SOCIAL
Apple crackdown on ChatGPT apps unlikely, new rules possible later

Apple CEO Tim Cook speaks at Apple’s Worldwide Developer Conference (WWDC) at the San Jose Convention Center in San Jose, California on Monday, June 4, 2018.
Josh Edelson | AFP | Getty Images
Large language models like ChatGPT can produce entire blocks of text that read like a human wrote them. Companies are racing to integrate ChatGPT into their apps, including Microsoft, Snap, and Shopify. But the trend could be stalled if Apple decides to restrict ChatGPT-based apps from its App Store, which is the only way to install software on an iPhone.
Blix, an email app maker that has regularly clashed with Apple over its App Store rules, says it ran into that hurdle this week.
Co-founder Ben Volach told the Wall Street Journal that Apple rejected an update to its BlueMail app because it integrated ChatGPT to help write emails, and it didn’t include content filtering over the output of the chatbot. Volach has also claimed on Twitter that Apple is “blocking” an AI update.
Apple said that without content filtering, the Blue Mail chatbot could produce words that aren’t appropriate for children, and the email app would have to raise its recommended age to 17 and up, according to the report.
Apple is investigating and the developers can appeal the decision, a spokesperson told CNBC.
Regardless, the Blue Mail episode isn’t a sign of an impending Apple crackdown on AI apps.
In fact, ChatGPT-powered features are already in Snapchat and the Microsoft Bing app, which are currently being distributed through the App Store. Other AI apps, such as Lensa, have also been distributed and have flourished in the App Store.
There is no formal AI or chatbot policy in Apple’s App Store Guidelines, a document that outlines what Apple permits on the App Store. Apple has employees in a department called App Review load up and briefly use all apps and updates before it approves them.
Apple could add AI-specific guidelines in the future. For crypto apps, for example, Apple explicitly introduced a section about cryptocurrency in the guidelines allowing wallet apps and banning on-device mining in a 2018 update. Apple introduced new rules about NFTs last year. The company often releases updates to its guidelines in June and October.
But the Blue Mail episode does reflect that Apple’s App Store is strict about content that’s generated at massive scale — either by users (in the case of social media apps, for example), or, more recently, by AI.
If an app can display content that infringes intellectual property, or messages that amount to cyberbullying, for example, then the app must have a way to filter that material and a way for users to report it, Apple says.
The content moderation rule was likely at the heart of a skirmish with Elon Musk’s Twitter late last year and was the reason Apple booted Parler from the App Store in 2021. Apple let Parler back on the App Store when it added content moderation.
Before it was released on the iPhone in the Bing app, the ChatGPT-based AI in Bing produced some creepy conversations, including threats against its users and pleas for help.
But Bing does have content moderation and filtering tools built into it. Microsoft’s AI allows users to downvote harmful responses, and includes a “safety system” that includes content filtering and abuse detection. Microsoft also updated its Bing chatbot in recent weeks to tamp down those creepy conversations, with the chatbot now often refusing to engage topics that could cause it to go off the rails.
SOCIAL
Snapchat Explores New Messaging Retention Feature: A Game-Changer or Risky Move?
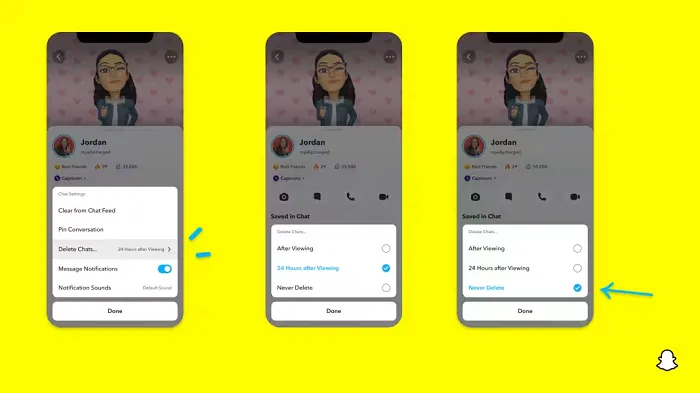
In a recent announcement, Snapchat revealed a groundbreaking update that challenges its traditional design ethos. The platform is experimenting with an option that allows users to defy the 24-hour auto-delete rule, a feature synonymous with Snapchat’s ephemeral messaging model.
The proposed change aims to introduce a “Never delete” option in messaging retention settings, aligning Snapchat more closely with conventional messaging apps. While this move may blur Snapchat’s distinctive selling point, Snap appears convinced of its necessity.
According to Snap, the decision stems from user feedback and a commitment to innovation based on user needs. The company aims to provide greater flexibility and control over conversations, catering to the preferences of its community.
Currently undergoing trials in select markets, the new feature empowers users to adjust retention settings on a conversation-by-conversation basis. Flexibility remains paramount, with participants able to modify settings within chats and receive in-chat notifications to ensure transparency.
Snapchat underscores that the default auto-delete feature will persist, reinforcing its design philosophy centered on ephemerality. However, with the app gaining traction as a primary messaging platform, the option offers users a means to preserve longer chat histories.
The update marks a pivotal moment for Snapchat, renowned for its disappearing message premise, especially popular among younger demographics. Retaining this focus has been pivotal to Snapchat’s identity, but the shift suggests a broader strategy aimed at diversifying its user base.
This strategy may appeal particularly to older demographics, potentially extending Snapchat’s relevance as users age. By emulating features of conventional messaging platforms, Snapchat seeks to enhance its appeal and broaden its reach.
Yet, the introduction of message retention poses questions about Snapchat’s uniqueness. While addressing user demands, the risk of diluting Snapchat’s distinctiveness looms large.
As Snapchat ventures into uncharted territory, the outcome of this experiment remains uncertain. Will message retention propel Snapchat to new heights, or will it compromise the platform’s uniqueness?
Only time will tell.
SOCIAL
Catering to specific audience boosts your business, says accountant turned coach

While it is tempting to try to appeal to a broad audience, the founder of alcohol-free coaching service Just the Tonic, Sandra Parker, believes the best thing you can do for your business is focus on your niche. Here’s how she did just that.
When running a business, reaching out to as many clients as possible can be tempting. But it also risks making your marketing “too generic,” warns Sandra Parker, the founder of Just The Tonic Coaching.
“From the very start of my business, I knew exactly who I could help and who I couldn’t,” Parker told My Biggest Lessons.
Parker struggled with alcohol dependence as a young professional. Today, her business targets high-achieving individuals who face challenges similar to those she had early in her career.
“I understand their frustrations, I understand their fears, and I understand their coping mechanisms and the stories they’re telling themselves,” Parker said. “Because of that, I’m able to market very effectively, to speak in a language that they understand, and am able to reach them.”Â
“I believe that it’s really important that you know exactly who your customer or your client is, and you target them, and you resist the temptation to make your marketing too generic to try and reach everyone,” she explained.
“If you speak specifically to your target clients, you will reach them, and I believe that’s the way that you’re going to be more successful.
Watch the video for more of Sandra Parker’s biggest lessons.
SOCIAL
Instagram Tests Live-Stream Games to Enhance Engagement

Instagram’s testing out some new options to help spice up your live-streams in the app, with some live broadcasters now able to select a game that they can play with viewers in-stream.
As you can see in these example screens, posted by Ahmed Ghanem, some creators now have the option to play either “This or That”, a question and answer prompt that you can share with your viewers, or “Trivia”, to generate more engagement within your IG live-streams.
That could be a simple way to spark more conversation and interaction, which could then lead into further engagement opportunities from your live audience.
Meta’s been exploring more ways to make live-streaming a bigger consideration for IG creators, with a view to live-streams potentially catching on with more users.
That includes the gradual expansion of its “Stars” live-stream donation program, giving more creators in more regions a means to accept donations from live-stream viewers, while back in December, Instagram also added some new options to make it easier to go live using third-party tools via desktop PCs.
Live streaming has been a major shift in China, where shopping live-streams, in particular, have led to massive opportunities for streaming platforms. They haven’t caught on in the same way in Western regions, but as TikTok and YouTube look to push live-stream adoption, there is still a chance that they will become a much bigger element in future.
Which is why IG is also trying to stay in touch, and add more ways for its creators to engage via streams. Live-stream games is another element within this, which could make this a better community-building, and potentially sales-driving option.
We’ve asked Instagram for more information on this test, and we’ll update this post if/when we hear back.
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress















