Key Google Analytics Features For Effectively Analyzing Data
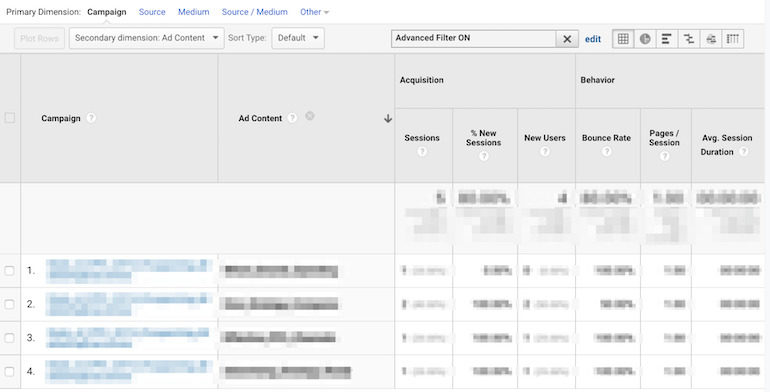
Being able to effectively analyze your data is critical when it comes to PPC performance. This article covers a few key Google Analytics features important for quickly analyzing your data in the interface. If you’ve used Analytics before but haven’t ventured in too deep then this article will help you better segment and view your performance.
Secondary Dimensions
Since this article is introductory I want to clarify what a dimension is versus a metric, but if you already know the difference feel free to skip to the next paragraph. A dimension is a data attribute such as a campaign, keyword, or source/medium. Those are the most common ones in PPC, but a dimension can also be a location, page URL, month, age, device, language, etc. Metrics are quantitative measurements, or numbers, associated with dimensions and are typically what people think of when they used the word “data”. The metrics are what tell us how something is performing.
The secondary dimension feature is probably the one I use the most when viewing data in an Analytics table. It simply allows you to quickly segment data one step further with an additional dimension option of your choice. If I was looking at Google Ads data using the campaign as my primary dimension I could add ad group as a secondary dimension to break the data down more. You could also do this for ad group and keyword, page and source/medium, among many many other combinations.
Various examples of primary and secondary dimension combinations:




Advanced Filters
This is my #2 most used Analytics feature and I’m usually using it in combination with a secondary dimension. Advanced filters are exactly what they sound like, filters that you can put in place to whittle down your data to specific segments of interest. For example, I might put a filter in place to include only campaigns that contain the word bananas. Once I do that all campaigns not containing bananas go away so I can see the data I’m interested in more clearly. The filter can be set to include or exclude items, and you have the choice of several options for how to filter:
Dimensions: containing, begins with, ends with, exactly matching, or regex
Metrics: greater than, less than, or equals
When you’re filtering, keep in mind that you can only filter for dimensions and metrics that are present in your data table. If you have a secondary dimension selected you can filter on both the primary and secondary dimensions simultaneously.
Dimension and metric filter options:



Example advanced filters:



Pivot View
I will be the first (but not the only one) to admit that I don’t love and don’t use the pivot view in Analytics. I much prefer to export my data and do my pivots in Excel or Google Sheets. But I realize not everyone, especially those just getting familiar with data analysis, may not be comfortable with pivots in Excel/Sheets and in that case it is a useful feature. It can also be useful if you need to pivot simple data quickly.
With the pivot view, you will select a dimension, pivot by, and a metric option. You can add up to two dimensions and two metrics. There are numerous combinations of options you can use and part of getting the hang of pivots is jumping in there and testing out combinations until you figure out what you need. Listed below are some simple pivot report options to get you started.
New vs Returning Visitor Analysis
Primary Dimension – Channel
Pivot by – User Type
Pivot Metric – Sessions
Second Pivot Metric – Goal Completions/Transactions
Example pivot view:

Channel Analysis
Primary Dimension – Channel
Pivot by – Source
Pivot Metric – Sessions
Landing Page Analysis
Primary Dimension – Landing Pages
Pivot by – Medium
Pivot Metrics – Sessions
Browser & Operating System Analysis
Primary Dimension – Browser
Pivot by – Operations system
Pivot metric – Sessions
Second Pivot metric – Goal Completions/Transactions
Conversion Analysis
Primary Dimension – Landing Pages
Secondary Dimension – Medium
Pivot by – Location
Pivot Metric – Sessions
Secondary Pivot Metric – Goal Completions/Transactions
Come Workshopping With Me!
If you enjoyed learning a few different ways to use Analytics to improve your data chops then you should join me at Hero Conf Austin in April 2020. I will be leading a half-day workshop all about using Analytics for PPC analysis. Our workshops are hands-on and personal so you get the attention you deserve.
AI
Exploring the Evolution of Language Translation: A Comparative Analysis of AI Chatbots and Google Translate

According to an article on PCMag, while Google Translate makes translating sentences into over 100 languages easy, regular users acknowledge that there’s still room for improvement.
In theory, large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT are expected to bring about a new era in language translation. These models consume vast amounts of text-based training data and real-time feedback from users worldwide, enabling them to quickly learn to generate coherent, human-like sentences in a wide range of languages.
However, despite the anticipation that ChatGPT would revolutionize translation, previous experiences have shown that such expectations are often inaccurate, posing challenges for translation accuracy. To put these claims to the test, PCMag conducted a blind test, asking fluent speakers of eight non-English languages to evaluate the translation results from various AI services.
The test compared ChatGPT (both the free and paid versions) to Google Translate, as well as to other competing chatbots such as Microsoft Copilot and Google Gemini. The evaluation involved comparing the translation quality for two test paragraphs across different languages, including Polish, French, Korean, Spanish, Arabic, Tagalog, and Amharic.
In the first test conducted in June 2023, participants consistently favored AI chatbots over Google Translate. ChatGPT, Google Bard (now Gemini), and Microsoft Bing outperformed Google Translate, with ChatGPT receiving the highest praise. ChatGPT demonstrated superior performance in converting colloquialisms, while Google Translate often provided literal translations that lacked cultural nuance.
For instance, ChatGPT accurately translated colloquial expressions like “blow off steam,” whereas Google Translate produced more literal translations that failed to resonate across cultures. Participants appreciated ChatGPT’s ability to maintain consistent levels of formality and its consideration of gender options in translations.
The success of AI chatbots like ChatGPT can be attributed to reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF), which allows these models to learn from human preferences and produce culturally appropriate translations, particularly for non-native speakers. However, it’s essential to note that while AI chatbots outperformed Google Translate, they still had limitations and occasional inaccuracies.
In a subsequent test, PCMag evaluated different versions of ChatGPT, including the free and paid versions, as well as language-specific AI agents from OpenAI’s GPTStore. The paid version of ChatGPT, known as ChatGPT Plus, consistently delivered the best translations across various languages. However, Google Translate also showed improvement, performing surprisingly well compared to previous tests.
Overall, while ChatGPT Plus emerged as the preferred choice for translation, Google Translate demonstrated notable improvement, challenging the notion that AI chatbots are always superior to traditional translation tools.
Source: https://www.pcmag.com/articles/google-translate-vs-chatgpt-which-is-the-best-language-translator
Google Implements Stricter Guidelines for Mass Email Senders to Gmail Users

Beginning in April, Gmail senders bombarding users with unwanted mass emails will encounter a surge in message rejections unless they comply with the freshly minted Gmail email sender protocols, Google cautions.
Fresh Guidelines for Dispatching Mass Emails to Gmail Inboxes In an elucidative piece featured on Forbes, it was highlighted that novel regulations are being ushered in to shield Gmail users from the deluge of unsolicited mass emails. Initially, there were reports surfacing about certain marketers receiving error notifications pertaining to messages dispatched to Gmail accounts. Nonetheless, a Google representative clarified that these specific errors, denoted as 550-5.7.56, weren’t novel but rather stemmed from existing authentication prerequisites.
Moreover, Google has verified that commencing from April, they will initiate “the rejection of a portion of non-compliant email traffic, progressively escalating the rejection rate over time.” Google elaborates that, for instance, if 75% of the traffic adheres to the new email sender authentication criteria, then a portion of the remaining non-conforming 25% will face rejection. The exact proportion remains undisclosed. Google does assert that the implementation of the new regulations will be executed in a “step-by-step fashion.”
This cautious and methodical strategy seems to have already kicked off, with transient errors affecting a “fraction of their non-compliant email traffic” coming into play this month. Additionally, Google stipulates that bulk senders will be granted until June 1 to integrate “one-click unsubscribe” in all commercial or promotional correspondence.
Exclusively Personal Gmail Accounts Subject to Rejection These alterations exclusively affect bulk emails dispatched to personal Gmail accounts. Entities sending out mass emails, specifically those transmitting a minimum of 5,000 messages daily to Gmail accounts, will be mandated to authenticate outgoing emails and “refrain from dispatching unsolicited emails.” The 5,000 message threshold is tabulated based on emails transmitted from the same principal domain, irrespective of the employment of subdomains. Once the threshold is met, the domain is categorized as a permanent bulk sender.
These guidelines do not extend to communications directed at Google Workspace accounts, although all senders, including those utilizing Google Workspace, are required to adhere to the updated criteria.
Augmented Security and Enhanced Oversight for Gmail Users A Google spokesperson emphasized that these requisites are being rolled out to “fortify sender-side security and augment user control over inbox contents even further.” For the recipient, this translates to heightened trust in the authenticity of the email sender, thus mitigating the risk of falling prey to phishing attempts, a tactic frequently exploited by malevolent entities capitalizing on authentication vulnerabilities. “If anything,” the spokesperson concludes, “meeting these stipulations should facilitate senders in reaching their intended recipients more efficiently, with reduced risks of spoofing and hijacking by malicious actors.”
Google’s Next-Gen AI Chatbot, Gemini, Faces Delays: What to Expect When It Finally Launches

In an unexpected turn of events, Google has chosen to postpone the much-anticipated debut of its revolutionary generative AI model, Gemini. Initially poised to make waves this week, the unveiling has now been rescheduled for early next year, specifically in January.
Gemini is set to redefine the landscape of conversational AI, representing Google’s most potent endeavor in this domain to date. Positioned as a multimodal AI chatbot, Gemini boasts the capability to process diverse data types. This includes a unique proficiency in comprehending and generating text, images, and various content formats, even going so far as to create an entire website based on a combination of sketches and written descriptions.
Originally, Google had planned an elaborate series of launch events spanning California, New York, and Washington. Regrettably, these events have been canceled due to concerns about Gemini’s responsiveness to non-English prompts. According to anonymous sources cited by The Information, Google’s Chief Executive, Sundar Pichai, personally decided to postpone the launch, acknowledging the importance of global support as a key feature of Gemini’s capabilities.
Gemini is expected to surpass the renowned ChatGPT, powered by OpenAI’s GPT-4 model, and preliminary private tests have shown promising results. Fueled by significantly enhanced computing power, Gemini has outperformed GPT-4, particularly in FLOPS (Floating Point Operations Per Second), owing to its access to a multitude of high-end AI accelerators through the Google Cloud platform.
SemiAnalysis, a research firm affiliated with Substack Inc., expressed in an August blog post that Gemini appears poised to “blow OpenAI’s model out of the water.” The extensive compute power at Google’s disposal has evidently contributed to Gemini’s superior performance.
Google’s Vice President and Manager of Bard and Google Assistant, Sissie Hsiao, offered insights into Gemini’s capabilities, citing examples like generating novel images in response to specific requests, such as illustrating the steps to ice a three-layer cake.
While Google’s current generative AI offering, Bard, has showcased noteworthy accomplishments, it has struggled to achieve the same level of consumer awareness as ChatGPT. Gemini, with its unparalleled capabilities, is expected to be a game-changer, demonstrating impressive multimodal functionalities never seen before.
During the initial announcement at Google’s I/O developer conference in May, the company emphasized Gemini’s multimodal prowess and its developer-friendly nature. An application programming interface (API) is under development, allowing developers to seamlessly integrate Gemini into third-party applications.
As the world awaits the delayed unveiling of Gemini, the stakes are high, with Google aiming to revolutionize the AI landscape and solidify its position as a leader in generative artificial intelligence. The postponed launch only adds to the anticipation surrounding Gemini’s eventual debut in the coming year.
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress















