NHS data breach: trusts shared patient details with Facebook without consent | Health
NHS trusts are sharing intimate details about patients’ medical conditions, appointments and treatments with Facebook without consent and despite promising never to do so.
An Observer investigation has uncovered a covert tracking tool in the websites of 20 NHS trusts which has for years collected browsing information and shared it with the tech giant in a major breach of privacy.
The data includes granular details of pages viewed, buttons clicked and keywords searched. It is matched to the user’s IP address – an identifier linked to an individual or household – and in many cases details of their Facebook account.
Information extracted by Meta Pixel can be used by Facebook’s parent company, Meta, for its own business purposes – including improving its targeted advertising services.
Records of information sent to the firm by NHS websites reveal it includes data which – when linked to an individual – could reveal personal medical details.
It was collected from patients who visited hundreds of NHS webpages about HIV, self-harm, gender identity services, sexual health, cancer, children’s treatment and more.
It also includes details of when web users clicked buttons to book an appointment, order a repeat prescription, request a referral or to complete an online counselling course. Millions of patients are potentially affected.
This weekend, 17 of the 20 NHS trusts that were using Meta Pixel confirmed they had pulled the tracking tool from their websites.
Eight issued apologies to patients. Multiple trusts said they had originally installed the tracking pixels to monitor recruitment or charity campaigns and were not aware that they were sending patient data to Facebook. The Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) is investigating.
The Observer can reveal:
In one case, Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS trust shared when a user viewed a patient handbook for HIV medication. The name of the drug and the NHS trust were sent to the company along with the user’s IP address and details of their Facebook user ID.
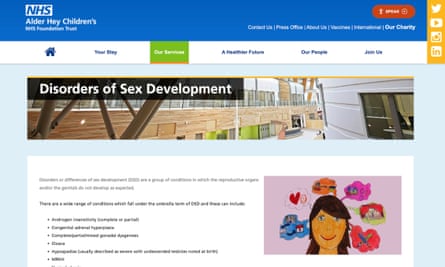
Alder Hey Children’s trust in Liverpool, sent Facebook details when users visited webpages for sexual development problems, crisis mental health services and eating disorders. It also shared data when users clicked to order repeat prescriptions.
The Tavistock and Portman NHS foundation trust in London shared data with Facebook when users clicked the information page for its gender identity service, which specialises in working with children who have gender dysphoria. Data was also shared when users viewed the webpage for the Portman Clinic, which “offers specialist help with disturbing sexual behaviours”, and clicked for details on how to be referred to the service.
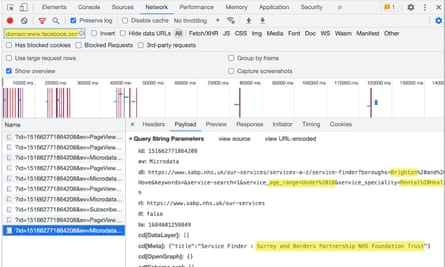
Surrey and Borders Partnership NHS trust shared data with Facebook when a patient clicked buttons indicating they were under 18, lived in Brighton and wanted to access mental health services.
Other NHS trusts sent detailed receipts to Facebook when users accessed pages for appointment bookings or completed online self-help courses. Barts Health NHS trust, which serves a population of 2.5 million in London, shared data with Facebook when a user clicked to “cancel or change an appointment” or added a visit to a particular hospital to their itinerary.
The Royal Marsden, a specialist cancer centre, sent data on patients requesting referrals, viewing information about private care and browsing pages for particular cancer types.
The findings have caused alarm among privacy experts who said they indicated widespread potential breaches of data protection and patient confidentiality that were “completely unacceptable”.
Information sent to the company is likely to include special category health data, which has extra protection in law and is defined as information “about an individual’s past, current or future health status”, including medical conditions, tests and treatment and “any related data which reveals anything about the state of someone’s health”. Using or sharing it without explicit consent or another lawful basis is illegal.
Once the data reaches Facebook’s servers, it is not possible to track exactly how it is used. The company says it prohibits organisations from sending it sensitive health information and has filters to weed such data out when it is received by mistake.
Professor David Leslie, director of ethics at the Alan Turing Institute, said the transfer of data to third parties by the NHS risked damaging the “delicate relationship of trust” with patients. “Our reasonable expectation when we’re accessing an NHS website is that our data won’t be extracted and shared with third-party commercial entities that could [use it] for targeting ads or linking our personal identities to health conditions,” he said.
Wolfie Christl, a data privacy expert who has investigated the ad tech industry, said: “This should have been stopped by regulators a long time ago. It is irresponsible, even negligent, and it must stop.”
He accused Meta of doing too little to monitor what information it was being sent. “Meta says we don’t permit certain types of data being sent to us but they haven’t spent enough on resources to audit this,” Christl said.
In most cases, the information sent to Facebook during a test by the Observer was transferred automatically upon loading a website – before the user had selected to “accept” or “decline” cookies – and without explicit consent. Only three of the 20 trusts mentioned Facebook or Meta in their privacy policies at all. Several of the trusts had previously promised patients that their information would not be shared or used for marketing.
Collectively, the 20 NHS trusts found using the tracking tool serve a population of more than 22 million people in England, stretching from Devon to the Pennines. Some had been using it for several years.
One of the trusts that pulled the tracking tool this weekend, Buckinghamshire Healthcare NHS trust, had previously said in its privacy policy that “confidential personal information about your health and care … would never be used for marketing purposes without your explicit consent”.
In a statement, the trust apologised to patients and said the Meta Pixel had been active on its website in error. “It was installed in relation to a recruitment campaign, and we were not aware that Meta was using this information for marketing purposes,” a spokesperson said. “Immediate action has been taken to remove it.”
Alder Hey said it asked visitors to its website for permission to use cookies and said patients’ names and addresses had not been shared. It has removed the tracking tool.
The Royal Marsden said it regularly reviewed its privacy policies but did not say whether it planned to remove the pixel. Barts said it was removing trackers from its website “following the disclosure that they were being used to extract personal information beyond the purpose for which they were originally installed, which was to measure responses to recruitment advertising campaigns.”
Several said they were unaware of how data would be used and apologised to patients for failing to get consent. Aside from the 17 who pulled or are pulling the tool, Hertfordshire Partnership trust and Royal Marsden said they were investigating the issues internally and only the Tavistock and Portman did not respond to requests for comment.
The ICO said it had “noted the findings” and was considering the matter. “People have the right to expect that organisations will handle their information securely and that it will only be used for the purpose they are told,” a spokesperson said.
Revelations about the NHS use of Meta Pixel come after regulators in the US issued warnings over the use of tracking tools there. Last summer, tech website The Markup exposed their use on the websites of healthcare providers. In December, the Biden administration warned that using tracking pixels to collect patient data without consent was a potential federal law violation.
Several leading US hospitals are currently being sued by their patients over their use of the pixels, which are tiny pieces of code that are invisible during normal browsing.
Meta is also facing legal action over accusations of knowingly receiving sensitive health information – including from pages within patient portals – and not taking steps to stop it. The plaintiffs claim Meta violated their medical privacy by intercepting “individually identifiable health information” from its partner websites and “monetising” it.
Jeffrey Koncius, a partner at Kiesel Law in California and one of the attorneys leading the action, said the data transfer by the NHS websites appeared similar to what was happening in the US. “Imagine if a hospital sent a letter to Mark Zuckerberg and said, ‘We want you to know that Jeff Koncius is our patient,’” he said. “That’s exactly what’s happening here. It’s just happening electronically.”
The Liberal Democrat health spokesperson Daisy Cooper described the findings as a “shocking discovery” that raised serious questions about the protection of patient information. “The NHS must investigate how this happened and how widespread this alleged data breach is,” she said.
NHS England said individual trusts were responsible for ensuring they followed data protection laws. “The NHS is looking into this issue and will take further action if necessary,” a spokesperson said.
Meta said it had contacted the trusts to remind them of its policies, which prohibited organisations from sending it health data. “We educate advertisers on properly setting up business tools to prevent this from occurring,” the spokesperson said. They added it was website owner’s responsibility to ensure it complied with data protection laws and had obtained consent before sending data.
The company did not answer questions about the effectiveness of its filters designed to weed out “potentially sensitive data”, or which types of information they would block from hospital websites – or say why it permitted NHS trusts to send it data at all, given the high risk it could reveal details about the web user’s health.
“Like any technology, our filters won’t be able to catch everything all of the time. However, we are constantly improving our mechanisms to make sure we catch as much as we can,” a spokesperson said.
The company offers its business tools to advertisers, saying they can help them use health-based advertising to “grow your business”. In one guide, it says data collected through its business tools can improve users’ Facebook experience by showing them ads they “might be interested in”. “You may see ads for hotel deals if you visit travel websites,” it explains.
Sam Smith, at medConfidential, a data privacy campaign group, said it was never appropriate for the tools to be used to collect health information. “There’s no benefit to NHS trusts in giving this information away. It’s like asking a tobacco company to sponsor a cancer ward,” he said. “NHS England is tacitly approving this by not enforcing anything better.”