SEO
Google Business Profile Suspended? Here’s How To Get Reinstated

For most small businesses, Google Business Profile (GBP) is their marketing lifeblood.
Because it’s free, many local businesses rely solely on their Google Business Profile to generate traffic and calls, as well as to bring customers to their business.
Marketers know it’s risky to put all your marketing eggs in one basket.
But for a local business that has a limited budget – or no marketing budget at all – a free GBP listing is often all they have to promote their business online.
When a business’s GBP listing gets suspended, it can literally make a company’s sales come to a screeching halt. And in some cases, I’ve seen companies go out of business due to a suspension.
A suspended GBP listing will cause the business owner a lot of stress and worry – especially when most aren’t sure why they were suspended in the first place.
What Is A Google Business Profile Suspension?
A Google Business Profile suspension is when your GBP listing is no longer visible on Google and Google Maps, or you have lost control of your listing (your business listing is essentially “unverified,” and you can’t manage it.)
You will know that your listing has been suspended when you see one of these notifications in your GBP dashboard:
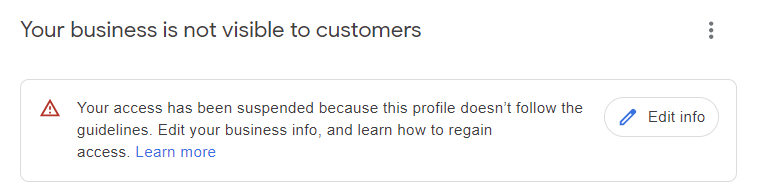
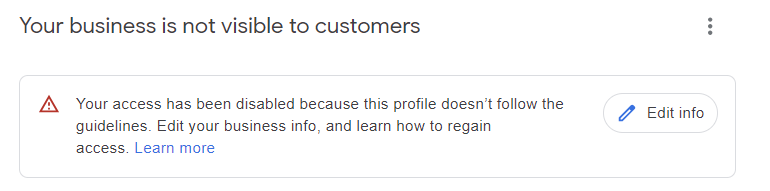 Screenshot from Google Business Profile dashboard, February 2024
Screenshot from Google Business Profile dashboard, February 2024
You will also get an email from Google letting you know that your GBP listing has been suspended.
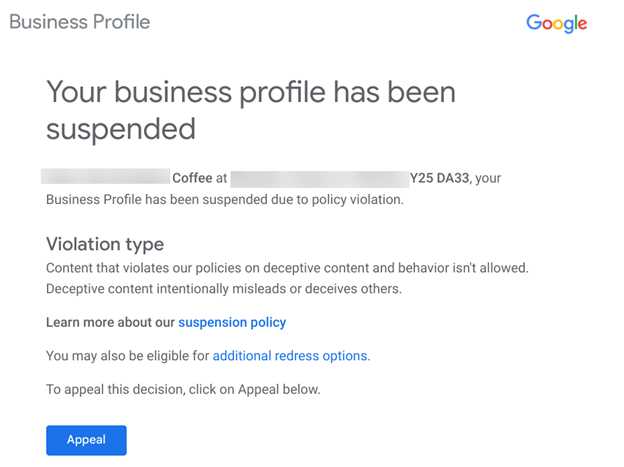 Screenshot of email, February 2024
Screenshot of email, February 2024
When your listing gets suspended, in the email you receive, Google will give you the “violation type.” This will give you a general idea of the reason your listing got suspended.
GBP listings can get suspended for various reasons – many of which have to do with spammy tactics or if the GBP listing owner breaks Google Business Profile Guidelines.
Google can also give you a Manual Suspension if it reviews your listing and finds an issue with it.
This review often comes after someone reports your listing through GBP’s Redressal Form.
It’s also possible for a user to report a listing on Google Maps or search through the Suggest an edit feature.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
If that person is “trusted” enough by Google, it is possible that their suggestion to remove the business listing or make negative edits could take effect almost immediately. Sometimes, these changes can cause a suspension.
Suspensions can also happen after you make changes to your listing.
For instance, one of my client’s listings was immediately suspended after he correctly changed his landscaping business from a storefront with a physical address (his home) to a service area business by deleting the address.
Immediately after he deleted the address from the listing, his GBP profile was suspended.
There are two types of suspensions:
- A hard suspension.
- A soft suspension.
What Is A Hard Suspension?
A hard suspension is when you do a search for your company’s name and city, and your Knowledge Panel/Business Profile doesn’t show up online – which is a very bad thing because potential customers won’t be able to find your GBP listing on Google Maps or search results.
Hard suspensions usually happen when Google determines that your business doesn’t qualify for a GBP listing or you’re using spammy tactics.
What Is A Soft Suspension?
A soft suspension is when your business’s Knowledge Panel/Business Profile still shows up online, and you can access it in your GBP dashboard, but it looks as if it hasn’t been verified and you can’t manage or update your listing.
If you have a soft suspension, your GBP profile can be subjected to user-suggested edits more easily – making it more vulnerable to incorrect changes and displaying incorrect information.
Also, some industries are more likely to get suspensions than others.
These categories are known to have more spam and fake listings, which makes them more prone to suspensions.
Google and SEO professionals have been trying to crack down on spammy and fake GBP listings, so if you’re in one of these industries, someone may report your profile if you are violating any Google Business Profile rules.
These spammy categories are typically Service Area Businesses (SABs) and include:
- Locksmiths.
- Lawyers.
- Plumbers.
- Pest control services.
- HVAC.
- Etc.
The Dreaded Google Business Profile Suspension Email Notification
If your listing hasn’t been suspended yet, you’re lucky.
Most listings, at some point or another, will face a suspension. (So it’s best to be prepared!)
Why Would Your Google Business Profile Get Suspended?
If your GBP listing gets suspended, you have likely done something that looks suspicious or spammy, you broke Google Business Profile guidelines, or you violated the terms of service of another Google product or service.
Google suspends listings for various reasons – especially if you are violating Google Business Profile Guidelines.
How Do You Know If Your GBP Profile Has Been Suspended?
Most business owners first notice a decrease in calls or visitors to their business.
They will then do a quick search online and may not find their listing at all, or they will log in to their Google Business Profile dashboard and see a notification that alerts them that their listing has been suspended:
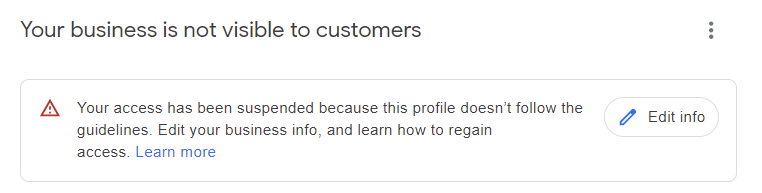 Screenshot from Google Business Profile dashboard, February 2024
Screenshot from Google Business Profile dashboard, February 2024
And they will receive an email letting them know that their listing was suspended, too.
This email contains valuable information about the “violation type” – or the general policy your listing violates.
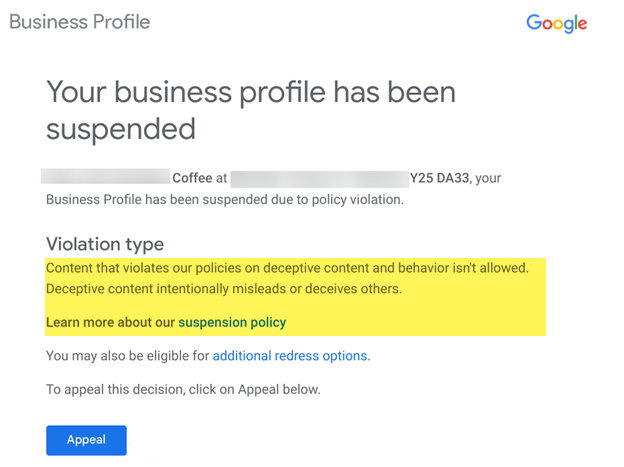 Screenshot from email, February 2024
Screenshot from email, February 2024
Common Reasons Why A GBP Listing Gets Suspended
There are many common reasons why a Google Business Profile may get suspended.
For instance, if you are in a high-spam industry like lawyers, locksmiths, or plumbers, you might get your listing suspended just because of the industry you’re in.
If you sat down at your computer and made several updates to the main information on your Google Business Profile listing in one sitting, that also can sometimes cause Google to be suspicious and trigger a suspension.
Here are some other reasons why GBP listings get suspended:
- Keyword stuffing your business name.
- Using a P.O. Box or UPS store address.
- You set up your listing at a virtual office or co-working space address.
- You have a Service Area Business (SAB) and are displaying a physical address.
- You have an online-only business.
- You are in a high-risk business category, like lawyers, plumbers, HVAC, locksmiths, rehab centers, etc.
- If another business shares your same address – especially if it’s a residential address.
- You have made a bunch of changes/edits to your GBP profile in one sitting.
- The URL you add to your GBP profile forwards/redirects to another website or links to a social media page.
- If you change your listing from a Storefront to a SAB – or vice versa.
- Having multiple GBPs in an area that has service areas overlapping.
- Your address or hours don’t match what is listed on your website or other online business directories/citations.
- You list your business hours as 24/7.
- A manager on your listing had their account suspended – so your listing was also suspended.
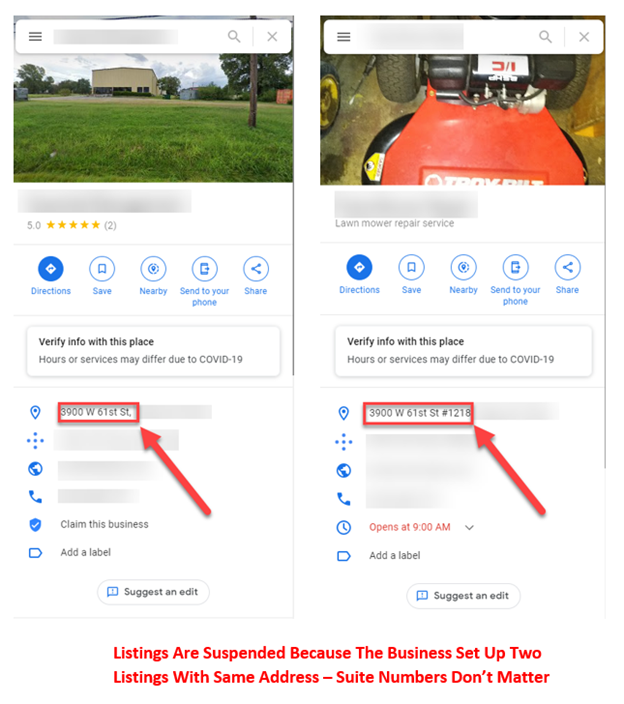
- You created multiple listings for the same business at the same address.
- You violated the terms of service of some other Google tool or service.
Seeing that suspension notice and email will probably cause you to panic – and you may be tempted to fill out the appeal form right away.
But wait!
Before you can apply for an appeal, you have to fix what’s wrong with your listing.
If you’ve done any of these things, you will need to fix the issues before you submit your appeal and try to get your GBP reinstated.
Now, many people who get their listings suspended think they should just create a new listing to avoid fixing the suspended profile.
Do not create a new listing!
Doing that will just complicate things and is a direct violation of Google’s guidelines. (Plus, chances are very high that if you do create a new GBP listing, that profile will immediately be suspended, too.)
When it comes to fixing what caused the suspension, you should first carefully read about the violation type identified in the email you received and next review the Google Business Profile Guidelines to make sure you didn’t violate any of those rules.
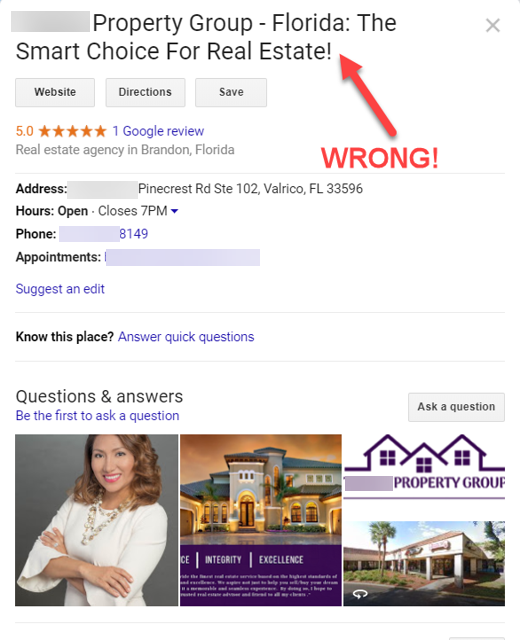
For instance, if you have keyword-stuffed your business name, you need to fix your company’s name to get your listing reinstated.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
In the example above, the real estate agent added extra, spammy words to the name of her business.
Before she submits her reinstatement form, she needs to delete the words “- Florida: The Smart Choice For Real Estate!” from her business name.
If you think you were suspended because you have your hours listed as 24/7, then you should adjust your hours to be something like 8:00 a.m.- 6:00 p.m. before you submit your appeal.
(Note: The hours you list on your GBP profile should be the hours that you have employees at your business location to meet with customers.
If you’re a SAB, it should be the hours that you are actually available to serve your customers at their location. Not when you answer your phone. Google wants to know when you have employees at your business to physically help customers.)
Do you have a duplicate listing problem, or have you set up more than one business at the same address?
You would need to fix these issues before you try to get your listing reinstated.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Once you think you’ve figured out the issues and have fixed your GBP, it’s time to fill out the appeal form.
The Appeal Tool Process
Once you’ve fixed the problems with your listing, it’s time to use the Appeals tool.
The Google Business Appeal process is pretty straightforward, but you must be prepared ahead of time. That’s why reading through this article in its entirety is important.
First, be sure to look at the Help document about the appeal process and become familiar with it. Next, let’s look at how the appeal process works.
When your GBP listing gets suspended, you will receive an email that looks like the one below. This email contains a blue button that says Appeal. You will need to click on the Appeal button that takes you to the Appeals tool.
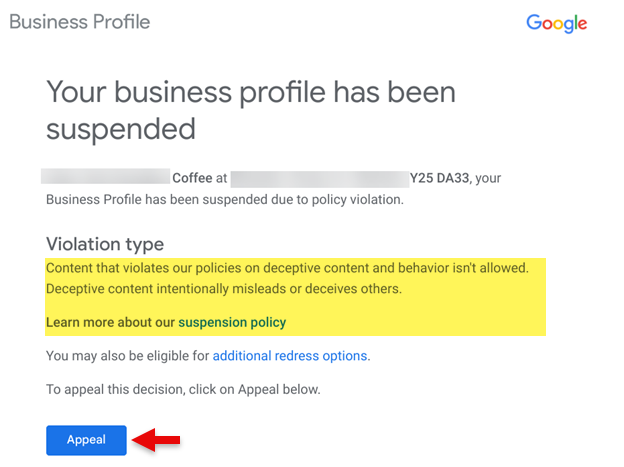 Screenshot from email, February 2024
Screenshot from email, February 2024
The Appeals tool will be your central headquarters for working on your appeal and checking the status of your appeal.
Before you begin, double-check to make sure you’re logged in using the email address that you use to manage the suspended GBP listing account, and then click Confirm.
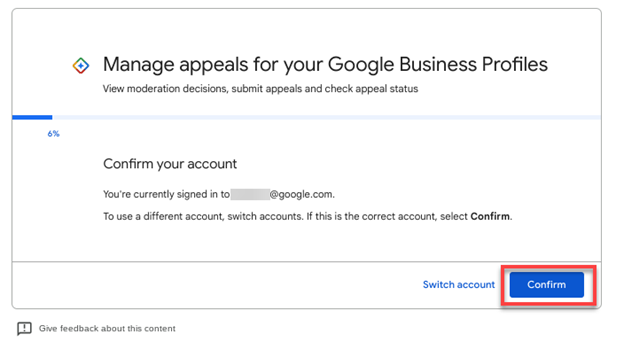 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Next, select the business profile that’s suspended. If you only have one business location, only the suspended location will appear here.
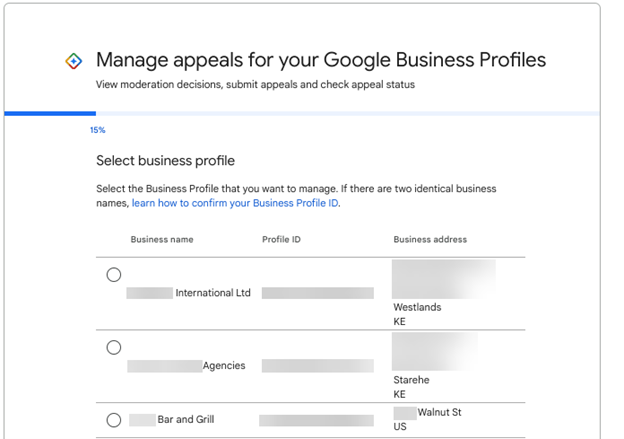 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
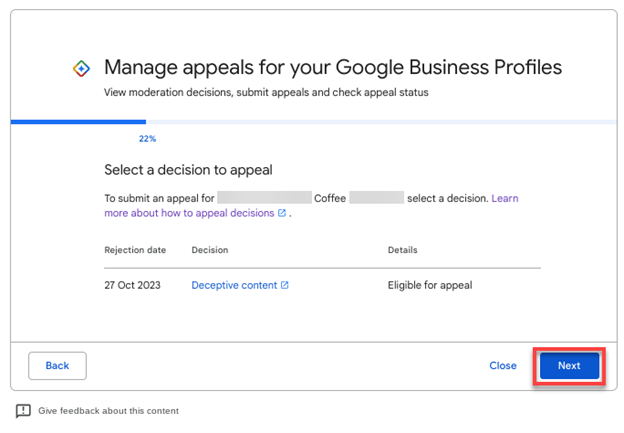
On the next screen, you will see when the Business Profile was suspended, the reason for the suspension, and the details/status:
- Cannot be appealed.
- Eligible for appeal.
Note that not all suspensions are eligible to be appealed.
If you see that your Google Business Profile can’t be appealed – you’re out of luck. You cannot create a new GBP; you are simply done with Google Business Profiles.
If the Details/Status says Eligible for Appeal, click Next to move forward through the appeal process.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
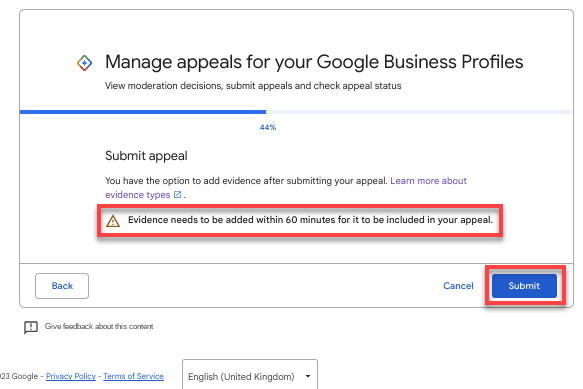
Pro Tip: This next section is very important. Once you click the Submit button on this next screen, you have exactly 60 minutes to upload official documents to prove you are a legitimate business.
If you are not sure if your evidence documents are the correct ones, are unsure of the process or whether your GBP listing complies, it’s best to hire a true product expert to help you with the Appeal process.
Do not move forward with this process without product expert help if you are uncertain about what’s required. This is just too important to the future of your business to leave to chance.
You will want to upload evidence to prove you are a legitimate business.
Google Business Profile Appeal Evidence List:
- Official business registration – shows you’re an officially established business.
- Business license – proves you’re authorized to operate your business.
- Tax certificate – shows your tax ID and that you’re validated.
- Utility bill at the business’s address – these can include electricity, phone, gas, water, sewage, trash, recycling, TV, or internet.
Your Business Registration/License must display the business name and address that matches the Business Profile you are appealing for. The utility bill must display the same business name and address as your registration/license or tax certificate.
Basically, all the documents you submit must match the business name and address on your Google Business Profile listing.
You must double-check all your documents to ensure that your business name and address match your GBP listing exactly.
It’s best to provide as many items as possible to ensure you have the greatest chance for reinstatement. You can upload a zipped file if you have more than two documents you want to upload.
Once you have all your documents gathered and are ready to upload, click the Submit button.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
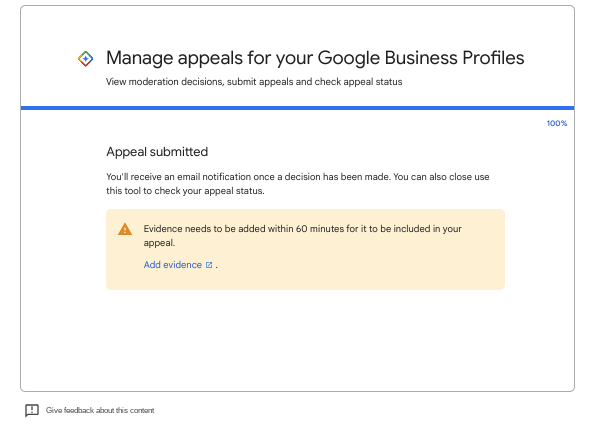
This is where you want to start a timer for 60 minutes.
It’s very important that you click on the very subtle Add Evidence link on this screen to open the form so you can upload your evidence documents.
If you choose not to submit any evidence, the chances of your Google Business Profile getting reinstated are slim.
Remember, you have one chance to upload the evidence, so do not miss this step.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
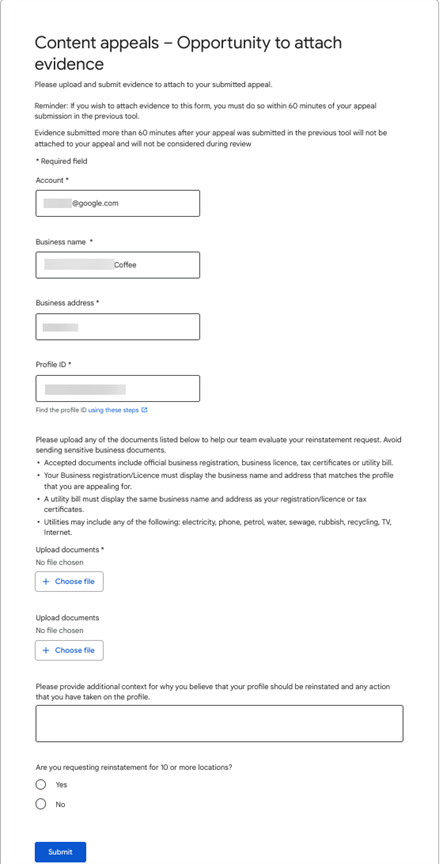
When the Evidence Form opens up, it’s pre-populated with your email address, business name, address, and Google Business Profile ID.
There are options to upload two files, but you can upload zipped files. So, if you have more than two files to upload, zip up those files and upload the zipped file. (The more evidence you can provide Google, the better!)
There is also a text box where you should provide a narrative as to why your profile should be reinstated, what you changed to fix your Business Profile to get it in compliance with GBP Guidelines, and any other information that would be helpful for Google to know.
Keep everything about the facts.
You are allowed 1,000 characters in this space, so use your words carefully.
Once you have uploaded your documents and filled out the rest of the form, click the Submit button.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
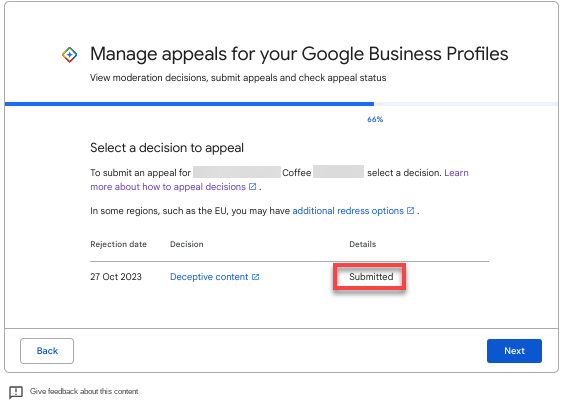
After you submit the evidence, you will be sent back to the Appeals tool, where your Details/Status should be changed to Submitted.
 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
The Google Support team will need several days to manually review the evidence you have submitted and to check your Business Profile to ensure your GBP listing complies with guidelines.
You can check the Appeals tool to see if the Details/Status has changed to either of the following:
Once Google has reviewed your evidence and GBP listing, you will receive one of two emails.
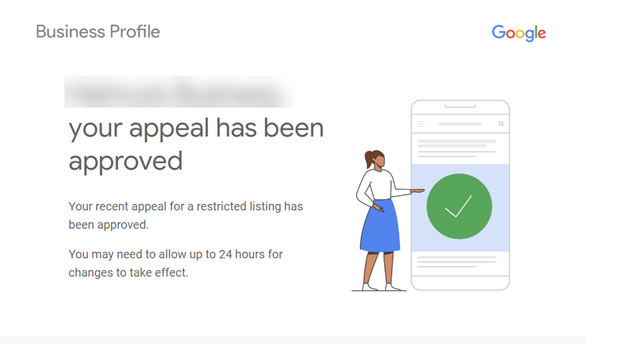
If your evidence proves that your business is legitimate and your Google Business Profile follows Google’s Guidelines, you will receive an email letting you know that your appeal was approved.
 Screenshot from email, February 2024
Screenshot from email, February 2024
The Appeals tool will show that your listing appeal was Approved.
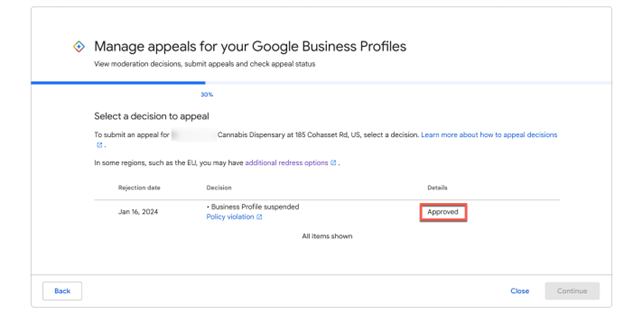 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
But if your GBP listing is still in violation of guidelines and/or your evidence does not satisfy Google’s requirements, you will receive an email denying your appeal.
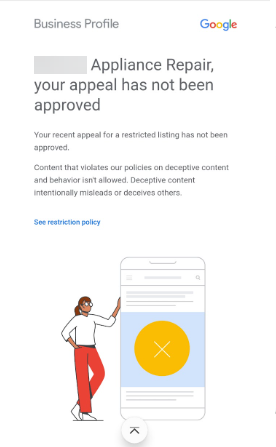 Screenshot from email, February 2024
Screenshot from email, February 2024
The Details in the Appeals tool will show that your appeal was Not Approved.
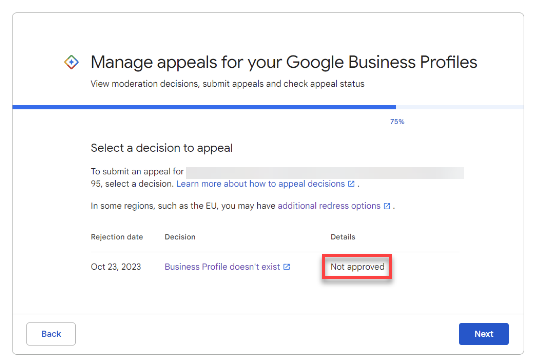 Screenshot from Google, February 2024
Screenshot from Google, February 2024
If your appeal is denied, you may have the option to have Google re-evaluate your appeal decision. However, we do not have details yet on how this process works.
Final Thoughts
Now that you know more about GBP suspensions, you will hopefully be better prepared should you see the Suspended notice in your dashboard.
Remember, GBP suspensions can sometimes happen for random reasons – like if you make too many changes at once, if a competitor suggests an edit, or even if there’s a glitch on Google’s end.
Make sure you’re prepared and that you are not just counting on Google Business Profile for all your online marketing efforts.
And always try to follow Google’s rules. Don’t forget that Google has the upper hand, as it makes this amazing – and free – marketing tool available to merchants.
More resources:
Featured Image: FabrikaSimf/Shutterstock

![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)















