SEO
Maximizing Your SEO Investment: Tips For Outsourcing Effectively

Outsourcing SEO to a team of experienced professionals is one of the most reliable ways to increase your digital footprint and drive meaningful traffic to your site.
But ensuring your SEO partner integrates seamlessly with your business and consistently meets your expectations is easier said than done.
To get the best returns on your SEO investment, you need to set clear goals, strategically choose the right partner, and, crucially, foster a collaborative working relationship that adapts to shifting business needs and market conditions.
In this post, we’ll explore various strategies for developing and maintaining a fruitful partnership with your outsourced SEO team.
Let’s dive straight in.
What Does It Mean To Outsource Your SEO?
Outsourcing SEO is the process of hiring a third-party SEO expert or agency to oversee some or all of your SEO activities. This includes keyword research, link building, local SEO, content strategy and marketing, and technical SEO.
Outsourcing your SEO can be trickier than the other aspects of your marketing (or business).
Why?
SEO is a multifaceted discipline that requires experience and a tactical approach to deliver real results. You’re more likely to find freelancers who are experts in specific areas of SEO, not all areas of SEO.
Also, you’re torn between two options:
- Hiring an expert to oversee the individual components you don’t want to do yourself.
- Hiring a managed SEO agency that handles everything from scratch to finish.
For instance, if you’re adept at creating content but struggle with technical SEO, hiring a technical SEO expert will be more cost-effective than hiring an SEO agency. But this also means you must oversee all other aspects of SEO yourself.
Why Should You Consider Outsourcing Your SEO?
Outsourcing your SEO can help you achieve your SEO goals and scale more rapidly.
Also, if you feel your competitors are outshining you on the search engine results pages (SERPs) despite all your efforts, outsourcing to experts can help you gain a competitive advantage and improve your overall performance.
How To Outsource Your SEO: 5 Tips To Make It Effective
1. Lay The Groundwork For SEO Before Outsourcing
Before engaging with an SEO provider, it’s essential to recognize that your SEO efforts should be geared toward supporting your broader business objectives.
For example, if your business priority is to expand into new geographic markets, your SEO strategy might focus on localizing content and optimizing for regional search terms.
Alternatively, if you want to increase online product sales, your strategy might focus on optimizing product pages, improving user experience, and targeting high-intent commercial keywords.
Establishing these objectives early on will not only guide your SEO strategy but will also allow you to select an SEO partner whose strengths and experience align with your business needs.
Once you’ve aligned your business goals with your SEO ambitions, you should evaluate the current state of your site. Setting these benchmarks will provide a good baseline for measuring progress and give your outsourced team a clear picture of where your website currently stands.
Remember, there’s no need to conduct a thorough website audit yourself. Instead, you can use readily available tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to quickly gather top-level data about organic traffic, keyword rankings, and conversion rates.
2. Choose The Right SEO Partnership Model
Once you’ve defined your SEO goals and understand how your site is currently performing, it’s time to search for a suitable SEO provider.
There are three types of providers to choose from. Each option offers different advantages depending on your specific needs.
- An independent contractor or freelancer: Ideal for small projects or companies with limited budgets. Working with an independent professional offers flexibility and a more personalized approach, but may lack the broader capabilities and manpower of multi-person agencies.
- A full-service digital marketing agency: These agencies provide SEO along with other services like social media management, PPC, and email marketing. This model is suitable for businesses looking for a complete digital marketing strategy that ensures all elements are integrated and aligned.
- A specialist SEO agency: These agencies are laser-focused on SEO and are usually on the cutting edge of trends and algorithm changes, offering a depth of knowledge and tactical proficiency that generalist agencies might not offer.
Whichever model suits your business best, there are a few common qualities to look for in any worthwhile SEO partner. When considering potential suitors, look for those that can satisfy the following criteria:
- Expertise: Look for an SEO company with a long track record of executing successful SEO campaigns. Review their case studies, client testimonials, and official credentials to gauge their level of technical expertise and project management abilities.
- Industry experience: Ideally, your SEO partner will have experience running campaigns for businesses within your industry. This familiarity will make it easier for them to develop strategies that are more likely to succeed in your specific context.
- Transparency and communication: Clear and consistent communication is vital for the success of any SEO project. Look for a provider that values transparency and offers regular (and honest!) updates on campaign progress.
- Flexibility: The organic search landscape is constantly changing. Any provider worth your time should be tuned in to what your competitors are doing and stay up to speed on the latest developments in the world of SEO. They should be ready to adapt to shifting circumstances and innovate as needed to keep your SEO efforts effective.
- Cultural fit: The relationship with your SEO provider should be collaborative and synergistic. Make sure their values and company culture align with yours, as this will enhance the working relationship and contribute to a smoother project flow.
- A focus on results: Ultimately, you want a provider who is focused on achieving your specific business outcomes. Ensure they understand your goals and are committed to driving the results you need, whether it’s increasing traffic, improving keyword rankings, or boosting conversions.
As a marketer/business owner, you don’t have the resources or time to invest in the wrong agency. So, how can you find the best fit for your business?
- Go beyond the search results. Ask for recommendations from industry peers, online communities, and forums (e.g., LinkedIn, Twitter, and Reddit are great platforms to start with).
 Screenshot from Twitter, July 2024
Screenshot from Twitter, July 2024 Screenshot from Twitter, July 2024
Screenshot from Twitter, July 2024- Check out your competitor pages on LinkedIn to see if they’re managing their SEO in-house or attributing success to a particular agency. Sometimes, these agencies refrain from taking on two similar clients simultaneously, but their profiles can give you a good head start in your search process.
- Attend SEO-related virtual events to connect with experts in the industry. And even if they can’t handle your SEO, they could give you quality referrals.
- Make a list (on a spreadsheet) of the agencies/contractors/freelancers you got from your search. Segment them according to their years of experience, service offered, portfolio, etc. Here’s some inspiration:
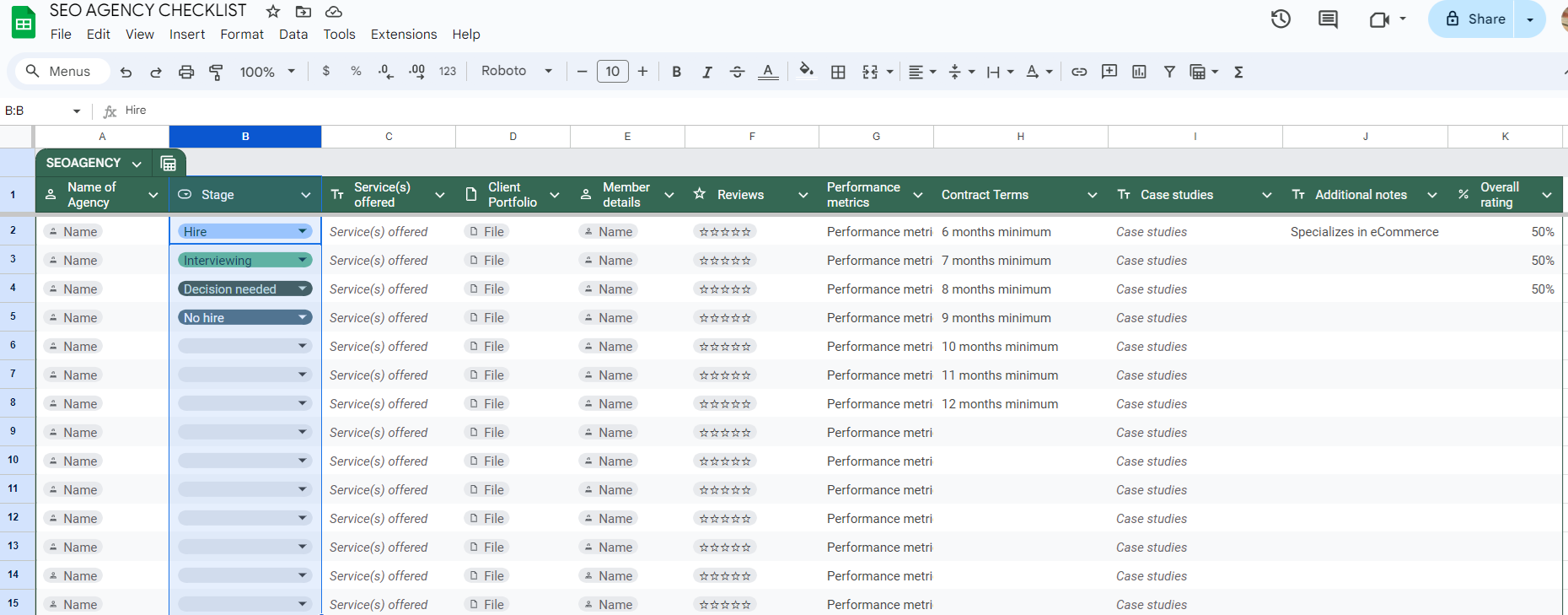 Screenshot from author, July 2024
Screenshot from author, July 20243. Vet The Shortlisted Agencies/Freelancers:
Now that you have a list, it’s time to go deeper into each to find the perfect fit for you.
Before I get into the details, keep in mind that any agency that guarantees results like a #1 rankings boost in your conversion rate after the first month is most likely a scam. Overall, anything that sounds too good to be true probably is.
- Check out the agency/freelancer service offerings. Some agencies/freelancers focus exclusively on specific areas of SEO, e.g., technical SEO, while others offer full-scale SEO. Unless you need specialized services, opt for those offering comprehensive services.
- How long have they been in the SEO industry? How many projects have they worked on within the period? If they can’t provide straightforward answers with proofs, tick them off your list.
- Next, examine their case studies (or portfolio). Have they worked with businesses similar to yours? Prioritize those with prior experience in your industry. This will shorten the learning curve and allow them to adopt strategies tailored to your needs.
- Sometimes, written words aren’t enough because anyone can claim to be an expert. Contact the agency/consultant for a one-on-one interview to discuss how they intend to achieve your SEO goals.
Ask questions like: ‘How would you solve my SEO goal?’ ‘Can you provide examples of successful SEO campaigns you’ve worked on?’ ‘How do you approach keyword research and selection for my business?’
- Go over their testimonials, too. What are people saying about them? Honest feedback from previous clients can give you a clear picture of what to expect when working with them. It’s also okay if they have one or two negative reviews – no one is perfect. What really matters is how they respond to them. So, be sure to check this out during your research.
- Add an extra layer of credibility to your search by checking out for industry-relevant awards.
4. Enhance Collaboration With Your SEO Partner
Once you’ve signed on with your new SEO provider, it’s essential to establish clear lines of communication from the get-go.
This means agreeing on a structured communication framework that defines how often you’ll interact and through what modes (e.g., email, phone, video calls).
Creating a regular schedule for updates and meetings will ensure that both parties stay informed and are able to make proactive adjustments to the SEO strategy.
Consider implementing a collaborative project management tool where both your internal employees and your SEO partner can view, track, and update progress on tasks.
Tools like Trello, Slack, or Asana can facilitate real-time updates and smooth communication. Note that some SEO providers will set up a customized reporting dashboard as part of their service offering.
It’s helpful to think of your SEO partner as an extension of your team rather than a separate entity. Try to encourage an open exchange of ideas, involve them in relevant internal discussions, and make sure they have ready access to necessary tools and data within your organization.
Remember, the goal is to create the most collaborative environment possible with minimal points of friction. Doing so will ensure that your SEO team can continually tweak their strategy to better meet your business needs and avoid unnecessary hold-ups in the progress of your campaign.
5. Leverage Your SEO Partner’s Expertise
Another way to maximize returns on your outsourced SEO investment is to take full advantage of the specialized knowledge your SEO partner brings to the table.
Your service agreement should include comprehensive, scheduled reporting focusing on critical SEO metrics such as keyword performance, traffic trends, and backlink acquisition.
However, the purpose of these reports isn’t just to provide data. They should serve as a foundation for strategic discussions that, if necessary, lead to tactical campaign adjustments. If you have questions about specific metrics or trends, or if you don’t understand the rationale behind a given strategy, these review sessions are the ideal time to ask for clarity.
Remember, a good SEO partner will have no qualms explaining their methodologies. After all, challenging assumptions are a healthy feature of any collaborative project.
Moreover, the more you and your team learn about the dynamics of SEO from your service provider, the better equipped you’ll be to integrate SEO thinking into broader marketing and business strategies.
This knowledge transfer not only optimizes your current investment but also prepares your team for future digital marketing challenges.
How Much Does Outsourcing SEO Cost?
There’s no fixed cost for outsourcing SEO, as the value depends on the level of expertise of the agency or freelancer, the scope of the project, etc.
On average, SEO consultants in the US charge $144.68/hour. Agencies charge a higher rate—$147.93/hour—primarily because of their massive talent pool, expertise, and access to advanced SEO tools.
Read more about SEO pricing here.
When Should You Outsource SEO?
You should outsource your SEO when you notice or get any of these results:
- You (or your marketing team) have a lot on your plate and need an extra hand.
- Your growth is stagnant, and you need fresh ideas to revitalize your current strategy.
- You want to scale but lack the expertise and resources to do so.
- Your SEO efforts are undefined, and you’re not seeing any positive results.
- You want to target new markets.
- You’re an SEO professional or agency experiencing a surge in client demand that exceeds your current capacity.
- Your team is great but not experts in SEO.
Final Thoughts
Outsourcing SEO allows you to benefit from expert, data-driven search strategies while keeping your focus on core business activities.
But making the most of your outsourced SEO investment sometimes feels like a whole new challenge in and of itself.
Fortunately, by following the tips outlined in this post, you can streamline the process, ensuring the partnership remains productive and stress-free.
More resources:
Featured Image: Ink Drop/Shutterstock
In-article screenshots taken by author



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













