TECHNOLOGY
Revolutionizing Cybersecurity for Today’s Hybrid Workforce

Zero Trust is a security framework founded on the principle of enforcing stringent access controls.
It adopts an initial stance of skepticism towards all individuals, eliminating the default assumption of trust.
The rise of remote work, cloud computing, and interconnected networks has necessitated a paradigm shift towards a more robust and proactive security model known as Zero Trust Architecture.
This article explores how Zero Trust Architecture is reinventing cybersecurity for the modern hybrid workforce, offering a comprehensive defense strategy that addresses the challenges posed by an increasingly decentralized digital environment.
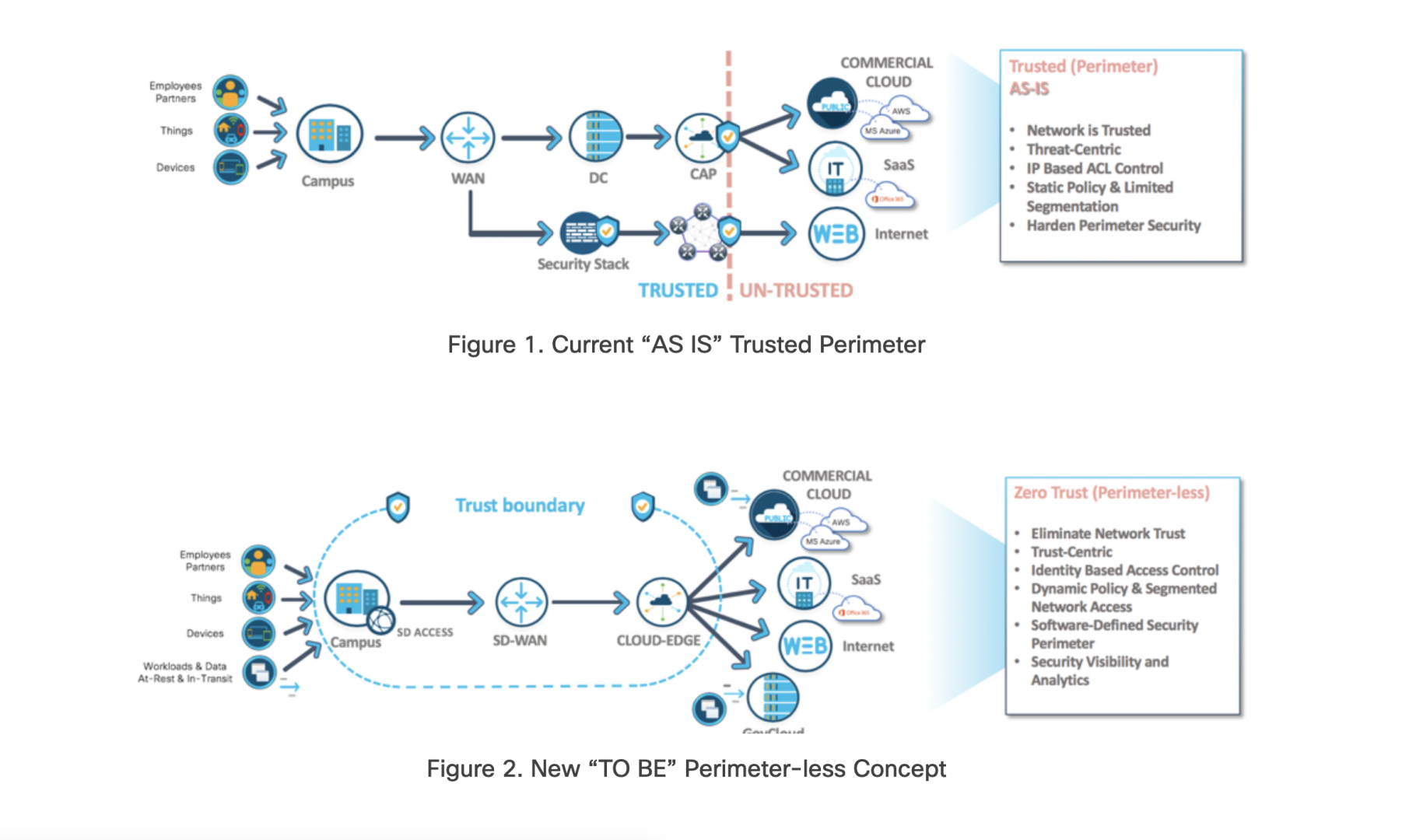
Beyond the Perimeter: The Need for a New Approach
The traditional approach to cybersecurity relied heavily on perimeter defenses, assuming that once within the network, users and devices were implicitly trusted. However, the proliferation of remote work, mobile devices, and cloud-based applications has blurred the lines of the traditional network perimeter, rendering it inadequate against today’s dynamic threat landscape.
Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture operates on the core principle of “never trust, always verify.” Instead of relying on implicit trust, every user, device, and application is treated as potentially malicious until proven otherwise. This approach enforces strict authentication, continuous monitoring, and least-privilege access, reducing the attack surface and minimizing the potential impact of breaches.
Securing the Hybrid Workforce
As remote and hybrid work arrangements become the norm, organizations must secure endpoints and access points beyond the corporate network. Zero Trust ensures that regardless of the user’s location, device, or network, access is granted based on verified identity and context, safeguarding sensitive data and applications.
Micro-Segmentation and Least-Privilege Access
Zero Trust involves segmenting the network into smaller, isolated zones, each with specific access controls. This micro-segmentation limits lateral movement within the network, preventing unauthorized access to critical assets. Additionally, least-privilege access ensures that users are granted only the permissions necessary for their roles, reducing the risk of privilege escalation.
Continuous Monitoring and Behavioral Analysis
Unlike traditional security models that rely on static rules, Zero Trust employs continuous monitoring and behavioral analysis to detect anomalies and potential threats in real-time. Machine learning and AI algorithms analyze user behavior, identifying deviations from the norm and triggering immediate responses to mitigate risks.
Protecting Data in Transit and at Rest
The Zero Trust model extends its security measures to data in transit and at rest. Strong encryption, secure authentication protocols, and data loss prevention techniques ensure that sensitive information remains protected throughout its lifecycle, regardless of its location.
Embracing a Future-Ready Approach

Zero Trust Architecture is not just a reactionary response to current challenges but a forward-thinking approach that can adapt to evolving threats. By reducing the attack surface, minimizing lateral movement, and prioritizing continuous monitoring, organizations are better equipped to withstand emerging cyber threats.
To Sum Up
As the boundaries between work and personal digital environments continue to blur, adopting a security model that aligns with the realities of the hybrid workforce is imperative. Zero Trust Architecture represents a fundamental shift from the traditional perimeter-based approach, offering a proactive, context-aware, and adaptable cybersecurity framework. By embracing this revolutionary approach, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of the digital era, safeguard their assets, and foster a secure and productive work environment for their hybrid workforce.

















