MARKETING
How To Build a Communication and Implementation Plan

You learn about a C-suite decision that will have a transformative impact on your content marketing team. Perhaps, the announcement included one or more of these directives:
- “We must produce more content and manage multi-platform distribution with greater agility. We plan to add ChatGPT to our editorial capabilities and implement a headless CMS.”
- “We’re updating our three-year business strategy and need all teams to align their operations around achieving a new set of goals.”
- “We’ve been acquired. We will be merging many of our business units and will need to relaunch our website so we can tell a more unified story.”
Or maybe it’s another substantive shift in strategy or operations. As a content team leader, whether excited or terrified, you must get your team on board and ensure the initiative succeeds.
Transformational changes are nearly impossible to implement without a clear plan that communicates the desired destination, the motivation to pursue it, and the path to reach it.
Jenny Magic, marketing strategist and professional coach, shares how to do that in a Content Marketing World presentation she co-developed with Melissa Breker.
You can watch the conversation (beginning at 2:30-minute mark) or scroll down to read her recommendations to gather support, clear obstacles, and keep efforts moving in the right direction.
5 sabotages that disrupt transformational changes
Every organization has unique conditions and challenges, but Jenny points out five common barriers that prevent the successful adoption of new priorities and practices:
- Forced change. When workers don’t understand or agree with the change, they won’t invest in the process, especially if it requires a lot of effort or a long-term investment.
- Misaligned goals. You can’t sell a change that benefits the company if employees don’t see how it helps them reach their personal or professional goals.
- Group-speak. Your team may nod in agreement when the CEO says, “We’re all going to do this together, right?” But that enthusiasm might not hold when the boss’ eyes are no longer on them.
- Rushed process. Team members already overwhelmed with responsibilities don’t give new tasks top priority. Jenny says if you can’t take something off their plate, communicate they won’t be pressured to rush it through.
- Lack of team alignment. Everyone must be on the same page regarding the direction, intention, and actions required. Without this alignment, tasks fall through the cracks, and all the hard work may not lead to achieving the goal.
Forced change, group-speak, rushed processes can all disrupt transformational changes, says @JennyLMagic via @joderama @CMIContent. Click To Tweet
For your change mission to succeed, your communications plan should account for how you’ll address (or avoid) these obstacles. These details will minimize the friction, lack of participation, and flagging enthusiasm you could have experienced during implementation.
ADVERTISEMENT
The marketer’s field manual to content operations
A hands-on primer for marketers to upgrade their content production process – by completing a self-audit and following our step-by-step best practices. Get the e-book.
Plan for the transformation journey
Jenny shares a three-part approach she uses to help her consultancy clients get big ideas off the drawing board, onto team members’ priority lists, and into the marketplace.
1. Establish the destination: What’s changing, why, and what’s involved
To get your team to join the journey of change, they need to know where they’re going. Create a change summary to help with that. The simple map summarizes the relevant details about the change, the phases of implementation, and the benefits gained when the goal is reached.
First, identify the most critical details to communicate. Answer these questions:
- What’s the nature of the change? What is being done differently, and what does that mean for the business and team? What isn’t changing that might be the stability anchor?
- Why is it happening? Why does the organization think this change is critical? Why is now the right time to do this?
- Who’s involved? Who will the change affect? What will they be expected to do? What about their roles, processes, and priorities? Why would they want to participate, and why might they be reluctant?
- When will it happen? Will the change occur all at once or gradually? What happens at each stage, and which ones will require the content marketing team’s involvement?
- What are the expected results? What is the organization looking to achieve? What benefits or advantages will it bring? What will the company and team see when the goal is reached?
With these answers, you can build a change summary to share in stakeholder and team member conversations. Any spreadsheet or presentation tool will do, though you can create a template based on the document Jenny uses for her client engagements (below).
The summary of what’s changing appears at the top of the page and details of the most critical elements appear below it. Bulleted notes detail what to expect with each element and the benefits for the business and your team. Lastly, a general timeline outlines each project phase.
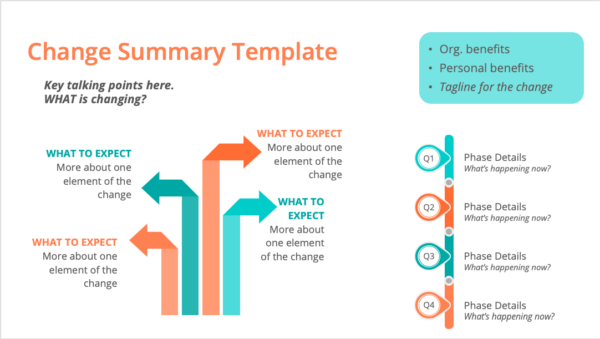
2. Load up the crew: Gather support and communicate benefits
To achieve the change goal, all players must agree to travel together and move in the same direction. “If our team is not aligned on where the heck we’re going, there’s literally no chance we’re going to get there,” Jenny says.
Team members who immediately see the value in the initiative might follow your lead without question. But some key players may need a little more convincing. Jenny offers a few ideas to get them on board.
Enlist the support of an active, visible sponsor: Social media shows putting the right influencer behind your pitch can move minds. The same goes for pushing through a big change within an organization. Research from Prosci finds projects with an extremely effective sponsor met or exceeded objectives more than twice as often as those with a very ineffective sponsor.
If you have the support of senior team leaders and high-profile company personnel, ask for their help socializing the change to others. They might seed relevant information in their newsletters and other content they share internally or help shape your change activities and messaging to improve their appeal.
Translate organizational goals into personal motivations: Some team members may reluctantly participate because they perceive an impact on their role. For example, workers may think the added work will strain their already demanding schedules. Others may be skeptical because of negative experiences with similar changes in the past or disbelief that the change might benefit them.
A series of stakeholder conversations can help identify the significant concerns and disconnects that might prevent them from engaging. They also can reveal specific challenges and motivations that you can address with more resonant and appealing messaging.
Translate organizational goals into personal motivations so team members can see how they’ll benefit, says @JennyLMagic via @joderama @CMIContent. Click To Tweet
Some marketing tools you use to influence an audience can help you facilitate those conversations. For example, Jenny says, personas can surface critical insights about who may be impacted by the change and what it might take to nurture them onto the path.
Her personas checklist includes these questions:
- Who’s leading the change? Do any key sponsors directly relate to the persona’s role?
- Will this persona be impacted more or less than others?
- Will they need information more frequently or in greater detail?
- What reactions will they have?
- How will you approach training for this persona? What support will be provided?
- At what phase of the change will they be most affected?

Jenny also recommends using your marketing communication and engagement tools. For example, the simple tracking sheet she developed (below) can help visualize the audience, delivery formats and channels, optimal messages, and approval and final sign-off requirements to mention in your stakeholder discussions.

Choose the right messenger – and a customized message: Sometimes, a disconnect occurs not because of the message but because of the message’s deliverer. For example, employees expect to hear about significant corporate initiatives from executives and senior leaders. But for changes impacting their day-to-day responsibilities, they may prefer to hear from a manager or supervisor who understands their role.
Other times, preventing a disconnect could require tailoring the message to the team’s needs. Jenny suggests focusing on the direct benefits once the initiative is activated. “Consider how it might help them further their career, address something they’re struggling with, or offer an opportunity to explore an area they’re passionate about,” Jenny says.
Surface hidden issues with confidential interviews: Valid concerns can remain hidden, especially for team members who are reluctant to voice their objections in team meetings. Working one-on-one with a neutral or external moderator – someone with no stake in the decision for change – might help them open up.
Ensure they know the confidential interview results will be aggregated so no individual responses will be identified. “It’s really helpful to get that confessional energy,” Jenny says. “It can help you surface individual reservations, causes of their reluctance, and personal motivations. “
A confidential one-on-one interview with an external moderator can help surface concerns from reluctant team members, says @JennyLMagic via @joderama @CMIContent. Click To Tweet
Jenny shares in her checklist (below) some preliminary questions for a moderator to assess during a confidential interview:
- How does the individual feel about the change?
- Is it the right change?
- Is it the right time?
- Is it supported enough to succeed?
- What risks do they predict?
- Do they have ideas about how we could reduce obstacles and challenges?
- What lessons from past change efforts can they share with us?
- Could they become a change champion?

The process can fuel opportunities to shift messaging, positioning, or delivery approach to help the outliers see how the change can benefit them and get them more excited about participating. Jenny says it can also reveal valid concerns that need to be solved so they don’t hinder progress.
3. Hit the road: Position and prepare your team for success
Big changes are always risky. They disrupt the status quo, and if they involve multiple teams and business functions, some changes may feel like a win for some at the expense of others.
Taking a few extra steps before executing your plans can keep those issues from diverting the goal or leaving any team members stranded along the way. “This is where we establish commitment and accountability and think about what could go wrong and how we’re going to deal with it,” Jenny says.
Own up to what you do and don’t know: Ultimately, you can’t plan for every contingency. “You’ll lose trust rapidly if you pretend you do,” Jenny says. She offers a few communication tips to set the right expectations from the start:
- Be clear and candid: Directly address what you do know, don’t know, and what is and isn’t possible with this change. Outline how you will communicate status updates and new information as they arise.
- Be receptive: Don’t take resistance personally. Listen to your team’s questions and respond to their feedback with an open mind.
- Be visible: Socialize progress across your team’s preferred communication channels, and make sure everyone knows how to reach you if they encounter a problem. You can regularly host town hall meetings, road-show presentations, or open forums to ensure everyone stays informed and has a chance to share their thoughts.
Position project requirements as opportunities and advantages: Jenny suggests exercising creative thinking to help concerned team members see the new responsibilities as a chance to benefit personally.
For example, if they need to learn additional skills to accomplish their tasks, provide in-house training or access to third-party educational tools. Position the opportunity as a chance to expand their capabilities to help them be more prepared for this change and to advance their careers in the long run.
You can also use the big change to rethink your org chart and rebalance team member responsibilities. “Every single person has work that they hate on their to-do list. I’ve found folks become more open if they’re offered an opportunity to do a task trade-off,” Jenny says.
Incentivize the journey – not just the destination: A lengthy and gradual implementation process should include incentives at regular intervals to motivate team members to stay the course.
Rewards can be specific and tangible, such as bonuses or loyalty program points. Or they can be intangible, such as shoutouts during monthly meetings or in internal newsletters. Arrange team happy hours or give comp time for extra hours worked. These appreciation efforts can make the added burden feel worthwhile.
Overcome obstacles in predictive planning: An element of science exists in the journey of change. You can’t reach your destination if the forces of resistance are stronger than the forces propelling you forward.
Jenny shares an innovation tool from a company called Gamestorming that can help quantify the balance of those forces at each phase. By working through this force-field analysis, you can take steps to ensure the winds of change will be in your favor.
An example of how it works is shown below. In the center, an illustration represents the change you want to implement – transitioning from hierarchical to more transparent hubs.
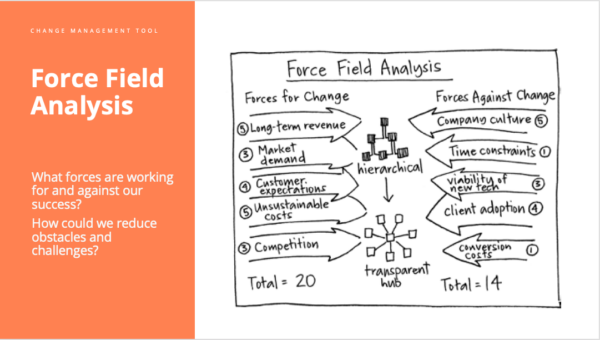
On one side, the forces of change – all the elements of the vision that characterize the importance of the change and how it works in your favor – are listed. In this example, those forces are:
- Improve long-term revenue
- Help meet market demand
- Satisfies customer expectations
- Addresses current unsustainable costs
- Give a competitive advantage in the marketplace
On the other side, the forces of resistance – conditions and constraints that may prevent realizing the vision – are listed. In the example, these forces include:
- Company culture
- Time constraints
- Viability of new tech
- Client adoption
- Current costs
Rank each element’s impact on the project’s success on a scale of one to five. Then add the rankings on each side and compare the scores to see whether you have a stronger chance of success than failure and identify where efforts should be made to overcome obstacles.
Plan the journey for a smoother arrival
Convincing your team to jump aboard the organizational-change train is rarely easy. But with a clear operational plan, aligned support, and open communication, you’ll help them see the benefits of participating and get them excited to reach their destination.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
MARKETING
Ecommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C

Understanding convergence
B2B and B2C ecommerce are two distinct models of online selling. B2B ecommerce is between businesses, such as wholesalers, distributors, and manufacturers. B2C ecommerce refers to transactions between businesses like retailers and consumer brands, directly to individual shoppers.
However, in recent years, the boundaries between these two models have started to fade. This is known as the convergence between B2B and B2C ecommerce and how they are becoming more similar and integrated.
Source: White Paper: The evolution of the B2B Consumer Buyer (ClientPoint, Jan 2024)
What’s driving this change?
Ever increasing customer expectations
Customers today expect the same level of convenience, speed, and personalization in their B2B transactions as they do in their B2C interactions. B2B buyers are increasingly influenced by their B2C experiences. They want research, compare, and purchase products online, seamlessly transitioning between devices and channels. They also prefer to research and purchase online, using multiple devices and channels.
Forrester, 68% of buyers prefer to research on their own, online . Customers today expect the same level of convenience, speed, and personalization in their B2B transactions as they do in their B2C interactions. B2B buyers are increasingly influenced by their B2C experiences. They want research, compare, and purchase products online, seamlessly transitioning between devices and channels. They also prefer to research and purchase online, using multiple devices and channels
Technology and omnichannel strategies
Technology enables B2B and B2C ecommerce platforms to offer more features and functionalities, such as mobile optimization, chatbots, AI, and augmented reality. Omnichannel strategies allow B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses to provide a seamless and consistent customer experience across different touchpoints, such as websites, social media, email, and physical stores.
However, with every great leap forward comes its own set of challenges. The convergence of B2B and B2C markets means increased competition. Businesses now not only have to compete with their traditional rivals, but also with new entrants and disruptors from different sectors. For example, Amazon Business, a B2B ecommerce platform, has become a major threat to many B2B ecommerce businesses, as it offers a wide range of products, low prices, and fast delivery
“Amazon Business has proven that B2B ecommerce can leverage popular B2C-like functionality” argues Joe Albrecht, CEO / Managing Partner, Xngage. . With features like Subscribe-and-Save (auto-replenishment), one-click buying, and curated assortments by job role or work location, they make it easy for B2B buyers to go to their website and never leave. Plus, with exceptional customer service and promotional incentives like Amazon Business Prime Days, they have created a reinforcing loyalty loop.
And yet, according to Barron’s, Amazon Business is only expected to capture 1.5% of the $5.7 Trillion addressable business market by 2025. If other B2B companies can truly become digital-first organizations, they can compete and win in this fragmented space, too.”
If other B2B companies can truly become digital-first organizations, they can also compete and win in this fragmented space
Joe AlbrechtCEO/Managing Partner, XNGAGE
Increasing complexity
Another challenge is the increased complexity and cost of managing a converging ecommerce business. Businesses have to deal with different customer segments, requirements, and expectations, which may require different strategies, processes, and systems. For instance, B2B ecommerce businesses may have to handle more complex transactions, such as bulk orders, contract negotiations, and invoicing, while B2C ecommerce businesses may have to handle more customer service, returns, and loyalty programs. Moreover, B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses must invest in technology and infrastructure to support their convergence efforts, which may increase their operational and maintenance costs.
How to win
Here are a few ways companies can get ahead of the game:
Adopt B2C-like features in B2B platforms
User-friendly design, easy navigation, product reviews, personalization, recommendations, and ratings can help B2B ecommerce businesses to attract and retain more customers, as well as to increase their conversion and retention rates.
According to McKinsey, ecommerce businesses that offer B2C-like features like personalization can increase their revenues by 15% and reduce their costs by 20%. You can do this through personalization of your website with tools like Product Recommendations that help suggest related products to increase sales.
Focus on personalization and customer experience
B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses need to understand their customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors, and tailor their offerings and interactions accordingly. Personalization and customer experience can help B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses to increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy, as well as to improve their brand reputation and competitive advantage. According to a Salesforce report, 88% of customers say that the experience a company provides is as important as its products or services.
Market based on customer insights
Data and analytics can help B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses to gain insights into their customers, markets, competitors, and performance, and to optimize their strategies and operations accordingly. Data and analytics can also help B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses to identify new opportunities, trends, and innovations, and to anticipate and respond to customer needs and expectations. According to McKinsey, data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers, six times more likely to retain customers, and 19 times more likely to be profitable.
What’s next?
The convergence of B2B and B2C ecommerce is not a temporary phenomenon, but a long-term trend that will continue to shape the future of ecommerce. According to Statista, the global B2B ecommerce market is expected to reach $20.9 trillion by 2027, surpassing the B2C ecommerce market, which is expected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2027. Moreover, the report predicts that the convergence of B2B and B2C ecommerce will create new business models, such as B2B2C, B2A (business to anyone), and C2B (consumer to business).
Therefore, B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses need to prepare for the converging ecommerce landscape and take advantage of the opportunities and challenges it presents. Here are some recommendations for B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses to navigate the converging landscape:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of your customers, competitors, and market, and identify the gaps and opportunities for convergence.
- Develop a clear vision and strategy for convergence, and align your goals, objectives, and metrics with it.
- Invest in technology and infrastructure that can support your convergence efforts, such as cloud, mobile, AI, and omnichannel platforms.
- Implement B2C-like features in your B2B platforms, and vice versa, to enhance your customer experience and satisfaction.
- Personalize your offerings and interactions with your customers, and provide them with relevant and valuable content and solutions.
- Leverage data and analytics to optimize your performance and decision making, and to innovate and differentiate your business.
- Collaborate and partner with other B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses, as well as with other stakeholders, such as suppliers, distributors, and customers, to create value and synergy.
- Monitor and evaluate your convergence efforts, and adapt and improve them as needed.
By following these recommendations, B2B and B2C ecommerce businesses can bridge the gap between their models and create a more integrated and seamless ecommerce experience for their customers and themselves.
MARKETING
Streamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results

How can businesses succeed nowadays when technology rules? With competition getting tougher and customers changing their preferences often, it’s a challenge. But using marketing automation can help make things easier and get better results. And in the future, it’s going to be even more important for all kinds of businesses.
So, let’s discuss how businesses can leverage marketing automation to stay ahead and thrive.
Benefits of automation marketing automation to boost your efforts
First, let’s explore the benefits of marketing automation to supercharge your efforts:
Marketing automation simplifies repetitive tasks, saving time and effort.
With automated workflows, processes become more efficient, leading to better productivity. For instance, automation not only streamlines tasks like email campaigns but also optimizes website speed, ensuring a seamless user experience. A faster website not only enhances customer satisfaction but also positively impacts search engine rankings, driving more organic traffic and ultimately boosting conversions.
Automation allows for precise targeting, reaching the right audience with personalized messages.
With automated workflows, processes become more efficient, leading to better productivity. A great example of automated workflow is Pipedrive & WhatsApp Integration in which an automated welcome message pops up on their WhatsApp
within seconds once a potential customer expresses interest in your business.
Increases ROI
By optimizing campaigns and reducing manual labor, automation can significantly improve return on investment.
Leveraging automation enables businesses to scale their marketing efforts effectively, driving growth and success. Additionally, incorporating lead scoring into automated marketing processes can streamline the identification of high-potential prospects, further optimizing resource allocation and maximizing conversion rates.
Harnessing the power of marketing automation can revolutionize your marketing strategy, leading to increased efficiency, higher returns, and sustainable growth in today’s competitive market. So, why wait? Start automating your marketing efforts today and propel your business to new heights, moreover if you have just learned ways on how to create an online business
How marketing automation can simplify operations and increase efficiency
Understanding the Change
Marketing automation has evolved significantly over time, from basic email marketing campaigns to sophisticated platforms that can manage entire marketing strategies. This progress has been fueled by advances in technology, particularly artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, making automation smarter and more adaptable.
One of the main reasons for this shift is the vast amount of data available to marketers today. From understanding customer demographics to analyzing behavior, the sheer volume of data is staggering. Marketing automation platforms use this data to create highly personalized and targeted campaigns, allowing businesses to connect with their audience on a deeper level.
The Emergence of AI-Powered Automation
In the future, AI-powered automation will play an even bigger role in marketing strategies. AI algorithms can analyze huge amounts of data in real-time, helping marketers identify trends, predict consumer behavior, and optimize campaigns as they go. This agility and responsiveness are crucial in today’s fast-moving digital world, where opportunities come and go in the blink of an eye. For example, we’re witnessing the rise of AI-based tools from AI website builders, to AI logo generators and even more, showing that we’re competing with time and efficiency.
Combining AI-powered automation with WordPress management services streamlines marketing efforts, enabling quick adaptation to changing trends and efficient management of online presence.
Moreover, AI can take care of routine tasks like content creation, scheduling, and testing, giving marketers more time to focus on strategic activities. By automating these repetitive tasks, businesses can work more efficiently, leading to better outcomes. AI can create social media ads tailored to specific demographics and preferences, ensuring that the content resonates with the target audience. With the help of an AI ad maker tool, businesses can efficiently produce high-quality advertisements that drive engagement and conversions across various social media platforms.
Personalization on a Large Scale
Personalization has always been important in marketing, and automation is making it possible on a larger scale. By using AI and machine learning, marketers can create tailored experiences for each customer based on their preferences, behaviors, and past interactions with the brand.
This level of personalization not only boosts customer satisfaction but also increases engagement and loyalty. When consumers feel understood and valued, they are more likely to become loyal customers and brand advocates. As automation technology continues to evolve, we can expect personalization to become even more advanced, enabling businesses to forge deeper connections with their audience. As your company has tiny homes for sale California, personalized experiences will ensure each customer finds their perfect fit, fostering lasting connections.
Integration Across Channels
Another trend shaping the future of marketing automation is the integration of multiple channels into a cohesive strategy. Today’s consumers interact with brands across various touchpoints, from social media and email to websites and mobile apps. Marketing automation platforms that can seamlessly integrate these channels and deliver consistent messaging will have a competitive edge. When creating a comparison website it’s important to ensure that the platform effectively aggregates data from diverse sources and presents it in a user-friendly manner, empowering consumers to make informed decisions.
Omni-channel integration not only betters the customer experience but also provides marketers with a comprehensive view of the customer journey. By tracking interactions across channels, businesses can gain valuable insights into how consumers engage with their brand, allowing them to refine their marketing strategies for maximum impact. Lastly, integrating SEO services into omni-channel strategies boosts visibility and helps businesses better understand and engage with their customers across different platforms.
The Human Element
While automation offers many benefits, it’s crucial not to overlook the human aspect of marketing. Despite advances in AI and machine learning, there are still elements of marketing that require human creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking.
Successful marketing automation strikes a balance between technology and human expertise. By using automation to handle routine tasks and data analysis, marketers can focus on what they do best – storytelling, building relationships, and driving innovation.
Conclusion
The future of marketing automation looks promising, offering improved efficiency and results for businesses of all sizes.
As AI continues to advance and consumer expectations change, automation will play an increasingly vital role in keeping businesses competitive.
By embracing automation technologies, marketers can simplify processes, deliver more personalized experiences, and ultimately, achieve their business goals more effectively than ever before.
MARKETING
Will Google Buy HubSpot? | Content Marketing Institute

Google + HubSpot. Is it a thing?
This week, a flurry of news came down about Google’s consideration of purchasing HubSpot.
The prospect dismayed some. It delighted others.
But is it likely? Is it even possible? What would it mean for marketers? What does the consideration even mean for marketers?
Well, we asked CMI’s chief strategy advisor, Robert Rose, for his take. Watch this video or read on:
Why Alphabet may want HubSpot
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, apparently is contemplating the acquisition of inbound marketing giant HubSpot.
The potential price could be in the range of $30 billion to $40 billion. That would make Alphabet’s largest acquisition by far. The current deal holding that title happened in 2011 when it acquired Motorola Mobility for more than $12 billion. It later sold it to Lenovo for less than $3 billion.
If the HubSpot deal happens, it would not be in character with what the classic evil villain has been doing for the past 20 years.
At first glance, you might think the deal would make no sense. Why would Google want to spend three times as much as it’s ever spent to get into the inbound marketing — the CRM and marketing automation business?
At a second glance, it makes a ton of sense.
I don’t know if you’ve noticed, but I and others at CMI spend a lot of time discussing privacy, owned media, and the deprecation of the third-party cookie. I just talked about it two weeks ago. It’s really happening.
All that oxygen being sucked out of the ad tech space presents a compelling case that Alphabet should diversify from third-party data and classic surveillance-based marketing.
Yes, this potential acquisition is about data. HubSpot would give Alphabet the keys to the kingdom of 205,000 business customers — and their customers’ data that almost certainly numbers in the tens of millions. Alphabet would also gain access to the content, marketing, and sales information those customers consumed.
Conversely, the deal would provide an immediate tip of the spear for HubSpot clients to create more targeted programs in the Alphabet ecosystem and upload their data to drive even more personalized experiences on their own properties and connect them to the Google Workspace infrastructure.
When you add in the idea of Gemini, you can start to see how Google might monetize its generative AI tool beyond figuring out how to use it on ads on search results pages.
What acquisition could mean for HubSpot customers
I may be stretching here but imagine this world. As a Hubspoogle customer, you can access an interface that prioritizes your owned media data (e.g., your website, your e-commerce catalog, blog) when Google’s Gemini answers a question).
Recent reports also say Google may put up a paywall around the new premium features of its artificial intelligence-powered Search Generative Experience. Imagine this as the new gating for marketing. In other words, users can subscribe to Google’s AI for free, but Hubspoogle customers can access that data and use it to create targeted offers.
The acquisition of HubSpot would immediately make Google Workspace a more robust competitor to Microsoft 365 Office for small- and medium-sized businesses as they would receive the ADDED capability of inbound marketing.
But in the world of rented land where Google is the landlord, the government will take notice of the acquisition. But — and it’s a big but, I cannot lie (yes, I just did that). The big but is whether this acquisition dance can happen without going afoul of regulatory issues.
Some analysts say it should be no problem. Others say, “Yeah, it wouldn’t go.” Either way, would anybody touch it in an election year? That’s a whole other story.
What marketers should realize
So, what’s my takeaway?
It’s a remote chance that Google will jump on this hard, but stranger things have happened. It would be an exciting disruption in the market.
The sure bet is this. The acquisition conversation — as if you needed more data points — says getting good at owned media to attract and build audiences and using that first-party data to provide better communication and collaboration with your customers are a must.
It’s just a matter of time until Google makes a move. They might just be testing the waters now, but they will move here. But no matter what they do, if you have your customer data house in order, you’ll be primed for success.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Limits News Links In California Over Proposed ‘Link Tax’ Law
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 12, 2024
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle Unplugs “Notes on Search” Experiment
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoCritical Display Error in Brand Safety Metrics On Twitter/X Corrected















You must be logged in to post a comment Login