MARKETING
How to Use Estimated Brand Reach as a Meaningful Marketing Metric

The author’s views are entirely his or her own (excluding the unlikely event of hypnosis) and may not always reflect the views of Moz.
Estimated brand reach is the most important high-level metric that everyone seems to either interpret incorrectly, or ignore altogether.
Why? Because it’s a tough nut to crack.
By definition, brand reach is a headcount of unique “individuals” who encounter your brand, and you cannot de-anonymize all the people on every one of your web channels. Simply put, two “sessions” or “users” in your analytics could really be from one person, and there’s just no way you could know.
Nevertheless, you can and most definitely should estimate your brand reach. And you should, and most definitely can, use that data in a meaningful way.
For instance, it’s how we confirmed that:
And that’s just the tip of the iceberg. Let’s dive in.
What is reach?
Reach counts the number of actual people who come in contact with a particular campaign. For example, if 1,500 people see a post on Instagram, your reach is 1,500. (Warning: Take any tool claiming to give you a “reach” number with a grain of salt. As we covered earlier, it’s really hard to count unique individuals on the web).
Impressions, on the other hand, is a count of views. One person can see an Instagram post multiple times. A post with a reach of 1,500 can easily have as many as 3,000 impressions if every one of those people see it twice.
Brand reach takes this a step further by tracking all the individual people who have encountered any and all of your company’s campaigns across all of your channels, in a given time period.
If you’re tracking brand reach correctly, every single person only gets counted once, and as far we know, that’s impossible.
Google Search Console, for instance, will show you exactly how many impressions your website has achieved on Google Search over a period of time. But it won’t count unique individuals over that period. Someone could easily search two different keywords that your site is ranking for and encounter your brand twice on Google. There is no way to tie those multiple sessions back to one individual user.
It would be even harder to track that individual across all of your channels. How, for instance, would you make sure that someone who found you on social, and then again on search, isn’t counted twice?
The short answer is that you can’t.
However, you can estimate brand reach, and it’s work worth doing. It will a) help you tie meaningful metrics to your overall brand awareness efforts, and b) give you an immense amount of insight into how that high-level brand awareness affects your deeper-funnel outcomes — something that is sorely missing in most marketing programs.
Using impressions as a stand-in for pure reach
We’ve accepted that we can’t count the number of users who encounter our brand. But we are confident in our ability to count total impressions, and crucially, we’ve deduced that there’s a strong relationship between impressions and reach.
Common sense tells us that, if you see changes in your brand’s total impressions, there are likely changes to your reach as well.
We tested this premise using one of the only channels where we can actually count pure reach vs impressions: our email marketing program.
In email marketing:
And, as we suspected, there is a near perfect correlation between the two, of 0.94.
Interestingly, there is also a near-perfect correlation between email impressions and email engagement (someone clicking on that email) of 0.87.
Admittedly, email is a very controlled channel relative to, say, search or social media.
So, I went one step further and looked at how our “impressions” in Google Search Console aligned with Google Analytics’ count of “New Users” over the course of one year (which we’ll use as a stand-in for pure reach, since it only counts users once in a given timeframe):
The Pearson Correlation Coefficient for impressions’ relationship to GA’s New Users is 0.69, which is very strong! In other words, more impressions typically means more unique users, (AKA, reach).
Meanwhile, the relationship between GA’s New Users and GSC clicks is an astonishing 0.992, which is just 0.008 off from a perfect correlation.
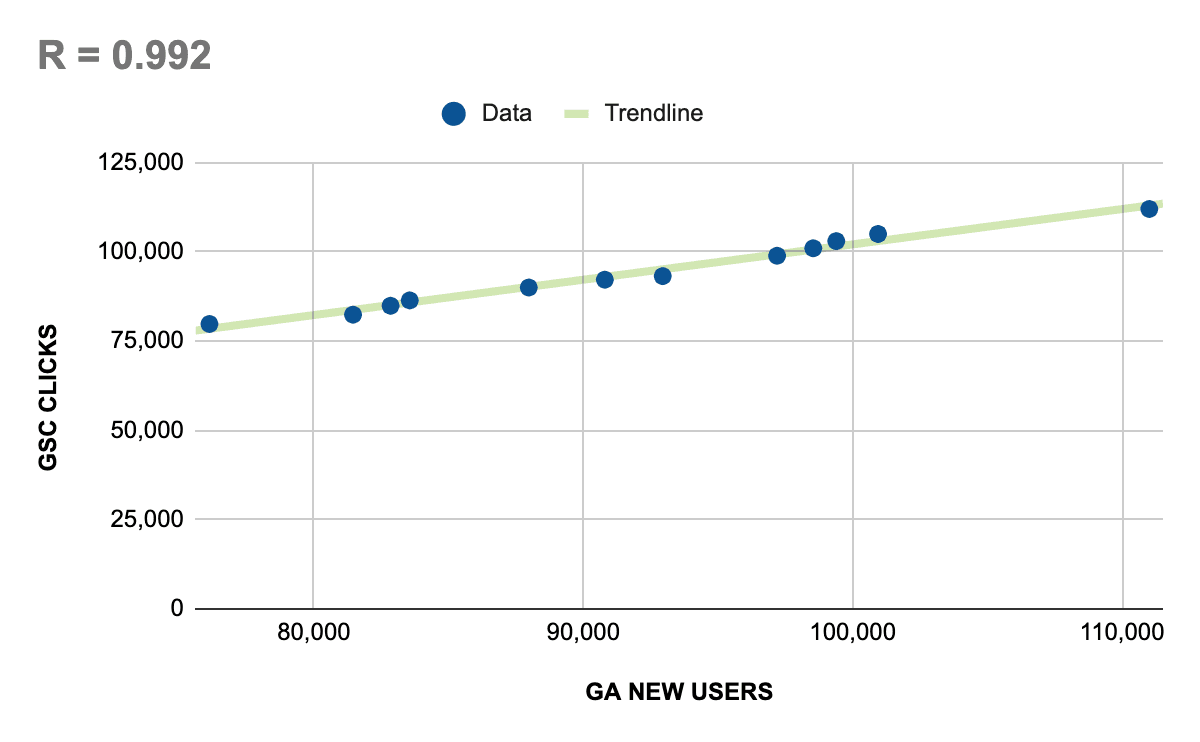
People much smarter than I have pointed out time and time again that GA’s user data must be taken with a grain of salt, for reasons I won’t get into here. Still, the point is that there’s ample evidence to suggest an extremely tight relationship between reach and impressions.
TL;DR: If impressions change negatively or positively, there is very likely to be a corresponding change in reach, and vice versa.
What we ended up with
Taking all of this knowledge into account, we started tracking impressions of every single channel (except email, where we can actually use pure reach) to help determine our estimated brand reach. The outcome? This graph of our brand reach as it changes over time:
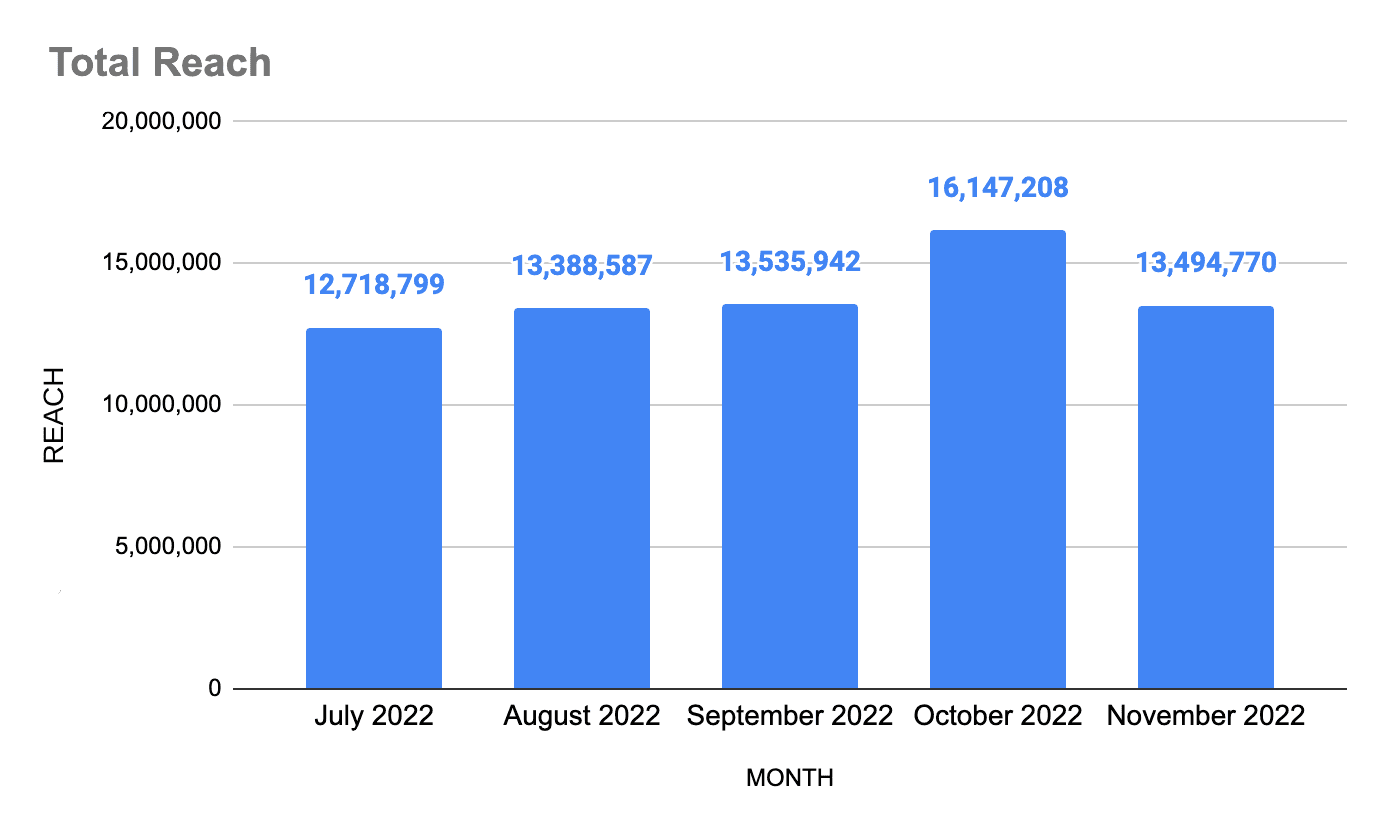
It’s extremely rewarding to have this type of number for your brand, even if it is an estimate.
But the greatest value here is not in the actual number; it’s in how that number changes from month to month, and more importantly, why it changes (more on this later in this post).
How to track estimated reach
The chart above displays our brand’s estimated reach across all our known marketing channels. Acquiring the data is as simple as going into each of these channels’ analytics properties once a month, and pulling out the impressions for the prior month.
Let’s go through the steps.
1. Have a spreadsheet where you can log everything. Here’s a template you can use. Feel free to update the info in the leftmost columns according to your channels. Columns G through L will populate automatically based on the data you add to columns C through F. We recommend using this layout, and tracking the data monthly, as it will make it easier for you to create pivot tables to help with your analysis.
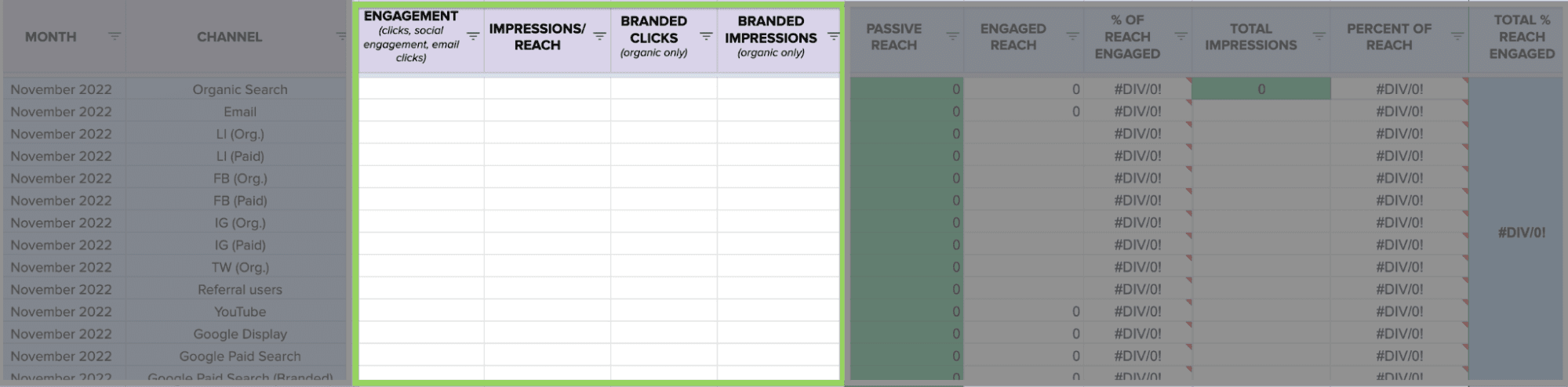
2. Access your impression data. Every marketing mix is different, but here’s how we would access impression data for the channels we rely on:
-
Organic search: Pull impressions for the month from Google Search Console.
-
Email marketing: Total number of unique contacts who have successfully received at least one email from you in the current month (this is one of the few channels where we use pure reach, as opposed to impressions).
-
Social media: Impressions pulled from Sprout, or from the native social media analytics platforms. Do the same for paid impressions.
-
Google Ads/Adroll/other ad platform: Impressions pulled from the ad-management platform of your choosing.
-
Website referrals: The sum of estimated page traffic from our backlinks each month. We use Ahrefs for this. The idea is that any backlink is a potential opportunity for someone to engage with our brand. Ahrefs estimates the traffic of each referring page. We can export this, and add it all up in a sheet, to get an estimate of the impressions we’re making on other websites.
-
YouTube: Impressions from Youtube Analytics.
Most of the above is self-explanatory, with a few exceptions.
First, there’s email. We use pure reach as opposed to impressions for two reasons:
-
Because we can.
-
Because using impressions for email would vastly inflate our estimated reach number. In any given month, we send 3 million or more email messages, but only reach around 400,000 people. Email, by its nature, entails regularly messaging the same group of people. Social media, while similar (your followers are your main audience), has a much smaller reach (we are under 30,000 each month).
Second, is Referral traffic. This is traffic that comes from other sites onto yours, but note that it excludes email, search-engine traffic and social media traffic. These are accounted for separately.
The referral source, more than any other channel, is a rough estimate. It only looks at the estimated organic page traffic, so it leaves out a large potential source of traffic in the form of other distribution channels (social, email, etc.) that website publishers may be using to promote a page.
But again, reach is most valuable as a relative metric — i.e., how it changes month to month — not as an absolute number.
To get the desired timeframe of one full month on Ahrefs, select “All” (so you’re actually seeing all current live links) and then show history for “last 3 months” like so:
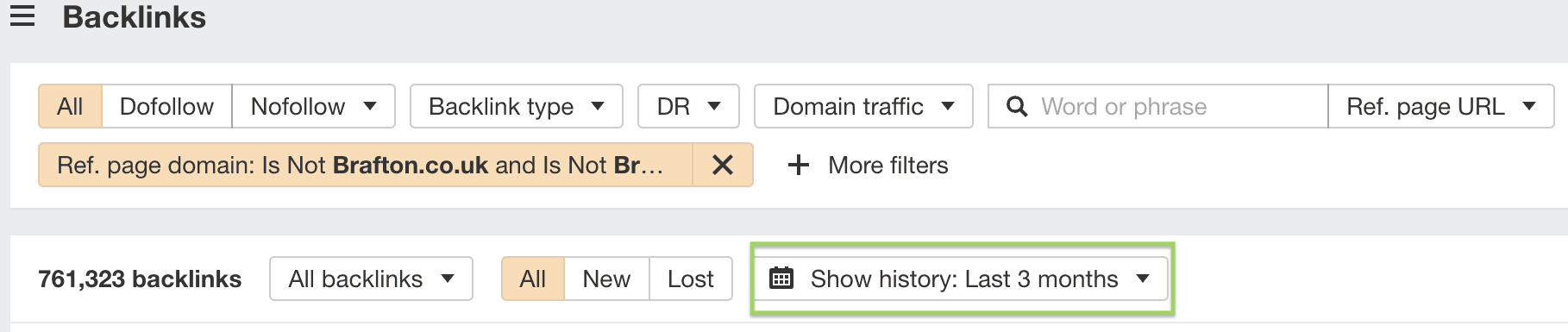
This is because Ahrefs, sadly, doesn’t let you provide custom dates on its backlink tool. My way of doing this adds a few steps, but they’re fairly intuitive once you get the hang of them (plus I made a video to help you).
Start by exporting the data into a spreadsheet. Next, filter out backlinks in your sheet that were first seen after the last day of the month you’re analyzing, or last seen before the first day of that month. Finally, add up all the Page Views, and that will be your total “impressions” from referral traffic.
The video below how we would pull these numbers for November, using Ahrefs:
Finally, you’ll notice “branded clicks” and “branded impressions” on the template:
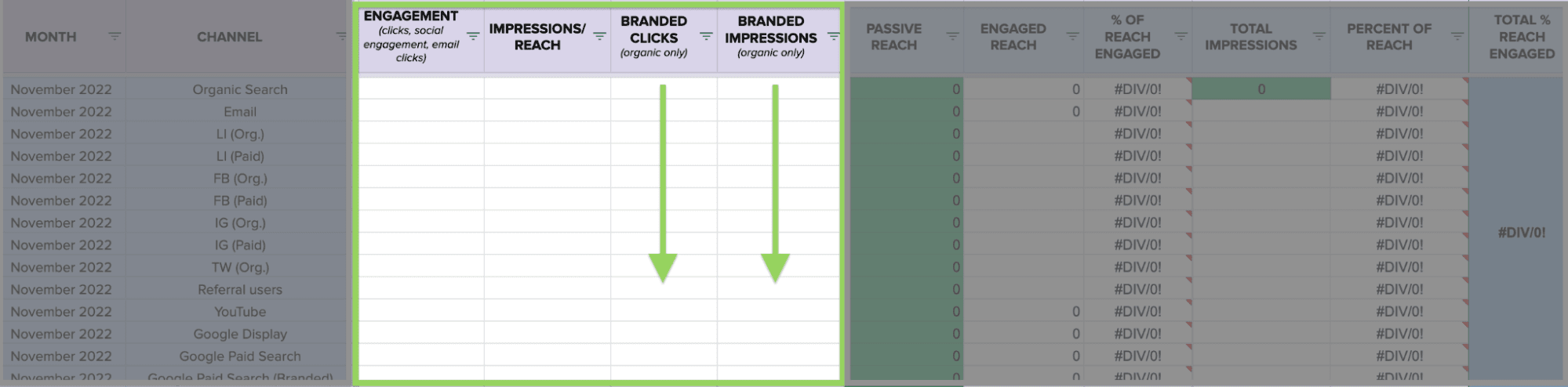
This data, which is easily pulled from GSC (filter for queries containing your brand name) can make for some interesting correlative data. It also helps us with engagement data, since we count branded search as a form of engagement. After all, if someone’s typing your brand name into Google Search, there’s likely some intent there.
How to evaluate estimated reach
Once you’ve filled in all your data, your sheet will look something like the image below:
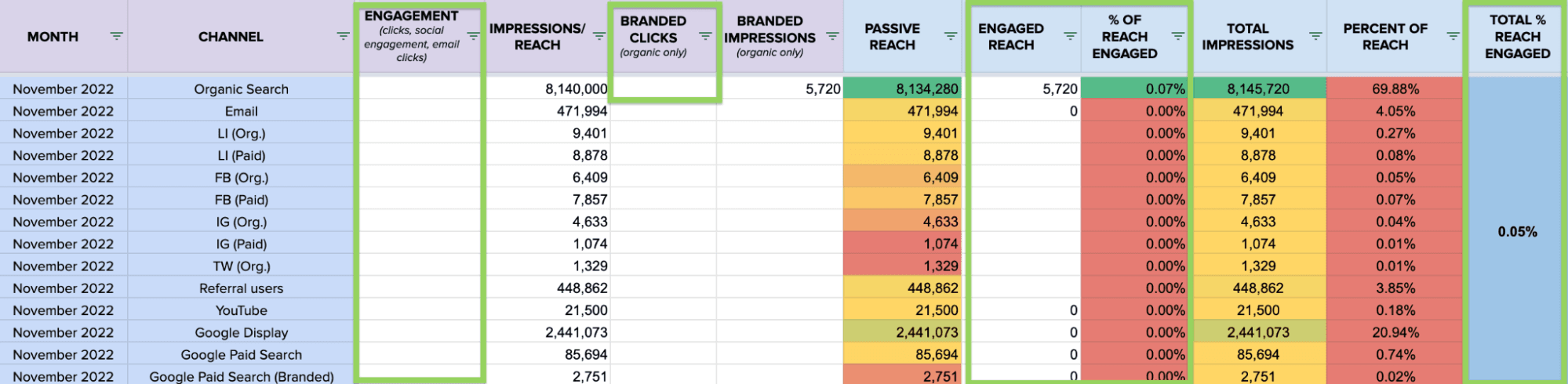
That’s enough to start creating very basic pivot tables (like adding up your total reach each month). But notice all the holes and zeros?
You can fill those by pulling in your engagement metrics. Let’s run through them:
-
Organic search: Pull clicks from Google Search Console. (Optional: I also recommend pulling branded search impressions, which we count as engagements in our spreadsheet, as well as branded clicks). New Users from GA is a viable alternative to clicks (remember that near-perfect relationship?), but you won’t be able to filter for your branded impressions and clicks this way.
-
Email marketing: Total number of “clicks” from the emails you’ve sent. We do this over opens, because opens have become less reliable; some email clients now technically open your emails before you do. Clicks in emails can be pulled from your email automation platform.
-
Social media: Engagements (link clicks, comments, likes and reposts) pulled from Sprout, or from each social platform’s native analytics. Do the same for paid engagements.
-
Google Ads/AdRoll/other ad platform: Interactions, or clicks, pulled from the ad platform of your choosing.
-
Website referrals: Referral traffic from Google Analytics (these are the people who encountered your brand on an external website and then engaged with it).
-
YouTube: Views from Youtube Analytics.
Once you’ve filled in this data, your spreadsheet will look more like this:
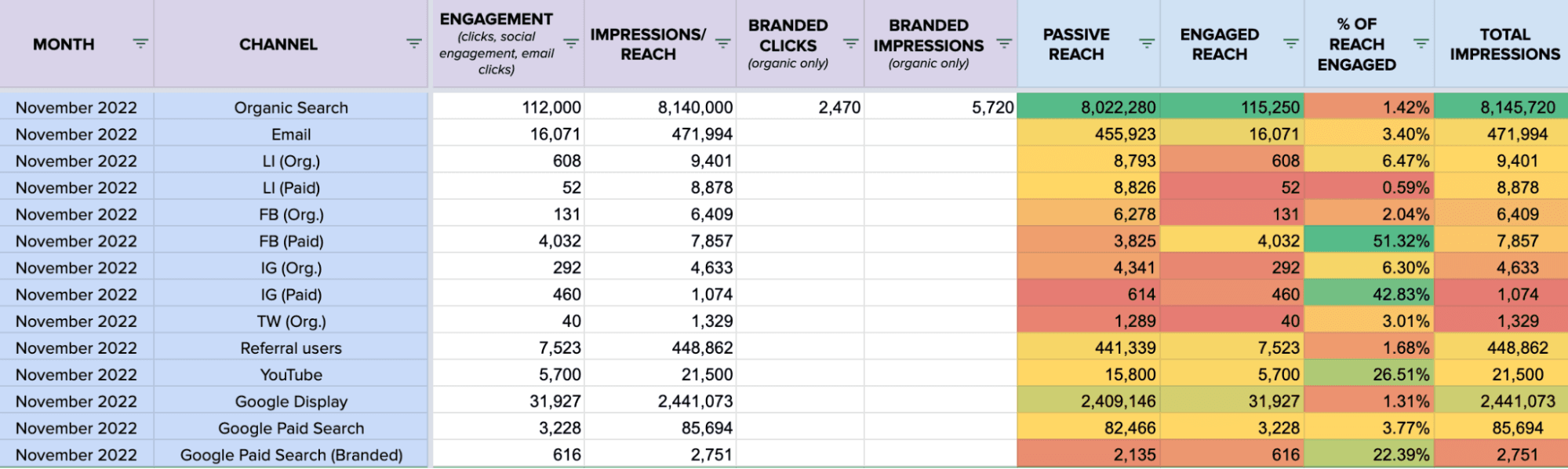
Now you have some new insights that you can create pivot tables around. Let’s look at a few:
1. Engaged reach
This is the portion of your total estimated reach that has engaged with your brand. You want to see this climb every month.
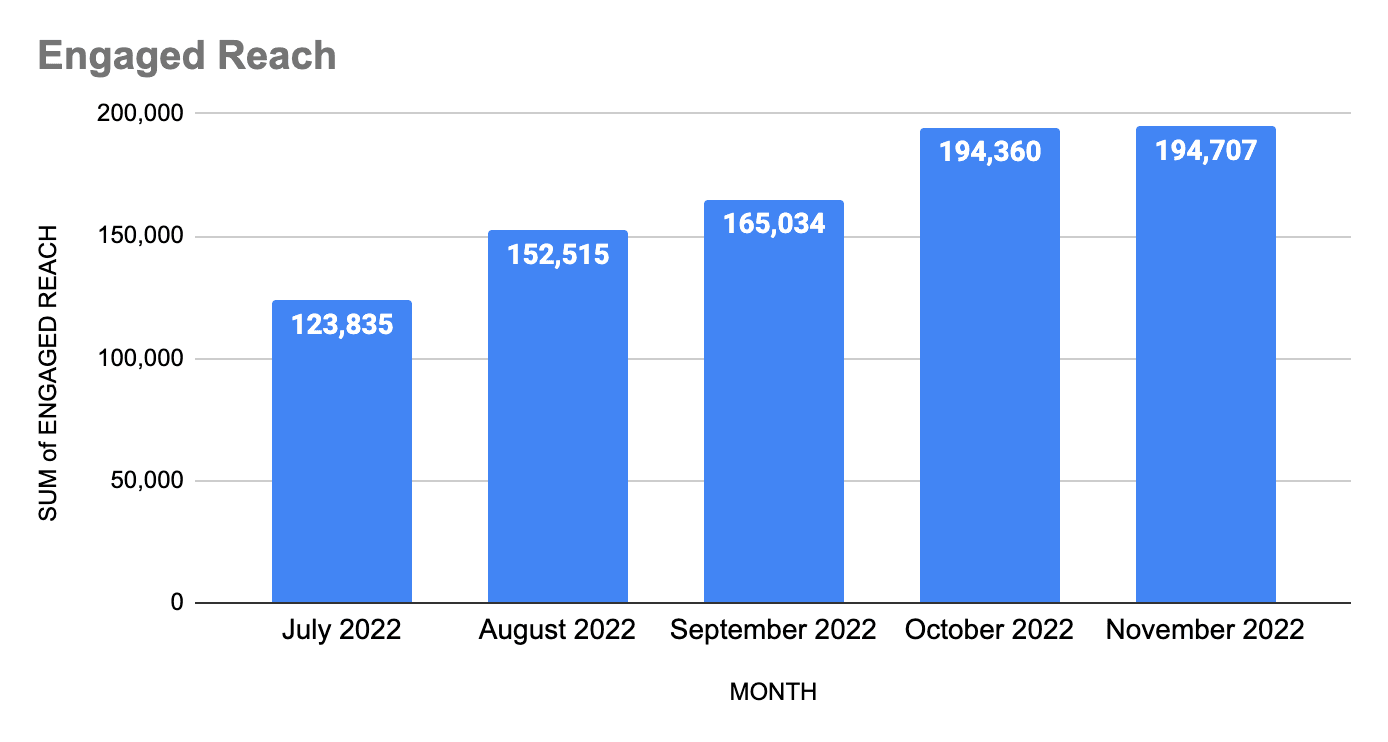
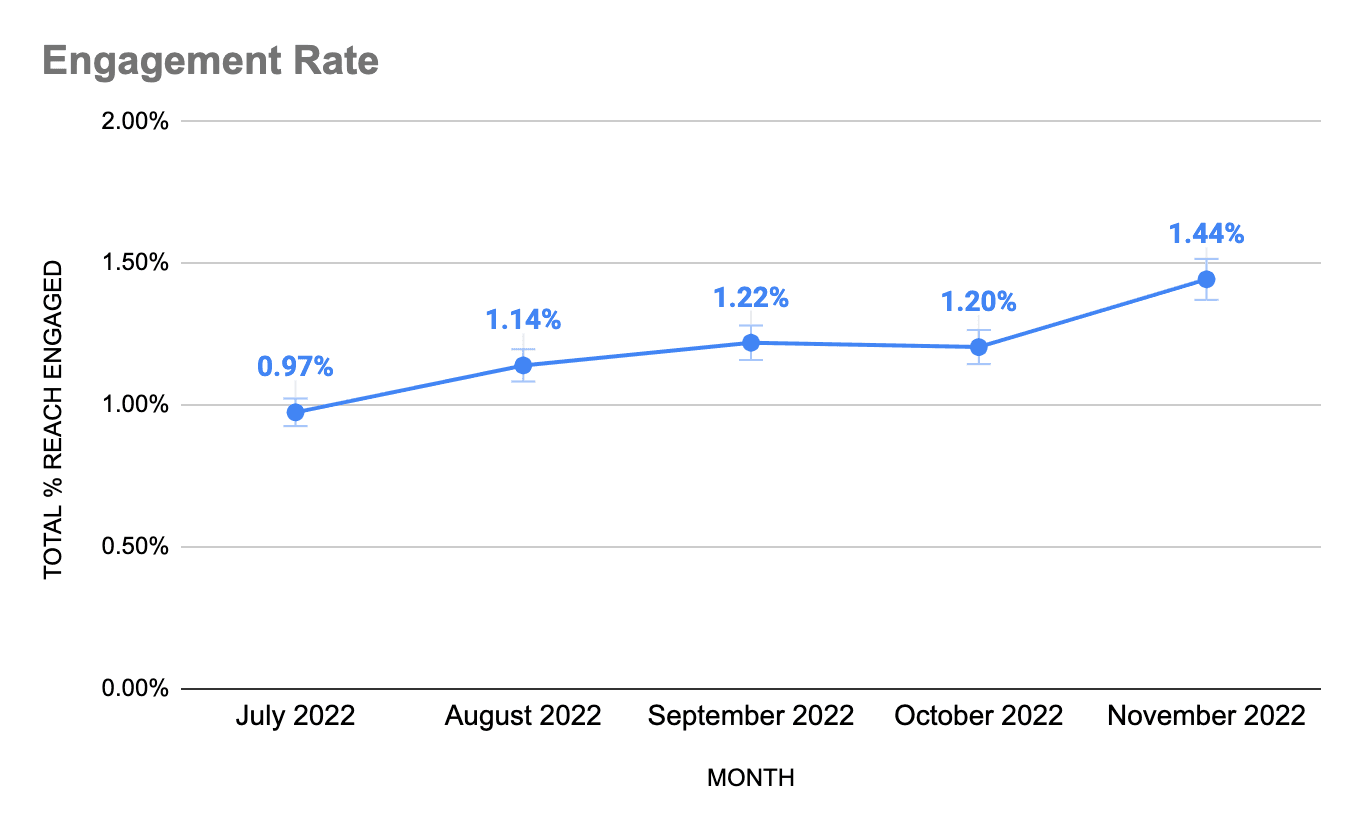
2. Engagement rate
This is the percentage of your estimated reach that is engaging with your brand. This is arguably your most important metric — the one you should be working to increase every month. The higher that percent, the more efficient use you’re making of the reach you have.
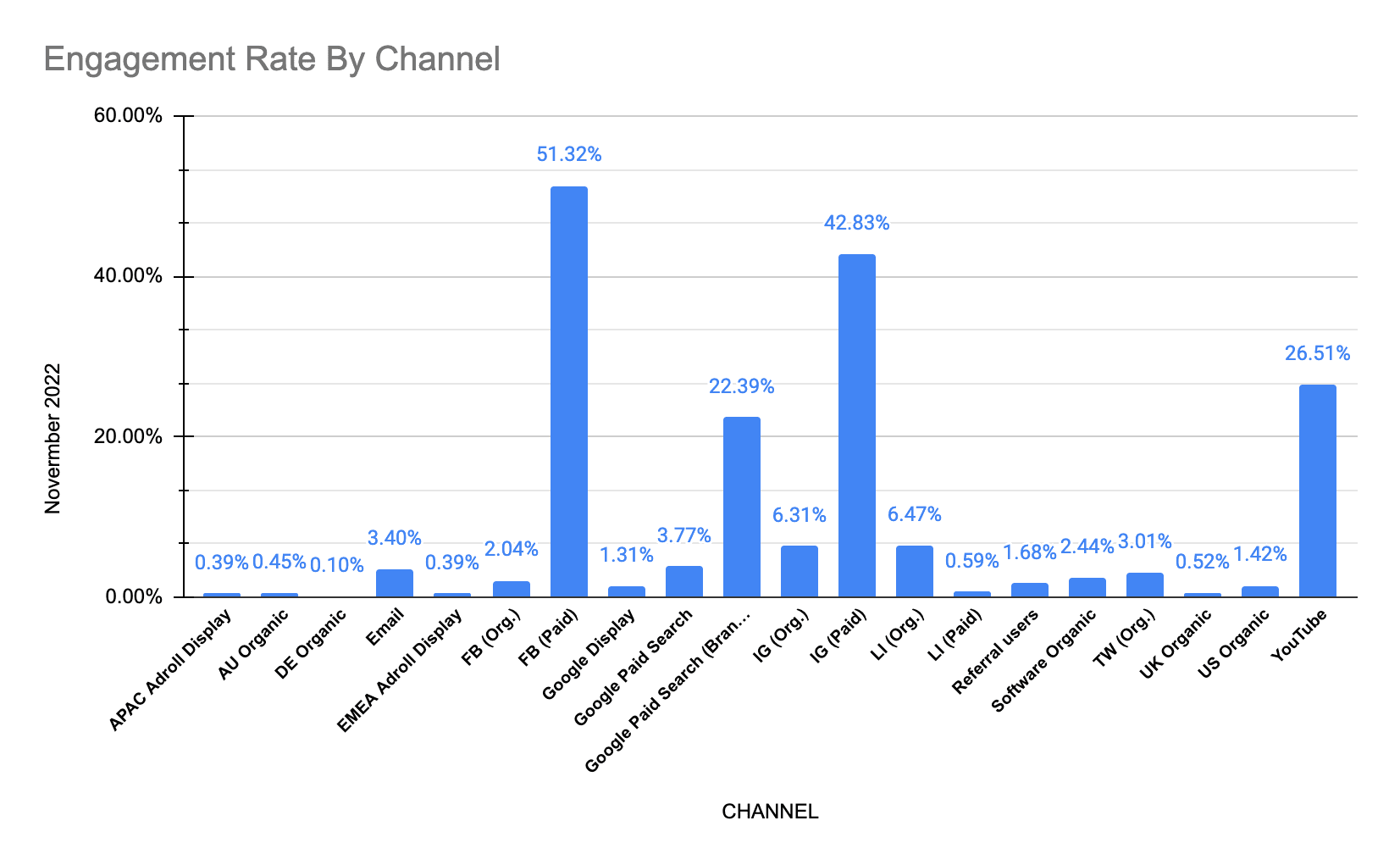
3. Engagement rate by channel
This shows you the channels with your highest engagement rate for the current month. You can use this to flag channels that are giving you what we might call “bad” or “inefficient” reach. It affirmed our decision, for instance, to drop an entire display channel (AdRoll) in favor of another (Google Display). Month after month, we saw low engagement rates on the former. Diverting our spend away from that display channel slightly increased our cost per thousand impressions, but the added cost was more than offset by a higher engagement rate.
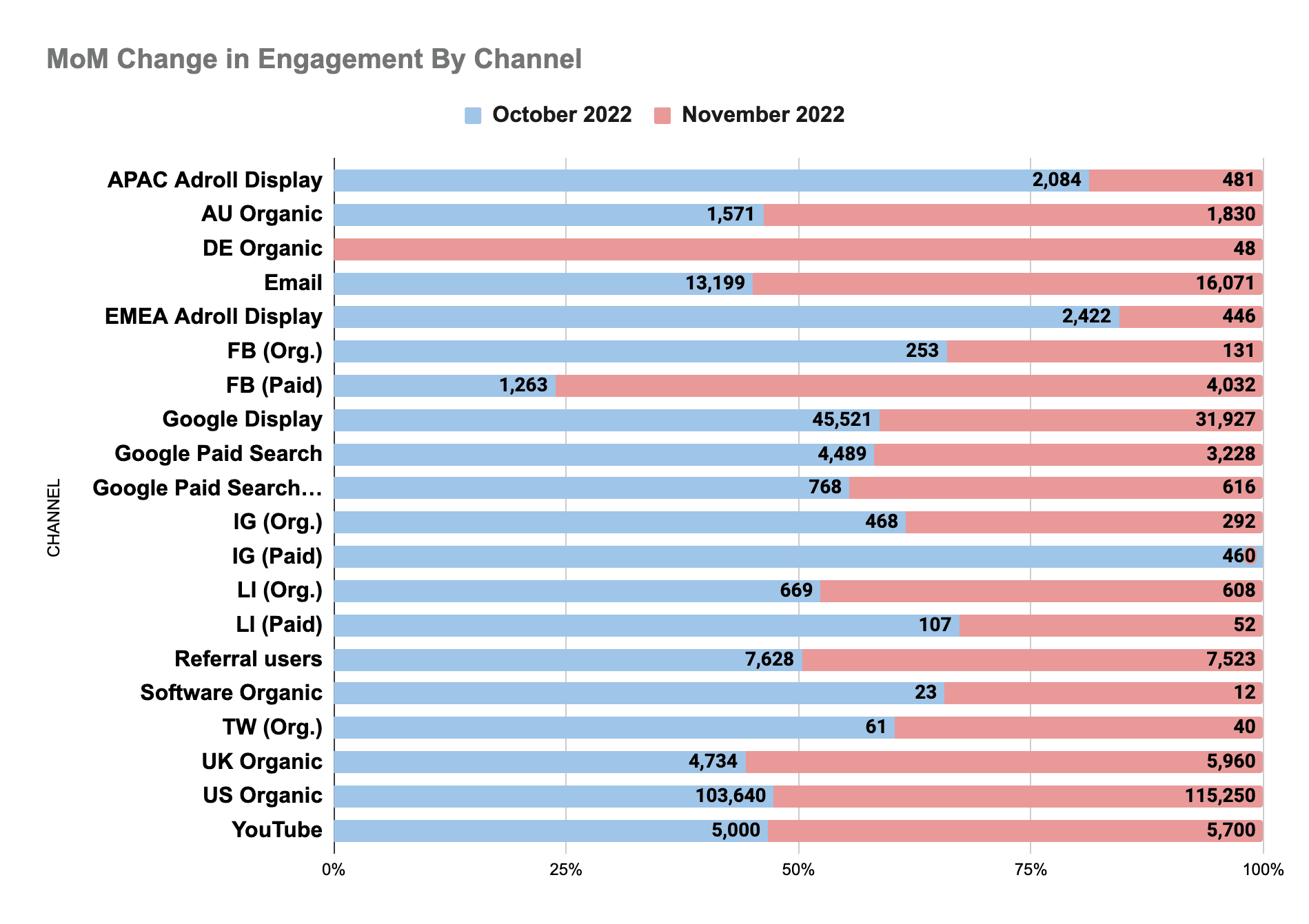
4. Winners and losers month-over-month
You can do this as a direct comparison for reach or for engagement. The chart below is a comparison of engagements between October (blue) and November (red). We always want the red (most recent color) to be bigger than the blue (unless, of course, you’ve pulled resources or spend from a particular channel, e.g., paid Instagram in the chart below):
5. Correlation data
This is where we get a little deeper into the funnel, and find some fascinating insights. There are many ways to search for correlations, and some of them are just common sense. For example, we noticed that our YouTube reach skyrocketed in a particular month. After looking into it, we determined that this was a result of running video ads on Google.
But reach and engagements’ most important relationships are to leads and, better yet, leads assigned to sales reps. Here’s an example using five months of our own data:
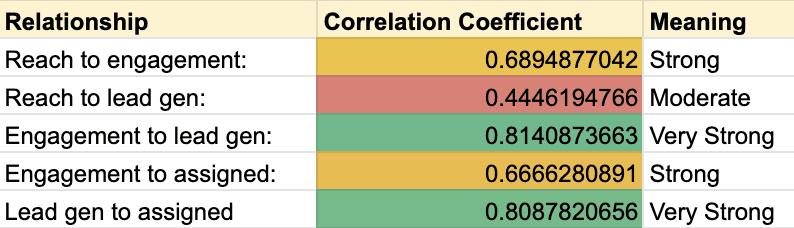
While we still need more data (5 months isn’t enough to close the book on these relationships), our current dataset suggests a few things:
-
More reach usually means more engagement. There’s a strong relationship between reach and engagement.
-
More reach usually means more lead gen. There’s a moderate relationship between reach and lead gen.
-
More engagement almost always means more lead gen. There is a very strong relationship between engagement and lead gen.
-
More engagement almost always means more assigned leads. There’s a strong relationship between engagement and leads that actually get assigned to sales people.
-
More lead gen almost always means more assigned leads. There’s a very strong relationship between lead gen and leads getting assigned to sales people.
This is just one of the ways we’ve sliced and diced the data, and it barely skims the surface of how you can evaluate your own brand reach and brand engagement data.
6. Collaborating with other marketers on your team
Some of the relationships and correlations are subtler, in the sense that they relate to specific levers pulled on specific channels.
For example, we were able to figure out that we can increase branded search by running broad-match-keyword Google paid search campaigns, specifically.
The only reason we know this is that we meet as a team regularly to look over this data, and we’re always debriefing one another on the types of actions we’re taking on different campaigns. This structured, frequent communication helps us pull insights from the data, and from each other, that we’d otherwise never uncover.
Why this work is so worth doing
If at some point while reading this article you’ve thought, “dang, this seems like a lot of work,” you wouldn’t necessarily be wrong. But you wouldn’t be right, either.
Because most of the actual work happens upfront — figuring out exactly which channels you’ll track, and how you’ll track them, and building out the pivot tables that will help you visualize your data month after month.
Pulling the data is a monthly activity, and once you have your methods documented (write down EVERYTHING, because a month is a long time to remember precisely how you’ve pulled data), it’s pretty easy.
One person on our team spends about one hour per month pulling this data, and then I spend maybe another two hours analyzing it, plus 15 minutes or so presenting it at the start of each month.
We’ve only been doing this for about half a year, but it’s already filled gaps in our reporting, and it’s provided us with clues on multiple occasions of where things might be going wrong, and where we should be doubling down on our efforts.
Eventually, we even hope to help use this as a forecasting tool, by understanding the relationship between reach and sales meetings, but also reach and the most meaningful metric of all: revenue.
How cool would that be?
MARKETING
5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails

Welcome to Creator Columns, where we bring expert HubSpot Creator voices to the Blogs that inspire and help you grow better.
I’ve tested 100s of psychological tactics on my email subscribers. In this blog, I reveal the five tactics that actually work.
You’ll learn about the email tactic that got one marketer a job at the White House.
You’ll learn how I doubled my 5 star reviews with one email, and why one strange email from Barack Obama broke all records for donations.
5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
Imagine writing an email that’s so effective it lands you a job at the White House.
Well, that’s what happened to Maya Shankar, a PhD cognitive neuroscientist. In 2014, the Department of Veterans Affairs asked her to help increase signups in their veteran benefit scheme.
Maya had a plan. She was well aware of a cognitive bias that affects us all—the endowment effect. This bias suggests that people value items higher if they own them. So, she changed the subject line in the Veterans’ enrollment email.
Previously it read:
- Veterans, you’re eligible for the benefit program. Sign up today.
She tweaked one word, changing it to:
- Veterans, you’ve earned the benefits program. Sign up today.
This tiny tweak had a big impact. The amount of veterans enrolling in the program went up by 9%. And Maya landed a job working at the White House

Inspired by these psychological tweaks to emails, I started to run my own tests.
Alongside my podcast Nudge, I’ve run 100s of email tests on my 1,000s of newsletter subscribers.
Here are the five best tactics I’ve uncovered.
1. Show readers what they’re missing.
Nobel prize winning behavioral scientists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky uncovered a principle called loss aversion.
Loss aversion means that losses feel more painful than equivalent gains. In real-world terms, losing $10 feels worse than how gaining $10 feels good. And I wondered if this simple nudge could help increase the number of my podcast listeners.
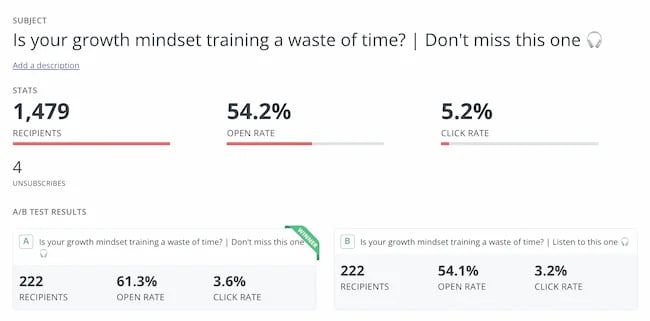
For my test, I tweaked the subject line of the email announcing an episode. The control read:
“Listen to this one”
In the loss aversion variant it read:
“Don’t miss this one”
It is very subtle loss aversion. Rather than asking someone to listen, I’m saying they shouldn’t miss out. And it worked. It increased the open rate by 13.3% and the click rate by 12.5%. Plus, it was a small change that cost me nothing at all.
2. People follow the crowd.
In general, humans like to follow the masses. When picking a dish, we’ll often opt for the most popular. When choosing a movie to watch, we tend to pick the box office hit. It’s a well-known psychological bias called social proof.
I’ve always wondered if it works for emails. So, I set up an A/B experiment with two subject lines. Both promoted my show, but one contained social proof.
The control read: New Nudge: Why Brands Should Flaunt Their Flaws
The social proof variant read: New Nudge: Why Brands Should Flaunt Their Flaws (100,000 Downloads)
I hoped that by highlighting the episode’s high number of downloads, I’d encourage more people to listen. Fortunately, it worked.
The open rate went from 22% to 28% for the social proof version, and the click rate, (the number of people actually listening to the episode), doubled.
3. Praise loyal subscribers.
The consistency principle suggests that people are likely to stick to behaviours they’ve previously taken. A retired taxi driver won’t swap his car for a bike. A hairdresser won’t change to a cheap shampoo. We like to stay consistent with our past behaviors.
I decided to test this in an email.
For my test, I attempted to encourage my subscribers to leave a review for my podcast. I sent emails to 400 subscribers who had been following the show for a year.
The control read: “Could you leave a review for Nudge?”
The consistency variant read: “You’ve been following Nudge for 12 months, could you leave a review?”
My hypothesis was simple. If I remind people that they’ve consistently supported the show they’ll be more likely to leave a review.
It worked.
The open rate on the consistency version of the email was 7% higher.
But more importantly, the click rate, (the number of people who actually left a review), was almost 2x higher for the consistency version. Merely telling people they’d been a fan for a while doubled my reviews.
4. Showcase scarcity.
We prefer scarce resources. Taylor Swift gigs sell out in seconds not just because she’s popular, but because her tickets are hard to come by.
Swifties aren’t the first to experience this. Back in 1975, three researchers proved how powerful scarcity is. For the study, the researchers occupied a cafe. On alternating weeks they’d make one small change in the cafe.
On some weeks they’d ensure the cookie jar was full.
On other weeks they’d ensure the cookie jar only contained two cookies (never more or less).
In other words, sometimes the cookies looked abundantly available. Sometimes they looked like they were almost out.
This changed behaviour. Customers who saw the two cookie jar bought 43% more cookies than those who saw the full jar.
It sounds too good to be true, so I tested it for myself.
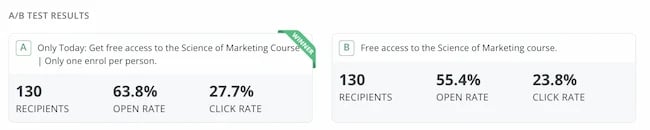
I sent an email to 260 subscribers offering free access to my Science of Marketing course for one day only.
In the control, the subject line read: “Free access to the Science of Marketing course”
For the scarcity variant it read: “Only Today: Get free access to the Science of Marketing Course | Only one enrol per person.”
130 people received the first email, 130 received the second. And the result was almost as good as the cookie finding. The scarcity version had a 15.1% higher open rate.
5. Spark curiosity.
All of the email tips I’ve shared have only been tested on my relatively small audience. So, I thought I’d end with a tip that was tested on the masses.
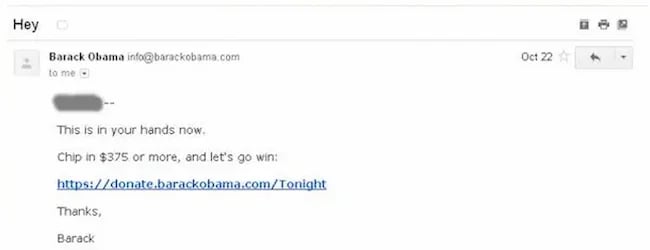
Back in 2012, Barack Obama and his campaign team sent hundreds of emails to raise funds for his campaign.
Of the $690 million he raised, most came from direct email appeals. But there was one email, according to ABC news, that was far more effective than the rest. And it was an odd one.
The email that drew in the most cash, had a strange subject line. It simply said “Hey.”
The actual email asked the reader to donate, sharing all the expected reasons, but the subject line was different.
It sparked curiosity, it got people wondering, is Obama saying Hey just to me?
Readers were curious and couldn’t help but open the email. According to ABC it was “the most effective pitch of all.”
Because more people opened, it raised more money than any other email. The bias Obama used here is the curiosity gap. We’re more likely to act on something when our curiosity is piqued.
Loss aversion, social proof, consistency, scarcity and curiosity—all these nudges have helped me improve my emails. And I reckon they’ll work for you.
It’s not guaranteed of course. Many might fail. But running some simple a/b tests for your emails is cost free, so why not try it out?
This blog is part of Phill Agnew’s Marketing Cheat Sheet series where he reveals the scientifically proven tips to help you improve your marketing. To learn more, listen to his podcast Nudge, a proud member of the Hubspot Podcast Network.
MARKETING
The power of program management in martech

As a supporter of the program perspective for initiatives, I recognize the value of managing related projects, products and activities as a unified entity.
While one-off projects have their place, they often involve numerous moving parts and in my experience, using a project-based approach can lead to crucial elements being overlooked. This is particularly true when building a martech stack or developing content, for example, where a program-based approach can ensure that all aspects are considered and properly integrated.
For many CMOs and marketing organizations, programs are becoming powerful tools for aligning diverse initiatives and driving strategic objectives. Let’s explore the essential role of programs in product management, project management and marketing operations, bridging technical details with business priorities.
Programs in product management
Product management is a fascinating domain where programs operate as a strategic framework, coordinating related products or product lines to meet specific business objectives.
Product managers are responsible for defining a product or product line’s strategy, roadmap and features. They work closely with program managers, who ensure alignment with market demands, customer needs and the company’s overall vision by managing offerings at a program level.
Program managers optimize the product portfolio, make strategic decisions about resource allocation and ensure that each product contributes to the program’s goals. One key aspect of program management in product management is identifying synergies between products.
Program managers can drive innovation and efficiency across the portfolio by leveraging shared technologies, customer insights, or market trends. This approach enables organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, seize emerging opportunities and maintain a competitive advantage. Product managers, in turn, use these insights to shape the direction of individual products.
Moreover, programs in product management facilitate cross-functional collaboration and knowledge sharing. Program managers foster a holistic understanding of customer needs and market dynamics by bringing together teams from various departments, such as engineering, marketing and sales.
Product managers also play a crucial role in this collaborative approach, ensuring that all stakeholders work towards common goals, ultimately leading to more successful product launches and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Dig deeper: Understanding different product roles in marketing technology acquisition
Programs in project management
In project management, programs provide a structured approach for managing related projects as a unified entity, supporting broader strategic objectives. Project managers are responsible for planning, executing and closing individual projects within a program. They focus on specific deliverables, timelines and budgets.
On the other hand, program managers oversee these projects’ coordination, dependencies and outcomes, ensuring they collectively deliver the desired benefits and align with the organization’s strategic goals.
A typical example of a program in project management is a martech stack optimization initiative. Such a program may involve integrating marketing technology tools and platforms, implementing customer data management systems and training employees on the updated technologies. Project managers would be responsible for the day-to-day management of each project.
In contrast, the program manager ensures a cohesive approach, minimizes disruptions and realizes the full potential of the martech investments to improve marketing efficiency, personalization and ROI.
The benefits of program management in project management are numerous. Program managers help organizations prioritize initiatives that deliver the greatest value by aligning projects with strategic objectives. They also identify and mitigate risks that span multiple projects, ensuring that issues in one area don’t derail the entire program. Project managers, in turn, benefit from this oversight and guidance, as they can focus on successfully executing their projects.
Additionally, program management enables efficient resource allocation, as skills and expertise can be shared across projects, reducing duplication of effort and maximizing value. Project managers can leverage these resources and collaborate with other project teams to achieve their objectives more effectively.
Dig deeper: Combining martech projects: 5 questions to ask
Programs in marketing operations
In marketing operations, programs play a vital role in integrating and managing various marketing activities to achieve overarching goals. Marketing programs encompass multiple initiatives, such as advertising, content marketing, social media and event planning. Organizations ensure consistent messaging, strategic alignment, and measurable results by managing these activities as a cohesive program.
In marketing operations, various roles, such as MOps managers, campaign managers, content managers, digital marketing managers and analytics managers, collaborate to develop and execute comprehensive marketing plans that support the organization’s business objectives.
These professionals work closely with cross-functional teams, including creative, analytics and sales, to ensure that all marketing efforts are coordinated and optimized for maximum impact. This involves setting clear goals, defining key performance indicators (KPIs) and continuously monitoring and adjusting strategies based on data-driven insights.
One of the primary benefits of a programmatic approach in marketing operations is maintaining a consistent brand voice and message across all channels. By establishing guidelines and standards for content creation, visual design and customer interactions, marketing teams ensure that the brand’s identity remains cohesive and recognizable. This consistency builds customer trust, reinforces brand loyalty and drives business growth.
Programs in marketing operations enable organizations to take a holistic approach to customer engagement. By analyzing customer data and feedback across various touchpoints, marketing professionals can identify opportunities for improvement and develop targeted strategies to enhance the customer experience. This customer-centric approach leads to increased satisfaction, higher retention rates and more effective marketing investments.
Dig deeper: Mastering the art of goal setting in marketing operations
Embracing the power of programs for long-term success
We’ve explored how programs enable marketing organizations to drive strategic success and create lasting impact by aligning diverse initiatives across product management, project management and marketing operations.
- Product management programs facilitate cross-functional collaboration and ensure alignment with market demands.
- In project management, they provide a structured approach for managing related projects and mitigating risks.
- In marketing operations, programs enable consistent messaging and a customer-centric approach to engagement.
Program managers play a vital role in maintaining strategic alignment, continuously assessing progress and adapting to changes in the business environment. Keeping programs aligned with long-term objectives maximizes ROI and drives sustainable growth.
Organizations that invest in developing strong program management capabilities will be better positioned to optimize resources, foster innovation and achieve their long-term goals.
As a CMO or marketing leader, it is important to recognize the strategic value of programs and champion their adoption across your organization. By aligning efforts across various domains, you can unlock the full potential of your initiatives and drive meaningful results. Try it, you’ll like it.
Fuel for your marketing strategy.
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily MarTech. Staff authors are listed here.
MARKETING
2 Ways to Take Back the Power in Your Business: Part 2


Before we dive into the second way to assume power in your business, let’s revisit Part 1.
Who informs your marketing strategy?
YOU, with your carefully curated strategy informed by data and deep knowledge of your brand and audience? Or any of the 3 Cs below?
- Competitors: Their advertising and digital presence and seemingly never-ending budgets consume the landscape.
- Colleagues: Their tried-and-true proven tactics or lessons learned.
- Customers: Their calls, requests, and ideas.
Considering any of the above is not bad, in fact, it can be very wise! However, listening quickly becomes devastating if it lends to their running our business or marketing department.
It’s time we move from defense to offense, sitting in the driver’s seat rather than allowing any of the 3 Cs to control.
It is one thing to learn from and entirely another to be controlled by.
In Part 1, we explored how knowing what we want is critical to regaining power.
1) Knowing what you want protects the bottom line.
2) Knowing what you want protects you from the 3 Cs.
3) Knowing what you want protects you from running on auto-pilot.
You can read Part 1 here; in the meantime, let’s dive in!
How to Regain Control of Your Business: Knowing Who You Are
Vertical alignment is a favorite concept of mine, coined over the last two years throughout my personal journey of knowing self.
Consider the diagram below.
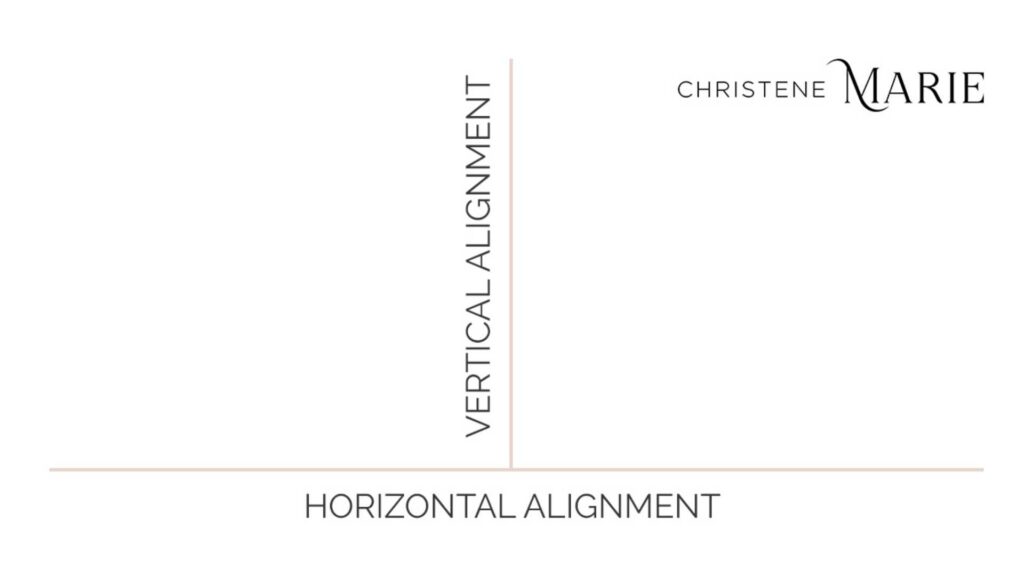

Vertical alignment is the state of internal being centered with who you are at your core.
Horizontal alignment is the state of external doing engaged with the world around you.
In a state of vertical alignment, your business operates from its core center, predicated on its mission, values, and brand. It is authentic and confident and cuts through the noise because it is entirely unique from every competitor in the market.
From this vertical alignment, your business is positioned for horizontal alignment to fulfill the integrity of its intended services, instituted processes, and promised results.
A strong brand is not only differentiated in the market by its vertical alignment but delivers consistently and reliably in terms of its products, offerings, and services and also in terms of the customer experience by its horizontal alignment.
Let’s examine what knowing who you are looks like in application, as well as some habits to implement with your team to strengthen vertical alignment.
1) Knowing who You are Protects You from Horizontal Voices.
The strength of “Who We Are” predicates the ability to maintain vertical alignment when something threatens your stability. When a colleague proposes a tactic that is not aligned with your values. When the customer comes calling with ideas that will knock you off course as bandwidth is limited or the budget is tight.
I was on a call with a gal from my Mastermind when I mentioned a retreat I am excited to launch in the coming months.
I shared that I was considering its positioning, given its curriculum is rooted in emotional intelligence (EQ) to inform personal brand development. The retreat serves C-Suite, but as EQ is not a common conversation among this audience, I was considering the best positioning.


She advised, “Sell them solely on the business aspects, and then sneak attack with the EQ when they’re at the retreat!”
At first blush, it sounds reasonable. After all, there’s a reason why the phrase, “Sell the people what they want, give them what they need,” is popular.
Horizontal advice and counsel can produce a wealth of knowledge. However, we must always approach the horizontal landscape – the external – powered by vertical alignment – centered internally with the core of who we are.
Upon considering my values of who I am and the vision of what I want for this event, I realized the lack of transparency is not in alignment with my values nor setting the right expectations for the experience.
Sure, maybe I would get more sales; however, my bottom line — what I want — is not just sales. I want transformation on an emotional level. I want C-Suite execs to leave powered from a place of emotional intelligence to decrease decisions made out of alignment with who they are or executing tactics rooted in guilt, not vision.
Ultimately, one of my core values is authenticity, and I must make business decisions accordingly.
2) Knowing who You are Protects You from Reactivity.
Operating from vertical alignment maintains focus on the bottom line and the strategy to achieve it. From this position, you are protected from reacting to the horizontal pressures of the 3 Cs: Competitors, Colleagues, and Customers.
This does not mean you do not adjust tactics or learn.


However, your approach to adjustments is proactive direction, not reactive deviations. To do this, consider the following questions:
First: How does their (any one of the 3 Cs) tactic measure against my proven track record of success?
If your colleague promotes adding newsletters to your strategy, lean in and ask, “Why?”
- What are their outcomes?
- What metrics are they tracking for success?
- What is their bottom line against yours?
- How do newsletters fit into their strategy and stage(s) of the customer journey?
Always consider your historical track record of success first and foremost.
Have you tried newsletters in the past? Is their audience different from yours? Why are newsletters good for them when they did not prove profitable for you?
Operate with your head up and your eyes open.
Maintain focus on your bottom line and ask questions. Revisit your data, and don’t just take their word for it.
2. Am I allocating time in my schedule?
I had coffee with the former CEO of Jiffy Lube, who built the empire that it is today.
He could not emphasize more how critical it is to allocate time for thinking. Just being — not doing — and thinking about your business or department.


Especially for senior leaders or business owners, but even still for junior staff.
The time and space to be fosters creative thinking, new ideas, and energy. Some of my best campaigns are conjured on a walk or in the shower.
Kasim Aslam, founder of the world’s #1 Google Ads agency and a dear friend of mine, is a machine when it comes to hacks and habits. He encouraged me to take an audit of my calendar over the last 30 days to assess how I spend time.
“Create three buckets,” he said. “Organize them by the following:
- Tasks that Generate Revenue
- Tasks that Cost Me Money
- Tasks that Didn’t Earn Anything”
He and I chatted after I completed this exercise, and I added one to the list: Tasks that are Life-Giving.
Friends — if we are running empty, exhausted, or emotionally depleted, our creative and strategic wherewithal will be significantly diminished. We are holistic creatures and, therefore, must nurture our mind, body, soul, and spirit to maintain optimum capacity for impact.


I shared this hack with a friend of mine. Not only did she identify meetings that were costing her money and thus needed to be eliminated, but she also identified that particular meetings could actually turn revenue-generating! She spent a good amount of time each month facilitating introductions; now, she is adding Strategic Partnerships to her suite of services.
ACTION: Analyze your calendar’s last 30-60 days against the list above.
Include what is life-giving!
How are you spending your time? What is the data showing you? Are you on the path to achieving what you want and living in alignment with who you want to be?
Share with your team or business partner for the purpose of accountability, and implement practical changes accordingly.
Finally, remember: If you will not protect your time, no one else will.
3) Knowing who You are Protects You from Lack.
“What are you proud of?” someone asked me last year.
“Nothing!” I reply too quickly. “I know I’m not living up to my potential or operating in the full capacity I could be.”


They looked at me in shock. “You need to read The Gap And The Gain.”
I silently rolled my eyes.
I already knew the premise of the book, or I thought I did. I mused: My vision is so big, and I have so much to accomplish. The thought of solely focusing on “my wins” sounded like an excuse to abdicate personal responsibility.
But I acquiesced.
The premise of this book is to measure one’s self from where they started and the success from that place to where they are today — the gains — rather than from where they hope to get and the seemingly never-ending distance — the gap.
Ultimately, Dr. Benjamin Hardy and Dan Sullivan encourage changing perspectives to assign success, considering the starting point rather than the destination.
The book opens with the following story:
Dan Jensen was an Olympic speed skater, notably the fastest in the world. But in each game spanning a decade, Jansen could not catch a break. “Flukes” — even tragedy with the death of his sister in the early morning of the 1988 Olympics — continued to disrupt the prediction of him being favored as the winner.


The 1994 Olympics were the last of his career. He had one more shot.
Preceding his last Olympics in 1994, Jansen adjusted his mindset. He focused on every single person who invested in him, leading to this moment. He considered just how very lucky he was to even participate in the first place. He thought about his love for the sport itself, all of which led to an overwhelming realization of just how much he had gained throughout his life.
He raced the 1994 Olympic games differently, as his mindset powering every stride was one of confidence and gratitude — predicated on the gains rather than the gap in his life.
This race secured him his first and only gold medal and broke a world record, simultaneously proving one of the most emotional wins in Olympic history.
Friends, knowing who we are on the personal and professional level, can protect us from those voices of shame or guilt that creep in.
PERSONAL ACTION: Create two columns. On one side, create a list of where you were when you started your business or your position at your company. Include skills and networks and even feelings about where you were in life. On the other side, outline where you are today.
Look at how far you’ve come.
COMPANY ACTION: Implement a quarterly meeting to review the past three months. Where did you start? Where are you now?
Celebrate the gain!
Only from this place of gain mindset, can you create goals for the next quarter predicated on where you are today.
Ultimately, my hope for you is that you deliver exceptional and memorable experiences laced with empathy toward the customer (horizontally aligned) yet powered by the authenticity of the brand (vertically aligned).
Aligning vertically maintains our focus on the bottom line and powers horizontal fulfillment.


Want to get certified in Content Marketing?
Leverage the tools and channels to predictably and profitably drive awareness, leads, sales, and referrals—EVERYTHING you need to know to become a true master of digital marketing. Click Here
Granted, there will be strategic times and seasons for adjustment; however, these changes are to be made on the heels of consulting who we are as a brand — not in reaction to the horizontal landscape of what is the latest and greatest in the industry.
In Conclusion…
Taking back control of your business and marketing strategies requires a conscious effort to resist external pressures and realign with what you want and who you are.
Final thoughts as we wrap up:
First, identify the root issue(s).
Consider which of the 3 Cs holds the most power: be it competition, colleagues, or customers.
Second, align vertically.
Vertical alignment facilitates individuality in the market and ensures you — and I — stand out and shine while serving our customers well.
Third, keep the bottom line in view.
Implement a routine that keeps you and your team focused on what matters most, and then create the cascading strategy necessary to accomplish it.
Fourth, maintain your mindsets.
Who You Are includes values for the internal culture. Guide your team in acknowledging the progress made along the way and embracing the gains to operate from a position of strength and confidence.
Fifth, maintain humility.
I cannot emphasize enough the importance of humility and being open to what others are doing. However, horizontal alignment must come after vertical alignment. Otherwise, we will be at the mercy of the whims and fads of everyone around us. Humility allows us to be open to external inputs and vertically aligned at the same time.
Buckle up, friends! It’s time to take back the wheel and drive our businesses forward.
The power lies with you and me.
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days ago10 WordPress Influencers to Follow in 2024 – WordPress.com News
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoFeeling Stuck: What to Do When You Don’t Know What to Do
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Image Search Adds Pixel Level Object Segmentation Animation
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoA History of Google AdWords and Google Ads: Revolutionizing Digital Advertising & Marketing Since 2000
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoMore Google March 2024 Core Update Ranking Volatility
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days agoCompetitor Monitoring: 7 ways to keep watch on the competition
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago31 Ready-to-Go Mother’s Day Messages for Social Media, Email, & More
-

 WORDPRESS6 days ago
WORDPRESS6 days agoThrive Architect vs Divi vs Elementor













![5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails → Download Now: The Beginner's Guide to Email Marketing [Free Ebook]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/11-Free-Email-Hacks-to-Step-Up-Your-Productivity.png)




You must be logged in to post a comment Login