The new app is called watchGPT and as I tipped off already, it gives you access to ChatGPT from your Apple Watch. Now the $10,000 question (or more accurately the $3.99 question, as that is the one-time cost of the app) is why having ChatGPT on your wrist is remotely necessary, so let’s dive into what exactly the app can do.
NEWS
Twitter now lets everyone limit replies to their tweets


Twitter may describe itself as the town square, but that doesn’t mean you have to talk to everyone walking past your seat at the cafe. Today, to increase the amount of “meaningful conversations” that take place on Twitter, and to help people weed out abuse and spam in their replies, the company announced that it is rolling out a new feature where users can limit who replies to their Tweets.
After a brief run in beta, the feature is rolling out globally starting today to users of the iOS and Android apps, as well as twitter.com, Suzanne Xie noted in a blog post announcing the feature. TweetDeck is not yet supported, Twitter tells me.
A small globe icon will start to appear at the bottom of your tweet, and if you do nothing, everyone will still be able to reply — this is the default option. Or, you can tap it and limit replies just to those who follow you; or just to those who you tag in the tweet itself.
And, if you pick the third of these and tag no one, it’s also a way to broadcast a tweet or a thread of tweets with no replies at all. (This all applies to “open” accounts; those that have locked who can view their tweets are limited by default; and it doesn’t seem to replace the option to hide replies, which Twitter launched last year. We asked and Twitter declined to make any update or statement on the “hide replies” functionality.)
Those who can’t reply will get a greyed-out icon, but they can still view, retweet, retweet with comment and “like” the tweets.
The basic idea behind limiting replies is more control. Specifically, setting parameters around those who can reply can help the original poster curtail abusive or trolling replies, or to limit replies to keep the conversation on track. Both can be especially critical in a number of use cases common on Twitter. Those tweeting about a sensitive issue or a political topic are classic scenarios that bring out trolls. And those trying to broadcast a conversation with a specific group (or indeed in a monologue) with the intention of making that conversation publicly viewable can now do it without interruption.
“Sometimes people are more comfortable talking about what’s happening when they can choose who can reply,” Xie wrote. “We’ve seen people use these settings to have conversations that weren’t really possible before. Starting today, everyone will be able to use these settings so unwanted replies don’t get in the way of meaningful conversations.”
Xie said that beta test feedback has been positive. Those using the feature said they felt more comfortable and protected from spam and abuse, and the feature is getting used: It found that those who have submitted abuse reports and had access to the new limit reply tool were three times more likely to use the settings.
It seems that limiting replies is more of a complement to, not a replacement for, muting and blocking: 60% of those using the limit replies feature weren’t already muting and blocking other users. Xie doesn’t mention how it is used alongside another spam-controlling feature Twitter launched last year, hiding replies.
People who are limited from replying directly can still retweet with a comment, and thus still inject whatever they want to say. But Xie noted that “these settings prevented an average of three potentially abusive replies while only adding one potentially abusive retweet with comment,” adding that there was no uptick in unwanted direct messages, either.
The feature getting announced today has been a while in the making, both from a product and even longer from an idealogical point of view.
The concept for limiting replies was first announced back at January at CES, when Kayvon Beykpour, Twitter’s VP of Product said that the primary motivation [for the feature] was control. “We want to build on the theme of authors getting more control and we’ve thought … that there are many analogs of how people have communications in life,” he said at the time.
The feature then formally started to roll out in a limited test in May, and the version that is getting turned on today looks just like that. (In fact, the screen shots are exactly the same, except with a more recent date on the tweets.)
But the bigger thinking behind the new feature stretches back earlier than this year.
Twitter has long (as in years now) been working on creating better ways to channel its open-ended social platform to keep it from getting exploited and abused.
The issue stems from the platform’s basic DNA: Twitter was built around the idea of anyone being able to reply to anyone else, regardless of whether two users follow each other, or whether someone wants to hear a certain response. The issue, some argue, is that Twitter has dragged its feet because the open-ended aspect is actually in Twitter’s best business interest, since it encourages more engagement and use. (For a recent example of that argument pertaining specifically to cancel culture conversations, see here.)
Admittedly, it can be one of the more empowering feelings you can have on this big internet of ours, to be able to reply to someone on Twitter when you have an opinion on something, or just a question. Never mind that the reply may never come, or come from an army of trolls. And indeed, that open-ended aspect hasn’t always played out as a positive every time.
People, some of whom might be vulnerable or going through difficult situations, can be singled out for negative responses by other users, leading some of them to leave Twitter altogether, sometimes in very high-profile incidents. At a time when social media has become ever more influential and is being criticized by many asking whether it is fair enough, responsible enough and responsive enough in relation to the (incendiary and other) content that bounces around its playing fields, it has been a bad look for Twitter, and it’s been trying for years now to fix it.
I’m guessing that some will decry the move to limit replies as a curtailing of free speech and free expression, that it might give a stronger voice to those who are actually using Twitter to disseminate abusive information themselves, by potentially limiting how people can respond.
There are a couple of counter arguments, though. One is that people can still see and retweet what someone says, one way of responding. A retweet with comment can still be pretty powerful: Sometimes these tweets can go viral and be seen even more than the original tweets themselves.
Xie noted that people will be able to see when replies have been limited, and that Twitter is working on ways of making that more obvious. That might well include pointing people to further information elsewhere. And the new timeline containing “Retweets with Comments” launched in May gets four times more visits on Tweets using these settings, Xie said.
There have, in fact, been a number of tweaks to reduce the amount of noise on the platform: Last year Twitter turned on the ability to hide replies, and over the years Twitter has improved the process for reporting harassment (including a number of updates and tests around harmful language), blocking people (although it seems this has some people contesting it) and muting people.
And it’s worth pointing out that Twitter has been making a lot of efforts to better detect and help users report original tweets that are abusive, discriminatory, contain fake news and the rest.
That might be the most important point here. This is a net positive for the platform, but still just one step in a long journey to work on improving the climate on Twitter overall.
Facebook Faces Yet Another Outage: Platform Encounters Technical Issues Again

Uppdated: It seems that today’s issues with Facebook haven’t affected as many users as the last time. A smaller group of people appears to be impacted this time around, which is a relief compared to the larger incident before. Nevertheless, it’s still frustrating for those affected, and hopefully, the issues will be resolved soon by the Facebook team.
Facebook had another problem today (March 20, 2024). According to Downdetector, a website that shows when other websites are not working, many people had trouble using Facebook.
This isn’t the first time Facebook has had issues. Just a little while ago, there was another problem that stopped people from using the site. Today, when people tried to use Facebook, it didn’t work like it should. People couldn’t see their friends’ posts, and sometimes the website wouldn’t even load.
Downdetector, which watches out for problems on websites, showed that lots of people were having trouble with Facebook. People from all over the world said they couldn’t use the site, and they were not happy about it.
When websites like Facebook have problems, it affects a lot of people. It’s not just about not being able to see posts or chat with friends. It can also impact businesses that use Facebook to reach customers.
Since Facebook owns Messenger and Instagram, the problems with Facebook also meant that people had trouble using these apps. It made the situation even more frustrating for many users, who rely on these apps to stay connected with others.
During this recent problem, one thing is obvious: the internet is always changing, and even big websites like Facebook can have problems. While people wait for Facebook to fix the issue, it shows us how easily things online can go wrong. It’s a good reminder that we should have backup plans for staying connected online, just in case something like this happens again.
NEWS
We asked ChatGPT what will be Google (GOOG) stock price for 2030

Investors who have invested in Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOG) stock have reaped significant benefits from the company’s robust financial performance over the last five years. Google’s dominance in the online advertising market has been a key driver of the company’s consistent revenue growth and impressive profit margins.
In addition, Google has expanded its operations into related fields such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. These areas show great promise as future growth drivers, making them increasingly attractive to investors. Notably, Alphabet’s stock price has been rising due to investor interest in the company’s recent initiatives in the fast-developing field of artificial intelligence (AI), adding generative AI features to Gmail and Google Docs.
However, when it comes to predicting the future pricing of a corporation like Google, there are many factors to consider. With this in mind, Finbold turned to the artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT to suggest a likely pricing range for GOOG stock by 2030. Although the tool was unable to give a definitive price range, it did note the following:
“Over the long term, Google has a track record of strong financial performance and has shown an ability to adapt to changing market conditions. As such, it’s reasonable to expect that Google’s stock price may continue to appreciate over time.”
GOOG stock price prediction
While attempting to estimate the price range of future transactions, it is essential to consider a variety of measures in addition to the AI chat tool, which includes deep learning algorithms and stock market experts.
Finbold collected forecasts provided by CoinPriceForecast, a finance prediction tool that utilizes machine self-learning technology, to anticipate Google stock price by the end of 2030 to compare with ChatGPT’s projection.
According to the most recent long-term estimate, which Finbold obtained on March 20, the price of Google will rise beyond $200 in 2030 and touch $247 by the end of the year, which would indicate a 141% gain from today to the end of the year.
Google has been assigned a recommendation of ‘strong buy’ by the majority of analysts working on Wall Street for a more near-term time frame. Significantly, 36 analysts of the 48 have recommended a “strong buy,” while seven people have advocated a “buy.” The remaining five analysts had given a ‘hold’ rating.
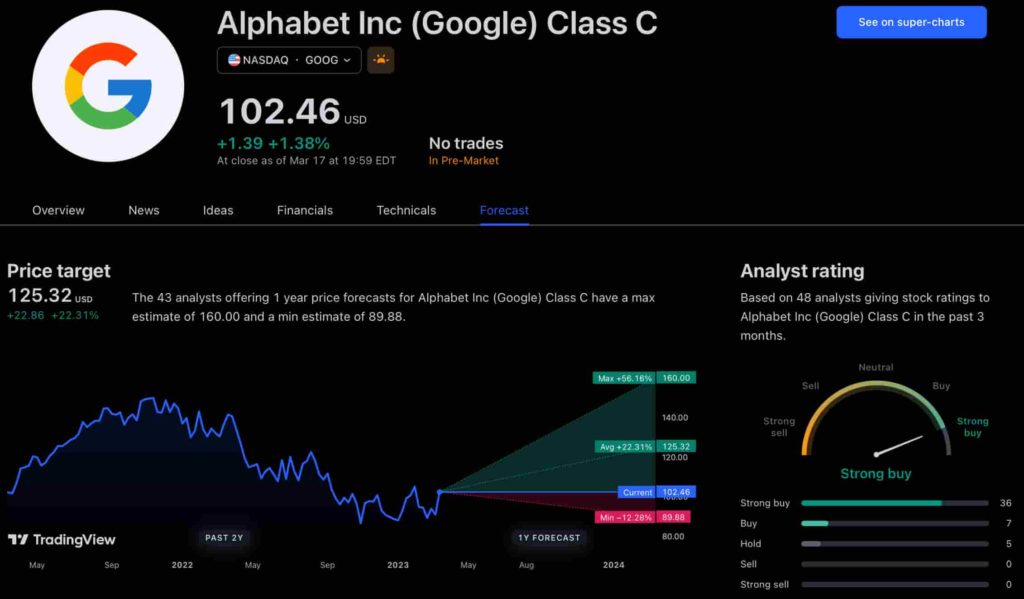
The average price projection for Alphabet stock over the last three months has been $125.32; this objective represents a 22.31% upside from its current price. It’s interesting to note that the maximum price forecast for the next year is $160, representing a gain of 56.16% from the stock’s current price of $102.46.
While the outlook for Google stock may be positive, it’s important to keep in mind that some potential challenges and risks could impact its performance, including competition from ChatGPT itself, which could affect Google’s price.
Disclaimer: The content on this site should not be considered investment advice. Investing is speculative. When investing, your capital is at risk.
NEWS
This Apple Watch app brings ChatGPT to your wrist — here’s why you want it

ChatGPT feels like it is everywhere at the moment; the AI-powered tool is rapidly starting to feel like internet connected home devices where you are left wondering if your flower pot really needed Bluetooth. However, after hearing about a new Apple Watch app that brings ChatGPT to your favorite wrist computer, I’m actually convinced this one is worth checking out.
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Limits News Links In California Over Proposed ‘Link Tax’ Law
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-
SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 12, 2024
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days ago2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2
-

 MARKETING4 days ago
MARKETING4 days ago5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoCritical Display Error in Brand Safety Metrics On Twitter/X Corrected
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoWeekend Google Core Ranking Volatility