A brand new course to help you successfully launch your newsletter. No registration required and it doesn’t cost a thing.
HOWTO'S
How to Prevent A/B Testing from Slowing Down Your Site

You’ve probably used tools like Google Optimize for A/B testing to increase conversion rates on your site.
These tools allow you to test content by showing different variations of the same page to visitors at random.
A/B testing helps prevent websites from spending time and resources on developing features that turn out to be unpopular with their users.
Sometimes, however, A/B testing can lead to a slower user experience if the page takes too long to load.
This often happens if the content is being tested too often or if the code is used in a way that slows down the site.
If your content takes too long to load, users may navigate off your site, increasing bounce rates and lowering your chance to convert them.
In this blog, we’ll cover how to prevent A/B testing from slowing down your site, using tactics such as:
- making sure that the scripts are implemented directly into the top of the head tag, not using a tag manager
- implementing the asynchronous GTM version of Google Optimize
- using animations can be used to prevent test experiences from loading too slowly and being too disruptive to user experience
Let’s get started.
How Can A/B Testing Slow Down Your Site?
A/B testing can cause an extra step in loading and displaying web pages.
This happens because two versions of content are being shown to users at random times, collecting data on which page performs better.
All of this back and forth communication can result in a lag in page load time.
It can also cause a flicker of original content (FOOC) that displays for a short moment before the page finishes loading.
A/B testing slows down your site in three ways:
- making the loading time of your site slower than normal
- creating a poor user experience that causes users to leave or prevent them from visiting again later on
- delaying any other events, such as an email campaign, because it’s taking longer for pages to load and finish rendering
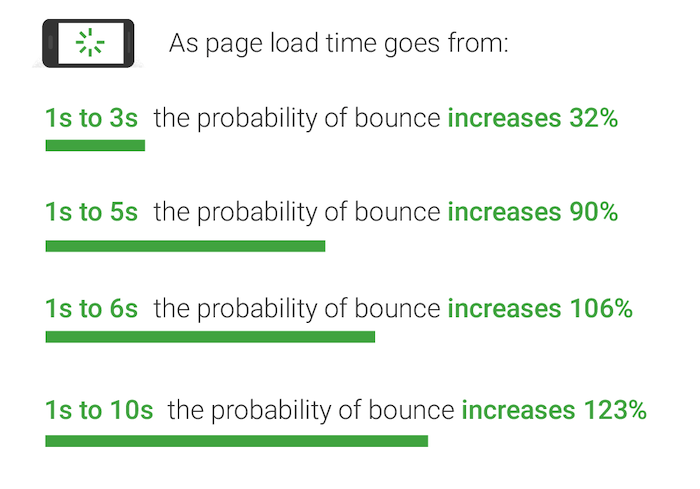
Page load time is an important metric for your conversions and SEO.
Research has shown the first five seconds of page load time has the biggest impact on conversion rates.
Similarly, 70 percent of consumers say page speed influences their desire to buy.
Ultimately, if you want users to stay on your site and purchase your products, you need to make sure your site is fast.
How to Prevent A/B Testing from Slowing Down Your Site
To prevent A/B testing from slowing down your site, it’s important to take extra steps to ensure your user experience is not impacted by these tests.
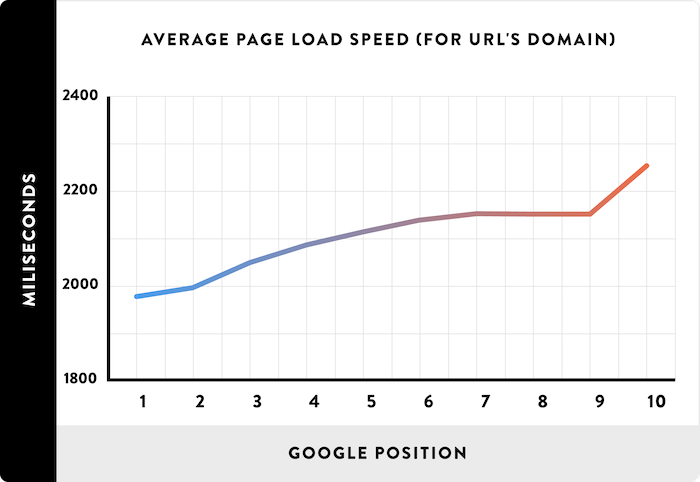
According to Backlinko, the average page load benchmark is 10.3 seconds on desktop and 27.3 seconds on mobile.
If you’re not hitting these markers, you may have a problem.
Whether you’re using Google Optimize or another A/B testing tool, there are a few ways to prevent your site from slowing down.
1. Implement Scripts in the Top of the Head Tag
When you add A/B testing scripts to your site, make sure they are at the top of your head tag and not a tag manager.
This is important because if you make changes to your site, the scripts will be overwritten.
A tag manager is an external script that loads in place of others which can overwrite them without warning and prevent scripts from functioning properly when you make changes to your website.
If you are using the synchronous version of the script, then make sure it is placed after your site’s scripts.
This will prevent any problems with delays caused by third-party resources on your page, such as ad networks.
2. Use Asynchronous Tracking
Google Optimize has two versions: synchronous and asynchronous.
The synchronous versions prevent any content from rendering until it has been fully loaded. This can prevent your A/B tests from loading in a reasonable time.
The asynchronous versions prevent any content from rendering until it is ready, but this does not prevent the other scripts on the page from being executed immediately.
The asynchronous version is recommended for most users. It loads in a separate thread from the rest of the website, so it does not prevent other critical tasks from being executed prior to its execution.
The async version will prevent certain animations from slowing down your test experiences while still allowing for other elements on the page to play.
If you use a tag manager like Google Tag Manager (GTM), or another JavaScript management system, it’s important these are implemented asynchronously and not using the standard version of the Optimize snippet.
There should be no delays in page load time when Google Optimize is running on your website. The async version can prevent this by adding asynchronous to each script call so they don’t block rendering.
This is particularly important if you don’t run any tests or if they are played in a non-interruptive manner across all pages.
3. Incorporate Animations to Improve UX
If you are using Google Optimize, then you can also use animations to prevent test experiences that may load slowly and be too disruptive to the user experience.
Animations can be used to prevent A/B testing from slowing down your site by giving users something fun to focus on while they wait for content delivery.
For example, you can use animations to keep users engaged before a site fully loads, like this.
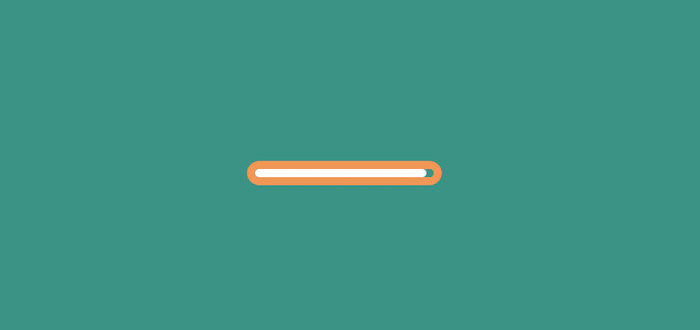
This will tell users their content is being loaded and prevent them from leaving the page.
Remember to always center your animations in a place where your user will be focused.
A loading page is a good example of this or a page where the user will be focused on a specific part of the design.
Remember to prevent animations from interrupting other tests and make sure they are implemented correctly across all pages.
4. Reduce the Size of the Snippet
When adding a snippet to your site, try to keep it as small as possible.
This will prevent the script from slowing down other parts of your site, and prevent other scripts on your page from being delayed or interrupted.
You can do this by using a tag manager, such as Google Tag Manager (GTM).
GTM will allow you to shorten the snippet or include the snippet only on specific pages.
Keep in mind that using a tag manager is not necessary for Google Optimize if you just want to add it once across all of your page’s head tags.
If you prefer to embed the script into each page directly then make sure they are implemented at the top of the head tag.
5. Test on the Server-Side
When conducting A/B tests on different server sides, the delay is often much less noticeable.
For example, you might be using PHP instead of JavaScript on your client-side to prevent content from loading slowly and interrupting users who are trying out their new site design.
Using different server sides works because the async version will prevent browsers from blocking on a callback function, which would prevent all other content from loading while it’s waiting for code to finish running.
The benefit of doing this is the server-side tests prevent users with slow connections or high latency from seeing delays when loading content.
If you can’t do this, it’s recommended to use Google Tag Manager to load these scripts asynchronously so they run after page rendering is complete and don’t affect performance.
Also keep in mind that when testing on different server sides, it might be more difficult to prevent a slower loading experience from interrupting users since there is no way of calling asynchronous JavaScript into service.
6. Consolidate and Optimize Variation Code
Consolidating and optimizing variation codes can help prevent A/B testing from slowing down your site.
Variation codes are the code that is used by Optimize for each variation.
The more complicated your website, the more variations you need to create and the more often these tests run — which results in slower site speed.
If too many changes are applied at once on a page it can prevent other scripts from running properly or even prevent the page from loading at all.
This is detrimental to your user experience and can prevent testing from allowing you to continue optimizing your website.
For example, if a user has JavaScript turned off or does not have it enabled they will never reach the variation that contains optimized content for them and this can set back optimizations by several weeks!
This is why it’s so important to consolidate all of your Optimize codes and scripts directly into the head tag of your site.
7. Keep All Data in a Single File
Your website is full of data and assets that need to load before the page is shown to a user.
When you run an A/B test these assets and data need to be shared between the two experiences, but can also cause a lot of issues if they aren’t carefully managed.
For example, say your old site used Font Awesome for all its icons and your new website uses Google Fonts as it is more web-friendly. If your site is running an A/B test, your old site will need to use the same Google Fonts as your new one.
If you don’t manage this correctly it can cause a considerable delay in how fast the page loads for users because of all these extra assets that are loaded on top of each other.
To prevent A/B testing from slowing down your site, keep all data in a single file. This means you prevent the page from having to make multiple requests for information.
All experiments should be stored in a single place that is easily accessible by everyone on your team. This can prevent a lot of issues from occurring, as well as making it much easier to track the progress and performance of each test you are running.
Frequently Asked Questions About Preventing A/B Testing from Slowing Down Your Site
Does Google Optimize slow down your site?
Google Optimize does not have a big effect on page load times. What’s more important is the time it takes your page to load, latency, and visitor connection speeds.
What should you do after an A/B test?
After you complete your A/B testing you should measure your results and take action based on your findings. It’s also recommended to strategize a new A/B test so you can continue learning.
How do I increase my Google page speed?
Page speed comes down to many factors, but optimizing your A/B tests can help prevent testing from slowing down your site.
When should you not use an A/B test?
If you lack meaningful traffic, don’t have the time or resources to dedicate to testing, don’t have a hypothesis to test, or don’t need more traffic, you should not use an A/B test.
How to Prevent A/B Testing from Slowing Down Your Site: Conclusion
A/B testing can be a great tool for driving conversions and it’s something every website owner should take advantage of.
Understanding how to prevent A/B tests from slowingdown your site, however, is equally important because slow test experiences are disruptive to the user experience.
Sites that use A/B testing effectively will see both an increase in traffic and greater audience insights.
How have you used A/B testing to improve site performance?
See How My Agency Can Drive Massive Amounts of Traffic to Your Website
- SEO – unlock massive amounts of SEO traffic. See real results.
- Content Marketing – our team creates epic content that will get shared, get links, and attract traffic.
- Paid Media – effective paid strategies with clear ROI.
AFFILIATE MARKETING
How to Add Affiliate Disclosure for Each Blog Post Automatically

Do you want to add an affiliate disclosure for each blog post automatically?
Affiliate marketing is one of the easiest ways to make money online. However, if you don’t disclose your affiliate links then you could end up in legal trouble.
In this article, we will show you how you can add an affiliate disclosure to all your WordPress blog posts.
Why Add an Affiliate Disclosure to Each WordPress Blog Post?
With affiliate marketing, you earn a commission every time someone clicks a referral link and makes a purchase. It’s a great way to make money online blogging with WordPress.
However, you must make it clear that your links are paid advertisements by adding an affiliate disclaimer. That just means posting a short notice explaining what affiliate marketing is, and that you get money from talking about the product or service.
Many countries have laws about failing to disclose paid endorsements. For example in the United States, you might get a fine from the Federal Trade Commission. You may even end up banned from reputable networks such as Amazon affiliates.
Even if you don’t get into legal trouble, customers who click on undisclosed affiliate links may feel tricked and stop visiting your WordPress website.
How to Add an Affiliate Disclosure to Each WordPress Blog Post
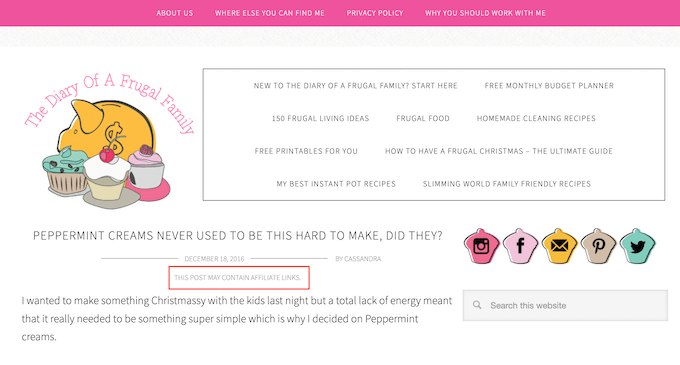
One option is to publish the affiliate disclaimer on its own page, as we do on WPBeginner.
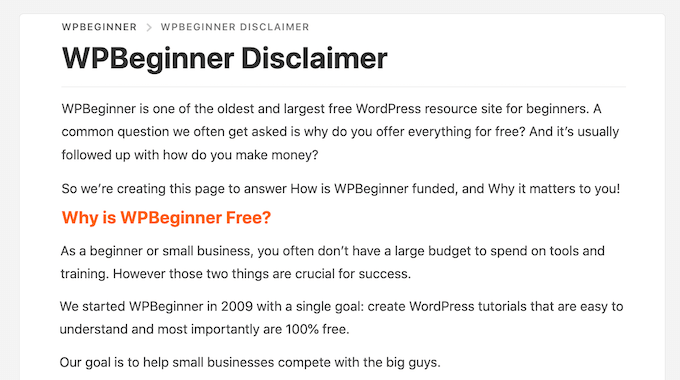
You can then add a link to every page that features an affiliate URL. This may be a good choice if you have a longer disclosure and don’t want to distract from the post’s content.
If yours is short, then you can often add the full text of the disclaimer to every post.
No matter which option you choose, you can save time and effort by adding the affiliate disclosure automatically. Simply use the quick links below to jump straight to the method you want to use.
Method 1. Add Affiliate Disclosure Using Pretty Links
Pretty Links is one of the best affiliate marketing plugins that can automate all your affiliate activities, including adding a disclosure.
Pretty Links comes with an advanced auto-linking feature that allows you to enter the keywords or phrases that you want to turn into affiliate URLs.
Every time you type this word or phrase, Pretty Links will turn it into an affiliate URL automatically. Even better, if you have created a disclosure notice page, Pretty Links can also add a link to it in the post.
For example, if you add “MacBook Pro” as a keyword and then use that phrase in a new post, then Pretty Links will automatically turn “MacBook Pro” into an affiliate URL and add a link to your disclosure notice page.
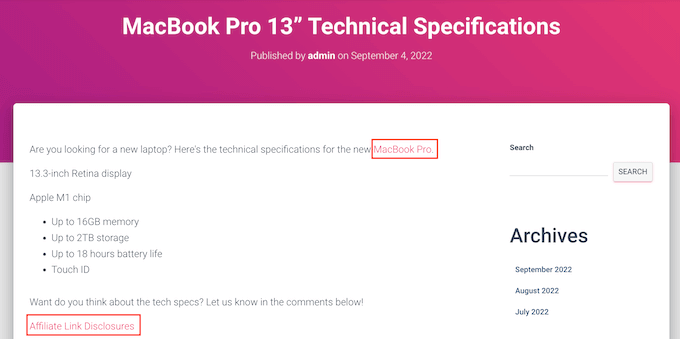
Note: Pretty Links won’t insert the disclosure link if you only add affiliate URLs manually. It only works when a post uses automatic keyword linking.
To get started, you’ll need to install and activate Pretty Links. If you need help, then please see our guide on how to install a WordPress plugin.
Upon activation, go to Pretty Links » Activate. You can then add your license key to the following field: ‘Enter Your Pretty Links Pro License Key.’
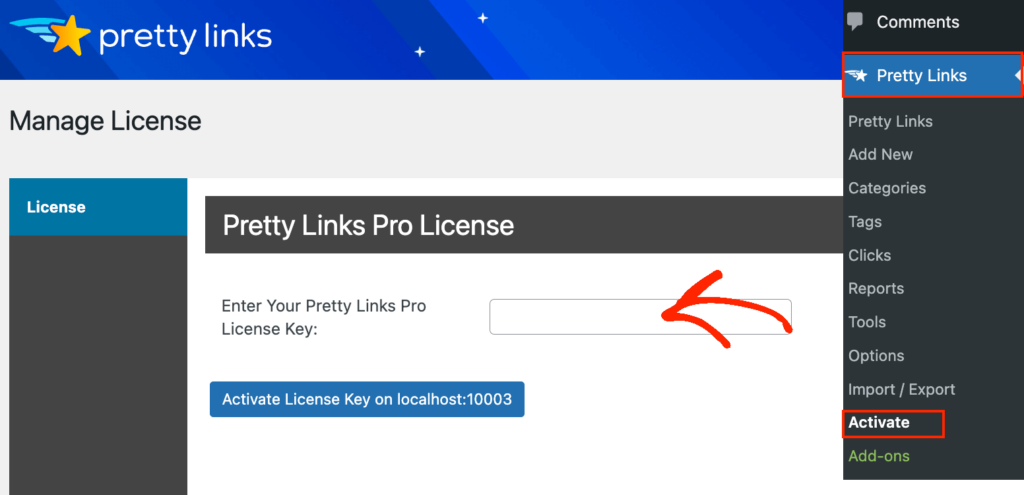
You can find this information under your account on the Pretty Links website. After typing in this information, click on the ‘Activate’ button.
With that done, you’ll need to go to Pretty Links » Add New and then add the first link you want to manage using the Pretty Links plugin.
For detailed step-by-step instructions, please see our guide on how to cloak affiliate links on your WordPress site.
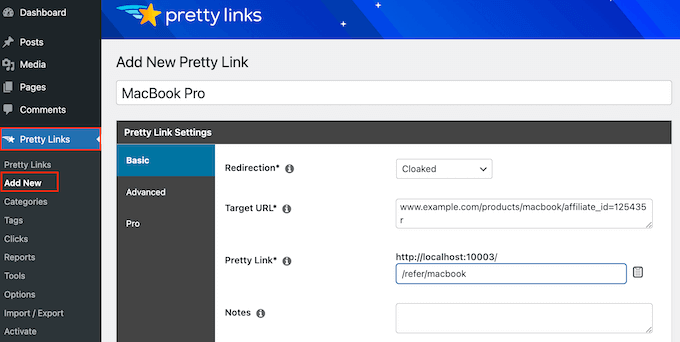
After that, click on the ‘Pro’ tab. In the ‘Keywords’ field, type in each word or phrase where you want to automatically insert this affiliate URL.
Simply repeat this process for all your affiliate links.
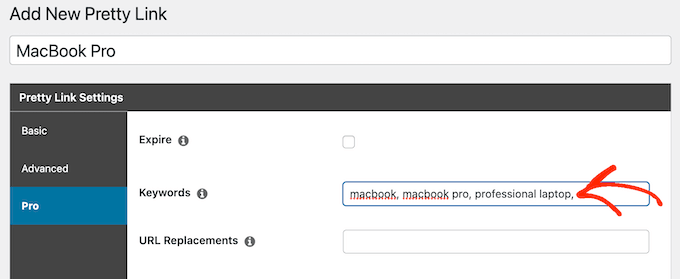
Every time it adds this affiliate URL, Pretty Links will also add a link to your disclosure notice.
The next step is creating the disclosure notice page that Pretty Links will link to. Simply go to Pages » Add New. You can then type in your affiliate disclaimer and add any categories or tags that you want to use.
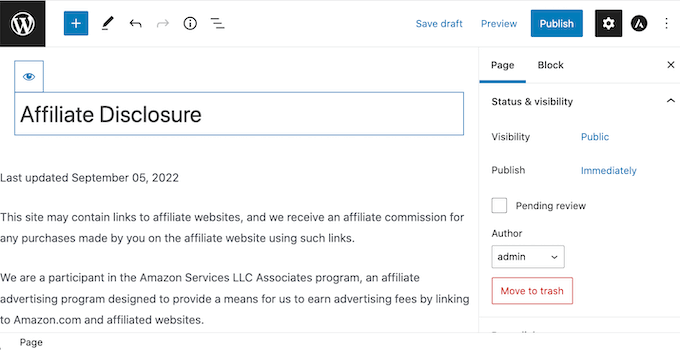
When you’re happy with your disclaimer, publish the page to make it live. It’s a good idea to make a note of the page’s URL, as you’ll need it in the next step.
Once you’ve done that, simply go to Pretty Links » Options. Then, click on the ‘Replacements’ tab.
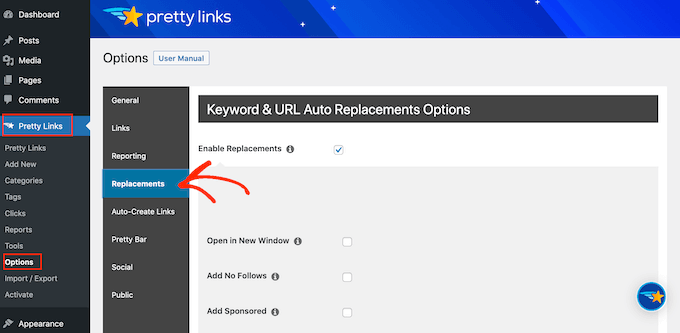
Here, check the ‘Enable Replacements’ box if it isn’t already selected.
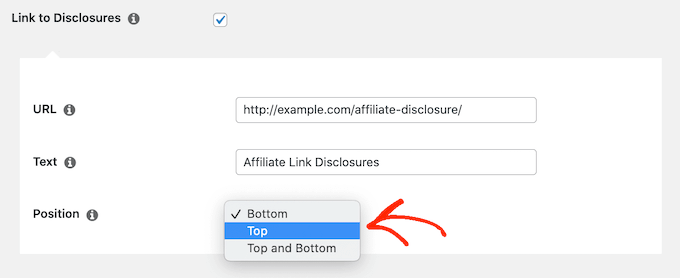
After that, check the ‘Link to Disclosures’ box. In the ‘URL’ box, go ahead and enter your affiliate disclosure URL.
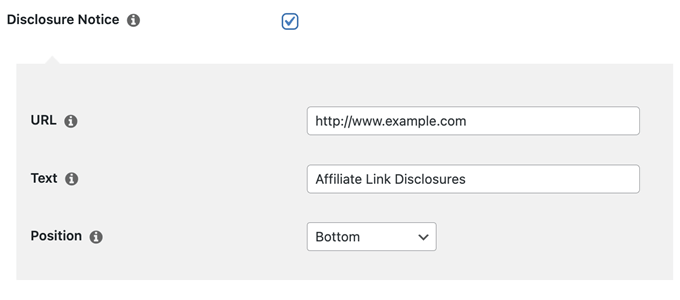
By default, Pretty Links will use ‘Affiliate Link Disclosures’ as your link’s text. However, you can change this to anything you want by typing into the ‘Text’ field.
You can also change where Pretty Links adds the affiliate disclaimer link. By default, it shows the URL at the bottom of the post, so it doesn’t distract visitors from the post’s content.
Another option is to add the disclaimer to the top of the post. This is where we include it on WPBeginner.
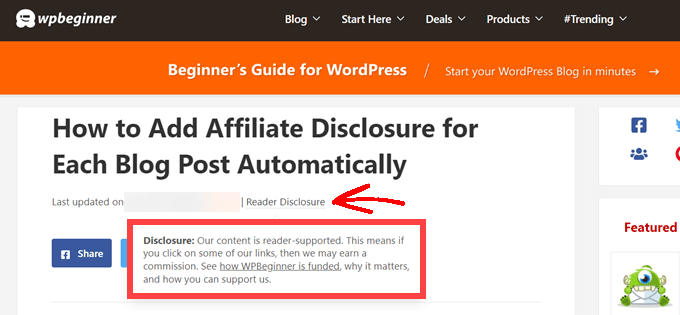
This lets visitors know the post contains an affiliate link before they start reading, which is a good way to build trust with your audience. However, some people may see the disclaimer and decide not to stay on the page, which can increase your bounce rate.
You can also add the disclaimer to both the top and bottom of each post. This may be a good idea if you write very long posts, but most sites don’t need multiple disclosures per page.
To place the affiliate URL, simply open the ‘Position’ dropdown and choose Bottom, Top, or Top and Bottom.
Once you’ve done that, just scroll to the bottom of the page.
Then, click on the ‘Update’ button.

Now, Pretty Links will add an affiliate disclosure link every time it auto-inserts an affiliate URL to your posts, pages, or custom post types.
Method 2. Add Affiliate Disclosure Using WPCode (More Customizable)
Sometimes you may want to add the affiliate disclosure to different areas of every blog post. For example, you might show the disclosure after you mention each affiliate product for the first time.
In this case, you can create a shortcode that adds your affiliate disclaimer. This gives you complete control over where the disclosure appears, without you having to type the entire text every single time.
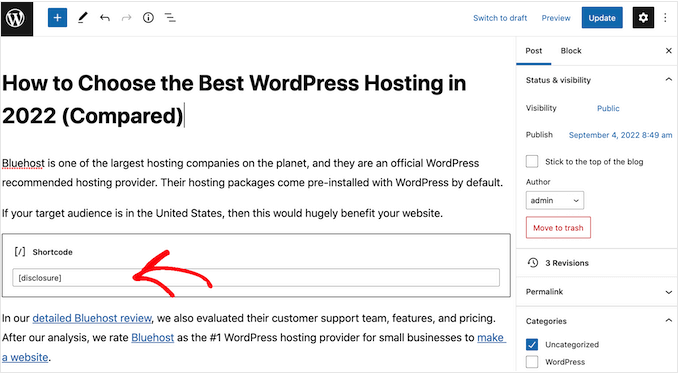
The easiest way to create a custom shortcode is using WPCode. This plugin lets you add code snippets to WordPress without editing your theme’s functions.php file.
WPCode also helps you avoid common errors by performing smart code snippet validation.
There are lots of ways to add an affiliate disclosure using WPCode. Besides the shortcode method, we’ll also share an easy way to automatically add the disclaimer to every post, page, or custom post type.
The first thing you need to do is install and activate the free WPCode plugin on your website. For more details, see our step-by-step guide on how to install a WordPress plugin.
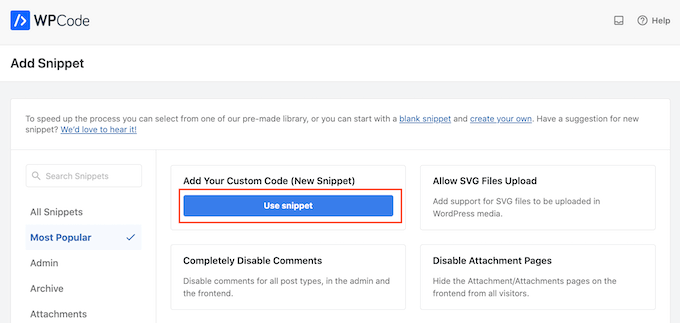
Upon activation, go to Code Snippets » Add Snippet.
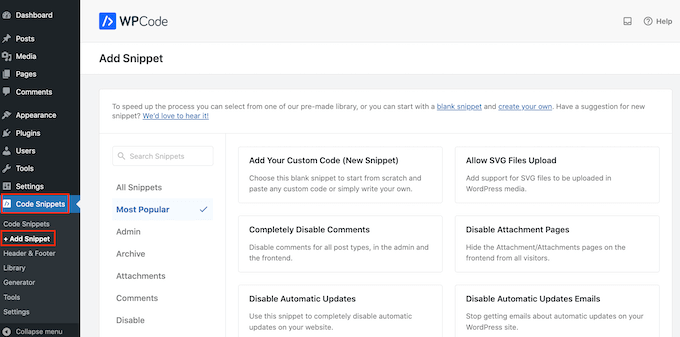
This will bring you to the ‘Add Snippet’ page where you can see all the ready-made snippets that you can use on your site.
Since we want to add custom code in WordPress, hover your mouse over ‘Add Your Custom Code (New Snippet).’ Then, click on ‘Use snippet’ when it appears.
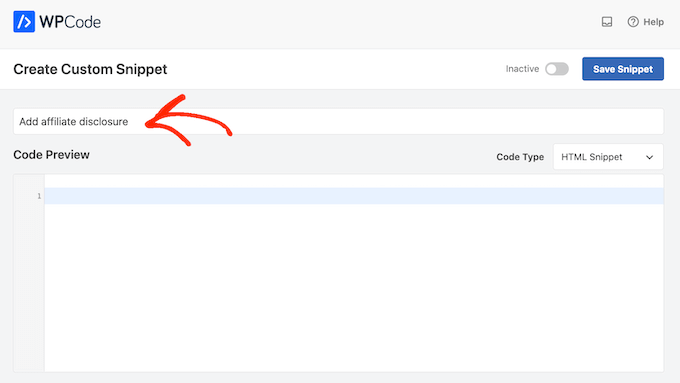
To start, enter a title for the custom code snippet.
This could be anything that helps you identify the snippet in the WordPress admin area.
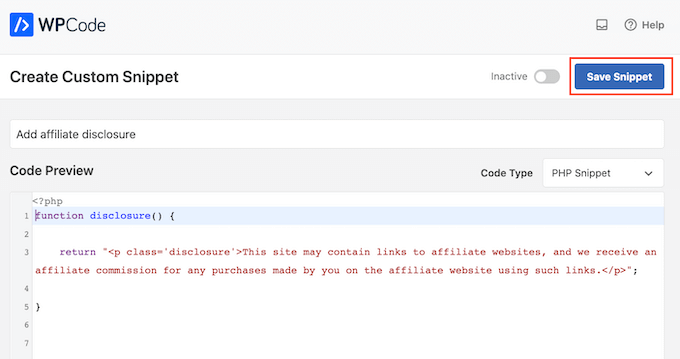
We’re going to add a PHP snippet, so open the ‘Code Type’ dropdown and choose the ‘PHP Snippet’ option.
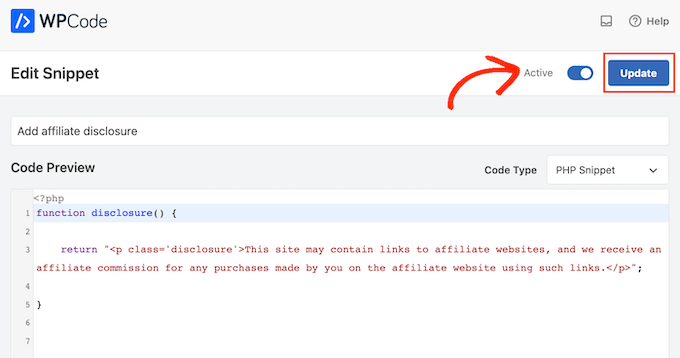
You can then go ahead and paste the following code into the code box:
function disclosure() {
return "<p class="disclosure">This site may contain links to affiliate websites, and we receive an affiliate commission for any purchases made by you on the affiliate website using such links.</p>";
}
add_shortcode( 'disclosure', 'disclosure' );
You can use any text as your affiliate disclaimer, simply by editing the code above. For example, you might want to add a link in HTML to your affiliate disclosure page.
Once you’ve done that, scroll to the ‘Insertion’ section and make sure ‘Auto Insert’ is selected.
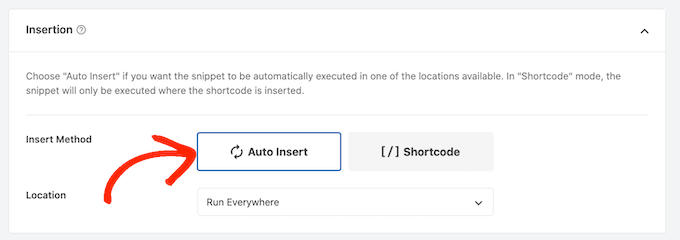
Then, open the ‘Location’ dropdown and choose ‘Frontend Only’ since we only want to use this code on our site’s frontend, which is what visitors see when they visit your site.
You can also organize your snippets by adding tags.
When you’re happy with how the snippet is set up, scroll to the top of the screen and click on ‘Save Snippet.’
After that, you can make the code snippet live by clicking the ‘Active’ toggle.
Finally, don’t forget to save the change by clicking on ‘Update.’
Now you can add the affiliate disclosure to any page, post, or custom post type using the [disclosure] shortcode. For more details on how to place the shortcode, you can see our guide on how to add a shortcode in WordPress.
How to Automatically Display the Affiliate Disclosure with WPCode
With WPCode, there are lots of different ways to add an affiliate disclosure to your WordPress website, including automatically adding it to every post.
This can save you a lot of time and effort, since you don’t need to add the shortcode manually. However, the disclosure will appear in the same location on every page.
To automatically add the disclaimer, simply create a new custom code snippet by following the same process described above. However, this time open the ‘Code Type’ dropdown and select ‘HTML Snippet.’
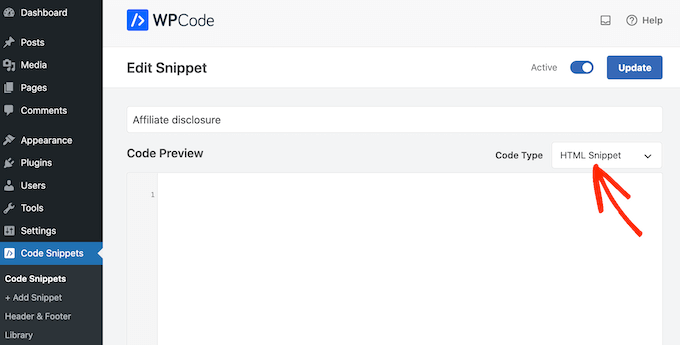
You can now add your disclaimer in the code editor, complete with the formatting that you want to use. For example, here we’re adding a simple disclaimer as a new paragraph:
<p>This site may contain links to affiliate websites, and we receive an affiliate commission for any purchases made by you on the affiliate website using such links.</p>
Next, scroll to the ‘Insertion’ section and open the ‘Location’ dropdown.
You can now choose where this disclaimer should appear, such as ‘Insert After Post’ or ‘Insert Before Content.’
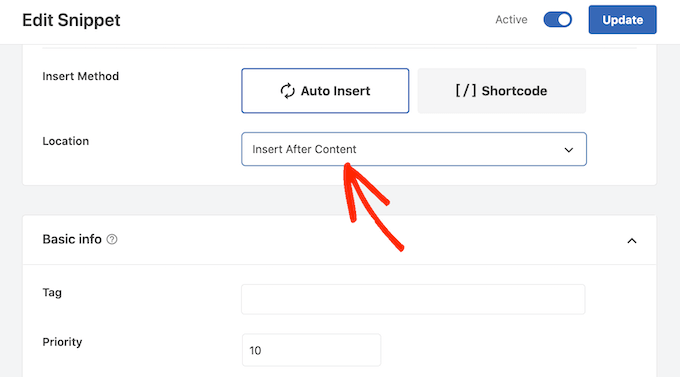
You can then go ahead and enable the snippet by following the same process described above. WPCode will now automatically show the disclaimer on every page, post, and custom post type, without you having to add the shortcode manually.
Method 3. Add Affiliate Disclosure Using Full-Site Editor (Block-Enabled Themes Only)
If you’re using a block-based theme like Hestia Pro, then you can add an affiliate disclosure to your theme’s blog post template.
This is a good choice if you want to show the exact same disclosure on every blog post. However, you won’t have the option to change the style or text on individual posts, so it’s not a good choice if you want to show different information on different pages.
To use this method, go to Themes » Editor in the WordPress dashboard.
By default, the full-site editor will show your theme’s home template, so you’ll typically want to select a new template.
If you want to show the affiliate disclosure across your entire website, then we recommend adding it to the footer template part.
However, if you just want to show the disclaimer on your blog posts, then click on Templates on the left-hand side of the screen in the Design section.
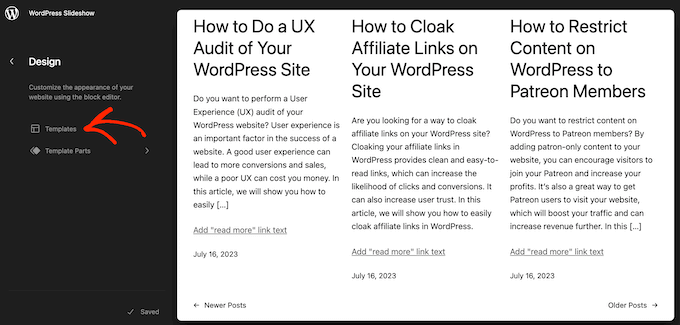
The editor will now show all the layouts that make up your WordPress theme.
Simply click go ahead and click on ‘Single.’

WordPress will now show a preview of the template.
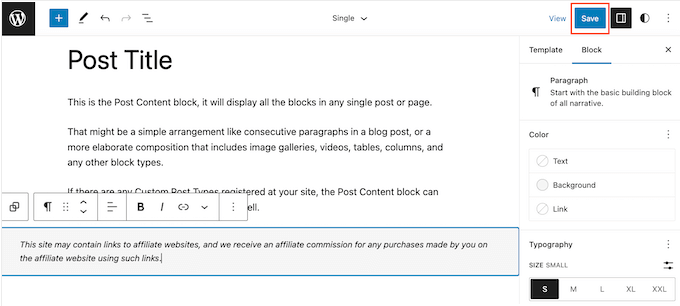
To edit this template, go ahead and click on the small pencil icon.

With that done, click on the blue ‘+’ icon in the top left corner.
In the search bar that appears, type in ‘Paragraph’ to find the right block.
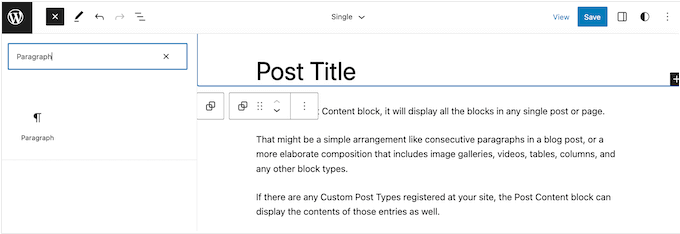
You can now drag and drop the block onto the area where you want to show the disclaimer.
Now, click on the block and type in your affiliate disclaimer.
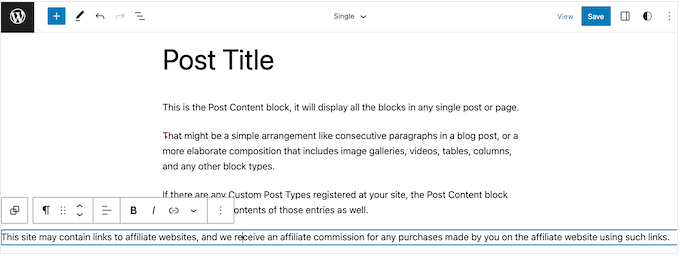
You may also want to change how the disclaimer looks.
To change the font size, background color, and more, simply click to select the paragraph block. Then, select the ‘Block’ tab in the right-hand menu.
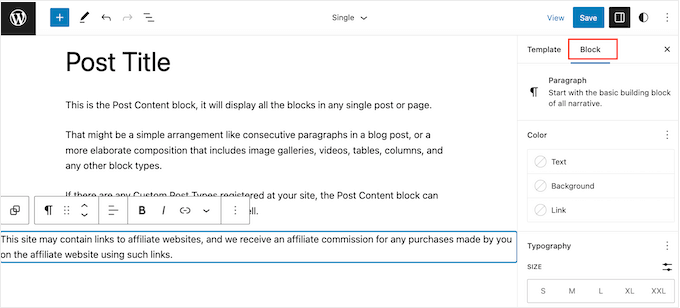
You can now change the background color and text color, or make the disclaimer bigger or smaller using the settings in the right-hand menu.
When you’re happy with how the disclaimer looks, click on the ‘Save’ button.
Now, if you visit any blog post on your affiliate website, you’ll see the disclaimer in action.
We hope this article helped you learn how to add affiliate disclosures for each blog post automatically. You can also go through our guide on the best giveaway and contest plugins and how to create an email newsletter the RIGHT way.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
HOWTO'S
What a 500 Internal Server Error is, and How to Fix it
No one likes opening a webpage and seeing a 500 internal server error message—especially when it’s on your own website.
The problem with seeing this is the mystery behind it: a 500 internal server error is a very general HTTP status code with no definitive clues as to what is causing it.
If you’re seeing one now and are stumped, don’t worry. We can help you find what’s wrong, and what you need to do to fix it.
What is a Website Status Code?
Also known as a HTTP status code, these are a series of numbers that equates to a certain status of a webpage that you are currently viewing.
Whenever you visit a website, your browser sends a request to its server. The server then processes it, and sends back the resources needed to load whichever page you’re requesting. Attached to that is an HTTP header as well as a status code.
If everything can load fine, that status code is a 200. If there’s something wrong, it could be a 500 status code.
Webmaster’s Note: This is part of our more comprehensive guide to Technical SEO, where I cover everything you need to know about crawlability, indexing, and page speed optimization, as well as helpful tips on how to troubleshoot common website errors.
What are 500 Internal Server Errors?
The 500 Internal Server Error, also known as HTTP Error 500, is a server response that indicates an unexpected problem preventing the server from fulfilling the user’s request.
In simpler words, it’s a general message from your server saying “There’s a problem, but I’m not sure what.”
So if you’re seeing one now, then it is important to understand that the issue is not due to the user’s browser, internet connection, or device. Instead, the problem lies with the server that hosts the website. This server-side error can manifest in various messages, as different websites may display their own variations of the 500 error.
Here are some of the different variations of the 500 Internal Server Error:
- 500 Internal Server Error
- Internal Server Error 500
- HTTP Error 500
- HTTP Status 500 – Internal Server Error
- Error 500 Internal Server Error
- 500 Error
- Temporary Error (500)
- 500 – Server Error
- The website cannot display the page – HTTP 500.
Causes of 500 Internal Server Errors
The generic 500 server error can be challenging to pinpoint, because it is a general error—it does not point to any specific cause from the get-go. This means you have to dig into your website to find the cause.
But the good news is there are some likely culprits you can look at first:
- Browser Cache: Clearing your browser cache can help resolve the issue by ensuring that you are accessing the most up-to-date version of the website.
- Database Issues: Incorrect login credentials or a corrupt database can trigger a 500 error. Double-check that the credentials are correct and consider repairing or optimizing the database.
- Corrupted Files: If the core files of a WordPress website become corrupted, it can lead to a 500 error. Restoring or updating these files can help resolve the issue.
- Server and Disk Space: Issues within the server, such as running out of disk space or PHP memory limit exhaustion, can result in a 500 error. Contact your hosting provider to address these server-related issues.
- File Permissions and .htaccess: Incorrect file or folder permissions, as well as a corrupt or broken .htaccess file, can cause a 500 error. Double-check these settings and make necessary adjustments.
- Third-Party Plugins and Themes: Compatibility issues or errors within third-party plugins or themes can trigger a 500 error. Disable or remove these elements one by one to identify the problematic ones.
- Malware infections: Malicious software can compromise your website’s functionality and trigger internal server errors. For example, if a hacker injects a piece of malicious code into your website’s files, it can disrupt the server’s operation and result in a 500 error.
- Broken script injections: Hackers can inject malicious scripts into your website’s code, which may cause conflicts and result in internal server errors.
By understanding these potential causes, you can take the necessary steps to address them and resolve the 500 internal server errors.
Troubleshooting 500 Internal Server Errors
To resolve 500 internal server errors and get your website back online, you could follow these detailed troubleshooting steps:
Clear Your Browser Cache

Before diving into complex troubleshooting steps, clearing your browser cache is a good starting point. By clearing the cache, you ensure that any previously stored data or cached versions of the website are removed, allowing for a fresh attempt at accessing the site.
This can be especially helpful if the error was caused by a previous version of the website being cached locally on your device.
- Example: Let’s say you are using Google Chrome. To clear your browser cache, you would click on the three dots icon at the top right of the browser window, go to “More tools,” select “Clear browsing data,” choose a time range or “All time” option, and finally, click “Clear data” to remove the cached files.
Reload the Page
After encountering a 500 error, it is worth waiting a minute and then attempting to reload the page.
The error can be temporary if it occurs due to server overload or maintenance. By reloading the page, you give the server a chance to resolve the issue and send a proper response.
- Example: You visit a news website and encounter a 500 internal server error while trying to access an article. Instead of immediately assuming a problem with your device, you wait for a moment and then press F5 or Ctrl + F5 to refresh the page. If the server overload was the cause, the website would likely be accessible again after the reload.
Check for Recently Installed or Updated Software
If the 500 error persists, it is important to investigate whether any recently installed or updated software on your website may be causing conflicts.
This could include plugins, themes, or any other website components that have undergone changes.
- Example: You recently updated the content management system (CMS) of your WordPress website, and shortly after, you start experiencing 500 Errors. To troubleshoot the issue, you can compare the date of the CMS update with the start of the errors. If they align, it may indicate that the update caused compatibility issues or conflicts with other plugins or themes.
Check for Server-side Errors
Review your server’s error logs to identify any specific error messages or patterns. These logs can provide valuable insights into the underlying issues causing Error 500.
- Example: A server error log indicating database connection failures may indicate a misconfiguration in your website’s database settings, leading to 500 internal server errors.
Review Error Logs

Look for recurring errors or warnings that may indicate underlying issues. Correlate timestamps with user-reported errors if applicable to pinpoint specific areas of concern.
- Example: If users consistently report a 500 error when submitting a contact form, reviewing error logs during those instances may reveal issues with the form submission script.
Identify and Fix .htaccess File Issues
Open the .htaccess file using a text editor and check for syntax errors or conflicting directives. Rectify any mistakes or consider renaming the file to regenerate it.
- Example: A website experiencing Error 500 after adding rewrite rules to the .htaccess file may have introduced syntax errors that disrupt the server’s operation.
Address Script Injection Problems
Inspect your website’s files and code for any suspicious or unrecognized scripts. Remove any injected code and ensure that your website’s security measures are robust.
- Example: If your website allows user-generated content and you notice unexpected scripts in certain posts or comments, it is possible that malicious users have injected their own code.
500 Error VS. Other 5xx Response Codes
If you’re seeing an error screen and none of these solutions worked, then you might be dealing with a different kind of 5xx error.
To have a better understanding of the differences between generic 500 errors and other internal server errors, it’s essential to know the most common 5xx response codes:
- 500 Error: This code indicates that the server encountered an unexpected problem that prevents it from fulfilling the request. It’s an unidentified issue without providing additional details.
- 501 Error: A “not implemented” HTTP status code, it shows that the server is unable to execute the request. This may happen due to an inability to identify the request’s objective or insufficient power to fulfill it.
- 502 Error: Known as a “bad gateway,” this response happens when an invalid response is detected by the server acting as a proxy or gateway. This means that the server received an invalid response from an upstream server, potentially indicating a problem with your server if you are using a web application firewall.
- 503 Error: Happens when a service is unavailable, which can be triggered by server overload, maintenance, or even a malware attack. The server is unable to handle additional tasks at that moment.
- 504 Error: A “gateway timeout” indicates that the server, operating as a proxy or gateway, was unable to identify the request within the specified time limit.
- 505 Error: This error happens when the server cannot recognize the HTTP protocol used in the request.
- 511 Error: An error for network authentication. This means that the server requires user authentication to access the requested resource.
How 500 Error Codes Can Impact Your SEO
Encountering frequent 500 internal server errors can have several negative implications for your website’s SEO:
- User Experience and Rankings – Internal server errors can significantly impact user experience, leading to a low engagement rate as visitors encounter a non-functioning website. User experience is a critical signal for search engines, as they aim to provide the most relevant and satisfying results to users. High bounce rates and decreased engagement can signal to search engines that the website may not be meeting users’ needs, potentially impacting its SEO rankings.
- Crawling and Indexing – Search engine crawlers could also encounter Error 500 as they attempt to access and index website content. If search engines repeatedly encounter these server errors during crawling, they may interpret it as a sign of poor website maintenance or technical issues. This can result in difficulty for search engines in indexing and ranking the site effectively. It also means that fresh content updates or changes may not be properly discovered or reflected in search results.
- Domain Authority and Reputation – A website that frequently experiences internal server errors can have a negative impact on its authority and reputation, both in the eyes of search engines and users.
If a site consistently delivers a poor user experience due to server errors, users may lose trust and credibility in the website. Search engines prioritize user satisfaction and may accordingly adjust rankings for websites that consistently provide a subpar experience. That’s why I consider engaging in ongoing technical SEO a must for any webmaster or SEO professional.
How to Prevent 500 Internal Server Errors
To minimize the risk of future 500 Internal Server Errors, implement these preventive measures:
Regularly Update and Maintain your Website
Keep your content management system (CMS), plugins, and themes up to date to prevent conflicts or vulnerabilities.
Remove any unused or outdated plugins or themes that may create conflicts or security vulnerabilities.
- Example: An e-commerce website should regularly update its CMS, such as WordPress, along with the associated plugins, to ensure that security vulnerabilities are patched and compatibility issues are avoided.
Implement Reliable Security Measures:
Install a reputable security plugin to protect your website from potential attacks and malware infections. Use strong, unique passwords for administrative access and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
If you’re using WordPress, here’s how to scan your WordPress site for better security and to prevent any malicious code.
- Example: Utilize a security plugin that can actively scan your website for vulnerabilities, block suspicious IP addresses, and provide real-time alerts for potential threats.
Backup your Website Regularly:
Establish a regular backup routine to ensure that you have a clean copy of your website to restore in case of issues or errors.
Store backups in secure off-site locations or use a reliable backup service.
- Example: Use backup plugins or backup your website manually by downloading both your website files and database, then store the backups on a secure cloud storage platform or external hard drive.
Key Takeaway
Encountering a 500 internal server error can be a frustrating experience, but by understanding its causes and following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article, you can effectively resolve these issues and minimize their impact on your website and SEO.
Prioritize regular maintenance, implement reliable security measures, and establish a backup routine to lessen the chances of having to deal with 500 Internal Server Errors.
HOWTO'S
How to Launch a Newsletter on WordPress.com

Unleash your inner creator! Dive into the exciting journey of crafting captivating newsletters with WordPress.com’s newest course: Newsletters 101: From Basics to Automation and Monetization.
This completely free online course is designed to share the key skills of creating, managing, and monetizing your newsletter. Whether you’re a blogger, entrepreneur, or part of a non-profit organization, this is your gateway to reaching the hearts and minds of your audience directly in their inboxes.
Let’s dive in!
The power of newsletters
Newsletters offer creators and businesses a unique advantage: a simple way to establish a personal, direct line of communication with their audience, free from the whims and distractions of social media algorithms. Publishing a newsletter can help you forge stronger relationships with your subscribers, nurturing a loyal following over time.
And newsletters are an invaluable tool for generating revenue, too. People who sign up for your newsletter are much more likely to be interested in what you have to offer, which means they’re more receptive to your ideas, recommendations, and products.
Get set up for success
In this course we’ll walk you through the basics of setting up a newsletter, even if you don’t have a website. And if you already have a website you’d like to turn into a newsletter, we’ll also guide you on how to do so with just a few clicks.
Our Newsletters 101 course will get you started with what you need no matter where you’re at or what your niche is. You’ll find pro tips, ideas, how-tos, and resources for getting the most out of your newsletter.
The best part? The course is free and no registration is required. Just click the button below and get started!
Unleash your monetization potential
Want to make money through your newsletter? We’ve got you covered! We’ll walk you through setting up paid subscriptions, so you can start generating recurring revenue by simply sharing what you’re passionate about.
We’ll also explore affiliate marketing, a way to earn commissions through carefully curated product recommendations. Plus, we’ll guide you on integrating ads or sponsored content, offering a win-win scenario where your audience benefits from valuable content, and you earn from your efforts.
Making it real
You might be thinking, “I’m not a techie, can I really do this?” Absolutely, yes! In this course, we break down everything into bite-sized pieces, making it simple to follow along, no matter your technical abilities.
And to support you on the way, we have an Education Community Forum where you can ask questions and celebrate your progress.
See you there!
PS: Get the best out of our learning resources by checking out all of our courses, live webinars, and recorded replays.
Join 100,487,100 other subscribers
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoCompetitor Monitoring: 7 ways to keep watch on the competition
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoTurkish startup ikas attracts $20M for its e-commerce platform designed for small businesses
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago31 Ready-to-Go Mother’s Day Messages for Social Media, Email, & More
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoA History of Google AdWords and Google Ads: Revolutionizing Digital Advertising & Marketing Since 2000
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoThrive Architect vs Divi vs Elementor
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoMore Google March 2024 Core Update Ranking Volatility
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Search Results Can Be Harmful & Dangerous In Some Cases








