TECHNOLOGY
Zero Trust Cybersecurity-Focused Leadership in the Digital Era

Zero trust cybersecurity is increasingly being adopted as a way to improve cybersecurity in organizations of all sizes and industries.
The impact of cybercrimes is expected to increase exponentially by 2025 and reach an estimated $10.5T. In CY 2022 cybersecurity breaches had a global economic impact evaluated at $6T and the average cost reported per cybersecurity breach was $4.35M. Investors have recognized the need and potential of this mega-industry which is equivalent to a nation’s GDP and larger than most country’s GDPs. We have witnessed an increase in venture capital , private equity and overall mergers and acquisitions, as well as a vibrant startup ecosystem offering a complex range of cyber-defense solutions.
Zero-trust cybersecurity is a security model that assumes that any network, device, or user may be compromised and therefore requires authentication and authorization for access to resources. As outlined by the World Economic Forum (WEF) there is an urgency for governments and business leaders to adopt zero trust cybersecurity in this current global economic and socio-political environment.
The zero-trust approach that encourages us to “never trust and always verify” can help restore digital trust by limiting access to sensitive information and systems to only those who have been verified and authorized, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. Additionally, it can also help organizations comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards for data security.
The principles that define a zero-trust architecture are:
-
All data and services are resources
-
All communications is secured regardless location
-
Access to enterprise resources is session based
-
Access to resources is determined dynamically
-
Continuous security posture monitoring
-
Strict authorization and access enforcement
-
Continuous data collection & enforcement enhancements
-
Integration with enterprise detection & response
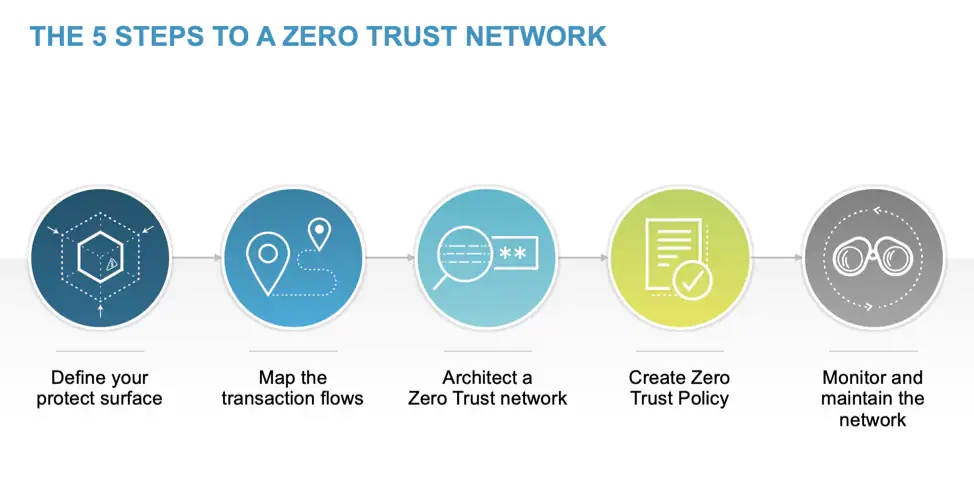
Investing in zero trust cybersecurity can include a variety of different technology solutions and services. Some common investments that organizations may make to implement a zero-trust model include:
-
Identity and access management (IAM) solutions: These solutions can be used to verify the identity of users and devices and control access to resources based on predefined policies.
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions: These solutions can be used to add an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before accessing resources.
-
Network segmentation solutions: These solutions can be used to segment networks and isolate sensitive data and systems from the rest of the network.
-
Endpoint security solutions: These solutions can be used to protect endpoint devices such as laptops and mobile devices from malware and other threats.
-
Cloud security solutions: These solutions can be used to secure cloud environments and protect data and systems that are hosted in the cloud.
-
Security information and event management (SIEM) solutions: These solutions can be used to monitor and analyze security-related data from various sources to detect and respond to threats.
-
Professional services: Organizations can also invest in professional services such as security assessments, penetration testing, and incident response planning to help identify vulnerabilities and develop a robust security strategy.
The zero-trust cybersecurity investment size and type will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the organization, the size of the organization, as well as the organization’s technological maturity, risk tolerance and results of a robust feasibility analysis.
The impact of zero-trust cybersecurity can vary depending on the specific industry sector and the types of data or systems that are being protected. Examples of implementing a zero-trust model in various industries include:
Zero-trust cybersecurity architecture, as outlined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology NIST can have a profound impact on data governance, as it can help to secure sensitive data and systems in various industries by verifying the identity of users and devices, and by limiting access to resources based on predefined policies related to regulatory guidelines or specific business rules.
However, there are numerous challenges encountered when deploying zero-trust cybersecurity, such as cost, interoperability, alignment with other enterprise strategic priorities, harmonization with ethics and risk programs, etc.
What can C-suite leaders do to be better prepared for success when planning a zero trust strategy? They can focus on creating a culture of cyber-resilience, which translates into increasing cyber-literacy and cyber-fluency for the general enterprise workforce, and optimize ( via upskilling and reskilling) cyber-specific skills for their technical team. The workforce management efforts should be complemented with a proactive digital ethics program deployment and an honest SWAT assessment in the face of increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks globally. Performing a robust FMEA analysis is an imperative for companies that wish to retain or gain competitive advantage. Evaluating and examining existing internal enterprise cyber-capabilities, versus the option to forge strategic partnerships or perhaps scout out for a potential cyber-acquisition should also be on the agenda. The design and deployment of cyber-metrics is a crucial step that requires alignment with other financial, operational and ethics enterprise dashboard metrics. Last, but certainly not least, forward thinking leaders must embed innovation and continuously improve their cyber-defense program to dynamically adjust to the rapidly evolving cyber landscape.
Futurists envision cyber-resilient programs that will most likely include satellite internet, human-computer interfaces, cyber-digital twins, quantum technology, federated learning, etc.
Globalists and ESG-conscious leaders are hoping that our transition to the next iterations of the world wide web, such as web 3.0 and web 4.0 will have state of the art cyber-defense programs and will align with both the UN SDG 2030, as well as with the net-zero UN 2050 agendas.
TECHNOLOGY
Next-gen chips, Amazon Q, and speedy S3

AWS re:Invent, which has been taking place from November 27 and runs to December 1, has had its usual plethora of announcements: a total of 21 at time of print.
Perhaps not surprisingly, given the huge potential impact of generative AI – ChatGPT officially turns one year old today – a lot of focus has been on the AI side for AWS’ announcements, including a major partnership inked with NVIDIA across infrastructure, software, and services.
Yet there has been plenty more announced at the Las Vegas jamboree besides. Here, CloudTech rounds up the best of the rest:
Next-generation chips
This was the other major AI-focused announcement at re:Invent: the launch of two new chips, AWS Graviton4 and AWS Trainium2, for training and running AI and machine learning (ML) models, among other customer workloads. Graviton4 shapes up against its predecessor with 30% better compute performance, 50% more cores and 75% more memory bandwidth, while Trainium2 delivers up to four times faster training than before and will be able to be deployed in EC2 UltraClusters of up to 100,000 chips.
The EC2 UltraClusters are designed to ‘deliver the highest performance, most energy efficient AI model training infrastructure in the cloud’, as AWS puts it. With it, customers will be able to train large language models in ‘a fraction of the time’, as well as double energy efficiency.
As ever, AWS offers customers who are already utilising these tools. Databricks, Epic and SAP are among the companies cited as using the new AWS-designed chips.
Zero-ETL integrations
AWS announced new Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Relational Database Services (Amazon RDS) for MySQL integrations with Amazon Redshift, AWS’ cloud data warehouse. The zero-ETL integrations – eliminating the need to build ETL (extract, transform, load) data pipelines – make it easier to connect and analyse transactional data across various relational and non-relational databases in Amazon Redshift.
A simple example of how zero-ETL functions can be seen is in a hypothetical company which stores transactional data – time of transaction, items bought, where the transaction occurred – in a relational database, but use another analytics tool to analyse data in a non-relational database. To connect it all up, companies would previously have to construct ETL data pipelines which are a time and money sink.
The latest integrations “build on AWS’s zero-ETL foundation… so customers can quickly and easily connect all of their data, no matter where it lives,” the company said.
Amazon S3 Express One Zone
AWS announced the general availability of Amazon S3 Express One Zone, a new storage class purpose-built for customers’ most frequently-accessed data. Data access speed is up to 10 times faster and request costs up to 50% lower than standard S3. Companies can also opt to collocate their Amazon S3 Express One Zone data in the same availability zone as their compute resources.
Companies and partners who are using Amazon S3 Express One Zone include ChaosSearch, Cloudera, and Pinterest.
Amazon Q
A new product, and an interesting pivot, again with generative AI at its core. Amazon Q was announced as a ‘new type of generative AI-powered assistant’ which can be tailored to a customer’s business. “Customers can get fast, relevant answers to pressing questions, generate content, and take actions – all informed by a customer’s information repositories, code, and enterprise systems,” AWS added. The service also can assist companies building on AWS, as well as companies using AWS applications for business intelligence, contact centres, and supply chain management.
Customers cited as early adopters include Accenture, BMW and Wunderkind.
Want to learn more about cybersecurity and the cloud from industry leaders? Check out Cyber Security & Cloud Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
TECHNOLOGY
HCLTech and Cisco create collaborative hybrid workplaces

Digital comms specialist Cisco and global tech firm HCLTech have teamed up to launch Meeting-Rooms-as-a-Service (MRaaS).
Available on a subscription model, this solution modernises legacy meeting rooms and enables users to join meetings from any meeting solution provider using Webex devices.
The MRaaS solution helps enterprises simplify the design, implementation and maintenance of integrated meeting rooms, enabling seamless collaboration for their globally distributed hybrid workforces.
Rakshit Ghura, senior VP and Global head of digital workplace services, HCLTech, said: “MRaaS combines our consulting and managed services expertise with Cisco’s proficiency in Webex devices to change the way employees conceptualise, organise and interact in a collaborative environment for a modern hybrid work model.
“The common vision of our partnership is to elevate the collaboration experience at work and drive productivity through modern meeting rooms.”
Alexandra Zagury, VP of partner managed and as-a-Service Sales at Cisco, said: “Our partnership with HCLTech helps our clients transform their offices through cost-effective managed services that support the ongoing evolution of workspaces.
“As we reimagine the modern office, we are making it easier to support collaboration and productivity among workers, whether they are in the office or elsewhere.”
Cisco’s Webex collaboration devices harness the power of artificial intelligence to offer intuitive, seamless collaboration experiences, enabling meeting rooms with smart features such as meeting zones, intelligent people framing, optimised attendee audio and background noise removal, among others.
Want to learn more about cybersecurity and the cloud from industry leaders? Check out Cyber Security & Cloud Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
TECHNOLOGY
Canonical releases low-touch private cloud MicroCloud

Canonical has announced the general availability of MicroCloud, a low-touch, open source cloud solution. MicroCloud is part of Canonical’s growing cloud infrastructure portfolio.
It is purpose-built for scalable clusters and edge deployments for all types of enterprises. It is designed with simplicity, security and automation in mind, minimising the time and effort to both deploy and maintain it. Conveniently, enterprise support for MicroCloud is offered as part of Canonical’s Ubuntu Pro subscription, with several support tiers available, and priced per node.
MicroClouds are optimised for repeatable and reliable remote deployments. A single command initiates the orchestration and clustering of various components with minimal involvement by the user, resulting in a fully functional cloud within minutes. This simplified deployment process significantly reduces the barrier to entry, putting a production-grade cloud at everyone’s fingertips.
Juan Manuel Ventura, head of architectures & technologies at Spindox, said: “Cloud computing is not only about technology, it’s the beating heart of any modern industrial transformation, driving agility and innovation. Our mission is to provide our customers with the most effective ways to innovate and bring value; having a complexity-free cloud infrastructure is one important piece of that puzzle. With MicroCloud, the focus shifts away from struggling with cloud operations to solving real business challenges” says
In addition to seamless deployment, MicroCloud prioritises security and ease of maintenance. All MicroCloud components are built with strict confinement for increased security, with over-the-air transactional updates that preserve data and roll back on errors automatically. Upgrades to newer versions are handled automatically and without downtime, with the mechanisms to hold or schedule them as needed.
With this approach, MicroCloud caters to both on-premise clouds but also edge deployments at remote locations, allowing organisations to use the same infrastructure primitives and services wherever they are needed. It is suitable for business-in-branch office locations or industrial use inside a factory, as well as distributed locations where the focus is on replicability and unattended operations.
Cedric Gegout, VP of product at Canonical, said: “As data becomes more distributed, the infrastructure has to follow. Cloud computing is now distributed, spanning across data centres, far and near edge computing appliances. MicroCloud is our answer to that.
“By packaging known infrastructure primitives in a portable and unattended way, we are delivering a simpler, more prescriptive cloud experience that makes zero-ops a reality for many Industries.“
MicroCloud’s lightweight architecture makes it usable on both commodity and high-end hardware, with several ways to further reduce its footprint depending on your workload needs. In addition to the standard Ubuntu Server or Desktop, MicroClouds can be run on Ubuntu Core – a lightweight OS optimised for the edge. With Ubuntu Core, MicroClouds are a perfect solution for far-edge locations with limited computing capabilities. Users can choose to run their workloads using Kubernetes or via system containers. System containers based on LXD behave similarly to traditional VMs but consume fewer resources while providing bare-metal performance.
Coupled with Canonical’s Ubuntu Pro + Support subscription, MicroCloud users can benefit from an enterprise-grade open source cloud solution that is fully supported and with better economics. An Ubuntu Pro subscription offers security maintenance for the broadest collection of open-source software available from a single vendor today. It covers over 30k packages with a consistent security maintenance commitment, and additional features such as kernel livepatch, systems management at scale, certified compliance and hardening profiles enabling easy adoption for enterprises. With per-node pricing and no hidden fees, customers can rest assured that their environment is secure and supported without the expensive price tag typically associated with cloud solutions.
Want to learn more about cybersecurity and the cloud from industry leaders? Check out Cyber Security & Cloud Expo taking place in Amsterdam, California, and London. Explore other upcoming enterprise technology events and webinars powered by TechForge here.
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days ago10 WordPress Influencers to Follow in 2024 – WordPress.com News
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Image Search Adds Pixel Level Object Segmentation Animation
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoFeeling Stuck: What to Do When You Don’t Know What to Do
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoA History of Google AdWords and Google Ads: Revolutionizing Digital Advertising & Marketing Since 2000
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoMore Google March 2024 Core Update Ranking Volatility
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoCompetitor Monitoring: 7 ways to keep watch on the competition
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago31 Ready-to-Go Mother’s Day Messages for Social Media, Email, & More
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoThrive Architect vs Divi vs Elementor













You must be logged in to post a comment Login