SOCIAL
Germany weighs ban on Telegram, tool of conspiracy theorists
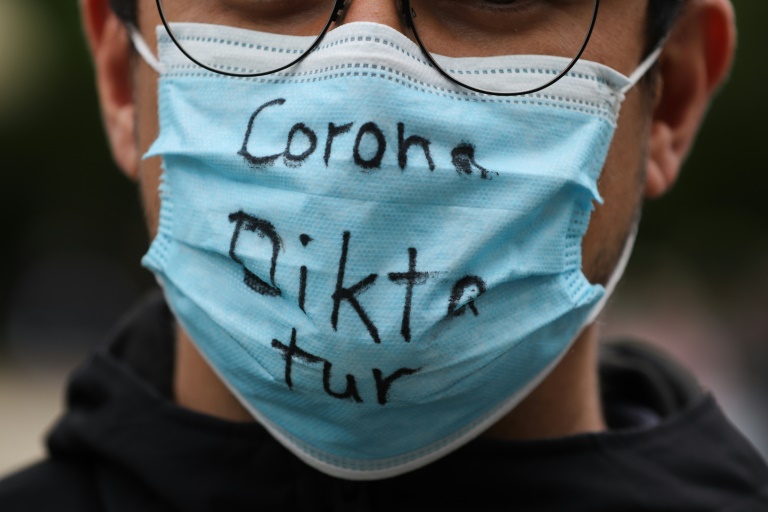

Germany has seen regular, sometimes violent, protests against Covid-related government restrictions – Copyright AFP Wakil KOHSAR
David COURBET
The German government is considering a ban on encrypted messaging app Telegram after it was repeatedly used as a channel for spreading anti-vaccine conspiracy theories and even death threats.
The app has also played a key role in mobilising turnout at some of the most violent protests in opposition to the German government’s Covid-19 policies since the start of the pandemic.
With parliament due to begin debating compulsory vaccination on Wednesday, authorities fear that the controversial issue could risk firing up another wave of rage.
With this in mind, politicians have set their sights on tighter controls on Telegram.
Interior Minister Nancy Faeser will unveil plans by Easter to require the app to delete messages that contain death threats or hate speech and identify their authors.
If Telegram fails to comply, the government could even ban the service completely.
“We will ensure that those spreading hate are identified and held accountable,” Faeser told the Bundestag lower house of parliament in mid-January.
She also told Die Zeit newspaper that Telegram could be deactivated in Germany if it failed to comply with local laws and “all other options have failed”.
Telegram chat groups, which can include up to 200,000 members, have been used by some anti-vaccine protesters to share false information and to encourage violence against politicians.
In December, German police seized weapons during raids in the eastern city of Dresden after a Telegram group was used to share death threats against a regional leader.
The same month, Telegram was used to mobilise a group of coronavirus-sceptics to mass outside the house of Petra Koepping, the health minister of Saxony state, armed with flaming torches.
A message viewed by 25,000 people had called for people opposing Covid restrictions to share private addresses of German “local MPs, politicians and other personalities” who they believed were “seeking to destroy” them through pandemic curbs.
– New avenues –
At the height of a refugee crisis that erupted in 2015, online social networking tools Facebook and Twitter fell foul of the authorities as they were seized by the far-right to spread virulent anti-immigrant content.
In 2017, Germany passed a controversial law that requires the social network giants to remove illegal content and report it to the police.
Facebook said in September it had deleted accounts, pages and groups linked to the “Querdenker” (Lateral Thinkers), a movement that has emerged as the loudest voice against the German government’s coronavirus curbs.
But that pushed opposing voices to other platforms, with Telegram emerging as the app of choice.
“Since the big platforms like Facebook no longer allow racist, anti-Semitic hate and far-right content like Holocaust denial, people who want to spread this are looking for new avenues,” Simone Rafael, digital manager for the Amadeu Antonio anti-racism foundation, told AFP.
“Currently, the most popular one in Germany is Telegram,” Rafael said.
While Facebook has an interest in maintaining a presence in Germany and has gradually submitted to national legislation, this is not the case with Telegram, the expert said.
“Telegram is not cooperating with the judicial or security authorities, even on indisputably punishable and reprehensible matters such as child pornography,” a behaviour that “deprives the state of any capacity for action”, Rafael said.
With Telegram not budging, German federal police are even planning to start flooding the company with requests for content deletion to push it into action, reported Die Welt daily.
– ‘Very bad signal’ –
One option for the government could be to require Google or Apple to remove Telegram from their app stores. However, this would not affect users who have already downloaded the app.
For Rafael, the only solution is to ban the app completely.
That would make Germany the first Western country to outlaw Telegram, created in 2013 by Russian brothers Nikolai and Pavel Durov, two opponents of Russian President Vladimir Putin who sought to avoid surveillance by their country’s secret services.
The company is currently headquartered in Dubai, with its parent group in British Virgin Islands.
Telegram is already banned or heavily regulated in China, India and Russia.
But a move against the app could also spark further dissent in Germany.
Such a drastic step would “send a very bad signal”, according to digital journalist Markus Reuter.
“On the one hand we are celebrating Telegram’s lack of censorship and its importance for democratic movements in Belarus and Iran, and on the other, we are then disabling the service here” in Germany, he said.
Source link
SOCIAL
Snapchat Explores New Messaging Retention Feature: A Game-Changer or Risky Move?
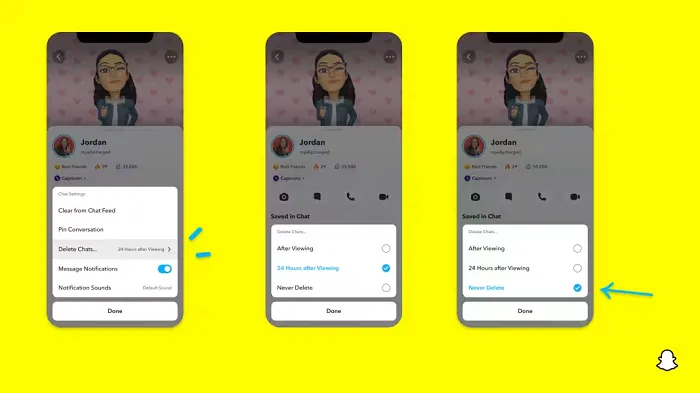
In a recent announcement, Snapchat revealed a groundbreaking update that challenges its traditional design ethos. The platform is experimenting with an option that allows users to defy the 24-hour auto-delete rule, a feature synonymous with Snapchat’s ephemeral messaging model.
The proposed change aims to introduce a “Never delete” option in messaging retention settings, aligning Snapchat more closely with conventional messaging apps. While this move may blur Snapchat’s distinctive selling point, Snap appears convinced of its necessity.
According to Snap, the decision stems from user feedback and a commitment to innovation based on user needs. The company aims to provide greater flexibility and control over conversations, catering to the preferences of its community.
Currently undergoing trials in select markets, the new feature empowers users to adjust retention settings on a conversation-by-conversation basis. Flexibility remains paramount, with participants able to modify settings within chats and receive in-chat notifications to ensure transparency.
Snapchat underscores that the default auto-delete feature will persist, reinforcing its design philosophy centered on ephemerality. However, with the app gaining traction as a primary messaging platform, the option offers users a means to preserve longer chat histories.
The update marks a pivotal moment for Snapchat, renowned for its disappearing message premise, especially popular among younger demographics. Retaining this focus has been pivotal to Snapchat’s identity, but the shift suggests a broader strategy aimed at diversifying its user base.
This strategy may appeal particularly to older demographics, potentially extending Snapchat’s relevance as users age. By emulating features of conventional messaging platforms, Snapchat seeks to enhance its appeal and broaden its reach.
Yet, the introduction of message retention poses questions about Snapchat’s uniqueness. While addressing user demands, the risk of diluting Snapchat’s distinctiveness looms large.
As Snapchat ventures into uncharted territory, the outcome of this experiment remains uncertain. Will message retention propel Snapchat to new heights, or will it compromise the platform’s uniqueness?
Only time will tell.
SOCIAL
Catering to specific audience boosts your business, says accountant turned coach

While it is tempting to try to appeal to a broad audience, the founder of alcohol-free coaching service Just the Tonic, Sandra Parker, believes the best thing you can do for your business is focus on your niche. Here’s how she did just that.
When running a business, reaching out to as many clients as possible can be tempting. But it also risks making your marketing “too generic,” warns Sandra Parker, the founder of Just The Tonic Coaching.
“From the very start of my business, I knew exactly who I could help and who I couldn’t,” Parker told My Biggest Lessons.
Parker struggled with alcohol dependence as a young professional. Today, her business targets high-achieving individuals who face challenges similar to those she had early in her career.
“I understand their frustrations, I understand their fears, and I understand their coping mechanisms and the stories they’re telling themselves,” Parker said. “Because of that, I’m able to market very effectively, to speak in a language that they understand, and am able to reach them.”Â
“I believe that it’s really important that you know exactly who your customer or your client is, and you target them, and you resist the temptation to make your marketing too generic to try and reach everyone,” she explained.
“If you speak specifically to your target clients, you will reach them, and I believe that’s the way that you’re going to be more successful.
Watch the video for more of Sandra Parker’s biggest lessons.
SOCIAL
Instagram Tests Live-Stream Games to Enhance Engagement

Instagram’s testing out some new options to help spice up your live-streams in the app, with some live broadcasters now able to select a game that they can play with viewers in-stream.
As you can see in these example screens, posted by Ahmed Ghanem, some creators now have the option to play either “This or That”, a question and answer prompt that you can share with your viewers, or “Trivia”, to generate more engagement within your IG live-streams.
That could be a simple way to spark more conversation and interaction, which could then lead into further engagement opportunities from your live audience.
Meta’s been exploring more ways to make live-streaming a bigger consideration for IG creators, with a view to live-streams potentially catching on with more users.
That includes the gradual expansion of its “Stars” live-stream donation program, giving more creators in more regions a means to accept donations from live-stream viewers, while back in December, Instagram also added some new options to make it easier to go live using third-party tools via desktop PCs.
Live streaming has been a major shift in China, where shopping live-streams, in particular, have led to massive opportunities for streaming platforms. They haven’t caught on in the same way in Western regions, but as TikTok and YouTube look to push live-stream adoption, there is still a chance that they will become a much bigger element in future.
Which is why IG is also trying to stay in touch, and add more ways for its creators to engage via streams. Live-stream games is another element within this, which could make this a better community-building, and potentially sales-driving option.
We’ve asked Instagram for more information on this test, and we’ll update this post if/when we hear back.
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login