SEO
What Are They & How Do You Get Them?

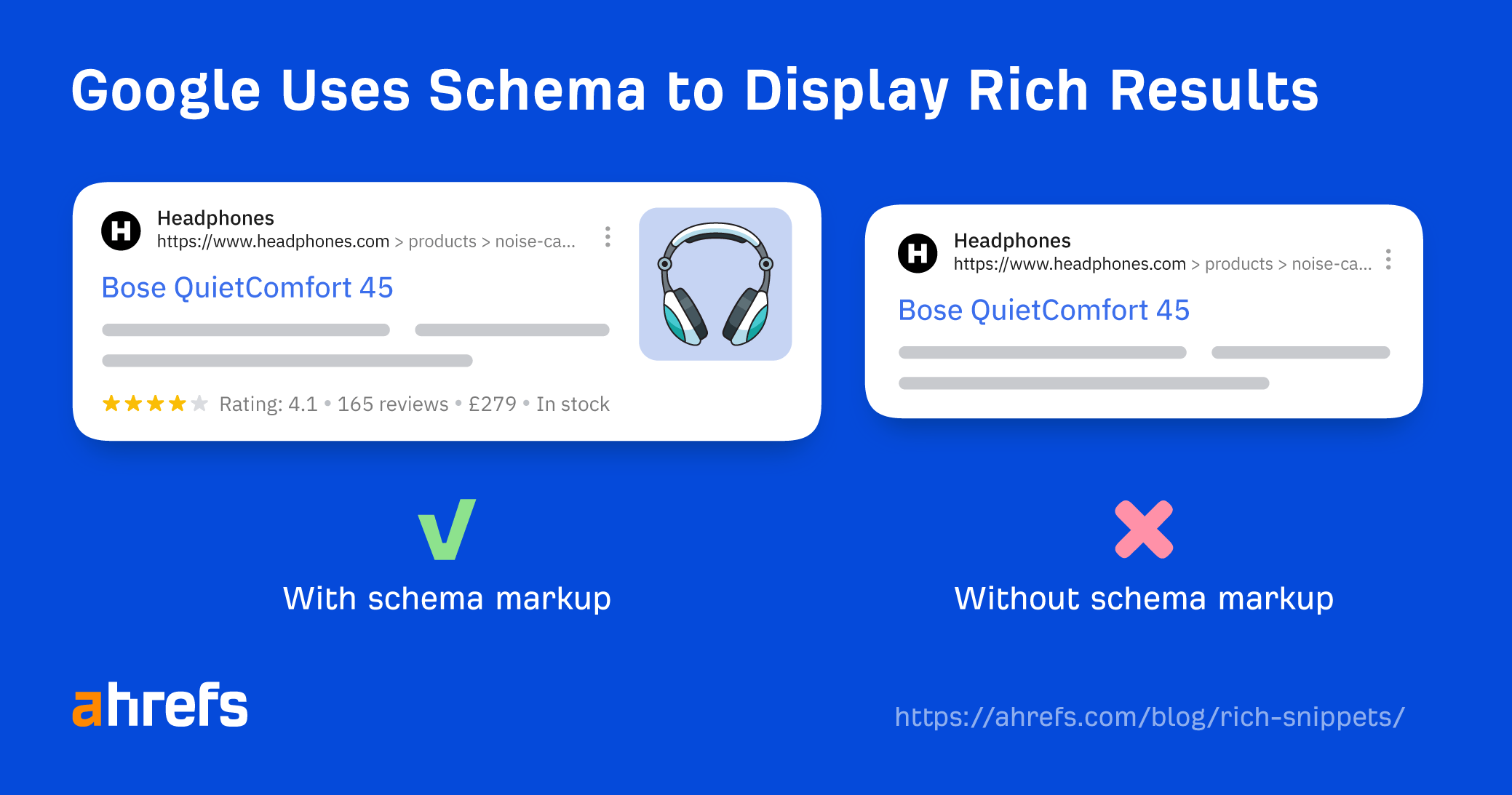
Rich snippets aren’t a Google ranking factor, but they can make your website’s search results stand out from the crowd.
So what exactly are rich snippets, how are they different from other SERP features, and how can you get them to show for your site?
Rich snippets, rich results, and SERP features are sometimes used interchangeably by SEOs, which can cause confusion.
So what are the differences?
- Rich snippets – Google’s glossary states that rich snippets are now known as rich results.
- Rich results – Google says rich results can include carousels, images, or other non-textual elements and that they are experiences that go beyond the standard blue link.
- SERP features – Provide additional and related information on the search query. Examples include the local pack, videos, and the knowledge panel.
Google supports different types of rich results within its search results. Let’s take a look at some of the most popular types.
Review
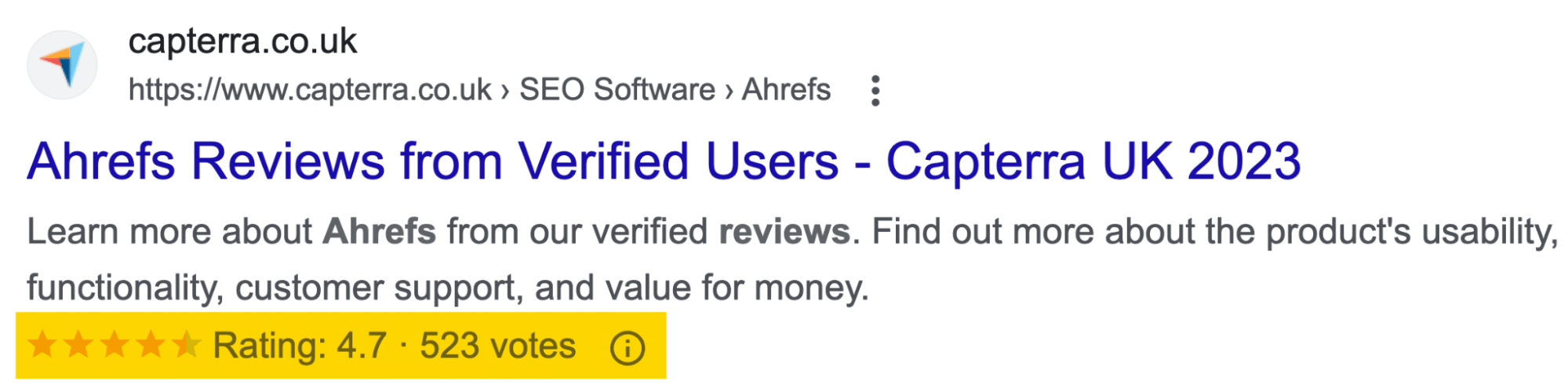
One of the most prominent examples of rich snippets is the Review snippet, which adds a yellow star rating to the search results with additional information about the reviews.
Here’s an example of what a Review snippet can look like, with the snippets highlighted.
Review snippets can appear for the following content types:
- Book
- Course
- Event
- How-to
- Local business (for sites that capture reviews about other local businesses)
- Movie
- Product
- Recipe
- Software app
Product
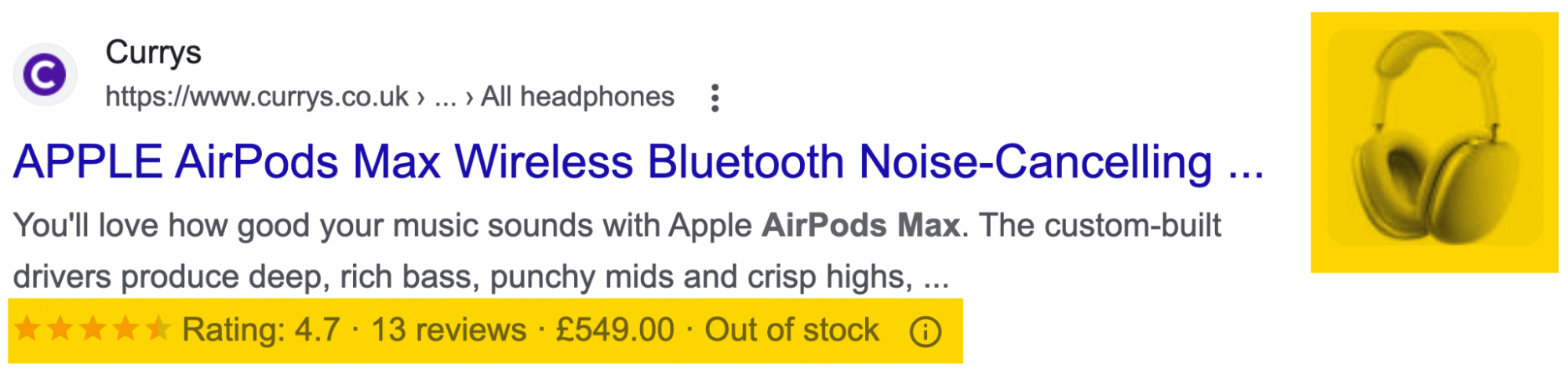
Product rich snippets are useful if you have an e-commerce website. They provide more information to your potential customers about your products—like whether the product is currently in stock, its shipping information, and its price.
Here’s an example of what a Product snippet result can look like in the search results, with the snippets highlighted.
Recipe
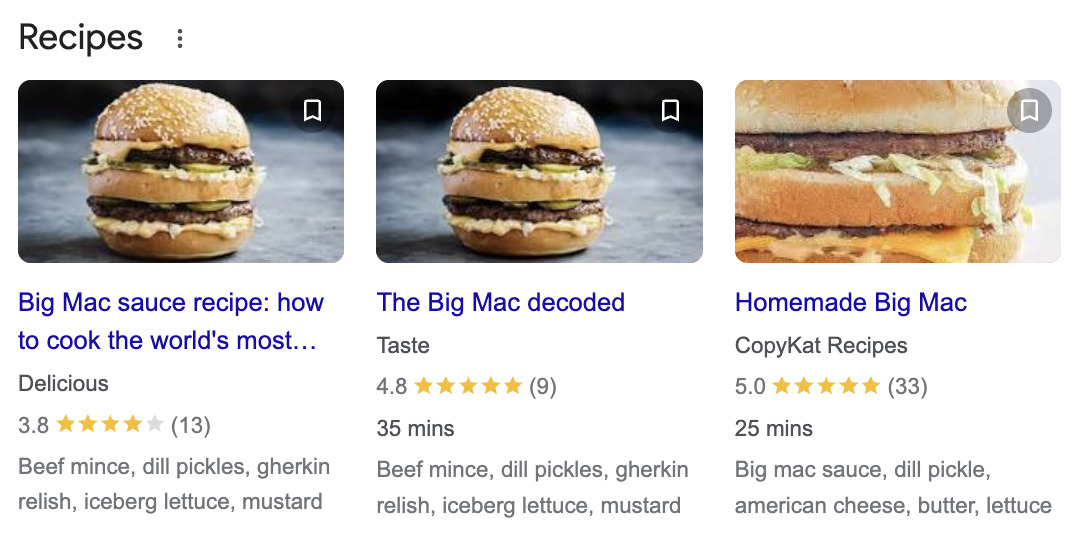
Recipe rich snippets give more information about the recipe on the page, such as how long it takes to prepare, its ingredients, and reviews.
Here’s an example of what a recipe result can look like in Google in the Recipes carousel.
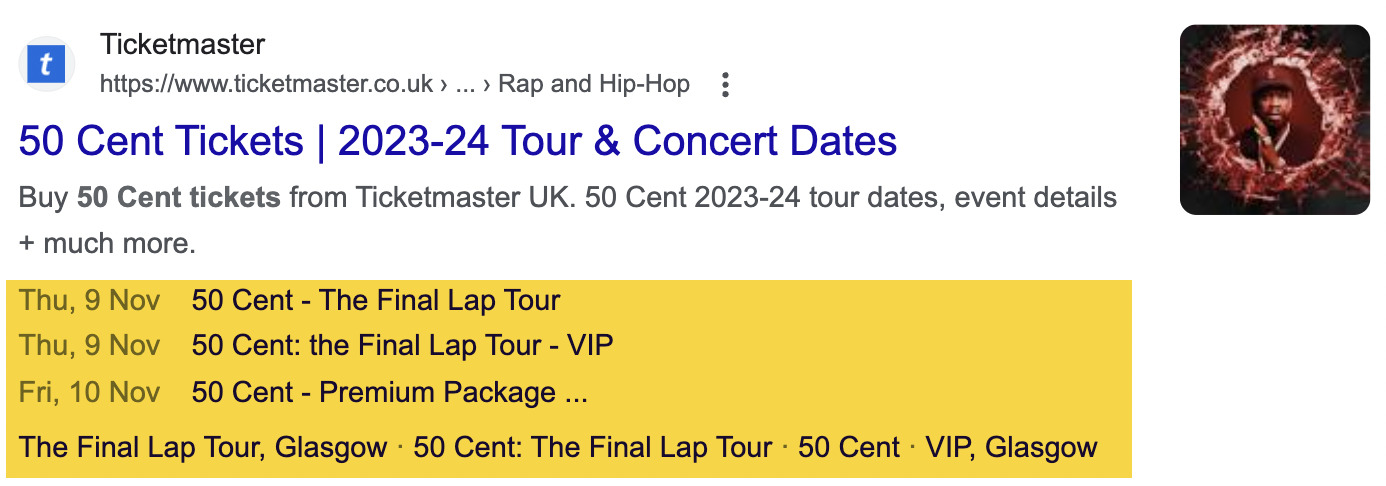
Event
Event snippets highlight the date and location of your events. They’re useful if you have ticketed events like concerts or shows.
Here’s an example of an Event snippet.
Sidenote.
FAQ and HowTo results are not included in this list, as Google announced it was reducing the visibility for them on August 8, 2023, to provide a “cleaner and more consistent” search experience.
To be eligible for rich snippets, you’ll need to add schema markup to your pages and ensure you follow Google’s structured data guidelines.
But before attempting to add the code, check whether your CMS has added it already.
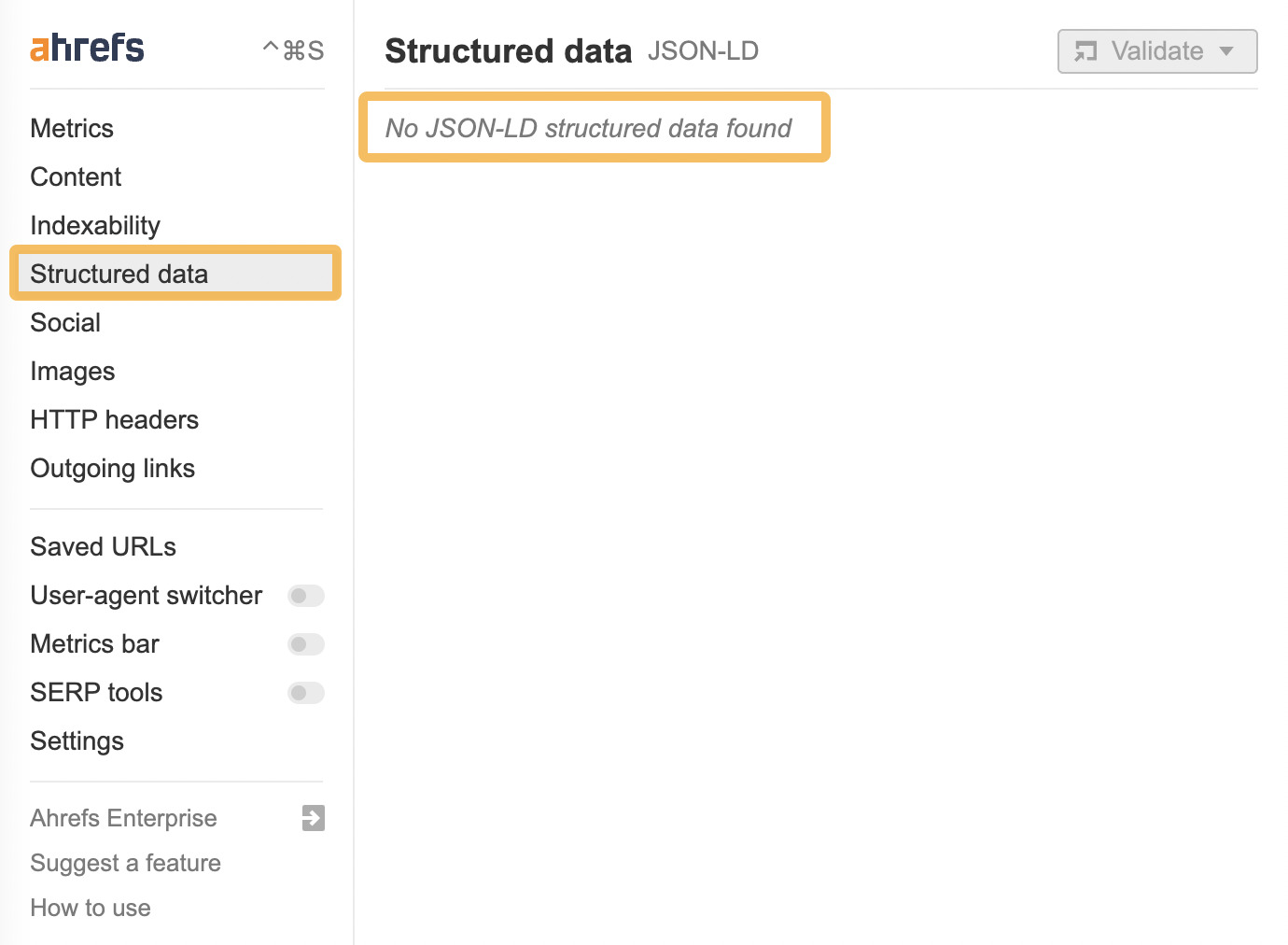
To do this, head to a page where you think there should be markup, open up Ahrefs’ SEO Toolbar, and go to the “Structured data” tab.
If there’s no structured data on the page, you’ll get a message that looks like the one below.
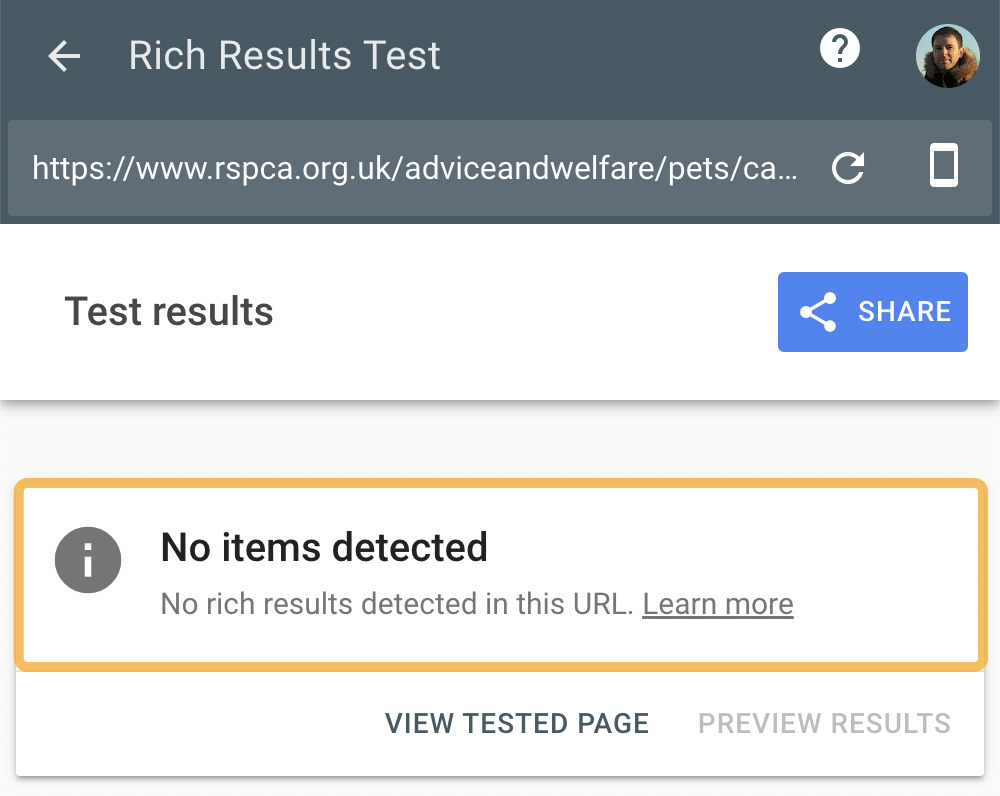
You can double-check this by running a page through the Rich Results Test tool.
If no markup is present on the page, the rich results test will display the message “No items detected.”
Assuming there are no rich results detected, you’re safe to add the code.
Here’s how you do it.
1. Generate the code
If you use a popular content management system (CMS) like WordPress, adding schema to your website is as easy as installing a schema plugin like this one.
If you already use a plugin like Rank Math, you can use its guide to generate and customize your schema.
If you don’t use one of the more popular CMSes, you may have to generate the code yourself.
Tip
If you are not confident with code, it’s worth talking to a developer or SEO consultant to help you implement these changes.
I’m using Merkle’s Schema Markup Generator to generate Product schema markup. But you can use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or even ChatGPT as well.
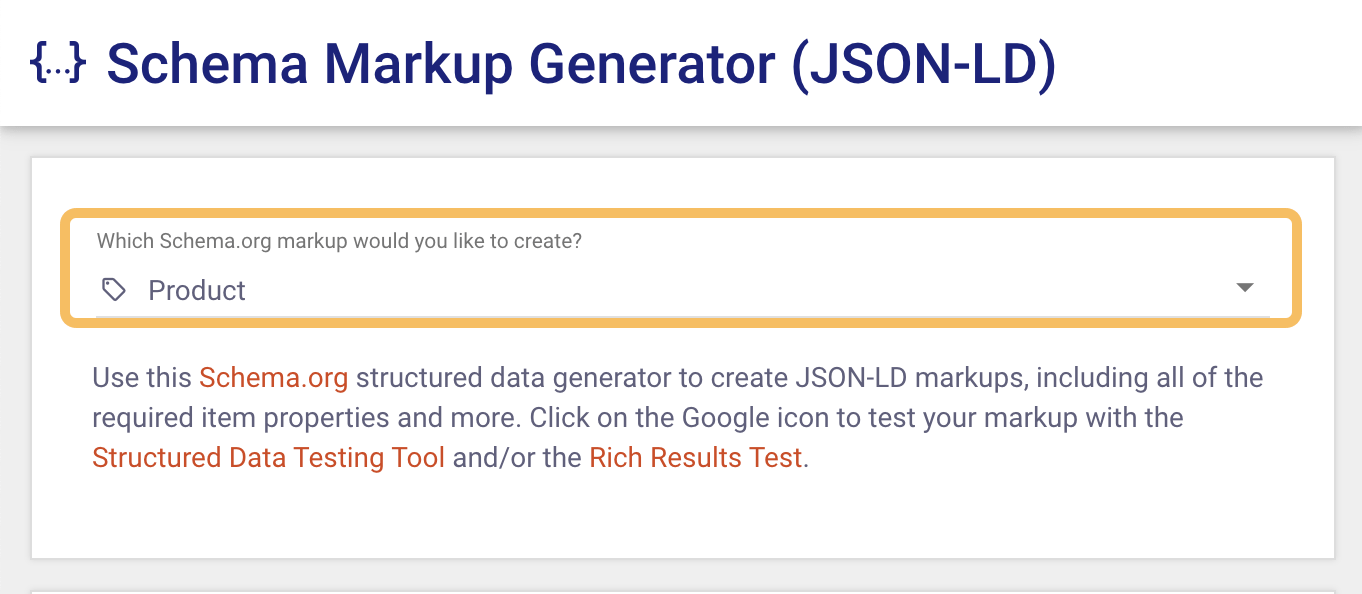
To generate the code, simply fill out the prompts from the tool.
Once you’ve finished, copy the JSON-LD code; this is the code format Google recommends for schema markup.
Sidenote.
Remember to only add code for content that’s visible to users and adheres to Google’s guidelines for the selected schema type.
2. Check and validate the markup
Once you’ve generated the code, it’s just a matter of checking if it’s valid. If it’s not valid, your page won’t be eligible for rich results.
If you generated your code with a plugin or through your CMS, you can check it by:
- Opening the SEO Toolbar on the page you want to check.
- Going to the Structured data tab.
- Clicking on Validate and then the Rich Results Test.

Clicking this will take you to Google’s Rich Results Test. If it’s valid, you’ll see a green tick.
Once you’ve confirmed it’s present and valid, you can skip to step #3 below.
If you’ve manually added your schema code, you’ll need to make two checks:
- Check the code is valid before you implement it
- Check the code is valid after it’s added to your website
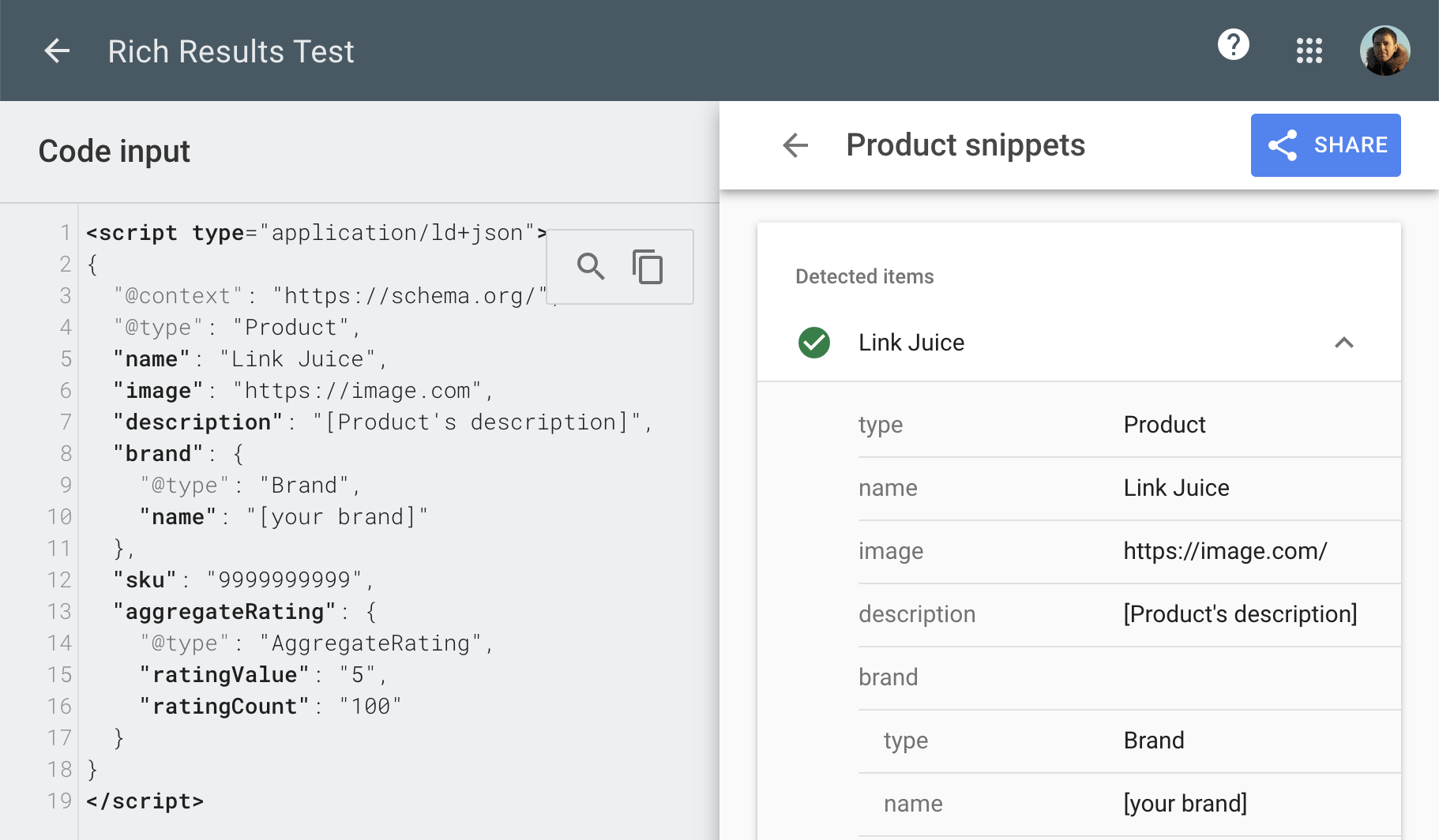
To see if your code snippet is valid, select “Code” on the Rich Results Test and paste your code snippet in.
If it’s valid, you’ll see a green tick appear under the subheadings “Detected items.”
Once you’ve validated your code, you can upload it to your website. Add it to the <head> or <body> of your website. Google has confirmed either is fine.
Once the code is added, you can run the page URL through the Rich Results Test to double-check it’s valid on-site.
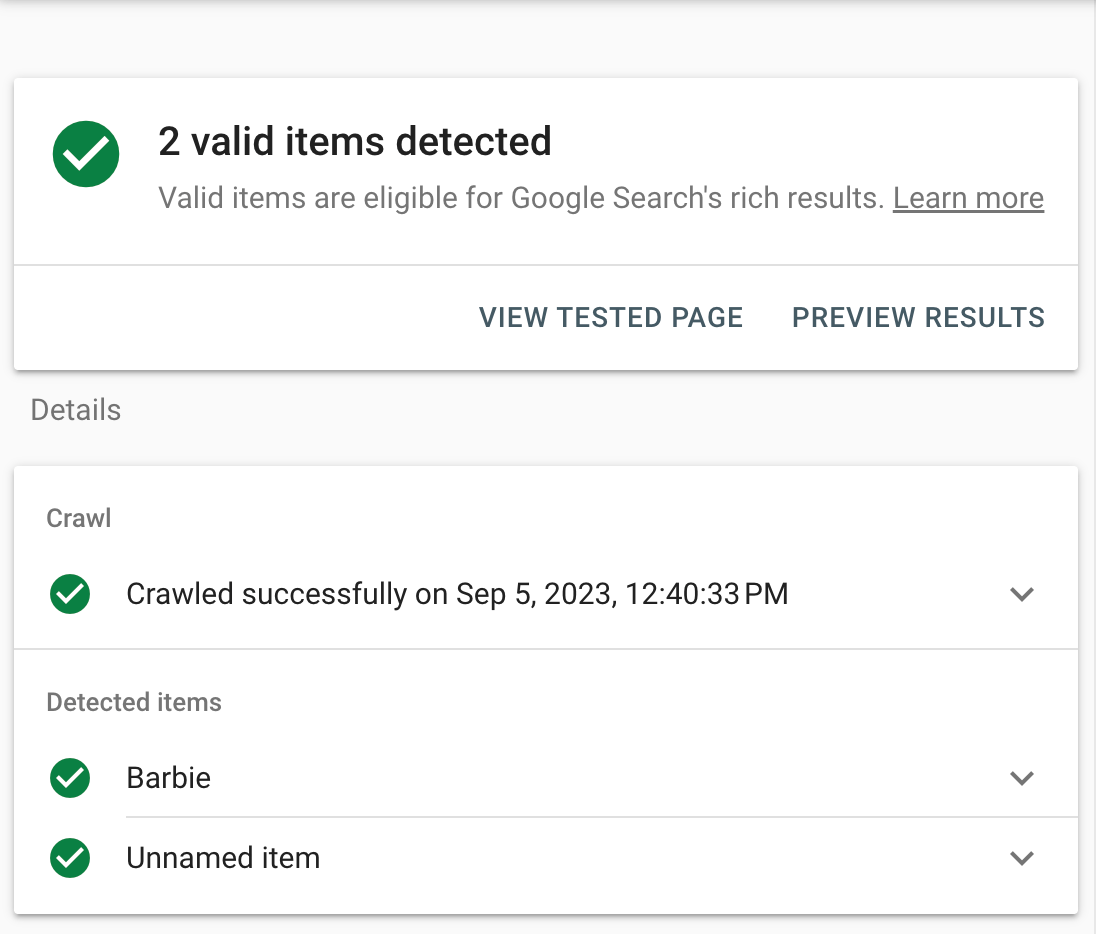
This time, select “URL,” and enter a URL you want to test.
If it’s valid, you’ll see a green tick.
3. Monitor marked-up pages for performance and errors using Ahrefs
There are two reasons monitoring your marked-up pages is important:
- Websites break easily – Even if your code is valid on day #1, it can break later on. There may be code on other pages that isn’t valid as well.
- Existing code may be invalid – Old schema markup may be invalid and need fixing.
The best way to run a check is by using Ahrefs’ Site Audit—you can access this for free using Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
Here’s how to check your website.
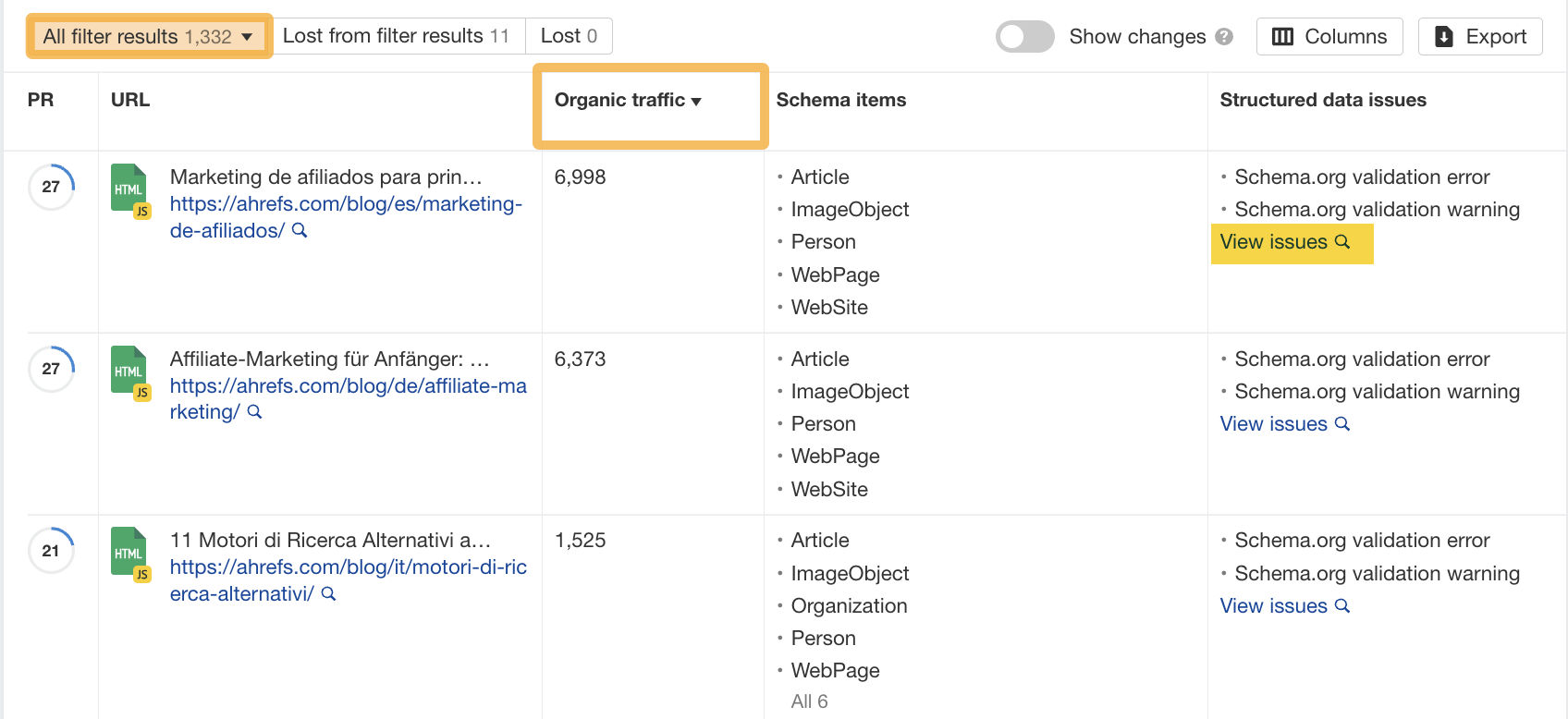
Once you’ve run your audit, head to the All issues report in Site Audit. If there are structured data issues, you’ll see a message like the one below.

Clicking on this issue will show all structured data issues on your website. There are 1,332 results in this example. I prioritize fixes for pages by sorting “Organic traffic” from high to low.
To do this, click on the “Organic traffic” header, then click “View issues” in the “Structured data issues” column to get more details about it.
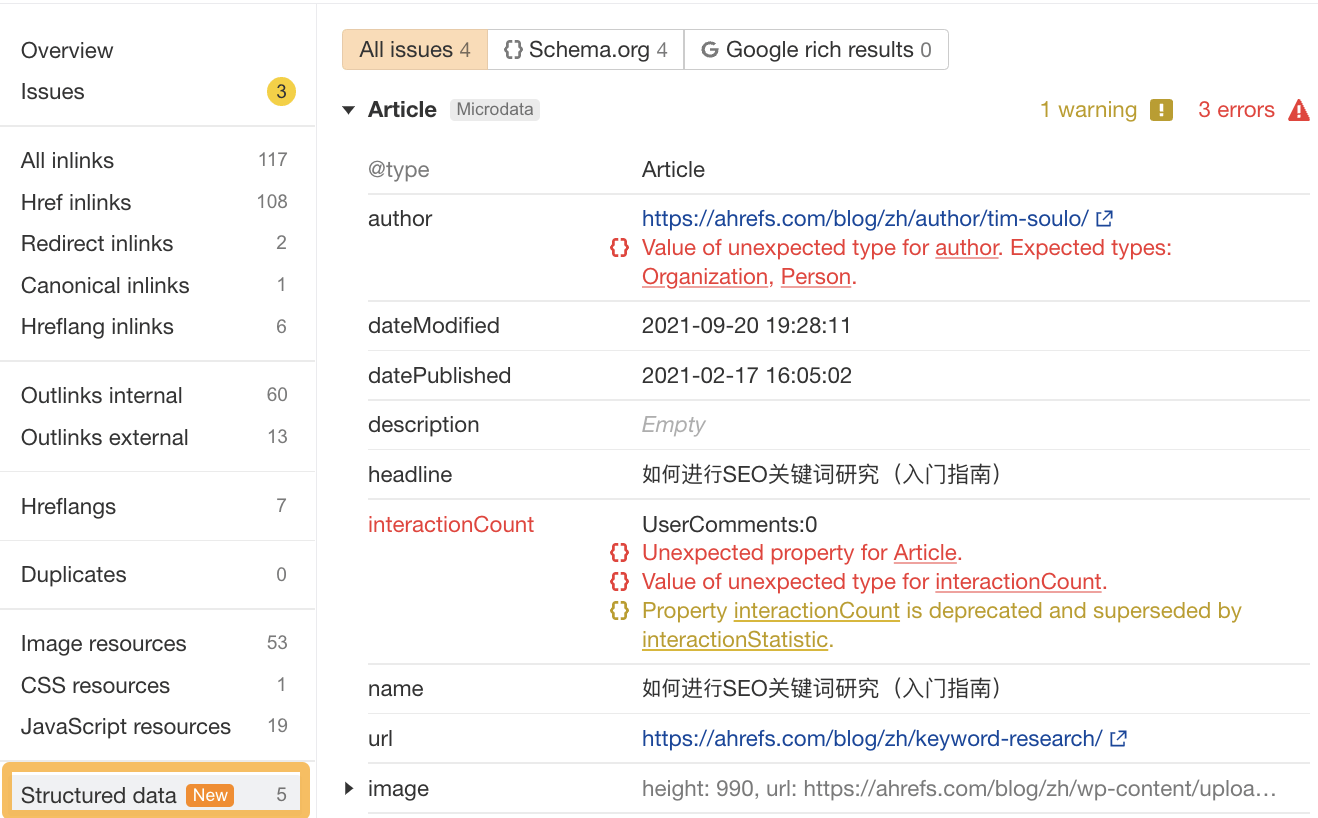
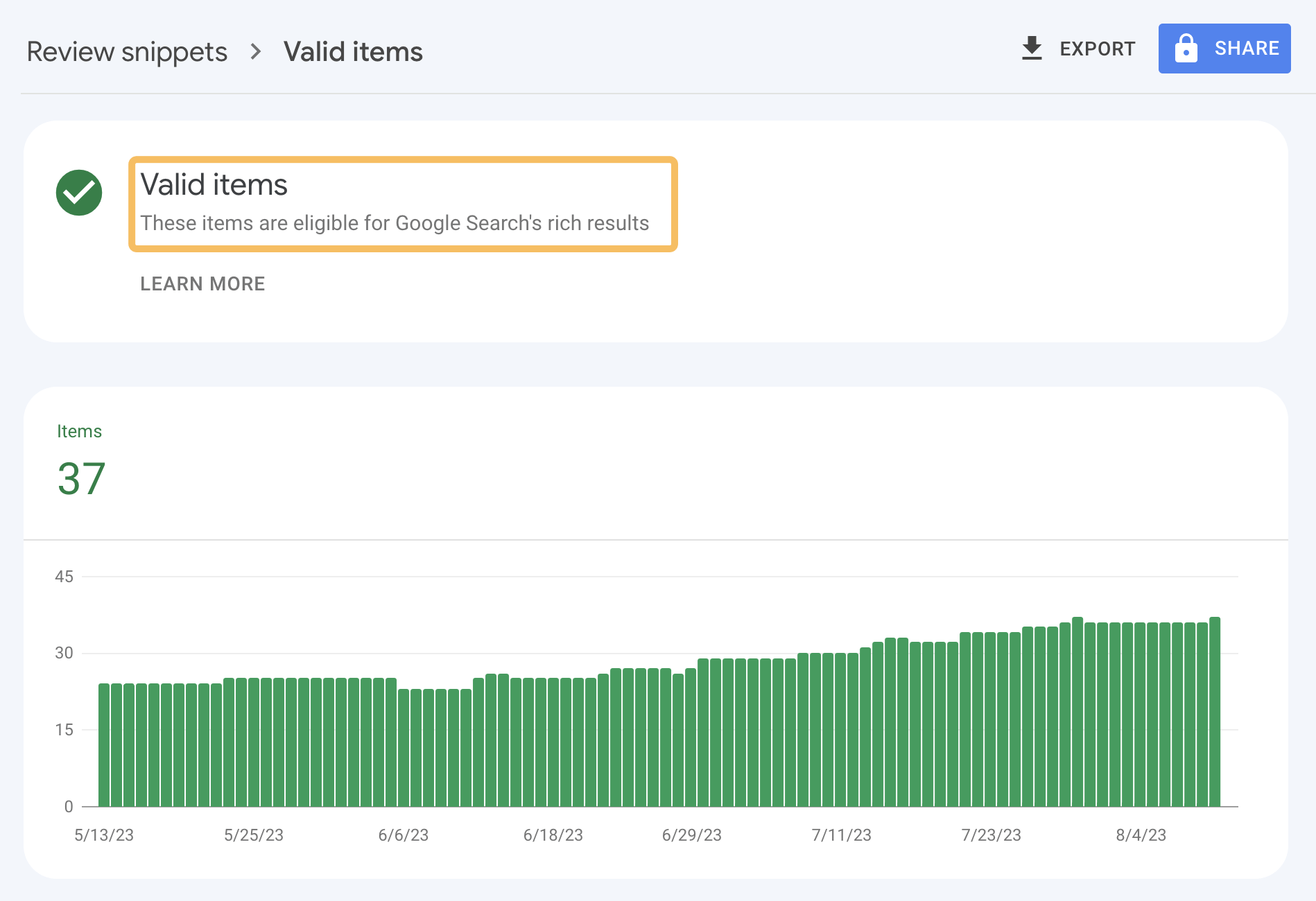
Although you can check rich results status using Google Search Console (GSC), the advantage of using Site Audit is that you can find and diagnose invalid schema code before it gets picked up by Google by scheduling regular crawls.
That way, when you go to GSC, you’ll see nothing but green “Valid items” that are eligible for Google’s rich results, as you’ve already fixed any invalid code.
Final thoughts
Rich snippets often get more clicks than traditional “blue link” results. But whether they’re worth implementing for your website depends on the type of content you have.
You don’t need to be a coding expert to get rich snippets for your website—but it takes some work to get started. Even once everything is set up, there’s no guarantee they’ll show. Tools like Ahrefs’ Site Audit are helpful here, as they can help you validate and monitor your code.



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













