SOCIAL
Clubhouse Finally Launches Android Version – But is it Already Too Late?
It’s taken some time – and no doubt some scrambling at Clubhouse HQ – but finally, an Android version of the audio social platform is now available, in limited beta for now, with a wider launch coming soon.

As explained by Clubhouse:
“Today, we are thrilled to share that Clubhouse for Android will start rolling out in beta immediately. We will begin gradually, with the U.S. today, followed by other English-speaking countries and then the rest of the world. Our plan over the next few weeks is to collect feedback from the community, fix any issues we see and work to add a few final features like payments and club creation before rolling it out more broadly.”
Clubhouse’s Android app does have some significant limitation at launch, including the lack of options to follow topics, inability to create or manage clubs, and no capacity to update your name or update username in-app, among others. But it is finally here, which has been a long time coming, and is a critical step for the next stage of the app’s development.
Clubhouse’s lack of an Android app has become a significant growth impediment of late, with Twitter, Facebook and Instagram all adding Clubhouse-like audio social options that could end up slowing the Clubhouse’s potential Android user take-up. If you can tune in to all the audio social rooms you want, in the apps that you’re already familiar with – which are available on your device right now – do you really need Clubhouse in your life?
The growing variety of audio social tools has now made this a real question, and while Clubhouse may have originated the audio social trend, these newer offerings are refining it, in various ways, which poses a major challenge for Clubhouse as it looks to capitalize on its early momentum, and maximize its audience growth.
Which is already slowing – according to data from Sensor Tower, Clubhouse’s total download numbers fell 72% in March, after peaking at 9.6 million in February.
You can see that same downward trend in the app’s daily download rankings:

As you can see, while Clubhouse is still seeing small boosts in download numbers, the downward trend here is clear.
This can largely be attributed to its lack of an Android app (though these, of course, are only iOS numbers), the rising competition within the audio social space, as noted, and Clubhouse’s invite-only approach, which is designed to both enhance the FOMO factor and fuel more interest in the app, while also alleviating stress on Clubhouse’s servers.
Which will still be in place for the new Android version:
“As a part of the effort to keep the growth measured, we will be continuing the waitlist and invite system, ensuring that each new community member can bring along a few close friends. As we head into the summer and continue to scale out the backend, we plan to begin opening up even further, welcoming millions more people in from the iOS waitlist, expanding language support, and adding more accessibility features, so that people worldwide can experience Clubhouse in a way that feels native to them.”
This was once one of Clubhouse’s key growth features, with its invite-only approach making Clubhouse invites a desired digital item, with many even being auctioned off on eBay for ridiculous prices. But with more audio social options arriving on the scene, it’s now become a limitation – though it does also serve a practical purpose, which Clubhouse further explains:
“Earlier this year, Clubhouse started growing very quickly, as people all over the world began inviting their friends faster than we had ever expected. This had its downsides, as the load stressed our systems- causing widespread server outages and notification failures, and surpassing the limits of our early discovery algorithms. It made us shift our focus to hiring, fixing, and company building, rather than the community meetups and product features that we normally like to focus on. It was an important time of investment, which we think will help us serve the community much better in the long run.”
This is a problem that its competitors don’t have, because most have already built the infrastructure to host multi-participant video streams, meaning that, if anything, downgrading their video tools to audio only is a step back from a data load perspective, while Clubhouse is working to keep up. That puts more pressure on the Clubhouse team to invest heavily in infrastructure to accelerate growth, which it can still do, but as Clubhouse itself notes, its sudden growth has put its systems under significant strain.
And if it can’t open up more widely, and maximize its recommendation algorithms, it’s at huge risk of being superseded by the bigger platforms, which are already starting from a stronger position, with broader reach, better, more personally attuned algorithms, and improved audio features. And those tools are being updated and refined every single day.
Can Clubhouse stay up with the bigger players, even with the arrival of its Android app?
The key likely comes down to two things: creator incentives and algorithm refinement.
On the first, Clubhouse has already announced the first round of finalists for its Creator Accelerator program, which will eventually see 20 Clubhouse-based projects receive training, funding and support to help develop their concepts. That will, ideally, help the platform keep more of its top broadcasters aligned with the app, while Clubhouse is also working on creator payments as another means to build incentive systems to keep broadcasters, and their audiences, coming back again and again.
On the second, many users have already noted that, even at this stage, its become more and more difficult to find Clubhouse rooms that are aligned with their interests. That will only get worse as the app opens up to more people, so Clubhouse needs to work on its algorithm tools to ensure that each user is being alerted to the most relevant content to them, in order to keep them active – and again, returning to the app.
As Clubhouse notes, it is working on this, while it’s also recently added scheduled room listings on user profiles and RSVP tools to help improve its systems. This will become an increasingly complex technological process as more users get access, but if Clubhouse wants to keep competing with its better-resourced competitors, it will need to invest heavily in this element, in order to maximize audience engagement.
That’s how TikTok has been able to stick around, and become a significant competitor in the social space. Because every TikTok clip is full-screen, TikTok is better able to determine user interests based on each and every clip, and the TikTok team has worked to build in a range of measurement factors based on the content of each clip, which has helped it build a highly responsive, and heavily refined, personalization algorithm that’s able to suck users in, and keep them coming back and scrolling through its video clips for hours on end.
Clubhouse doesn’t have the same advantages that TikTok does in this respect, but it can work to establish connections between the rooms each person visits, how long they spend in each, the people they regularly listen to, etc. Using these factors, Clubhouse can create an effective personal recommendation algorithm, which could still see it become a more significant audio social option over time.
But the path ahead is not easy, and Clubhouse seems like it’s already stretched as it works to keep pace.
It can still win out, with a dedicated audience, and expanding reach, along with engaged creators and a ‘cool factor’ that the other, legacy social apps simply don’t have at this stage.
But the challenge is significant, and rising.
Hopefully, the arrival of an Android app, slightly ahead of schedule, is a sign of more good things to come for the Clubhouse team.
Android users can download Clubhouse for Android and sign up now to be alerted once it’s available to you, while you can read more about the app’s Android release here.
SOCIAL
Snapchat Explores New Messaging Retention Feature: A Game-Changer or Risky Move?
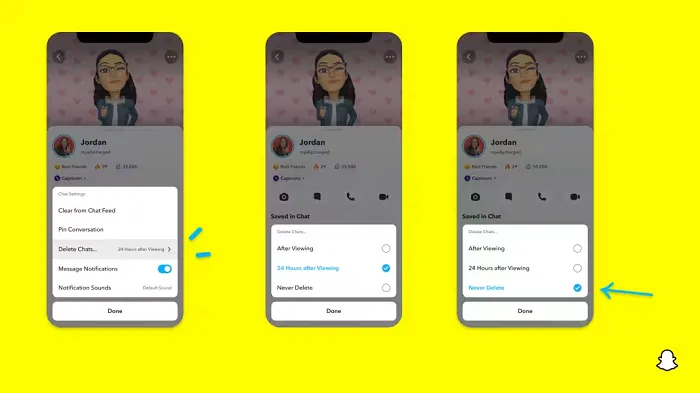
In a recent announcement, Snapchat revealed a groundbreaking update that challenges its traditional design ethos. The platform is experimenting with an option that allows users to defy the 24-hour auto-delete rule, a feature synonymous with Snapchat’s ephemeral messaging model.
The proposed change aims to introduce a “Never delete” option in messaging retention settings, aligning Snapchat more closely with conventional messaging apps. While this move may blur Snapchat’s distinctive selling point, Snap appears convinced of its necessity.
According to Snap, the decision stems from user feedback and a commitment to innovation based on user needs. The company aims to provide greater flexibility and control over conversations, catering to the preferences of its community.
Currently undergoing trials in select markets, the new feature empowers users to adjust retention settings on a conversation-by-conversation basis. Flexibility remains paramount, with participants able to modify settings within chats and receive in-chat notifications to ensure transparency.
Snapchat underscores that the default auto-delete feature will persist, reinforcing its design philosophy centered on ephemerality. However, with the app gaining traction as a primary messaging platform, the option offers users a means to preserve longer chat histories.
The update marks a pivotal moment for Snapchat, renowned for its disappearing message premise, especially popular among younger demographics. Retaining this focus has been pivotal to Snapchat’s identity, but the shift suggests a broader strategy aimed at diversifying its user base.
This strategy may appeal particularly to older demographics, potentially extending Snapchat’s relevance as users age. By emulating features of conventional messaging platforms, Snapchat seeks to enhance its appeal and broaden its reach.
Yet, the introduction of message retention poses questions about Snapchat’s uniqueness. While addressing user demands, the risk of diluting Snapchat’s distinctiveness looms large.
As Snapchat ventures into uncharted territory, the outcome of this experiment remains uncertain. Will message retention propel Snapchat to new heights, or will it compromise the platform’s uniqueness?
Only time will tell.
SOCIAL
Catering to specific audience boosts your business, says accountant turned coach

While it is tempting to try to appeal to a broad audience, the founder of alcohol-free coaching service Just the Tonic, Sandra Parker, believes the best thing you can do for your business is focus on your niche. Here’s how she did just that.
When running a business, reaching out to as many clients as possible can be tempting. But it also risks making your marketing “too generic,” warns Sandra Parker, the founder of Just The Tonic Coaching.
“From the very start of my business, I knew exactly who I could help and who I couldn’t,” Parker told My Biggest Lessons.
Parker struggled with alcohol dependence as a young professional. Today, her business targets high-achieving individuals who face challenges similar to those she had early in her career.
“I understand their frustrations, I understand their fears, and I understand their coping mechanisms and the stories they’re telling themselves,” Parker said. “Because of that, I’m able to market very effectively, to speak in a language that they understand, and am able to reach them.”Â
“I believe that it’s really important that you know exactly who your customer or your client is, and you target them, and you resist the temptation to make your marketing too generic to try and reach everyone,” she explained.
“If you speak specifically to your target clients, you will reach them, and I believe that’s the way that you’re going to be more successful.
Watch the video for more of Sandra Parker’s biggest lessons.
SOCIAL
Instagram Tests Live-Stream Games to Enhance Engagement

Instagram’s testing out some new options to help spice up your live-streams in the app, with some live broadcasters now able to select a game that they can play with viewers in-stream.
As you can see in these example screens, posted by Ahmed Ghanem, some creators now have the option to play either “This or That”, a question and answer prompt that you can share with your viewers, or “Trivia”, to generate more engagement within your IG live-streams.
That could be a simple way to spark more conversation and interaction, which could then lead into further engagement opportunities from your live audience.
Meta’s been exploring more ways to make live-streaming a bigger consideration for IG creators, with a view to live-streams potentially catching on with more users.
That includes the gradual expansion of its “Stars” live-stream donation program, giving more creators in more regions a means to accept donations from live-stream viewers, while back in December, Instagram also added some new options to make it easier to go live using third-party tools via desktop PCs.
Live streaming has been a major shift in China, where shopping live-streams, in particular, have led to massive opportunities for streaming platforms. They haven’t caught on in the same way in Western regions, but as TikTok and YouTube look to push live-stream adoption, there is still a chance that they will become a much bigger element in future.
Which is why IG is also trying to stay in touch, and add more ways for its creators to engage via streams. Live-stream games is another element within this, which could make this a better community-building, and potentially sales-driving option.
We’ve asked Instagram for more information on this test, and we’ll update this post if/when we hear back.
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoWill Google Buy HubSpot? | Content Marketing Institute
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 16, 2024
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Clarifies Vacation Rental Structured Data
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoStreamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago97 Marvelous May Content Ideas for Blog Posts, Videos, & More


