The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Senate Explores Changing DMCA

A Senate committee is investigating updating the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). The goal is to modernize the DMCA to make it easier to protect copyrighted content while also defending fair use rights. The Internet Archive responded to a call for feedback by encouraging the committee to keep things as they are.
Copyright Reform
The chair of the Senate Judiciary Committee’s Intellectual Property Panel, Thom Tillis, signaled his intention of overhauling copyright law in order to better address how today’s Internet has evolved, as well as new technologies like software and the rights of those users.
The breadth of change under discussion seeks to keep up to date with modern technology and how users interact with it.
Senator Thom Tillis wrote:
“Rather, than tinker around the edges of existing provisions, I believe Congress should reform copyright law’s framework to better encourage the creation of copyrightable works and to protect users and consumers making lawful uses of copyrighted goods and software-enabled products, respectively.”
The first part that is relevant to online publishers seeks to address differences in needs between smaller and larger stakeholders.
What Thom Tillis wants to do is streamline the takedown process and make it into a staydown system, where a copyright holder only needs to notify an Online Service Provider (OSP) once about infringing material.
Thereafter, it becomes the OSPs responsibility to monitor for repeat infringements and take them down without having to burden the copyright holder.
Furthermore, he said that the needs of a small stakeholder and those of the small OSP have things in common and that the laws should be crafted to reflect that.
This is how the Senator explained it:
“The record established in my DMCA reform hearings indicated that an overarching principle of any reform should be making digital copyright less one-size-fits-all. The law needs to account for the fact that small copyright owners and small online services providers (OSPs) may have more in common with each other than they do with big copyright owners and big OSPs, respectively.
Accordingly, I think we should consider whether copyright law should be revised to account for such differences among stakeholders. “
The Internet Archive disagreed and downplayed problems with the DMCA as a perception of a problem and questioned if problems with the DMCA actually existed.
The Internet Archive refers to “perceived” problems in their response, which is to say that what looks like a problem is only a perception of a problem but not actually a problem.
Internet Archive response:
“The idea of dividing the world into “large” vs. “small” online service providers and copyright owners is intuitively appealing as a solution to some of the perceived problems with the DMCA…”
The non-profit then questions whether problems with the DMCA actually exists:
“However, it is unclear exactly what problems these changes would solve.”
The Internet Archive then states how “large” organizations are already able to handle DMCA requests in a manner that results in a staydown.
“Most of the large platforms such as YouTube and Facebook have already voluntarily developed technology and entered into agreements with large rights holders in order to go above and beyond the requirements of
the statute because it has been in their business interest to do so.YouTube’s much discussed Content ID program is just one such example.
Smaller and non-profit organizations likely have not invested in these responses because they do not have the resources.”
While the Internet Archive’s intent might have been to show how the current system is working because large organizations are being proactive, they also highlighted the lack of resources that smaller organizations have to be proactive in the manner that larger organizations are able to.
That answer seems to agree with the Senator’s premise that small copyright holders and small OSPs have a common interest in that small organizations have less resources than large organizations to send out take down notices and to institute staydown policies.
Replace Takedown Notices with Staydown Notices
The committee chair proposed streamlining the process so that copyright holders needn’t have to shoulder the burden of constantly sending out take down notices to the same organizations. That way, once a notice has been served it becomes the burden of the OSP to take down repeat infringers.
The Senator’s suggestion does not address how a smaller OSP would be able to keep track of multiple infringements.
This is the change under discussion:
“Section 512 places the burden on copyright owners to identify infringing materials and affirmatively ask the OSP to remove the material or disable access to it. This burden appears to strike the correct balance, but the burden that the notice-and-takedown system itself places on copyright owners is too heavy; the system is also woefully inefficient for both copyright owners and service providers.
I believe U.S. copyright law should move towards some type of a notice-and-staydown system—in other words, once a copyright owner notifies a service provider that a use of a copyrighted work is infringing, the service provider must, without further prompting, remove subsequent infringing uses absent a statement from the user (whether the copyright owner or not) that they believe the use is licensed or otherwise authorized by law (e.g., fair use).”
The Internet Archive argued that a staydown approach would be unworkable for five reasons:
1. By making content removal automatic in a staydown approach, it removes the human element from judging whether something is indeed fair use or a copyright infringement. They argue that manual inspection cannot be scaled, meaning that the burden should remain on the copyright holder to identify violations.
The Internet Archive cited having received DMCA notices that were in error or applied to a small part of a larger work, implying that an automatic staydown response would unfairly remove non-infringing content.
2. They argued that an automatic staydown could result in “broad censorship” in that OSPs would have to use an algorithm developed by a third party to make the decision. Furthermore, this kind of system doesn’t have a context for or make allowances for how to file a counter-notification against taking the content down in an automated staydown approach.
3. Filtering technologies can be bypassed with links to infringing content.
4. Notice and Staydown systems would be burdensome and costly for OSPs. They cite that YouTube spent $60 million dollars developing their Content ID anti-infringement system.
5. They noted that there is no evidence whether a notice and staydown approach is effective.
Many DMCA Changes Suggested
These are just some of the changes to the DMCA that are being discussed. Other changes involve creating better mechanisms for contesting a takedown request, automating the takedown process. Among the changes to accomplish this is to remove the litigation from Federal courts and move them to small claims court.
There is also a nod toward increasing the privacy of those involved by not removing personally identifiable information including addresses.
Then there is also the goal of protecting fair use. Because the DMCA agreements between the infringed creator and the OSP don’t address third parties that may be entitled to fair use of the work, the concern is that the DMCA law may discourage fair use and lead to increased automatic takedowns of work that does not infringe on the copyright holder.
That concern is one of the issues that the Internet Archive raised as well.
Here is what the senator wrote:
“One concern with the voluntary agreements that copyright owners and OSPs adopt to supplement section 512 is that third-party interests are not often represented in the agreements.
That can lead to concerns that certain copyright owners may be shutout from utilizing an OSP or including their works in an OSP’s monetization program, or that the speech of specific users and consumers may be censored.
I am interested in protecting these interests possibly by allowing for regulatory review to ensure that voluntary agreements do not prohibit uses authorized by law (e.g., fair use) or otherwise unduly burden third parties, including copyright owners not party to an agreement.”
Should the DMCA Be Updated?
Twenty two years have passed since the creation of the DMCA. Much has changed about the Internet, how users share content and many other considerations. Additionally, there may be ways to improve the system by making it easier for stakeholders to defend their fair use of content. Being able to litigate in Small Claims court also takes away the fear that a DMCA request might turn into an expensive Federal court case.
But the Internet Archive says that there is no evidence that this kind of notice and staydown system will work.
“…we do not have any evidence as to whether “staydown” systems work at all. The Copyright Office reported that it does not have sufficient empirical evidence on the efficacy of staydown requirements…the prudent course of action for Congress would be to wait and see what evidence develops from jurisdictions that have invested in staydown approaches…”
How do you feel about the DMCA? Do you feel it can be improved?
Citation
Read the Senate Committee reform suggestions and the answers by the Internet Archive here:
Re: DMCA Reform Bill Questions from Senator Tillis for Stakeholders
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
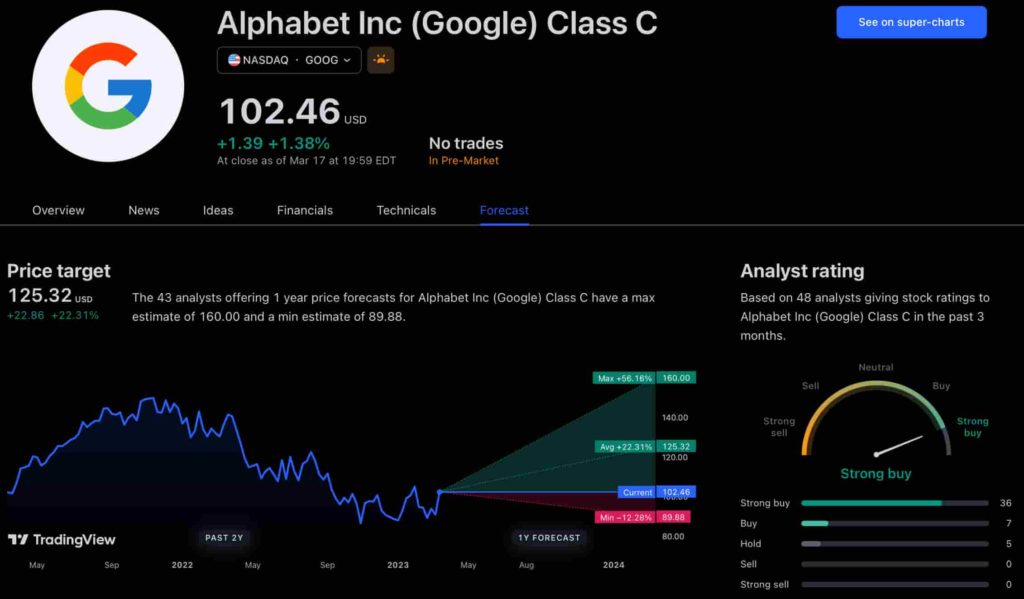
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days ago10 WordPress Influencers to Follow in 2024 – WordPress.com News
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoFeeling Stuck: What to Do When You Don’t Know What to Do
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoCompetitor Monitoring: 7 ways to keep watch on the competition
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoA History of Google AdWords and Google Ads: Revolutionizing Digital Advertising & Marketing Since 2000
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoThrive Architect vs Divi vs Elementor
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoMore Google March 2024 Core Update Ranking Volatility
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago31 Ready-to-Go Mother’s Day Messages for Social Media, Email, & More
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoTurkish startup ikas attracts $20M for its e-commerce platform designed for small businesses