SEO
Programmatic SEO, Explained for Beginners

Programmatic SEO refers to the creation of keyword-targeted pages in an automatic (or near automatic) way.
It provides a way for companies to create thousands of website pages targeted at thousands of keywords—without having to design, write, and publish pages manually. Companies like Zapier, Zillow, and G2 use programmatic SEO to generate millions of pageviews each year.
Programmatic pages are usually created from data in a database, like product prices, weather, or location information. To create programmatic content at a large scale, it helps to be a web developer, but there are less technical ways to learn some of the core principles.
We’ll show you how.
Programmatic SEO is a new term for an old idea. If you’ve ever visited Amazon, Yelp, or TripAdvisor, you’ve visited a programmatic page. In fact, if a company offers thousands of products, or provides services in thousands of locations, a programmatic approach to content creation is virtually necessary.
But you don’t have to be an ecommerce giant to find programmatic content useful.
Nomadlist’s location pages
URL: https://nomadlist.com/chiang-mai
Estimated pages: 25,873
Estimated monthly organic traffic: 41,200
Nomadlist helps aspiring digital nomads work out which countries and cities to visit. The website has thousands of programmatic pages sharing the same core information—like internet speeds, average temperatures, and common languages—for towns and cities across the world.
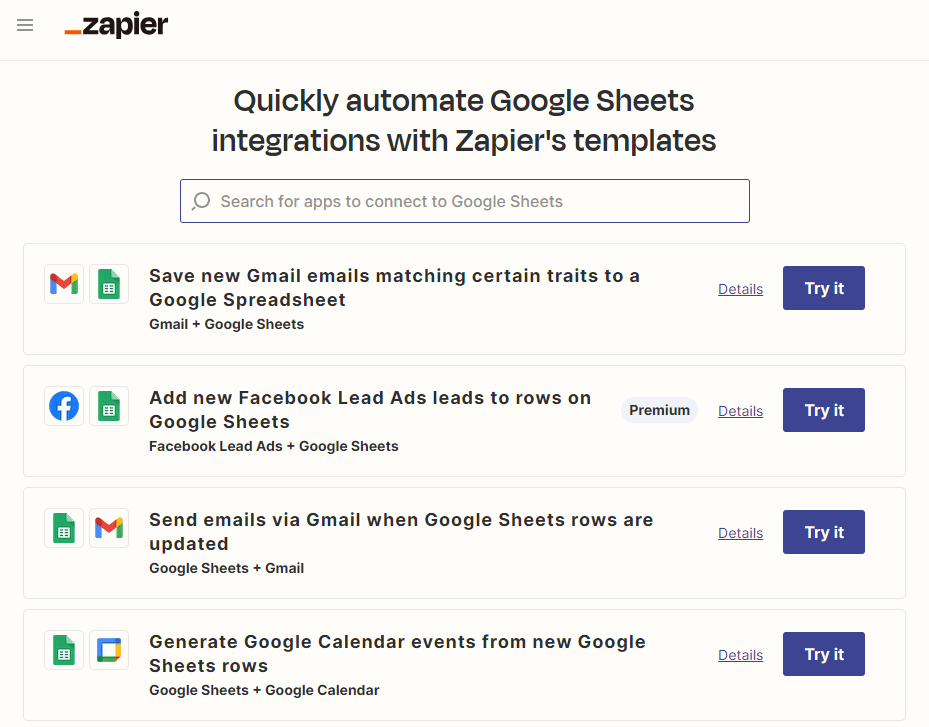
Zapier’s app directory
Estimated pages: 800,632
Estimated monthly organic traffic: 306,000
Zapier is a workflow automation tool that connects different software products together (allowing you to automatically save new emails into a Google Sheet, for example). The company has programmatically created landing pages for each of the thousands of products they integrate with, showing the tools they connect to, and the workflows that can be triggered.

Webflow’s website templates
URL: https://webflow.com/made-in-webflow/website
Estimated pages: 31,516
Estimated monthly organic traffic: 27,600
Webflow is a no-code website builder. They’ve used programmatic SEO to build unique landing pages for thousands of website templates created by their users. Their strategy generates a good amount of traffic, but also makes it easy for visitors to clone the templates and become a Webflow user.


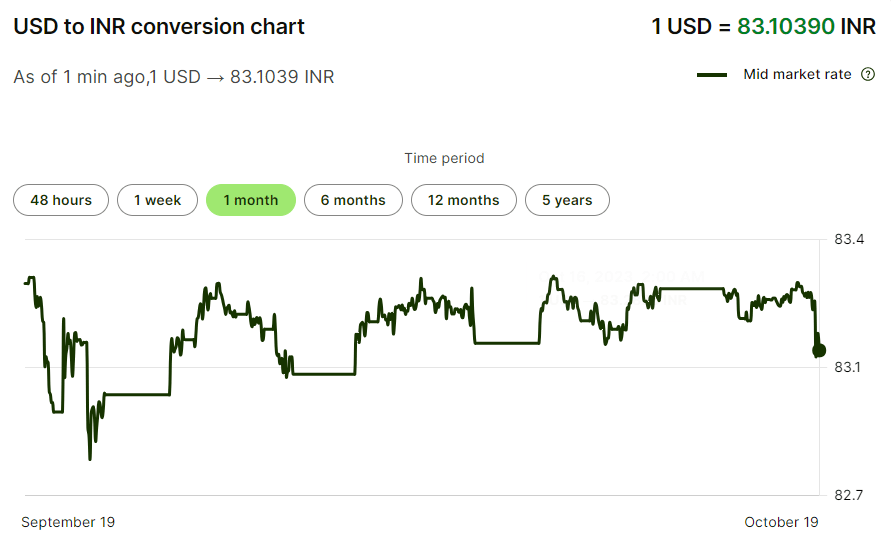
Wise’s currency conversion pages
URL: https://wise.com/us/currency-converter/
Estimated pages: 14,888
Estimated monthly organic traffic: 4,667,719
Wise offer international banking services, including currency conversion. They generate millions of monthly pageviews by programmatically creating landing pages to help users convert between different currencies—from US Dollars to Indian Rupees, from Indian Rupees to Mexican Pesos, and so on. Virtually every currency pair has its own unique page.

Before you get too excited about the prospect of publishing thousands of pages, it’s worth considering the words of Google’s John Mueller: “Programmatic SEO is often a fancy banner for spam.”
Any company that publishes a huge number of very similar pages runs the risk of creating thin content: content that offers little to no value to the end user. Like any other page, programmatic content needs to satisfy user intent (and not violate Google’s spam policies).
If you’re wondering what sets “good” programmatic content apart from bad, the answer often boils down to data and relevancy.
Sites like Wise and Zapier can generate millions of pageviews from programmatic content largely because they offer good, product-relevant data in a format that’s useful to the reader:
- Wise’s currency conversion pages also include historical conversion rate data, rate comparisons with other banks, and the ability to actually send money using Wise.
- Zapier’s app pages are more than basic lists of tools: they show dozens of useful workflows and allow the reader to actually set them up for themselves.
Today, it’s technically possible to generate huge numbers of website pages with little more than a ChatGPT subscription, a Google Sheet, and a simple script (which ChatGPT can even help you to write). But just because you can, theoretically, put content creation on autopilot, it doesn’t mean that good results will follow.
This type of thin content isn’t likely to generate meaningful traffic for a sustained period of time. Relevant, unique data is usually what makes the difference between helpful content and spam.
True programmatic content creation can get very complicated, very quickly. Thousands (even millions) of data points need to be sourced, synced, and updated. Thousands of URLs need to be indexed, and thousands of internal links need to be built. To create something like Wise or Zapier have built, you need developers.
But not every programmatic project has to be quite so complicated. You can attract plenty of traffic with just a few hundred or a few thousand pages.
Here’s a simple no-code process to get started with programmatic SEO. It will help you identify great keywords for programmatic SEO, automatically build prototype pages, and even communicate more effectively with the developers who’ll bring your vision to life.
1. Find keywords that scale
Programmatic content works by targeting thousands of similar keywords with one basic page template. So to get started, you need to find relevant keywords that have hundreds (or even thousands) of similar variations.
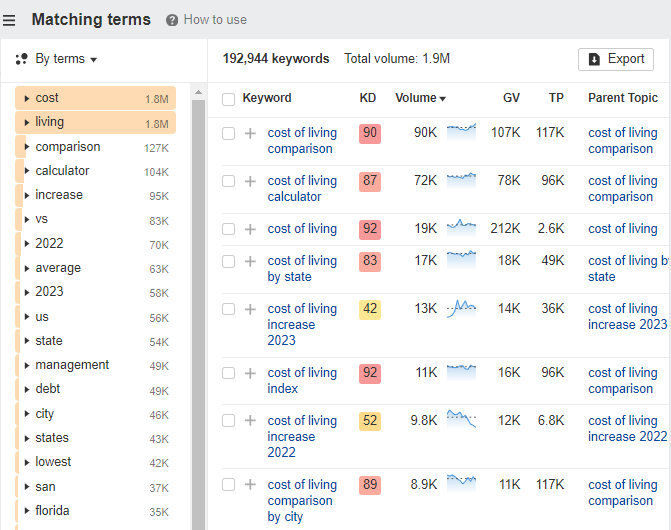
Start by entering your seed keywords into Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. For a personal finance website, you might use terms like debt management, cost of living and expense tracking. Then expand your list of possible keywords by selecting the Matching Terms report:

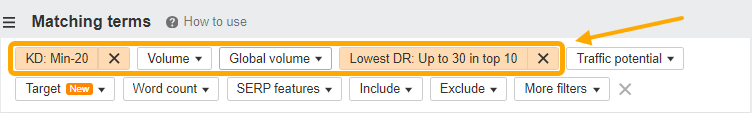
If you’re not confident in your ability to rank for high-competition keywords, it can be useful to filter your results by setting the Keyword Difficulty to <20 and the DR of top-ranking sites to <30. This will show keywords that most websites could rank for—even those without lots of backlinks:

Browse through the keyword list and look for patterns in the keywords. In this case, many of the “cost of living” keywords reference a particular location:
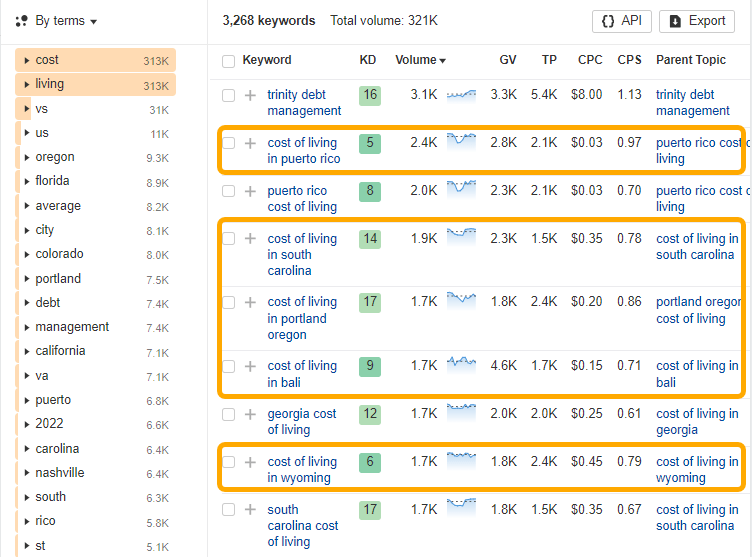

To home in on just these types of keywords, we can use the Include filter to show all keywords that include “cost of living in”:
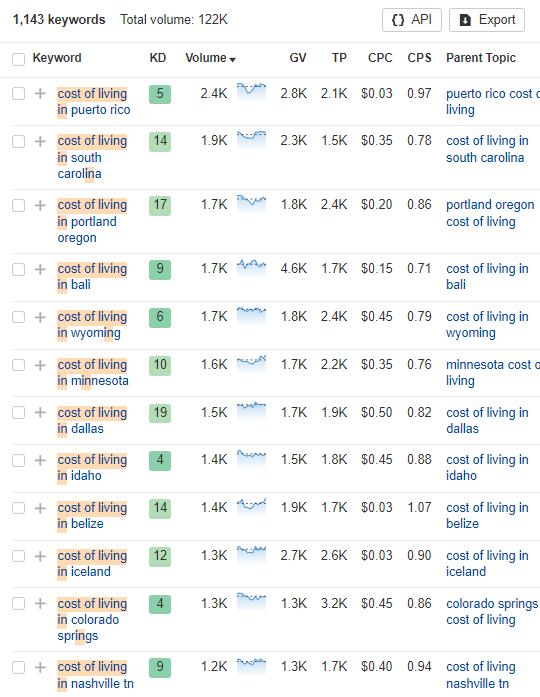

Looking at this example, we’ve found 1,143 keywords with a combined monthly search volume of 122,000. Successfully ranking for even a few dozen of these terms could generate substantial traffic for your website.
These keywords are perfect for programmatic SEO. The type of content that would best help someone searching for “cost of living in arizona” is likely to be very similar to the type of content that would help someone searching for “cost of living in california.”
The data on each page would need to be different, but the structure and main ideas would be the same.
2. Check search intent
Next, you need to work out what type of content would help people searching for these keywords. If you look at the SERP for a few of your “cost of living” keywords, many of the search results contain the same types of information:
- A cost of living score on a 0–100 scale
- Comparisons with nearby states
- Typical costs for major expenses like property, food, and healthcare


These data points give us an idea of the type of information required to meet the searcher’s intent. Searchers want a way to quickly compare cost of living between states, and beyond that, to see how those costs break out across core categories.
For your programmatic content, you should probably include these data points on every page.
3. Find relevant data
Next, you need to source that data. There are three types of data you have at our disposal:
- Proprietary data: original data that is unique to you, your company, or your product. This is the most desirable data type: you can provide information no one else has.
- Public data: publicly available data that is licensed for commercial use. This is usually the easiest data to find, but that means that other companies may be using it in a similar context.
- Scraped data: data extracted from websites using web scraping tools. This can be useful but may introduce issues with copyright.
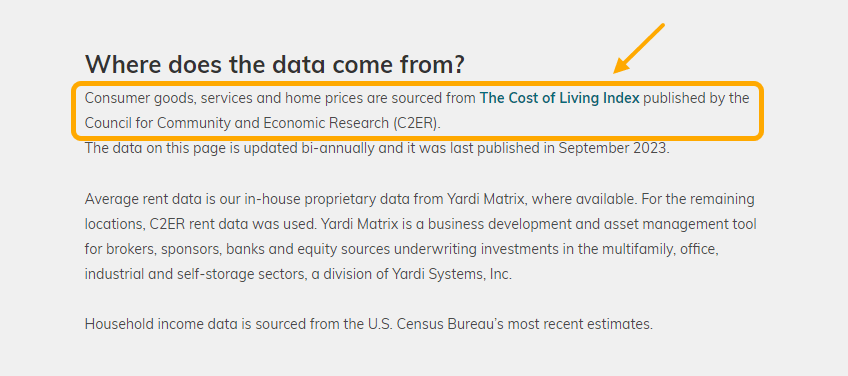
Looking at the search results for these keywords, many of the top-ranking articles contain data from the same public data source: the Cost of Living Index published by the Council for Community and Economic Research. It’s likely that you’ll be able to use this same data in your programmatic content.

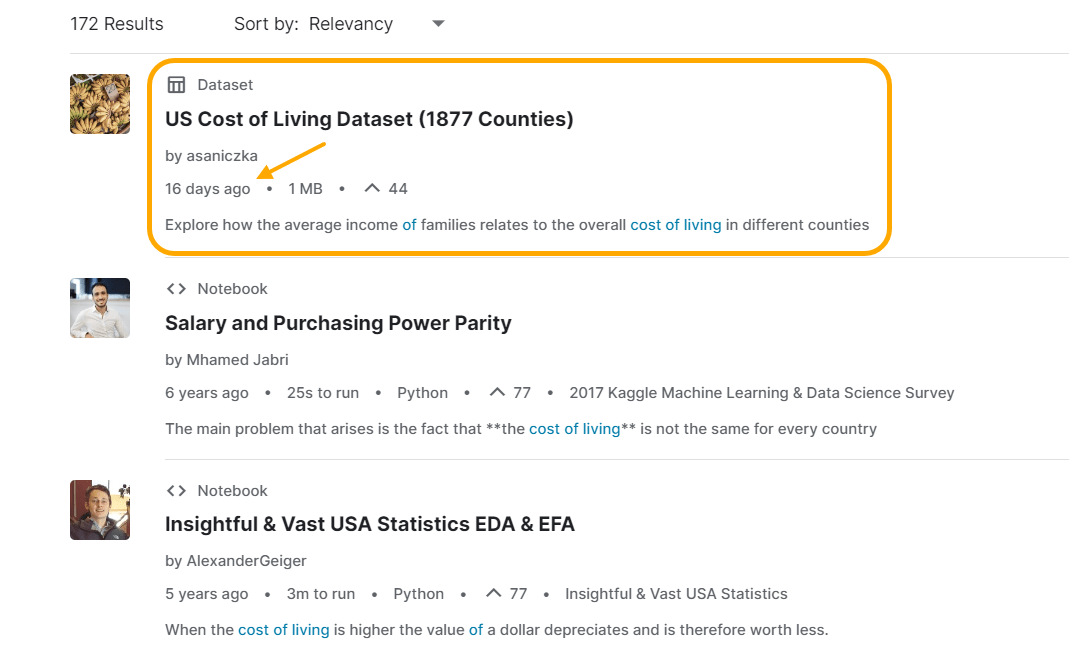
If you want to go a step further, you could consider adding new data that other top-ranking articles don’t have. Sites like Kaggle provide data sets for use in training AI and machine learning models, but they can also provide extra data points for your content.
Run a quick search for “cost of living” on Kaggle, and several useful data sets appear. You can order by age to find new data that other companies are unlikely to be using:

Armed with your data sources, you can combine all of your desired data points together in a single place.
4. Build your pages
Next, you need to map your data sources to relevant parts of your page. At this point, it would be helpful to enlist a web developer—but we’ll show a simplified example using Google Sheets as a basic database.
In the first tab of the spreadsheet, we have our keyword data, which you can use to build page titles and URLs. In the next tab, we have our cost of living data.
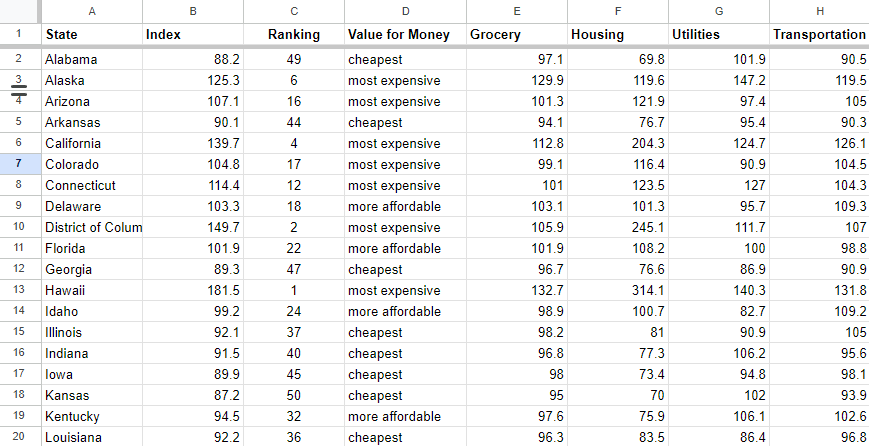

Based on our intent analysis, we want each page to include three “buckets” of information:
- Cost of living score
- Comparison with other US states
- Breakdown of costs across key categories
So in the third tab, we’ve created a formula that pulls relevant data from our different sheets into a simple page template.


Sidenote.
If you aren’t very familiar with Google Sheets formulas, in the fourth tab we’ve included a ChatGPT prompt that can do this for you.
This body copy correctly references data from the cost of living sheet, showing the cost of living score, ranking it relative to the other 49 states, determining whether a state is cheap, mid-priced, or expensive, and sharing cost indices across six major categories.
If you add additional states to the list by dragging down the formula in column A, new URLs, page titles, and body copy are automatically generated. By combining your data sources with a single page template, you can create 50 different pages with the drag of a mouse.


Crucially, the content we’ve generated here is the definition of “thin”, containing lots of duplicated text and non-original data. But if you were to add unique data, create helpful data visualizations, and provide unique written context, then these pages might stand a fighting chance at helping readers and ranking for their target keywords.
5. Publish content to your website
The final step is to publish your newly created content to your website. Depending on the content management system you use, there are a few no-code tools that can help with this process:
- If you already use WordPress for your website, try WP All Import.
- If you use Webflow CMS, set up a Zapier integration to connect to your spreadsheet.
- If you want to build a website straight from your spreadsheet, try Softr.
Once configured, each of these tools will automatically publish a new website page whenever a new row of data is added to your spreadsheet.
Final thoughts
Programmatic SEO is not money for nothing. Managing data and pages at large scales is deceptively complicated. In order for your content to rank—and actually help people—you’ll need relevant, interesting data to share. (And it helps to be a web developer.)
But the combination of “scalable” keywords and great data is a force to be reckoned with. With a little know-how, it’s possible to generate thousands (even millions) of pageviews from a single page template. Pretty cool.
SEO
WordPress Insiders Discuss WordPress Stagnation

A recent webinar featuring WordPress executives from Automattic and Elementor, along with developers and Joost de Valk, discussed the stagnation in WordPress growth, exploring the causes and potential solutions.
Stagnation Was The Webinar Topic
The webinar, “Is WordPress’ Market share Declining? And What Should Product Businesses Do About it?” was a frank discussion about what can be done to increase the market share of new users that are choosing a web publishing platform.
Yet something that came up is that there are some areas that WordPress is doing exceptionally well so it’s not all doom and gloom. As will be seen later on, the fact that the WordPress core isn’t progressing in terms of specific technological adoption isn’t necessarily a sign that WordPress is falling behind, it’s actually a feature.
Yet there is a stagnation as mentioned at the 17:07 minute mark:
“…Basically you’re saying it’s not necessarily declining, but it’s not increasing and the energy is lagging. “
The response to the above statement acknowledged that while there are areas of growth like in the education and government sectors, the rest was “up for grabs.”
Joost de Valk spoke directly and unambiguously acknowledged the stagnation at the 18:09 minute mark:
“I agree with Noel. I think it’s stagnant.”
That said, Joost also saw opportunities with ecommerce, with the performance of WooCommerce. WooCommerce, by the way, outperformed WordPress as a whole with a 6.80% year over year growth rate, so there’s a good reason that Joost was optimistic of the ecommerce sector.
A general sense that WordPress was entering a stall however was not in dispute, as shown in remarks at the 31:45 minute mark:
“… the WordPress product market share is not decreasing, but it is stagnating…”
Facing Reality Is Productive
Humans have two ways to deal with a problem:
- Acknowledge the problem and seek solutions
- Pretend it’s not there and proceed as if everything is okay
WordPress is a publishing platform that’s loved around the world and has literally created countless jobs, careers, powered online commerce as well as helped establish new industries in developing applications that extend WordPress.
Many people have a stake in WordPress’ continued survival so any talk about WordPress entering a stall and descent phase like an airplane that reached the maximum altitude is frightening and some people would prefer to shout it down to make it go away.
Acknowledging facts and not brushing them aside is what this webinar achieved as a step toward identifying solutions. Everyone in the discussion has a stake in the continued growth of WordPress and their goal was to put it out there for the community to also get involved.
The live webinar featured:
- Miriam Schwab, Elementor’s Head of WP Relations
- Rich Tabor, Automattic Product Manager
- Joost de Valk, founder of Yoast SEO
- Co-hosts Matt Cromwell and Amber Hinds, both members of the WordPress developer community moderated the discussion.
WordPress Market Share Stagnation
The webinar acknowledged that WordPress market share, the percentage of websites online that use WordPress, was stagnating. Stagnation is a state at which something is neither moving forward nor backwards, it is simply stuck at an in between point. And that’s what was openly acknowledged and the main point of the discussion was understanding the reasons why and what could be done about it.
Statistics gathered by the HTTPArchive and published on Joost de Valk’s blog show that WordPress experienced a year over year growth of 1.85%, having spent the year growing and contracting its market share. For example, over the latest month over month period the market share dropped by -0.28%.
Crowing about the WordPress 1.85% growth rate as evidence that everything is fine is to ignore that a large percentage of new businesses and websites coming online are increasingly going to other platforms, with year over year growth rates of other platforms outpacing the rate of growth of WordPress.
Out of the top 10 Content Management Systems, only six experienced year over year (YoY) growth.
CMS YoY Growth
- Webflow: 25.00%
- Shopify: 15.61%
- Wix: 10.71%
- Squarespace: 9.04%
- Duda: 8.89%
- WordPress: 1.85%
Why Stagnation Is A Problem
An important point made in the webinar is that stagnation can have a negative trickle-down effect on the business ecosystem by reducing growth opportunities and customer acquisition. If fewer of the new businesses coming online are opting in for WordPress are clients that will never come looking for a theme, plugin, development or SEO service.
It was noted at the 4:18 minute mark by Joost de Valk:
“…when you’re investing and when you’re building a product in the WordPress space, the market share or whether WordPress is growing or not has a deep impact on how easy it is to well to get people to, to buy the software that you want to sell them.”
Perception Of Innovation
One of the potential reasons for the struggle to achieve significant growth is the perception of a lack of innovation, pointed out at the 16:51 minute mark that there’s still no integration with popular technologies like Next JS, an open-source web development platform that is optimized for fast rollout of scalable and search-friendly websites.
It was observed at the 16:51 minute mark:
“…and still today we have no integration with next JS or anything like that…”
Someone else agreed but also expressed at the 41:52 minute mark, that the lack of innovation in the WordPress core can also be seen as a deliberate effort to make WordPress extensible so that if users find a gap a developer can step in and make a plugin to make WordPress be whatever users and developers want it to be.
“It’s not trying to be everything for everyone because it’s extensible. So if WordPress has a… let’s say a weakness for a particular segment or could be doing better in some way. Then you can come along and develop a plug in for it and that is one of the beautiful things about WordPress.”
Is Improved Marketing A Solution
One of the things that was identified as an area of improvement is marketing. They didn’t say it would solve all problems. It was simply noted that competitors are actively advertising and promoting but WordPress is by comparison not really proactively there. I think to extend that idea, which wasn’t expressed in the webinar, is to consider that if WordPress isn’t out there putting out a positive marketing message then the only thing consumers might be exposed to is the daily news of another vulnerability.
Someone commented in the 16:21 minute mark:
“I’m missing the excitement of WordPress and I’m not feeling that in the market. …I think a lot of that is around the product marketing and how we repackage WordPress for certain verticals because this one-size-fits-all means that in every single vertical we’re being displaced by campaigns that have paid or, you know, have received a a certain amount of funding and can go after us, right?”
This idea of marketing being a shortcoming of WordPress was raised earlier in the webinar at the 18:27 minute mark where it was acknowledged that growth was in some respects driven by the WordPress ecosystem with associated products like Elementor driving the growth in adoption of WordPress by new businesses.
They said:
“…the only logical conclusion is that the fact that marketing of WordPress itself is has actually always been a pain point, is now starting to actually hurt us.”
Future Of WordPress
This webinar is important because it features the voices of people who are actively involved at every level of WordPress, from development, marketing, accessibility, WordPress security, to plugin development. These are insiders with a deep interest in the continued evolution of WordPress as a viable platform for getting online.
The fact that they’re talking about the stagnation of WordPress should be of concern to everybody and that they are talking about solutions shows that the WordPress community is not in denial but is directly confronting situations, which is how a thriving ecosystem should be responding.
Watch the webinar:
Is WordPress’ Market share Declining? And What Should Product Businesses Do About it?
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Krakenimages.com
SEO
Google’s New Support For AVIF Images May Boost SEO

Google announced that images in the AVIF file format will now be eligible to be shown in Google Search and Google Images, including all platforms that surface Google Search data. AVIF will dramatically lower image sizes and improve Core Web Vitals scores, particularly Largest Contentful Paint.
How AVIF Can Improve SEO
Getting pages crawled and indexed are the first step of effective SEO. Anything that lowers file size and speeds up web page rendering will help search crawlers get to the content faster and improve the amount of pages crawled.
Google’s crawl budget documentation recommends increasing the speeds of page loading and rendering as a way to avoid receiving “Hostload exceeded” warnings.
It also says that faster loading times enables Googlebot to crawl more pages:
Improve your site’s crawl efficiency
Increase your page loading speed
Google’s crawling is limited by bandwidth, time, and availability of Googlebot instances. If your server responds to requests quicker, we might be able to crawl more pages on your site.
What Is AVIF?
AVIF (AVI Image File Format) is a next generation open source image file format that combines the best of JPEG, PNG, and GIF image file formats but in a more compressed format for smaller image files (by 50% for JPEG format).
AVIF supports transparency like PNG and photographic images like JPEG does but does but with a higher level of dynamic range, deeper blacks, and better compression (meaning smaller file sizes). AVIF even supports animation like GIF does.
AVIF Versus WebP
AVIF is generally a better file format than WebP in terms of smaller files size (compression) and image quality. WebP is better for lossless images, where maintaining high quality regardless of file size is more important. But for everyday web usage, AVIF is the better choice.
See also: 12 Important Image SEO Tips You Need To Know
Is AVIF Supported?
AVIF is currently supported by Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and Safari browsers. Not all content management systems support AVIF. However, both WordPress and Joomla support AVIF. In terms of CDN, Cloudflare also already supports AVIF.
I couldn’t at this time ascertain whether Bing supports AVIF files and will update this article once I find out.
Current website usage of AVIF stands at 0.2% but now that it’s available to surfaced in Google Search, expect that percentage to grow. AVIF images will probably become a standard image format because of its high compression will help sites perform far better than they currently do with JPEG and PNG formats.
Research conducted in July 2024 by Joost de Valk (founder of Yoast, ) discovered that social media platforms don’t all support AVIF files. He found that LinkedIn, Mastodon, Slack, and Twitter/X do not currently support AVIF but that Facebook, Pinterest, Threads and WhatsApp do support it.
AVIF Images Are Automatically Indexable By Google
According to Google’s announcement there is nothing special that needs to be done to make AVIF image files indexable.
“Over the recent years, AVIF has become one of the most commonly used image formats on the web. We’re happy to announce that AVIF is now a supported file type in Google Search, for Google Images as well as any place that uses images in Google Search. You don’t need to do anything special to have your AVIF files indexed by Google.”
Read Google’s announcement:
Supporting AVIF in Google Search
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Cast Of Thousands
SEO
CMOs Called Out For Reliance On AI Content For SEO

Eli Schwartz, Author of Product-Led SEO, started a discussion on LinkedIn about there being too many CMOs (Chief Marketing Officers) who believe that AI written content is an SEO strategy. He predicted that there will be reckoning on the way after their strategies end in failure.
This is what Eli had to say:
“Too many CMOs think that AI-written content is an SEO strategy that will replace actual SEO.
This mistake is going to lead to an explosion in demand for SEO strategists to help them fix their traffic when they find out they might have been wrong.”
Everyone in the discussion, which received 54 comments, strongly agreed with Eli, except for one guy.
What Is Google’s Policy On AI Generated Content?
Google’s policy hasn’t changed although they did update their guidance and spam policies on March 5, 2024 at the same time as the rollout of the March 2024 Core Algorithm Update. Many publishers who used AI to create content subsequently reported losing rankings.
Yet it’s not said that using AI is enough to merit poor rankings, it’s content that is created for ranking purposes.
Google wrote these guidelines specifically for autogenerated content, including AI generated content (Wayback machine copy dated March 6, 2024)
“Our long-standing spam policy has been that use of automation, including generative AI, is spam if the primary purpose is manipulating ranking in Search results. The updated policy is in the same spirit of our previous policy and based on the same principle. It’s been expanded to account for more sophisticated scaled content creation methods where it isn’t always clear whether low quality content was created purely through automation.
Our new policy is meant to help people focus more clearly on the idea that producing content at scale is abusive if done for the purpose of manipulating search rankings and that this applies whether automation or humans are involved.”
Many in Eli’s discussion were in agreement that reliance on AI by some organizations may come to haunt them, except for that one guy in the discussion
Read the discussion on LinkedIn:
Too many CMOs think that AI-written content is an SEO strategy that will replace actual SEO
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Cast Of Thousands
-

 SEO7 days ago
SEO7 days agoGoogle’s Revamped Documentation Shows 4 Reasons To Refresh Content
-
SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: August 26, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Ranking Bug Fixed, August Core Update Swings, AI Overviews, Google Ads Bug & More
-
SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: August 27, 2024
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoHow to Secure Your WordPress Store
-

 AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days ago
AFFILIATE MARKETING7 days agoBusiness Owners are Batting 1,000 With This All-in-One Management Hub
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Migrating All To Google Merchant Center Next By September
-

 WORDPRESS5 days ago
WORDPRESS5 days ago10 Best StudioPress Alternatives (Genesis Framework)














