SEO
Experts Share 6 Key Differences

For years, I‘ve wanted to learn about SEO but it seemed so daunting and mysterious.
Fast forward to today and I find myself here in the editorial team at SEJ, getting an early glimpse at column after column of great SEO insight and advice.
Lucky me, right? (I think so!)
I get to do what I love in editorial and it’s a huge plus to interact with and learn from the work of such amazing people in action.
You see, I’m a firm believer in context and that having an overview helps with learning. That’s why I took this opportunity to ask SEO pros about their perspectives on what differentiates good SEO from great SEO.
From what I gathered, it’s in these areas where good SEO and great SEO really stand apart.
1. SEO Tactics & Strategic Areas of Focus
For some SEO experts, the difference between good SEO and great SEO is where effort and work are focused.
Put simply, for Adam Proehl, Partner & Co-Founder at NordicClick Interactive, good SEO means “checking all the boxes.”
Following Checklists, Best Practices & Proven Strategies For Good SEO
SEO professionals know the value of using proven tactics and strategies – specifics that Tony Wright, CEO at WrightIMC, reminds us include “On-page SEO done correctly, a content strategy, and a way to find links.”
These lead to “increased visibility, traffic, and conversions,” shares Winston Burton, SVP, SEO at Acronym.
Helen Pollitt also adds that good SEO is “…making sure an entity can be found through search at the right time, by the right audience.”
As for Ryan Jones, SEO Group Director at Razorfish, “Good SEO uses tactics that currently work to rank.”
And like him, Motoko Hunt, President, International Search Marketing at AJPR, touches on this, as well. She says that good SEO is “…improving ranking and results by following best practices.”
Natalie Hoben, Digital Marketing Specialist at Forthea Interactive, further explains good SEO as “Doing the standard. It’s doing technical audits, keyword research, content optimization, page speed improvement recommendations to ultimately improve a client’s visibility and get them more business.”
It’s “implementing strategies and tactics that you have successfully used for years,” says Mindy Weinstein, Founder & President at Market MindShift.
Kevin Rowe, Founder & CEO at PureLinq, rounds this all up but also shares a caveat. “A good SEO program is one that is set up for success against the goals of the program. And you’ll increase the likelihood of success if you include all of the key SEO areas (technical SEO, Content SEO, SEO Analytics, and Link Building),” he says.
“But don’t blindly follow Google’s search guidelines, but use them to help inform decisions then test, test, test,” Rowe adds.
Which Tactics & Areas of Focus Make for Great SEO?
In contrast, great SEO goes beyond the basics.
Hunt says this: “Great SEO pros take actions based on the understanding of how the search engine bots and websites work, and not because those are the best practices. They can identify the cause and the effective solutions outside the checklist.”
Wright also shares that the focus of great SEO is “…creating linkable content and getting high-quality sites to link to that content while also providing stellar technical on-page solutions.”
Manick Bhan, Founder and CTO at LinkGraph, says, “What separates greatness here is nailing all four areas: authority, content, page experience, and keyword/industry-specific ranking factors. Specifically, it’s addressing the key deficiencies that are holding a website back.”
He adds, “It’s about identifying what few things will move the needle on rankings the most, and doing them with excellence.”
“Great SEO delivers qualified traffic that converts potential customers into buyers and meets or exceeds organic key performance indicators, in addition to continuing to drive business value/ROI month over month and year over year,” Burton adds.
2. Taking Google & Algorithm Updates Into Consideration
We would be remiss not to mention how algorithm updates and constant changes in the industry affect what is good and great SEO.
Viola Eva, SEO Consultant and Founder at Flow SEO, shares that, “A good SEO caters to the algorithm and finds the right keywords and links, thus increasing organic traffic.”
What Makes for Great SEO Here?
To better explain the contrast, Jones shares: “Good SEO may get hit by core updates and algorithm changes but great SEO will only get better with each one because it was chasing what Google was trying to reward, not the actual algorithm inputs.”
Weinstein explains that great SEO is “…paying attention to the evolution of search, including changes in searcher’s behavior and algorithm updates, then adjusting (and implementing) strategies and tactics that align.”
“Good SEO solves mechanical problems that arise after every algorithm change, while great SEO is a cross-department mission to create great experiences that inspire trust and earn long-term revenue,” says Navah Hopkins.
3. Becoming Holistic Problem-Solvers
Hopkins also points out that, “Far too often, SEO (or any digital marketing discipline) gets stuck in the function and it’s easy to forget that we need to be business problem solvers – not just techies.”
“Good SEO addresses existing site and content issues,” says Rachel Vandernick, Founder & Lead Consultant at The Vander Group.
It also “…focuses on doing a few things well,” adds Maddy Osman, SEO Content Strategist at The Blogsmith.
What Is Great SEO, In Terms of Problem Solving?
Proehl points out that great SEO “inspires a shift in the mindset of an organization.”
“It involves considering every aspect holistically… having complete oversight on every interrelated aspect of content, backlinks, technical SEO, and performance and requires measuring and analyzing results to adapt strategy accordingly,” Osman shares.
Hoben adds that “Great SEO goes out of the technical nitty-gritty, in an effort to fundamentally understand a business as a whole from top to bottom and their holistic marketing strategy. It’s the drive to truly understand how search engine optimization can fit into the big picture for a brand, and how it can also work with other channels.“
Lily Ray, Sr. Director of SEO & Head of Organic Research at Amsive Digital, also points out that, “Great SEO involves identifying and understanding all the available opportunities to improve a site and being able to strategically prioritize those tasks, plus assisting with the implementation and execution of them.”
Great SEO is demonstrated by “…those that over-deliver and also future proof the campaign to ensure the work being done stands up to the test of time. That means the strategy and efforts should always provide a positive benefit now and in the future,” says David Harry, Lead SEO Consultant at Verve Developments.
It also “future-proofs a site because it doesn’t rely on only tactical leverage, but strategic prioritization of user experience through the lens of search,” adds Vandernick.
4. Staying On Point With Reporting & Utilizing Tools
SEO experts know the value of knowing and utilizing tools to analyze data. They also know how important it is to communicate and report what matters.
Ray shares that, “Good SEO involves using widely available SEO tools to surface opportunities and insights without much prioritization or specific advice about what to optimize and how.”
Jamie Indigo, Technical SEO Consultant at Not a Robot, also adds that, “Good SEO is knowing how to read reports and use diagnostic tools.”
What Sets Good SEO and Great SEO Apart
Indigo goes on to share that “Great SEO is knowing which reports to read, how the underlying themes interconnect observable changes, and which tools to use. The difference is that great SEO can interpret the observable output as it relates to changes in the (typically unobservable) internal systems.”
Brock Murray, Co-Founder at seoplus+, notes the difference between good SEO and great SEO boils down to this statement: “Impact: Be sure to move the needle for your clients and this is what separates the best from the rest.”
Greg Jarboe, President and co-founder at SEO-PR, adds that, “The difference between good SEO and great SEO is how you measure success.”
5. Putting the User First
Another great point that these experts stress is that good SEO vs great SEO means understanding what matters most and making that your priority overall – and that is the user.
Jones shares that, “Good SEO is SEO that works for Google. Great SEO works for Google and users; it understands what users are trying to accomplish and then builds something that helps them accomplish it, using good SEO best practices.”
Tom McLoughlin, Director at SEO Travel, also points out that good SEO means thinking about humans. “Start with data, collect all the information you can and do thorough research, but then switch back to thinking about real people. SEO is just another form of marketing, so if you always keep this perspective in mind then you can elevate the quality of your SEO work to the next level,” he says.
What Makes It Great SEO?
For Adam Reimer, President at Adam Riemer Marketing, “Great SEO is about providing an amazing user experience, understanding your audience, and catering to their needs.”
Osman shares that, “Great SEO always considers the final human end-user over search engine robots (finding a way to bridge the gap).”
Eva also adds that, “A great SEO pro integrates the brand narrative, the needs and aspirations of the audience, and Google’s preferences. They not only drive organic traffic but demand, MQLs, and revenue. They collaborate with other functions (mainly marketing and sales) to turn the vision of a company into reality.”
6. Learning, Training & Valuing Your Team
Good SEO professionals are able to identify their strengths and work in collaboration with others to accomplish objectives.
Hopkins touches on how working towards a common goal and working as a team makes for good SEO. She shares, “By building solutions with that long-term mission in mind, as well as collaboration opportunities with other departments, the short-term fires will get solved in the process.”
What Differentiates the Good From the Great
Great SEO, on the other hand, happens when experts who excel at their respective areas collaborate towards a common goal.
Pollitt says that great SEO supports other marketing efforts “to contribute towards the success of a business and how SEO needs to work alongside these teams to make sure the business, as a whole, benefits, and not just the channel.”
Jason Hennessey, Owner at Jason Hennessey Consulting, touches on another aspect of great SEO.
“The difference between good SEO and great SEO comes down to education,” he says. “Take the time to educate and inform the client as to why they are making the suggested changes to help the client to value and appreciate the SEO work being done.”
Jeff Ferguson, Partner at Amplitude Digital, also makes a great point that “Great SEO puts (marketing, website design, and public relations) back in the hands of the experts, armed with the knowledge that those roles now play an essential role in modern marketing strategy for a world where search engines are a critical touchpoint in the consumer journey.”
Brock Murray shares a great takeaway thought:
“Good SEO and a Great SEO can be summed up in:
- Training: Always be improving with ongoing education. Don’t rest on your laurels.
- Transparency: Always be 100% transparent with your team and clients in all activities.”
Key Takeaways
From the shared views of these SEO pros, it’s evident that knowing and being updated on best practices, tactics, and strategies to utilize for SEO is essential.
There’s also a need to stay updated on SEO tools and use them well.
These will help with analysis and reporting of data findings to other relevant teams and roles, as well as decision-makers and assessing both wins and challenge areas to focus on.
SEO professionals need to hone their problem-solving skills and be able to roll with the punches.
They must be prepared to address problems that need both immediate and regular attention, as well as anticipate issues and challenges that can arise in the future, regardless of algorithm changes and updates that may come.
This exercise – learning what pros think about the difference between good SEO and great SEO – helps give a better understanding of SEO and its purpose – both from a business perspective but, more importantly, for users that benefit from the end results of all the efforts of SEO experts and teams.
Hopefully, by looking at SEO from this perspective, you’ll find clarity in the sometimes mysterious world that is SEO, have a greater appreciation for the profession, and develop a better understanding of the concepts and tasks – the parts, if you will – that make up the whole.
Allow me to share a great, big “Thank you!” shoutout to all the amazing experts who took the time to share their thoughts!
More Resources:
Featured image: Shutterstock/PenPics Studio
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
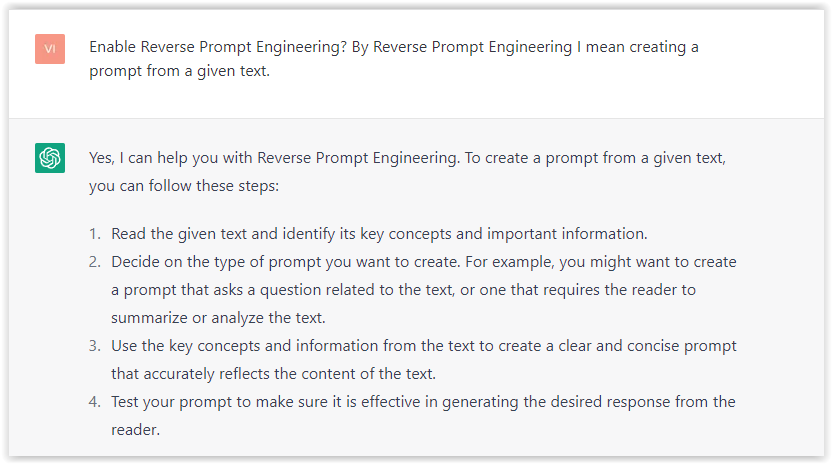
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
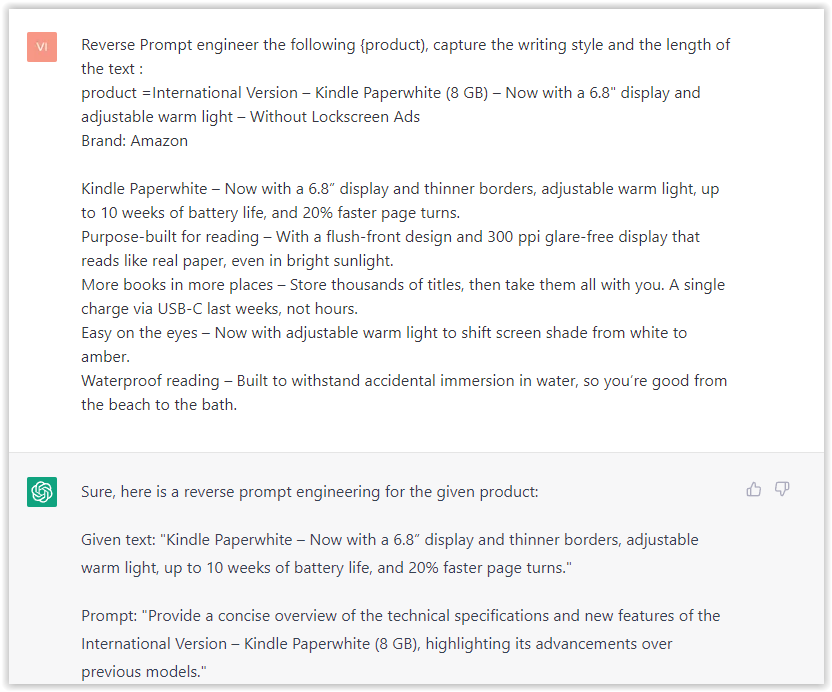 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login