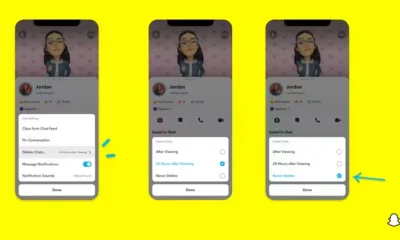
The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
With kids and adults staying at home, are virtual worlds ready for primetime?

We’ve been diligently following the development of virtual worlds, also known as the “metaverse,” on TechCrunch.
Hanging out within the virtual worlds of games has become more popular in recent years with the growth of platforms like Roblox and open-world games like Fortnite, but it still isn’t a mainstream way to socialize outside of the young-adult demographic.
Three weeks ago, TechCrunch media columnist Eric Peckham published an in-depth report that positioned virtual worlds as the next era of social media. In an eight-part series, he looked at the history of virtual worlds and why games are already social networks, why social networks want more gaming, what the next few years looks like for the industry and why isn’t it mainstream already, how these virtual worlds will lead to healthier social relations, what the future of virtual economies will be and which companies are poised for success in this new market.
Given all that has changed in just the last three weeks — who would have thought that large swaths of the knowledge economy would suddenly find themselves entirely interacting virtually? — I wanted to get a sense of what the rising popularity of virtual worlds looks like in the midst of the outbreak of novel coronavirus. Eric and I had a call to discuss this and decided to share our conversation publicly.
Danny Crichton: So let’s talk about timing a bit. You wrote this eight-article series around virtual worlds and then all of a sudden post-publication there is this massive event — the novel coronavirus pandemic — causing a large portion of the human population to stay at home and interact only online. What’s happening now in the space?
Eric Peckham: I wrote my series on the multiverse because I was already seeing a surge of interest, both in terms of consumer demand for open-world MMO games and in terms of social media giants like Facebook and Snap trying to incorporate virtual worlds and social games into their platforms. Large companies are planning for virtual worlds in a way that is actionable and not just a futuristic vision. Over the last couple of years there has also been a lot of VC investment into a handful of startups focused on building next-generation virtual worlds for people to spend time in, virtual worlds with complex societies shaped by users’ contributions.
Talking to founders and investors in the gaming space, there has been a huge increase in usage over the last few weeks as more people hang out at home playing games, whether it’s on the adult side or the kid side.
Most of these next-generation virtual worlds are still in private beta but already popular platforms like Roblox, Minecraft, and Fortnite are getting substantially more use than normal. A large portion of people stuck at home are escaping via the virtual worlds of games.
You wrote this whole analysis before you knew the extent of the pandemic — how has the outlook changed for this industry?
This accelerates the timeline of virtual worlds being a mainstream place to hang out and socialize in daily life. I think people will be at home for multiple months, not just a couple of weeks, and it’s going to change people’s perspectives on socializing and working from home.
That’s a really powerful cultural shift. It’s getting more people beyond the core gaming community excited about spending time in virtual worlds and hanging out with their friends there.
We have seen this most heavily with the youngest generation of internet users. The majority of kids 9-12 years old are users of Minecraft and Roblox who hang out there with friends after school. We’ll see that expand to older demographics more quickly than it was going to before.
One of the complaints that I’ve seen on Twitter is that even though we have one of the largest global human lockdowns of all time, all the VR headsets are basically gone. Is VR a key component of virtual worlds?
Well, you don’t need VR headsets in order to spend meaningful time with others in a virtual space. Hundreds of millions of people already do it through their mobile phones and through PCs and consoles.
This is at the heart of the gaming industry: creating virtual worlds for people to spend time in, both pursuing the mission of whatever a game is designed for but also interacting with others. Among the most popular mobile and PC games last year were massively multiplayer online (MMO) games.
Talking about gaming, one facet of the story that I thought was particularly interesting was the fact that gaming was still not that high in terms of market penetration in the population.
More than two billion people play video games in the context of a year. There’s incredible market penetration in that sense. But, at least for the data I’ve seen for the U.S., the percent of the population who play games on a given day is still much lower than the percent of the population who use social media on a given day.
The more that games become virtual worlds for socializing and hanging out beyond just the mission of the gameplay, the more who will turn to virtual worlds as a social and entertainment outlet when they have five minutes free to do something on their phone. Social media fills these small moments in life. MMO games right now don’t because they are so oriented around the gameplay, which takes time and uninterrupted focus. Virtual worlds in the vein of those on Roblox where you just hang out and explore with friends compete for that time with Instagram more directly.
Theater chains like Regal and AMC announced this week that they are entirely shutting down to wait out the pandemic. Is that going to affect these virtual world companies?
I think they are separate parts of media. Cinema attendance has been declining quite substantially for years, and the way the industry has made up for that is trying to turn cinemas into these premium experiences and increasing ticket prices. Kids are just as likely, if not more likely, to play a game together on a Friday night as they are to go to the cinema. Cinemas are less culturally relevant to young people than they once were.
We’ve seen a massive experiment in work from home, which is a form of virtual world, or at least, a virtual workplace. When it comes to popularizing virtual worlds, is it going to come from the entertainment side or the more productivity-oriented platforms?
It will come from the entertainment side, and from younger people using it to socialize, in part because there’s less fear around cultural etiquette compared to people meeting in a business setting who are worried about a virtual world context not feeling as professional. Over time, as virtual worlds become pervasive in our social lives they will become more natural places to chat with people about business as well.
As more and more people are working online and interacting virtually, a big question is how you get beyond Zoom calls or the technology that’s currently in the market for virtual conferences to something that feels more like walking around and chatting with people in person. It’s tough to do without the ability to walk around a virtual space. You can’t have those unplanned small group or one-on-one interactions with people you don’t know if you’re just boxes within a Zoom call or some other broadcast. It will be interesting to see what develops around virtual business conferences that stems from virtual world technology. I’ve seen a few teams exploring this.
Last question here, but we are looking at a major recession in the economy, and so how does the landscape of people earning money from virtual worlds change with coronavirus?
The second-to-last article in my series is about the virtual economies around virtual worlds. Any virtual world inherently has commerce and people have already been making real-world money from games and from early virtual worlds like Second Life.
Both people staying home amid the coronavirus and the recession that we seem to be entering are pressures that will push more people to look online for ways to make money. That will only increase the activity of virtual economies around some of these worlds, whether those are formally built into the game or they’re happening in a gray or black market around the games (which is more common).
Thanks, Eric.
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
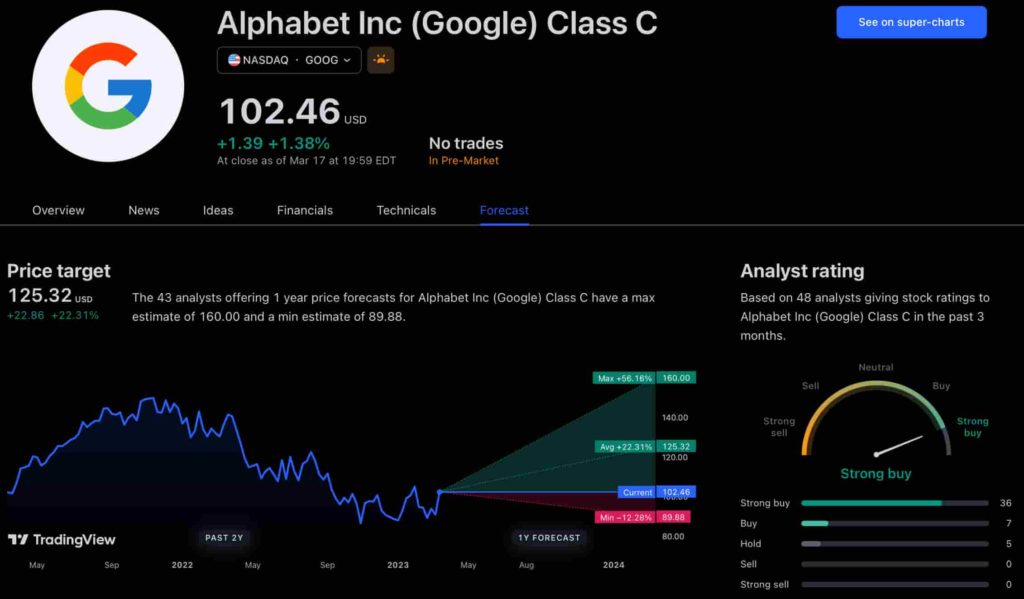
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago25 WordPress Alternatives Best For SEO