SEO
A Technical SEO Guide To Lighthouse Performance Metrics

Maybe you’re here because you’re a die-hard fan of performance metrics. Or maybe you don’t know what Lighthouse is and are too afraid to ask.
Either is an excellent option. Welcome!
Together, we’re hoping to take your performance improvement efforts from “make all the numbers green” to some clear and meaningful action items.
Note: This article was updated for freshness in January 2022 to represent versions 8 and 9.
Technical SEO and Google Data Studio nerd Rachel Anderson joined me on this merry adventure into demystifying developer documentation.
We’re going to answer:
- What is Lighthouse?
- How is Lighthouse different from Core Web Vitals?
- Why doesn’t Lighthouse match Search Console/Crux reports?
- How is Performance Score calculated?
- Why is my score different each time I test?
- Lighthouse Performance metrics explained
- How to test performance using Lighthouse
What Is Lighthouse?
Performance is about measuring how quickly a browser can assemble a webpage.
Lighthouse uses a web browser called Chromium to build pages and runs tests on the pages as they’re built. The tool is open-source (meaning it is maintained by the community and free to use).
Each audit falls into one of five categories:
- Performance.
- Accessibility.
- Best Practices.
- SEO.
- Progressive Web App.
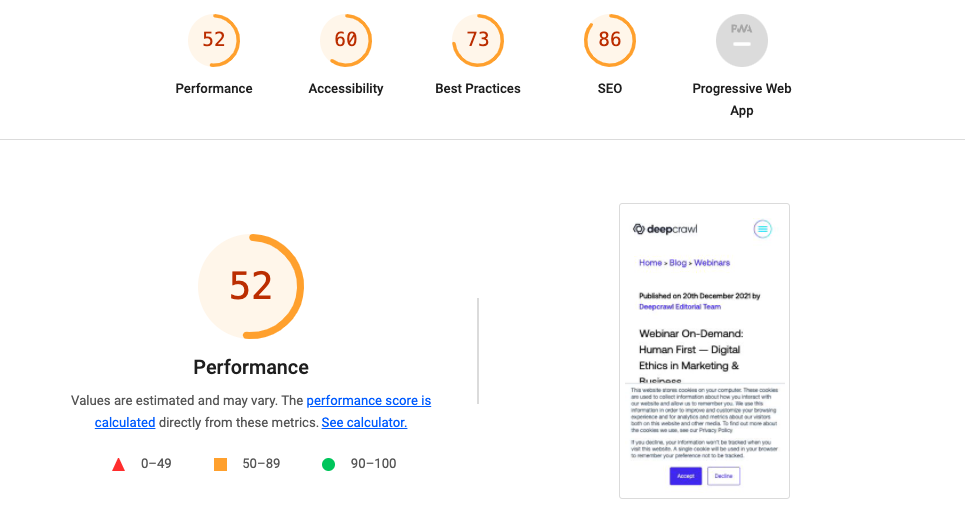
For the purposes of this article, we’re going to use the name Lighthouse to refer to the series of tests executed by the shared Github repo, regardless of the execution method.
Version 9 is currently out on Github and is slated for large-scale rollout with the stable Chrome 98 release in February 2022.
Lighthouse And Web Core Vitals
On May 5, 2020, the Chromium project announced a set of three metrics with which the Google-backed open-source browser would measure performance.
The metrics, known as Web Vitals, are part of a Google initiative designed to provide unified guidance for quality signals.
The goal of these metrics is to measure web performance in a user-centric manner.
Within two weeks, Lighthouse v6 rolled out with a modified version of Web Core Vitals at the heart of the update.
July 2020 saw Lighthouse v6’s unified metrics adopted across Google products with the release of Chrome 84.
Chrome DevTools Audits panel was renamed to Lighthouse. Pagespeed insights and Google Search Console also reference these unified metrics.
This change in focus sets new, more refined goals.
How Is Lighthouse Different Than Core Web Vitals?
The three metrics represented by Core Web Vital are part of Lighthouse performance scoring.
Largest Contentful Paint, Total Blocking Time, and Cumulative Layout Shift comprise 70% of Lighthouse’s weighted performance score.
The scores you’ll see for CWV in Lighthouse are the result of emulated tests.
It’s the same metric but measured off a single page load rather than calculated from page loads around the world.
Why Doesn’t Lighthouse Match Search Console/Crux reports?
For real users, how quickly a page assembles is based on factors like their network connection, the device’s network processing power, and even the user’s physical distance to the site’s servers.
Lighthouse performance data doesn’t account for all these factors.
Instead, the tool emulates a mid-range device and throttles CPU in order to simulate the average user.
These are lab tests collected within a controlled environment with predefined device and network settings.
Lab data is helpful for debugging performance issues.
It does not mean that the experience on your local machine in a controlled environment represents the experiences of real humans in the wild.
The good news is you don’t have to choose between Lighthouse and Core Web Vitals. They’re designed to be part of the same workflow.
Always start with field data from the Chrome User Experience Report to identify issues impacting real uses.
Then leverage the expanded testing capabilities of Lighthouse to identify the code causing the issue.
If you’re working on a site pre-launch or QAing changes in a non-public environment, Lighthouse will be your new best #webperf friend.
 Screenshot from Lighthouse, January 2022
Screenshot from Lighthouse, January 2022How Is Lighthouse Performance Metrics Calculated?
 Lighthouse, January 2022
Lighthouse, January 2022In versions 8 and 9, Lighthouse’s performance score is made of seven metrics with each contributing a percentage of the total performance score.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022Why Is My Score Different Each Time I Test?
Your score may change each time you test.
Browser extensions, internet connection, A/B tests, or even the ads displayed on that specific page load have an impact.
If you’re curious/furious to know more, check out the documentation on performance testing variability.
Lighthouse Performance Metrics Explained
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- What it represents: A user’s perception of loading experience.
- Lighthouse Performance score weighting: 25%
- What it measures: The point in the page load timeline when the page’s largest image or text block is visible within the viewport.
- How it’s measured: Lighthouse extracts LCP data from Chrome’s tracing tool.
- Is Largest Contentful Paint a Web Core Vital? Yes!
- LCP Scoring
- Goal: Achieve LCP in < 2.5 seconds.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022What Elements Can Be Part Of LCP?
- Text.
- Images.
- Videos.
- Background images.
What Counts As LCP On Your Page?
It depends! LCP typically varies by page template.
This means that you can measure a handful of pages using the same template and define LCP.
Lighthouse will provide you with the exact HTML of the LCP element, but it can be useful to know the node as well when communicating with developers.
The node name will be consistent while the exact on-page image or text may change depending on which content is rendered by the template.
How To Define LCP Using Chrome Devtools
- Open the page in Chrome.
- Navigate to the Performance panel of Dev Tools (Command + Option + I on Mac or Control + Shift + I on Windows and Linux).
- Hover over the LCP marker in the Timings section.
- The element(s) that correspond to LCP is detailed in the Related Node field.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022What Causes Poor LCP?
Poor LCP typically comes from four issues:
- Slow server response times.
- Render-blocking JavaScript and CSS.
- Resource load times.
- Client-side rendering.
How To Fix Poor LCP
If the cause is slow server response time:
- Optimize your server.
- Route users to a nearby CDN.
- Cache assets.
- Serve HTML pages cache-first.
- Establish third-party connections early.
If the cause is render-blocking JavaScript and CSS:
- Minify CSS.
- Defer non-critical CSS.
- Inline critical CSS.
- Minify and compress JavaScript files.
- Defer unused JavaScript.
- Minimize unused polyfills.
If the cause is resource load times:
- Optimize and compress images.
- Preload important resources.
- Compress text files.
- Deliver different assets based on the network connection (adaptive serving).
- Cache assets using a service worker.
If the cause is client-side rendering:
Resources For Improving LCP
Total Blocking Time (TBT)
- What it represents: Responsiveness to user input.
- Lighthouse Performance score weighting: 30%
- What it measures: TBT measures the time between First Contentful Paint and Time to Interactive. TBT is the lab equivalent of First Input Delay (FID) – the field data used in the Chrome User Experience Report and Google’s upcoming Page Experience ranking signal.
- How it’s measured: The total time in which the main thread is occupied by tasks taking more than 50ms to complete. If a task takes 80ms to run, 30ms of that time will be counted toward TBT. If a task takes 45ms to run, 0ms will be added to TBT.
- Is Total Blocking Time a Web Core Vital? Yes! It’s the lab data equivalent of First Input Delay (FID).
TBT Scoring
- Goal: Achieve TBT score of less than 300 milliseconds.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022First Input Delay, the field data equivalent to TBT, has different thresholds.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022Long Tasks And Total Blocking Time
TBT measures long tasks – those taking longer than 50ms.
When a browser loads your site, there is essentially a single line queue of scripts waiting to be executed.
Any input from the user has to go into that same queue.
When the browser can’t respond to user input because other tasks are executing, the user perceives this as lag.
Essentially, long tasks are like that person at your favorite coffee shop who takes far too long to order a drink.
Like someone ordering a 2% venti four-pump vanilla, five-pump mocha whole-fat froth, long tasks are a major source of bad experiences.
 Screenshot by author, January 2022
Screenshot by author, January 2022What Causes A High TBT On Your Page?
Heavy JavaScript.
That’s it.
How To See TBT Using Chrome Devtools
 Screenshot from Chrome Devtools, January 2022
Screenshot from Chrome Devtools, January 2022How To Fix Poor TBT
- Break up Long Tasks.
- Optimize your page for interaction readiness.
- Use a web worker.
- Reduce JavaScript execution time.
Resources For Improving TBT
First Contentful Paint (FCP)
- What it represents: FCP marks the time at which the first text or image is painted (visible).
- Lighthouse Performance score weighting: 10%
- What it measures: The time when I can see the page I requested is responding. My thumb can stop hovering over the back button.
- How it’s measured: Your FCP score in Lighthouse is measured by comparing your page’s FCP to FCP times for real website data stored by the HTTP Archive.
- Your FCP increases if it is faster than other pages in the HTTP Archive.
- Is First Contentful Paint a Web Core Vital? No
FCP Scoring
- Goal: Achieve FCP in < 2 seconds.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022What Elements Can Be Part Of FCP?
The time it takes to render the first visible element to the DOM is the FCP.
Anything that happens before an element that renders non-white content to the page (excluding iframes) is counted toward FCP.
Since iframes are not considered part of FCP, if they are the first content to render, FCP will continue counting until the first non-iframe content loads, but the iframe load time isn’t counted toward the FCP.
The documentation around FCP also calls out that is often impacted by font load time and there are tips for improving font loads.
FCP Using Chrome Devtools
- Open the page in Chrome.
- Navigate to the Performance panel of Dev Tools (Command + Option + I on Mac or Control + Shift + I on Windows and Linux).
- Click on the FCP marker in the Timings section.
- The summary tab has a timestamp with the FCP in ms.
How To Improve FCP
In order for content to be displayed to the user, the browser must first download, parse, and process all external stylesheets it encounters before it can display or render any content to a user’s screen.
The fastest way to bypass the delay of external resources is to use in-line styles for above-the-fold content.
To keep your site sustainably scalable, use an automated tool like penthouse and Apache’s mod_pagespeed.
These solutions will come with some restrictions to functionalities, require testing, and may not be for everyone.
Universally, we can all improve our site’s time to First Contentful Paint by reducing the scope and complexity of style calculations.
If a style isn’t being used, remove it.
You can identify unused CSS with Chrome Dev Tool’s built-in Code Coverage functionality.
Use better data to make better decisions.
Similar to TTI, you can capture real user metrics for FCP using Google Analytics to correlate improvements with KPIs.
Resources For Improving FCP
Speed Index
- What it represents: How much is visible at a time during load.
- Lighthouse Performance score weighting: 10%
- What it measures: The Speed Index is the average time at which visible parts of the page are displayed.
- How it’s measured: Lighthouse’s Speed Index measurement comes from a node module called Speedline.
You’ll have to ask the kindly wizards at webpagetest.org for the specifics but roughly, Speedline scores vary by the size of the viewport (read as device screen) and have an algorithm for calculating the completeness of each frame.
 Screenshot by author, January 2022
Screenshot by author, January 2022- Is Speed Index a Web Core Vital? No.
SI Scoring
- Goal: achieve SI in < 4.3 seconds.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022How To Improve SI
Speed score reflects your site’s Critical Rendering Path.
A “critical” resource means that the resource is required for the first paint or is crucial to the page’s core functionality.
The longer and denser the path, the slower your site will be to provide a visual page.
If your path is optimized, you’ll give users content faster and score higher on Speed Index.
How The Critical Path Affects Rendering
 Screenshot by author, January 2022
Screenshot by author, January 2022Lighthouse recommendations commonly associated with a slow Critical Rendering Path include:
- Minimize main-thread work.
- Reduce JavaScript execution time.
- Minimize Critical Requests Depth.
- Eliminate Render-Blocking Resources.
- Defer offscreen images.
Resources For Improving SI
Time To Interactive
- What it represents: Load responsiveness; identifying where a page looks responsive but isn’t yet.
- Lighthouse Performance score weighting: 10%
- What it measures: The time from when the page begins loading to when its main resources have loaded and are able to respond to user input.
- How it’s measured: TTI measures how long it takes a page to become fully interactive. A page is considered fully interactive when:
1. The page displays useful content, which is measured by the First Contentful Paint.
2. Event handlers are registered for most visible page elements.
3. The page responds to user interactions within 50 milliseconds.
- Is Time to Interactive a Web Core Vital? No
TTI Scoring
Goal: achieve TTI score of less than 3.8 seconds.
Resources For Improving TTI
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- What it represents: A user’s perception of a page’s visual stability.
- Lighthouse Performance score weighting: 15%
- What it measures: It quantifies shifting page elements through the end of page load.
- How it’s measured: Unlike other metrics, CLS isn’t measured in time. Instead, it’s a calculated metric based on the number of frames in which elements move and the total distance in pixels the elements moved.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022CLS Scoring
- Goal: achieve CLS score of less than 0.1.
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022What Elements Can Be Part Of CLS?
Any visual element that appears above the fold at some point in the load.
That’s right – if you’re loading your footer first and then the hero content of the page, your CLS is going to hurt.
Causes Of Poor CLS
- Images without dimensions.
- Ads, embeds, and iframes without dimensions.
- Dynamically injected content.
- Web Fonts causing FOIT/FOUT.
- Actions waiting for a network response before updating DOM.
How To Define CLS Using Chrome Devtools
- Open the page in Chrome.
- Navigate to the Performance panel of Dev Tools (Command + Option + I on Mac or Control + Shift + I on Windows and Linux).
- Hover and move from left to right over the screenshots of the load (make sure the screenshots checkbox is checked).
- Watch for elements bouncing around after the first paint to identify elements causing CLS.
How To Improve CLS
Once you identify the element(s) at fault, you’ll need to update them to be stable during the page load.
For example, if slow-loading ads are causing the high CLS score, you may want to use placeholder images of the same size to fill that space as the ad loads to prevent the page shifting.
Some common ways to improve CLS include:
- Always include width and height size attributes on images and video elements.
- Reserve space for ad slots (and don’t collapse it).
- Avoid inserting new content above existing content.
- Take care when placing non-sticky ads near the top of the viewport.
- Preload fonts.
CLS Resources
How To Test Performance Using Lighthouse
Methodology Matters
Out of the box, Lighthouse audits a single page at a time.
A single page score doesn’t represent your site, and a fast homepage doesn’t mean a fast site.
Test multiple page types within your site.
Identify your major page types, templates, and goal conversion points (signup, subscribe, and checkout pages).
If 40% of your site is blog posts, make 40% of your testing URLs blog pages!
Example Page Testing Inventory
 Created by author, January 2022
Created by author, January 2022Before you begin optimizing, run Lighthouse on each of your sample pages and save the report data.
Record your scores and the to-do list of improvements.
Prevent data loss by saving the JSON results and utilizing Lighthouse Viewer when detailed result information is needed.
Get Your Backlog to Bite Back Using ROI
Getting development resources to action SEO recommendations is hard.
An in-house SEO professional could destroy their pancreas by having a birthday cake for every backlogged ticket’s birthday. Or at least learn to hate cake.
In my experience as an in-house enterprise SEO pro, the trick to getting performance initiatives prioritized is having the numbers to back the investment.
This starting data will become dollar signs that serve to justify and reward development efforts.
With Lighthouse testing, you can recommend specific and direct changes (Think preload this font file) and associate the change to a specific metric.
Chances are you’re going to have more than one area flagged during tests. That’s okay!
If you’re wondering which changes will have the most bang for the buck, check out the Lighthouse Scoring Calculator.
How To Run Lighthouse Tests
This is a case of many roads leading to Oz.
Sure, some scarecrow might be particularly loud about a certain shade of brick but it’s about your goals.
Looking to test an entire staging site? Time to learn some NPM.
Have less than five minutes to prep for a prospective client meeting? A couple of one-off reports should do the trick.
Whichever way you execute, default to mobile unless you have a special use-case for desktop.
For One-Off Reports: PageSpeed Insights
Test one page at a time on PageSpeed Insights. Simply enter the URL.
 Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, January 2022
Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, January 2022Pros Of Running Lighthouse From PageSpeed Insights
- Detailed Lighthouse report is combined with URL-specific data from the Chrome User Experience Report.
- Opportunities and Diagnostics can be filtered to specific metrics. This is exceptionally useful when creating tickets for your engineers and tracking the resulting impact of the changes.
- PageSpeed Insights is running already version 9.
 Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, January 2022
Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, January 2022
Cons Of Running Lighthouse From PageSpeed Insights
- One report at a time.
- Only Performance tests are run (if you need SEO, Accessibility, or Best Practices, you’ll need to run those separately)
- You can’t test local builds or authenticated pages.
- Reports can’t be saved in JSON, HTML, or Gist format. (Save as PDF via browser functionality is an option.
- Requires you to manually save results.
For Comparing Test Results: Chrome DevTools Or Web.dev
Because the report will be emulating a user’s experience using your browser, use an incognito instance with all extensions, and the browser’s cache disabled.
Pro-tip: Create a Chrome profile for testing. Keep it local (no sync enabled, password saving, or association to an existing Google account) and don’t install extensions for the user.
How To Run A Test Lighthouse Using Chrome DevTools
- Open an incognito instance of Chrome.
- Navigate to the Network panel of Chrome Dev Tools (Command + Option + I on Mac or Control + Shift + I on Windows and Linux).
- Tick the box to disable cache.
- Navigate to the Lighthouse panel.
- Click Generate Report.
- Click the dots to the right of the URL in the report
- Save in your preferred format (JSON, HTML, or Gist)
 Screenshot from Lighthouse Reports, January 2022
Screenshot from Lighthouse Reports, January 2022
Note that your version of Lighthouse may change depending on what version of Chrome you’re using. v8.5 is used on Chrome 97.
Lighthouse v9 will ship with DevTools in Chrome 98.
How To Run A Test Lighthouse Using Web.Dev
It’s just like DevTools but you don’t have to remember to disable all those pesky extensions!
- Go to web.dev/measure.
- Enter your URL.
- Click Run Audit.
- Click View Report.
 Screenshot by author, January 2022
Screenshot by author, January 2022
Pros Of Running Lighthouse From DevTools/web.dev
- You can test local builds or authenticated pages.
- Saved reports can be compared using the Lighthouse CI Diff tool.
 Screenshot from Lighthouse CI Diff, January 2022
Screenshot from Lighthouse CI Diff, January 2022
Cons Of Running Lighthouse From DevTools/web.dev
- One report at a time.
- Requires you to manually save results.
For Testing At Scale (and Sanity): Node Command Line
1. Install npm.
(Mac Pro-tip: Use homebrew to avoid obnoxious dependency issues.)
2. Install the Lighthouse node module with npm
install -g lighthouse
3. Run a single text with
lighthouse <url>
4. Run tests on lists of usings by running tests programmatically.
Pros Of Running Lighthouse From Node
- Many reports can be run at once.
- Can be set to run automatically to track change over time.
Cons Of Running Lighthouse From Node
- Requires some coding knowledge.
- More time-intensive setup.
Conclusion
The complexity of performance metrics reflects the challenges facing all sites.
We use performance metrics as a proxy for user experience – that means factoring in some unicorns.
Tools like Google’s Test My Site and What Does My Site Cost? can help you make the conversion and customer-focused arguments for why performance matters.
Hopefully, once your project has traction, these definitions will help you translate Lighthouse’s single performance metric into action tickets for a skilled and collaborative engineering team.
Track your data and shout it from the rooftops.
As much as Google struggles to quantify qualitative experiences, SEO professionals and devs must decode how to translate a concept into code.
Test, iterate, and share what you learn! I look forward to seeing what you’re capable of, you beautiful unicorn.
More resources:
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
SEO
Google Confirms Links Are Not That Important

Google’s Gary Illyes confirmed at a recent search marketing conference that Google needs very few links, adding to the growing body of evidence that publishers need to focus on other factors. Gary tweeted confirmation that he indeed say those words.
Background Of Links For Ranking
Links were discovered in the late 1990’s to be a good signal for search engines to use for validating how authoritative a website is and then Google discovered soon after that anchor text could be used to provide semantic signals about what a webpage was about.
One of the most important research papers was Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment by Jon M. Kleinberg, published around 1998 (link to research paper at the end of the article). The main discovery of this research paper is that there is too many web pages and there was no objective way to filter search results for quality in order to rank web pages for a subjective idea of relevance.
The author of the research paper discovered that links could be used as an objective filter for authoritativeness.
Kleinberg wrote:
“To provide effective search methods under these conditions, one needs a way to filter, from among a huge collection of relevant pages, a small set of the most “authoritative” or ‘definitive’ ones.”
This is the most influential research paper on links because it kick-started more research on ways to use links beyond as an authority metric but as a subjective metric for relevance.
Objective is something factual. Subjective is something that’s closer to an opinion. The founders of Google discovered how to use the subjective opinions of the Internet as a relevance metric for what to rank in the search results.
What Larry Page and Sergey Brin discovered and shared in their research paper (The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine – link at end of this article) was that it was possible to harness the power of anchor text to determine the subjective opinion of relevance from actual humans. It was essentially crowdsourcing the opinions of millions of website expressed through the link structure between each webpage.
What Did Gary Illyes Say About Links In 2024?
At a recent search conference in Bulgaria, Google’s Gary Illyes made a comment about how Google doesn’t really need that many links and how Google has made links less important.
Patrick Stox tweeted about what he heard at the search conference:
” ‘We need very few links to rank pages… Over the years we’ve made links less important.’ @methode #serpconf2024″
Google’s Gary Illyes tweeted a confirmation of that statement:
“I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that”
Why Links Matter Less
The initial state of anchor text when Google first used links for ranking purposes was absolutely non-spammy, which is why it was so useful. Hyperlinks were primarily used as a way to send traffic from one website to another website.
But by 2004 or 2005 Google was using statistical analysis to detect manipulated links, then around 2004 “powered-by” links in website footers stopped passing anchor text value, and by 2006 links close to the words “advertising” stopped passing link value, links from directories stopped passing ranking value and by 2012 Google deployed a massive link algorithm called Penguin that destroyed the rankings of likely millions of websites, many of which were using guest posting.
The link signal eventually became so bad that Google decided in 2019 to selectively use nofollow links for ranking purposes. Google’s Gary Illyes confirmed that the change to nofollow was made because of the link signal.
Google Explicitly Confirms That Links Matter Less
In 2023 Google’s Gary Illyes shared at a PubCon Austin that links were not even in the top 3 of ranking factors. Then in March 2024, coinciding with the March 2024 Core Algorithm Update, Google updated their spam policies documentation to downplay the importance of links for ranking purposes.
The documentation previously said:
“Google uses links as an important factor in determining the relevancy of web pages.”
The update to the documentation that mentioned links was updated to remove the word important.
Links are not just listed as just another factor:
“Google uses links as a factor in determining the relevancy of web pages.”
At the beginning of April Google’s John Mueller advised that there are more useful SEO activities to engage on than links.
Mueller explained:
“There are more important things for websites nowadays, and over-focusing on links will often result in you wasting your time doing things that don’t make your website better overall”
Finally, Gary Illyes explicitly said that Google needs very few links to rank webpages and confirmed it.
I shouldn’t have said that… I definitely shouldn’t have said that
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (so official, trust me) (@methode) April 19, 2024
Why Google Doesn’t Need Links
The reason why Google doesn’t need many links is likely because of the extent of AI and natural language undertanding that Google uses in their algorithms. Google must be highly confident in its algorithm to be able to explicitly say that they don’t need it.
Way back when Google implemented the nofollow into the algorithm there were many link builders who sold comment spam links who continued to lie that comment spam still worked. As someone who started link building at the very beginning of modern SEO (I was the moderator of the link building forum at the #1 SEO forum of that time), I can say with confidence that links have stopped playing much of a role in rankings beginning several years ago, which is why I stopped about five or six years ago.
Read the research papers
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Environment – Jon M. Kleinberg (PDF)
The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine
Featured Image by Shutterstock/RYO Alexandre
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Clarifies Vacation Rental Structured Data
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 16, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoStreamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago97 Marvelous May Content Ideas for Blog Posts, Videos, & More
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login