TECHNOLOGY
Overview of Generative AI and ChatGPT
AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and natural language understanding.
AI is based on the idea of creating intelligent machines that can work and learn like humans. These machines can be trained to recognize patterns, understand speech, interpret data, and make decisions based on that data.
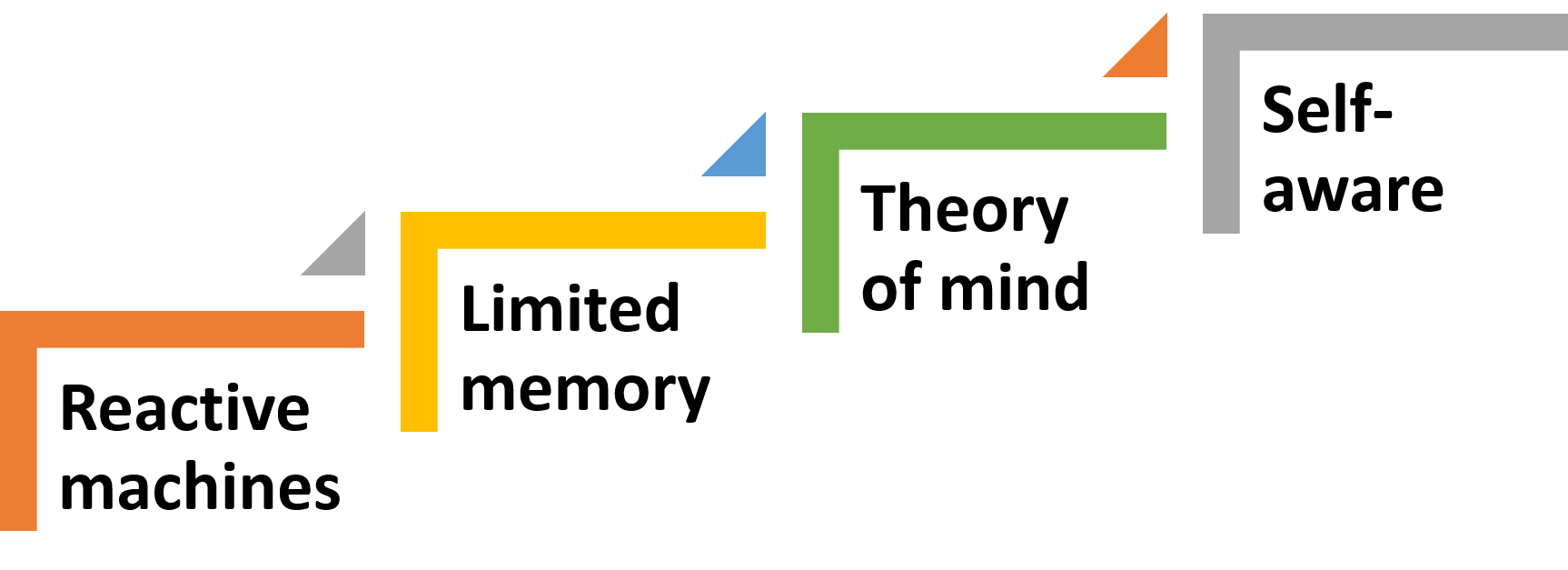
AI can be classified into different categories, such as:
1. Reactive machines: These machines can only react to specific situations based on pre-programmed rules.
2. Limited memory: These machines can learn from previous data and make decisions based on that data.
3. Theory of mind: These machines can understand human emotions and respond accordingly.
4. Self-aware: These machines can understand their own existence and modify their behavior accordingly.
AI has many practical applications, including speech recognition, image recognition, natural language processing, autonomous vehicles, and robotics, to name a few.
Another Classification of AI
Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, is an AI system designed to perform a specific task or set of tasks. These tasks are often well-defined and narrow in scope, such as image recognition, speech recognition, or language translation. Narrow AI systems rely on specific algorithms and techniques to solve problems and make decisions within their domain of expertise. These systems do not possess true intelligence, but rather mimic intelligent behavior within a specific domain.
General AI, also known as strong AI or human-level AI, is an AI system that can perform any intellectual task that a human can do. General AI would have the ability to reason, learn, and understand any intellectual task that a human can perform. It would be capable of solving problems in a variety of domains, and would be able to apply its knowledge to new and unfamiliar situations. General AI is often thought of as the ultimate goal of AI research, but is currently only a theoretical concept.
Super AI, also known as artificial superintelligence, is an AI system that surpasses human intelligence in all areas. Super AI would be capable of performing any intellectual task with ease, and would have an intelligence level far beyond that of any human being. Super AI is often portrayed in science fiction as a threat to humanity, as it could potentially have its own goals and motivations that could conflict with those of humans. Super AI is currently only a theoretical concept, and the development of such a system is seen as a long-term goal of AI research.

Technical Types of AI
1. Rule-based AI: Rule-based AI, also known as expert systems, is a type of AI that relies on a set of pre-defined rules to make decisions or recommendations. These rules are typically created by human experts in a particular domain, and are encoded into a computer program. Rule-based AI is useful for tasks that require a lot of domain-specific knowledge, such as medical diagnosis or legal analysis.
2. Supervised Learning: Supervised learning is a type of machine learning that involves training a model on a labeled dataset. This means that the dataset includes both input data and the correct output for each example. The model learns to map input data to output data, and can then make predictions on new, unseen data. Supervised learning is useful for tasks such as image recognition or natural language processing.
3. Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning that involves training a model on an unlabeled dataset. This means that the dataset only includes input data, and the model must find patterns or structure in the data on its own. Unsupervised learning is useful for tasks such as clustering or anomaly detection.
4. Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning that involves training a model to make decisions based on rewards and punishments. The model learns by receiving feedback in the form of rewards or punishments based on its actions, and adjusts its behavior to maximize its reward. Reinforcement learning is useful for tasks such as game playing or robotics.
5. Deep Learning: Deep learning is a type of machine learning that involves training deep neural networks on large datasets. Deep neural networks are neural networks with multiple layers, allowing them to learn complex patterns and structures in the data. Deep learning is useful for tasks such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
6. Generative AI: Generative AI is a type of AI that is used to generate new content, such as images, videos, or text. It works by using a model that has been trained on a large dataset of examples, and then uses this knowledge to generate new content that is similar to the examples it has been trained on. Generative AI is useful for tasks such as computer graphics, natural language generation, and music composition.
Generative AI
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that is used to generate new content, such as images, videos, or even text. It works by using a model that has been trained on a large dataset of examples, and then uses this knowledge to generate new content that is similar to the examples it has been trained on.
One of the most exciting applications of generative AI is in the field of computer graphics. By using generative models, it is possible to create realistic images and videos that look like they were captured in the real world. This can be incredibly useful for a wide range of applications, from creating realistic game environments to generating lifelike product images for e-commerce websites.
Another application of generative AI is in the field of natural language processing. By using generative models, it is possible to generate new text that is similar in style and tone to a particular author or genre. This can be useful for a wide range of applications, from generating news articles to creating marketing copy.
One of the key advantages of generative AI is its ability to create new content that is both creative and unique. Unlike traditional computer programs, which are limited to following a fixed set of rules, generative AI is able to learn from examples and generate new content that is similar, but not identical, to what it has seen before. This can be incredibly useful for applications where creativity and originality are important, such as in the arts or in marketing.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to generative AI. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the content generated by these models is not biased or offensive. Because these models are trained on a dataset of examples, they may inadvertently learn biases or stereotypes that are present in the data. This can be especially problematic in applications like natural language processing, where biased language could have real-world consequences.
Another challenge is ensuring that the content generated by these models is of high quality. Because these models are based on statistical patterns in the data, they may occasionally produce outputs that are nonsensical or even offensive. This can be especially problematic in applications like chatbots or customer service systems, where errors or inappropriate responses could damage the reputation of the company or organization.
Despite these challenges, however, the potential benefits of generative AI are enormous. By using generative models, it is possible to create new content that is both creative and unique, while also being more efficient and cost-effective than traditional methods. With continued research and development, generative AI could play an increasingly important role in a wide range of applications, from entertainment and marketing to scientific research and engineering.
One of the challenges in creating effective generative AI models is choosing the right architecture and training approach. There are many different types of generative models, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common types of generative models include variational autoencoders, generative adversarial networks, and autoregressive models.
Variational autoencoders are a type of generative model that uses an encoder-decoder architecture to learn a compressed representation of the input data, which can then be used to generate new content. This approach is useful for applications where the input data is high-dimensional, such as images or video.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are another popular approach to generative AI. GANs use a pair of neural networks to generate new content. One network generates new content, while the other network tries to distinguish between real and fake content. By training these networks together, GANs are able to generate content that is both realistic and unique.
Autoregressive models are a type of generative model that uses a probabilistic model to generate new content. These models work by predicting the probability of each output.
Future of Generative AI
Generative AI is a rapidly advancing field that holds enormous potential for many different applications. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see some exciting advancements and trends in the future of generative AI. Here are some possible directions for the field: Improved Natural Language Processing (NLP): Natural language processing is one area where generative AI is already making a big impact, and we can expect to see this trend continue in the future. Advancements in nlp will allow for more natural-sounding and contextually appropriate responses from chatbots, virtual assistants, and other AI-powered communication tools. Increased Personalization: As generative AI systems become more sophisticated, they will be able to generate content that is more tailored to individual users. This could mean everything from personalized news articles to custom video game levels that are generated on the fly. Enhanced Creativity: Generative AI is already being used to generate music, art, and other forms of creative content. As the technology improves, we can expect to see more and more AI-generated works of art that are indistinguishable from those created by humans. Better Data Synthesis: As data sets become increasingly complex, generative AI will become an even more valuable tool for synthesizing and generating new data. This could be especially important in scientific research, where AI-generated data could help researchers identify patterns and connections that might otherwise go unnoticed. Increased Collaboration: One of the most exciting possibilities for generative AI is its potential to enhance human creativity and collaboration. By providing new and unexpected insights, generative AI could help artists, scientists, and other creatives work together in novel ways to generate new ideas and solve complex problems.
The future of generative AI looks bright, with plenty of opportunities for innovation and growth in the years ahead.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a specific implementation of Generative AI that is designed to generate text in response to user input in a conversational setting. ChatGPT is based on the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture, which is a type of neural network that has been pre-trained on a massive amount of text data. This pre-training allows ChatGPT to generate high-quality text that is both fluent and coherent.
In other words, ChatGPT is a specific application of Generative AI that is designed for conversational interactions. Other applications of Generative AI may include language translation, text summarization, or content generation for marketing purposes.
ChatGPT is a powerful tool for natural language processing that can be used in a wide range of applications, from customer service to education to healthcare.
As an AI language model, ChatGPT’s future is constantly evolving and growing. Temperature is a parameter used in chatting with chatgpt to control the quality of the results (0.0 conservative, while 1.0 is creative ). With a temperature of 0.9, ChatGPT has the potential to generate more imaginative and unexpected responses, albeit at the cost of potentially introducing errors and inconsistencies.
In the future, ChatGPT will likely continue to improve its natural language processing capabilities, allowing it to understand and respond to increasingly complex and nuanced queries. It may also become more personalized, utilizing data from users’ interactions to tailor responses to individual preferences and needs.
However, as with any emerging technology, ChatGPT will face challenges, such as ethical concerns surrounding its use, potential biases in its responses, and the need to ensure user privacy and security.
The future of ChatGPT is exciting and full of potential. With continued development and improvement, ChatGPT has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology and each other, making communication faster, more efficient, and more personalized.
As with any emerging technology, ChatGPT will face challenges and limitations. Some potential issues include:
1. Ethical concerns: There are ethical concerns surrounding the use of AI language models like ChatGPT, particularly with regards to issues like privacy, bias, and the potential for misuse.
2. Accuracy and reliability: ChatGPT is only as good as the data it is trained on, and it may not always provide accurate or reliable information. Ensuring that ChatGPT is trained on high-quality data and that its responses are validated and verified will be crucial to its success.
3. User experience: Ensuring that users have a positive and seamless experience interacting with ChatGPT will be crucial to its adoption and success. This may require improvements in natural language processing and user interface design.
The future of ChatGPT is full of potential and promise. With continued development and improvement, ChatGPT has the potential to transform the way we interact with technology and each other, making communication faster, more efficient, and more personalized than ever before.
TECHNOLOGY
Next-gen chips, Amazon Q, and speedy S3

AWS re:Invent, which has been taking place from November 27 and runs to December 1, has had its usual plethora of announcements: a total of 21 at time of print.
Perhaps not surprisingly, given the huge potential impact of generative AI – ChatGPT officially turns one year old today – a lot of focus has been on the AI side for AWS’ announcements, including a major partnership inked with NVIDIA across infrastructure, software, and services.
Yet there has been plenty more announced at the Las Vegas jamboree besides. Here, CloudTech rounds up the best of the rest:
Next-generation chips
This was the other major AI-focused announcement at re:Invent: the launch of two new chips, AWS Graviton4 and AWS Trainium2, for training and running AI and machine learning (ML) models, among other customer workloads. Graviton4 shapes up against its predecessor with 30% better compute performance, 50% more cores and 75% more memory bandwidth, while Trainium2 delivers up to four times faster training than before and will be able to be deployed in EC2 UltraClusters of up to 100,000 chips.
The EC2 UltraClusters are designed to ‘deliver the highest performance, most energy efficient AI model training infrastructure in the cloud’, as AWS puts it. With it, customers will be able to train large language models in ‘a fraction of the time’, as well as double energy efficiency.
As ever, AWS offers customers who are already utilising these tools. Databricks, Epic and SAP are among the companies cited as using the new AWS-designed chips.
Zero-ETL integrations
AWS announced new Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Relational Database Services (Amazon RDS) for MySQL integrations with Amazon Redshift, AWS’ cloud data warehouse. The zero-ETL integrations – eliminating the need to build ETL (extract, transform, load) data pipelines – make it easier to connect and analyse transactional data across various relational and non-relational databases in Amazon Redshift.
A simple example of how zero-ETL functions can be seen is in a hypothetical company which stores transactional data – time of transaction, items bought, where the transaction occurred – in a relational database, but use another analytics tool to analyse data in a non-relational database. To connect it all up, companies would previously have to construct ETL data pipelines which are a time and money sink.
The latest integrations “build on AWS’s zero-ETL foundation… so customers can quickly and easily connect all of their data, no matter where it lives,” the company said.
Amazon S3 Express One Zone
AWS announced the general availability of Amazon S3 Express One Zone, a new storage class purpose-built for customers’ most frequently-accessed data. Data access speed is up to 10 times faster and request costs up to 50% lower than standard S3. Companies can also opt to collocate their Amazon S3 Express One Zone data in the same availability zone as their compute resources.
Companies and partners who are using Amazon S3 Express One Zone include ChaosSearch, Cloudera, and Pinterest.
Amazon Q
A new product, and an interesting pivot, again with generative AI at its core. Amazon Q was announced as a ‘new type of generative AI-powered assistant’ which can be tailored to a customer’s business. “Customers can get fast, relevant answers to pressing questions, generate content, and take actions – all informed by a customer’s information repositories, code, and enterprise systems,” AWS added. The service also can assist companies building on AWS, as well as companies using AWS applications for business intelligence, contact centres, and supply chain management.
Customers cited as early adopters include Accenture, BMW and Wunderkind.
Want to learn more about cybersecurity and the cloud from industry leaders? Check out Cyber Security & Cloud Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
TECHNOLOGY
HCLTech and Cisco create collaborative hybrid workplaces

Digital comms specialist Cisco and global tech firm HCLTech have teamed up to launch Meeting-Rooms-as-a-Service (MRaaS).
Available on a subscription model, this solution modernises legacy meeting rooms and enables users to join meetings from any meeting solution provider using Webex devices.
The MRaaS solution helps enterprises simplify the design, implementation and maintenance of integrated meeting rooms, enabling seamless collaboration for their globally distributed hybrid workforces.
Rakshit Ghura, senior VP and Global head of digital workplace services, HCLTech, said: “MRaaS combines our consulting and managed services expertise with Cisco’s proficiency in Webex devices to change the way employees conceptualise, organise and interact in a collaborative environment for a modern hybrid work model.
“The common vision of our partnership is to elevate the collaboration experience at work and drive productivity through modern meeting rooms.”
Alexandra Zagury, VP of partner managed and as-a-Service Sales at Cisco, said: “Our partnership with HCLTech helps our clients transform their offices through cost-effective managed services that support the ongoing evolution of workspaces.
“As we reimagine the modern office, we are making it easier to support collaboration and productivity among workers, whether they are in the office or elsewhere.”
Cisco’s Webex collaboration devices harness the power of artificial intelligence to offer intuitive, seamless collaboration experiences, enabling meeting rooms with smart features such as meeting zones, intelligent people framing, optimised attendee audio and background noise removal, among others.
Want to learn more about cybersecurity and the cloud from industry leaders? Check out Cyber Security & Cloud Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
TECHNOLOGY
Canonical releases low-touch private cloud MicroCloud

Canonical has announced the general availability of MicroCloud, a low-touch, open source cloud solution. MicroCloud is part of Canonical’s growing cloud infrastructure portfolio.
It is purpose-built for scalable clusters and edge deployments for all types of enterprises. It is designed with simplicity, security and automation in mind, minimising the time and effort to both deploy and maintain it. Conveniently, enterprise support for MicroCloud is offered as part of Canonical’s Ubuntu Pro subscription, with several support tiers available, and priced per node.
MicroClouds are optimised for repeatable and reliable remote deployments. A single command initiates the orchestration and clustering of various components with minimal involvement by the user, resulting in a fully functional cloud within minutes. This simplified deployment process significantly reduces the barrier to entry, putting a production-grade cloud at everyone’s fingertips.
Juan Manuel Ventura, head of architectures & technologies at Spindox, said: “Cloud computing is not only about technology, it’s the beating heart of any modern industrial transformation, driving agility and innovation. Our mission is to provide our customers with the most effective ways to innovate and bring value; having a complexity-free cloud infrastructure is one important piece of that puzzle. With MicroCloud, the focus shifts away from struggling with cloud operations to solving real business challenges” says
In addition to seamless deployment, MicroCloud prioritises security and ease of maintenance. All MicroCloud components are built with strict confinement for increased security, with over-the-air transactional updates that preserve data and roll back on errors automatically. Upgrades to newer versions are handled automatically and without downtime, with the mechanisms to hold or schedule them as needed.
With this approach, MicroCloud caters to both on-premise clouds but also edge deployments at remote locations, allowing organisations to use the same infrastructure primitives and services wherever they are needed. It is suitable for business-in-branch office locations or industrial use inside a factory, as well as distributed locations where the focus is on replicability and unattended operations.
Cedric Gegout, VP of product at Canonical, said: “As data becomes more distributed, the infrastructure has to follow. Cloud computing is now distributed, spanning across data centres, far and near edge computing appliances. MicroCloud is our answer to that.
“By packaging known infrastructure primitives in a portable and unattended way, we are delivering a simpler, more prescriptive cloud experience that makes zero-ops a reality for many Industries.“
MicroCloud’s lightweight architecture makes it usable on both commodity and high-end hardware, with several ways to further reduce its footprint depending on your workload needs. In addition to the standard Ubuntu Server or Desktop, MicroClouds can be run on Ubuntu Core – a lightweight OS optimised for the edge. With Ubuntu Core, MicroClouds are a perfect solution for far-edge locations with limited computing capabilities. Users can choose to run their workloads using Kubernetes or via system containers. System containers based on LXD behave similarly to traditional VMs but consume fewer resources while providing bare-metal performance.
Coupled with Canonical’s Ubuntu Pro + Support subscription, MicroCloud users can benefit from an enterprise-grade open source cloud solution that is fully supported and with better economics. An Ubuntu Pro subscription offers security maintenance for the broadest collection of open-source software available from a single vendor today. It covers over 30k packages with a consistent security maintenance commitment, and additional features such as kernel livepatch, systems management at scale, certified compliance and hardening profiles enabling easy adoption for enterprises. With per-node pricing and no hidden fees, customers can rest assured that their environment is secure and supported without the expensive price tag typically associated with cloud solutions.
Want to learn more about cybersecurity and the cloud from industry leaders? Check out Cyber Security & Cloud Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days ago5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoWeekend Google Core Ranking Volatility
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoThe power of program management in martech
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 15, 2024
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days agoWordPress Releases A Performance Plugin For “Near-Instant Load Times”









![The Current State of Google's Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] The Current State of Google's Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It-400x240.jpg)
![The Current State of Google's Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] The Current State of Google's Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It-80x80.jpg)




You must be logged in to post a comment Login