SEO
Ranking Factors & The Myths We Found

Yandex is the search engine with the majority of market share in Russia and the fourth-largest search engine in the world.
On January 27, 2023, it suffered what is arguably one of the largest data leaks that a modern tech company has endured in many years – but is the second leak in less than a decade.
In 2015, a former Yandex employee attempted to sell Yandex’s search engine code on the black market for around $30,000.
The initial leak in January this year revealed 1,922 ranking factors, of which more than 64% were listed as unused or deprecated (superseded and best avoided).
This leak was just the file labeled kernel, but as the SEO community and I delved deeper, more files were found that combined contain approximately 17,800 ranking factors.
When it comes to practicing SEO for Yandex, the guide I wrote two years ago, for the most part, still applies.
Yandex, like Google, has always been public with its algorithm updates and changes, and in recent years, how it has adopted machine learning.
Notable updates from the past two-three years include:
- Vega (which doubled the size of the index).
- Mimicry (penalizing fake websites impersonating brands).
- Y1 update (introducing YATI).
- Y2 update (late 2022).
- Adoption of IndexNow.
- A fresh rollout and assumed update of the PF filter.
On a personal note, this data leak is like a second Christmas.
Since January 2020, I’ve run an SEO news website as a hobby dedicated to covering Yandex SEO and search news in Russia with 600+ articles, so this is probably the peak event of the hobby site.
I’ve also spoken twice at the Optimization conference – the largest SEO conference in Russia.
This is also a good test to see how closely Yandex’s public statements match the codebase secrets.
In 2019, working with Yandex’s PR team, I was able to interview engineers in their Search team and ask a number of questions sourced from the wider Western SEO community.
You can read the interview with the Yandex Search team here.
Whilst Yandex is primarily known for its presence in Russia, the search engine also has a presence in Turkey, Kazakhstan, and Georgia.
The data leak was believed to be politically motivated and the actions of a rogue employee, and contains a number of code fragments from Yandex’s monolithic repository, Arcadia.
Within the 44GB of leaked data, there’s information relating to a number of Yandex products including Search, Maps, Mail, Metrika, Disc, and Cloud.
What Yandex Has Had To Say
As I write this post (January 31st, 2023), Yandex has publicly stated that:
the contents of the archive (leaked code base) correspond to the outdated version of the repository – it differs from the current version used by our services
And:
It is important to note that the published code fragments also contain test algorithms that were used only within Yandex to verify the correct operation of the services.
So, how much of this code base is actively used is questionable.
Yandex has also revealed that during its investigation and audit, it found a number of errors that violate its own internal principles, so it is likely that portions of this leaked code (that are in current use) may be changing in the near future.
Factor Classification
Yandex classifies its ranking factors into three categories.
This has been outlined in Yandex’s public documentation for some time, but I feel is worth including here, as it better helps us understand the ranking factor leak.
- Static factors – Factors that are related directly to the website (e.g. inbound backlinks, inbound internal links, headers, and ads ratio).
- Dynamic factors – Factors that are related to both the website and the search query (e.g. text relevance, keyword inclusions, TF*IDF).
- User search-related factors – Factors relating to the user query (e.g. where is the user located, query language, and intent modifiers).
The ranking factors in the document are tagged to match the corresponding category, with TG_STATIC and TG_DYNAMIC, and then TG_QUERY_ONLY, TG_QUERY, TG_USER_SEARCH, and TG_USER_SEARCH_ONLY.
Yandex Leak Learnings So Far
From the data thus far, below are some of the affirmations and learnings we’ve been able to make.
There is so much data in this leak, it is very likely that we will be finding new things and making new connections in the next few weeks.
These include:
- PageRank (a form of).
- At some point Yandex utilized TF*IDF.
- Yandex still uses meta keywords, which are also highlighted in its documentation.
- Yandex has specific factors for medical, legal, and financial topics (YMYL).
- It also uses a form of page quality scoring, but this is known (ICS score).
- Links from high-authority websites have an impact on rankings.
- There’s nothing new to suggest Yandex can crawl JavaScript yet outside of already publicly documented processes.
- Server errors and excessive 4xx errors can impact ranking.
- The time of day is taken into consideration as a ranking factor.
Below, I’ve expanded on some other affirmations and learnings from the leak.
Where possible, I’ve also tied these leaked ranking factors to the algorithm updates and announcements that relate to them, or where we were told about them being impactful.
MatrixNet
MatrixNet is mentioned in a few of the ranking factors and was announced in 2009, and then superseded in 2017 by Catboost, which was rolled out across the Yandex product sphere.
This further adds validity to comments directly from Yandex, and one of the factor authors DenPlusPlus (Den Raskovalov), that this is, in fact, an outdated code repository.
MatrixNet was originally introduced as a new, core algorithm that took into consideration thousands of ranking factors and assigned weights based on the user location, the actual search query, and perceived search intent.
It is typically seen as an early version of Google’s RankBrain, when they are indeed two very different systems. MatrixNet was launched six years before RankBrain was announced.
MatrixNet has also been built upon, which isn’t surprising, given it is now 14 years old.
In 2016, Yandex introduced the Palekh algorithm that used deep neural networks to better match documents (webpages) and queries, even if they didn’t contain the right “levels” of common keywords, but satisfied the user intents.
Palekh was capable of processing 150 pages at a time, and in 2017 was updated with the Korolyov update, which took into account more depth of page content, and could work off 200,000 pages at once.
URL & Page-Level Factors
From the leak, we have learned that Yandex takes into consideration URL construction, specifically:
- The presence of numbers in the URL.
- The number of trailing slashes in the URL (and if they are excessive).
- The number of capital letters in the URL is a factor.
The age of a page (document age) and the last updated date are also important, and this makes sense.
As well as document age and last update, a number of factors in the data relate to freshness – particularly for news-related queries.
Yandex formerly used timestamps, specifically not for ranking purposes but “reordering” purposes, but this is now classified as unused.
Also in the deprecated column are the use of keywords in the URL. Yandex has previously measured that three keywords from the search query in the URL would be an “optimal” result.
Internal Links & Crawl Depth
Whilst Google has gone on the record to say that for its purposes, crawl depth isn’t explicitly a ranking factor, Yandex appears to have an active piece of code that dictates that URLs that are reachable from the homepage have a “higher” level of importance.
 Screenshot from author, January 2023
Screenshot from author, January 2023This mirrors John Mueller’s 2018 statement that Google gives “a little more weight” to pages found more than one click from the homepage.
The ranking factors also highlight a specific token weighting for webpages that are “orphans” within the website linking structure.
Clicks & CTR
In 2011, Yandex released a blog post talking about how the search engine uses clicks as part of its rankings and also addresses the desires of the SEO pros to manipulate the metric for ranking gain.
Specific click factors in the leak look at things like:
- The ratio of the number of clicks on the URL, relative to all clicks on the search.
- The same as above, but broken down by region.
- How often do users click on the URL for the search?
Manipulating Clicks
Manipulating user behavior, specifically “click-jacking”, is a known tactic within Yandex.
Yandex has a filter, known as the PF filter, that actively seeks out and penalizes websites that engage in this activity using scripts that monitor IP similarities and then the “user actions” of those clicks – and the impact can be significant.
The below screenshot shows the impact on organic sessions (сессии) after being penalized for imitating user clicks.
-
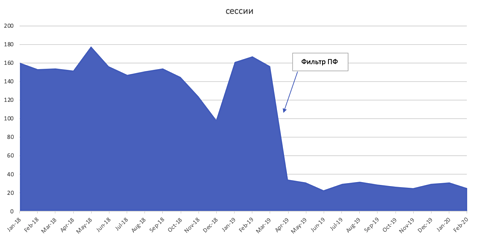 Image from Russian Search News, January 2023
Image from Russian Search News, January 2023
User Behavior
The user behavior takeaways from the leak are some of the more interesting findings.
User behavior manipulation is a common SEO violation that Yandex has been combating for years. At the 2020 Optimization conference, then Head of Yandex Webmaster Tools Mikhail Slevinsky said the company is making good progress in detecting and penalizing this type of behavior.
Yandex penalizes user behavior manipulation with the same PF filter used to combat CTR manipulation.
Dwell Time
102 of the ranking factors contain the tag TG_USERFEAT_SEARCH_DWELL_TIME, and reference the device, user duration, and average page dwell time.
All but 39 of these factors are deprecated.
 Screenshot from author, January 2023
Screenshot from author, January 2023Bing first used the term Dwell time in a 2011 blog, and in recent years Google has made it clear that it doesn’t use dwell time (or similar user interaction signals) as ranking factors.
YMYL
YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) is a concept well-known within Google and is not a new concept to Yandex.
Within the data leak, there are specific ranking factors for medical, legal, and financial content that exist – but this was notably revealed in 2019 at the Yandex Webmaster conference when it announced the Proxima Search Quality Metric.
Metrika Data Usage
Six of the ranking factors relate to the usage of Metrika data for the purposes of ranking. However, one of them is tagged as deprecated:
- The number of similar visitors from the YandexBar (YaBar/Ябар).
- The average time spent on URLs from those same similar visitors.
- The “core audience” of pages on which there is a Metrika counter [deprecated].
- The average time a user spends on a host when accessed externally (from another non-search site) from a specific URL.
- Average ‘depth’ (number of hits within the host) of a user’s stay on the host when accessed externally (from another non-search site) from a particular URL.
- Whether or not the domain has Metrika installed.
In Metrika, user data is handled differently.
Unlike Google Analytics, there are a number of reports focused on user “loyalty” combining site engagement metrics with return frequency, duration between visits, and source of the visit.
For example, I can see a report in one click to see a breakdown of individual site visitors:
 Screenshot from Metrika, January 2023
Screenshot from Metrika, January 2023Metrika also comes “out of the box” with heatmap tools and user session recording, and in recent years the Metrika team has made good progress in being able to identify and filter bot traffic.
With Google Analytics, there is an argument that Google doesn’t use UA/GA4 data for ranking purposes because of how easy it is to modify or break the tracking code – but with Metrika counters, they are a lot more linear, and a lot of the reports are unchangeable in terms of how the data is collected.
Impact Of Traffic On Rankings
Following on from looking at Metrika data as a ranking factor; These factors effectively confirm that direct traffic and paid traffic (buying ads via Yandex Direct) can impact organic search performance:
- Share of direct visits among all incoming traffic.
- Green traffic share (aka direct visits) – Desktop.
- Green traffic share (aka direct visits) – Mobile.
- Search traffic – transitions from search engines to the site.
- Share of visits to the site not by links (set by hand or from bookmarks).
- The number of unique visitors.
- Share of traffic from search engines.
News Factors
There are a number of factors relating to “News”, including two that mention Yandex.News directly.
Yandex.News was an equivalent of Google News, but was sold to the Russian social network VKontakte in August 2022, along with another Yandex product “Zen”.
So, it’s not clear if these factors related to a product no longer owned or operated by Yandex, or to how news websites are ranked in “regular” search.
Backlink Importance
Yandex has similar algorithms to combat link manipulation as Google – and has since the Nepot filter in 2005.
From reviewing the backlink ranking factors and some of the specifics in the descriptions, we can assume that the best practices for building links for Yandex SEO would be to:
- Build links with a more natural frequency and varying amounts.
- Build links with branded anchor texts as well as use commercial keywords.
- If buying links, avoid buying links from websites that have mixed topics.
Below is a list of link-related factors that can be considered affirmations of best practices:
- The age of the backlink is a factor.
- Link relevance based on topics.
- Backlinks built from homepages carry more weight than internal pages.
- Links from the top 100 websites by PageRank (PR) can impact rankings.
- Link relevance based on the quality of each link.
- Link relevance, taking into account the quality of each link, and the topic of each link.
- Link relevance, taking into account the non-commercial nature of each link.
- Percentage of inbound links with query words.
- Percentage of query words in links (up to a synonym).
- The links contain all the words of the query (up to a synonym).
- Dispersion of the number of query words in links.
However, there are some link-related factors that are additional considerations when planning, monitoring, and analyzing backlinks:
- The ratio of “good” versus “bad” backlinks to a website.
- The frequency of links to the site.
- The number of incoming SEO trash links between hosts.
The data leak also revealed that the link spam calculator has around 80 active factors that are taken into consideration, with a number of deprecated factors.
This creates the question as to how well Yandex is able to recognize negative SEO attacks, given it looks at the ratio of good versus bad links, and how it determines what a bad link is.
A negative SEO attack is also likely to be a short burst (high frequency) link event in which a site will unwittingly gain a high number of poor quality, non-topical, and potentially over-optimized links.
Yandex uses machine learning models to identify Private Blog Networks (PBNs) and paid links, and it makes the same assumption between link velocity and the time period they are acquired.
Typically, paid-for links are generated over a longer period of time, and these patterns (including link origin site analysis) are what the Minusinsk update (2015) was introduced to combat.
Yandex Penalties
There are two ranking factors, both deprecated, named SpamKarma and Pessimization.
Pessimization refers to reducing PageRank to zero and aligns with the expectations of severe Yandex penalties.
SpamKarma also aligns with assumptions made around Yandex penalizing hosts and individuals, as well as individual domains.
Onpage Advertising
There are a number of factors relating to advertising on the page, some of them deprecated (like the screenshot example below).
 Screenshot from author, January 2023
Screenshot from author, January 2023It’s not known from the description exactly what the thought process with this factor was, but it could be assumed that a high ratio of adverts to visible screen was a negative factor – much like how Google takes umbrage if adverts obfuscate the page’s main content, or are obtrusive.
Tying this back to known Yandex mechanisms, the Proxima update also took into consideration the ratio of useful and advertising content on a page.
Can We Apply Any Yandex Learnings To Google?
Yandex and Google are disparate search engines, with a number of differences, despite the tens of engineers who have worked for both companies.
Because of this fight for talent, we can infer that some of these master builders and engineers will have built things in a similar fashion (though not direct copies), and applied learnings from previous iterations of their builds with their new employers.
What Russian SEO Pros Are Saying About The Leak
Much like the Western world, SEO professionals in Russia have been having their say on the leak across the various Runet forums.
The reaction in these forums has been different to SEO Twitter and Mastodon, with a focus more on Yandex’s filters, and other Yandex products that are optimized as part of wider Yandex optimization campaigns.
It is also worth noting that a number of conclusions and findings from the data match what the Western SEO world is also finding.
Common themes in the Russian search forums:
- Webmasters asking for insights into recent filters, such as Mimicry and the updated PF filter.
- The age and relevance of some of the factors, due to author names no longer being at Yandex, and mentions of long-retired Yandex products.
- The main interesting learnings are around the use of Metrika data, and information relating to the Crawler & Indexer.
- A number of factors outline the usage of DSSM, which in theory was superseded by the release of Palekh in 2016. This was a search algorithm utilizing machine learning, announced by Yandex in 2016.
- A debate around ICS scoring in Yandex, and whether or not Yandex may provide more traffic to a site and influence its own factors by doing so.
The leaked factors, particularly around how Yandex evaluates site quality, have also come under scrutiny.
There is a long-standing sentiment in the Russian SEO community that Yandex oftentimes favors its own products and services in search results ahead of other websites, and webmasters are asking questions like:
Why does it bother going to all this trouble, when it just nails its services to the top of the page anyway?
In loosely translated documents, these are referred to as the Sorcerers or Yandex Sorcerers. In Google, we’d call these search engine results pages (SERPs) features – like Google Hotels, etc.
In October 2022, Kassir (a Russian ticket portal) claimed ₽328m compensation from Yandex due to lost revenue, caused by the “discriminatory conditions” in which Yandex Sorcerers took the customer base away from the private company.
This is off the back of a 2020 class action in which multiple companies raised a case with the Federal Antimonopoly Service (FAS) for anticompetitive promotion of its own services.
More resources:
Featured Image: FGC/Shutterstock
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
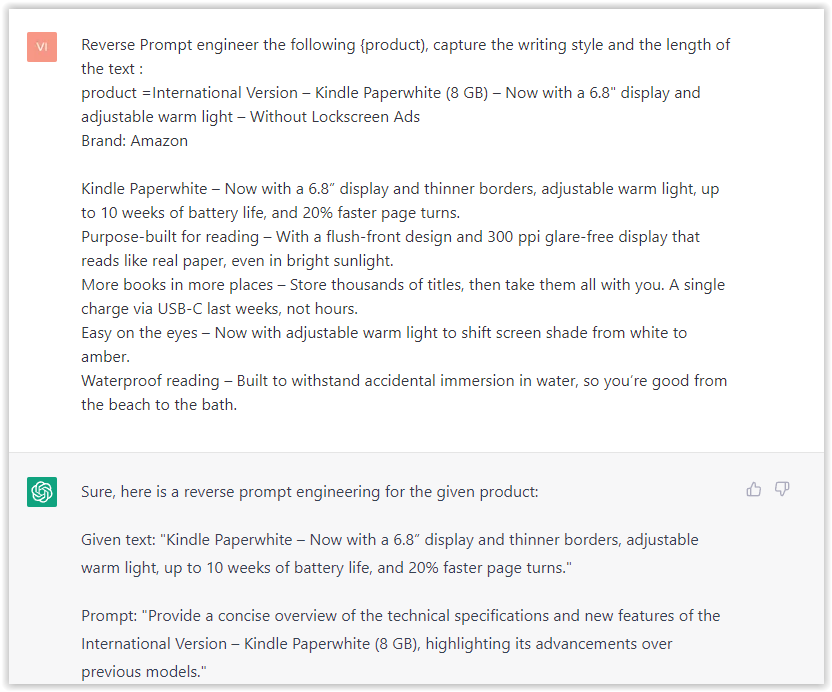 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoStreamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days ago97 Marvelous May Content Ideas for Blog Posts, Videos, & More
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024















You must be logged in to post a comment Login