SEO
A Simple (But Effective) 14-Step SEO Audit & Checklist
An SEO audit is where you find opportunities to improve a site’s search performance. It involves finding technical, on-page, content, and link-related issues to fix or improve.
Everyone’s SEO audit process differs, as there’s no universal approach. But there are a handful of basic issues all site owners should look for.
You’ll learn how to check for 14 of them in this guide.
Manual actions are when a human reviewer at Google decides that your site doesn’t comply with their webmaster guidelines. The result is that some or all of your site won’t be shown in Google’s search results.
You’re unlikely to have a manual action unless you’ve done something drastically wrong. But it’s still arguably the best first thing to check because if you have one, you’re dead in the water before you even start.
To check for manual actions, go to the Manual actions report in Google Search Console.

If it says anything other than “No issues detected,” read our Google penalties guide.
Google updates its search algorithms all the time. Many of these updates target specific things like link spam or content quality.
For that reason, it’s important to check for organic traffic drops coinciding with known Google updates, as these may point to specific issues.
For example, the core update in August 2018 appeared to largely affect health, fitness, and medical sites that failed to demonstrate expertise, authoritativeness, and trust (E-A-T). In fact, Barry Schwartz, a prominent blogger, dubbed it the “Medic” update.
The update all but destroyed some sites, like this one:

You can check your organic traffic trend for free in Google Search Console. Just go to the Search results report and set the period to the past year or two.

You can also see an estimated traffic graph in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, where you can also overlay known Google updates to more easily diagnose issues.
For example, we can see that this site’s traffic drop coincided with a core update:

If you spot a big traffic drop coinciding with a Google update, check our Google Algorithm Updates History page to see the focus of the update.
HTTPS is a secure protocol for transferring data to and from visitors. It helps to keep things like passwords and credit card details secure, and it’s been a small Google ranking factor since 2014.
You can check if your website uses HTTPS by visiting it. If there’s a “lock” icon in the address bar, it’s secure.

However, some websites face issues where certain pages load securely, but other pages and resources don’t. So we recommend digging a bit deeper to make sure there are no HTTPS-related issues. Here’s how:
- Sign up for a free Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account
- Crawl your site with Site Audit
- Go to the Internal pages report
From here, check the “Protocols distribution” graph to see whether any pages are using HTTP. Ideally, you want to see an all-green graph.

Recommendation
- Click on “HTTP”
- Sort the report by status code from low to high
- Add a column for “Final redirect URL”
If the lowest HTTP status code is “301” and the final redirect URLs all begin with HTTPS, everything is fine.

Next, hit the “Issues” tab and look for the “HTTPS/HTTP mixed content” issue. This indicates that while your initial HTML is loading over a secure HTTPS connection, some resource files like images load over an unsecure one.

If you see either of these issues, read our HTTPS guide to learn more about dealing with them.
People should only be able to access one of these four versions of your website:
http://domain.com http://www.domain.com https://domain.com https://www.domain.com
The other three variations should redirect to the canonical (master) version.
This is important because Google sees all four of these as separate site versions. Having more than one accessible can cause crawling and indexing issues. In some cases, it can even dilute link equity and, thus, may negatively impact rankings.
To check that everything works as it should, install Ahrefs’ SEO Toolbar, type each URL version into your browser, then check the HTTP headers to make sure they all redirect to the same “master” version.
For example, if we visit http://ahrefs.com, it redirects to the secure version at https://ahrefs.com.

The same happens if we visit the secure www version (https://www.ahrefs.com).

If this doesn’t happen, you’ll need to implement redirects.
Learn more: Redirects for SEO: A Simple (But Complete) Guide
Google search results come from its index, which is a database of hundreds of billions of webpages. Your pages need to be in this index to stand any chance at ranking.
It’s also important to keep pages that aren’t valuable for searchers out of Google’s index, as this can also cause SEO issues.
Indexing issues can get quite complicated, but you can check for basic issues fairly easily.
First, check the Indexability report in Site Audit for “Noindex page” warnings.

Google can’t index pages with this warning, so it’s worth checking they’re not pages you want indexed. If they are, remove or edit the meta robots tag.
Second, check the number of indexable URLs in the same report.

Investigate further if this looks abnormally high.
For example, given that we only have around 500 published blog posts, 2,164 indexable URLs seem high for the Ahrefs blog. But if we click the number, we see that it’s because it includes versions of our blog in other languages.

If we exclude those pages, along with author, category, and pagination pages, the number of indexable URLs looks pretty much spot on.

Mobile-friendliness has been a ranking factor everywhere since Google moved to mobile-first indexing in 2019.
Checking for mobile-friendliness is easily done. Just go to the Mobile Usability report in Google Search Console. It tells you whether any URLs have errors that affect mobile usability.

If you don’t have access to Google Search Console, plug any page from your website into Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.

In general, assuming that other pages on your website use the same design and layout, the result should apply to most, if not all, of your pages.
Learn more: Mobile-First Indexing: What You Need to Know
Page speed has been a small ranking factor on desktop since 2010 and mobile since 2018. However, there’s no official threshold for how fast a page should load, and there are a confusing number of metrics you can use as a proxy.
For example, Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool shows all kinds of metrics:

The other downside of this tool is that you can only test one page at a time.
For that reason, it’s better to start with a tool that’ll give you speed metrics on all your pages. You can do this in Ahrefs’ Site Audit, which you can use for free with an Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account. Here’s how:
- Crawl your website with Site Audit
- Go to the Performance report
- Check the “Time to first byte” and “Load time distribution” graphs

As a general rule, the more green you see here, the better. If you see lots of red, you may want to work on improving your page speed.
Core Web Vitals are metrics that Google uses to measure user experience. They measure a page’s load time, interactivity, and the stability of the content as it loads.
As they’re currently a weak ranking signal, you shouldn’t obsess over them. But it’s still worth taking a quick look at your site’s performance.
To do this, check the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console.

As this report is based on Chrome User Experience (CrUX) data, there’s a chance you may see a “Not enough data collected” or “Not enough recent usage data” message instead of data.
If that happens, head over to the Performance report in Ahrefs’ Site Audit and check the Lighthouse scores. As this is lab data, it doesn’t rely on user experience data from Google.

Having broken pages on your site is never good. If these pages have backlinks, they are effectively wasted because they point to nothing.
To find broken pages on your website, head to the Internal pages report in Site Audit and click the number under “Broken.”

If you want to see the number of backlinks to each of these pages, add the “No. of referring domains” column to the report.

You can also find broken URLs with backlinks in Site Explorer. Just plug in your domain, go to the Best by links report, add a “404 not found” filter, then sort the report by referring domains from high to low.

The benefit of using Site Explorer is that it shows URLs that people linked to accidentally.
For example, we have links from three referring domains to this URL:

This page never existed. The linkers just linked to the wrong URL. It should have an “s” at the end.
Here’s our recommended process for dealing with broken links:

A sitemap lists the pages that you want search engines to index. It shouldn’t list things like redirects, non-canonicals, or dead pages because those send mixed signals to Google.
To check for sitemap issues, head to the All issues report in Site Audit and scroll to the “Other” section.

You’ll see any issues here relating to:
- Dead or inaccessible pages in the sitemap.
- Noindexed pages in the sitemap.
- Non-canonical pages in the sitemap.
If you have any of these issues, hit the caret and follow the advice on fixing them.
Every indexable page on your site should have a title tag, meta description, and H1 tag. These basic on-page elements help Google understand your content and help you to win more clicks from your rankings.
To check for issues, head to the “Issues” tab in the Content report in Site Audit.

For example, the website above has 724 pages with a missing or empty title tag. This isn’t ideal because Google shows them in the search results, so the site could be missing out on clicks as a result.
It also has the same number of pages with an empty or missing meta description, and thousands with a missing or empty H1 tag.
Google often shows meta descriptions in the search results, so you should try to write an enticing one for every important page. Missing H1 tags, on the other hand, usually point to bigger issues like an improperly coded theme.
You can see which URLs are affected by clicking an issue and hitting “View affected URLs.”

If you want to prioritize fixes, sort the report by estimated organic traffic from high to low.

Rankings rarely last forever. As content becomes outdated, its search traffic will often start to drop off. But you can often solve this by refreshing and republishing the content.
For example, our list of top Google searches declined massively in 2021.

This is because we didn’t update the post for over a year, so the content became outdated. The recent spike in traffic is a result of us updating and republishing the piece.
Here’s an easy way to find declining content in Google Search Console:
- Go to the Search results report
- Set the date filter to compare mode
- Choose “Compare last 6 months to previous period”
- Click the “Pages” tab
- Sort the table by “Clicks Difference” from low to high
For example, this shows us that our list of the most visited websites has declined massively over the last six months. So this is probably ripe for an update.

If you’re a WordPress user, you can automate this process with our free SEO plugin. It monitors for pages that no longer perform well and gives recommendations on how to fix them.
For example, it’s suggesting that we rewrite our list of the best keyword tools because it used to rank in the top three for its target keyword but now doesn’t even rank in the top 100.

Content gaps occur when you miss important subtopics in your content. The result is that you don’t rank for as many long-tail keywords and potentially not as high as you could for your main target keyword.
Here’s an easy way to find content gaps:
- Paste one of your page’s URLs into Site Explorer
- Go to the Content Gap report
- Paste in the URLs of a few similar pages outranking you

Hit “Show keywords.” You’ll see all of the keywords that these pages rank for where yours don’t.
Many of these will just be different ways of searching for the same thing, but some may represent subtopics you’ve missed.
For example, when we do this for our page about “what is seo,” we see that competing pages are ranking for quite a few keywords relating to what SEO stands for.

This is an interesting case because we kind of covered this in our definition on the page:

However, we didn’t explicitly state that this is what SEO stands for. Many of our competitors did.


For that reason, it may be worth us stating this in a more explicit way.
Many other technical issues can hinder your rankings. That’s why it’s always worth crawling your site with a tool like Ahrefs’ Site Audit to check for other SEO issues.
For example, if we do this for Ahrefs’ blog, we find a redirect loop:

Redirect loops are something you’re unlikely to spot by chance. So this issue would have likely gone unnoticed without a crawl-based audit.
It looks like we also have missing alt text on over 2,400 images:

This is arguably not a huge problem, but the sheer number of affected images in this instance points to a likely hole in our processes.
Final thoughts
Running this SEO audit gives you three things to take action on to improve SEO.
- Technical SEO issues – Fixing these may boost your site’s overall search performance.
- On-page SEO issues – Fixing these may increase your organic clicks.
- Content opportunities – Pursuing these may rank pages higher and for more keywords.
If you want to run a deeper audit, read our guide to running a technical SEO audit.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.
SEO
brightonSEO Live Blog

Hello everyone. It’s April again, so I’m back in Brighton for another two days of Being the introvert I am, my idea of fun isn’t hanging around our booth all day explaining we’ve run out of t-shirts (seriously, you need to be fast if you want swag!). So I decided to do something useful and live-blog the event instead.
Follow below for talk takeaways and (very) mildly humorous commentary. sun, sea, and SEO!
SEO
Google Further Postpones Third-Party Cookie Deprecation In Chrome

Google has again delayed its plan to phase out third-party cookies in the Chrome web browser. The latest postponement comes after ongoing challenges in reconciling feedback from industry stakeholders and regulators.
The announcement was made in Google and the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) joint quarterly report on the Privacy Sandbox initiative, scheduled for release on April 26.
Chrome’s Third-Party Cookie Phaseout Pushed To 2025
Google states it “will not complete third-party cookie deprecation during the second half of Q4” this year as planned.
Instead, the tech giant aims to begin deprecating third-party cookies in Chrome “starting early next year,” assuming an agreement can be reached with the CMA and the UK’s Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO).
The statement reads:
“We recognize that there are ongoing challenges related to reconciling divergent feedback from the industry, regulators and developers, and will continue to engage closely with the entire ecosystem. It’s also critical that the CMA has sufficient time to review all evidence, including results from industry tests, which the CMA has asked market participants to provide by the end of June.”
Continued Engagement With Regulators
Google reiterated its commitment to “engaging closely with the CMA and ICO” throughout the process and hopes to conclude discussions this year.
This marks the third delay to Google’s plan to deprecate third-party cookies, initially aiming for a Q3 2023 phaseout before pushing it back to late 2024.
The postponements reflect the challenges in transitioning away from cross-site user tracking while balancing privacy and advertiser interests.
Transition Period & Impact
In January, Chrome began restricting third-party cookie access for 1% of users globally. This percentage was expected to gradually increase until 100% of users were covered by Q3 2024.
However, the latest delay gives websites and services more time to migrate away from third-party cookie dependencies through Google’s limited “deprecation trials” program.
The trials offer temporary cookie access extensions until December 27, 2024, for non-advertising use cases that can demonstrate direct user impact and functional breakage.
While easing the transition, the trials have strict eligibility rules. Advertising-related services are ineligible, and origins matching known ad-related domains are rejected.
Google states the program aims to address functional issues rather than relieve general data collection inconveniences.
Publisher & Advertiser Implications
The repeated delays highlight the potential disruption for digital publishers and advertisers relying on third-party cookie tracking.
Industry groups have raised concerns that restricting cross-site tracking could push websites toward more opaque privacy-invasive practices.
However, privacy advocates view the phaseout as crucial in preventing covert user profiling across the web.
With the latest postponement, all parties have more time to prepare for the eventual loss of third-party cookies and adopt Google’s proposed Privacy Sandbox APIs as replacements.
Featured Image: Novikov Aleksey/Shutterstock
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
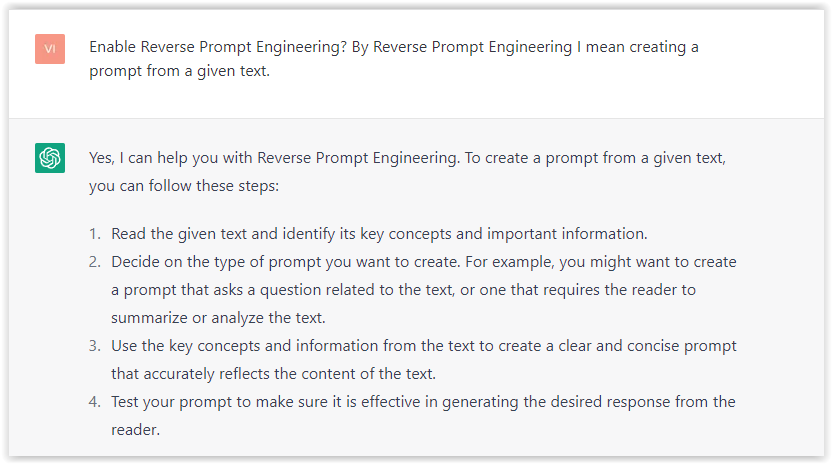 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
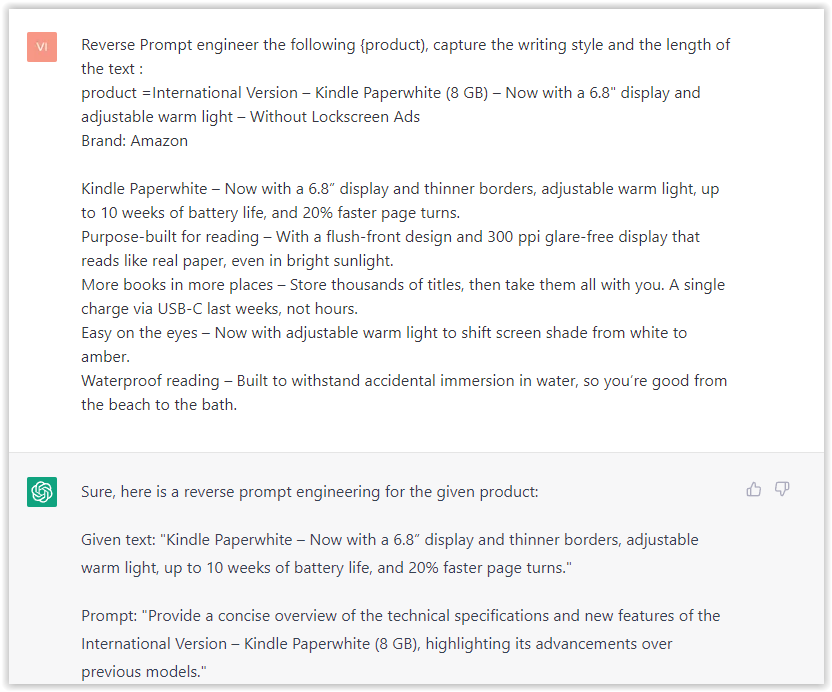 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago25 WordPress Alternatives Best For SEO
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago7 Best WooCommerce Points and Rewards Plugins (Free & Paid)
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login