The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Is This Why Some Content Ranks in Google?
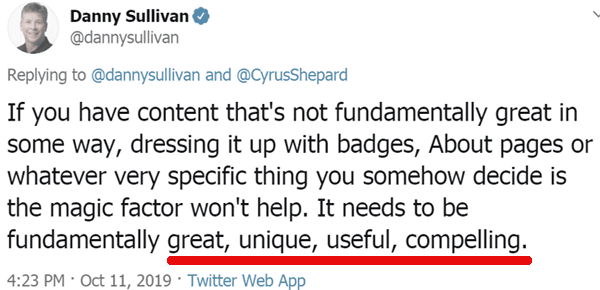
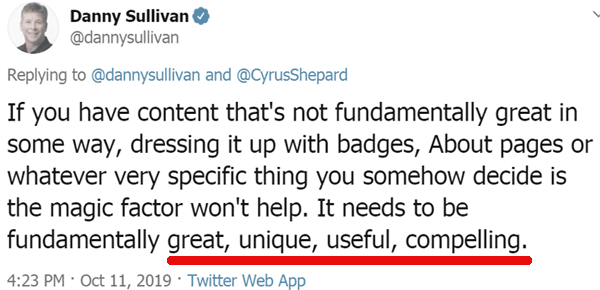
Google’s Danny Sullivan tweeted that SEOs should focus on content that is “great, unique, useful, compelling.” Some in the search community pushed back on the idea.
Ranking Factors and Content
The context of Danny Sullivan’s statement is in responding to a tweet by Cyrus Shepard:
“Google’s statements on ranking factors are like onions. They have layers. And when you peel too many layers, you start to cry”
Danny asserted that what SEOs should focus on is making great content that is useful, compelling, etc.
Danny Sullivan tweeted this response:
“If you have content that’s not fundamentally great in some way, dressing it up with badges, About pages or whatever very specific thing you somehow decide is the magic factor won’t help.
It needs to be fundamentally great, unique, useful, compelling.“
Great Content is Not Always Comprehensive
A common mistake made with content is understanding greatness as being comprehensive. Comprehensive means covering a topic from beginning to end.
However, not every topic needs to be comprehensive. The reason why short content sometimes beats comprehensive content is because sometimes a search query is satisfied by a 400 word answer.
This is particularly true in “how to” type search queries that are highly specific. If those kinds of queries can be expressed in short steps (step 1, step 2, etc.), then your users may be happier to see it answered that way.
Why Comprehensive Content Loses Rankings
Comprehensive content can tend to drift off topic. Content that ranks well tends to be on topic. Content that ranks on page two of the search results tends to contain “side topics” that aren’t essential to the main topic.
For example, if the keyword phrase is “how to catch striped bass,” introducing place names (entities) like Cape Cod, Montauk and Rhode Island into your “comprehensive” web page about catching striped bass will alter the topic of the web page.
The page won’t necessarily rank for “how to catch striped bass” but it may begin to rank for the keyword phrase plus those geographic locations (entities).
Off Topic Metaphors, Jargon, and Analogies
In my opinion, another way publishers kill their content is by using wildly off topic metaphors, jargon, and analogies. Doing it once is probably okay.
But peppering the entire web page with multiple instances of off topic elements is, in my opinion from studying why some sites are high ranked and some are low ranked, a sure way to lower the relevance of the page.
This is a common mistake of content that lost rankings in Google broad core updates. Every time Google tightens it’s association between content and search queries, web pages with off topic content starts to lose rankings.
I’m not saying being off topic is the only reason why web pages lose rankings. I’m pointing out that this is one reason out of many that pages tend to lose rankings.
Some pages lose rankings for other reasons entirely. But that’s outside of the focus of this article.
Returning to the example of “how to catch striped bass,” a common jargon in New England for a big striped bass is the word, cow.
But Google does not understand that the word “cow” in the context of fishing. Do a search for the phrase “how to fish for a cow” or “how to catch a cow from shore” and you’ll see that Google strongly associates the word (entity) cow with livestock.
So if your web page uses the word “cow” and livestock related phrases (rounding up cow stripers) in an article, it’s possible that Google may begin to associate your web page about catching striped bass with the animals that moo.
Content that Ranks is Concise and On Topic
There are many reasons why great content loses rankings in Google core algorithm updates. When doing site audits, one reason that I see now and then is the tendency to confuse “comprehensive” with being useful. Another reason I see some sites lose rankings is because the content is off topic.
Content that Ranks is Relevant to Users
Another common mistake is writing content about keywords. I find that it’s useful to write to the user intent.
When you’re talking about user intent, in my opinion you’re really talking about:
Answer the appropriate question for the keyword phrase and you’ll be closer to answering the actual reason why the user is searching.
Let’s “de-jargonize” this: Understand WHY the user is making a search query then provide the solution. Let the search results be your guide to what the user means when they type a certain search query.
Great means being above average, standing above and apart from others. In my opinion, true greatness lies in serving the user and that means focusing on aspirations, needs and goals in a way that is delivered quickly and efficiently.
Danny Sullivan suggested it was a good idea to create content that is useful. Focusing on being useful is the first step toward creating content that ranks well.
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
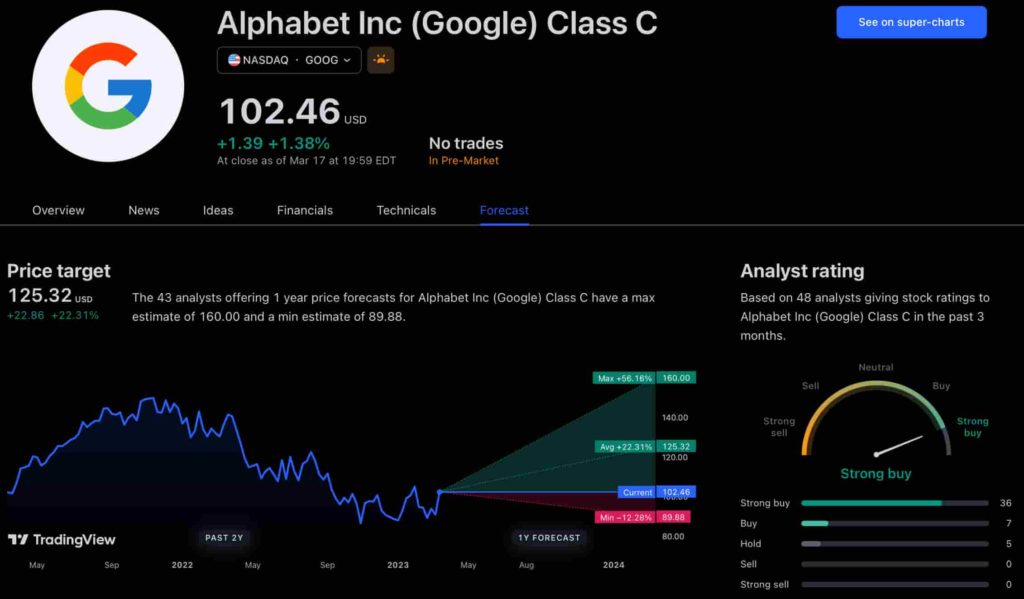
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 PPC7 days ago
PPC7 days agoCompetitor Monitoring: 7 ways to keep watch on the competition
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoA History of Google AdWords and Google Ads: Revolutionizing Digital Advertising & Marketing Since 2000
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago31 Ready-to-Go Mother’s Day Messages for Social Media, Email, & More
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoMore Google March 2024 Core Update Ranking Volatility
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoTurkish startup ikas attracts $20M for its e-commerce platform designed for small businesses
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoThrive Architect vs Divi vs Elementor
-

 MARKETING5 days ago
MARKETING5 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Search Results Can Be Harmful & Dangerous In Some Cases