MARKETING
How to Win Potential Consumers with Customer Journey Mapping on Google
The author’s views are entirely his or her own (excluding the unlikely event of hypnosis) and may not always reflect the views of Moz.
If your website is like most others, there is likely a mismatch between the content you provide, and what your prospective customers search for on Google.
This article is about understanding your potential customers and their conversation with Google by using the customer journey mapping method to provide them with the best content. The idea came to me when watching internal user experience teams at our agency, and I hope it will inspire you as an SEO to leave your spreadsheets for a moment and start working with sticky notes (yeah, sticky notes).
Later in the article, as an example of the method, I will show you how a Danish insurance firm managed to come out of nowhere and dominate the conversation for a strategically important insurance product.
I have built +100 customer journey maps over the last year, so I am excited to share my knowledge with you.

I will come back to this later, but let’s get a few definitions in place first:
What is a customer journey?
The customer journey is a model, which describes the stages a prospective customer goes through in order to convert to your solution. It is a way for us as marketers to understand what challenges a user confronts during their journey. When we understand it, we know how our marketing efforts should show up at every stage.
There are many different customer journey models, but I prefer the classic AIDA model, adding the Loyalty stage at the end.

Here is a description of the five stages with examples of typical Google queries:
Awareness: The prospects realize that they have a problem or desire and actively start searching on Google. For example, they may think, “Hey, I’m coughing. How do I get rid of it?” and search for “How to stop coughing?” (40K monthly queries in the US).
Interest: The prospects start searching for simple solution queries. An example is “cough medicine” (59K monthly queries). In this stage, they will also look for substitutes (e.g. “honey ginger tea”).
Desire: The prospects become more educated and refine their search to find the right solution for them. They search for different attributes of the product such as segments (“infant cough medicine”) and types (“non drowsy cough medicine”). This is also the customer journey stage where users subsequently get into the buying mode with best/cheapest/discount queries (e.g. “best coughing medicine for dry cough”). They also begin to search for brands. Typical queries on Google could be “Delsym cough medicine” (5.2K monthly queries) and comparison queries, like “Delsym vs Robitussin” (1.6K monthly queries).
Action: The prospects have made their choice and are ready to take action. A typical search would be “Delsym near me” (90 monthly queries).
Loyalty: The prospects have turned into clients and could have questions about the newly purchased product. A typical example could be “Delsym side effects”.
What is customer journey mapping on Google?
Customer journey mapping is a traditional exercise when working with user experience (UX), trying to visualize the typical touchpoints for a user and thereby understand how to create a frictionless experience.
As I mentioned in the intro, I had a light bulb moment watching our UX teams. Why couldn’t SEOs adopt this practice and map up the customer journey with Google data? Where UX teams use qualitative interviews, eye tracking, client feedback and gut feeling, Google data is the hard data that’s missing.
The idea of doing customer journey mapping on Google was born.

We have the data right at our feet. With Google’s own data sources (e.g. Google Search Console) and third party tools (e.g. Moz Keyword Explorer), SEOs can map out a large part of the customer journey.
Just look at your user data in Google Analytics, and you will see how dominant Google is. According to a study by GrowthBadger, across industries 50-90% of all traffic came from Google. While social media is a great activation channel in 2022, prospects still go to Google when they need to educate themselves before they contact you.
By mapping the entire customer journey on Google we understand:
-
What are the major topics that potential clients are querying on Google?
-
What is the search intent behind the conversation potential clients are having with Google, that might match our USPs?
-
Where are the “peak ends”, meaning the most important conversation touchpoints on Google, that can win or lose a future customer?
-
What is the timeline of search intent, so we understand how to prioritize content development?
Why you should use customer journey mapping on Google
There are three main arguments for why you should use customer journey mapping.
1) Targeting specific keywords is outdated. We need to focus on owning user intent instead.
Especially with Google’s introduction of BERT in September 2019, they understand searches better than ever. And with their MUM update, the search experience will become even more impressive. This also means that we, the SEOs, have to adapt to these advances, focus less on targeting specific keywords, and instead focus on the user intent.
To give an example, all the keywords below have the same intent and should be seen as one:
The total monthly search volume for this search intent is 4,000 monthly queries in the US, so this is a big touchpoint to overlook in your content, if you sell sleeping bags.
2) We need to share SEO data insights with marketing teams – and do it fast.
It should be our aim to break out of the SEO silo and ensure that SEO supports marketing strategies and activities.
People in your marketing department may not even know that Google Search Console exists, and even fewer may have access, so SEOs need to share the insights from this goldmine of data.
SEO silo analysis can take weeks, but when aligning with the rest of the company, speed is crucial. Decisions in marketing are made on a daily basis, so SEOs need to be able to provide data quickly. A customer journey map can be created inside a few hours, and is a great way to visualize data in ways that any non-SEO can understand.
3) Topic clustering doesn’t give you the full picture.
Are you already working with topic clustering and think that customer journey mapping sounds like the same? It’s not.
A normal topic cluster only covers the Interest/Desire stages in the customer journey. A topic cluster consists of the main page (the money page), which ranks for the most important keyword (e.g. “car insurance”) and various supporting pages (pillar pages), which will rank for secondary keywords (e.g. “car insurance for teens” and “car insurance calculator”).
Customer journey mapping covers the full customer journey including the early part of the funnel and the post-sales stage. These two stages are important to pay attention to, in order to be seen as a topical authority by Google, and of course to help your prospective consumer along their entire journey.
Early-funnel
Studies have shown that helping a user early in the process will make them remember you later on. At an early stage of the journey, the prospect is not yet aware of the solution, so they will do symptom queries. This type of query isn’t so easy to identify, but this also means that your competitors are probably missing out on them. This can be a great opportunity for extra traffic.
To research symptom queries you need to think like your prospect. What would they search for when they aren’t sure what they’re looking for? A way to validate if the symptom queries are relevant for you, check in “Related searches” at the bottom of page one on Google, if any solution queries are listed. It is an indicator, if it is a relevant query or not.
Another important aspect is to educate the prospect so they won’t choose the wrong solution. In my last Moz Blog post on SEO sprints, I showed an example of prospects searching for yellow-tinted glasses for driving at night. This is the wrong solution, because opposing cars have blue lights. This is important content to provide your audience, in order to lead prospects in the right direction. What is a misconception in your industry?
Post-sale
The post-sale queries are very valuable, because these are queries done by actual clients. This is not only about helping them out with their actual problem, but it is also an important touchpoint to warm them up for their next conversion.
If you want to identify post-sale queries quickly, then use this regex formula in your Google Search Console:
b(clean|broken|wash off|shattered|polish|problem|treat|doesn’t work|replace|doesn’t start|scratch|repair|manual|fix|protect|renew|coverage|warranty)[” “]
If you do not rank well for the queries that show up, then you most likely have a content gap.
Not all of your content will convert directly. Some content is more apt for micro conversions (see a video, read another piece of content, download pdf). With customer journey mapping, you’re forced to place the search intent in order of appearance. This will help you understand how to structure your content and what a piece of content should do.
How to build a customer journey map using Google data
Let me walk you through the process.
Step 1 : Define your persona and your objective

What do we want to obtain, and who is our persona/s? This important first step ensures that we create the scope for the mapping.
Step 2 : Get the data and map out the intents
Next up is to map out the user intent. I will initially use the client’s Google Search Console.
I will filter 12 months of data for a specific keyword. I will then go through my keyword list. In this example I am doing a map for “Natural playgrounds”. One intent is “natural playground equipment”. I have marked three queries below, which have the same intent: Natural playground equipment, Nature playground equipment and Nature play equipment.

This is one intent identified. Usually, I write the intent on a sticky note with the search volume and the average ranking. Here is an example below from a session.

When I am not able to find more intents in Google Search Console I will add data from third party tools such as Moz Explorer. Here I have inserted the keyword “Natural playground” in the suggestion box, and a list of relevant keywords appear.

Step 3 : Map the post-its in a funnel
I then draw up a sales funnel on a whiteboard, where I place the sticky notes. I will move them around and cluster them, where it makes sense. I will eventually revisit my tools to get more data, if I see gaps in the funnel. This should be a quick process. This is how my whiteboard ends up looking:

When I have completed this exercise I have a great understanding of the prospects’ conversation with Google. The next step is to insert the intents in PowerPoint, so it can be presented to the client. Here is an example. The traffic lights show how the site performs (Green = Rank 1-3 in Google. Yellow = Rest of page 1. Red = Page 2 or worse.). The size of the bubbles represent the search volume.

When a map like this is presented, it will naturally kick-start a focus on how we can convert all the intents to green.
How a Danish insurance firm won prospects with customer journey mapping
Købstædernes Forsikring is one of the oldest insurance firms in Denmark, established in 1731. Historically, they have not focused on SEO, so when I started helping them, they had very little non-branded presence on Google.
Step 1 – We want to own the conversation on Google for “salary insurance”
“Salary insurance” is a product offered by all the insurance industry players. If you lose your job, then with this insurance, you can cover 90% of your salary. This is a strategically important product for Købstædernes, and Google is a big touchpoint in their prospects’ customer journey.
Step 2 – Let’s get the data for “salary insurance” and create a customer journey map
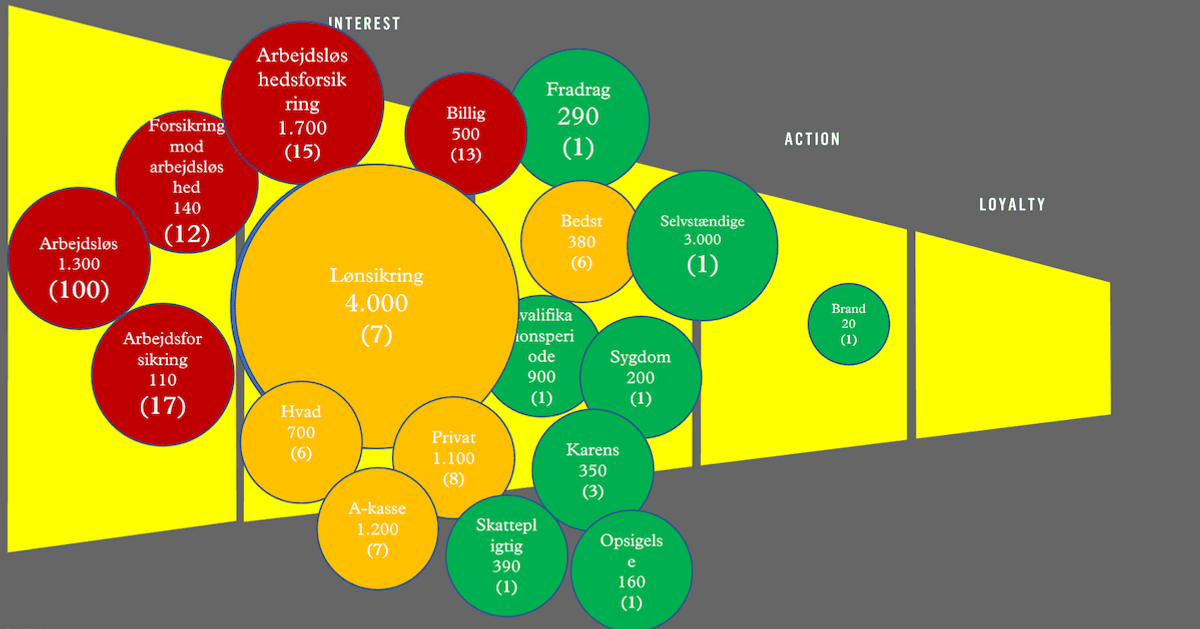
To get an understanding of potential customer search intent, we created the following customer journey map. Each bubble represents a search intent. The size of the bubble shows the relative search volume and the color represents their average ranking. I use traffic light colors to visualize this (Green: ranks in top 3, Yellow: Rank 4-10, Red: Outside page 1 on Google).

To map out the conversation with Google, I used their Google Search Console data, supported with third party tools such as Moz Keyword Explorer. Furthermore, I held an interview with the product team to understand the potential client profiles better, so I could identify the initial symptom searches.
Since the marketing team at Købstædernes are not SEO savvy, then a customer journey map was a great way to explain that we were not part of the conversation at all. They immediately grasped our starting point, and could help by identifying the interesting conversations we should be part of. Furthermore, they could take the conversation insights and use them in the rest of their marketing mix.
Step 3 – Executing on the insights from the customer journey map
When the marketing team signed off on the journey map, we moved on to the second part, which was to understand what content to build, repurpose, and optimize. To be able to match topics between prospects’ conversation with Google and the content on the website, we needed to optimize 10 pages and create five new pages.
As with most organizations, Købstædernes does not have unlimited resources. Thus, the customer journey map was a great asset to understand how to prioritize their efforts. Content in the lower funnel should be produced first.
Over a period of two months, my small team managed to perform these tasks. While it is not the topic of this article I would like to mention that a project management tool such as Asana, Monday.com, Trello or other is necessary to ensure an efficient process. If you use a spreadsheet (Excel, Google Sheets or other) focus on tasks can easily be forgotten. With a project management tool you can assign tasks, set deadlines, describe tasks and sub tasks, insert tags etc. I see it time and time again that when key employees leave a SEO project is put on hold. I would therefore strongly urge you to use one of these tools to avoid brain drain and focus.
The results after 10 months
Here is the development after 10 months. As you can see, we have managed to own a big chunk of the conversation:

Traffic has gradually increased, with 100% growth for the last three months compared to the prior period.

In summary
Google is by far the biggest touchpoint in most customer journeys across industries, so it is obvious that hard data from Google Search Console and third-party tools such as Moz Keyword Explorer can help us understand user intent. Customer journey mapping on Google is a model to enable the data by visualizing it, ensuring that the full marketing team understands the prospects’ conversation with Google.
At the same time, it gives a clear overview of content prioritization, which is an important point, since most teams have limited resources.
Let me end with a few tips about customer journey maps:
-
Make sure you have a clear goal with your customer journey. If there is more than one goal, break the customer journey into several different customer journey maps.
-
Understand your USPs to focus on the relevant search intent. If necessary, break down the broader user intents into smaller ones on underlying customer journey maps, to get a better overview.
I hope this blog post about customer journey mapping has inspired you to think about how you can understand your prospects’ conversation with Google in a new way. Happy mapping!
Source link

















You must be logged in to post a comment Login