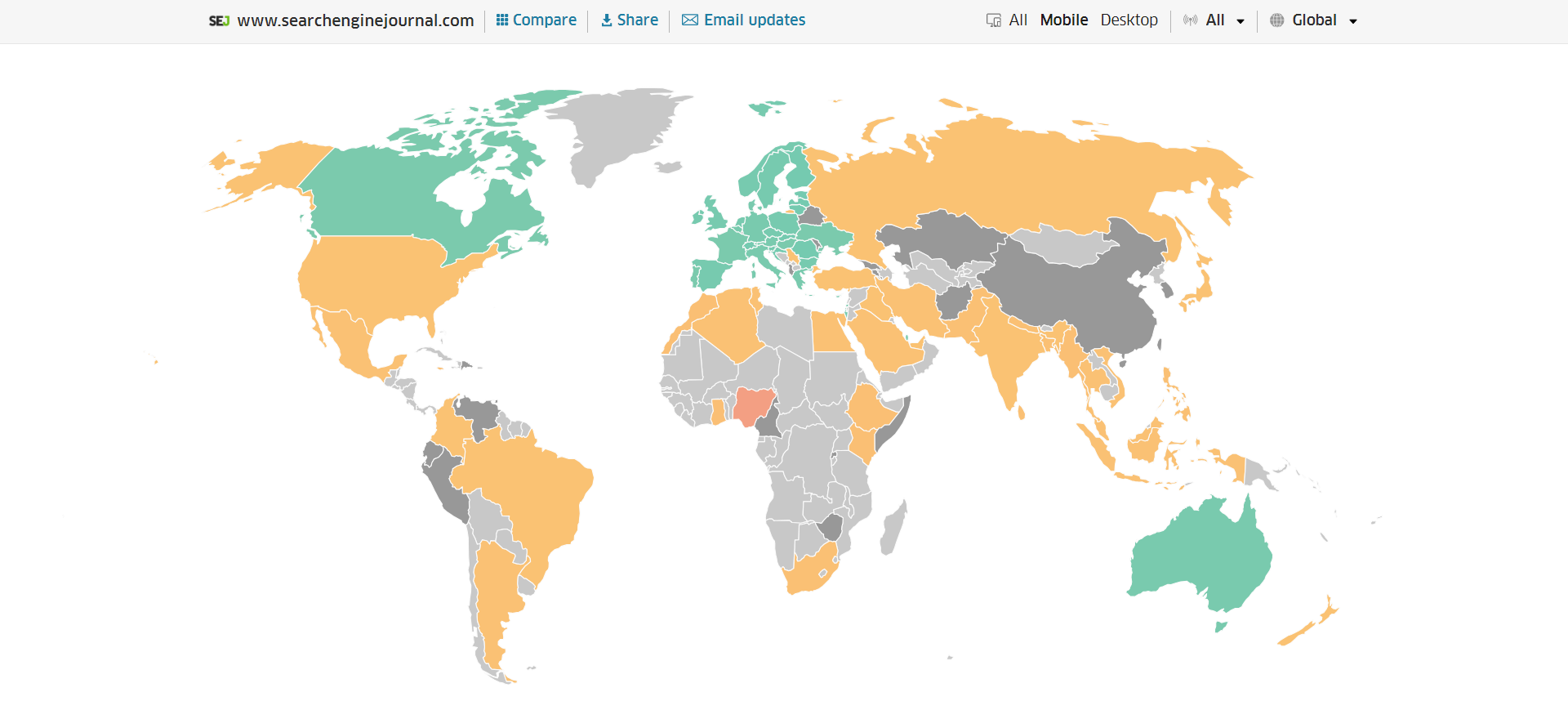 INP scores by Geos
INP scores by GeosRead more: How To Improve Interaction To Next Paint (INP)
Image Optimization
Images add a lot of value to the content on your site and can greatly affect the user experience.
From page speeds to image quality, you could adversely affect the user experience if you haven’t optimized your images.
This is especially true for the mobile experience. Images need to adjust to smaller screens, varying resolutions, and screen orientation.
- Use responsive images
- Implement lazy loading
- Compress your images (use WebP)
- Add your images into sitemap
Optimizing images is an entire science, and I advise you to read our comprehensive guide on image SEO how to implement the mentioned recommendations.
Avoid Intrusive Interstitials
Google rarely uses concrete language to state that something is a ranking factor or will result in a penalty, so you know it means business about intrusive interstitials in the mobile experience.
Intrusive interstitials are basically pop-ups on a page that prevent the user from seeing content on the page.
John Mueller, Google’s Senior Search Analyst, stated that they are specifically interested in the first interaction a user has after clicking on a search result.

Not all pop-ups are considered bad. Interstitial types that are considered “intrusive” by Google include:
- Pop-ups that cover most or all of the page content.
- Non-responsive interstitials or pop-ups that are impossible for mobile users to close.
- Pop-ups that are not triggered by a user action, such as a scroll or a click.
Read more: 7 Tips To Keep Pop-Ups From Harming Your SEO
Structured Data
Most of the tips provided in this guide so far are focused on usability and speed and have an additive effect, but there are changes that can directly influence how your site appears in mobile search results.
Search engine results pages (SERPs) haven’t been the “10 blue links” in a very long time.
They now reflect the diversity of search intent, showing a variety of different sections to meet the needs of users. Local Pack, shopping listing ads, video content, and more dominate the mobile search experience.
As a result, it’s more important than ever to provide structured data markup to the search engines, so they can display rich results for users.
In this example, you can see that both Zojirushi and Amazon have included structured data for their rice cookers, and Google is displaying rich results for both.
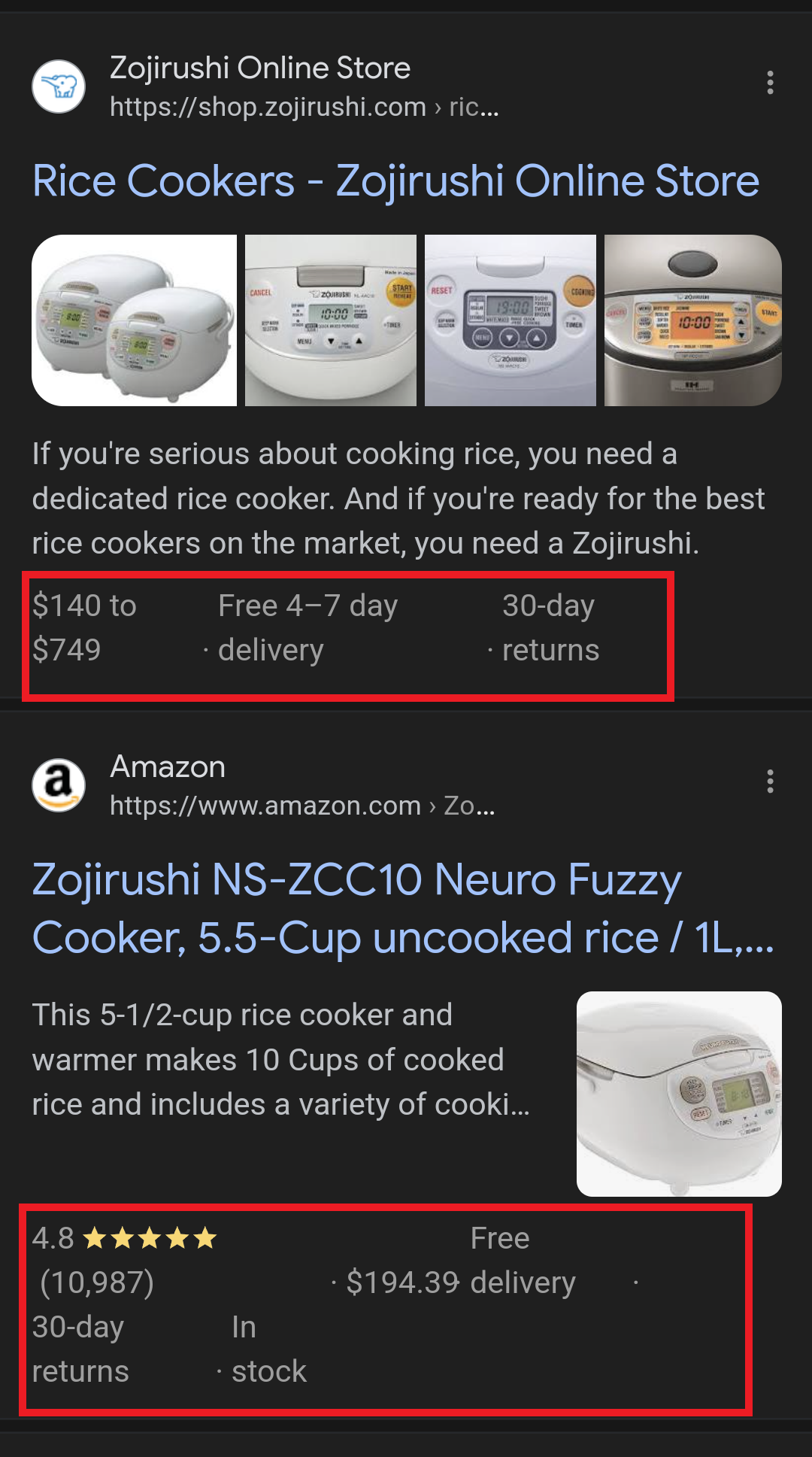 Screenshot from search for [Japanese rice cookers], Google, March 2024
Screenshot from search for [Japanese rice cookers], Google, March 2024Adding structured data markup to your site can influence how well your site shows up for local searches and product-related searches.
Using JSON-LD, you can mark up the business, product, and services data on your pages in Schema markup.
If you use WordPress as the content management system for your site, there are several plugins available that will automatically mark up your content with structured data.
Read more: What Structured Data To Use And Where To Use It?
Content Style
When you think about your mobile users and the screens on their devices, this can greatly influence how you write your content.
Rather than long, detailed paragraphs, mobile users prefer concise writing styles for mobile reading.
Each key point in your content should be a single line of text that easily fits on a mobile screen.
Your font sizes should adjust to the screen’s resolution to avoid eye strain for your users.
If possible, allow for a dark or dim mode for your site to further reduce eye strain.
Headers should be concise and address the searcher’s intent. Rather than lengthy section headers, keep it simple.
Finally, make sure that your text renders in a font size that’s readable.
Read more: 10 Tips For Creating Mobile-Friendly Content
Tap Targets
As important as text size, the tap targets on your pages should be sized and laid out appropriately.
Tap targets include navigation elements, links, form fields, and buttons like “Add to Cart” buttons.
Targets smaller than 48 pixels by 48 pixels and targets that overlap or are overlapped by other page elements will be called out in the Lighthouse report.
Tap targets are essential to the mobile user experience, especially for ecommerce websites, so optimizing them is vital to the health of your online business.
Read more: Google’s Lighthouse SEO Audit Tool Now Measures Tap Target Spacing
Prioritizing These Tips
If you have delayed making your site mobile-friendly until now, this guide may feel overwhelming. As a result, you may not know what to prioritize first.
As with so many other optimizations in SEO, it’s important to understand which changes will have the greatest impact, and this is just as true for mobile SEO.
Think of SEO as a framework in which your site’s technical aspects are the foundation of your content. Without a solid foundation, even the best content may struggle to rank.
- Responsive or Dynamic Rendering: If your site requires the user to zoom and scroll right or left to read the content on your pages, no number of other optimizations can help you. This should be first on your list.
- Content Style: Rethink how your users will consume your content online. Avoid very long paragraphs. “Brevity is the soul of wit,” to quote Shakespeare.
- Image Optimization: Begin migrating your images to next-gen image formats and optimize your content display network for speed and responsiveness.
- Tap Targets: A site that prevents users from navigating or converting into sales won’t be in business long. Make navigation, links, and buttons usable for them.
- Structured Data: While this element ranks last in priority on this list, rich results can improve your chances of receiving traffic from a search engine, so add this to your to-do list once you’ve completed the other optimizations.
Summary
From How Search Works, “Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
If Google’s primary mission is focused on making all the world’s information accessible and useful, then you know they will prefer surfacing sites that align with that vision.
Since a growing percentage of users are on mobile devices, you may want to infer the word “everywhere” added to the end of the mission statement.
Are you missing out on traffic from mobile devices because of a poor mobile experience?
If you hope to remain relevant, make mobile SEO a priority now.
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal
SEO
HARO Has Been Dead for a While

I know nothing about the new tool. I haven’t tried it. But after trying to use HARO recently, I can’t say I’m surprised or saddened by its death. It’s been a walking corpse for a while.
I used HARO way back in the day to build links. It worked. But a couple of months ago, I experienced the platform from the other side when I decided to try to source some “expert” insights for our posts.
After just a few minutes of work, I got hundreds of pitches:
So, I grabbed a cup of coffee and began to work through them. It didn’t take long before I lost the will to live. Every other pitch seemed like nothing more than lazy AI-generated nonsense from someone who definitely wasn’t an expert.
Here’s one of them:


Seriously. Who writes like that? I’m a self-confessed dullard (any fellow Dull Men’s Club members here?), and even I’m not that dull…
I don’t think I looked through more than 30-40 of the responses. I just couldn’t bring myself to do it. It felt like having a conversation with ChatGPT… and not a very good one!
Despite only reviewing a few dozen of the many pitches I received, one stood out to me:


Believe it or not, this response came from a past client of mine who runs an SEO agency in the UK. Given how knowledgeable and experienced he is (he actually taught me a lot about SEO back in the day when I used to hassle him with questions on Skype), this pitch rang alarm bells for two reasons:
- I truly doubt he spends his time replying to HARO queries
- I know for a fact he’s no fan of Neil Patel (sorry, Neil, but I’m sure you’re aware of your reputation at this point!)
So… I decided to confront him 😉
Here’s what he said:
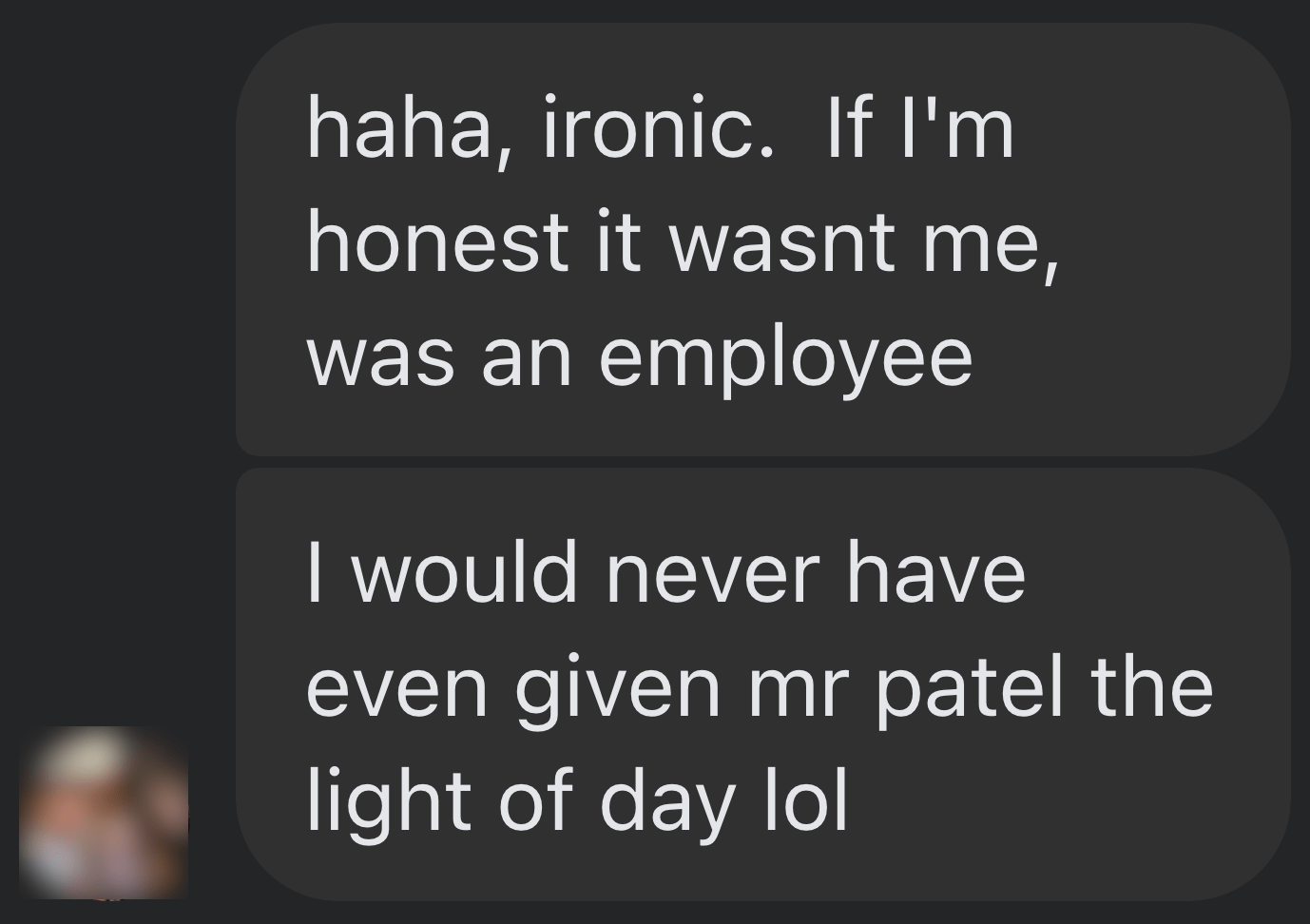

Shocker.
I pressed him for more details:
I’m getting a really good deal and paying per link rather than the typical £xxxx per month for X number of pitches. […] The responses as you’ve seen are not ideal but that’s a risk I’m prepared to take as realistically I dont have the time to do it myself. He’s not native english, but I have had to have a word with him a few times about clearly using AI. On the low cost ones I don’t care but on authority sites it needs to be more refined.
I think this pretty much sums up the state of HARO before its death. Most “pitches” were just AI answers from SEOs trying to build links for their clients.
Don’t get me wrong. I’m not throwing shade here. I know that good links are hard to come by, so you have to do what works. And the reality is that HARO did work. Just look at the example below. You can tell from the anchor and surrounding text in Ahrefs that these links were almost certainly built with HARO:
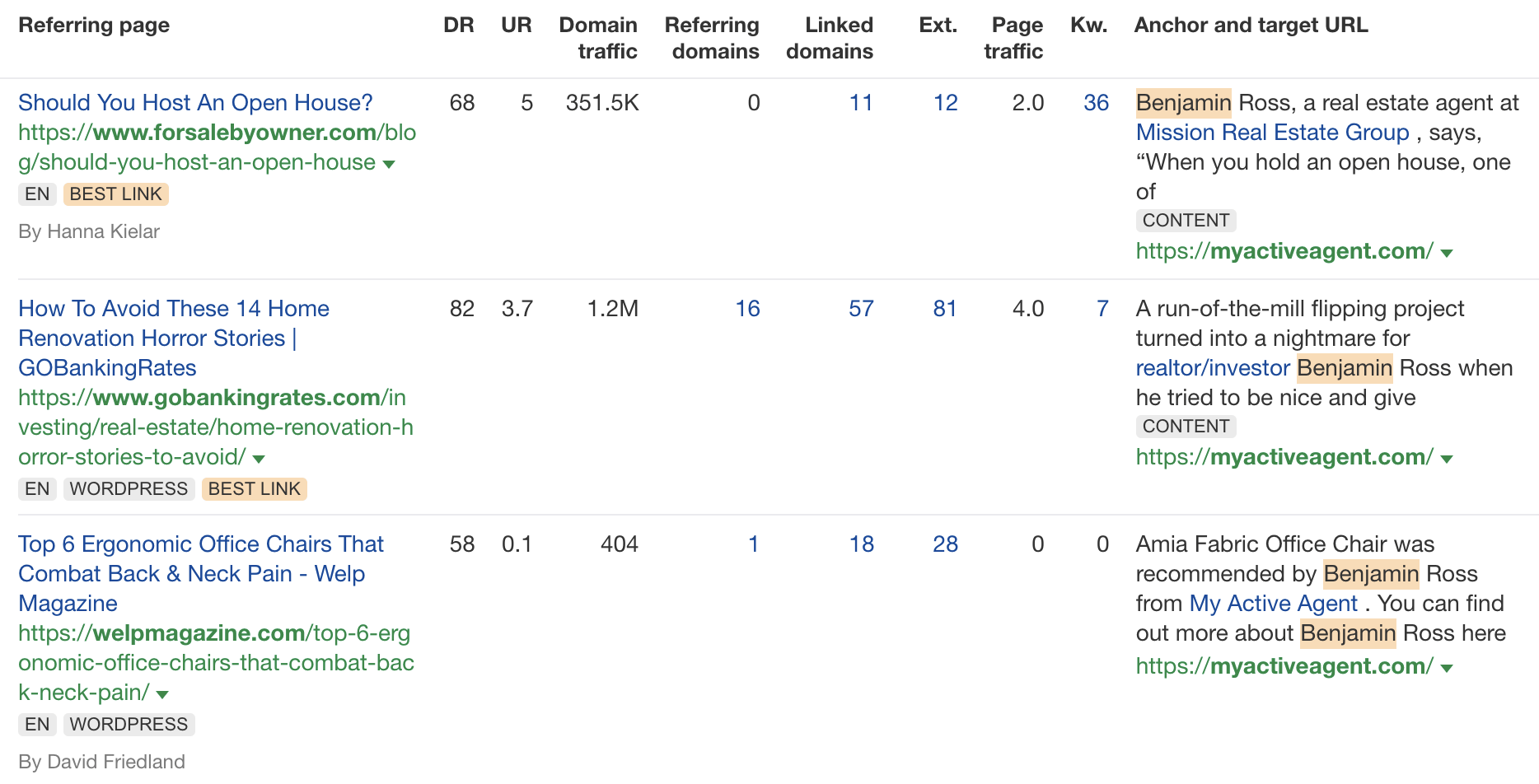

But this was the problem. HARO worked so well back in the day that it was only a matter of time before spammers and the #scale crew ruined it for everyone. That’s what happened, and now HARO is no more. So…
If you’re a link builder, I think it’s time to admit that HARO link building is dead and move on.
No tactic works well forever. It’s the law of sh**ty clickthroughs. This is why you don’t see SEOs having huge success with tactics like broken link building anymore. They’ve moved on to more innovative tactics or, dare I say it, are just buying links.
Sidenote.
Talking of buying links, here’s something to ponder: if Connectively charges for pitches, are links built through those pitches technically paid? If so, do they violate Google’s spam policies? It’s a murky old world this SEO lark, eh?
If you’re a journalist, Connectively might be worth a shot. But with experts being charged for pitches, you probably won’t get as many responses. That might be a good thing. You might get less spam. Or you might just get spammed by SEOs with deep pockets. The jury’s out for now.
My advice? Look for alternative methods like finding and reaching out to experts directly. You can easily use tools like Content Explorer to find folks who’ve written lots of content about the topic and are likely to be experts.
For example, if you look for content with “backlinks” in the title and go to the Authors tab, you might see a familiar name. 😉
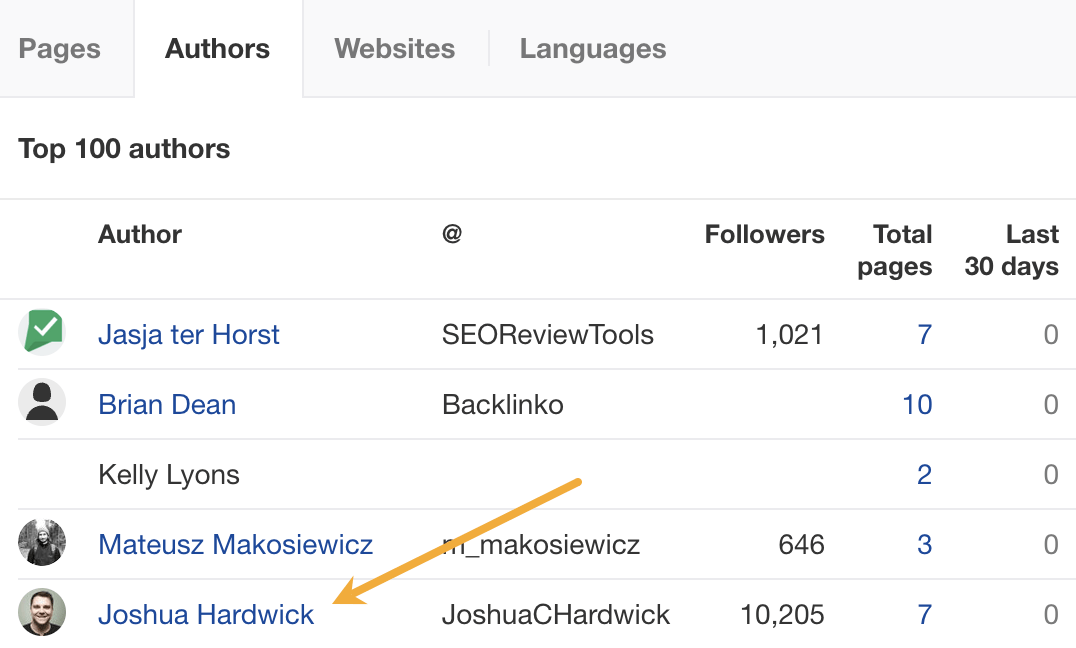

I don’t know if I’d call myself an expert, but I’d be happy to give you a quote if you reached out on social media or emailed me (here’s how to find my email address).
Alternatively, you can bait your audience into giving you their insights on social media. I did this recently with a poll on X and included many of the responses in my guide to toxic backlinks.
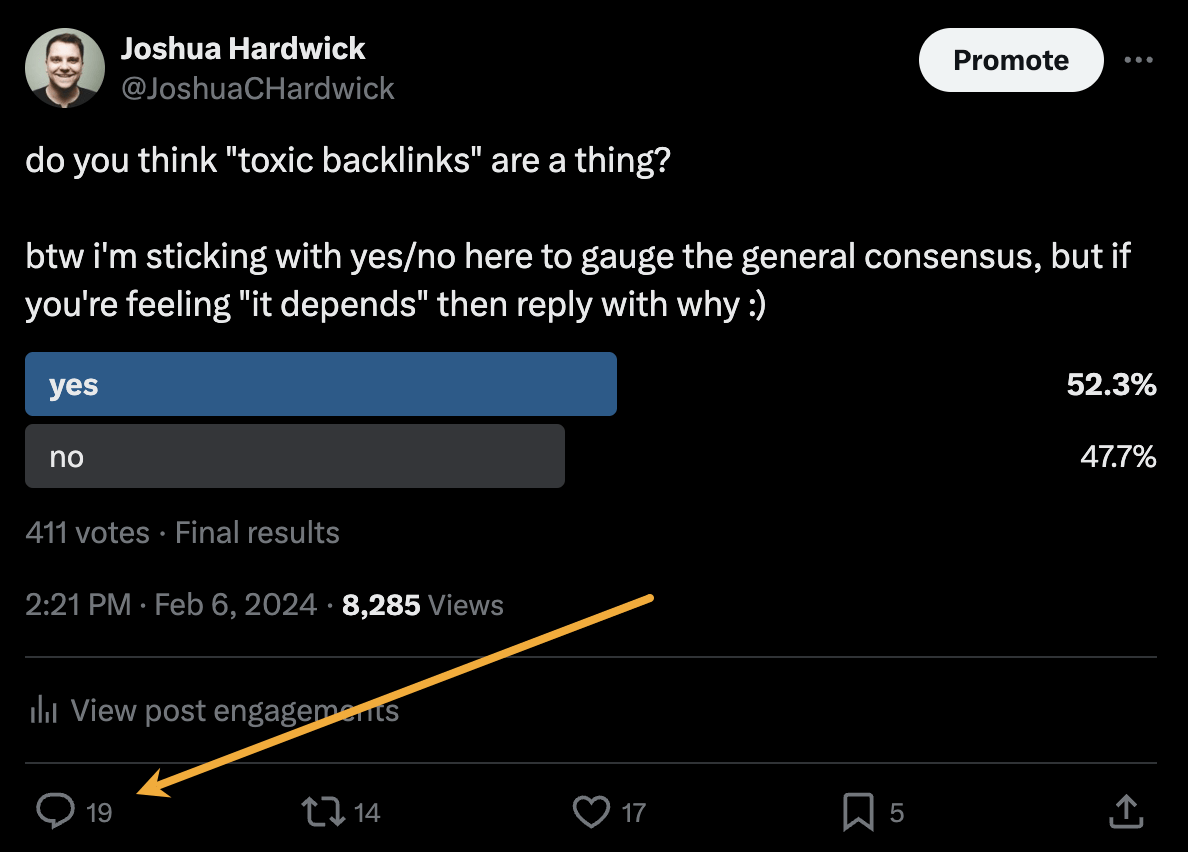
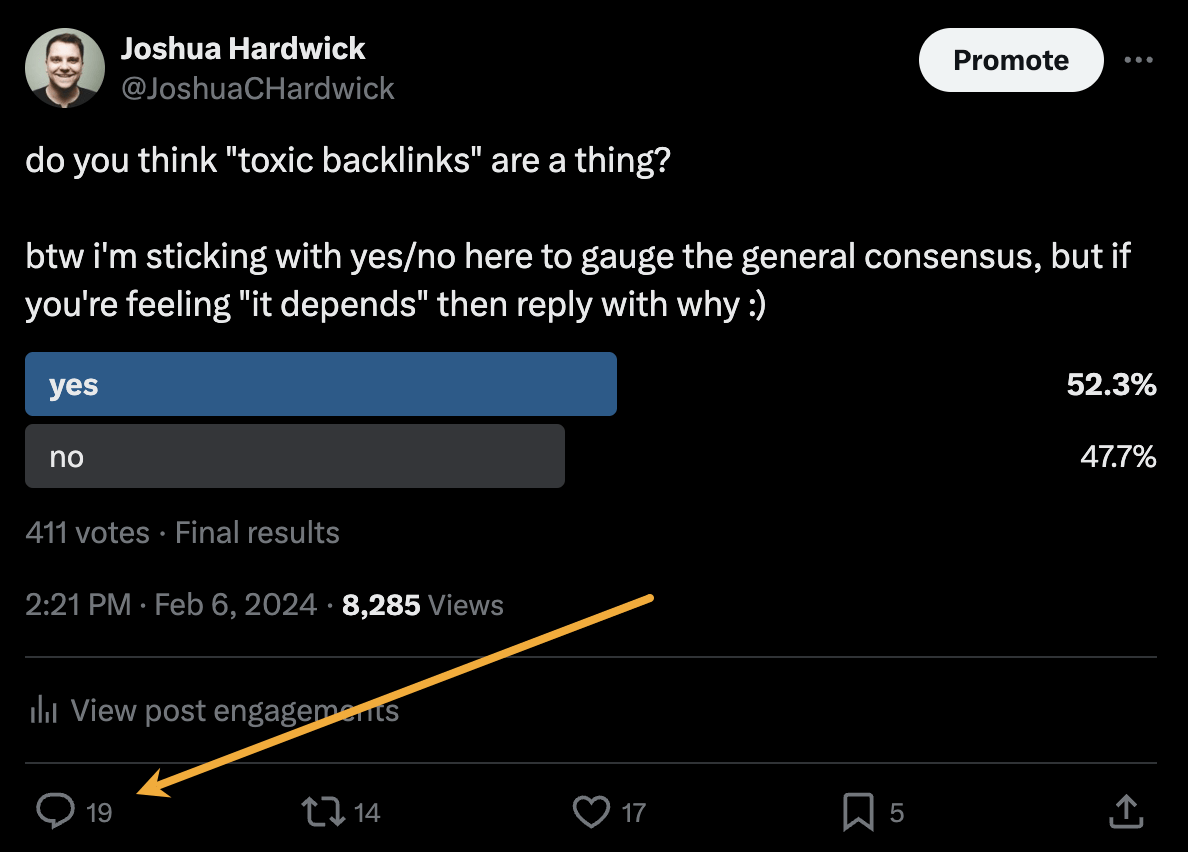
Either of these options is quicker than using HARO because you don’t have to sift through hundreds of responses looking for a needle in a haystack. If you disagree with me and still love HARO, feel free to tell me why on X 😉
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Limits News Links In California Over Proposed ‘Link Tax’ Law
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 12, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days ago5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoCritical Display Error in Brand Safety Metrics On Twitter/X Corrected













You must be logged in to post a comment Login