MARKETING
How to Write Simple Queries

How to Query a SQL Database:
- Make sure that you have a database management application (ex. MySQL Workbench, Sequel Pro).
- If not, download a database management application and work with your company to connect your database.
- Understand your database and its hierarhcy.
- Find out which fields are in your tables.
- Begin writing a SQL query to pull your desired data.
Ever heard of SQL? You may have heard about it in the context of data analysis, but never thought it would apply to you as a marketer. Or, you may have thought, “That’s for the advanced data users. I could never do that.”
Well, you couldn’t be more wrong! The most successful marketers are data-driven, and one of the most important parts of being data-driven is collecting data from databases quickly. SQL is the most popular tool out there for doing just that.
If your company already stores data in a database, you may need to learn SQL to access the data. But not to worry — you’re in the right place to get started. Let’s jump right in.
Why Use SQL?
SQL (often pronounced like “sequel”) stands for Structured Query Language, and it’s used when companies have a ton of data that they want to manipulate. The beauty of SQL is that anyone working at a company that stores data in a relational database can use it. (And chances are, yours does.)
For example, if you work for a software company and want to pull usage data on your customers, you can do that with SQL. If you’re helping develop a website for an ecommerce company that has data about customer purchases, you can use SQL to find out which customers are purchasing which products. Of course, these are just a few of many possible applications.
Think about it this way: Have you ever opened a very large data set in Excel, only for your computer to freeze or even shut down? SQL allows you to access only certain parts of your data at a time so you don’t have to download all the data into a CSV, manipulate it, and possibly overload Excel. In other words, SQL takes care of the data analysis that you may be used to doing in Excel.
How to Write Simple SQL Queries
Before we begin, make sure you have a database management application that will allow you to pull data from your database. Some options include MySQL or Sequel Pro.
Start by downloading one of these options, then talk to your company’s IT department about how to connect to your database. The option you choose will depend on your product’s back end, so check with your product team to make sure you select the correct one.
Understand the hierarchy of your database
Next, it’s important to become accustomed to your database and its hierarchy. If you have multiple databases of data, you’ll need to hone in on the location of the data you want to work with.
For example, let’s pretend we’re working with multiple databases about people in the United States. Enter the query “SHOW DATABASES;”. The results may show that you have a couple of databases for different locations, including one for New England.
Within your database, you’ll have different tables containing the data you want to work with. Using the same example above, let’s say we want to find out which information is contained in one of the databases. If we use the query “SHOW TABLES in NewEngland;”, we’ll find that we have tables for each state in New England: people_connecticut, people_maine, people_massachusetts, people_newhampshire, people_rhodeisland, and people_vermont.
Finally, you need to find out which fields are in the tables. Fields are the specific pieces of data that you can pull from your database. For example, if you want to pull someone’s address, the field name may not just be “address” — it may be separated into address_city, address_state, address_zip. In order to figure this out, use the query “Describe people_massachusetts;”. This provides a list of all of the data that you can pull using SQL.
Let’s do a quick review of the hierarchy using our New England example:
- Our database is: NewEngland.
- Our tables within that database are: people_connecticut, people_maine, people_massachusetts, people_newhampshire, people_rhodeisland, and people_vermont.
- Our fields within the people_massachusetts table include: address_city, address_state, address_zip, hair_color, age, first_name, and last_name.
Now, let’s write some simple SQL queries to pull data from our NewEngland database.
Basic SQL Queries
To learn how to write a SQL query, let’s use the following example:
Who are the people who have red hair in Massachusetts and were born in 2003 organized in alphabetical order?
SELECT
SELECT chooses the fields that you want displayed in your chart. This is the specific piece of information that you want to pull from your database. In the example above, we want to find the people who fit the rest of the criteria.
Here is our SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
;
FROM
FROM pinpoints the table that you want to pull the data from. In the earlier section, we learned that there were six tables for each of the six states in New England: people_connecticut, people_maine, people_massachusetts, people_newhampshire, people_rhodeisland, and people_vermont. Because we’re looking for people in Massachusetts specifically, we’ll pull data from that specific table.
Here is our SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
;
WHERE
WHERE allows you to filter a query to be more specific. In our example, we want to filter our query to include only people with red hair who were born in 2003. Let’s start with the red hair filter.
Here is our SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color=”red”
;
hair_color could have been part of your initial SELECT statement if you’d wanted to look at all of the people in Massachusetts along with their hair color. But if you want to filter to see only people with red hair, you can do so with a WHERE statement.
BETWEEN
Besides equals (=), BETWEEN is another operator you can use for conditional queries. A BETWEEN statement is true for values that fall between the specified minimum and maximum values.
In our case, we can use BETWEEN to pull records from a specific year, like 2003. Here’s the query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
;
AND
AND allows you to add additional criteria to your WHERE statement. Remember, we want to filter by people who had red hair in addition to people who were born in 2003. Since our WHERE statement is taken up by the red hair criteria, how can we filter by a specific year of birth as well?
That’s where the AND statement comes in. In this case, the AND statement is a date property — but it doesn’t necessarily have to be. (Note: Check the format of your dates with your product team to make sure they are in the correct format.)
Here is our SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color=”red”
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
;
OR
OR can also be used with a WHERE statement. With AND, both conditions must be true to appear in results (e.g., hair color must be red and must be born in 2003). With OR, either condition must be true to appear in results (e.g., hair color must be red or must be born in 2003).
Here’s what an OR statement looks like in action:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color = ‘red’
OR
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
;
NOT
NOT is used in a WHERE statement to display values in which the specified condition is untrue. If we wanted to pull up all Massachusetts residents without red hair, we can use the following query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE NOT
hair_color = ‘red’
;
ORDER BY
Calculations and organization also can be done within a query. That’s where the ORDER BY and GROUP BY functions come in. First, we’ll look at our SQL queries with the ORDER BY and then GROUP BY functions. Then, we’ll take a brief look at the difference between the two.
An ORDER BY clause allows you to sort by any of the fields that you have specified in the SELECT statement. In this case, let’s order by last name.
Here is our SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color = ‘red’
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
ORDER BY
last_name
;
GROUP BY
GROUP BY is similar to ORDER BY, but aggregates data that has similarities. For example, if you have any duplicates in your data, you can use GROUP BY to count the number of duplicates in your fields.
Here is your SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color = ‘red’
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
GROUP BY
last_name
;
ORDER BY VS. GROUP BY
To show the difference between an ORDER BY statement and a GROUP BY statement, let’s step outside our Massachusetts example briefly to look at a very simple dataset. Below is a list of four employees’ ID numbers and names.

If we were to use an ORDER BY statement on this list, the names of the employees would get sorted in alphabetical order. The result would look like this:

If we were to use a GROUP BY statement instead, the employees would be counted based on the number of times they appeared in the initial table. Note that Peter appeared twice in the initial table, so the result would look like this:

With me so far? Okay, let’s return to the SQL query we’ve been creating about red-haired people in Massachusetts who were born in 2003.
LIMIT
Depending on the amount of data you have in your database, it may take a long time to run your queries. This can be frustrating, especially if you’ve made an error in your query and now need to wait before continuing. If you want to test a query, the LIMIT function lets you limit the number of results you get.
For example, if we suspect there are thousands of people who have red hair in Massachusetts, we may want to test out our query using LIMIT before we run it in full to make sure we’re getting the information we want. Let’s say, for instance, we only want to see the first 100 people in our result.
Here is our SQL query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color = ‘red’
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
ORDER BY
last_name
LIMIT
100
;
INSERT INTO
In addition to retrieving information from a relational database, SQL can also be used to modify the contents of a database. Of course, you’ll need permissions to make changes to your company’s data. But, in case you’re ever in charge of managing the contents of a database, we’ll share some queries you should know.
First is the INSERT INTO statement, which is for putting new values into your database. If we want to add a new person to the Massachusetts table, we can do so by first providing the name of the table we want to modify, and the fields within the table we want to add to. Next, we write VALUE with each respective value we want to add.
Here’s what that query could look like:
INSERT INTO
people_massachusetts (address_city, address_state, address_zip, hair_color, age, first_name, last_name)
VALUES
(Cambridge, Massachusetts, 02139, blonde, 32, Jane, Doe)
;
Alternatively, if you are adding a value to every field in the table, you don’t need to specify fields. The values will be added to columns in the order that they are listed in the query.
INSERT INTO
people_massachusetts
VALUES
(Cambridge, Massachusetts, 02139, blonde, 32, Jane, Doe)
;
If you only want to add values to specific fields, you must specify these fields. Say we only want to insert a record with first_name, last_name, and address_state — we can use the following query:
INSERT INTO
people_massachusetts (first_name, last_name, address_state)
VALUES
(Jane, Doe, Massachusetts)
;
UPDATE
If you want to replace existing values in your database with different values, you can use UPDATE. What if, for example, someone is recorded in the database as having red hair when they actually have brown hair? We can update this record with UPDATE and WHERE statements:
UPDATE
people_massachusetts
SET
hair_color = ‘brown’
WHERE
first_name = ‘Jane’
AND
last_name = ‘Doe’
;
Or, say there’s a problem in your table where some values for “address_state” appear as “Massachusetts” and others appear as “MA”. To change all instances of “MA” to “Massachusetts” we can use a simple query and update multiple records at once:
UPDATE
people_massachusetts
SET
address_state = ‘Massachusetts’
WHERE
address_state = MA
;
Be careful when using UPDATE. If you don’t specify which records to change with a WHERE statement, you’ll change all values in the table.
DELETE
DELETE removes records from your table. Like with UPDATE, be sure to include a WHERE statement, so you don’t accidentally delete your entire table.
Or, if we happened to find several records in our people_massachusetts table who actually lived in Maine, we can delete these entries quickly by targeting the address_state field, like so:
DELETE FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
address_state = ‘maine’
;
Bonus: Advanced SQL Tips
Now that you’ve learned how to create a simple SQL query, let’s discuss some other tricks that you can use to take your queries up a notch, starting with the asterisk.
* (asterisk)
When you add an asterisk character to your SQL query, it tells the query that you want to include all the columns of data in your results.
In the Massachusetts example we’ve been using, we’ve only had two column names: first_name and last_name. But let’s say we had 15 columns of data that we want to see in our results — it would be a pain to type all 15 column names in the SELECT statement. Instead, if you replace the names of those columns with an asterisk, the query will know to pull all of the columns into the results.
Here’s what the SQL query would look like:
SELECT
*
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color=”red”
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
ORDER BY
last_name
LIMIT
100
;
% (percent symbol)
The percent symbol is a wildcard character, meaning it can represent one or more characters in a database value. Wildcard characters are helpful for locating records that share common characters. They are typically used with the LIKE operator to find a pattern in the data.
For instance, if we wanted to get the names of every person in our table whose zip code begins with “02”, we can write this query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
WHERE
address_zip LIKE ‘02%’
;
Here, “%” stands in for any group of digits that follow “02”, so this query turns up any record with a value for address_zip that begins with “02”.
LAST 30 DAYS
Once I started using SQL regularly, I found that one of my go-to queries involved trying to find which people took an action or fulfilled a certain set of criteria within the last 30 days.
Let’s pretend today is December 1, 2021. You could create these parameters by making the birth_date span between November 1, 2021 and November 30, 2021. That SQL query would look like this:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color=”red”
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2021-11-01’ AND ‘2021-11-30’
ORDER BY
last_name
LIMIT
100
;
But, that would require thinking about which dates cover the last 30 days, and you’d have to update this query constantly.
Instead, to make the dates automatically span the last 30 days no matter which day it is, you can type this under AND: birth_date >= (DATE_SUB(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 30))
(Note: You’ll want to double-check this syntax with your product team because it may differ based on the software you use to pull your SQL queries.)
Your full SQL query would therefore look like this:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
WHERE
hair_color=”red”
AND
birth_date >= (DATE_SUB(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 30))
ORDER BY
last_name
LIMIT
100
;
COUNT
In some cases, you may want to count the number of times that a criterion of a field appears. For example, let’s say you want to count the number of times the different hair colors appear for the people you are tallying up from Massachusetts. In this case, COUNT will come in handy so you don’t have to manually add up the number of people who have different hair colors or export that information to Excel.
Here’s what that SQL query would look like:
SELECT
hair_color,
COUNT(hair_color)
FROM
people_massachusetts
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
GROUP BY
hair_color
;
AVG
AVG calculates the average of an attribute in the results of your query, excluding NULL values (empty). In our example, we could use AVG to calculate the average age of Massachusetts residents in our query.
Here’s what our SQL query could look like:
SELECT
AVG(age)
FROM
people_massachusetts
;
SUM
SUM is another simple calculation you can do in SQL. It calculates the total value of all attributes from your query. So, if we wanted to add up all the ages of Massachusetts residents, we can use this query:
SELECT
SUM(age)
FROM
people_massachusetts
;
MIN and MAX
MIN and MAX are two SQL functions that give you the smallest and largest values of a given field. We can use it to identify the oldest and youngest members of our Massachusetts table:
This query will give us the record of the oldest:
SELECT
MIN(age)
FROM
people_massachusetts
;
And this query gives us the oldest:
SELECT
MAX(age)
FROM
people_massachusetts
;
JOIN
There may be a time when you need to access information from two different tables in one SQL query. In SQL, you can use a JOIN clause to do this.
(For those familiar with Excel formulas, this is similar to using the VLOOKUP formula when you need to combine information from two different sheets in Excel.)
Let’s say we have one table that has data of all Massachusetts residents’ user IDs and their birthdates. In addition, we have an entirely separate table containing all Massachusetts residents’ user IDs and their hair color.
If we want to figure out the hair color of Massachusetts residents born in the year 2003, we’d need to access information from both tables and combine them. This works because both tables share a matching column: user IDs.
Because we’re calling out fields from two different tables, our SELECT statement is also going to change slightly. Instead of just listing out the fields we want to include in our results, we’ll need to specify which table they’re coming from. (Note: The asterisk function may come in handy here so your query includes both tables in your results.)
To specify a field from a specific table, all we have to do is combine the name of the table with the name of the field. For example, our SELECT statement would say “table.field” — with the period separating the table name and the field name.
We’re also assuming a few things in this case:
- The Massachusetts birthdate table includes the following fields: first_name, last_name, user_id, birthdate
- The Massachusetts hair color table includes the following fields: user_id, hair_color
Your SQL query would therefore look like:
SELECT
birthdate_massachusetts.first_name,
birthdate_massachusetts.last_name
FROM
birthdate_massachusetts JOIN haircolor_massachusetts USING (user_id)
WHERE
hair_color=”red”
AND
birth_date BETWEEN ‘2003-01-01’ AND ‘2003-12-31’
ORDER BY
last_name
;
This query would join the two tables using the field “user_id” which appears in both the birthdate_massachusetts table and the haircolor_massachusetts table. You’re then able to see a table of people born in 2003 who have red hair.
CASE
Use a CASE statement when you want to return different results to your query based on which condition is met. Conditions are evaluated in order. Once a condition is met, the corresponding result is returned and all following conditions are skipped over.
You can include an ELSE condition at the end in case no conditions are met. Without an ELSE, the query will return NULL if no conditions are met.
Here’s an example of using CASE to return a string based on the query:
SELECT
first_name,
last_name
FROM
people_massachusetts
CASE
WHEN hair_color = ‘brown’ THEN ‘This person has brown hair.’
WHEN hair_color = ‘blonde’ THEN ‘This person has blonde hair.’
WHEN hair_color = ‘red’ THEN ‘This person has red hair.’
ELSE ‘Hair color not known.’
END
;
Basic SQL Queries Marketers Should Know
Congratulations. you’re ready to run your own SQL queries! While there’s a lot more you can do with SQL, I hope you found this overview of the basics helpful so you can get your hands dirty. With a strong foundation of the basics, you’ll be able to navigate SQL better and work toward some of the more complex examples.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in March 25 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Source link
MARKETING
How to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds

Welcome to Creator Columns, where we bring expert HubSpot Creator voices to the Blogs that inspire and help you grow better.
It’s the age of AI, and our job as marketers is to keep up.
My team at Foundation Marketing recently conducted an AI Marketing study surveying hundreds of marketers, and more than 84% of all leaders, managers, SEO experts, and specialists confirmed that they used AI in the workplace.
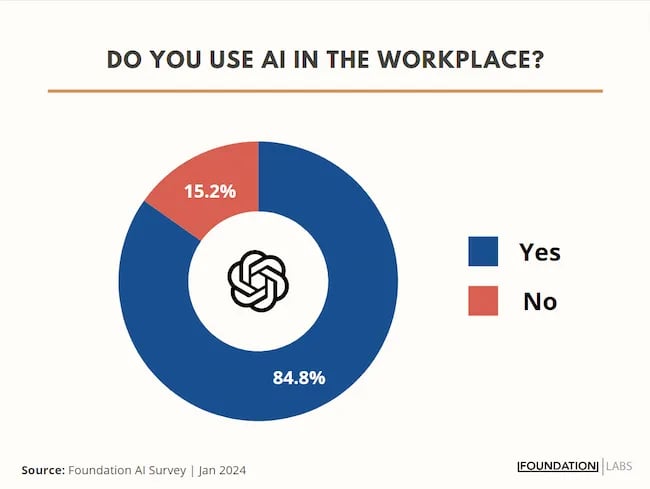
If you can overlook the fear-inducing headlines, this technology is making social media marketers more efficient and effective than ever. Translation: AI is good news for social media marketers.
In fact, I predict that the marketers not using AI in their workplace will be using it before the end of this year, and that number will move closer and closer to 100%.
Social media and AI are two of the most revolutionizing technologies of the last few decades. Social media has changed the way we live, and AI is changing the way we work.
So, I’m going to condense and share the data, research, tools, and strategies that the Foundation Marketing Team and I have been working on over the last year to help you better wield the collective power of AI and social media.
Let’s jump into it.
What’s the role of AI in social marketing strategy?
In a recent episode of my podcast, Create Like The Greats, we dove into some fascinating findings about the impact of AI on marketers and social media professionals. Take a listen here:
Let’s dive a bit deeper into the benefits of this technology:
Benefits of AI in Social Media Strategy
AI is to social media what a conductor is to an orchestra — it brings everything together with precision and purpose. The applications of AI in a social media strategy are vast, but the virtuosos are few who can wield its potential to its fullest.
AI to Conduct Customer Research
Imagine you’re a modern-day Indiana Jones, not dodging boulders or battling snakes, but rather navigating the vast, wild terrain of consumer preferences, trends, and feedback.
This is where AI thrives.
Using social media data, from posts on X to comments and shares, AI can take this information and turn it into insights surrounding your business and industry. Let’s say for example you’re a business that has 2,000 customer reviews on Google, Yelp, or a software review site like Capterra.
Leveraging AI you can now have all 2,000 of these customer reviews analyzed and summarized into an insightful report in a matter of minutes. You simply need to download all of them into a doc and then upload them to your favorite Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) to get the insights and data you need.
But that’s not all.
You can become a Prompt Engineer and write ChatGPT asking it to help you better understand your audience. For example, if you’re trying to come up with a persona for people who enjoy marathons but also love kombucha you could write a prompt like this to ChatGPT:

The response that ChatGPT provided back is quite good:
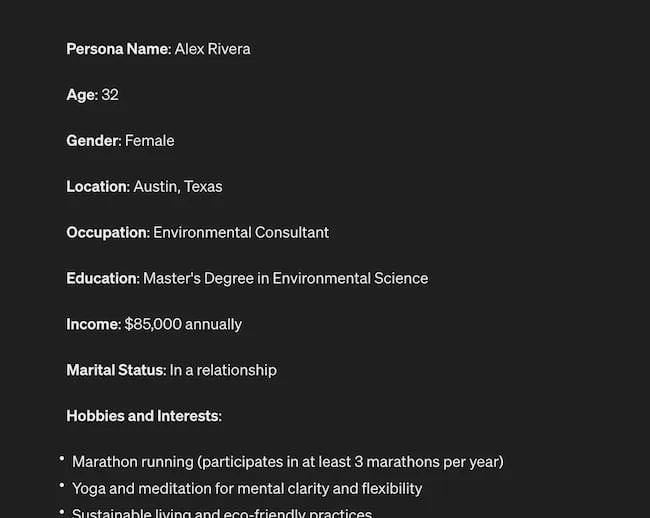
Below this it went even deeper by including a lot of valuable customer research data:
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Consumer behaviors
- Needs and preferences
And best of all…
It also included marketing recommendations.
The power of AI is unbelievable.
Social Media Content Using AI
AI’s helping hand can be unburdening for the creative spirit.
Instead of marketers having to come up with new copy every single month for posts, AI Social Caption generators are making it easier than ever to craft catchy status updates in the matter of seconds.
Tools like HubSpot make it as easy as clicking a button and telling the AI tool what you’re looking to create a post about:
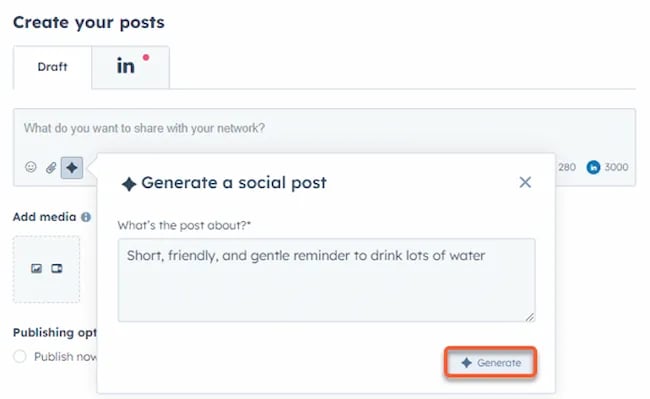
The best part of these AI tools is that they’re not limited to one channel.
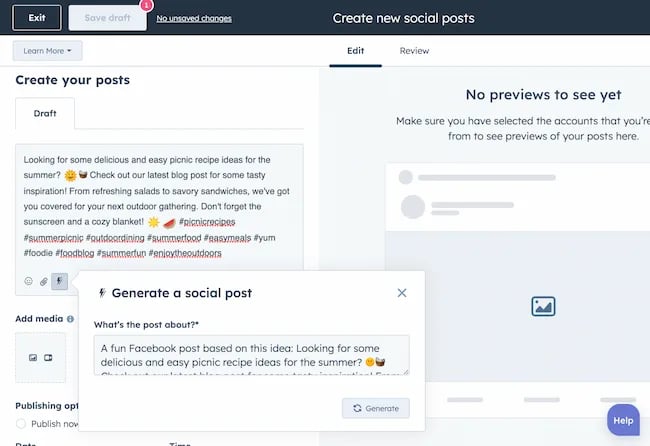
Your AI social media content assistant can help you with LinkedIn content, X content, Facebook content, and even the captions that support your post on Instagram.
It can also help you navigate hashtags:
With AI social media tools that generate content ideas or even write posts, it’s not about robots replacing humans. It’s about making sure that the human creators on your team are focused on what really matters — adding that irreplaceable human touch.
Enhanced Personalization
You know that feeling when a brand gets you, like, really gets you?
AI makes that possible through targeted content that’s tailored with a level of personalization you’d think was fortune-telling if the data didn’t paint a starker, more rational picture.
What do I mean?
Brands can engage more quickly with AI than ever before. In the early 2000s, a lot of brands spent millions of dollars to create social media listening rooms where they would hire social media managers to find and engage with any conversation happening online.
Thanks to AI, brands now have the ability to do this at scale with much fewer people all while still delivering quality engagement with the recipient.
Analytics and Insights
Tapping into AI to dissect the data gives you a CSI-like precision to figure out what works, what doesn’t, and what makes your audience tick. It’s the difference between guessing and knowing.
The best part about AI is that it can give you almost any expert at your fingertips.
If you run a report surrounding the results of your social media content strategy directly from a site like LinkedIn, AI can review the top posts you’ve shared and give you clear feedback on what type of content is performing, why you should create more of it, and what days of the week your content is performing best.
This type of insight that would typically take hours to understand.
Now …
Thanks to the power of AI you can upload a spreadsheet filled with rows and columns of data just to be met with a handful of valuable insights a few minutes later.
Improved Customer Service
Want 24/7 support for your customers?
It’s now possible without human touch.
Chatbots powered by AI are taking the lead on direct messaging experiences for brands on Facebook and other Meta properties to offer round-the-clock assistance.
The fact that AI can be trained on past customer queries and data to inform future queries and problems is a powerful development for social media managers.
Advertising on Social Media with AI
The majority of ad networks have used some variation of AI to manage their bidding system for years. Now, thanks to AI and its ability to be incorporated in more tools, brands are now able to use AI to create better and more interesting ad campaigns than ever before.
Brands can use AI to create images using tools like Midjourney and DALL-E in seconds.
Brands can use AI to create better copy for their social media ads.
Brands can use AI tools to support their bidding strategies.
The power of AI and social media is continuing to evolve daily and it’s not exclusively found in the organic side of the coin. Paid media on social media is being shaken up due to AI just the same.
How to Implement AI into Your Social Media Strategy
Ready to hit “Go” on your AI-powered social media revolution?
Don’t just start the engine and hope for the best. Remember the importance of building a strategy first. In this video, you can learn some of the most important factors ranging from (but not limited to) SMART goals and leveraging influencers in your day-to-day work:
The following seven steps are crucial to building a social media strategy:
- Identify Your AI and Social Media Goals
- Validate Your AI-Related Assumptions
- Conduct Persona and Audience Research
- Select the Right Social Channels
- Identify Key Metrics and KPIs
- Choose the Right AI Tools
- Evaluate and Refine Your Social Media and AI Strategy
Keep reading, roll up your sleeves, and follow this roadmap:
1. Identify Your AI and Social Media Goals
If you’re just dipping your toes into the AI sea, start by defining clear objectives.
Is it to boost engagement? Streamline your content creation? Or simply understand your audience better? It’s important that you spend time understanding what you want to achieve.
For example, say you’re a content marketing agency like Foundation and you’re trying to increase your presence on LinkedIn. The specificity of this goal will help you understand the initiatives you want to achieve and determine which AI tools could help you make that happen.
Are there AI tools that will help you create content more efficiently? Are there AI tools that will help you optimize LinkedIn Ads? Are there AI tools that can help with content repurposing? All of these things are possible and having a goal clearly identified will help maximize the impact. Learn more in this Foundation Marketing piece on incorporating AI into your content workflow.
Once you have identified your goals, it’s time to get your team on board and assess what tools are available in the market.
Recommended Resources:
2. Validate Your AI-Related Assumptions
Assumptions are dangerous — especially when it comes to implementing new tech.
Don’t assume AI is going to fix all your problems.
Instead, start with small experiments and track their progress carefully.
3. Conduct Persona and Audience Research
Social media isn’t something that you can just jump into.
You need to understand your audience and ideal customers. AI can help with this, but you’ll need to be familiar with best practices. If you need a primer, this will help:
Once you understand the basics, consider ways in which AI can augment your approach.
4. Select the Right Social Channels
Not every social media channel is the same.
It’s important that you understand what channel is right for you and embrace it.
The way you use AI for X is going to be different from the way you use AI for LinkedIn. On X, you might use AI to help you develop a long-form thread that is filled with facts and figures. On LinkedIn however, you might use AI to repurpose a blog post and turn it into a carousel PDF. The content that works on X and that AI can facilitate creating is different from the content that you can create and use on LinkedIn.
The audiences are different.
The content formats are different.
So operate and create a plan accordingly.
Recommended Tools and Resources:
5. Identify Key Metrics and KPIs
What metrics are you trying to influence the most?
Spend time understanding the social media metrics that matter to your business and make sure that they’re prioritized as you think about the ways in which you use AI.
These are a few that matter most:
- Reach: Post reach signifies the count of unique users who viewed your post. How much of your content truly makes its way to users’ feeds?
- Clicks: This refers to the number of clicks on your content or account. Monitoring clicks per campaign is crucial for grasping what sparks curiosity or motivates people to make a purchase.
- Engagement: The total social interactions divided by the number of impressions. This metric reveals how effectively your audience perceives you and their readiness to engage.
Of course, it’s going to depend greatly on your business.
But with this information, you can ensure that your AI social media strategy is rooted in goals.
6. Choose the Right AI Tools
The AI landscape is filled with trash and treasure.
Pick AI tools that are most likely to align with your needs and your level of tech-savviness.
For example, if you’re a blogger creating content about pizza recipes, you can use HubSpot’s AI social caption generator to write the message on your behalf:
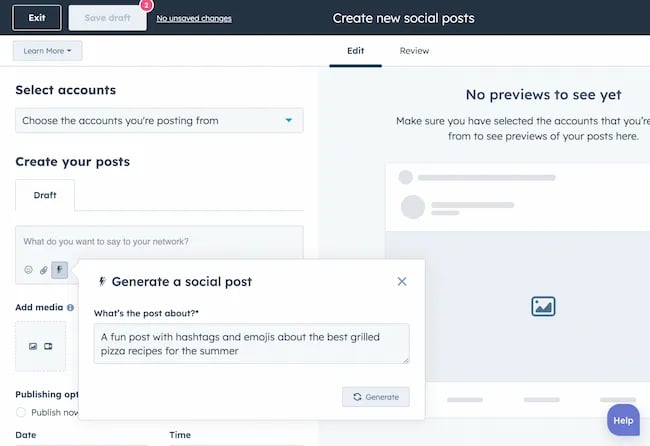
The benefit of an AI tool like HubSpot and the caption generator is that what at one point took 30-40 minutes to come up with — you can now have it at your fingertips in seconds. The HubSpot AI caption generator is trained on tons of data around social media content and makes it easy for you to get inspiration or final drafts on what can be used to create great content.
Consider your budget, the learning curve, and what kind of support the tool offers.
7. Evaluate and Refine Your Social Media and AI Strategy
AI isn’t a magic wand; it’s a set of complex tools and technology.
You need to be willing to pivot as things come to fruition.
If you notice that a certain activity is falling flat, consider how AI can support that process.
Did you notice that your engagement isn’t where you want it to be? Consider using an AI tool to assist with crafting more engaging social media posts.
Make AI Work for You — Now and in the Future
AI has the power to revolutionize your social media strategy in ways you may have never thought possible. With its ability to conduct customer research, create personalized content, and so much more, thinking about the future of social media is fascinating.
We’re going through one of the most interesting times in history.
Stay equipped to ride the way of AI and ensure that you’re embracing the best practices outlined in this piece to get the most out of the technology.
MARKETING
Advertising in local markets: A playbook for success

Many brands, such as those in the home services industry or a local grocery chain, market to specific locations, cities or regions. There are also national brands that want to expand in specific local markets.
Regardless of the company or purpose, advertising on a local scale has different tactics than on a national scale. Brands need to connect their messaging directly with the specific communities they serve and media to their target demo. Here’s a playbook to help your company succeed when marketing on a local scale.
1. Understand local vs. national campaigns
Local advertising differs from national campaigns in several ways:
- Audience specificity: By zooming in on precise geographic areas, brands can tailor messaging to align with local communities’ customs, preferences and nuances. This precision targeting ensures that your message resonates with the right target audience.
- Budget friendliness: Local advertising is often more accessible for small businesses. Local campaign costs are lower, enabling brands to invest strategically within targeted locales. This budget-friendly nature does not diminish the need for strategic planning; instead, it emphasizes allocating resources wisely to maximize returns. As a result, testing budgets can be allocated across multiple markets to maximize learnings for further market expansion.
- Channel selection: Selecting the correct channels is vital for effective local advertising. Local newspapers, radio stations, digital platforms and community events each offer advantages. The key lies in understanding where your target audience spends time and focusing efforts to ensure optimal engagement.
- Flexibility and agility: Local campaigns can be adjusted more swiftly in response to market feedback or changes, allowing brands to stay relevant and responsive.
Maintaining brand consistency across local touchpoints reinforces brand identity and builds a strong, recognizable brand across markets.
2. Leverage customized audience segmentation
Customized audience segmentation is the process of dividing a market into distinct groups based on specific demographic criteria. This marketing segmentation supports the development of targeted messaging and media plans for local markets.
For example, a coffee chain might cater to two distinct segments: young professionals and retirees. After identifying these segments, the chain can craft messages, offers and media strategies relating to each group’s preferences and lifestyle.
To reach young professionals in downtown areas, the chain might focus on convenience, quality coffee and a vibrant atmosphere that is conducive to work and socializing. Targeted advertising on Facebook, Instagram or Connected TV, along with digital signage near office complexes, could capture the attention of this demographic, emphasizing quick service and premium blends.
Conversely, for retirees in residential areas, the chain could highlight a cozy ambiance, friendly service and promotions such as senior discounts. Advertisements in local print publications, community newsletters, radio stations and events like senior coffee mornings would foster a sense of community and belonging.
Dig deeper: Niche advertising: 7 actionable tactics for targeted marketing
3. Adapt to local market dynamics
Various factors influence local market dynamics. Brands that navigate changes effectively maintain a strong audience connection and stay ahead in the market. Here’s how consumer sentiment and behavior may evolve within a local market and the corresponding adjustments brands can make.
- Cultural shifts, such as changes in demographics or societal norms, can alter consumer preferences within a local community. For example, a neighborhood experiencing gentrification may see demand rise for specific products or services.
- Respond by updating your messaging to reflect the evolving cultural landscape, ensuring it resonates with the new demographic profile.
- Economic conditions are crucial. For example, during downturns, consumers often prioritize value and practicality.
- Highlight affordable options or emphasize the practical benefits of your offerings to ensure messaging aligns with consumers’ financial priorities. The impact is unique to each market and the marketing message must also be dynamic.
- Seasonal trends impact consumer behavior.
- Align your promotions and creative content with changing seasons or local events to make your offerings timely and relevant.
- New competitors. The competitive landscape demands vigilance because new entrants or innovative competitor campaigns can shift consumer preferences.
- Differentiate by focusing on your unique selling propositions, such as quality, customer service or community involvement, to retain consumer interest and loyalty.
4. Apply data and predictive analytics
Data and predictive analytics are indispensable tools for successfully reaching local target markets. These technologies provide consumer behavior insights, enabling you to anticipate market trends and adjust strategies proactively.
- Price optimization: By analyzing consumer demand, competitor pricing and market conditions, data analytics enables you to set prices that attract customers while ensuring profitability.
- Competitor analysis: Through analysis, brands can understand their positioning within the local market landscape and identify opportunities and threats. Predictive analytics offer foresight into competitors’ potential moves, allowing you to strategize effectively to maintain a competitive edge.
- Consumer behavior: Forecasting consumer behavior allows your brand to tailor offerings and marketing messages to meet evolving consumer needs and enhance engagement.
- Marketing effectiveness: Analytics track the success of advertising campaigns, providing insights into which strategies drive conversions and sales. This feedback loop enables continuous optimization of marketing efforts for maximum impact.
- Inventory management: In supply chain management, data analytics predict demand fluctuations, ensuring inventory levels align with market needs. This efficiency prevents stockouts or excess inventory, optimizing operational costs and meeting consumer expectations.
Dig deeper: Why you should add predictive modeling to your marketing mix
5. Counter external market influences
Consider a clothing retailer preparing for a spring collection launch. By analyzing historical weather data and using predictive analytics, the brand forecasts an unseasonably cool start to spring. Anticipating this, the retailer adjusts its campaign to highlight transitional pieces suitable for cooler weather, ensuring relevance despite an unexpected chill.
Simultaneously, predictive models signal an upcoming spike in local media advertising rates due to increased market demand. Retailers respond by reallocating a portion of advertising budgets to digital channels, which offer more flexibility and lower costs than traditional media. This shift enables brands to maintain visibility and engagement without exceeding budget, mitigating the impact of external forces on advertising.
6. Build consumer confidence with messaging
Localized messaging and tailored customer service enhance consumer confidence by demonstrating your brand’s understanding of the community. For instance, a grocery store that curates cooking classes featuring local cuisine or sponsors community events shows commitment to local culture and consumer interests.
Similarly, a bookstore highlighting local authors or topics relevant to the community resonates with local customers. Additionally, providing service that addresses local needs — such as bilingual service and local event support — reinforces the brand’s values and response to the community.
Through these localized approaches, brands can build trust and loyalty, bridging the gap between corporate presence and local relevance.
7. Dominate with local advertising
To dominate local markets, brands must:
- Harness hyper-targeted segmentation and geo-targeted advertising to reach and engage precise audiences.
- Create localized content that reflects community values, engage in community events, optimize campaigns for mobile and track results.
- Fine-tune strategies, outperform competitors and foster lasting relationships with customers.
These strategies will enable your message to resonate with local consumers, differentiate you in competitive markets and ensure you become a major player in your specific area.
Dig deeper: The 5 critical elements for local marketing success
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily MarTech. Staff authors are listed here.
MARKETING
Battling for Attention in the 2024 Election Year Media Frenzy


As we march closer to the 2024 U.S. presidential election, CMOs and marketing leaders need to prepare for a significant shift in the digital advertising landscape. Election years have always posed unique challenges for advertisers, but the growing dominance of digital media has made the impact more profound than ever before.
In this article, we’ll explore the key factors that will shape the advertising environment in the coming months and provide actionable insights to help you navigate these turbulent waters.
The Digital Battleground
The rise of cord-cutting and the shift towards digital media consumption have fundamentally altered the advertising landscape in recent years. As traditional TV viewership declines, political campaigns have had to adapt their strategies to reach voters where they are spending their time: on digital platforms.
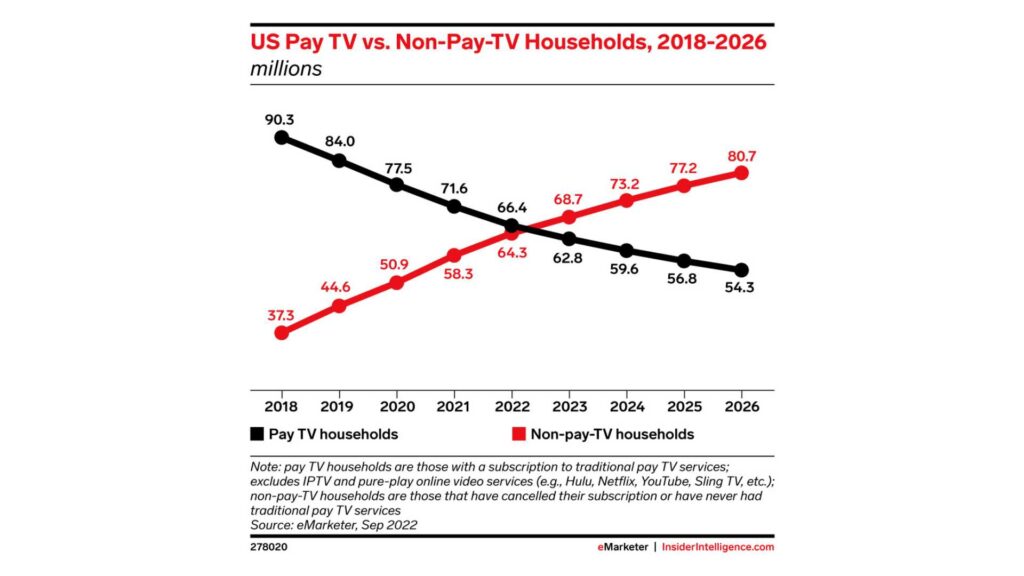

According to a recent report by eMarketer, the number of cord-cutters in the U.S. is expected to reach 65.1 million by the end of 2023, representing a 6.9% increase from 2022. This trend is projected to continue, with the number of cord-cutters reaching 72.2 million by 2025.
Moreover, a survey conducted by Pew Research Center in 2023 found that 62% of U.S. adults do not have a cable or satellite TV subscription, up from 61% in 2022 and 50% in 2019. This data further underscores the accelerating shift away from traditional TV and towards streaming and digital media platforms.
As these trends continue, political advertisers will have no choice but to follow their audiences to digital channels. In the 2022 midterm elections, digital ad spending by political campaigns reached $1.2 billion, a 50% increase from the 2018 midterms. With the 2024 presidential election on the horizon, this figure is expected to grow exponentially, as campaigns compete for the attention of an increasingly digital-first electorate.
For brands and advertisers, this means that the competition for digital ad space will be fiercer than ever before. As political ad spending continues to migrate to platforms like Meta, YouTube, and connected TV, the cost of advertising will likely surge, making it more challenging for non-political advertisers to reach their target audiences.
To navigate this complex and constantly evolving landscape, CMOs and their teams will need to be proactive, data-driven, and willing to experiment with new strategies and channels. By staying ahead of the curve and adapting to the changing media consumption habits of their audiences, brands can position themselves for success in the face of the electoral advertising onslaught.
Rising Costs and Limited Inventory
As political advertisers flood the digital market, the cost of advertising is expected to skyrocket. CPMs (cost per thousand impressions) will likely experience a steady climb throughout the year, with significant spikes anticipated in May, as college students come home from school and become more engaged in political conversations, and around major campaign events like presidential debates.


For media buyers and their teams, this means that the tried-and-true strategies of years past may no longer be sufficient. Brands will need to be nimble, adaptable, and willing to explore new tactics to stay ahead of the game.
Black Friday and Cyber Monday: A Perfect Storm
The challenges of election year advertising will be particularly acute during the critical holiday shopping season. Black Friday and Cyber Monday, which have historically been goldmines for advertisers, will be more expensive and competitive than ever in 2024, as they coincide with the final weeks of the presidential campaign.
To avoid being drowned out by the political noise, brands will need to start planning their holiday campaigns earlier than usual. Building up audiences and crafting compelling creative assets well in advance will be essential to success, as will a willingness to explore alternative channels and tactics. Relying on cold audiences come Q4 will lead to exceptionally high costs that may be detrimental to many businesses.
Navigating the Chaos
While the challenges of election year advertising can seem daunting, there are steps that media buyers and their teams can take to mitigate the impact and even thrive in this environment. Here are a few key strategies to keep in mind:
Start early and plan for contingencies: Begin planning your Q3 and Q4 campaigns as early as possible, with a focus on building up your target audiences and developing a robust library of creative assets.
Be sure to build in contingency budgets to account for potential cost increases, and be prepared to pivot your strategy as the landscape evolves.


Embrace alternative channels: Consider diversifying your media mix to include channels that may be less impacted by political ad spending, such as influencer marketing, podcast advertising, or sponsored content. Investing in owned media channels, like email marketing and mobile apps, can also provide a direct line to your customers without the need to compete for ad space.
Owned channels will be more important than ever. Use cheaper months leading up to the election to build your email lists and existing customer base so that your BF/CM can leverage your owned channels and warm audiences.
Craft compelling, shareable content: In a crowded and noisy advertising environment, creating content that resonates with your target audience will be more important than ever. Focus on developing authentic, engaging content that aligns with your brand values and speaks directly to your customers’ needs and desires.
By tapping into the power of emotional triggers and social proof, you can create content that not only cuts through the clutter but also inspires organic sharing and amplification.
Reflections
The 2024 election year will undoubtedly bring new challenges and complexities to the world of digital advertising. But by staying informed, adaptable, and strategic in your approach, you can navigate this landscape successfully and even find new opportunities for growth and engagement.
As a media buyer or agnecy, your role in steering your brand through these uncharted waters will be critical. By starting your planning early, embracing alternative channels and tactics, and focusing on creating authentic, resonant content, you can not only survive but thrive in the face of election year disruptions.
So while the road ahead may be uncertain, one thing is clear: the brands that approach this challenge with creativity, agility, and a steadfast commitment to their customers will be the ones that emerge stronger on the other side.
-

 PPC4 days ago
PPC4 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 16, 2024
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Clarifies Vacation Rental Structured Data
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoStreamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 17, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoAn In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago97 Marvelous May Content Ideas for Blog Posts, Videos, & More
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024















![How to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds Download Now: The 2024 State of Social Media Trends [Free Report]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-to-Use-AI-For-a-More-Effective-Social-Media.png)



You must be logged in to post a comment Login