SEO
8 Experiments To Improve Organic Traffic

Imagine the results you could achieve if you knew the Google search algorithm.
Just think of the organic traffic you could drive to your site if you knew exactly what Google was taking into account when generating search engine results, the precise amount each factor plays on rankings, and precisely what it would take to get to the top.
But of course, Google would never let you see behind the curtain. Not only could a bad actor use this information for nefarious purposes, but it would take all the fun out of search engine optimization.
So instead, every time there’s a new algorithm update, it’s up to us to figure out what exactly has changed and how to best leverage this to our advantage.
And because we in the search engine optimization world are a community, we tend to figure these things out collectively.
And because there are no (or very few, anyway) absolute answers, a lot of optimization comes down to best practices, theories, and outright guesswork.
Luckily, there’s a great way to determine if these theories are based on reality or just sheer conjecture. Of course, we’re talking about experimentation.
(Insert mad scientist laugh here.)
Before you get carried away and rush to put on your safety goggles and lab coats, relax. No bubbling beakers full of mystery liquids are involved, and your risk of accidentally creating a monster is very low.
(I would say zero, but I’ve seen the “Terminator” series, and it never explicitly says that a search engine optimizer didn’t create Skynet, so let’s play it safe.)
All your SEO experiments can be done from your desk chair’s comfort (and safety).
But before we dive into those, let’s first talk about how to test your SEO.
Steps For A Successful SEO Experiment
Thankfully, we don’t have to develop an entirely new framework for devising, conducting, and measuring our SEO tests – we can repurpose the scientific method you’re probably already familiar with.
Been a while since high school chemistry? Don’t worry; these five steps are sure to sound familiar:
- Make an observation. (E.g., my site is not on the first page of Google search results.)
- Ask a question and form a hypothesis. Is my meta description optimized for ranking? If I write better meta descriptions, it will improve my ranking.
- Gather data. Upon changing these descriptions, track the change in ranking position and site visits.
- Analyze the data. Create tables, graphs, and diagrams to help you understand the link between what was changed and changing results.
- Draw conclusions. Does the evidence support your prediction? Why or why not? Was site traffic increased due to your new meta descriptions, or did you also receive national news coverage during your testing period?)
You’ll want to do what marketers call A/B testing for accurate results. This means creating two versions of the same page, with only one difference, so you can see which gets the better response.
Before you start, keep one thing in mind: Incremental changes are essential. If you go wild and change all of these at once, you’ll have no idea which one(s) is making a difference.
Play it slowly and be patient. Test one, then wait for the results before moving on to the next. This will give you an obvious idea of what you need to do moving forward to ensure you’re always claiming front-page real estate.
With that out of the way, here’s a look at eight different things you can test to improve the ranking of your site:
1. SEO Title
Have you ever written what you thought was an amazing page title, only for Google to rewrite it in search results? That usually happens when the search engine doesn’t feel like your title was a good reflection of the page’s content.
But you can change this anytime you like.
And even if Google does replace the one you created, Google’s John Mueller confirmed the original title is still used for ranking purposes. This means even if you’re getting your SEO titles changed, it’s still a good idea to try to optimize them.
Here are a few things you can test to see if they generate results:
- Include your target keyword.
- Change their length (shorter is not always better).
- Experiment with brand name positioning or remove it altogether.
- Get click-baity (e.g., Do you want to lose 20 lbs. fast?).
- Add published date to demonstrate information relevancy.
- Get creative (people love what’s new and whimsical).
2. SEO Meta Description
Now, wait just a minute – you’re probably saying right now – Search Engine Journal has been clear that Google hasn’t used meta description in its rankings since sometime between 1999 and 2004.
Put down your pitchforks. Just because they aren’t a direct factor in SERPs doesn’t mean meta descriptions aren’t an essential SEO element.
For example, they can help improve your click-through rate, compel searchers, generate brand exposure, and help differentiate you from the competition. And all of these impact user behavior, which is a signal that Google factors in.
There have been entire articles written about creating awesome meta descriptions. But for our purposes, here are a few things you can A/B test to see if you can improve your organic traffic:
- Try different lengths. Traditional SEO wisdom suggests character count between 156-165 – see what works for you.
- Add keywords.
- Change your tone. Generally speaking, your style should match your brand’s voice, but for a specific page, maybe this isn’t the case.
- Get specific – are you getting a lot of visits from one long-tail keyword? Add that to your meta description.
3. Internal Anchor Text
You may know anchor text as the visible, clickable (usually blue) text in a hyperlink like this.
Not only is this useful for giving additional context to users, but Google has confirmed: Anchor text helps it better understand a page’s content, allowing it to rank those pages for relevant searches.
For example, in the paragraph above, “Google has confirmed” is the anchor text attached to the target link, which directs to a link proving that confirmation.
There are several types of anchor text you can use, including those with exact or partial-match keywords, branded (Search Engine Journal), images, generic (“click here”), and naked links (https://www.searchenginejournal.com).
To experiment with the impact, internal anchor text can have on your organic traffic. You can try things like:
- Changing their length (though shorter is often better).
- Adding keywords, particularly low-density keywords.
- Increasing specificity.
- Changing them to be more target link-specific.
4. Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of structured data used by Google and other search engines.
Following guidelines established by Schema.org, it is essentially a lingua franca for search engines. It’s an established standard that uses a unique vocabulary to help search engines more clearly understand your content.
It’s used to create rich snippets for adding information about events, recipes, people, videos, reviews, and products, among other things. These, in turn, make your link appear more prominent in SERPs.
And while schema is not directly factored into your ranking score, like SEO title, it can improve your click-through rate and impact your user behavior scores.
Experiment with adding schema markup to your pages and see if it improves your results.
5. Images
A picture is worth a thousand words – everyone knows that. This is because humans are visual creatures. And web designers and SEO professionals have recognized the importance of including images on webpages for a long time.
And it’s not just because they add visual interest and grab attention; they can also improve your search ranking.
Original (not stock), high-quality images optimized for SEO can reap the rewards.
Here are some things you can try with your images to improve your traffic:
- Add images. You should add images to every page. No one wants to read a wall of text.
- Choose a different file name. You want to immediately make it clear to Google what your image is depicting. Try adding your keywords.
- Change your formatting. There is no one-size-fits-all for digital images. You may want to change your file type depending on your image needs. JPEGs are good for larger photos. PNG files preserve background transparency.
- Compress files when possible. In general, smaller files are always better.
- Ensure responsiveness. With mobile search being such an essential factor in modern SEO, you want to ensure your images always look great on phones and desktops.
- Add alt text if the image can’t be displayed for some reason.
6. Headers
Your headlines and subheads give your page structure. This makes it easier for humans to browse and for search engines to understand what each section is about.
Google’s John Mueller was very clear about this, emphasizing the presence of any headings, not just H1s, sends a strong signal about the page’s content. It would be best if you took special care with all your H tags, from H1 down to H6. This is because they also serve as an accessibility aid and navigational tool in addition to their structural benefits.
Once upon a time, your headers were a massive factor in your ranking. But then, like always, people abused them, and Google started cracking down on keyword stuffing, overuse, and other dirty heading tricks.
That said, while they are far from the only factor Google takes into account, there is no question they are essential.
Here are a few things you can play with to try and improve your SEO results:
- Add more headings (except H1s). Improve the structure and clarity of your content by adding more subheads.
- Try using them to break up blocks of text. No one likes massive text blocks. H2s, H3s, etc., are the perfect solution.
- Add keywords. Like nearly everything else we’ve discussed, you should experiment with the use of keywords in your headings.
- Optimize for featured snippets. Grab attention and draw new traffic by claiming those special boxes on search results. Write your headers to land these.
- Get creative. Try making your headings and subheads more interesting.
7. Word Count
You already know content is the essential thing in any SEO strategy. But you may not have thought much about how the number of words you use can impact your ranking and traffic.
While you shouldn’t expect word count to push you over the top and take you from page six to the top result, it can help define your site as relevant and valuable to a search query – and draw in readers.
What do we mean by this? Again, it’s not a direct ranking factor, according to John Mueller.
With that said, longer-form copy tends to rank higher. This is because using more words provides Google with more information on what your page is about.
And if these longer pieces are well-written (like the one you’re reading in the author’s ever-so-humble opinion), they’ll help establish you as an authority on the topic.
And experimentation is easy. Take one of your existing articles or blog posts and duplicate it. On the second one, expound at greater length upon your topic.
Please note, we’re not talking about using your word count tricks from college (e.g., “at a later date” instead of just “later”). Instead, you should expand on ideas and topics, add examples and cite additional sources.
Then, see which one performs better on search engines. Chances are, it will be the longer one.
Read this piece for more on using word count for SEO optimization.
8. URL
Some SEO experts will swear URLs with keywords perform better than generic ones. Is this the case?
Well, yes and no.
On the one hand, Google has confirmed when it performs its initial crawl of a site, keywords in URLs help it understand what the site is about.
However, as this is only factored in when a new site is crawled, its role in an ongoing SEO strategy is minimal.
But again, this doesn’t mean you can’t use them to your advantage. Clear URLs create a better user experience and can be used as naked anchor tags much more accessible than one with 75 random numbers and letters tacked on at the end.
Experiment with your URLs. Take some of your old, non-descriptive links and add keywords to them. Shorten long URLs.
If you’re worried about losing links from the old page, add a 301-redirect pointing to the new one.
Don’t Be Afraid To Try Something New
Search engine optimization is a constantly shifting landscape. Changing trends can change how people interact with your website.
As algorithms change and new technologies emerge, your strategy needs to evolve.
There has never been, and probably never will be, “set it and forget it” search engine optimization. It will always require forward-thinkers and people willing to experiment to find new ways to get their websites to the top of the rankings.
Who says you can’t be one of them? Someone had to be the first to figure out that keyword stuffing helped rankings, and someone else had to figure out when it stopped working.
If you’re willing to experiment and try new things, you may find the next brilliant new strategy. Just don’t forget to share it with us.
More Resources:
Featured Image: Tatyana Vyc/Shutterstock
SEO
25 WordPress Alternatives Best For SEO

WordPress powers hundreds of millions of websites, but it is not the only content management system (CMS) option.
There’s a diverse marketplace of publishing platforms for those seeking alternatives. This review provides an overview of 25 leading alternatives to WordPress across key website categories.
We explore user-friendly website builders like Wix, Squarespace, and Weebly, which offer drag-and-drop simplicity. We look at flexible open-source options for developers and tech-savvy users, including Joomla, Drupal, and Hugo.
Ecommerce merchants can choose between hosted platforms like Shopify or open-source solutions like Magento. We also cover blogging-focused options like Ghost and Tumblr, web hosting providers like Bluehost, and community management tools like vBulletin.
For each alternative, we summarize the key features, benefits, and drawbacks to consider. Factors like budget, technical abilities, and website goals are examined to help identify the best fit based on individual needs.
While WordPress powers a large share of sites, there’s no shortage of quality options for creating the perfect online presence for those seeking alternatives.
Why Consider A WordPress Alternative?
There are several reasons why someone might consider a WordPress alternative for their website:
- Specific needs: While WordPress is versatile, some websites may have particular requirements for which other platforms are better suited.
- Ease of use: Some users may find WordPress challenging, especially if they lack technical skills.
- Maintenance and security: As an open-source platform, WordPress requires users to handle updates, backups, and security measures themselves.
- Built-in features: Some alternatives come with built-in features that WordPress requires plugins for.
- Customization: While WordPress offers many customization options, some users may prefer platforms that allow more granular control over the website’s appearance and functionality.
- Simplicity: Other publishing platforms might be a better fit for users who want a simple platform to publish content without dealing with the complexities of managing a website.
How To Choose An Alternative To WordPress
Choosing the right WordPress alternative depends on your specific needs and goals. To help you make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
- Purpose of your website: Determine its primary purpose. Is it a blog, an online store, a portfolio, or a complex business website?
- Budget: Consider your budget for building and maintaining your website. Some alternatives are free, while others require a subscription or a one-time payment.
- Technical skills: Assess your technical skills and those of your team. Some alternatives are designed for users with little coding experience, while others may require more technical knowledge.
- Customization and flexibility: Evaluate how much control you want over your website’s appearance and functionality.
- Scalability: Consider your website’s potential for growth. If you anticipate a significant increase in traffic or content, choose a platform that can scale with your needs.
- Support and community: Look into the level of support and the size of the community surrounding each alternative.
- Hosting: Decide whether you prefer a self-hosted solution or a hosted platform.
- Features: List the features your website requires. Ensure that your alternative offers these features natively or through extensions.
Once you’ve considered these factors, research various WordPress alternatives and compare them based on your requirements.
Read reviews, explore user communities, and, if possible, test out the platforms through free trials or demos.
This will help you better understand how each alternative works and whether it aligns with your needs and expectations.
25 Best WordPress Alternatives
1. Wix
Wix is best suited for individuals, small businesses, and entrepreneurs who want to create a professional-looking website without extensive technical skills or a large budget.
The platform’s user-friendly drag-and-drop interface makes it easy for users to design and customize their websites, offering various templates and design elements suitable for multiple purposes.
As a hosted platform, Wix takes care of technical aspects like server maintenance and security updates, making it ideal for those who don’t want to deal with these issues.
Wix also offers a free plan, allowing users to create a website without cost, although with limitations such as Wix branding and a non-custom domain.
One nuance to remember when using Wix is that once you’ve chosen a template and started building your site, it can be challenging to switch to a different template without redesigning your content.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available for all plans.
- Free custom domain available with paid plans.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- There is no option to retain complete control of your site as you can with WordPress.
- No access to source code.
2. Squarespace
 Screenshot from: squarespace.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: squarespace.com, March 2024.Squarespace is best suited for creatives, bloggers, and small business owners who want to create visually stunning websites with minimal technical knowledge.
The platform is known for its sleek, modern templates, which showcase content beautifully and are optimized for mobile devices.
As an all-in-one platform, Squarespace includes hosting, domain registration, and various tools for managing your website.
While Squarespace offers a high degree of customization, it may not be as flexible as some alternatives. The platform has a specific structure and set of features, which can be limiting for those who require advanced functionality or integrations.
Nonetheless, for most users, Squarespace’s built-in features and integrations are more than sufficient.
One tip for getting the most out of Squarespace is to use its built-in SEO and marketing tools, such as custom meta descriptions, alt tags, and automatic sitemaps.
Key Features:
- Complete hosting solution (including video).
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available for all plans.
- Free custom domain available with an annual subscription.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- There is no option to retain complete control of your site as you can with WordPress.
- No custom coding.
- No access to source code.
- No third-party extensions.
3. Weebly
 Screenshot from: weebly.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: weebly.com, March 2024.Weebly is best suited for individuals, small businesses, and entrepreneurs who want to create a simple, functional website without investing much time or money.
The platform’s drag-and-drop interface and intuitive editor make it beginner-friendly and easy to use, even for those without website-building experience.
However, it may not be as powerful or flexible as other alternatives, with a limited set of features and integrations that can be restrictive for those requiring advanced functionality or custom solutions.
One tip for getting the most out of Weebly is to explore its app center, which offers a range of third-party apps and integrations to extend your website’s functionality, including tools for marketing, social media, and ecommerce.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available.
- Inexpensive premium plans are as low as $6.00 per month.
- Free custom domain available with premium plans.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No option to retain complete control of your site as you can with WordPress.
- No access to source code.
- The free version restricts you to a maximum of five pages.
4. Google Sites
 Screenshot from: workspace.google.com/intl/en_ph/lp/sites/, March 2024.
Screenshot from: workspace.google.com/intl/en_ph/lp/sites/, March 2024.Google Sites is best suited for individuals, educators, and small businesses who need a simple, easy-to-use platform for creating basic websites or intranets. Its seamless integration with other Google tools, like Google Docs, Sheets, and Drive, makes it an excellent choice for those familiar with and heavily using these tools.
Google Sites also offers collaboration features, allowing multiple users to work on the same website simultaneously, making it ideal for team projects or class websites.
However, it’s a relatively basic website builder compared to other alternatives, with limited features and customization options. It may not be the best choice for those needing advanced functionality or design flexibility.
Additionally, it lacks built-in ecommerce features, making it less suitable for online stores.
One tip for getting the most out of Google Sites is leveraging its integration with other Google tools, such as embedding Google Docs, Sheets, or Slides into your web pages or using Google Forms to collect visitor data.
Key Features:
- The creator has complete control over page access and permissions.
- Tools can be accessed anywhere.
- It can be used as a basic project management program.
- Plenty of web development and deployment options.
- Real-time editing.
- Uses website speed optimization tools to minimize loading times.
Pros:
- Fast to get started and easy to use.
- Free to use.
- Integrated with other Google products.
Cons:
- Limited functionality compared to other website builders.
- It may not work with non-Google apps.
- Limited customization options.
- No SEO tools, and you can’t edit metadata.
- It cannot integrate Facebook pixels.
5. Jekyll
 Screenshot from: jekyllrb.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: jekyllrb.com, March 2024.Jekyll is best suited for developers, bloggers, and tech-savvy individuals who prefer a lightweight, flexible website creation platform. It’s particularly popular among the GitHub community, as it can be easily integrated with GitHub Pages for free hosting.
Jekyll requires specific technical knowledge, as users must be comfortable working with the command line and writing code. While Jekyll offers plugins and themes to extend its functionality, users may need to rely on their coding skills to customize their website fully.
One tip for getting the most out of Jekyll is to utilize its built-in blogging features, which offer a simple, intuitive way to create and manage blog posts using Markdown.
Another nuance to remember is that Jekyll generates static pages that may not be the best choice for websites requiring frequent updates or complex functionality.
Key Features:
- No programming is involved.
- SEO is built-in.
- GitHub manages redirects.
- Easy setup of custom domains.
Pros:
- No server maintenance.
- Very fast.
- Secure.
- Free hosting.
- Free SSL certificate.
- Works with GitHub as CMS.
Cons:
- It can’t create contact forms.
- No dynamic content options.
- Posts cannot be scheduled.
- Does not include image manipulation functionality.
6. Hugo
 Screenshot from: gohugo.io, March 2024.
Screenshot from: gohugo.io, March 2024.Hugo is best suited for developers, bloggers, and content creators who value speed, flexibility, and simplicity. Its lightning-fast build times and static page generation make it ideal for those who frequently update their site or publish new content regularly.
While Hugo offers themes and templates to help users get started, creating a unique design may require coding skills.
One tip for getting the most out of Hugo is to leverage its built-in shortcodes, which allow users to easily add complex functionality to their web pages without writing extensive code.
Another nuance to remember is that, as a static site generator, Hugo may not be the best choice for websites that require dynamic features like user authentication or real-time data updates.
Key Features:
- Can build most websites in seconds.
- Cross-platform with easy installation.
- Allows you to host your site anywhere.
- Customizable URLs.
- “Minutes to Read” and “WordCount” functionality.
- Integrated Google Analytics and Disqus comment support.
Pros:
- It easily integrates with Google Calendar and other apps.
- Easy to use with responsive customer service.
- Multilingual capabilities are built-in.
- Extendable as needed.
Cons:
- It can’t create one-off tasks.
- It can be confusing upon initial use, particularly in templating syntax.
- No plugins are available.
- Limited text formatting features.
7. Webflow
 Screenshot from: webflow.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: webflow.com, March 2024.Webflow is best suited for freelance designers and small agencies who want complete control over their website’s design without worrying about hosting, security, or performance.
One nuance of Webflow is that extending a site’s functionality is not as straightforward as installing a plugin like WordPress.
Users must either set up integrations between their Webflow site and other platforms using third-party tools like Zapier, or they can embed custom code blocks on pages to add features.
A key aspect to note about Webflow is its pricing structure. Building a site is completely free, and users only need to purchase a site plan and custom domain when they are ready to launch.
This makes it an attractive option for freelancers and small teams who want to design and prototype sites without upfront costs, paying only when they are ready to go live.
Key Features:
- More than 100 templates to choose from.
- Design is prioritized, with animation, interaction, and parallax scrolling options.
- Offers automatically generated sitemaps and customizable 301 redirects.
- Multiple payment options for ecommerce sites and automatic tax calculation.
Pros:
- Affordable plans range from free to $235 for top-tier ecommerce plans.
- Free starter plan.
- Numerous learning and help resources.
- Good range of templates.
- Good security.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Integration with social media can be frustrating.
- Advanced capabilities aren’t built-in and require integration.
8. Joomla
 Screenshot from: joomla.org, March 2024.
Screenshot from: joomla.org, March 2024.Joomla is best suited for creating social networking, community, and membership sites. With its built-in multilingual support and advanced user and content management options, Joomla enables site owners to manage hundreds of users, create custom post types, and publish content in multiple languages.
One nuance of Joomla is that it has a steeper learning curve compared to more beginner-friendly CMSs like WordPress.
While Joomla aims to combine the power and flexibility of Drupal with the user-friendliness of WordPress, users with some web development experience will be better equipped to understand and take full advantage of Joomla’s built-in features and settings.
Users can choose from over 6,000 extensions available in the official directory to extend a Joomla site’s functionality. However, unlike WordPress plugins that can be installed with just a few clicks, Joomla extensions must be installed via the backend.
This process requires more technical know-how and may be challenging for beginners.
Key Features:
- Almost 6,000 extensions are available.
- Traditional content editing (no drag-and-drop visual editor).
- Optimized for mobile (depending on the template).
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- Free, open-source software.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Access to source code.
Cons:
- No free subdomains or custom domains are available.
- No customer support.
- Requires a PHP-enable server to run.
- Fewer templates and extensions than WordPress.
9. Drupal
 Screenshot from: drupal.org, March 2024.
Screenshot from: drupal.org, March 2024.Drupal is best suited for large corporations, government agencies, and universities with dedicated teams of developers. With its extensive customization options and ability to handle large data and heavy traffic, Drupal is ideal for complex, high-performance websites.
One key nuance of Drupal is its steep learning curve. Drupal is designed for developers or users with a strong understanding of HTML, CSS, and PHP.
Customizing a Drupal site involves working with numerous modules and themes, which can be highly configurable but require technical expertise to set up and maintain.
For organizations with the necessary technical resources, Drupal’s flexibility and robustness make it a top choice for building highly secure and customized websites.
Key Features:
- Content management system (CMS).
- Over 47,000 modules are available.
- Traditional content editing (no drag-and-drop visual editor).
- Optimized for mobile (depending on the theme you choose).
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- Free, open-source software.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Access to source code.
- Strong security and data encryption.
Cons:
- No free subdomains.
- No customer support.
- Requires a PHP-enabled server to run.
10. DataLife Engine
 Screenshot from: dle-news.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: dle-news.com, March 2024.DataLife Engine (DLE) is best suited for media companies, news websites, and blogs, prioritizing SEO, security, and performance. The platform’s focus on handling high traffic levels with minimal server load makes it an attractive choice for websites that expect significant visitors and must ensure a smooth user experience.
DLE’s user-friendly interface and content management features suit organizations with multiple users involved in creating and publishing well-suited content.
The platform’s ability to track statistics and automatically filter words in comments can benefit media websites and blogs that need to moderate user-generated content and analyze audience engagement.
However, there are some nuances to consider when using DLE. The limited number of plugins and themes may restrict how much websites can customize their appearance and functionality compared to other CMSs like WordPress.
It’s also important to note that while DLE supports English users, they are considered a secondary focus.
Key Features:
- Content management system (CMS).
- Designed for multiple users.
- SEO-focused.
- Tracks statistics.
- Automatically filters words in comments.
- It supports an unlimited number of categories.
- Low server load.
- Allows plugins.
Pros:
- Stores data using MySQL.
- Excellent user experience
- Websites load quickly, even on low-end servers.
- Excellent for publishing news and blog posts.
Cons:
- No free version licenses vary from $79 for basic to $199 for unlimited.
- English users are a secondary focus.
- A limited number of plugins and themes.
- The lowest license doesn’t include customer support.
11. Sitefinity
 Screenshot from: progress.com/sitefinity-cms/, March 2024.
Screenshot from: progress.com/sitefinity-cms/, March 2024.Progress’ Sitefinity is best suited for organizations that manage multiple websites, brands, or marketing channels from a single platform.
The CMS’s ability to sync assets across pages and sites makes it an attractive choice for companies with a diverse online presence. It streamlines content management and ensures consistency across various touchpoints.
One notable advantage of Sitefinity is its low-cost license compared to other CMS options, which may make it an attractive choice for budget-conscious organizations.
Additionally, the minimal coding required for integration and the flexible deployment time can help businesses reduce development costs and bring their websites to market faster.
However, Sitefinity setup and administration can be challenging. Organizations may need to invest time and resources into training their teams or hiring experienced professionals to ensure a smooth implementation and ongoing management of the platform.
Key Features:
- Manage multiple sites from one location.
- Sync assets across pages and sites.
- It makes personalization simpler.
- Integrated analytics and optimization.
- Four versions include basic, marketing-focused, PaaS, and ecommerce.
- Multilingual capabilities.
Pros:
- Low-cost license compared to other CMS.
- No setup fee.
- Minimal coding is required for integration.
- Flexible deployment time shortens time to market.
- Options for marketing automation.
Cons:
- Free trial, but no free version.
- Setup and administration can be challenging.
- No mobile interface.
12. CMS Hub
 Screenshot from: hubspot.com/products/cms, March 2024.
Screenshot from: hubspot.com/products/cms, March 2024.CMS Hub, previously known as Hubspot CMS, is best suited for businesses that already use HubSpot’s marketing, sales, or service tools and want to integrate their website with their existing HubSpot ecosystem.
It combines the ease of use of a drag-and-drop website builder with the flexibility and performance of a CMS.
CMS Hub seamlessly integrates with HubSpot’s CRM platform, allowing businesses to create personalized content experiences, optimize marketing efforts, and streamline sales processes.
It also focuses on security and performance, with HubSpot handling website hosting, SSL certification, and CDN configuration.
However, while CMS Hub offers customization options, it may not be as flexible as other CMSs like WordPress or Drupal, potentially limiting businesses with particular design or functionality requirements.
Additionally, CMS Hub’s pricing model can be expensive compared to other CMS options, so companies must carefully consider their budget and weigh the benefits of its all-in-one approach.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based.
- Includes SEO recommendations.
- Includes numerous themes and responsive templates.
- Fully integrated CRM.
- Drag-and-drop webpage editor.
- Built-in security.
Pros:
- Adaptive A/B testing helps you identify the best page layout.
- All-in-one publishing tools.
- Built-in SEO tools.
- Supports smart content with personalized rules.
- Mobile pages supported with Google AMP.
Cons:
- Does not support ecommerce.
- No automatic backup and recovery.
13. Contentful
 Screenshot from: contentful.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: contentful.com, March 2024.Contentful is a headless CMS best suited for businesses and developers requiring a flexible, scalable, and customizable content management solution.
It’s particularly well-suited for organizations delivering content across multiple channels, such as websites, mobile apps, and IoT devices.
One of Contentful’s key advantages is its content modeling capabilities. The platform allows users to create custom content models that can be easily adapted to their needs.
When using Contentful, it’s important to remember that it’s a headless CMS that focuses on content management and delivery rather than providing a built-in front end or presentation layer.
Developers must build a front end using their preferred tools and frameworks and then integrate with Contentful’s API to retrieve and display the content.
Another aspect to consider is the learning curve associated with Contentful. While the platform is designed to be user-friendly, it may take some time for content editors and managers to become familiar with its interface and content modeling concepts.
Features:
- RESTful API gives you complete control over assets, translations, and versions.
- Customizable interface and framework that works across third-party component providers.
- It provides regional autonomy, so pieces in multiple languages and time zones can be published globally.
- Content modeling allows you to structure content by channel.
- Single sign-on and secure access.
Pros:
- Focus on integration simplifies the technology stack.
- User-friendly with a clean interface.
- Free version for up to five users.
- Good scalability.
Cons:
- Expensive for an upgraded version ($489/month).
- Poor internal search tools.
- Modeling content can be tricky.
14. Adobe Experience Manager
 Screenshot from: business.adobe.com/products/experience-manager/adobe-experience-manager.html, March 2024
Screenshot from: business.adobe.com/products/experience-manager/adobe-experience-manager.html, March 2024Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) is an enterprise-level CMS best suited for large organizations with complex content management needs and a significant budget. AEM’s target audience includes global brands, financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies.
One of AEM’s key strengths is its tight integration with other Adobe products, such as Analytics, Target, and Creative Cloud.
This integration allows organizations to leverage the full power of Adobe’s digital marketing suite, enabling them to create, manage, and optimize content and experiences across the entire customer journey.
AEM also offers advanced features like intelligent content delivery, AI-powered content tagging, and multi-site management, making it a comprehensive solution for enterprise content management.
The platform’s complexity and extensive feature set can overwhelm smaller organizations or teams with limited resources. Additionally, AEM’s licensing and implementation costs are among the highest in the market, making it a significant investment for any organization.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive marketing platform.
- End-to-end digital document solution.
- Enterprise-level security.
- Analytics included.
- Intelligent search.
- Scalable to your needs.
Pros:
- Streamlines workflows by keeping everything on one platform.
- Individual marketers can handle authoring and publishing.
- Easy authorization of workflow.
- Can handle massive content loads.
- Can manage multiple sites at once.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Requires different sign-ins to access other areas.
- Doesn’t integrate well with external DAMs.
- Not ideal for communities and forums.
Ecommerce Platforms
15. BigCommerce
 Screenshot from: bigcommerce.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: bigcommerce.com, March 2024.BigCommerce is a hosted ecommerce platform best suited for businesses of all sizes looking to create and manage an online store. It caters to many users, from small and medium-sized businesses to large enterprises.
One of BigCommerce’s key advantages is its scalability. The platform accommodates businesses as they grow, offering features like unlimited products, file storage, and bandwidth.
BigCommerce also provides a range of advanced ecommerce functionalities, such as multi-channel selling, abandoned cart recovery, and built-in SEO tools, which can help businesses optimize their online sales performance.
When considering BigCommerce, it’s important to remember that while the platform offers a wide range of features, some of the more advanced functionalities may require a higher-tier plan or additional costs.
BigCommerce also enforces certain design limitations on its themes, which may restrict the level of customization available without diving into custom coding.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- High level of customization options.
- Over 100 themes to choose from (including some free).
- No platform commission fees.
- Free subdomain available.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No free version is available.
- No access to source code.
- Pricing is based on revenue, which isn’t great if you have tight margins.
16. Shopify
 Screenshot from: shopify.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: shopify.com, March 2024.Shopify is an ecommerce platform well-suited for entrepreneurs and small business owners who want to establish an online presence quickly without extensive technical expertise.
Shopify’s extensive app marketplace allows businesses to extend its functionality and customize their online store to meet specific needs.
The platform also provides built-in features like inventory management, payment processing, and abandoned cart recovery to help streamline operations and optimize sales performance.
When using Shopify, consider the platform’s transaction fees, which vary depending on the payment gateway. Some advanced design changes may require HTML, CSS, and Liquid knowledge.
Despite these considerations, Shopify remains a top choice for businesses seeking a reliable, scalable, and feature-rich ecommerce platform.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No free version is available.
- No access to source code.
- Platform commission fees.
17. Magento
 Screenshot from: business.adobe.com/products/magento/magento-commerce.html, March 2024
Screenshot from: business.adobe.com/products/magento/magento-commerce.html, March 2024Magento is an open-source ecommerce platform best suited for medium to large enterprises with complex online selling needs.
Magento’s flexibility and scalability come with a steeper learning curve than other ecommerce platforms. It requires more technical expertise to set up, customize, and maintain, making it less suitable for small businesses or users without web development knowledge.
When using Magento, remember that its powerful features and customization options can impact website performance if not optimized properly.
Choosing a reliable hosting provider and working with experienced Magento developers is crucial for ensuring optimal store performance and security.
Key Features:
- Option to pay for Magento Commerce for a complete hosting platform or download the free, open-source software to install on your web server.
- Drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Ecommerce store.
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one ecommerce platform or open-source ecommerce software package.
- Free version available.
- Designed for large-scale ecommerce.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available (mainly for setup and testing purposes).
- Customer support (paid version only).
- Access to source code with the downloadable version.
Cons:
- No blog module, although you can add it as an extension.
- Not optimized for web projects or website purposes outside of ecommerce.
- The steep learning curve for inexperienced users.
- A large investment for small-scale ecommerce.
18. PrestaShop
 Screenshot from: prestashop.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: prestashop.com, March 2024.PrestaShop is an open-source ecommerce platform best suited for small to medium-sized businesses looking for a cost-effective and customizable solution.
PrestaShop offers a wide range of themes and modules, allowing businesses to customize their online store’s appearance and functionality. The platform also has a strong community of developers and users, providing support and resources for store owners.
While PrestaShop is generally easy to use, some advanced customizations may require coding knowledge. Additionally, the number of installed modules can impact the platform’s performance.
Key Features:
- Customizable to your needs, including themes and features.
- Includes backend tools like payments, shipping and data.
- Community of translators for multilanguage digital stores.
- Secure payment modules.
- Scalable.
- Includes demographic assistance.
Pros:
- Free version available.
- Open source so that you can customize your site to your needs.
- 5,000+ themes, modules, and services are available with the premium plan.
- Excellent user experience.
Cons:
- Limited scalability.
- No support team.
- Initial setup requires some programming knowledge.
19. OpenCart
 Screenshot from: opencart.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: opencart.com, March 2024.OpenCart is a free, open-source ecommerce platform best suited for small—to medium-sized businesses with limited budgets.
OpenCart offers a decent range of features and extensions, allowing businesses to customize their online store. However, its marketplace is smaller than other platforms, which may limit advanced functionality options.
When using OpenCart, be mindful of its performance limitations as the store grows. Optimizing and carefully selecting extensions may be required to maintain a smooth user experience.
Additionally, its simplicity may not be suitable for businesses with complex ecommerce needs.
Features:
- The administrator dashboard gives you information at a glance.
- User management allows you to assign permissions and separate access.
- Allows you to run multiple stores from one dashboard.
- Customizable variables let you include options for sizes, colors, or anything else.
Pros:
- The platform is entirely free, as are many add-ons.
- Extensive metrics and reports were provided.
- Works with your current payment gateway.
- Comes with dedicated technical support.
- Flexible.
Cons:
- Often creates duplicate pages, which can cause SEO problems.
- Not all extensions, modules, plugins, and add-ons work well together.
- Checkout can be slow, particularly if you have numerous plugins.
- Can be difficult to import a list of inventory.
- Requires some degree of technical ability for optimal use.
Blogging Platforms
20. Medium
 Screenshot from: medium.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: medium.com, March 2024.Medium is a publishing platform best suited for individual bloggers, writers, and content creators who want to share their ideas and stories with a built-in audience.
Medium’s clean and minimalistic interface allows readers to concentrate on the content. The platform also offers a built-in social network, making it easy for writers to connect with readers and other creators.
However, this simplicity comes with limited customization options for branding and design.
When using Medium, it’s important to understand that the platform controls the distribution and monetization of content. While this can lead to increased exposure, it also means less control over the presentation and ownership of your content compared to self-hosted solutions.
Key Features:
- Full hosting solution.
- No software to self-install.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Limited social media tools.
Pros:
- A community site for blogs.
- Free version available.
- Medium Partner Program to earn revenue.
- Customer support.
Cons:
- No extensions.
- No ecommerce stores.
- No premade designs or themes.
- No free subdomains.
- No third-party extensions.
- No access to source code.
21. Ghost
 Screenshot from: ghost.org, March 2024.
Screenshot from: ghost.org, March 2024.Ghost is a lightweight, open-source publishing platform best suited for bloggers, writers, and small publications who value simplicity and performance. It’s designed for users who want a clean, focused writing experience without the complexity of more feature-rich CMS platforms.
Ghost offers a simple, intuitive editor and a minimalistic default theme, allowing users to create and publish content quickly.
The platform also provides built-in SEO features and supports memberships and subscriptions, making it a good choice for content creators looking to monetize their work.
As Ghost primarily focuses on publishing, it may not be the best fit for users who require extensive customization options or advanced functionality beyond blogging.
Key Features:
- You can subscribe through Ghost’s hosting platform or download the free, open-source software to install on your web server.
- Basic drag-and-drop visual builder.
- Extensions are available through integrations with other tools.
- Optimized for mobile.
- Blog module.
- Ecommerce store (subscription only).
- Social media tools.
Pros:
- All-in-one website builder and platform.
- Free version available.
- Premade designs and templates.
- Free subdomain available with the paid version.
- Customer support.
- Access to source code.
Cons:
- Not compatible with all third-party web hosts.
- Highly specialized with limited capabilities beyond blogging.
- Not built to scale up into a business site or complex website.
22. Tumblr
 Screenshot from: tumblr.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: tumblr.com, March 2024.Tumblr is a microblogging and social networking platform best suited for younger audiences who enjoy sharing short-form multimedia content.
Tumblr’s emphasis on community and content discovery makes it easy for users to connect with others who share similar interests. The platform’s reblogging feature spreads content quickly, increasing visibility and engagement.
When using Tumblr, it’s important to understand the platform’s unique culture and demographics. Tumblr is known for its diverse, often niche communities, which can be both a strength and a challenge for brands and marketers.
Additionally, while Tumblr offers some customization options, it may not be the best choice for users who require a highly professional or branded online presence.
Key Features:
- Features strong social media functionality.
- Customizable.
- Google Analytics Integration.
- Unlimited storage.
- Ad-free blog themes.
- Free SSL certification.
Pros:
- Free to use; no upgrades are required to access all features.
- Free web hosting.
- User-friendly and easy to set up.
- No storage limits.
- Can post audio, video, images, gifs, and more.
Cons:
- Daily posting limit (250/day).
- Files must be under 10 MB.
- No plugins.
- Safety and security leave something to be desired.
- Unsuited to long-form content.
23. Bluehost
 Screenshot from: bluehost.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: bluehost.com, March 2024.Bluehost is a web hosting provider best suited for beginners and small businesses looking for an affordable, easy-to-use hosting solution.
Bluehost’s advantages are its user-friendly interface and one-click installations for popular CMS platforms like WordPress.
This makes it easy for users with limited technical knowledge to set up and manage their websites. Bluehost also provides 24/7 customer support and a free SSL certificate with each hosting plan.
While Bluehost is known for its reliability and performance, it may not be the best choice for websites with high traffic or complex requirements. Some users have reported issues with slow loading speeds and limited storage space on shared hosting plans.
Key Features:
- Domain names can be purchased through Bluehost.
- Versatile hosting options let you choose what works best for you.
- Dedicated servers and virtual private servers are available.
- A variety of plans are available based on your needs.
- Comes with customer service chat options.
Pros:
- The first term is inexpensive.
- Lots of storage and unlimited bandwidth.
- Good uptime.
- Free SSL certificates.
Cons:
- Extra features come with added costs, which can get pricey.
- High renewal rates.
- Speed could be better.
- All servers are U.S.-based.
24. Blogger
 Screenshot from: blogger.com, March 2024.
Screenshot from: blogger.com, March 2024.Blogger is a free, beginner-friendly blogging platform best suited for hobbyists, casual bloggers, and those who want to start a blog without investing in a self-hosted solution. It’s ideal for users who prioritize simplicity and ease of use over advanced customization options.
Blogger offers a straightforward, intuitive interface that makes it easy for users to create and publish blog posts.
The platform provides a selection of customizable templates and allows users to add gadgets and widgets to enhance their blog’s functionality. However, unlike other blogging platforms, Blogger’s design and customization options are relatively limited.
Blogger’s simplicity and lack of advanced features may make it unsuitable for professional bloggers or those looking to create a more sophisticated online presence.
Features:
- Clear analytics.
- Included layout/themes.
- Monetization options, including Google Adsense integration.
- Uses Google security.
- Unlimited storage.
Pros:
- Free to use.
- Extremely user-friendly.
- Free SSL security.
- Good uptime.
Cons:
- You don’t own your website.
- Fewer options and control over design.
- Limited support.
- Hard to port to a different platform.
Community Management
25. vBulletin
vBulletin is a proprietary forum software best suited for businesses, organizations, and communities looking to create and manage an online discussion platform.
vBulletin offers many features, including private messaging, user groups, and content management tools, making it a powerful solution for managing large, active communities.
The platform also provides a high level of customization, allowing administrators to tailor the look and feel of their forum to match their brand or website.
One of the primary considerations when using vBulletin is its licensing cost, which can be a significant investment for some users.
Additionally, while vBulletin offers a range of customization options, some technical knowledge may be required to optimize and maintain the platform entirely.
Key Features:
- Built-in SEO and security.
- Includes a chat app.
- Easy to get started.
- Built-in applications.
- Optimized for mobile users.
- Blogging functionality.
- Fully customizable.
Pros:
- Frequent patches and bug fixes.
- Customer support.
- Easy to install and get started.
- Designed to host forums.
- Includes templates.
Cons:
- No free option.
- Limited features compared to some other platforms.
- Requires some tech skills to take full advantage of the functionality.
- It can’t customize code for the cloud-based version.
Which One Is Right For You?
With so many options, determining the right alternative to WordPress depends on your specific needs and goals.
For individuals and small businesses seeking an easy-to-use website builder, Wix, Squarespace, or Weebly offer intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces. Those prioritizing simplicity and speed may prefer static site generators like Jekyll or Hugo.
Developers and tech-savvy users who value flexibility and customization can explore headless CMS options like Contentful or more robust open-source platforms like Joomla and Drupal.
Ecommerce merchants must evaluate features like inventory management, payment processing, and scalability when choosing between Shopify, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, and others.
No matter your requirements, there is likely a WordPress alternative that is well-suited to your needs. Thoroughly assessing your website goals, budget, and technical abilities will help you select the right platform to build your ideal online presence.
With some research and planning, you can find the perfect alternative to take your website beyond what WordPress offers.
More Resources:
Featured Image: GaudiLab/Shutterstock
SEO
2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making

WordPress security scanner WPScan’s 2024 WordPress vulnerability report calls attention to WordPress vulnerability trends and suggests the kinds of things website publishers (and SEOs) should be looking out for.
Some of the key findings from the report were that just over 20% of vulnerabilities were rated as high or critical level threats, with medium severity threats, at 67% of reported vulnerabilities, making up the majority. Many regard medium level vulnerabilities as if they are low-level threats and that’s a mistake because they’re not low level and should be regarded as deserving attention.
The WPScan report advised:
“While severity doesn’t translate directly to the risk of exploitation, it’s an important guideline for website owners to make an educated decision about when to disable or update the extension.”
WordPress Vulnerability Severity Distribution
Critical level vulnerabilities, the highest level of threat, represented only 2.38% of vulnerabilities, which is essentially good news for WordPress publishers. Yet as mentioned earlier, when combined with the percentages of high level threats (17.68%) the number or concerning vulnerabilities rises to almost 20%.
Here are the percentages by severity ratings:
- Critical 2.38%
- Low 12.83%
- High 17.68%
- Medium 67.12%
Authenticated Versus Unauthenticated
Authenticated vulnerabilities are those that require an attacker to first attain user credentials and their accompanying permission levels in order to exploit a particular vulnerability. Exploits that require subscriber-level authentication are the most exploitable of the authenticated exploits and those that require administrator level access present the least risk (although not always a low risk for a variety of reasons).
Unauthenticated attacks are generally the easiest to exploit because anyone can launch an attack without having to first acquire a user credential.
The WPScan vulnerability report found that about 22% of reported vulnerabilities required subscriber level or no authentication at all, representing the most exploitable vulnerabilities. On the other end of the scale of the exploitability are vulnerabilities requiring admin permission levels representing a total of 30.71% of reported vulnerabilities.
Permission Levels Required For Exploits
Vulnerabilities requiring administrator level credentials represented the highest percentage of exploits, followed by Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) with 24.74% of vulnerabilities. This is interesting because CSRF is an attack that uses social engineering to get a victim to click a link from which the user’s permission levels are acquired. This is a mistake that WordPress publishers should be aware of because all it takes is for an admin level user to follow a link which then enables the hacker to assume admin level privileges to the WordPress website.
The following is the percentages of exploits ordered by roles necessary to launch an attack.
Ascending Order Of User Roles For Vulnerabilities
- Author 2.19%
- Subscriber 10.4%
- Unauthenticated 12.35%
- Contributor 19.62%
- CSRF 24.74%
- Admin 30.71%
Most Common Vulnerability Types Requiring Minimal Authentication
Broken Access Control in the context of WordPress refers to a security failure that can allow an attacker without necessary permission credentials to gain access to higher credential permissions.
In the section of the report that looks at the occurrences and vulnerabilities underlying unauthenticated or subscriber level vulnerabilities reported (Occurrence vs Vulnerability on Unauthenticated or Subscriber+ reports), WPScan breaks down the percentages for each vulnerability type that is most common for exploits that are the easiest to launch (because they require minimal to no user credential authentication).
The WPScan threat report noted that Broken Access Control represents a whopping 84.99% followed by SQL injection (20.64%).
The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) defines Broken Access Control as:
“Access control, sometimes called authorization, is how a web application grants access to content and functions to some users and not others. These checks are performed after authentication, and govern what ‘authorized’ users are allowed to do.
Access control sounds like a simple problem but is insidiously difficult to implement correctly. A web application’s access control model is closely tied to the content and functions that the site provides. In addition, the users may fall into a number of groups or roles with different abilities or privileges.”
SQL injection, at 20.64% represents the second most prevalent type of vulnerability, which WPScan referred to as both “high severity and risk” in the context of vulnerabilities requiring minimal authentication levels because attackers can access and/or tamper with the database which is the heart of every WordPress website.
These are the percentages:
- Broken Access Control 84.99%
- SQL Injection 20.64%
- Cross-Site Scripting 9.4%
- Unauthenticated Arbitrary File Upload 5.28%
- Sensitive Data Disclosure 4.59%
- Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) 3.67%
- Remote Code Execution 2.52%
- Other 14.45%
Vulnerabilities In The WordPress Core Itself
The overwhelming majority of vulnerability issues were reported in third-party plugins and themes. However, there were in 2023 a total of 13 vulnerabilities reported in the WordPress core itself. Out of the thirteen vulnerabilities only one of them was rated as a high severity threat, which is the second highest level, with Critical being the highest level vulnerability threat, a rating scoring system maintained by the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
The WordPress core platform itself is held to the highest standards and benefits from a worldwide community that is vigilant in discovering and patching vulnerabilities.
Website Security Should Be Considered As Technical SEO
Site audits don’t normally cover website security but in my opinion every responsible audit should at least talk about security headers. As I’ve been saying for years, website security quickly becomes an SEO issue once a website’s ranking start disappearing from the search engine results pages (SERPs) due to being compromised by a vulnerability. That’s why it’s critical to be proactive about website security.
According to the WPScan report, the main point of entry for hacked websites were leaked credentials and weak passwords. Ensuring strong password standards plus two-factor authentication is an important part of every website’s security stance.
Using security headers is another way to help protect against Cross-Site Scripting and other kinds of vulnerabilities.
Lastly, a WordPress firewall and website hardening are also useful proactive approaches to website security. I once added a forum to a brand new website I created and it was immediately under attack within minutes. Believe it or not, virtually every website worldwide is under attack 24 hours a day by bots scanning for vulnerabilities.
Read the WPScan Report:
WPScan 2024 Website Threat Report
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Ljupco Smokovski
SEO
An In-Depth Guide And Best Practices For Mobile SEO

Over the years, search engines have encouraged businesses to improve mobile experience on their websites. More than 60% of web traffic comes from mobile, and in some cases based on the industry, mobile traffic can reach up to 90%.
Since Google has completed its switch to mobile-first indexing, the question is no longer “if” your website should be optimized for mobile, but how well it is adapted to meet these criteria. A new challenge has emerged for SEO professionals with the introduction of Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which replaced First Input Delay (FID) starting March, 12 2024.
Thus, understanding mobile SEO’s latest advancements, especially with the shift to INP, is crucial. This guide offers practical steps to optimize your site effectively for today’s mobile-focused SEO requirements.
What Is Mobile SEO And Why Is It Important?
The goal of mobile SEO is to optimize your website to attain better visibility in search engine results specifically tailored for mobile devices.
This form of SEO not only aims to boost search engine rankings, but also prioritizes enhancing mobile user experience through both content and technology.
While, in many ways, mobile SEO and traditional SEO share similar practices, additional steps related to site rendering and content are required to meet the needs of mobile users and the speed requirements of mobile devices.
Does this need to be a priority for your website? How urgent is it?
Consider this: 58% of the world’s web traffic comes from mobile devices.
If you aren’t focused on mobile users, there is a good chance you’re missing out on a tremendous amount of traffic.
Mobile-First Indexing
Additionally, as of 2023, Google has switched its crawlers to a mobile-first indexing priority.
This means that the mobile experience of your site is critical to maintaining efficient indexing, which is the step before ranking algorithms come into play.
Read more: Where We Are Today With Google’s Mobile-First Index
How Much Of Your Traffic Is From Mobile?
How much traffic potential you have with mobile users can depend on various factors, including your industry (B2B sites might attract primarily desktop users, for example) and the search intent your content addresses (users might prefer desktop for larger purchases, for example).
Regardless of where your industry and the search intent of your users might be, the future will demand that you optimize your site experience for mobile devices.
How can you assess your current mix of mobile vs. desktop users?
An easy way to see what percentage of your users is on mobile is to go into Google Analytics 4.
- Click Reports in the left column.
- Click on the Insights icon on the right side of the screen.
- Scroll down to Suggested Questions and click on it.
- Click on Technology.
- Click on Top Device model by Users.
- Then click on Top Device category by Users under Related Results.
- The breakdown of Top Device category will match the date range selected at the top of GA4.
You can also set up a report in Looker Studio.
- Add your site to the Data source.
- Add Device category to the Dimension field.
- Add 30-day active users to the Metric field.
- Click on Chart to select the view that works best for you.
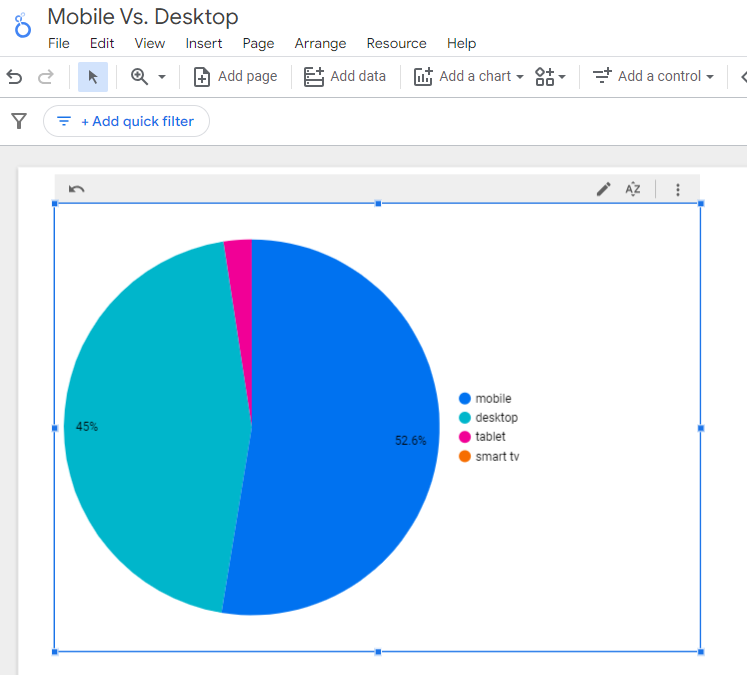 Screenshot from Looker Studio, March 2024
Screenshot from Looker Studio, March 2024You can add more Dimensions to really dig into the data to see which pages attract which type of users, what the mobile-to-desktop mix is by country, which search engines send the most mobile users, and so much more.
Read more: Why Mobile And Desktop Rankings Are Different
How To Check If Your Site Is Mobile-Friendly
Now that you know how to build a report on mobile and desktop usage, you need to figure out if your site is optimized for mobile traffic.
While Google removed the mobile-friendly testing tool from Google Search Console in December 2023, there are still a number of useful tools for evaluating your site for mobile users.
Bing still has a mobile-friendly testing tool that will tell you the following:
- Viewport is configured correctly.
- Page content fits device width.
- Text on the page is readable.
- Links and tap targets are sufficiently large and touch-friendly.
- Any other issues detected.
Google’s Lighthouse Chrome extension provides you with an evaluation of your site’s performance across several factors, including load times, accessibility, and SEO.
To use, install the Lighthouse Chrome extension.
- Go to your website in your browser.
- Click on the orange lighthouse icon in your browser’s address bar.
- Click Generate Report.
- A new tab will open and display your scores once the evaluation is complete.
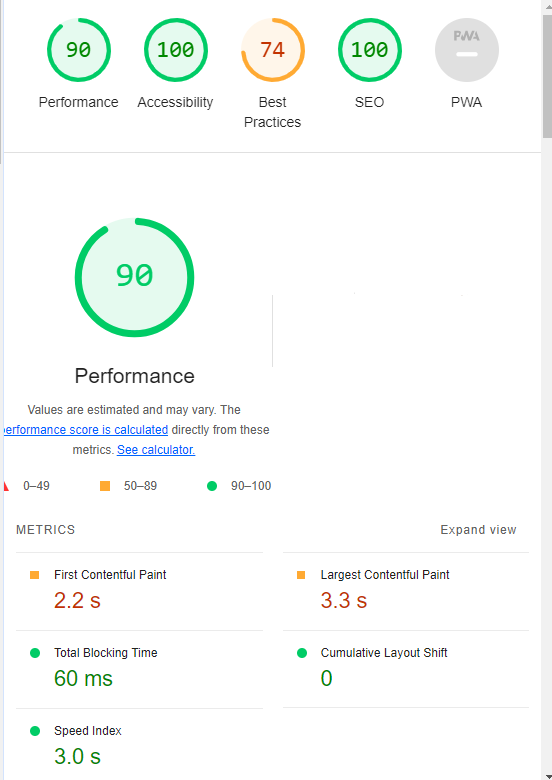 Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024
Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024You can also use the Lighthouse report in Developer Tools in Chrome.
- Simply click on the three dots next to the address bar.
- Select “More Tools.”
- Select Developer Tools.
- Click on the Lighthouse tab.
- Choose “Mobile” and click the “Analyze page load” button.
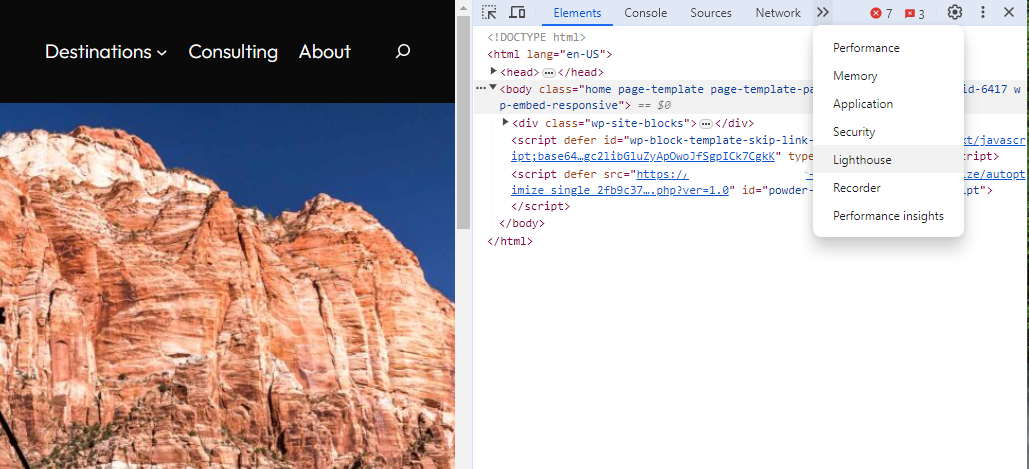 Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024
Screenshot from Lighthouse, March 2024Another option that Google offers is the PageSpeed Insights (PSI) tool. Simply add your URL into the field and click Analyze.
PSI will integrate any Core Web Vitals scores into the resulting view so you can see what your users are experiencing when they come to your site.
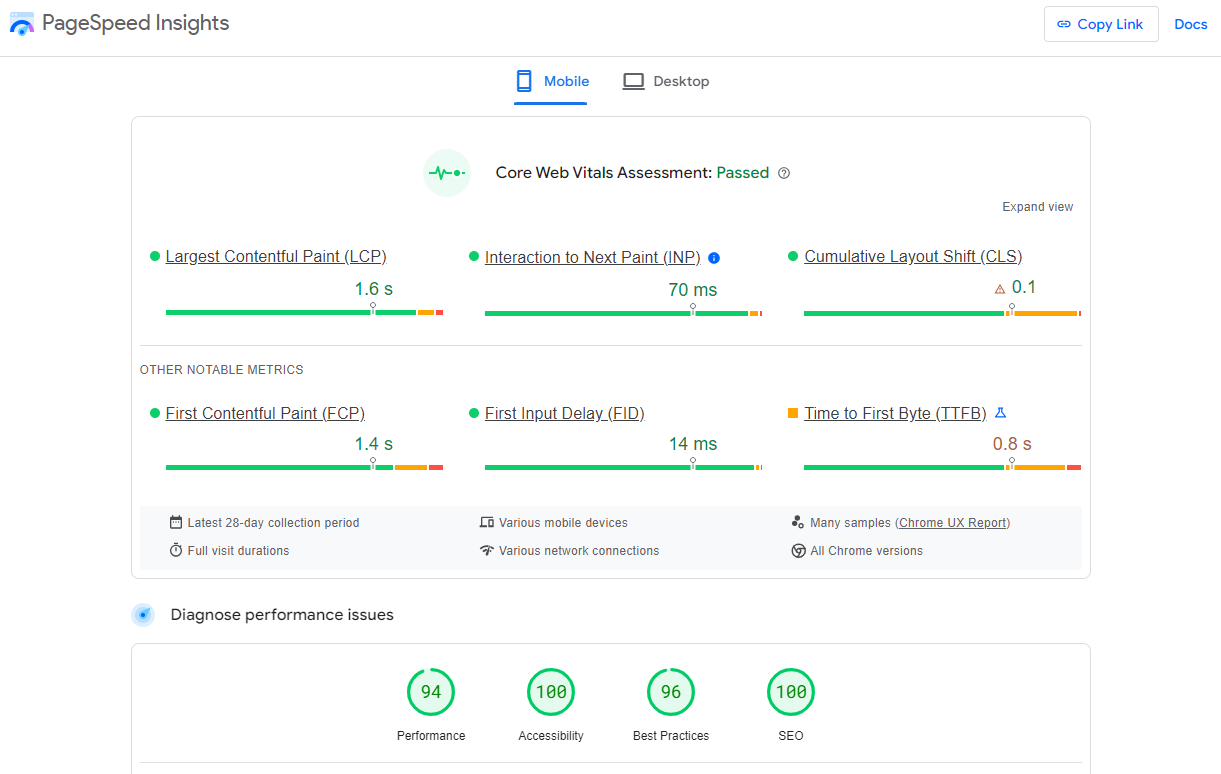 Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, March 2024
Screenshot from PageSpeed Insights, March 2024Other tools, like WebPageTest.org, will graphically display the processes and load times for everything it takes to display your webpages.
With this information, you can see which processes block the loading of your pages, which ones take the longest to load, and how this affects your overall page load times.
You can also emulate the mobile experience by using Developer Tools in Chrome, which allows you to switch back and forth between a desktop and mobile experience.
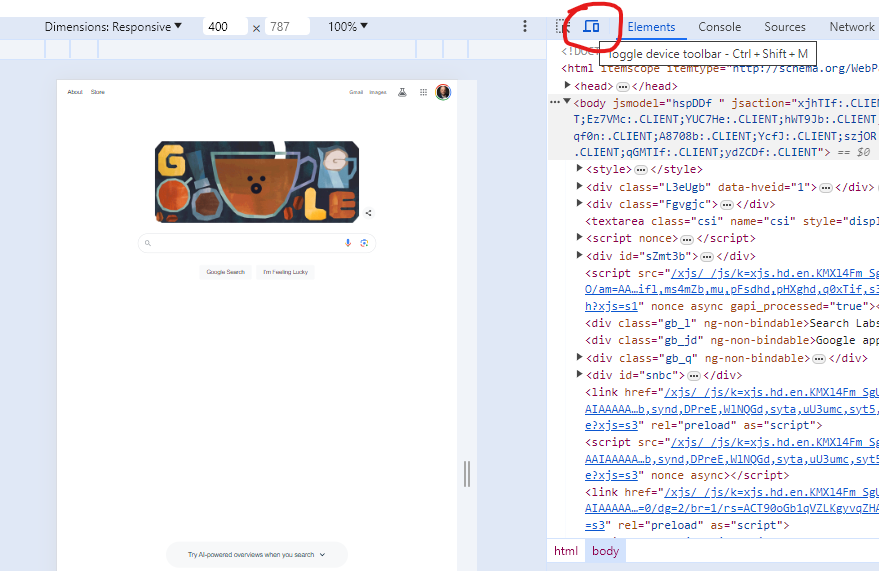 Screenshot from Google Chrome Developer Tools, March 2024
Screenshot from Google Chrome Developer Tools, March 2024Lastly, use your own mobile device to load and navigate your website:
- Does it take forever to load?
- Are you able to navigate your site to find the most important information?
- Is it easy to add something to cart?
- Can you read the text?
Read more: Google PageSpeed Insights Reports: A Technical Guide
How To Optimize Your Site Mobile-First
With all these tools, keep an eye on the Performance and Accessibility scores, as these directly affect mobile users.
Expand each section within the PageSpeed Insights report to see what elements are affecting your score.
These sections can give your developers their marching orders for optimizing the mobile experience.
While mobile speeds for cellular networks have steadily improved around the world (the average speed in the U.S. has jumped to 27.06 Mbps from 11.14 Mbps in just eight years), speed and usability for mobile users are at a premium.
Read more: Top 7 SEO Benefits Of Responsive Web Design
Best Practices For Mobile Optimization
Unlike traditional SEO, which can focus heavily on ensuring that you are using the language of your users as it relates to the intersection of your products/services and their needs, optimizing for mobile SEO can seem very technical SEO-heavy.
While you still need to be focused on matching your content with the needs of the user, mobile search optimization will require the aid of your developers and designers to be fully effective.
Below are several key factors in mobile SEO to keep in mind as you’re optimizing your site.
Site Rendering
How your site responds to different devices is one of the most important elements in mobile SEO.
The two most common approaches to this are responsive design and dynamic serving.
Responsive design is the most common of the two options.
Using your site’s cascading style sheets (CSS) and flexible layouts, as well as responsive content delivery networks (CDN) and modern image file types, responsive design allows your site to adjust to a variety of screen sizes, orientations, and resolutions.
With the responsive design, elements on the page adjust in size and location based on the size of the screen.
You can simply resize the window of your desktop browser and see how this works.
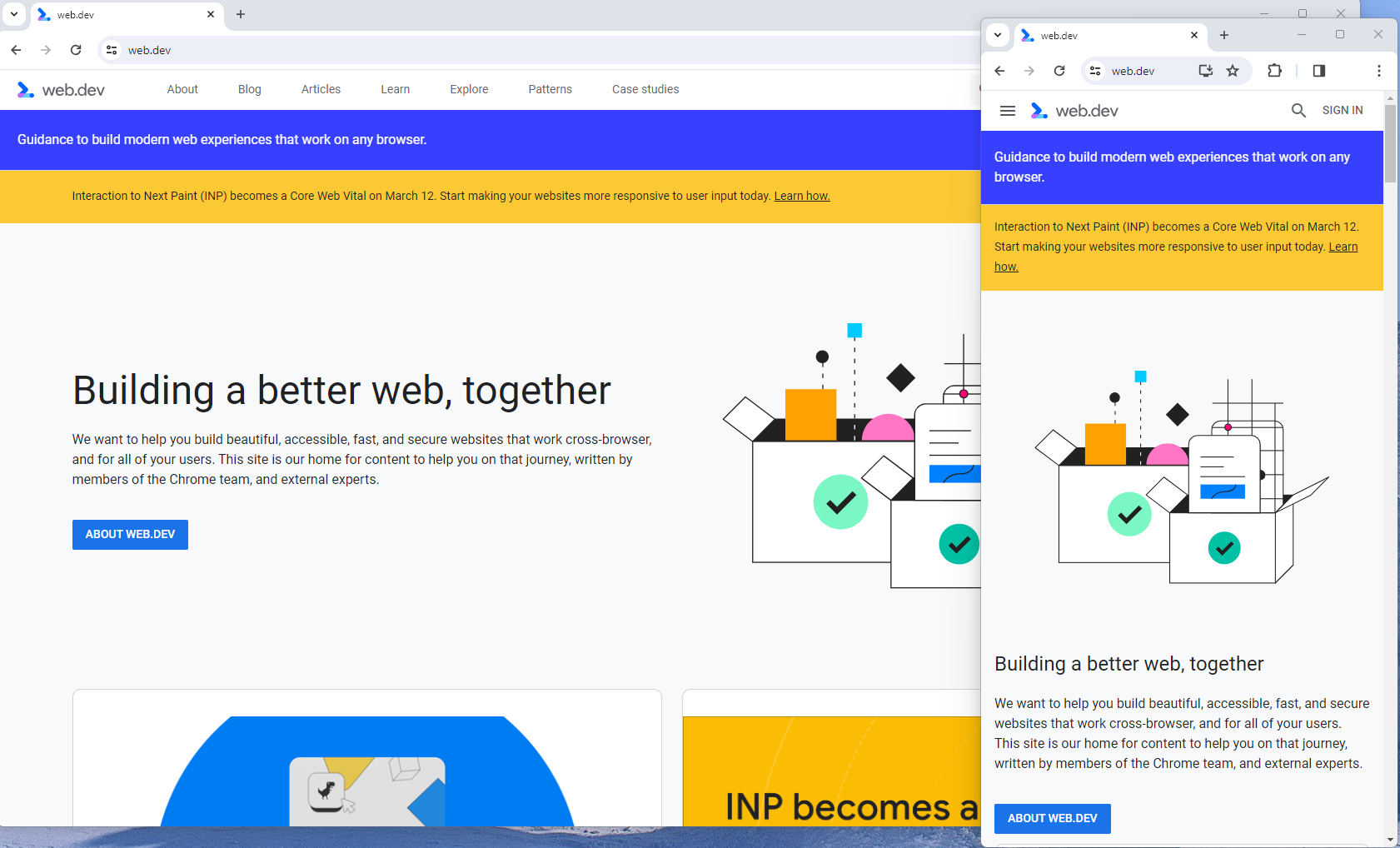 Screenshot from web.dev, March 2024
Screenshot from web.dev, March 2024This is the approach that Google recommends.
Adaptive design, also known as dynamic serving, consists of multiple fixed layouts that are dynamically served to the user based on their device.
Sites can have a separate layout for desktop, smartphone, and tablet users. Each design can be modified to remove functionality that may not make sense for certain device types.
This is a less efficient approach, but it does give sites more control over what each device sees.
While these will not be covered here, two other options:
- Progressive Web Apps (PWA), which can seamlessly integrate into a mobile app.
- Separate mobile site/URL (which is no longer recommended).
Read more: An Introduction To Rendering For SEO
Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
Google has introduced Interaction to Next Paint (INP) as a more comprehensive measure of user experience, succeeding First Input Delay. While FID measures the time from when a user first interacts with your page (e.g., clicking a link, tapping a button) to the time when the browser is actually able to begin processing event handlers in response to that interaction. INP, on the other hand, broadens the scope by measuring the responsiveness of a website throughout the entire lifespan of a page, not just first interaction.
Note that actions such as hovering and scrolling do not influence INP, however, keyboard-driven scrolling or navigational actions are considered keystrokes that may activate events measured by INP but not scrolling which is happeing due to interaction.
Scrolling may indirectly affect INP, for example in scenarios where users scroll through content, and additional content is lazy-loaded from the API. While the act of scrolling itself isn’t included in the INP calculation, the processing, necessary for loading additional content, can create contention on the main thread, thereby increasing interaction latency and adversely affecting the INP score.
What qualifies as an optimal INP score?
- An INP under 200ms indicates good responsiveness.
- Between 200ms and 500ms needs improvement.
- Over 500ms means page has poor responsiveness.
and these are common issues causing poor INP scores:
- Long JavaScript Tasks: Heavy JavaScript execution can block the main thread, delaying the browser’s ability to respond to user interactions. Thus break long JS tasks into smaller chunks by using scheduler API.
- Large DOM (HTML) Size: A large DOM ( starting from 1500 elements) can severely impact a website’s interactive performance. Every additional DOM element increases the work required to render pages and respond to user interactions.
- Inefficient Event Callbacks: Event handlers that execute lengthy or complex operations can significantly affect INP scores. Poorly optimized callbacks attached to user interactions, like clicks, keypress or taps, can block the main thread, delaying the browser’s ability to render visual feedback promptly. For example when handlers perform heavy computations or initiate synchronous network requests such on clicks.
and you can troubleshoot INP issues using free and paid tools.
As a good starting point I would recommend to check your INP scores by geos via treo.sh which will give you a great high level insights where you struggle with most.
 INP scores by Geos
INP scores by GeosRead more: How To Improve Interaction To Next Paint (INP)
Image Optimization
Images add a lot of value to the content on your site and can greatly affect the user experience.
From page speeds to image quality, you could adversely affect the user experience if you haven’t optimized your images.
This is especially true for the mobile experience. Images need to adjust to smaller screens, varying resolutions, and screen orientation.
- Use responsive images
- Implement lazy loading
- Compress your images (use WebP)
- Add your images into sitemap
Optimizing images is an entire science, and I advise you to read our comprehensive guide on image SEO how to implement the mentioned recommendations.
Avoid Intrusive Interstitials
Google rarely uses concrete language to state that something is a ranking factor or will result in a penalty, so you know it means business about intrusive interstitials in the mobile experience.
Intrusive interstitials are basically pop-ups on a page that prevent the user from seeing content on the page.
John Mueller, Google’s Senior Search Analyst, stated that they are specifically interested in the first interaction a user has after clicking on a search result.

Not all pop-ups are considered bad. Interstitial types that are considered “intrusive” by Google include:
- Pop-ups that cover most or all of the page content.
- Non-responsive interstitials or pop-ups that are impossible for mobile users to close.
- Pop-ups that are not triggered by a user action, such as a scroll or a click.
Read more: 7 Tips To Keep Pop-Ups From Harming Your SEO
Structured Data
Most of the tips provided in this guide so far are focused on usability and speed and have an additive effect, but there are changes that can directly influence how your site appears in mobile search results.
Search engine results pages (SERPs) haven’t been the “10 blue links” in a very long time.
They now reflect the diversity of search intent, showing a variety of different sections to meet the needs of users. Local Pack, shopping listing ads, video content, and more dominate the mobile search experience.
As a result, it’s more important than ever to provide structured data markup to the search engines, so they can display rich results for users.
In this example, you can see that both Zojirushi and Amazon have included structured data for their rice cookers, and Google is displaying rich results for both.
 Screenshot from search for [Japanese rice cookers], Google, March 2024
Screenshot from search for [Japanese rice cookers], Google, March 2024Adding structured data markup to your site can influence how well your site shows up for local searches and product-related searches.
Using JSON-LD, you can mark up the business, product, and services data on your pages in Schema markup.
If you use WordPress as the content management system for your site, there are several plugins available that will automatically mark up your content with structured data.
Read more: What Structured Data To Use And Where To Use It?
Content Style
When you think about your mobile users and the screens on their devices, this can greatly influence how you write your content.
Rather than long, detailed paragraphs, mobile users prefer concise writing styles for mobile reading.
Each key point in your content should be a single line of text that easily fits on a mobile screen.
Your font sizes should adjust to the screen’s resolution to avoid eye strain for your users.
If possible, allow for a dark or dim mode for your site to further reduce eye strain.
Headers should be concise and address the searcher’s intent. Rather than lengthy section headers, keep it simple.
Finally, make sure that your text renders in a font size that’s readable.
Read more: 10 Tips For Creating Mobile-Friendly Content
Tap Targets
As important as text size, the tap targets on your pages should be sized and laid out appropriately.
Tap targets include navigation elements, links, form fields, and buttons like “Add to Cart” buttons.
Targets smaller than 48 pixels by 48 pixels and targets that overlap or are overlapped by other page elements will be called out in the Lighthouse report.
Tap targets are essential to the mobile user experience, especially for ecommerce websites, so optimizing them is vital to the health of your online business.
Read more: Google’s Lighthouse SEO Audit Tool Now Measures Tap Target Spacing
Prioritizing These Tips
If you have delayed making your site mobile-friendly until now, this guide may feel overwhelming. As a result, you may not know what to prioritize first.
As with so many other optimizations in SEO, it’s important to understand which changes will have the greatest impact, and this is just as true for mobile SEO.
Think of SEO as a framework in which your site’s technical aspects are the foundation of your content. Without a solid foundation, even the best content may struggle to rank.
- Responsive or Dynamic Rendering: If your site requires the user to zoom and scroll right or left to read the content on your pages, no number of other optimizations can help you. This should be first on your list.
- Content Style: Rethink how your users will consume your content online. Avoid very long paragraphs. “Brevity is the soul of wit,” to quote Shakespeare.
- Image Optimization: Begin migrating your images to next-gen image formats and optimize your content display network for speed and responsiveness.
- Tap Targets: A site that prevents users from navigating or converting into sales won’t be in business long. Make navigation, links, and buttons usable for them.
- Structured Data: While this element ranks last in priority on this list, rich results can improve your chances of receiving traffic from a search engine, so add this to your to-do list once you’ve completed the other optimizations.
Summary
From How Search Works, “Google’s mission is to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
If Google’s primary mission is focused on making all the world’s information accessible and useful, then you know they will prefer surfacing sites that align with that vision.
Since a growing percentage of users are on mobile devices, you may want to infer the word “everywhere” added to the end of the mission statement.
Are you missing out on traffic from mobile devices because of a poor mobile experience?
If you hope to remain relevant, make mobile SEO a priority now.
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days ago5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoWeekend Google Core Ranking Volatility
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoWordPress Releases A Performance Plugin For “Near-Instant Load Times”
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoThe power of program management in martech
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 15, 2024
















You must be logged in to post a comment Login