SEO
9 Best Use Cases (And 4 Suboptimal Ones)

I’ll have to admit: ChatGPT is cool. I don’t think we expected AI to come this far so soon.
But it doesn’t mean every free “ChatGPT prompt” ebook you see on Gumroad is the future. Many of the use cases are simply engagement bait.
So in this post, we’ll look at the actual best use cases of ChatGPT for SEO. I’ll also cover cases where you shouldn’t use ChatGPT.
Editor’s Note
Prefer watching a video instead? Here’s Sam Oh on the best and worst cases of ChatGPT for SEO:

Here are some of our favorite ChatGPT use cases for SEO that we have found at Ahrefs.
1. Construct regex
A regular expression (regex) is a sequence of characters used to find patterns within text. For example, the pattern /b[aeiou]t/ will find words like “bat, bet, bit, bot, but” on a page.
If we want to find keywords phrased as a question in Google Search Console (GSC), we can ask ChatGPT:
What is the regular expression to show matches that contain any of the following words in it: how, what, who, when, where, why, do? These words should be the first word in the match.
And here’s ChatGPT’s answer:
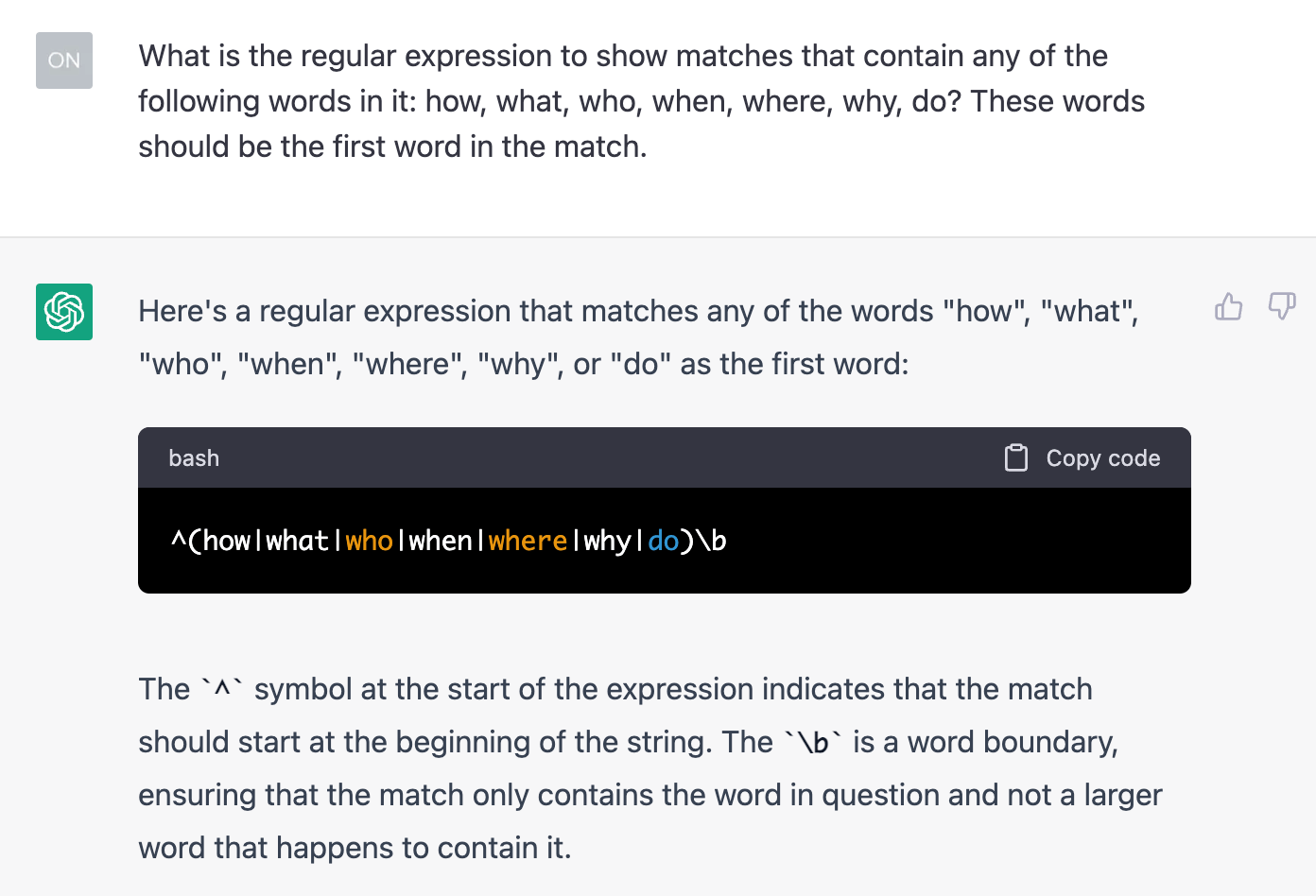
With this answer, we can go to GSC and paste the custom regex with the Query filter:
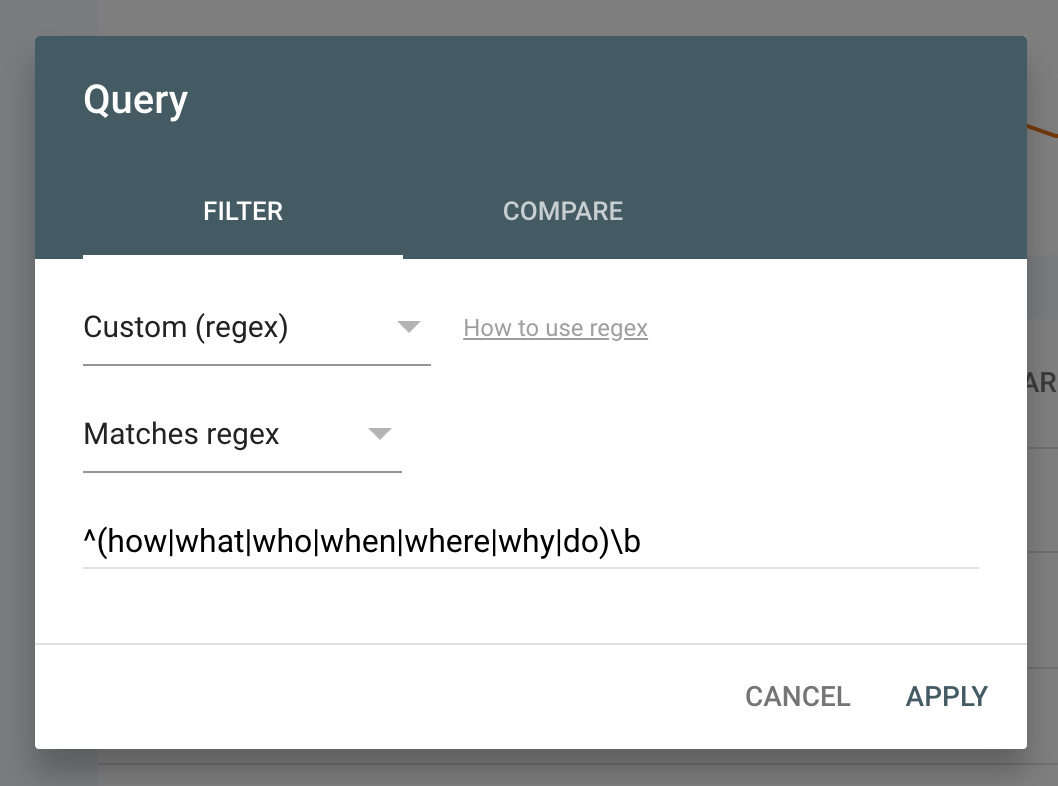
Then, we’ll set the Positions filter to >10 and sort the list in ascending order.
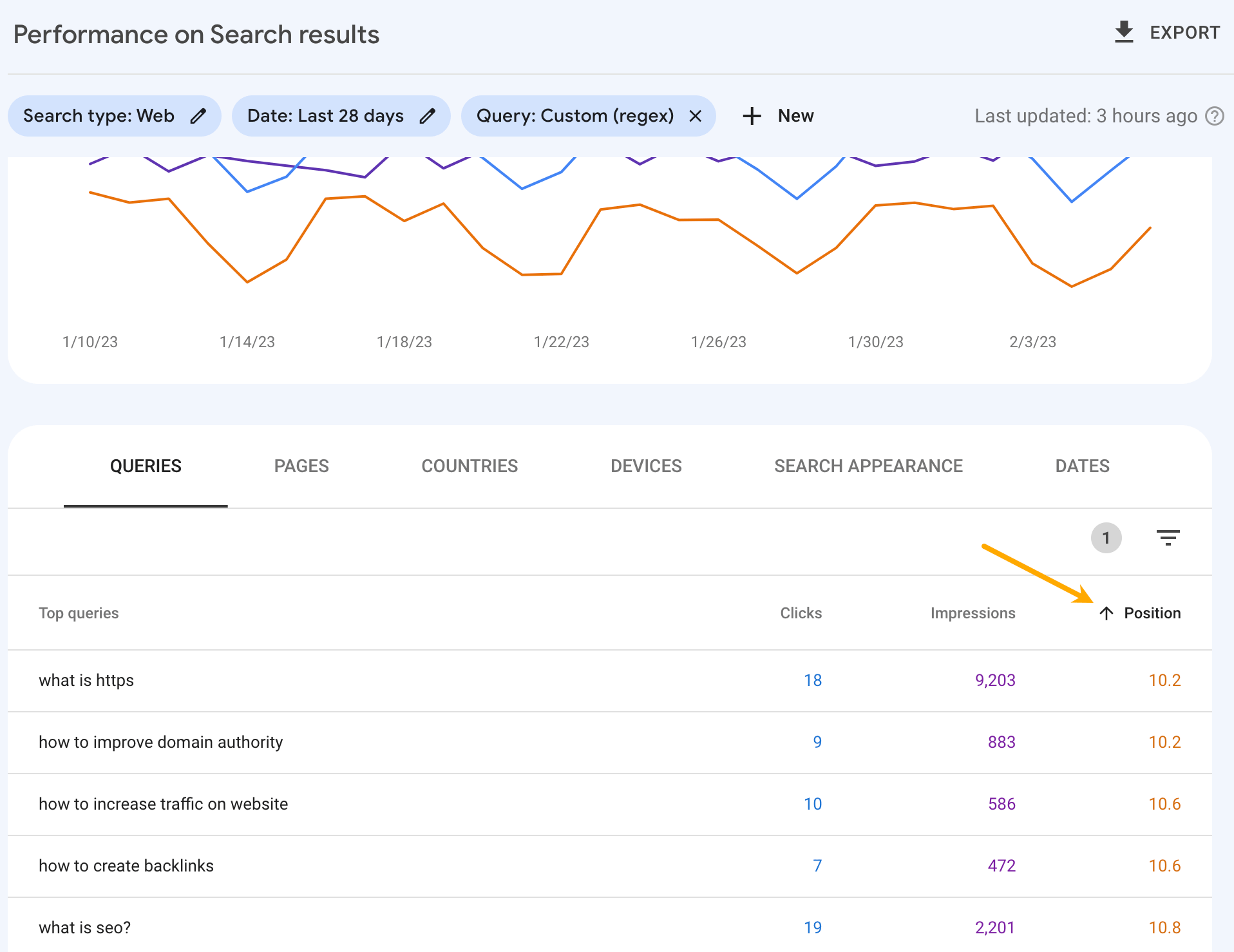
We now have a list of informational keywords we can work on to bring those pages from page two to page one of Google.
2. Create automations
ChatGPT can write code too.
If you’re tech-savvy, you’ll already see plenty of ways to use this to improve your processes. Here’s a quick example.
Let’s say you’re working on a link building campaign. You’ve collected the URL, domain, and first and last names of the authors you want to contact. Now you want to find their emails.
The inefficient method is to go through them one by one in a web app or Chrome Extension. The better way would be to code something in App Scripts to connect to an email-finding API, like Hunter.io.
We can use ChatGPT to write the code. Here’s a sample prompt:
Using Hunter.io’s Email Finder API, write a function called findEmail in Google Appscripts to return a person’s email address. If no email exists, then return “THEY DON’T WANT TO BE CONTACTED.” I will provide the first name, last name, and domain name. BTW, my API key is [MUTED]. Go!
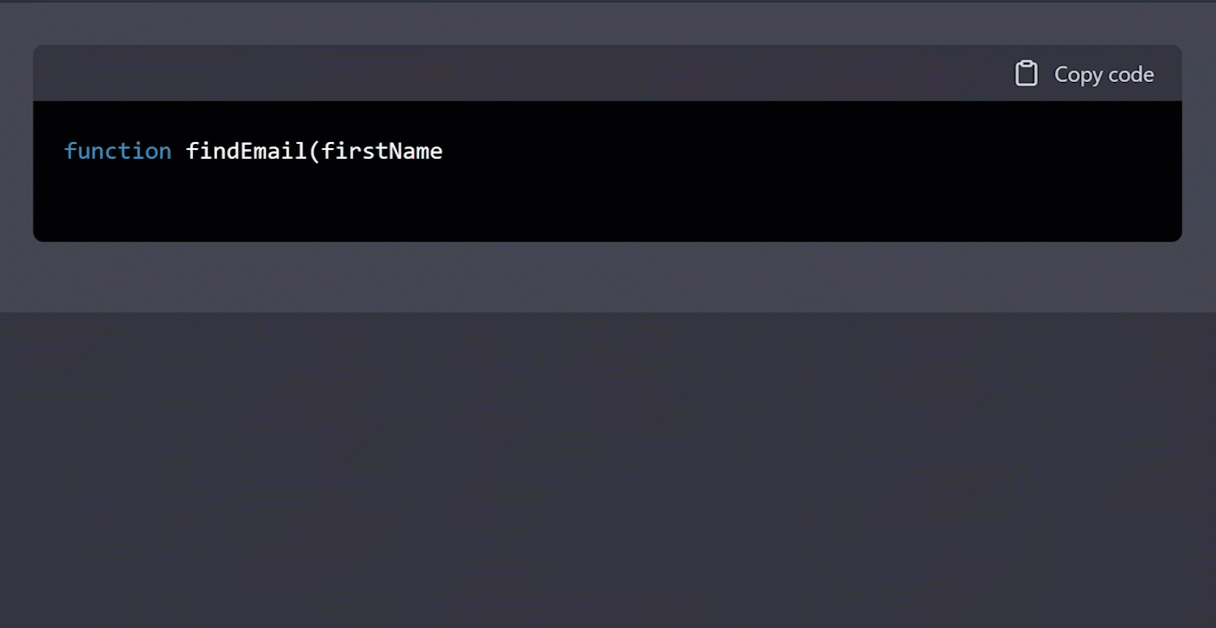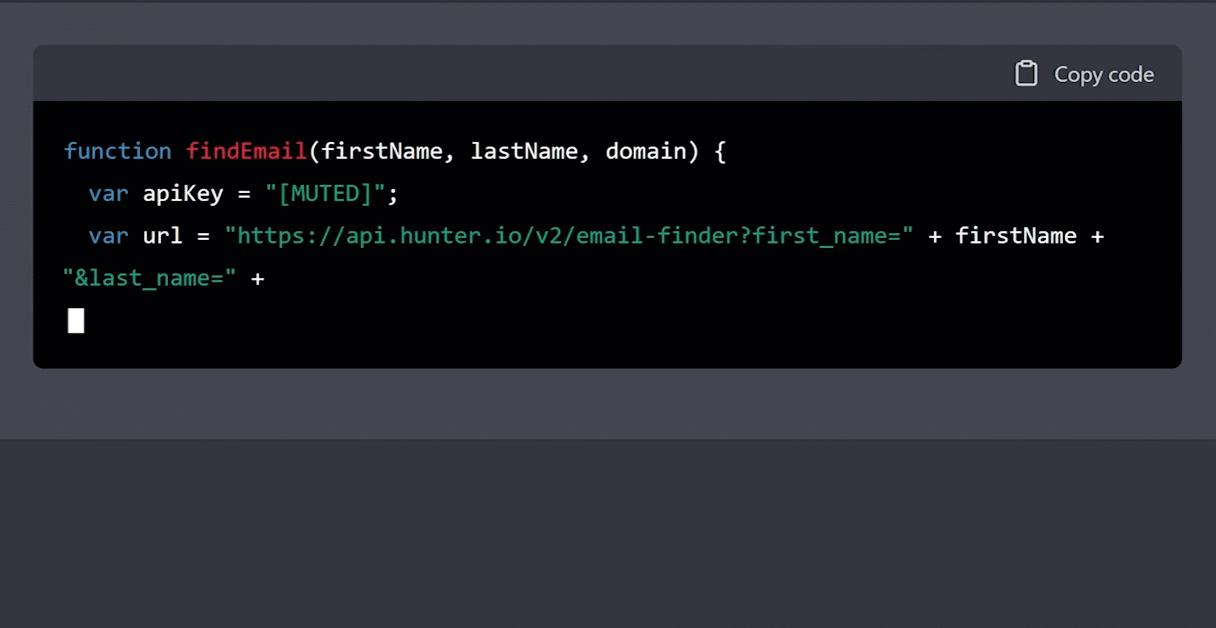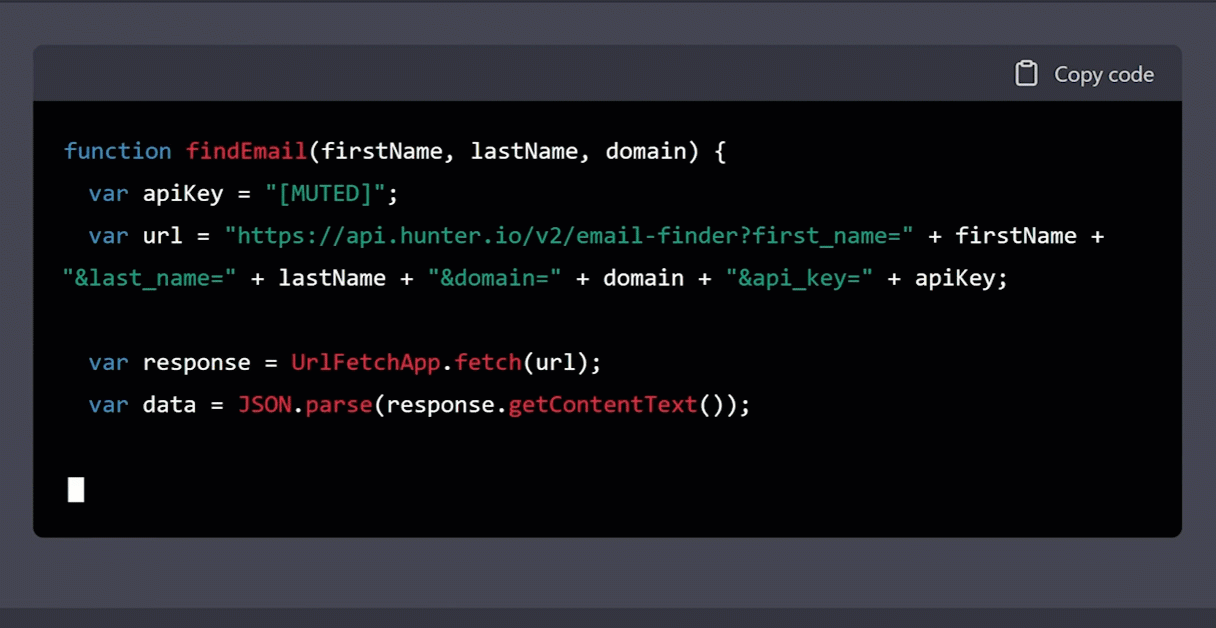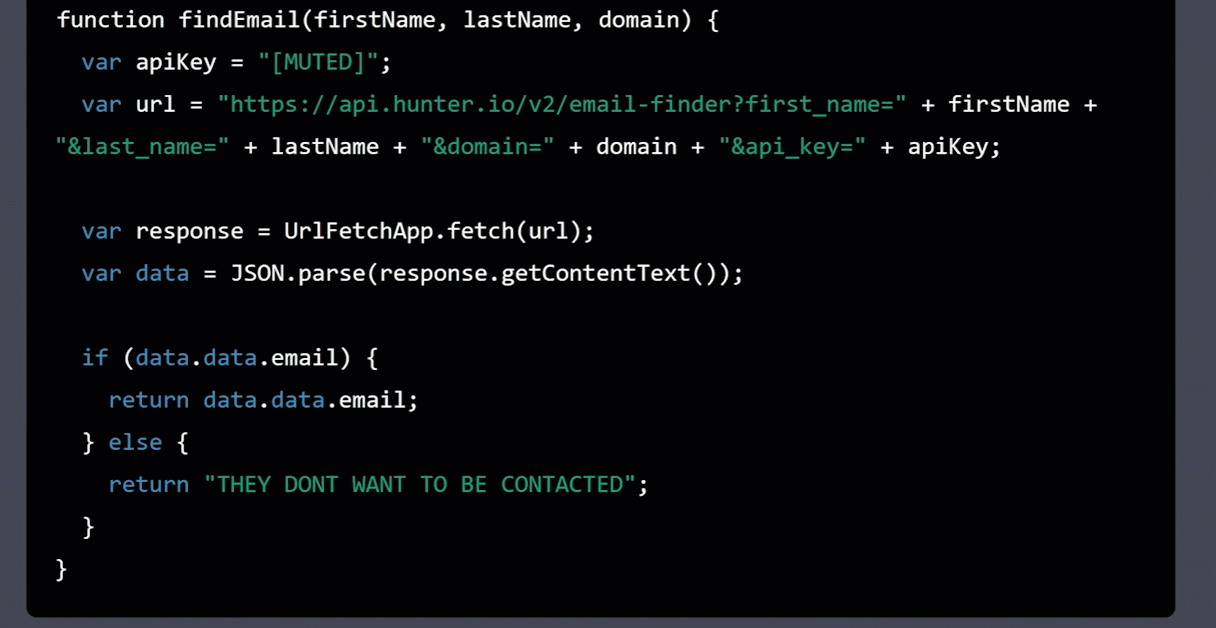
Then, we’ll take the generated code and open App Scripts:
- First, paste in the code, save the file, and go back to the Google Sheets.
- In the email column, type in “findEmail,” open parentheses, click the first name, last name, and the domain.
- Then hit enter.
- As for the rest of the list, just drag the formula down.
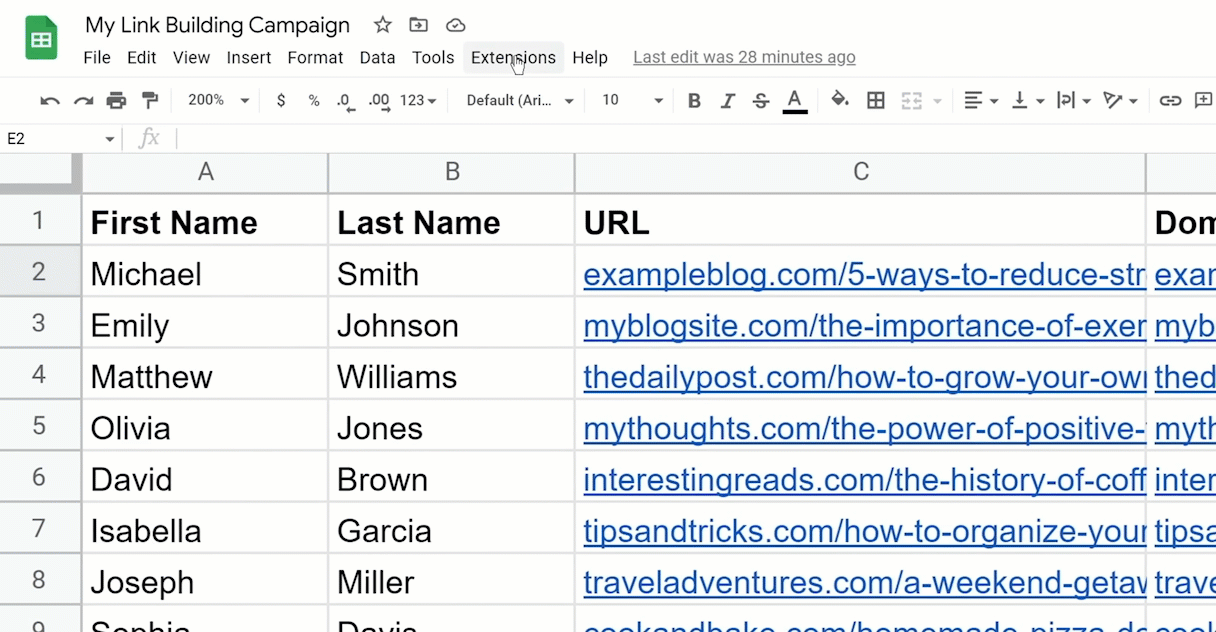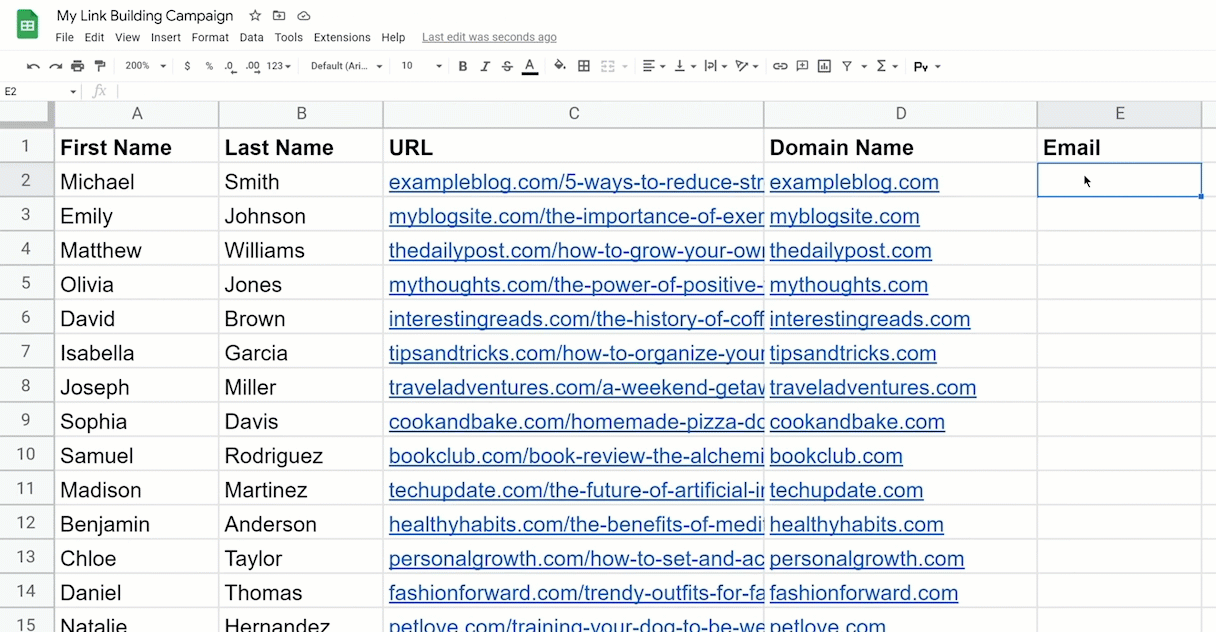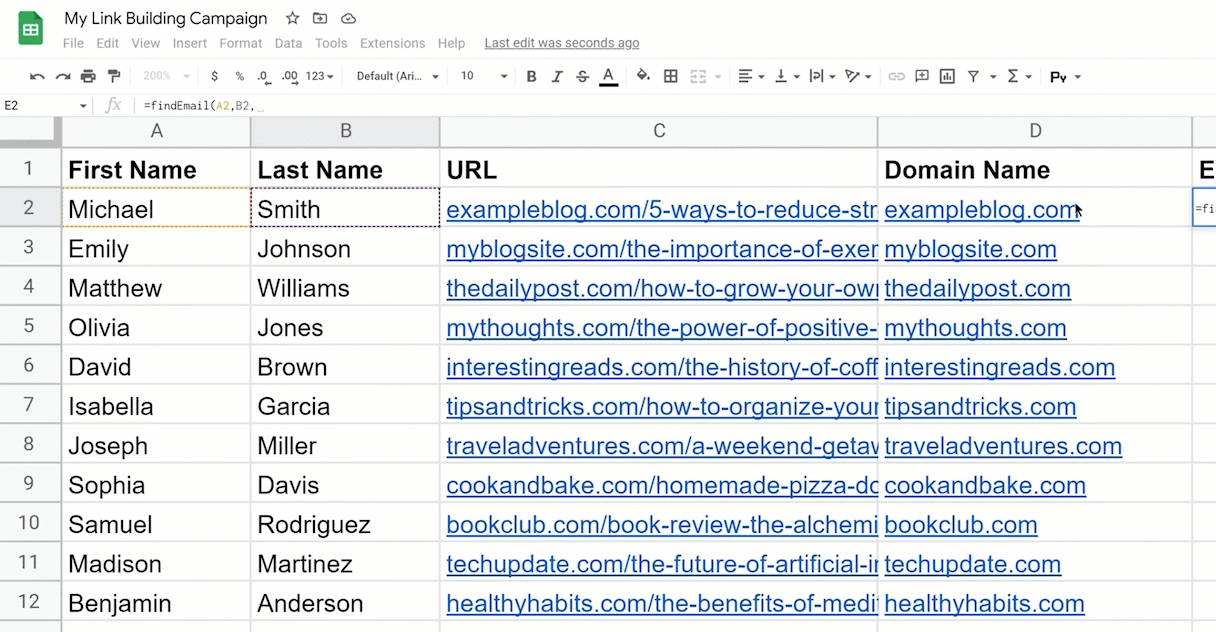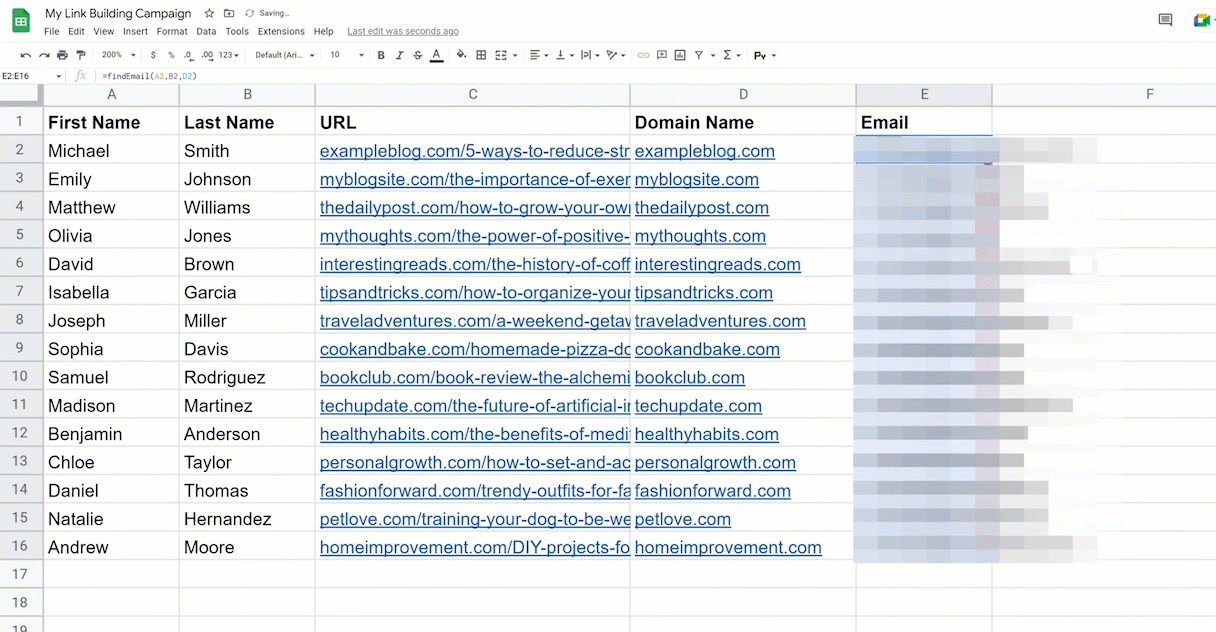
This is merely the tip of the iceberg. There are plenty more you can do—for example, SEOs are combining it with Python to do tons of cool stuff:
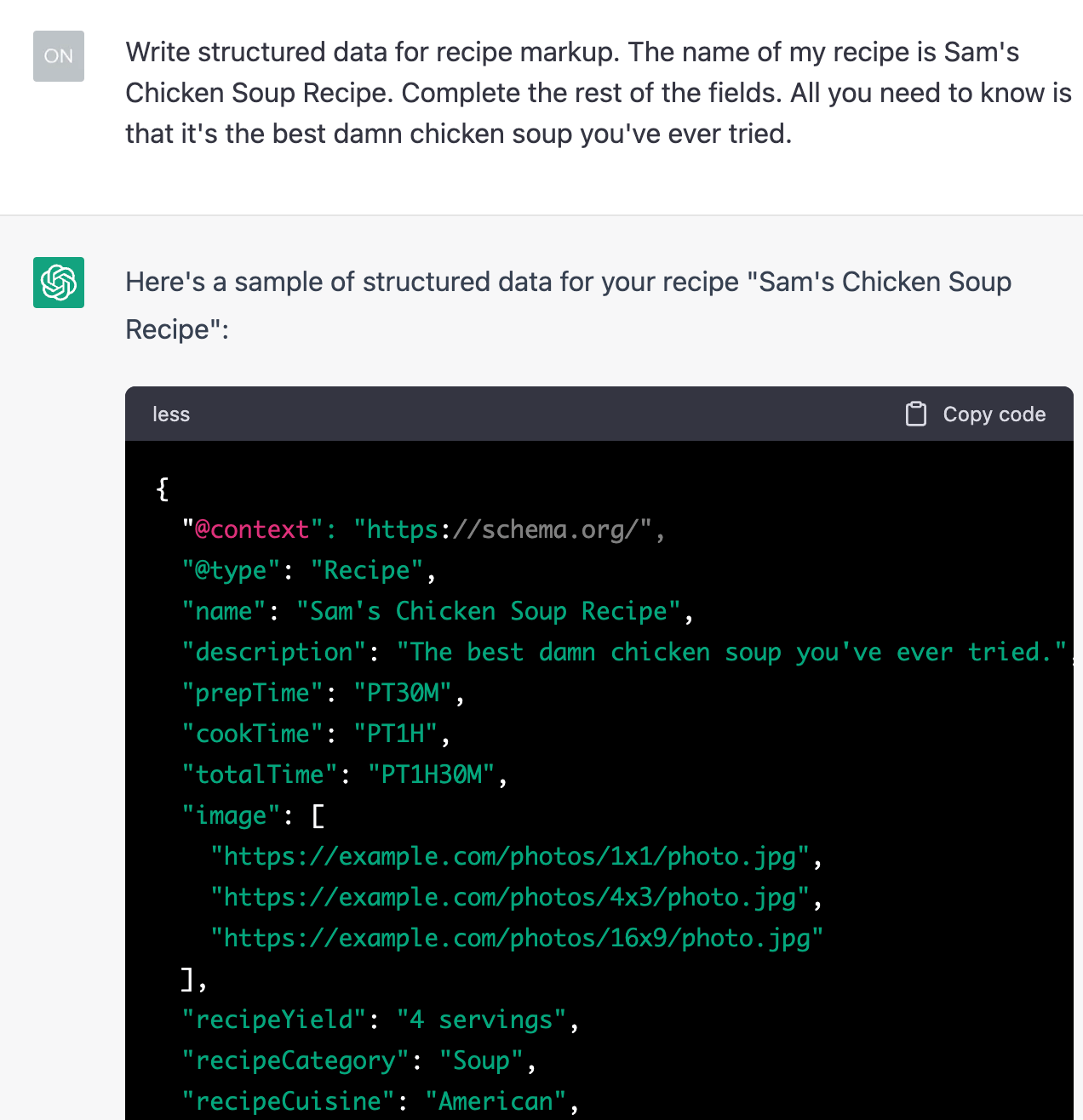
3. Whip up quick snippets of code
ChatGPT’s ability to write code means you can use it to quickly create snippets of code, such as schema markup:
And hreflang snippets:

More examples in the article below.
4. Write click-worthy titles
Writing the perfect headline can take longer than you think. So we can use ChatGPT to create click-worthy titles in seconds—and it outperforms human-written titles:
You can use ChatGPT to write click-worthy titles for your blog posts, podcasts, or YouTube videos. For best results, give it a working title.
Here’s a sample prompt:
Write 10 click-worthy titles for my blog post on the best marketing books. My working title is Best Marketing Books.

You can also ask ChatGPT to front-load keywords or make your titles sound like someone else. So let’s ask ChatGPT to make the above titles sound like Tim Ferriss:

Pretty cool.
5. Create quick outlines
If you like any of the titles ChatGPT suggested, you can ask it to create an outline. I’m sure many SEOs are salivating at the thought of using ChatGPT to create content briefs (or even blog posts—more on that later). But my point is this: think of ChatGPT as your creative sparring partner.
I like #7 from the above example, so let’s ask ChatGPT to expand on it:

It’s a decent outline, but there’s a problem: It’s repetitive. For example, I won’t organize the outline like this. Instead, I’ll probably make each book the H2, then go into the details (summary of the book, some key takeaways, how I used the takeaway to improve my marketing and career, etc.).
The suggested intro seems boring too—I’ll probably start with the story of my transformation rather than sound so academic and prescriptive.
By the way, I’m interested in ChatGPT’s book recommendations, so I’ll ask it to expand on II:

Again, decent suggestions that you’ll find on many marketing booklists. I agree with the recommendations, but my honest opinion is that everyone probably already knows these books. Of course, you don’t want to lie if these books really transformed your career. But if there are lesser-known ones, you’ll do better highlighting them.
Otherwise, you’re just like everyone else, and there’s no point in reading your content.
In summary, use ChatGPT as your ideation partner, but don’t rely on its suggested content 100%.
6. Suggest seed keywords
We don’t recommend using ChatGPT to do keyword research (more on that later), but that’s not to say it isn’t a good way to gather potential seed keywords.
For example, we can ask ChatGPT to give us “technical terms related to coffee”:

We can then use these terms as “seed keywords” to find more keyword ideas in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer:
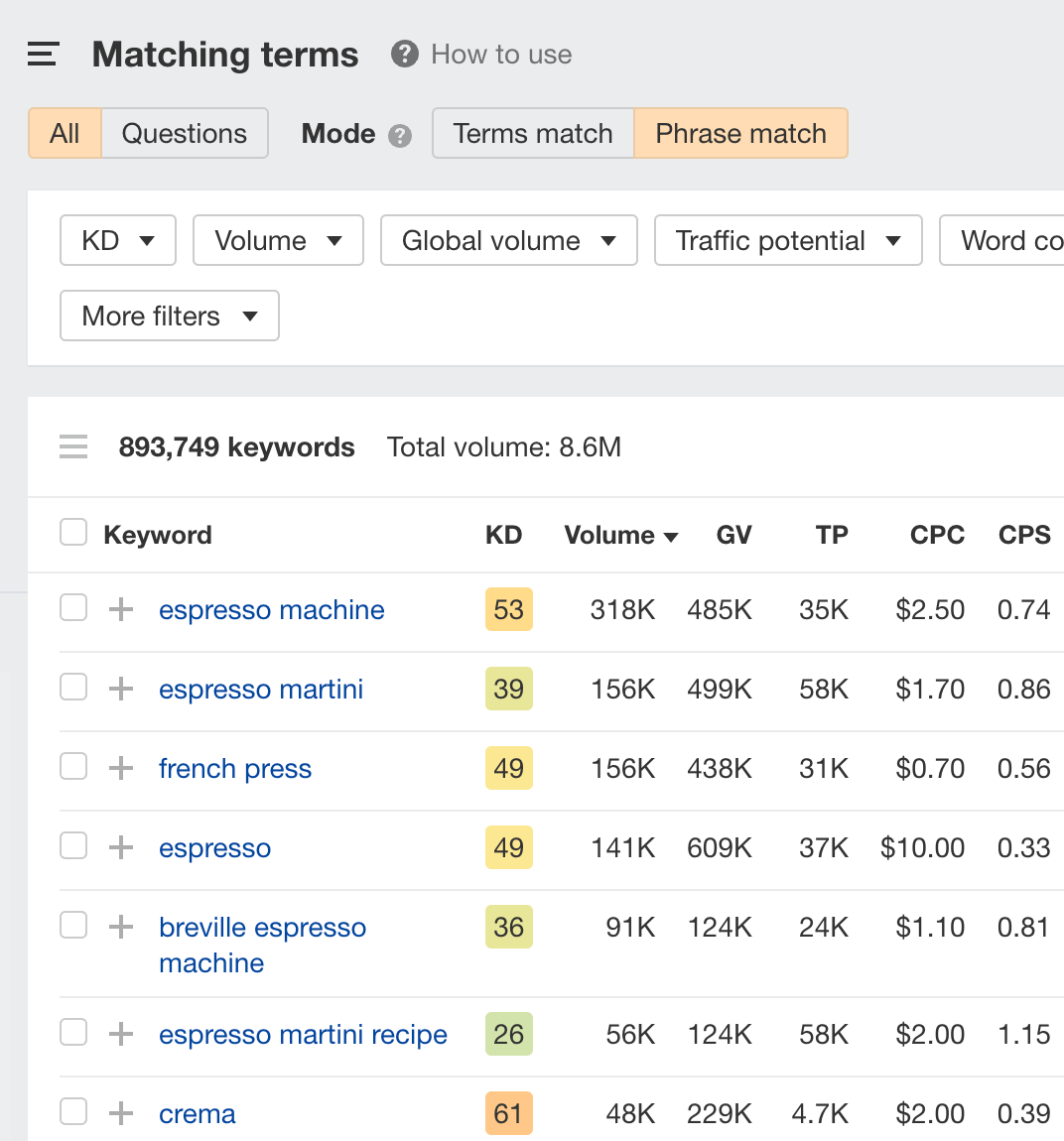
7. Generate short-form content
No matter how much you love writing, some types of content are just boring to create. Examples include meta descriptions, product descriptions, ad copy variations, and more.
For example, we have almost 300 pages on our site that don’t have meta descriptions.
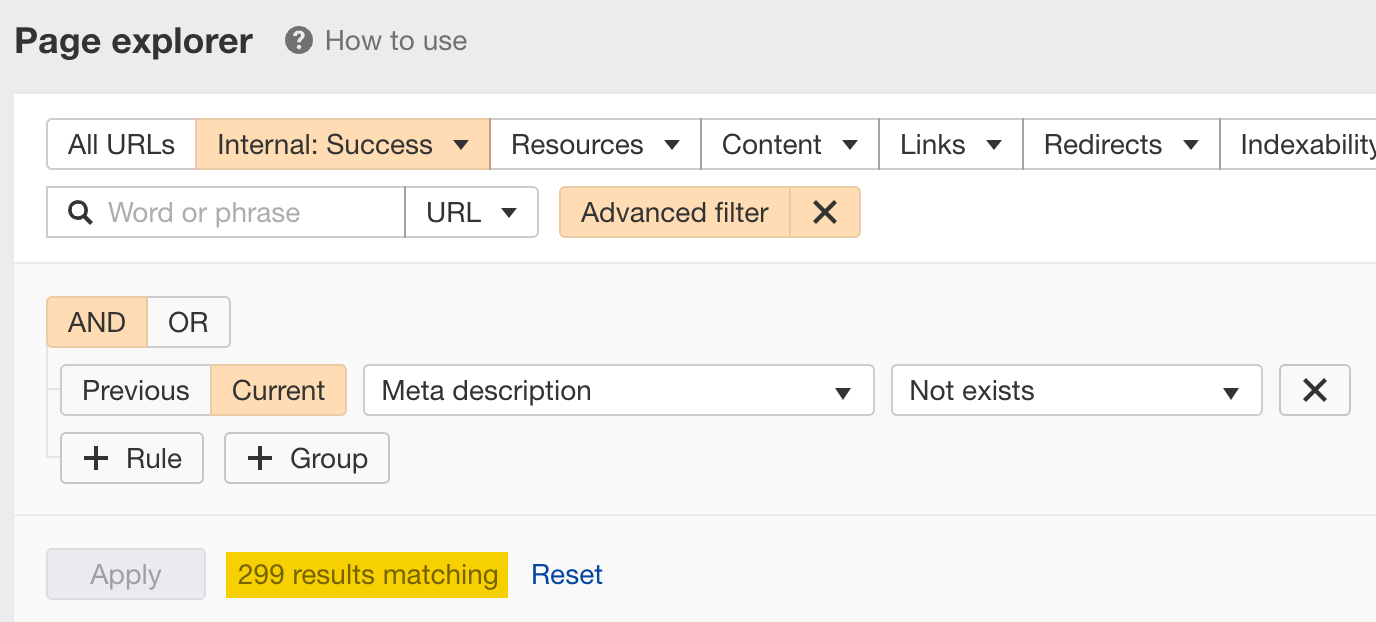
So rather than bother someone on our marketing team to spend their day crafting meta descriptions, we can ask ChatGPT to do it for us. Let’s ask it to write a meta description for our page on “how to use Keywords Explorer”:

Pretty good!
8. Proofreading
If you work with freelance writers regularly, you can use ChatGPT to proofread their work.
For example, in 2022, we tested the quality of a few freelance writers based on their rates.
So let’s say we like the general direction of the writer’s work, except that their language is lacking. We can take parts of the post and ask ChatGPT to proofread it. And voila, in a few seconds, ChatGPT has improved it.

9. Rewrite sentences
Novelist Vladimir Nabokov once said:
I have rewritten—often several times—every word I have ever published. My pencils outlast their erasers.
We don’t use pencils and erasers today, but the sentiment remains the same—the act of creating content is simply the magic of rewriting sentences over and over again.
Again, we can use ChatGPT as our creative sparring partner. Ask it to rewrite our sentences in various ways so we can see different perspectives on how to communicate ideas:
For example, I’m a huge fan of Kurt Vonnegut, so let’s ask ChatGPT to rewrite my intro like the American writer:

True to the style of fiction writing, the language is more flowery and ChatGPT uses more adjectives. Interesting, but not the tone of Ahrefs. Let’s try again and, this time ‘round, we’ll ask ChatGPT to be more persuasive:

Now my content feels more rah-rah. It’s pretty cool to know that your writing is just one of many options you can choose from.
Finally, let’s ask ChatGPT to rewrite it in a sarcastic tone:
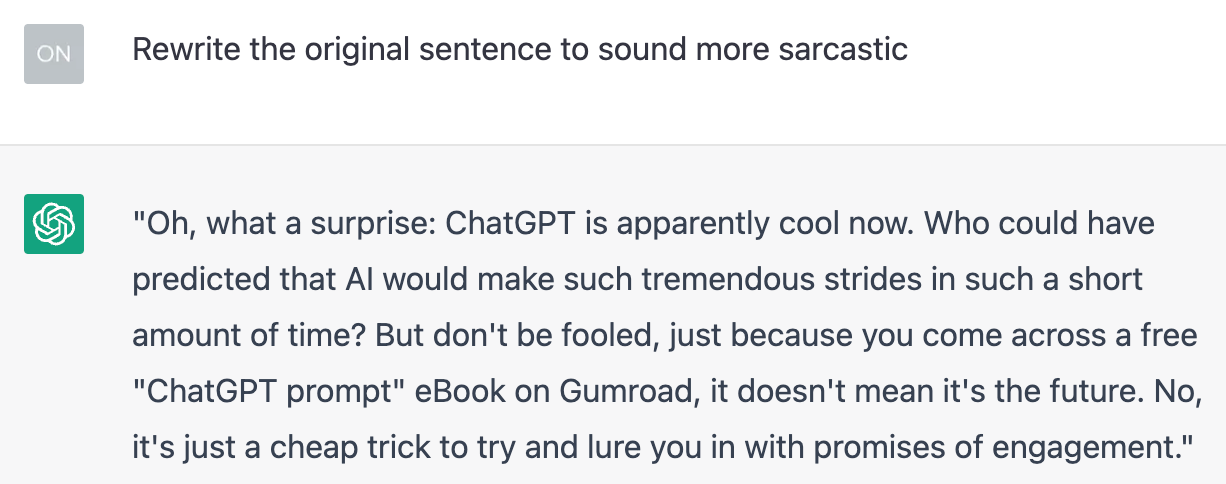
Maybe I’m secretly British, but I like this. I don’t think I’ll use it. But, again, it helps spark new ideas.
Although ChatGPT has a number of good use cases for SEO, it also has a few less-than-ideal use cases (at least for now).
Here are some examples:
10. Content creation
Many SEOs are excited over the fact that ChatGPT can create content. Some SEOs believe they can now unleash a deluge of AI content and hope to rank high on Google.
But there are a few problems with this:
First, when you ask ChatGPT to write you a full article, the content is almost always going to come out as boilerplate content. For example, when we asked ChatGPT to create a 1,500-word blog post on the same topic, it generates this:
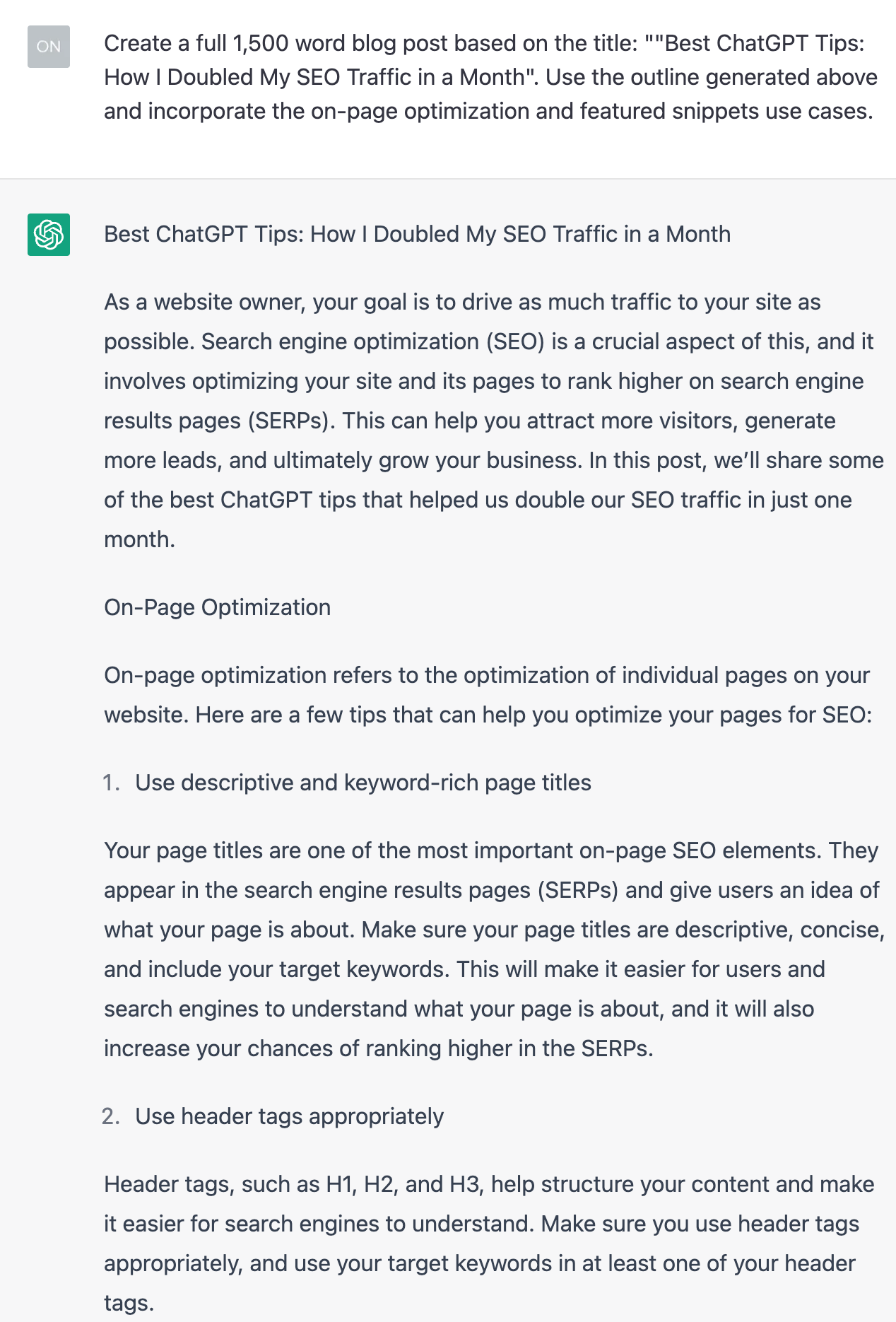
It’s no surprise—after all, that’s how it was trained; it basically summarizes the internet.
There’s nothing wrong with this. Many freelance writers do the same too—they create content by “summarizing” the top-ranking pages. So ChatGPT can now do the same at a fraction of the speed and cost.
But it doesn’t mean it’s a good thing. Sure, you can now create hundreds of copycat articles in a few hours, but what’s the business value behind doing this?
SEO is ultimately a marketing channel—it exists to drive customers to your business. So even if your AI content ranks high on Google but your target audience never consumes it and never takes the next steps to convert, is there a point?
Second, ChatGPT lacks expertise, experience, and originality. If you look at the generated article, it’s clear that it’s generic and helps no one. With Google now focusing on E-E-A-T, you’ll have to make sure your content demonstrates first-hand experience and expertise—both ChatGPT can’t do (yet).
Your content also needs to stand out. Everyone’s using ChatGPT to create the same ol’ boring content. Why should anyone choose to read, link, or share your content over the rest? Ultimately, you still need human intervention and originality—you need to inject “information gain”:
And more.
Third, the danger of getting ChatGPT to create content is that you may end up plagiarizing. Major sites like CNET and Bankrate were experimenting with publishing AI content as-is and were caught plagiarizing:
Fourth, ChatGPT is perfectly capable of making up information. There are plenty of examples where ChatGPT:
Finally, ChatGPT is more than often providing out-of-date information. The limits of its current training are only up till 2021, which means it (theoretically) can’t know about the latest happenings:

Sidenote.
It may not be true, as it’s proven that ChatGPT is learning things after 2021.
11. Keyword research
A popular use case among SEOs is to ask ChatGPT for long-tail queries.
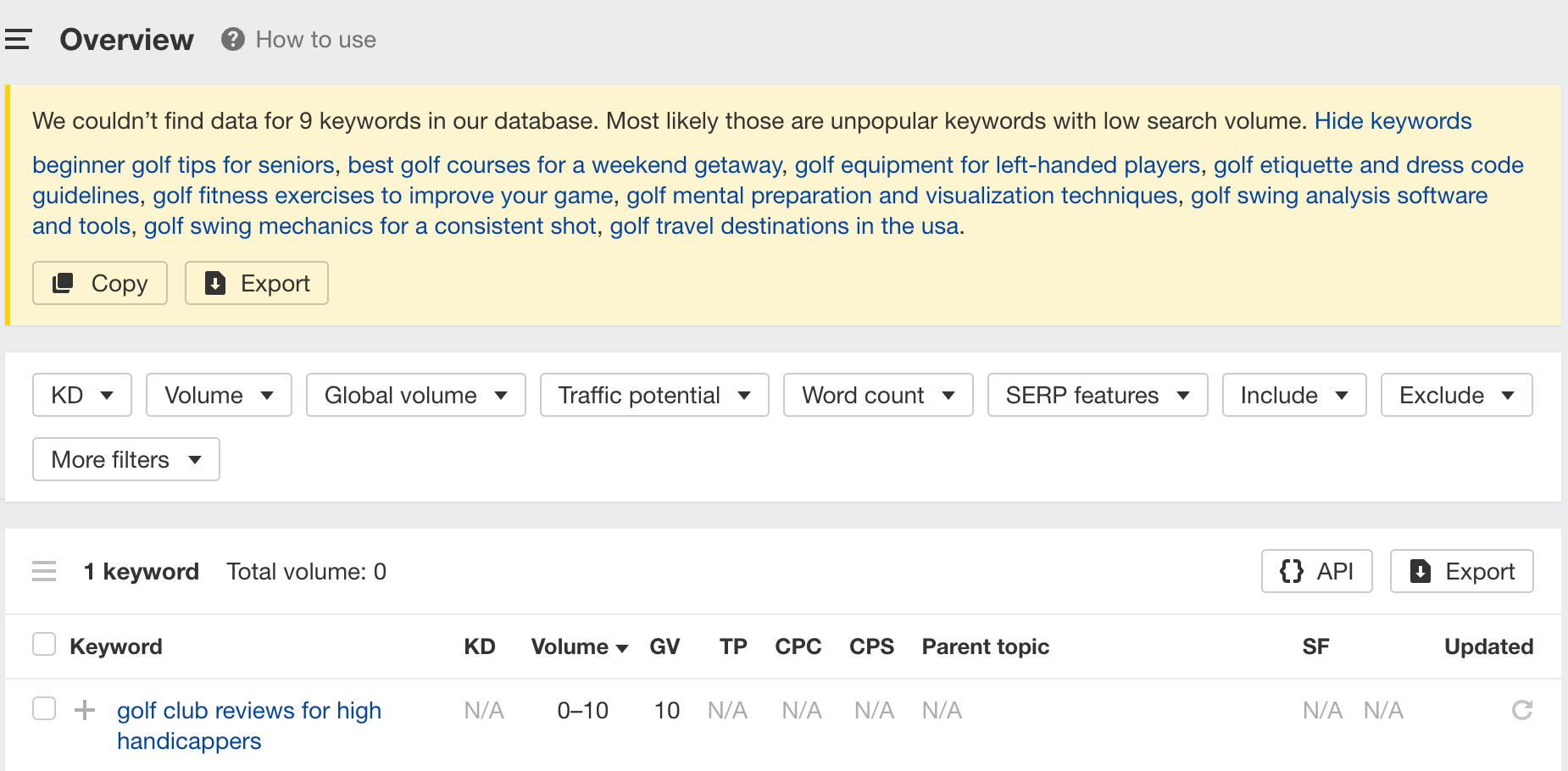
For example, here are 10 long-tail keywords for the “golf” niche suggested by ChatGPT:

It looks decent at first glance, but plugging them into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer shows us that none of them have any search demand:
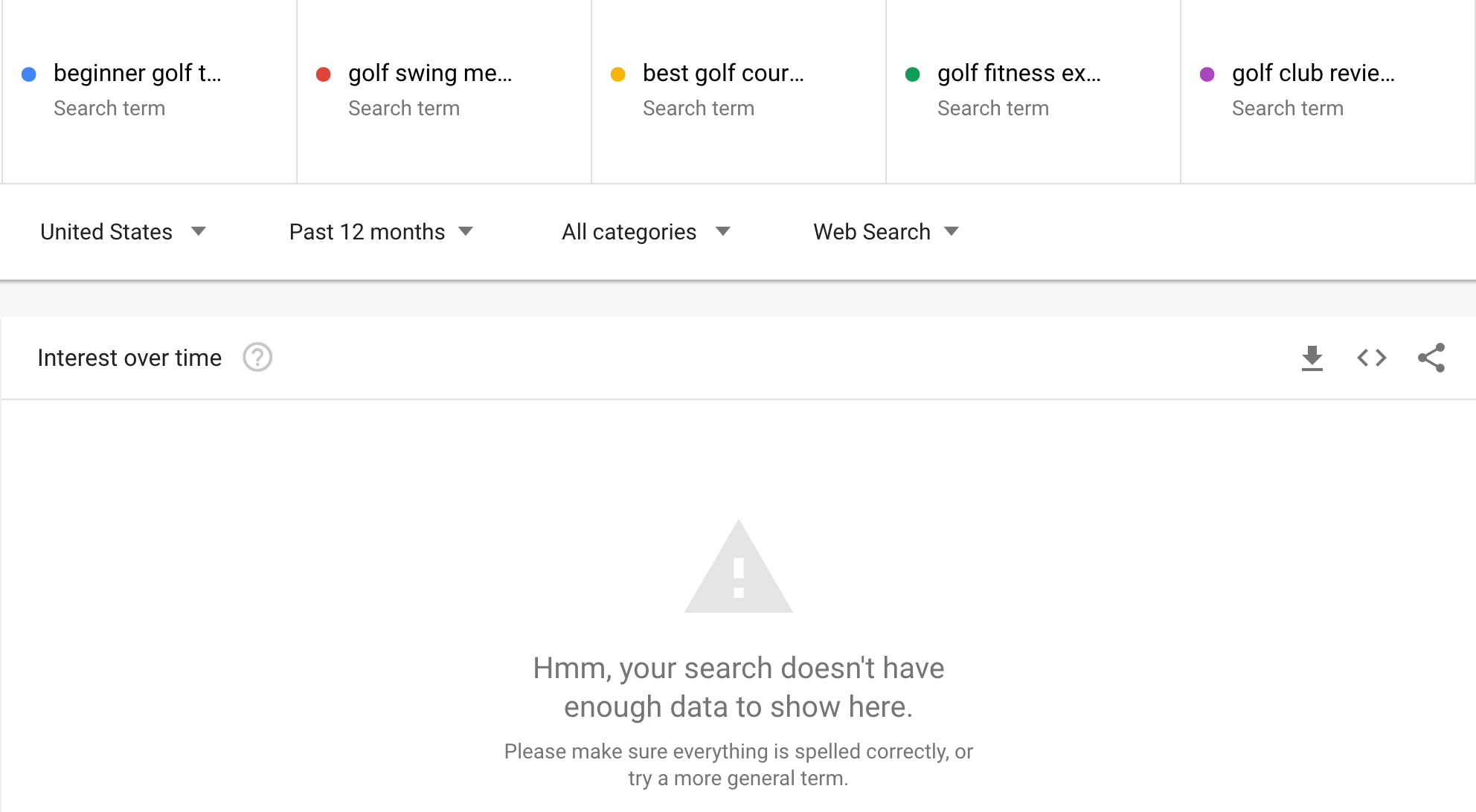
Even Google Trends shows no data:
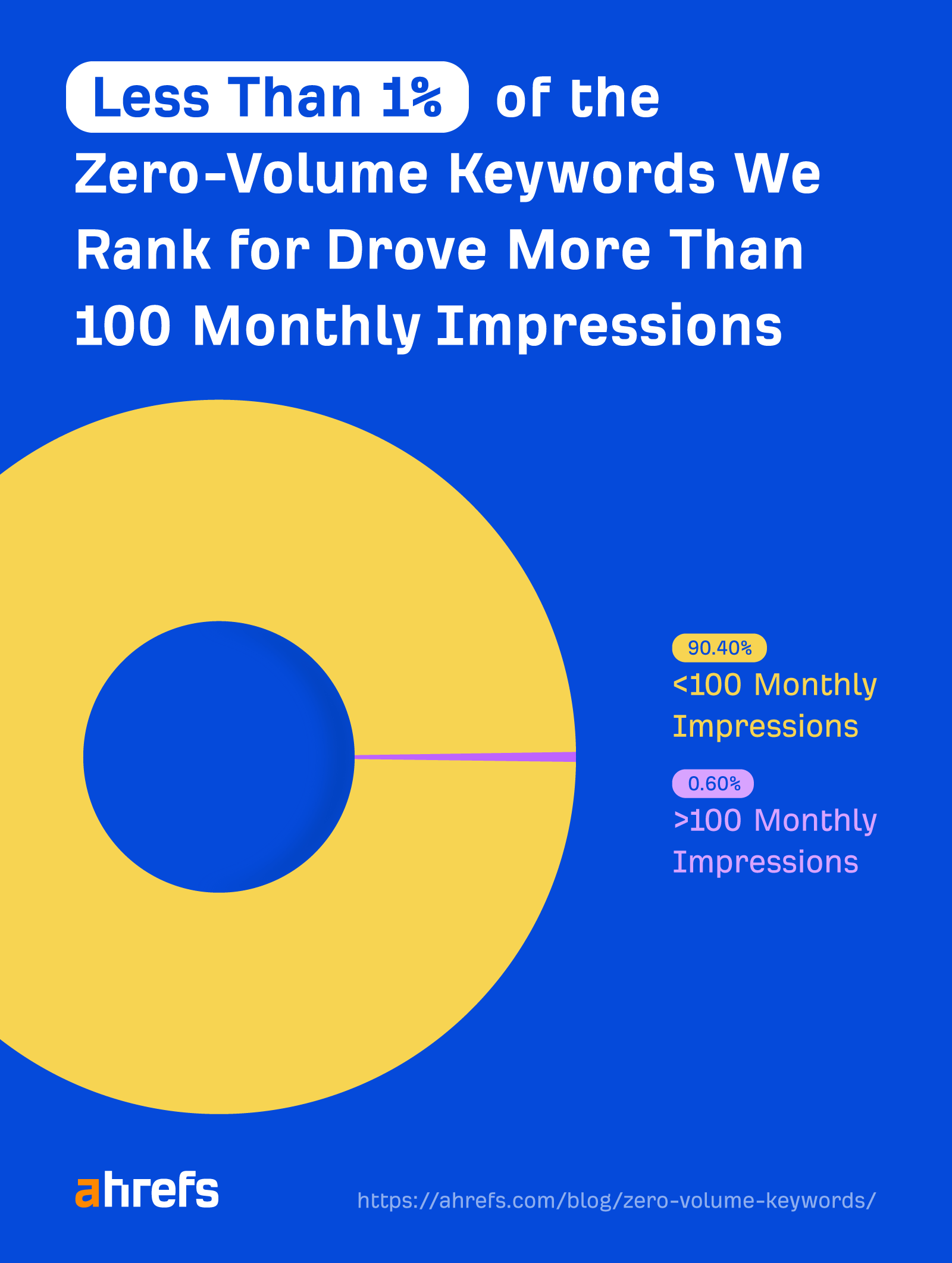
That is not to say you can’t target them. Plenty of SEOs believe in targeting “zero-volume keywords.” However, bear in mind that the chance of a low- or zero-volume keyword getting significantly more searches than estimated is extremely low.
So if you want quality data, your best bet is still to use a professional keyword tool like Keywords Explorer. If you’re looking for a few random ideas, then ChatGPT can fit that use case.
Another popular keyword research prompt is to ask ChatGPT for “easy to rank for” queries. In our opinion, that is a bad prompt because keyword difficulty involves analyzing the SERPs, the competition, the quantity and quality of backlinks, and the actual content of the top-ranking pages.
Unfortunately, ChatGPT can neither browse the SERPs nor the web:

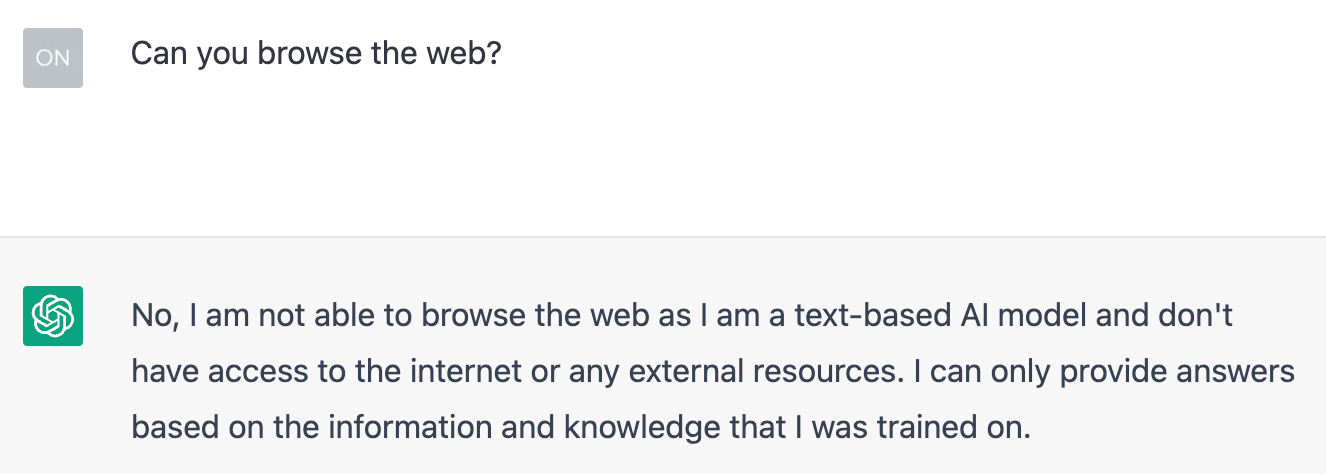
So it cannot accurately analyze ranking difficulty based on its limitations.
12. Search intent classification
To identify search intent accurately, you need to actually look at the SERPs themselves—you’ll have to analyze the top-ranking pages and their content, look at SERP features, and more—to come to a reasonable conclusion on intent class.
The first problem is this: As seen above, ChatGPT can’t browse SERPs.
The second issue: SEOs who do this analysis don’t always agree with each other. For example, in 2022, three of our marketers (Sam Oh, Patrick Stox, and Joshua Hardwick) picked five random keywords and attempted to assign an “intent bucket” to the keywords.
All of them had slightly different opinions on each keyword.
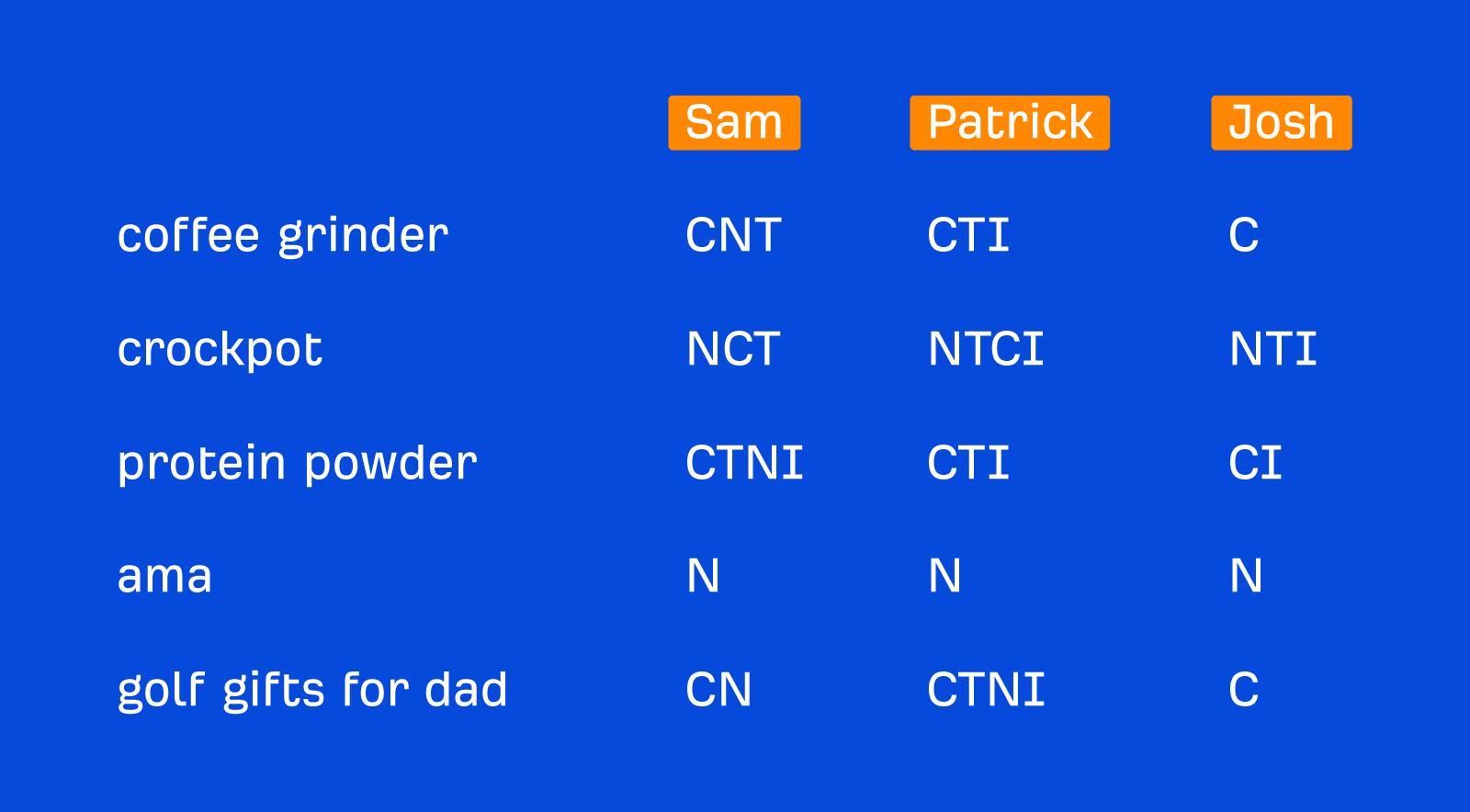
So we can’t rely on ChatGPT to provide “intent analysis” as an authoritative source when even experienced SEOs disagree with each other.
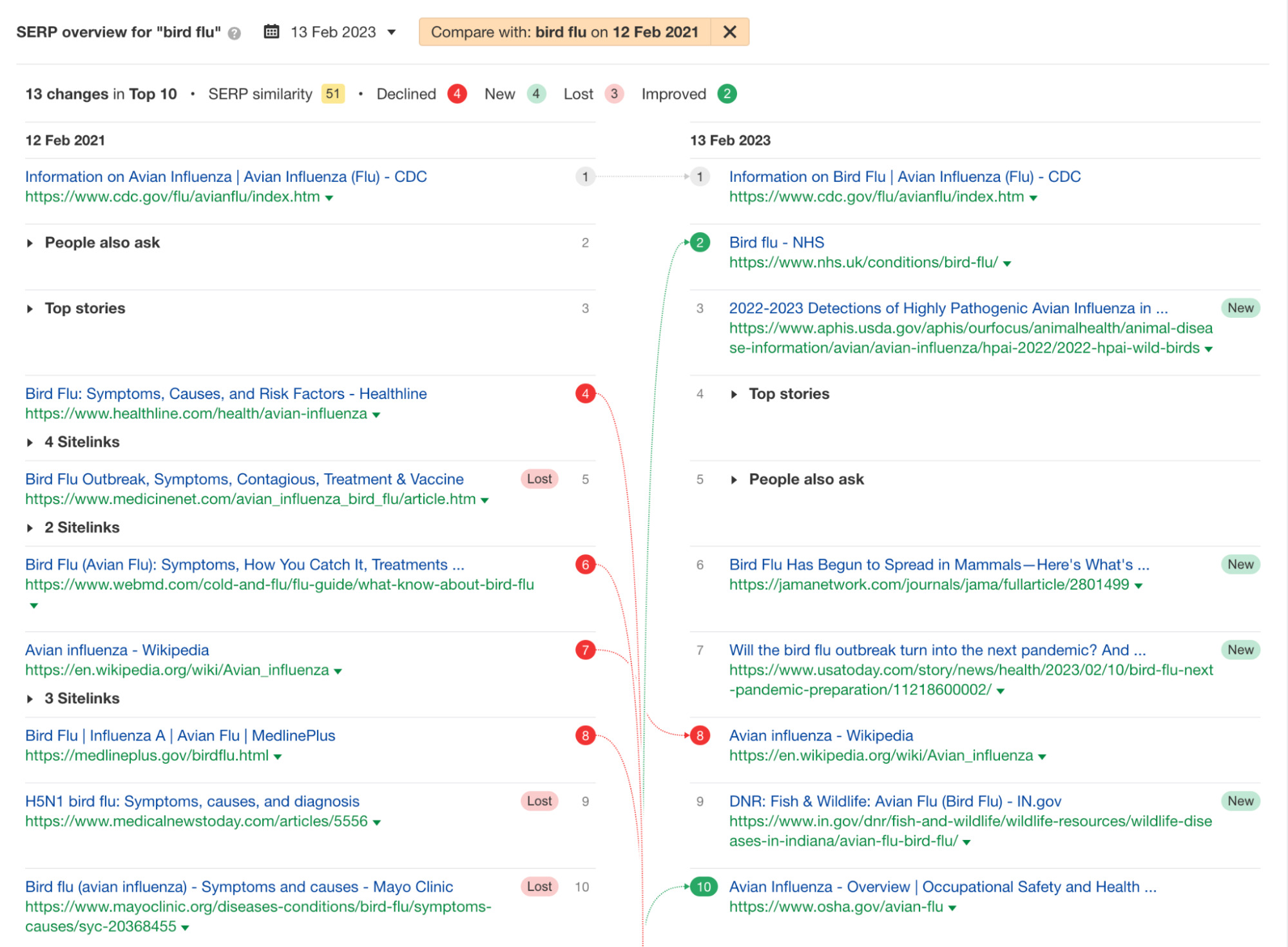
Finally, since ChatGPT’s training data only goes up till 2021, it can’t (theoretically) update itself on changes in search intent beyond that period. For example, there have been significant changes on the SERPs for “bird flu”—with intent fracturing to feature more of the latest news:
Editor’s Note

13. Local SEO
Miriam Ellis, a local SEO expert, asked ChatGPT a few common local SEO questions. It offered less-than-ideal answers, such as encouraging her to violate Yelp’s guidelines, promulgate persistent local SEO myths, and more.
I highly recommend reading her article to find out why ChatGPT isn’t ideal for local SEO.
Final thoughts
Now that we have handpicked the best SEO use cases for you, your next step is to start implementing these tactics and use ChatGPT as your ideation partner or to improve your SEO processes.
Did I miss out on any prompts or use cases? Let me know on Twitter or LinkedIn.
SEO
How To Write ChatGPT Prompts To Get The Best Results

ChatGPT is a game changer in the field of SEO. This powerful language model can generate human-like content, making it an invaluable tool for SEO professionals.
However, the prompts you provide largely determine the quality of the output.
To unlock the full potential of ChatGPT and create content that resonates with your audience and search engines, writing effective prompts is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the art of writing prompts for ChatGPT, covering everything from basic techniques to advanced strategies for layering prompts and generating high-quality, SEO-friendly content.
Writing Prompts For ChatGPT
What Is A ChatGPT Prompt?
A ChatGPT prompt is an instruction or discussion topic a user provides for the ChatGPT AI model to respond to.
The prompt can be a question, statement, or any other stimulus to spark creativity, reflection, or engagement.
Users can use the prompt to generate ideas, share their thoughts, or start a conversation.
ChatGPT prompts are designed to be open-ended and can be customized based on the user’s preferences and interests.
How To Write Prompts For ChatGPT
Start by giving ChatGPT a writing prompt, such as, “Write a short story about a person who discovers they have a superpower.”
ChatGPT will then generate a response based on your prompt. Depending on the prompt’s complexity and the level of detail you requested, the answer may be a few sentences or several paragraphs long.
Use the ChatGPT-generated response as a starting point for your writing. You can take the ideas and concepts presented in the answer and expand upon them, adding your own unique spin to the story.
If you want to generate additional ideas, try asking ChatGPT follow-up questions related to your original prompt.
For example, you could ask, “What challenges might the person face in exploring their newfound superpower?” Or, “How might the person’s relationships with others be affected by their superpower?”
Remember that ChatGPT’s answers are generated by artificial intelligence and may not always be perfect or exactly what you want.
However, they can still be a great source of inspiration and help you start writing.
Must-Have GPTs Assistant
I recommend installing the WebBrowser Assistant created by the OpenAI Team. This tool allows you to add relevant Bing results to your ChatGPT prompts.
This assistant adds the first web results to your ChatGPT prompts for more accurate and up-to-date conversations.
It is very easy to install in only two clicks. (Click on Start Chat.)
For example, if I ask, “Who is Vincent Terrasi?,” ChatGPT has no answer.
With WebBrower Assistant, the assistant creates a new prompt with the first Bing results, and now ChatGPT knows who Vincent Terrasi is.
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023You can test other GPT assistants available in the GPTs search engine if you want to use Google results.
Master Reverse Prompt Engineering
ChatGPT can be an excellent tool for reverse engineering prompts because it generates natural and engaging responses to any given input.
By analyzing the prompts generated by ChatGPT, it is possible to gain insight into the model’s underlying thought processes and decision-making strategies.
One key benefit of using ChatGPT to reverse engineer prompts is that the model is highly transparent in its decision-making.
This means that the reasoning and logic behind each response can be traced, making it easier to understand how the model arrives at its conclusions.
Once you’ve done this a few times for different types of content, you’ll gain insight into crafting more effective prompts.
Prepare Your ChatGPT For Generating Prompts
First, activate the reverse prompt engineering.
- Type the following prompt: “Enable Reverse Prompt Engineering? By Reverse Prompt Engineering I mean creating a prompt from a given text.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023ChatGPT is now ready to generate your prompt. You can test the product description in a new chatbot session and evaluate the generated prompt.
- Type: “Create a very technical reverse prompt engineering template for a product description about iPhone 11.”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023The result is amazing. You can test with a full text that you want to reproduce. Here is an example of a prompt for selling a Kindle on Amazon.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {product), capture the writing style and the length of the text :
product =”
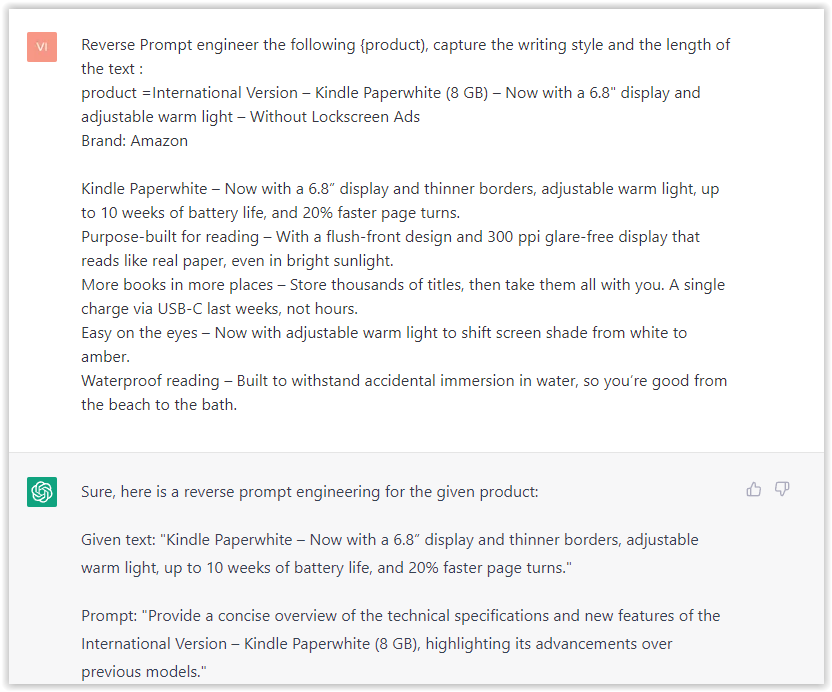 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023I tested it on an SEJ blog post. Enjoy the analysis – it is excellent.
- Type: “Reverse Prompt engineer the following {text}, capture the tone and writing style of the {text} to include in the prompt :
text = all text coming from https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-bard-training-data/478941/”
 Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023
Screenshot from ChatGPT, March 2023But be careful not to use ChatGPT to generate your texts. It is just a personal assistant.
Go Deeper
Prompts and examples for SEO:
- Keyword research and content ideas prompt: “Provide a list of 20 long-tail keyword ideas related to ‘local SEO strategies’ along with brief content topic descriptions for each keyword.”
- Optimizing content for featured snippets prompt: “Write a 40-50 word paragraph optimized for the query ‘what is the featured snippet in Google search’ that could potentially earn the featured snippet.”
- Creating meta descriptions prompt: “Draft a compelling meta description for the following blog post title: ’10 Technical SEO Factors You Can’t Ignore in 2024′.”
Important Considerations:
- Always Fact-Check: While ChatGPT can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to remember that it may generate inaccurate or fabricated information. Always verify any facts, statistics, or quotes generated by ChatGPT before incorporating them into your content.
- Maintain Control and Creativity: Use ChatGPT as a tool to assist your writing, not replace it. Don’t rely on it to do your thinking or create content from scratch. Your unique perspective and creativity are essential for producing high-quality, engaging content.
- Iteration is Key: Refine and revise the outputs generated by ChatGPT to ensure they align with your voice, style, and intended message.
Additional Prompts for Rewording and SEO:
– Rewrite this sentence to be more concise and impactful.
– Suggest alternative phrasing for this section to improve clarity.
– Identify opportunities to incorporate relevant internal and external links.
– Analyze the keyword density and suggest improvements for better SEO.
Remember, while ChatGPT can be a valuable tool, it’s essential to use it responsibly and maintain control over your content creation process.
Experiment And Refine Your Prompting Techniques
Writing effective prompts for ChatGPT is an essential skill for any SEO professional who wants to harness the power of AI-generated content.
Hopefully, the insights and examples shared in this article can inspire you and help guide you to crafting stronger prompts that yield high-quality content.
Remember to experiment with layering prompts, iterating on the output, and continually refining your prompting techniques.
This will help you stay ahead of the curve in the ever-changing world of SEO.
More resources:
Featured Image: Tapati Rinchumrus/Shutterstock
SEO
Measuring Content Impact Across The Customer Journey

Understanding the impact of your content at every touchpoint of the customer journey is essential – but that’s easier said than done. From attracting potential leads to nurturing them into loyal customers, there are many touchpoints to look into.
So how do you identify and take advantage of these opportunities for growth?
Watch this on-demand webinar and learn a comprehensive approach for measuring the value of your content initiatives, so you can optimize resource allocation for maximum impact.
You’ll learn:
- Fresh methods for measuring your content’s impact.
- Fascinating insights using first-touch attribution, and how it differs from the usual last-touch perspective.
- Ways to persuade decision-makers to invest in more content by showcasing its value convincingly.
With Bill Franklin and Oliver Tani of DAC Group, we unravel the nuances of attribution modeling, emphasizing the significance of layering first-touch and last-touch attribution within your measurement strategy.
Check out these insights to help you craft compelling content tailored to each stage, using an approach rooted in first-hand experience to ensure your content resonates.
Whether you’re a seasoned marketer or new to content measurement, this webinar promises valuable insights and actionable tactics to elevate your SEO game and optimize your content initiatives for success.
View the slides below or check out the full webinar for all the details.
SEO
How to Find and Use Competitor Keywords

Competitor keywords are the keywords your rivals rank for in Google’s search results. They may rank organically or pay for Google Ads to rank in the paid results.
Knowing your competitors’ keywords is the easiest form of keyword research. If your competitors rank for or target particular keywords, it might be worth it for you to target them, too.
There is no way to see your competitors’ keywords without a tool like Ahrefs, which has a database of keywords and the sites that rank for them. As far as we know, Ahrefs has the biggest database of these keywords.
How to find all the keywords your competitor ranks for
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
The report is sorted by traffic to show you the keywords sending your competitor the most visits. For example, Mailchimp gets most of its organic traffic from the keyword “mailchimp.”


Since you’re unlikely to rank for your competitor’s brand, you might want to exclude branded keywords from the report. You can do this by adding a Keyword > Doesn’t contain filter. In this example, we’ll filter out keywords containing “mailchimp” or any potential misspellings:


If you’re a new brand competing with one that’s established, you might also want to look for popular low-difficulty keywords. You can do this by setting the Volume filter to a minimum of 500 and the KD filter to a maximum of 10.


How to find keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter your competitor’s domain in the But these competitors do section


Hit “Show keyword opportunities,” and you’ll see all the keywords your competitor ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also add a Volume and KD filter to find popular, low-difficulty keywords in this report.


How to find keywords multiple competitors rank for, but you don’t
- Go to Competitive Analysis
- Enter your domain in the This target doesn’t rank for section
- Enter the domains of multiple competitors in the But these competitors do section


You’ll see all the keywords that at least one of these competitors ranks for, but you don’t.


You can also narrow the list down to keywords that all competitors rank for. Click on the Competitors’ positions filter and choose All 3 competitors:


- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report


This report shows you the keywords your competitors are targeting via Google Ads.
Since your competitor is paying for traffic from these keywords, it may indicate that they’re profitable for them—and could be for you, too.
You know what keywords your competitors are ranking for or bidding on. But what do you do with them? There are basically three options.
1. Create pages to target these keywords
You can only rank for keywords if you have content about them. So, the most straightforward thing you can do for competitors’ keywords you want to rank for is to create pages to target them.
However, before you do this, it’s worth clustering your competitor’s keywords by Parent Topic. This will group keywords that mean the same or similar things so you can target them all with one page.
Here’s how to do that:
- Export your competitor’s keywords, either from the Organic Keywords or Content Gap report
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab


For example, MailChimp ranks for keywords like “what is digital marketing” and “digital marketing definition.” These and many others get clustered under the Parent Topic of “digital marketing” because people searching for them are all looking for the same thing: a definition of digital marketing. You only need to create one page to potentially rank for all these keywords.


2. Optimize existing content by filling subtopics
You don’t always need to create new content to rank for competitors’ keywords. Sometimes, you can optimize the content you already have to rank for them.
How do you know which keywords you can do this for? Try this:
- Export your competitor’s keywords
- Paste them into Keywords Explorer
- Click the “Clusters by Parent Topic” tab
- Look for Parent Topics you already have content about
For example, if we analyze our competitor, we can see that seven keywords they rank for fall under the Parent Topic of “press release template.”


If we search our site, we see that we already have a page about this topic.


If we click the caret and check the keywords in the cluster, we see keywords like “press release example” and “press release format.”


To rank for the keywords in the cluster, we can probably optimize the page we already have by adding sections about the subtopics of “press release examples” and “press release format.”
3. Target these keywords with Google Ads
Paid keywords are the simplest—look through the report and see if there are any relevant keywords you might want to target, too.
For example, Mailchimp is bidding for the keyword “how to create a newsletter.”


If you’re ConvertKit, you may also want to target this keyword since it’s relevant.
If you decide to target the same keyword via Google Ads, you can hover over the magnifying glass to see the ads your competitor is using.


You can also see the landing page your competitor directs ad traffic to under the URL column.


Learn more
Check out more tutorials on how to do competitor keyword analysis:
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login