The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Core Web Vitals Might Include Noindexed Pages via @martinibuster
Webmaster Trends Analyst John Mueller answered questions about Core Web Vitals and how the scores are calculated. He also discussed the possibility of noindexed pages being be used as part of the Core Web Vitals calculation in the new ranking signal that is coming soon.
Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals are user experience metrics. They are a group of metrics that Google chose to represent how well a web page downloads and presents a good user experience for site visitors.
There are three Core Web Vitals metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
How fast a web page is perceived to load - First Input Delay (FID)
How soon a visitor can interact with a web page - Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
How stable web page elements (like buttons, text and images) are while the page is downloading, without shifting about.
Those three metrics are scheduled to become ranking factors sometime in 2021. That is why many publishers and SEOs are concerned about how Google calculates the core web vitals score because, as a ranking factor, there is a possibility that it may impact rankings in certain scenarios.
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Screenshot of Google’s John Mueller Discussing Noindexed Pages and Core Web Vitals
 Screenshot of Google’s John Mueller discussing why noindexed pages might be used to calculate Core Web Vitals score
Screenshot of Google’s John Mueller discussing why noindexed pages might be used to calculate Core Web Vitals score
Lab Data and Field Data
Knowing what lab data and field data are is key to understanding John Mueller’s answer.
Lab data, in reference to web vitals scores is an estimate of the score. The lab data scores are generated in a simulated environment.
The goal with lab data is to give a publisher an idea of what could be problematic.
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Field Data is a score based on actual site visitors under real-world conditions.
It’s the field data that Google will be using to calculate the associated ranking signal score.
Publishers concerned about their ability to rank are concerned with how field data is calculated.
- Does Google use actual page score?
- Does Google use an average of several pages to calculate the core web vitals score?
Noindex and Core Web Vitals
Noindex is a signal that a publisher can use to tell Google not to include a web page in Google’s search results.
According to Google’s official documentation:
“You can prevent a page from appearing in Google Search by including a noindex meta tag in the page’s HTML code, or by returning a noindex header in the HTTP request.
When Googlebot next crawls that page and sees the tag or header, Googlebot will drop that page entirely from Google Search results, regardless of whether other sites link to it.”
The question asked of Google’s John Mueller was whether a noindexed page will be used to calculate the web vitals score.
What made this question important was that the publisher was blocking these pages because they were very slow and the publisher did not want those pages used as part of the calculation of the core web vitals score.
This is the first question:
“With regards to core web vitals, field data is going to be the one to pay attention to, correct (in terms of ranking signals)?”
John Mueller’s response:
“Yes, yes, it’s the field data.”
Google May Aggregate Pages for Core Web Vitals
In the follow up question Mueller reveals how Google may in some cases calculate the core web vitals score as an average of multiple pages.
This is the question:
“When this becomes a ranking signal… is it going to be page level or domain level?”
Mueller answered:
“…What happens with the field data is we don’t have data points for every page.
So we, for the most part, we need to have kind of groupings of individual pages.
And depending on the amount of data that we have, that can be a grouping of the whole website (kind of the domain).
…I think in the Chrome User Experience Report they use the origin which would be the subdomain and the protocol there.
So that would be kind of the overarching kind of grouping.
And if we have more data for individual parts of a website then we’ll try to use that.
And I believe that’s something you also see in search console where we’ll show like one URL and say… there’s so many other pages that are associated with that. And that’s kind of the grouping that we would use there.”
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Mueller is clear that the core web vitals score may not always be calculated on a page by page basis.
Will Slow Pages Affect Overall CWV Score?
The person asking the follow up question then related that they have a set of pages that are slow and are no-indexed and asked if those pages can impact the core web vitals score.
“We gave this set of pages that they are slow. And these we have a noindex on them… they are very slow. And that’s why we don’t want it to be accounted for.”
Mueller responded:
“I don’t know for sure how we would do things with a noindex there. But it’s not something you can easily determine ahead of time.
Like, will we see this as one website or will we see it as different groupings there.
Sometimes with the Chrome User Experience Report data you can see like, Does Google have data points for those noindex pages? Does Google have data points for the other pages there?
And then you can kind of figure out like okay, it can recognize that there is separate kinds of pages and can treat them individually.
And if that’s the case, then I don’t see a problem with that.
If it’s a smaller website where we just don’t have a lot of signals for the website then those noindex pages could be playing a role there as well.
So I’m not 100% sure but my understanding is that in the Chrome User Experience Report data we do include all kinds of pages that users access.
So there’s no specific kind of, will this page be indexed like this or not check that happens there because the indexability is sometimes quite complex with regards to canonicals and all of that.
So it’s not trivial to determine… on the Chrome side if this page will be indexed or not.
It might be the case that if a page has a clear noindex then even in Chrome we would be able to recognize that. But I’m not 100% sure if we actually do that.
I would also check the Chrome User Experience Report data. I think you can download data into BigQuery and you can play with that a little bit and figure out how is that happening for other sites, for similar sites that kind of fall in the same category as the site that you’re working on.”
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Pages that Users Access
While Mueller hedged by saying that he wasn’t 100% certain if Google used noindexed pages, he did affirm that the Chrome User Experience Report included all kinds of pages (which in this context presumably includes noindexed pages).
The reason they are included is because, according to Mueller:
“…we do include all kinds of pages that users access.”
The logic behind using noindexed pages can be that because users can access a page then it is going to be measured. The reason is because a user will experience the noindexed pages, regardless if those web pages are blocked to Google.
Though Mueller wasn’t 100% certain, until there is further clarification, it may be prudent to assume that noindexed pages will be measured as part of the core web vitals ranking score.
Citation
Watch the Office Hours Hangout
[embedded content]Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
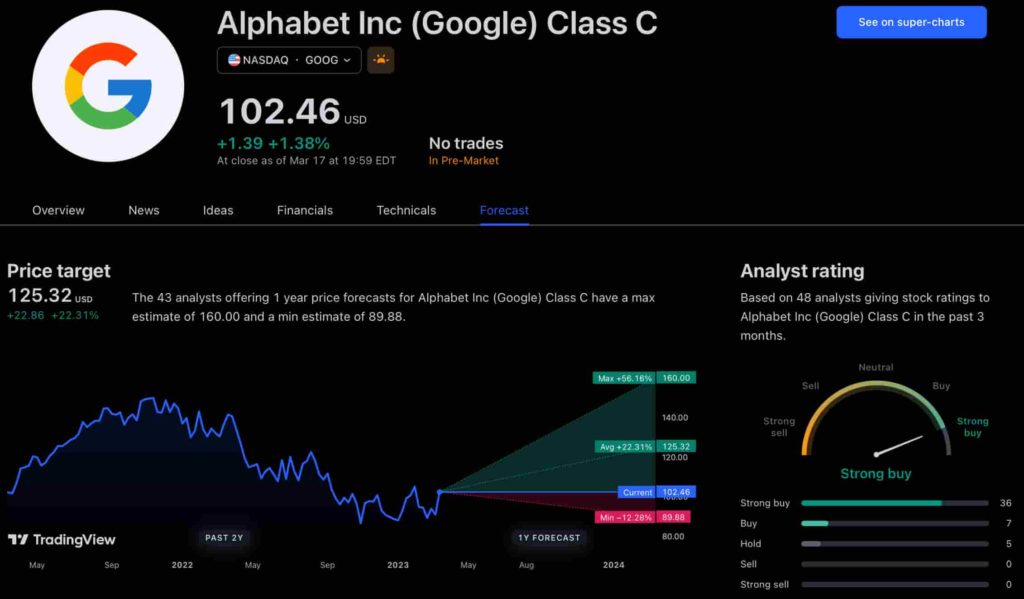
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days ago5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoWeekend Google Core Ranking Volatility
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoWordPress Releases A Performance Plugin For “Near-Instant Load Times”
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoThe power of program management in martech
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 15, 2024