SEO
5 Best SEO Certifications in 2023

Since university degrees in SEO are rare, certifications are a popular way to prove your knowledge or expertise in SEO. However, the problem is that such certifications can be provided by anyone.
So if you want to take an SEO certification, you want to make sure you’re completing those where:
- The course material is comprehensive, accurate, and actually teaches you the basics of SEO.
- They’re well regarded in the industry.
To find courses that fit the bill, we polled our 200K+ newsletter subscribers on the best SEO certifications they would recommend.
Here are the five that our subscribers gave the most votes:
1. Ahrefs Certification Course

Duration: 7 hours 4 minutes
Price: Free with an Ahrefs Webmaster Tools account
Instructor(s): Sam Oh
Level: All levels
This is our own certification course that teaches how Ahrefs’ tools and data work. It’s split into modules representing each of our tools.
Our certification course is currently in beta. So you won’t be able to take an exam and acquire a certificate (for now). Don’t worry, though; we plan to add the certificate in the near future.
2. Google SEO Fundamentals by UC Davis
Duration: 29 hours
Price: Free
Instructor(s): Rebekah May
Level: Beginner SEOs
Created by the University of California, Davis, and powered by Coursera, this course teaches the fundamentals of SEO. There are four modules in this course and four assessments to complete. Once you’ve passed, you can earn a career certificate that you can add to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV. For example, here’s one given to my colleague, Joshua Hardwick:

While the course is well regarded and prestigious, it comes at a huge time cost of 29 hours. You could build and potentially rank a website in that amount of time. It might be better to consider the other certifications on this list.
Many SEOs used to mistakenly claim that they were “Google certified” after completing this course. This was likely because Google used to recommend it, even as late as July 2023:
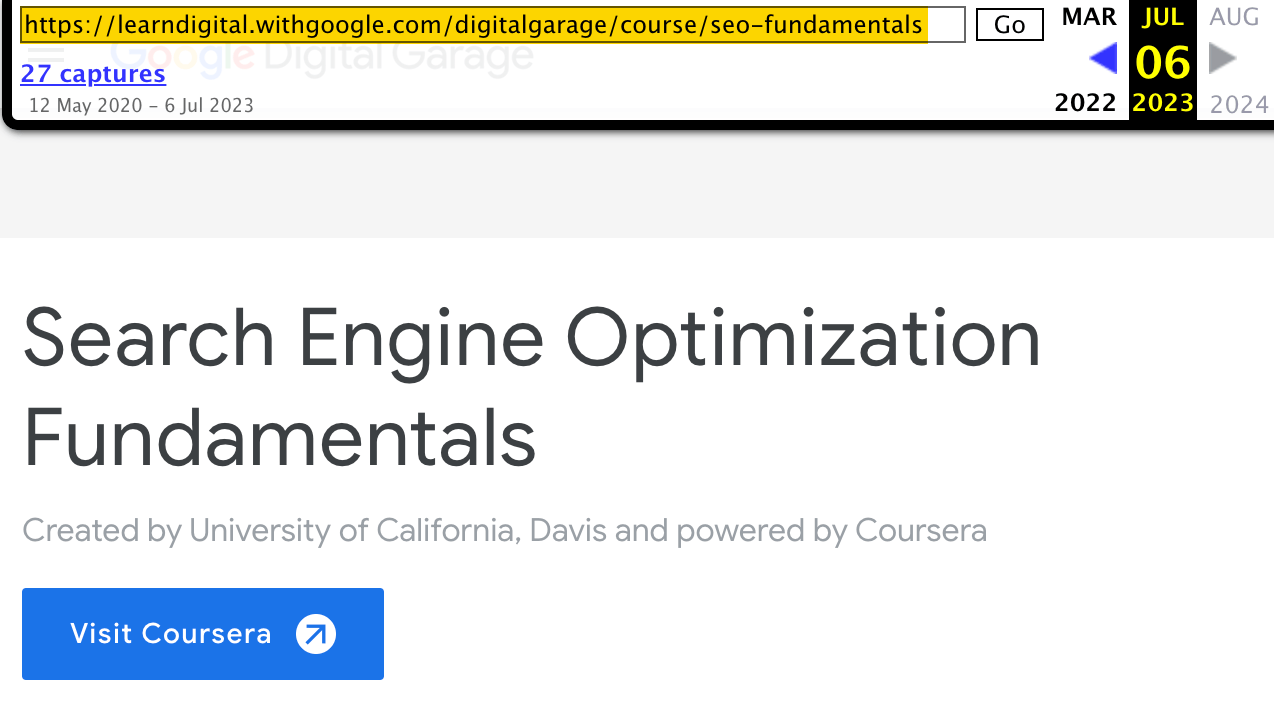
However, Google has since redirected this page somewhere else and, as a result, stopped recommending this course.
3. SEO Certification Course by HubSpot
Duration: 3 hours 51 minutes
Price: Free
Instructor(s): Rachel Sheldon, Matthew Howells-Barby
Level: Beginner SEOs
This SEO certification course is part of HubSpot, a SaaS company known for inbound marketing (the founders even wrote a book about it).
With six lessons and 26 videos, the course runs at close to four hours. There are also five quizzes to complete, after which you can gain a certificate. For example, my colleague, Joshua, took this certification and obtained this certificate:

The course is free, but you’ll have to sign up for a HubSpot Academy account.
4. All-Around SEO Training by Yoast

Duration: 3 hours
Price: $99/year
Instructor(s): Joost de Valk
Level: Beginner and intermediate SEOs
This is the first paid SEO certification on this list. It costs $99 per year, and you get a certificate, badge, and access to the course for one year. (You can share this on LinkedIn, your resume, CV, etc.). You also get access to all other Yoast academy courses and Yoast’s premium plugin.
Considering that Yoast is probably the most used SEO plugin, this may actually sound like a steal.
If you’re unsure about dropping that amount of money on an SEO course, Yoast also offers a free sample lesson for you to try:

5. SEO Foundations on LinkedIn
Duration: 1 hour 32 minutes
Price: ~$40
Instructor(s): David Booth
Level: Beginner SEOs
Part of LinkedIn Learning, this course has five modules and five chapter quizzes to assess your knowledge. Passing the course means acquiring a LinkedIn Learning Certificate of Completion, which you can easily add to your LinkedIn profile.

Unfortunately, this is a paid course—but it’s relatively affordable. You can even start a one-month free trial on LinkedIn Learning and complete the course within that period.
Let’s be straight:
Most SEO certifications aren’t worth it.
Here are a few reasons why.
1. Most employers don’t care about SEO certifications
We asked 15 SEO hiring managers for the skills and requirements that they deem important when hiring an SEO specialist. In all, 86% said that SEO certifications aren’t important, with the rest saying that they’re only somewhat important.
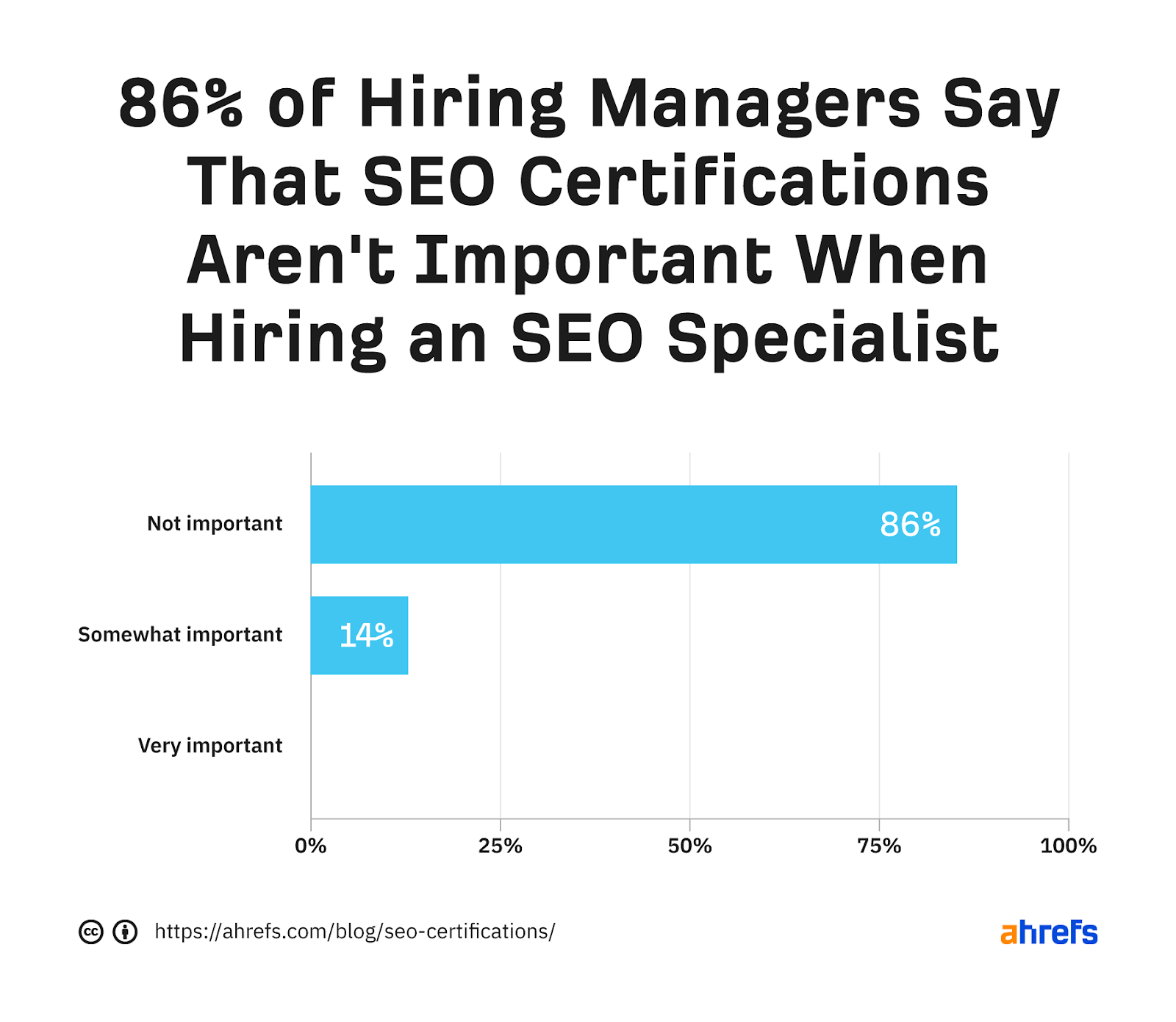
Not one hiring manager said they were very important.
So if you want an SEO certification to add to your resume and LinkedIn to attract job offers, I have bad news.
2. SEO certifications don’t guarantee a good SEO education
Getting an SEO certificate doesn’t necessarily mean that you learned anything useful. It just means that you learned something.
So don’t let the allure of a certificate cloud your judgment when learning SEO. If the syllabus doesn’t look helpful, don’t bother.
3. SEO certifications only teach you theory, not practical skills
Knowing the theory only gets you so far.
If you want to become an SEO expert, our advice is to start a website as soon as possible after learning the basics of SEO. Getting your hands dirty and trying to rank a website will teach you more than an SEO certification.
4. SEO certifications take a lot of time
There are 13 hours of material in Google’s SEO Fundamentals certification.
That’s not a negligible amount of time. You could spend that time building and ranking a website. And it’s probably a better use of your time if you already know the basics of SEO.
5. SEO certifications often have bad questions
Look at this question from an SEO exam:
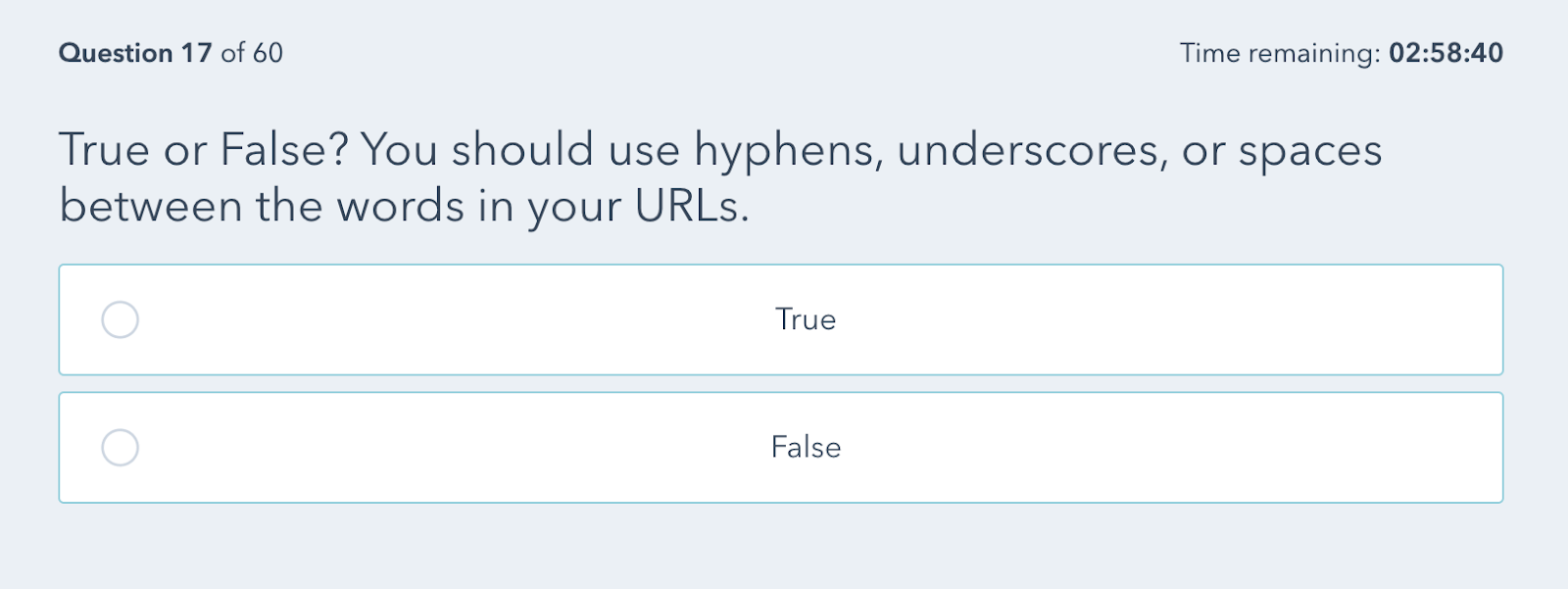
Google actually recommends you use hyphens rather than underscores in URLs. So it’s not a true or false question.
Here’s another question, this time from Google’s SEO Fundamentals certification:
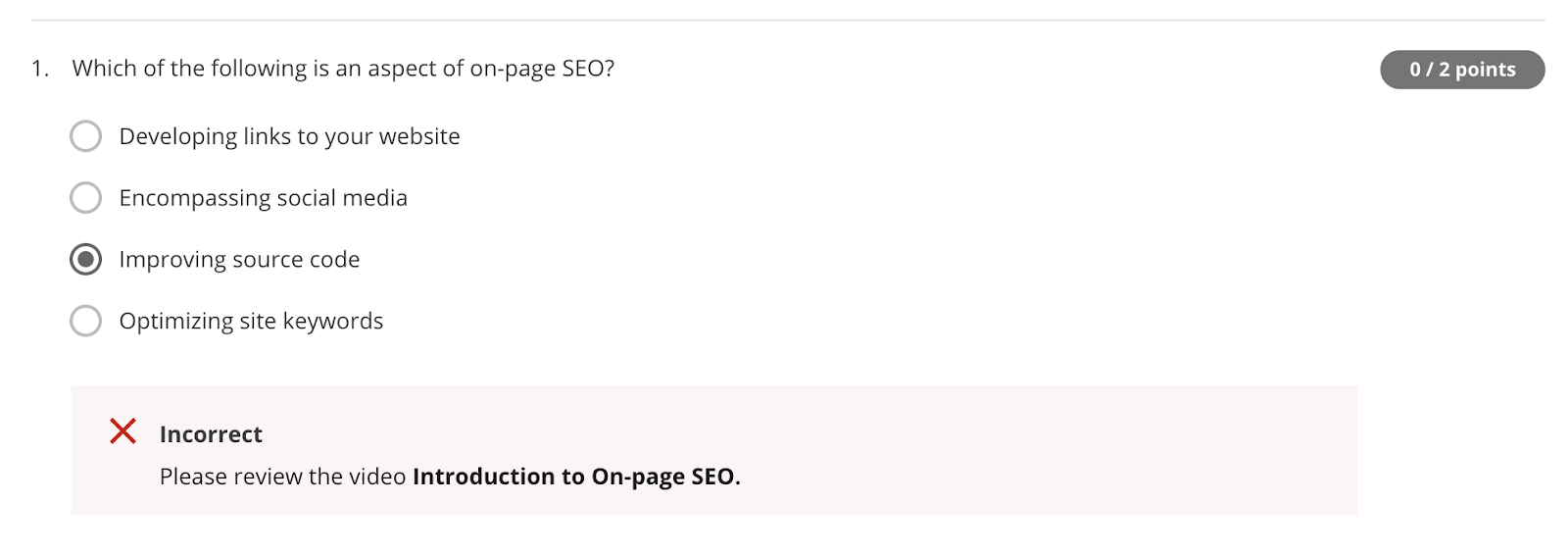
You can see we got the answer wrong. If we must guess, the correct answer is likely “optimizing site keywords.” But that’s a terrible answer—it sounds like something you’d see in 2009, not now.
If you are a hiring manager and see such questions in the quiz, will you trust the certification? And by extension, will you trust the knowledge of the person with such certifications?
Probably not.
6. SEO certifications are too easy to pass
For most certifications, if you failed the exam, you could retake it shortly after your initial attempt (between 0 and 12 hours).
This sounds great if you’re a “test taker.” But since most questions are multiple-choice, it’s only a matter of time before you pass the exam via trial and error or Googling.
This diminishes the value of your certification. Imagine if it was this easy for college exams. The job market would soon become saturated with graduates, and degrees would lose much of their value.
7. SEO certifications are often just marketing ploys
Passing an SEO certification gets you a certificate (and sometimes a badge too). You can show this off on your resume, LinkedIn profile, or website. That raises brand awareness for the creator of the SEO certification.
This is probably why many of them are easy to pass. Passes lead to brand awareness.
Here are some commonly asked questions about SEO certifications.
What is an SEO certification?
An SEO certification is awarded to a person who passes an assessment after completing an SEO course.
The proof of achievement, either in the form of a certificate or badge, is what differentiates an SEO certification from an SEO course.
Is there a Google SEO certification?
Kind of.
Google offers a free “Fundamentals of Digital Marketing” certification through the Google Digital Garage. It includes 26 modules, ~14 hours of material, and covers many aspects of digital marketing—with three of them solely dedicated to SEO. It’s accredited by the Interactive Advertising Bureau Europe and The Open University.
If you’re looking to learn Google Analytics, there’s also the Google Analytics Certification.
Should you pay for an SEO certification?
Judge the course by its material, not by the certification. If the course contains material you didn’t know before or can likely teach you new skills, then it’s worth paying for.
Final thoughts
Most SEO hiring managers see certifications as unimportant when hiring SEO specialists. We agree.
So here’s our advice:
If you want to grow your SEO knowledge, find a good SEO course (here’s our free one) and then execute what you learn.
If you want to get a job, do the same thing because results speak louder than an “SEO certification.”
Any questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter (X) or Threads.



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













