MARKETING
Everything You Need to Know about Brand Experience

Online sales are reaching all-time highs as buyers become more comfortable with digital transactions — in 2021, for example, consumers spent a collective $14 billion online across Black Friday and Cyber Monday.
For businesses, the shift to online-first purchasing offers substantive potential, but also underpins prospective problems: As the number of digital product offerings ramps up, competition for customer conversions is also on the rise.
The result? A battlefield for brand experience. If companies can create a lasting positive impression among potential customers, they can drive sales and set the stage for long-term loyalty. But what exactly is brand experience? What does effective design require and what does it look like in practice? Most importantly, how do brands create experience strategies that deliver reliable results over time?
What is Brand Experience?
Brand experience is the lasting impression customers have of your brand. It includes thoughts, feelings, perceptions, and reactions to everything from direct marketing efforts to large-scale ad campaigns and specific product launches.
While brand experience is similar to user experience, it encompasses a broader perception of your brand at large. Where user experience speaks to the takeaways — positive or negative — of a user when they interact with your website or social media profiles, brand experience refers to the impression of your brand as a whole. Not surprisingly, positive user experiences inform better brand experiences (and vice versa) but the two are distinct concepts.
It’s also important to understand that brand experience is subjective. While it’s possible to create experiences that produce reactions along a generalized spectrum, individual users will have different reactions to your efforts. In practice, this means that no matter how carefully you curate brand experience efforts, there will always be customers who come away with a negative reaction. As a result, the goal isn’t to create a universal experience but rather to create one that resonates positively with the largest number of target customers.
Breaking Down Brand Experience Design
Just 39% of business decision-makers say their brand effectively resonates with prospective buyers. This is a problem: If customers don’t connect your brand with positive thoughts, feelings, and reactions, they’re less likely to remember your products and services when it comes time to make a purchase.
Worth noting? Neutrality isn’t enough. While negative impressions of your brand can drive customers away from your site, neutral impressions are just as problematic — even if consumers see your brand listed in search engine results or advertised online, the absence of a positive brand impression means they won’t seek you out over companies that offer better connective messaging.
So what does effective brand experience design look like? Four components are critical:

Perception
Perception forms a key part of the experience. This includes audio, visual, and tactical interactions that allow customers to connect a specific sense to advertising campaigns. In much the same way that particular smells can bring back memories of childhood experiences, brands that successfully merge senses with marketing can create connections that drive sales.
Participation
It’s also more likely that customers will walk away with a positive brand experience if they’re able to participate in some way rather than simply watch. This might include the ability to submit suggestions online or interact in real-time online question forums, or it could feature the use of physical installations that allow consumers to touch your product or provide direct feedback.
Personalization
Generic marketing campaigns can produce steady returns, but personalization can help encourage connection across different customer segments. By leveraging both user-provided data (with their consent) along with social media interactions and other engagement data, it’s possible to create more personalized efforts that help create connections between consumer needs and current product offerings.
Prioritization
Brand experience can’t be all things to all people. Attempts to capture every consumer in every circumstance actually undermine experience-driven efforts — as a result, it’s worth selecting specific brand metrics such as positive social mentions or repeat purchases to prioritize.
Creating a Brand Experience Strategy
So how do you build an effective brand experience strategy?
First up is identifying areas where your current experience isn’t meeting customer expectations. Social media interactions and customer service calls can help pinpoint potential problems — if consistent concerns around brand interaction or reaction arise, this can help frame the foundation of brand experience strategy.
Next is targeting an area for improvement. While there may be more than one aspect of brand experience that could use a refresh or redesign, attempting to do everything at once can spread strategy efforts too thin and deliver less-than-ideal results. For example, you might choose to increase positive social mentions across specific channels such as Facebook or Instagram. While the eventual goal could be a larger social impact from initial contact to eventual conversion, easily-accessible social platforms provide an ideal starting point.
Effective measurement follows to ensure efforts are bearing fruit. In the case of our social media example above, this means tracking user views, reactions, and responses to social media posts along with the sentiment — positive, negative, or neutral — that goes along with them. This is also the time to explore and innovate by testing multiple strategies to see which one sticks. From video campaigns to personalized storytelling to marketing efforts all designed to elicit specific emotions, it’s worth finding that resonates with your customer base and then fine-tuning your efforts to deliver ideal outcomes.
Exploring Brand Experience Examples
- Red Bull
- Lean Cuisine
- Dove
- Cadbury India
- WestJet
It’s one thing to talk about brand experience building, but it’s another to see it in action. Here’s a look at five brand experiences efforts that offer effective in-practice examples.
1. Red Bull
In 2012, the company went all-in on its tagline “Red Bull gives you wings by sending skydiver Alex Baumgartner 24 miles above the Earth’s surface to pull off the highest skydive ever recorded and become the first person to break the sound barrier during freefall.
While his record was broken two years later by an executive from Google, it doesn’t change the fact that Red Bull did something no one had ever done before and created a unique brand experience that aligned with its core marketing message.
2. Lean Cuisine
While healthy eating has taken off in recent years, messaging around this effort is often the opposite. With a focus on weight loss instead of overall health, many brands find themselves reinforcing harmful stereotypes that equate weight loss with personal worth.
Lean Cuisine’s #WeighThis campaign looked to change the narrative by placing “scales” around New York’s Grand Central Station that encouraged women to “weigh in”.
The catch? These scales were actually boards that let women write down how they would prefer to be measured — such as by their own persistence, accomplishments or efforts.
Even better? Lean Cuisine marketers were smart enough to stay out of the way. There were no samples on offer, no surveys to fill out; women simply saw the scales and interacted with them, in turn boosting Lean Cuisine’s overall brand experience.
3. Dove
Dove’s Campaign for Real Beauty took a similar approach to Lean Cuisine but opted for the use of viral video that highlighted beauty of all types — beauty that goes beyond photoshoots and photoshop. The campaign earned praise for both its authenticity and efforts to help boost self-esteem among young girls.
By choosing emotional experience over a simple sales effort, Dove was able to better connect with its target customer base and boost overall customer loyalty.
4. Cadbury India
Cadbury India opted for consumer suggestions in creating their new chocolate bar flavor. Customers were encouraged to visit the company’s dedicated chocolate bar platform that let them select ingredients and create a recipe. Cadbury then tried all suggested recipes and selected the best of those submitted.
By prioritizing interaction over simple reaction, Cadbury facilitated consumer connection and encouraged customers to view chocolate bar making as a collaborative effort rather than a corporate endeavor, in turn creating a community-based brand experience.
5. WestJet
Canadian commercial airline WestJet has been running its “Christmas Miracle” campaign since 2013. It’s 2021 version sees the company asking people what they miss the most during the holidays — not surprisingly, many mention absent family members. WestJet staff then provide plane tickets to help loved ones reconnect, and the end of the video features a tearful reunion in progress.
Overall, it’s a feel-good experience designed to bring out emotions already close to the surface for many customers and in turn, boost the overall brand experience.
Building a Better Brand Experience
The right brand experience makes all the difference when it comes to cultivating long-term customer relationships. By understanding where current efforts don’t deliver, prioritizing areas for improvement and tracking engagement metrics over time, it’s possible to build a brand experience that boosts customer connection and encourages long-term loyalty.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in February 2016 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Source link
MARKETING
Effective Communication in Business as a Crisis Management Strategy

Everyday business life is full of challenges. These include data breaches, product recalls, market downturns and public relations conflicts that can erupt at any moment. Such situations pose a significant threat to a company’s financial health, brand image, or even its further existence. However, only 49% of businesses in the US have a crisis communications plan. It is a big mistake, as such a strategy can build trust, minimize damage, and even strengthen the company after it survives the crisis. Let’s discover how communication can transform your crisis and weather the chaos.
The ruining impact of the crisis on business
A crisis can ruin a company. Naturally, it brings losses. But the actual consequences are far worse than lost profits. It is about people behind the business – they feel the weight of uncertainty and fear. Employees start worrying about their jobs, customers might lose faith in the brand they once trusted, and investors could start looking elsewhere. It can affect the brand image and everything you build from the branding, business logo, social media can be ruined. Even after the crisis recovery, the company’s reputation can suffer, and costly efforts might be needed to rebuild trust and regain momentum. So, any sign of a coming crisis should be immediately addressed. Communication is one of the crisis management strategies that can exacerbate the situation.
The power of effective communication
Even a short-term crisis may have irreversible consequences – a damaged reputation, high employee turnover, and loss of investors. Communication becomes a tool that can efficiently navigate many crisis-caused challenges:
- Improved trust. Crisis is a synonym for uncertainty. Leaders may communicate trust within the company when the situation gets out of control. Employees feel valued when they get clear responses. The same applies to the customers – they also appreciate transparency and are more likely to continue cooperation when they understand what’s happening. In these times, documenting these moments through event photographers can visually reinforce the company’s messages and enhance trust by showing real, transparent actions.
- Reputation protection. Crises immediately spiral into gossip and PR nightmares. However, effective communication allows you to proactively address concerns and disseminate true information through the right channels. It minimizes speculation and negative media coverage.
- Saved business relationships. A crisis can cause unbelievable damage to relationships with employees, customers, and investors. Transparent communication shows the company’s efforts to find solutions and keeps stakeholders informed and engaged, preventing misunderstandings and painful outcomes.
- Faster recovery. With the help of communication, the company is more likely to receive support and cooperation. This collaborative approach allows you to focus on solutions and resume normal operations as quickly as possible.
It is impossible to predict when a crisis will come. So, a crisis management strategy mitigates potential problems long before they arise.
Tips on crafting an effective crisis communication plan.
To effectively deal with unforeseen critical situations in business, you must have a clear-cut communication action plan. This involves things like messages, FAQs, media posts, and awareness of everyone in the company. This approach saves precious time when the crisis actually hits. It allows you to focus on solving the problem instead of intensifying uncertainty and panic. Here is a step-by-step guide.
Identify your crisis scenarios.
Being caught off guard is the worst thing. So, do not let it happen. Conduct a risk assessment to pinpoint potential crises specific to your business niche. Consider both internal and external factors that could disrupt normal operations or damage the online reputation of your company. Study industry-specific issues, past incidents, and current trends. How will you communicate in each situation? Knowing your risks helps you prepare targeted communication strategies in advance. Of course, it is impossible to create a perfectly polished strategy, but at least you will build a strong foundation for it.
Form a crisis response team.
The next step is assembling a core team. It will manage communication during a crisis and should include top executives like the CEO, CFO, and CMO, and representatives from key departments like public relations and marketing. Select a confident spokesperson who will be the face of your company during the crisis. Define roles and responsibilities for each team member and establish communication channels they will work with, such as email, telephone, and live chat. Remember, everyone in your crisis response team must be media-savvy and know how to deliver difficult messages to the stakeholders.
Prepare communication templates.
When a crisis hits, things happen fast. That means communication needs to be quick, too. That’s why it is wise to have ready-to-go messages prepared for different types of crises your company may face. These messages can be adjusted to a particular situation when needed and shared on the company’s social media, website, and other platforms right away. These templates should include frequently asked questions and outline the company’s general responses. Make sure to approve these messages with your legal team for accuracy and compliance.
Establish communication protocols.
A crisis is always chaotic, so clear communication protocols are a must-have. Define trigger points – specific events that would launch the crisis communication plan. Establish a clear hierarchy for messages to avoid conflicting information. Determine the most suitable forms and channels, like press releases or social media, to reach different audiences. Here is an example of how you can structure a communication protocol:
- Immediate alert. A company crisis response team is notified about a problem.
- Internal briefing. The crisis team discusses the situation and decides on the next steps.
- External communication. A spokesperson reaches the media, customers, and suppliers.
- Social media updates. A trained social media team outlines the situation to the company audience and monitors these channels for misinformation or negative comments.
- Stakeholder notification. The crisis team reaches out to customers and partners to inform them of the incident and its risks. They also provide details on the company’s response efforts and measures.
- Ongoing updates. Regular updates guarantee transparency and trust and let stakeholders see the crisis development and its recovery.
Practice and improve.
Do not wait for the real crisis to test your plan. Conduct regular crisis communication drills to allow your team to use theoretical protocols in practice. Simulate different crisis scenarios and see how your people respond to these. It will immediately demonstrate the strong and weak points of your strategy. Remember, your crisis communication plan is not a static document. New technologies and evolving media platforms necessitate regular adjustments. So, you must continuously review and update it to reflect changes in your business and industry.
Wrapping up
The ability to handle communication well during tough times gives companies a chance to really connect with the people who matter most—stakeholders. And that connection is a foundation for long-term success. Trust is key, and it grows when companies speak honestly, openly, and clearly. When customers and investors trust the company, they are more likely to stay with it and even support it. So, when a crisis hits, smart communication not only helps overcome it but also allows you to do it with minimal losses to your reputation and profits.
MARKETING
Should Your Brand Shout Its AI and Marketing Plan to the World?

To use AI or not to use AI, that is the question.
Let’s hope things work out better for you than they did for Shakespeare’s mad Danish prince with daddy issues.
But let’s add a twist to that existential question.
CMI’s chief strategy officer, Robert Rose, shares what marketers should really contemplate. Watch the video or read on to discover what he says:
Should you not use AI and be proud of not using it? Dove Beauty did that last week.
Should you use it but keep it a secret? Sports Illustrated did that last year.
Should you use AI and be vocal about using it? Agency giant Brandtech Group picked up the all-in vibe.
Should you not use it but tell everybody you are? The new term “AI washing” is hitting everywhere.
What’s the best option? Let’s explore.
Dove tells all it won’t use AI
Last week, Dove, the beauty brand celebrating 20 years of its Campaign for Real Beauty, pledged it would NEVER use AI in visual communication to portray real people.
In the announcement, they said they will create “Real Beauty Prompt Guidelines” that people can use to create images representing all types of physical beauty through popular generative AI programs. The prompt they picked for the launch video? “The most beautiful woman in the world, according to Dove.”
I applaud them for the powerful ad. But I’m perplexed by Dove issuing a statement saying it won’t use AI for images of real beauty and then sharing a branded prompt for doing exactly that. Isn’t it like me saying, “Don’t think of a parrot eating pizza. Don’t think about a parrot eating pizza,” and you can’t help but think about a parrot eating pizza right now?
Brandtech Group says it’s all in on AI
Now, Brandtech Group, a conglomerate ad agency, is going the other way. It’s going all-in on AI and telling everybody.
This week, Ad Age featured a press release — oops, I mean an article (subscription required) — with the details of how Brandtech is leaning into the takeaway from OpenAI’s Sam Altman, who says 95% of marketing work today can be done by AI.
A Brandtech representative talked about how they pitch big brands with two people instead of 20. They boast about how proud they are that its lean 7,000 staffers compete with 100,000-person teams. (To be clear, showing up to a pitch with 20 people has never been a good thing, but I digress.)
OK, that’s a differentiated approach. They’re all in. Ad Age certainly seemed to like it enough to promote it. Oops, I mean report about it.
False claims of using AI and not using AI
Offshoots of the all-in and never-will approaches also exist.
The term “AI washing” is de rigueur to describe companies claiming to use AI for something that really isn’t AI. The US Securities and Exchange Commission just fined two companies for using misleading statements about their use of AI in their business model. I know one startup technology organization faced so much pressure from their board and investors to “do something with AI” that they put a simple chatbot on their website — a glorified search engine — while they figured out what they wanted to do.
Lastly and perhaps most interestingly, companies have and will use AI for much of what they create but remain quiet about it or desire to keep it a secret. A recent notable example is the deepfake ad of a woman in a car professing the need for people to use a particular body wipe to get rid of body odor. It was purported to be real, but sharp-eyed viewers suspected the fake and called out the company, which then admitted it. Or was that the brand’s intent all along — the AI-use outrage would bring more attention?
This is an AI generated influencer video.
Looks 100% real. Even the interior car detailing.
UGC content for your brand is about to get really cheap. ☠️ pic.twitter.com/2m10RqoOW3
— Jon Elder | Amazon Growth | Private Label (@BlackLabelAdvsr) March 26, 2024
To yell or not to yell about your brand’s AI decision
Should a brand yell from a mountaintop that they use AI to differentiate themselves a la Brandtech? Or should a brand yell they’re never going to use AI to differentiate themselves a la Dove? Or should a brand use it and not yell anything? (I think it’s clear that a brand should not use AI and lie and say it is. That’s the worst of all choices.)
I lean far into not-yelling-from-mountaintop camp.
When I see a CEO proudly exclaim that they laid off 90% of their support workforce because of AI, I’m not surprised a little later when the value of their service is reduced, and the business is failing.
I’m not surprised when I hear “AI made us do it” to rationalize the latest big tech company latest rounds of layoffs. Or when a big consulting firm announces it’s going all-in on using AI to replace its creative and strategic resources.
I see all those things as desperate attempts for short-term attention or a distraction from the real challenge. They may get responses like, “Of course, you had to lay all those people off; AI is so disruptive,” or “Amazing. You’re so out in front of the rest of the pack by leveraging AI to create efficiency, let me cover your story.” Perhaps they get this response, “Your company deserves a bump in stock price because you’re already using this fancy new technology.”
But what happens if the AI doesn’t deliver as promoted? What happens the next time you need to lay off people? What happens the next time you need to prove your technologically forward-leaning?
Yelling out that you’re all in on a disruptive innovation, especially one the public doesn’t yet trust a lot is (at best) a business sugar high. That short-term burst of attention may or may not foul your long-term brand value.
Interestingly, the same scenarios can manifest when your brand proclaims loudly it is all out of AI, as Dove did. The sugar high may not last and now Dove has itself into a messaging box. One slip could cause distrust among its customers. And what if AI gets good at demonstrating diversity in beauty?
I tried Dove’s instructions and prompted ChatGPT for a picture of “the most beautiful woman in the world according to the Dove Real Beauty ad.”
It gave me this. Then this. And this. And finally, this.
She’s absolutely beautiful, but she doesn’t capture the many facets of diversity Dove has demonstrated in its Real Beauty campaigns. To be clear, Dove doesn’t have any control over generating the image. Maybe the prompt worked well for Dove, but it didn’t for me. Neither Dove nor you can know how the AI tool will behave.
To use AI or not to use AI?
When brands grab a microphone to answer that question, they work from an existential fear about the disruption’s meaning. They do not exhibit the confidence in their actions to deal with it.
Let’s return to Hamlet’s soliloquy:
Thus conscience doth make cowards of us all;
And thus the native hue of resolution
Is sicklied o’er with the pale cast of thought,
And enterprises of great pith and moment
With this regard their currents turn awry
And lose the name of action.
In other words, Hamlet says everybody is afraid to take real action because they fear the unknown outcome. You could act to mitigate or solve some challenges, but you don’t because you don’t trust yourself.
If I’m a brand marketer for any business (and I am), I’m going to take action on AI for my business. But until I see how I’m going to generate value with AI, I’m going to be circumspect about yelling or proselytizing how my business’ future is better.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
MARKETING
How to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds

Welcome to Creator Columns, where we bring expert HubSpot Creator voices to the Blogs that inspire and help you grow better.
It’s the age of AI, and our job as marketers is to keep up.
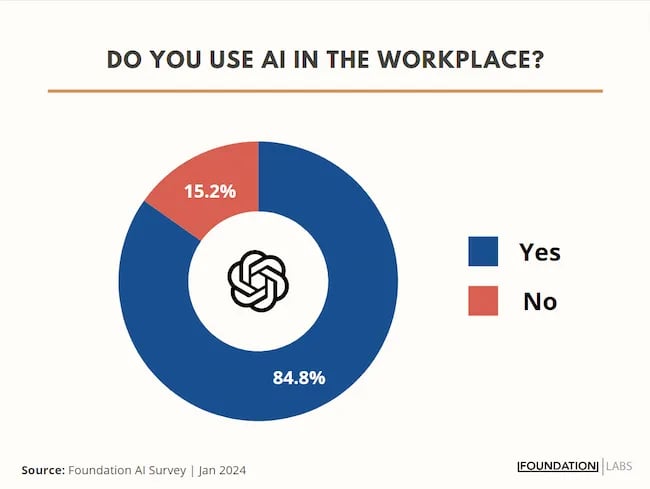
My team at Foundation Marketing recently conducted an AI Marketing study surveying hundreds of marketers, and more than 84% of all leaders, managers, SEO experts, and specialists confirmed that they used AI in the workplace.
If you can overlook the fear-inducing headlines, this technology is making social media marketers more efficient and effective than ever. Translation: AI is good news for social media marketers.
In fact, I predict that the marketers not using AI in their workplace will be using it before the end of this year, and that number will move closer and closer to 100%.
Social media and AI are two of the most revolutionizing technologies of the last few decades. Social media has changed the way we live, and AI is changing the way we work.
So, I’m going to condense and share the data, research, tools, and strategies that the Foundation Marketing Team and I have been working on over the last year to help you better wield the collective power of AI and social media.
Let’s jump into it.
What’s the role of AI in social marketing strategy?
In a recent episode of my podcast, Create Like The Greats, we dove into some fascinating findings about the impact of AI on marketers and social media professionals. Take a listen here:
Let’s dive a bit deeper into the benefits of this technology:
Benefits of AI in Social Media Strategy
AI is to social media what a conductor is to an orchestra — it brings everything together with precision and purpose. The applications of AI in a social media strategy are vast, but the virtuosos are few who can wield its potential to its fullest.
AI to Conduct Customer Research
Imagine you’re a modern-day Indiana Jones, not dodging boulders or battling snakes, but rather navigating the vast, wild terrain of consumer preferences, trends, and feedback.
This is where AI thrives.
Using social media data, from posts on X to comments and shares, AI can take this information and turn it into insights surrounding your business and industry. Let’s say for example you’re a business that has 2,000 customer reviews on Google, Yelp, or a software review site like Capterra.
Leveraging AI you can now have all 2,000 of these customer reviews analyzed and summarized into an insightful report in a matter of minutes. You simply need to download all of them into a doc and then upload them to your favorite Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) to get the insights and data you need.
But that’s not all.
You can become a Prompt Engineer and write ChatGPT asking it to help you better understand your audience. For example, if you’re trying to come up with a persona for people who enjoy marathons but also love kombucha you could write a prompt like this to ChatGPT:

The response that ChatGPT provided back is quite good:
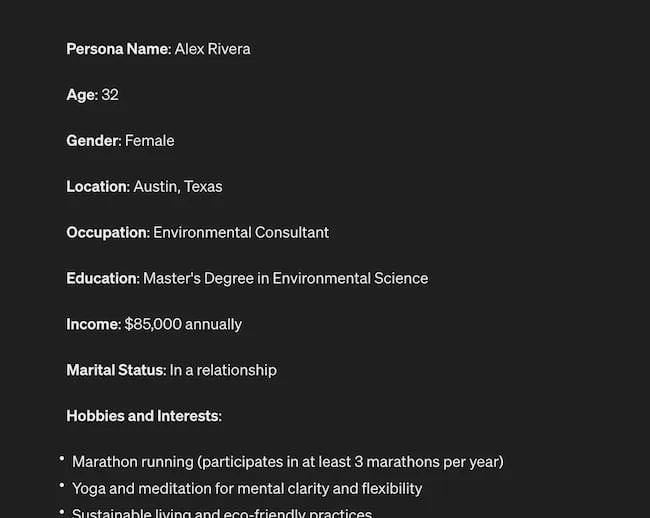
Below this it went even deeper by including a lot of valuable customer research data:
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Consumer behaviors
- Needs and preferences
And best of all…
It also included marketing recommendations.
The power of AI is unbelievable.
Social Media Content Using AI
AI’s helping hand can be unburdening for the creative spirit.
Instead of marketers having to come up with new copy every single month for posts, AI Social Caption generators are making it easier than ever to craft catchy status updates in the matter of seconds.
Tools like HubSpot make it as easy as clicking a button and telling the AI tool what you’re looking to create a post about:
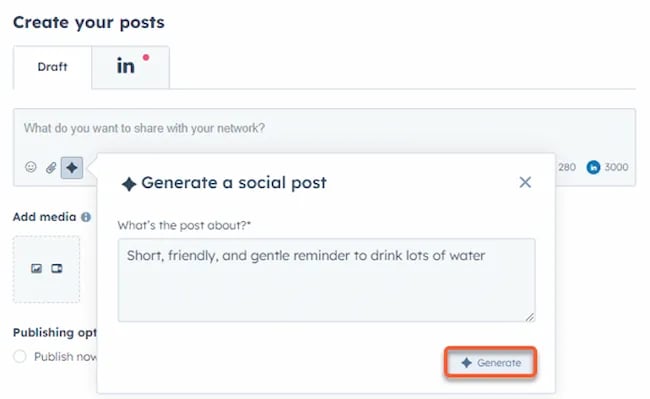
The best part of these AI tools is that they’re not limited to one channel.
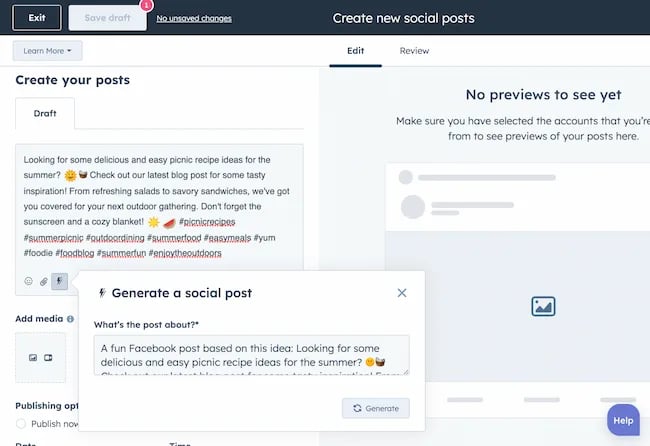
Your AI social media content assistant can help you with LinkedIn content, X content, Facebook content, and even the captions that support your post on Instagram.
It can also help you navigate hashtags:
With AI social media tools that generate content ideas or even write posts, it’s not about robots replacing humans. It’s about making sure that the human creators on your team are focused on what really matters — adding that irreplaceable human touch.
Enhanced Personalization
You know that feeling when a brand gets you, like, really gets you?
AI makes that possible through targeted content that’s tailored with a level of personalization you’d think was fortune-telling if the data didn’t paint a starker, more rational picture.
What do I mean?
Brands can engage more quickly with AI than ever before. In the early 2000s, a lot of brands spent millions of dollars to create social media listening rooms where they would hire social media managers to find and engage with any conversation happening online.
Thanks to AI, brands now have the ability to do this at scale with much fewer people all while still delivering quality engagement with the recipient.
Analytics and Insights
Tapping into AI to dissect the data gives you a CSI-like precision to figure out what works, what doesn’t, and what makes your audience tick. It’s the difference between guessing and knowing.
The best part about AI is that it can give you almost any expert at your fingertips.
If you run a report surrounding the results of your social media content strategy directly from a site like LinkedIn, AI can review the top posts you’ve shared and give you clear feedback on what type of content is performing, why you should create more of it, and what days of the week your content is performing best.
This type of insight that would typically take hours to understand.
Now …
Thanks to the power of AI you can upload a spreadsheet filled with rows and columns of data just to be met with a handful of valuable insights a few minutes later.
Improved Customer Service
Want 24/7 support for your customers?
It’s now possible without human touch.
Chatbots powered by AI are taking the lead on direct messaging experiences for brands on Facebook and other Meta properties to offer round-the-clock assistance.
The fact that AI can be trained on past customer queries and data to inform future queries and problems is a powerful development for social media managers.
Advertising on Social Media with AI
The majority of ad networks have used some variation of AI to manage their bidding system for years. Now, thanks to AI and its ability to be incorporated in more tools, brands are now able to use AI to create better and more interesting ad campaigns than ever before.
Brands can use AI to create images using tools like Midjourney and DALL-E in seconds.
Brands can use AI to create better copy for their social media ads.
Brands can use AI tools to support their bidding strategies.
The power of AI and social media is continuing to evolve daily and it’s not exclusively found in the organic side of the coin. Paid media on social media is being shaken up due to AI just the same.
How to Implement AI into Your Social Media Strategy
Ready to hit “Go” on your AI-powered social media revolution?
Don’t just start the engine and hope for the best. Remember the importance of building a strategy first. In this video, you can learn some of the most important factors ranging from (but not limited to) SMART goals and leveraging influencers in your day-to-day work:
The following seven steps are crucial to building a social media strategy:
- Identify Your AI and Social Media Goals
- Validate Your AI-Related Assumptions
- Conduct Persona and Audience Research
- Select the Right Social Channels
- Identify Key Metrics and KPIs
- Choose the Right AI Tools
- Evaluate and Refine Your Social Media and AI Strategy
Keep reading, roll up your sleeves, and follow this roadmap:
1. Identify Your AI and Social Media Goals
If you’re just dipping your toes into the AI sea, start by defining clear objectives.
Is it to boost engagement? Streamline your content creation? Or simply understand your audience better? It’s important that you spend time understanding what you want to achieve.
For example, say you’re a content marketing agency like Foundation and you’re trying to increase your presence on LinkedIn. The specificity of this goal will help you understand the initiatives you want to achieve and determine which AI tools could help you make that happen.
Are there AI tools that will help you create content more efficiently? Are there AI tools that will help you optimize LinkedIn Ads? Are there AI tools that can help with content repurposing? All of these things are possible and having a goal clearly identified will help maximize the impact. Learn more in this Foundation Marketing piece on incorporating AI into your content workflow.
Once you have identified your goals, it’s time to get your team on board and assess what tools are available in the market.
Recommended Resources:
2. Validate Your AI-Related Assumptions
Assumptions are dangerous — especially when it comes to implementing new tech.
Don’t assume AI is going to fix all your problems.
Instead, start with small experiments and track their progress carefully.
3. Conduct Persona and Audience Research
Social media isn’t something that you can just jump into.
You need to understand your audience and ideal customers. AI can help with this, but you’ll need to be familiar with best practices. If you need a primer, this will help:
Once you understand the basics, consider ways in which AI can augment your approach.
4. Select the Right Social Channels
Not every social media channel is the same.
It’s important that you understand what channel is right for you and embrace it.
The way you use AI for X is going to be different from the way you use AI for LinkedIn. On X, you might use AI to help you develop a long-form thread that is filled with facts and figures. On LinkedIn however, you might use AI to repurpose a blog post and turn it into a carousel PDF. The content that works on X and that AI can facilitate creating is different from the content that you can create and use on LinkedIn.
The audiences are different.
The content formats are different.
So operate and create a plan accordingly.
Recommended Tools and Resources:
5. Identify Key Metrics and KPIs
What metrics are you trying to influence the most?
Spend time understanding the social media metrics that matter to your business and make sure that they’re prioritized as you think about the ways in which you use AI.
These are a few that matter most:
- Reach: Post reach signifies the count of unique users who viewed your post. How much of your content truly makes its way to users’ feeds?
- Clicks: This refers to the number of clicks on your content or account. Monitoring clicks per campaign is crucial for grasping what sparks curiosity or motivates people to make a purchase.
- Engagement: The total social interactions divided by the number of impressions. This metric reveals how effectively your audience perceives you and their readiness to engage.
Of course, it’s going to depend greatly on your business.
But with this information, you can ensure that your AI social media strategy is rooted in goals.
6. Choose the Right AI Tools
The AI landscape is filled with trash and treasure.
Pick AI tools that are most likely to align with your needs and your level of tech-savviness.
For example, if you’re a blogger creating content about pizza recipes, you can use HubSpot’s AI social caption generator to write the message on your behalf:
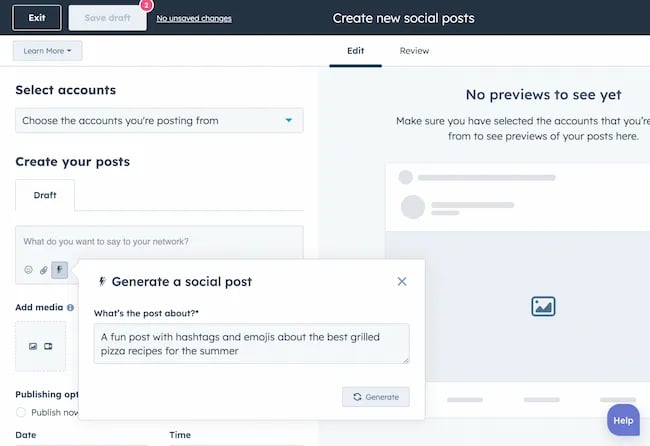
The benefit of an AI tool like HubSpot and the caption generator is that what at one point took 30-40 minutes to come up with — you can now have it at your fingertips in seconds. The HubSpot AI caption generator is trained on tons of data around social media content and makes it easy for you to get inspiration or final drafts on what can be used to create great content.
Consider your budget, the learning curve, and what kind of support the tool offers.
7. Evaluate and Refine Your Social Media and AI Strategy
AI isn’t a magic wand; it’s a set of complex tools and technology.
You need to be willing to pivot as things come to fruition.
If you notice that a certain activity is falling flat, consider how AI can support that process.
Did you notice that your engagement isn’t where you want it to be? Consider using an AI tool to assist with crafting more engaging social media posts.
Make AI Work for You — Now and in the Future
AI has the power to revolutionize your social media strategy in ways you may have never thought possible. With its ability to conduct customer research, create personalized content, and so much more, thinking about the future of social media is fascinating.
We’re going through one of the most interesting times in history.
Stay equipped to ride the way of AI and ensure that you’re embracing the best practices outlined in this piece to get the most out of the technology.
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days ago19 Best SEO Tools in 2024 (For Every Use Case)
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoEcommerce evolution: Blurring the lines between B2B and B2C
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 19, 2024
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 18, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days agoHow to Make $5000 of Passive Income Every Month in WordPress
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days ago2024 WordPress Vulnerability Report Shows Errors Sites Keep Making
-
 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 Amazing WordPress Design Resouces – WordPress.com News
-
WORDPRESS7 days ago
[GET] The7 Website And Ecommerce Builder For WordPress















![How to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds Download Now: The 2024 State of Social Media Trends [Free Report]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-to-Use-AI-For-a-More-Effective-Social-Media.png)



You must be logged in to post a comment Login