TECHNOLOGY
Transforming the Future of Technology and Connectivity

The Rise of Edge Computing: Transforming the Future of Technology and Connectivity
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the need for efficient data processing and reduced latency has become paramount.
As a response to this demand, a new computing paradigm known as edge computing has emerged. Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, enabling real-time processing and reduced reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure. This article will delve into the rise of edge computing, its implications for various industries, and how it is transforming the future of technology and connectivity.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing can be defined as a decentralized computing model that places computational resources and data storage closer to the edge of the network, near the source of data generation.

Unlike traditional centralized cloud computing, where data is processed in remote data centers, edge computing performs computation and analysis at or near the edge devices themselves. This decentralized architecture aims to bring processing power and storage capabilities closer to the data source, enabling faster and more efficient data processing.
Advantages and Benefits of Edge Computing
One of the key advantages of edge computing is reduced latency. By processing data closer to the edge devices, the time it takes for data to travel to and from remote cloud servers is minimized. This reduction in latency enables faster response times, making it ideal for real-time applications where immediate processing and decision-making are crucial.
Edge computing also enhances reliability. By distributing computing resources across multiple edge devices, the system becomes less reliant on a single central server. This redundancy improves system reliability, as failures in individual edge devices do not lead to complete service disruptions. It also mitigates the risks associated with network connectivity issues or latency problems that can occur when relying solely on centralized cloud infrastructure.
Furthermore, edge computing enables real-time decision making. By analyzing and processing data at the edge, immediate insights and actions can be taken without the need for constant communication with remote cloud servers. This capability is particularly valuable in time-sensitive applications such as autonomous vehicles, where split-second decisions can significantly impact safety and efficiency.
Applications and Use Cases of Edge Computing
Edge computing has a wide range of applications across various industries. In the Internet of Things (IoT) domain, edge computing plays a crucial role. By performing local data processing and analysis at the edge devices, it reduces the need for constant communication with the cloud, improving efficiency, reducing bandwidth requirements, and enhancing security.
Autonomous vehicles also heavily rely on edge computing. The ability to process data in real-time at the edge enables object recognition, collision detection, and immediate response times, making autonomous driving safer and more efficient.
In the healthcare industry, edge computing has the potential to revolutionize patient care. Remote patient monitoring, real-time diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans can all benefit from the fast and localized processing capabilities of edge computing. By analyzing health data at the edge, healthcare professionals can provide timely interventions and improve patient outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers numerous advantages, it also comes with challenges that need to be addressed. Security and privacy are major concerns, as sensitive data is processed and stored closer to the edge devices. Proper encryption, data protection measures, and secure communication protocols are essential to mitigate these risks.
Scalability and management of distributed edge infrastructure can also be challenging. As the number of edge devices increases, ensuring seamless integration, network connectivity, and device management becomes crucial. Standardization and interoperability among different edge computing solutions are necessary to create a cohesive and scalable ecosystem.
What’s Next for Edge Computing?
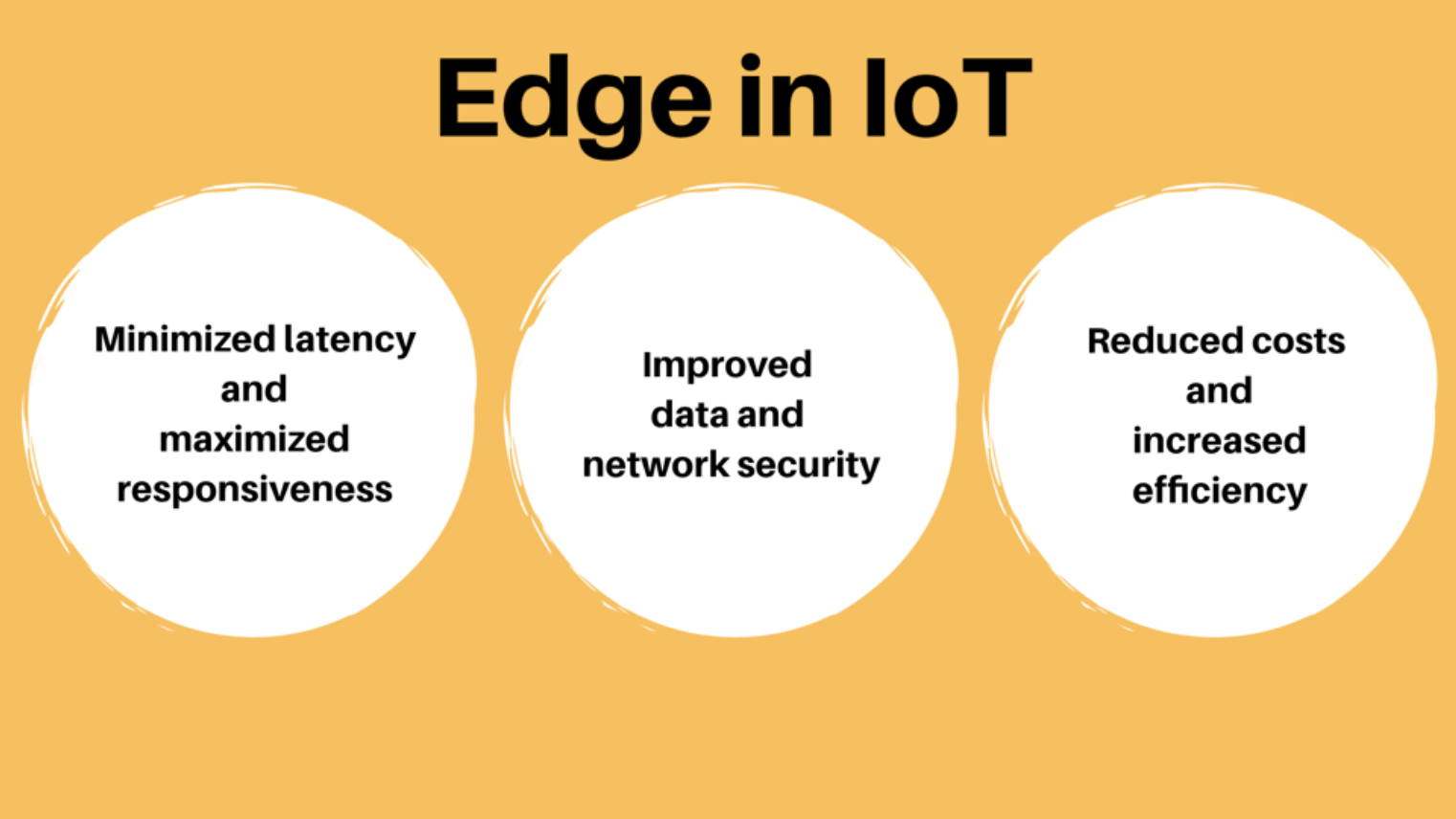
Organizations using edge computing to power their IoT systems can minimize the latency of their network, i.e., they can minimize the time for response between client and server devices. The rise of edge computing represents a significant shift in the way data is processed, analyzed, and utilized. By bringing computation closer to the edge of the network, edge computing offers reduced latency, improved reliability, and real-time decision-making capabilities. With applications spanning across IoT, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and beyond, edge computing is reshaping the future of technology and connectivity.