AMAZON
Selecting the Best Method for Structured Data Retrieval Using Generative AI
Organizations today are looking for simple ways to get direct answers to their business questions without needing to write complex SQL queries or use complicated business intelligence (BI) dashboards. They have many types of structured data like tables, databases, and data warehouses that fit specific formats.
With the rise of large language models (LLMs), users can ask questions in everyday language, such as “Which region has the highest revenue?” and get quick and meaningful answers. However, setting up these systems needs careful thought about what your organization needs. Here are some important considerations:
- Do you need to pull information from other systems?
- Who will use the data – internal staff or external clients?
- How complex are the questions users will ask?
- Should the answers be adjusted for specific business needs?
In this article, we will explore how to use LLMs for structured data queries, specifically focusing on solutions offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Understanding the Business Challenge
Many organizations find it hard to give non-technical users access to structured data due to several reasons:
- Employees often don’t know how to write SQL queries.
- They might depend on BI teams or data scientists, which delays getting insights.
- Existing dashboards limit their ability to explore data freely.
- Users may not even know what questions to ask or where to find the data they need.
An Effective Solution
A good solution should achieve the following:
- Conversational Interface: Allow employees to ask questions without needing technical skills.
- Natural Language Processing: Give accurate answers when questions are asked in simple language.
- Visualizations: Automatically create charts and graphs to show insights clearly.
- Unified Data Access: Combine information from different sources into one view.
- Easy Integration: Work smoothly with existing systems.
- Access Control: Ensure data is accessed appropriately based on roles and permissions.
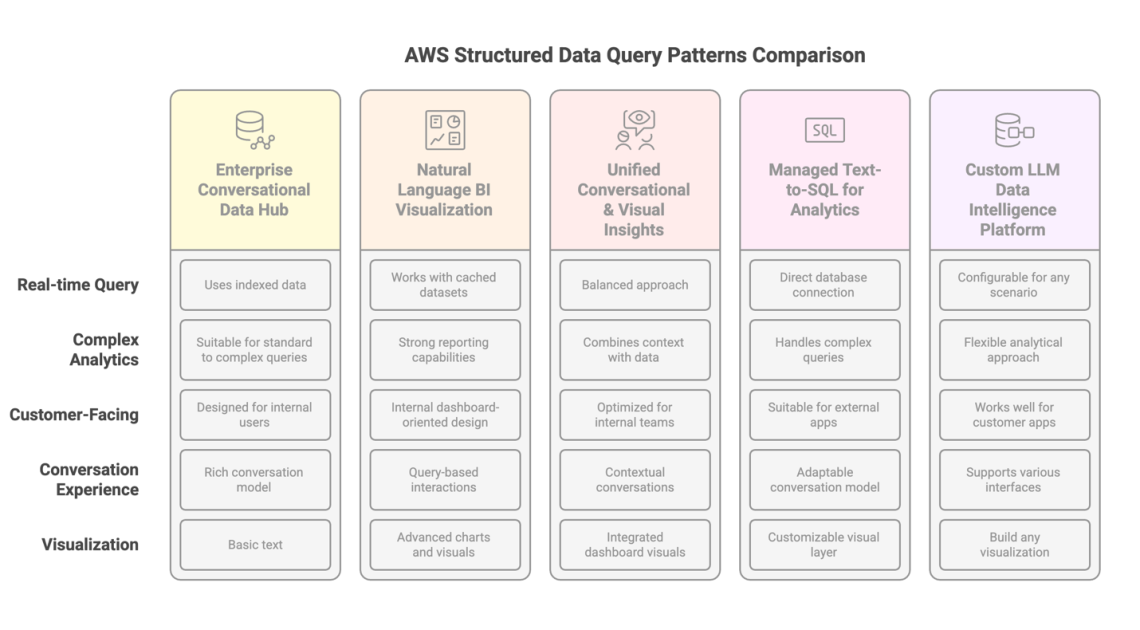
The Patterns for Data Retrieval
Let’s look at five patterns to help meet these needs:
Pattern 1: Direct Conversational Interface with Amazon Q Business
This pattern uses Amazon Q Business, a generative AI assistant. It allows users to chat about data sources directly. For instance, HR can ask, “What’s our parental leave policy and how many employees used it last quarter?” The assistant pulls the answer from both the policy documents and the employee database.
Benefits:
- Direct connections to data sources.
- Easy to manage with built-in tools.
- Supports both structured and unstructured data.
Pattern 2: Enhancing BI Tools with Natural Language Queries
This approach integrates Amazon Q into QuickSight, letting users ask questions directly in the QuickSight interface. For example, a sales executive can inquire, “What were our top 5 regions by revenue last quarter?” and quickly receive visual responses.
Benefits:
- Generates visualizations without needing coding skills.
- Perfect for immediate analysis and reporting.
- Works seamlessly within existing QuickSight dashboards.
Pattern 3: Combining BI Visualization with Conversational AI
This pattern merges BI visualization with conversational AI by linking Amazon Q in QuickSight with Amazon Q Business. It allows for richer data discussions where users can ask complex questions combining visual data displayed through QuickSight with insights from documents.
Benefits:
- Unifies answers from various data sources.
- Maintains conversational context while switching topics.
Pattern 4: Building Knowledge Bases with Managed Text-to-SQL
Using Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases, this pattern offers a managed text-to-SQL service. Users can ask complicated queries, and the system generates the necessary SQL code, executes it, and presents the results.
Benefits:
- No need for model training.
- Directly queries data without moving it.
- Supports complex analytical queries.
Pattern 5: Custom Text-to-SQL Implementation
This pattern allows organizations to create their own solutions using foundation models to convert natural language to SQL and execute queries. Amazon Bedrock provides predefined models, while Amazon SageMaker offers a customizable approach.
Benefits:
- Maximum flexibility in model selection and system design.
- Ideal for specific application needs or user interactions.
Making the Right Choice
Each pattern serves different needs based on your organization’s circumstances:
- Data Types: Where is your data stored? Are you using operating databases or a data warehouse?
- User Base: Is your audience internal (employees) or external (customers)?
- Technical Expertise: Do you have ML specialists on hand, or do you need a managed service?
- Governance: How much control do you need over the data output?
Conclusion
By understanding these patterns and their trade-offs, you can make informed decisions that align with your business goals. Choose the approach that best fits your data needs, user preferences, and available resources.
About the Authors
Akshara Shah is a Senior Solutions Architect at AWS, helping customers create AI services tailored to their needs.
Sanghwa Na is a Generative AI Specialist Solutions Architect at AWS, focusing on integrating AI that brings real value to businesses.
By keeping these insights in mind, organizations can navigate the complexities of generative AI and structured data retrieval successfully.