SEO
5 Types of Blogs That Make Money

- About 15% of bloggers make a full-time income from blogging ($30K a year).
- About 31% of bloggers make a decent side income from blogging ($6K a year).
- 6%–10% of bloggers make over $10K a month.
- You can realistically make $25K–$50K in your first year of blogging.
- The most successful blogs make over $100K a month.
Looks like professional blogging may actually be a good idea. You can make a full-time income or a decent side income. You can even own several blogs, hire copywriters, and multiply your earnings.
But like in every other business, nobody can guarantee your blogging business will work out. It usually takes years to be financially independent through blogging. Your first step is deciding on the type of blog you want to run.
With that said, here are the five types proven to make money.
Probably the most popular type of blog created with the purpose of making money. This kind of blog will take a deep dive into a particular niche or theme to cover as many topics as possible (to maximize traffic) or just the ones that are fit for the blog’s angle.
Topics are usually picked by the criteria of:
- Traffic potential (mostly organic traffic from search engines).
- The ability to monetize traffic (for instance, some topics will earn only from ads while others will also be a good fit for product placement).
- Popular requests from readers.
- Trends.
Here are some profitable blog niches with a list of typical content and blog examples:
| Niche | Typical content | Blog example | Last monthly income report | Pageviews (from last income report) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food and cooking | Recipes categorized by type of meal and diet, cookware reviews, tips and tricks, listicles | Pinch of Yum | $95,196 (source) | 4.245M |
| Health and wellness | Food, relationships, fitness, beauty, psychology | Hot Beauty Health | $9,655 (source) | 208.6K |
| Parenting | Pregnancy, child raising advice, product reviews, food recipes, stay-at-home parent jobs, kid activities, household tips | The Soccer Mom Blog | $11,288 (source) | 500K |
| News | Anything newsworthy in one niche or multiple niches (also gossip) | HuffPost | Acquired by AOL in 2011 for $315M, then acquired by BuzzFeed (source). According to this source, it generates $14M/mo. | 5.8M (monthly organic traffic March 2023, via Ahrefs) |
| Tech | Software and hardware reviews, exclusive deals, how to use software tools, comparisons, listicles, making money online, tech news, buying guides, gaming | 99signals | $5,242 (source) | 18K (monthly organic traffic on the date of the report, via Ahrefs) |
| Personal development | Life hacks, financial freedom, wellness, psychology, motivation, spirituality, fitness | Let’s Reach Success | $6,652 (source) | 115.5K |
| Pets | Pet health, product reviews, activities for pets, traveling with pets, pet adoption, training, tips, listicles | You Did What With Your Weiner | $7,720 (includes income outside of the content, source) | 40K (monthly organic traffic on the date of the report, via Ahrefs) |
| Entrepreneurship | Making money online, starting a business, interviews, complete courses, how-tos, inspiration | Smart Passive Income | $166,559 (source) | 68K (monthly organic traffic on the date of the report, all blogs, via Ahrefs) |
| Finance | Investing, saving money, retirement, financial product reviews, buying guides, family finance, mortgages, gig economy, debt, career advice, entrepreneurship, financial freedom | Millennial Money | $33,473 on average (source) | 1.5M visits in 2017 |
| Fashion | Outfit ideas, home decor, beauty, style tips, gift ideas, listicles, buyer guides | Chic Pursuit | $11,376 (source) | 135.3K |
| Lifestyle | Anything related to solving life’s problems and living a happier life | Abby Organizes | $41.7K (source) | Over 400K |
| Travel | City guides, listicles, traveling tips, gear and location reviews, life on the road, digital nomadism | Local Adventurer | $41K (source) | 541.8K |
| DIY/crafts | DIY decorations, DIY weekend projects, handcraft tutorials, life hacks, product reviews, food recipes, DIY repairs, renovations | Jennifer Maker | $15,158 (source) | 125.4K |
Recommendation
If you’re serious about blogging, take some time to read through the income reports linked above. At least a few of them. You’ll find some unique and inspiring stories and often great business tips.
The above list most probably doesn’t show all possible lucrative niches. But here’s a quick tip to check if a niche is profitable: search for affiliate programs in that niche.
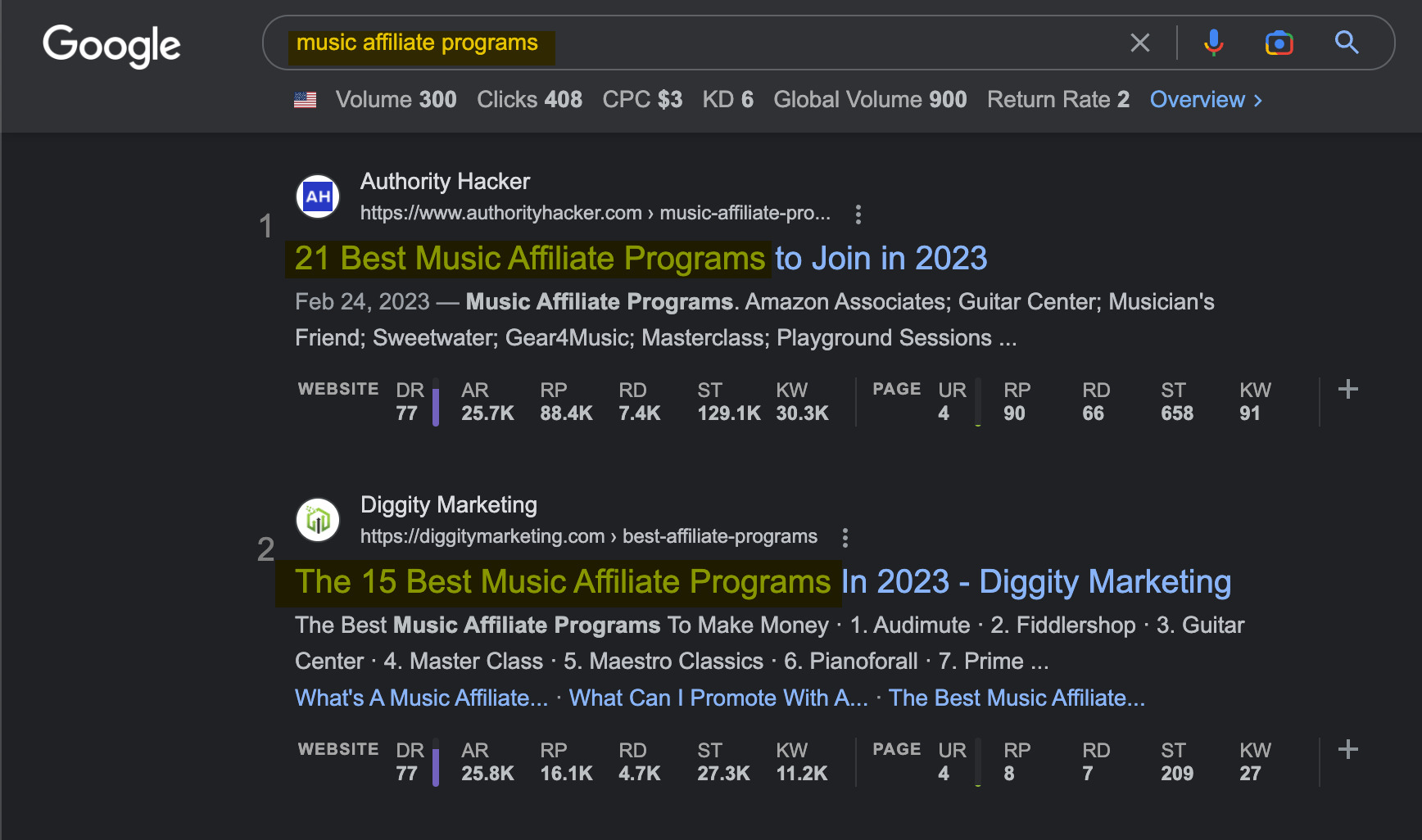
While practically every niche blog will review products to earn commissions, there are blogs that focus only on that (and turn it into art).
But why reviews? There are two reasons.
Number #1 is the demand. People turn to in-depth reviews made by people with first-hand experience to help them make a choice. Especially if the product is expensive or there are a lot of alternatives.
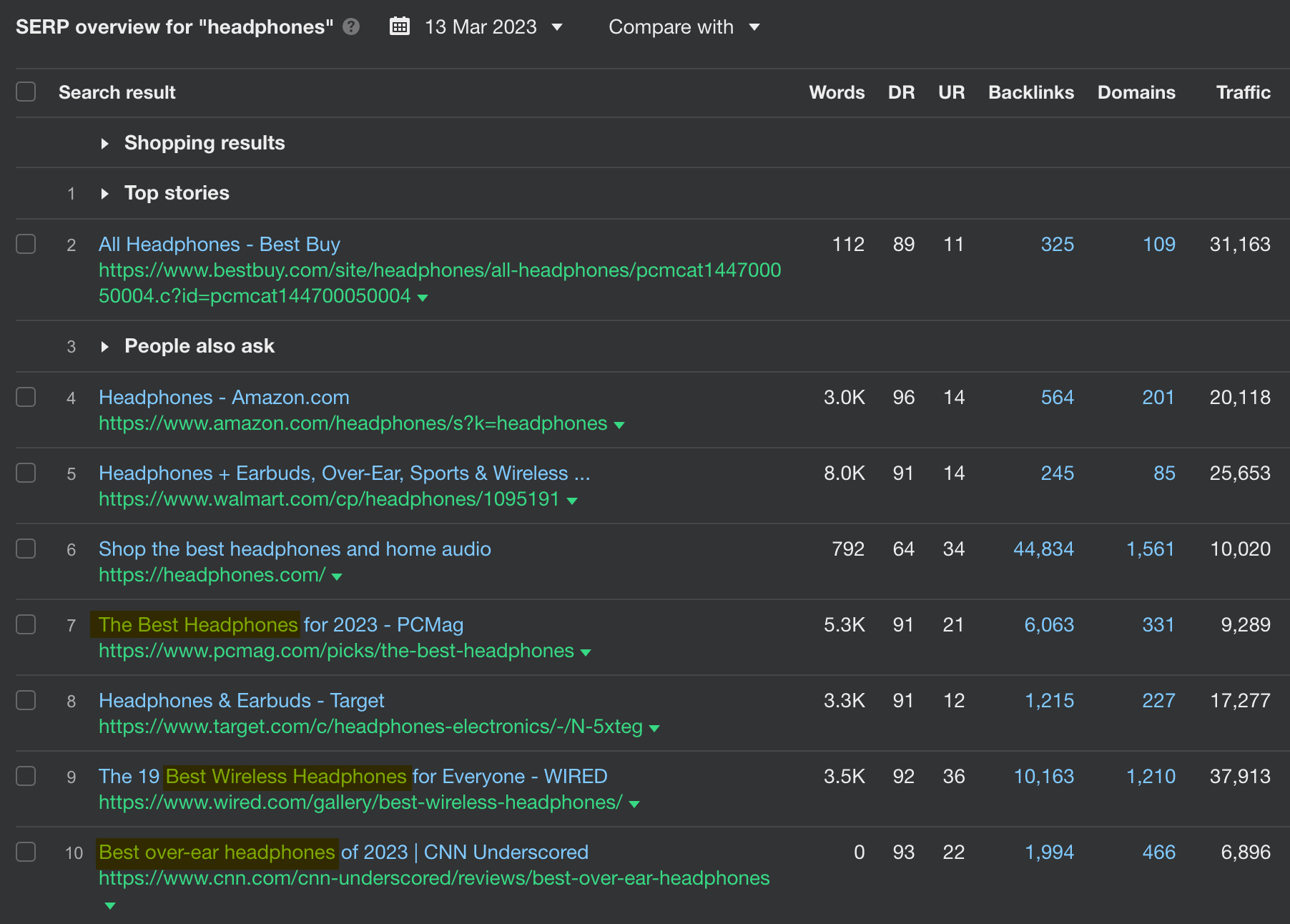
For instance, a single page on the best headphones for 2023 can generate over 12K in organic visits each month, ranking for hundreds of keywords related to headphone reviews. You can get a sense of the demand for this kind of service when you look at the search volume of some keywords in the U.S. alone:

In fact, the entire #1 page on Google for “headphones” shows commercial search intent with reviews showing up as well.
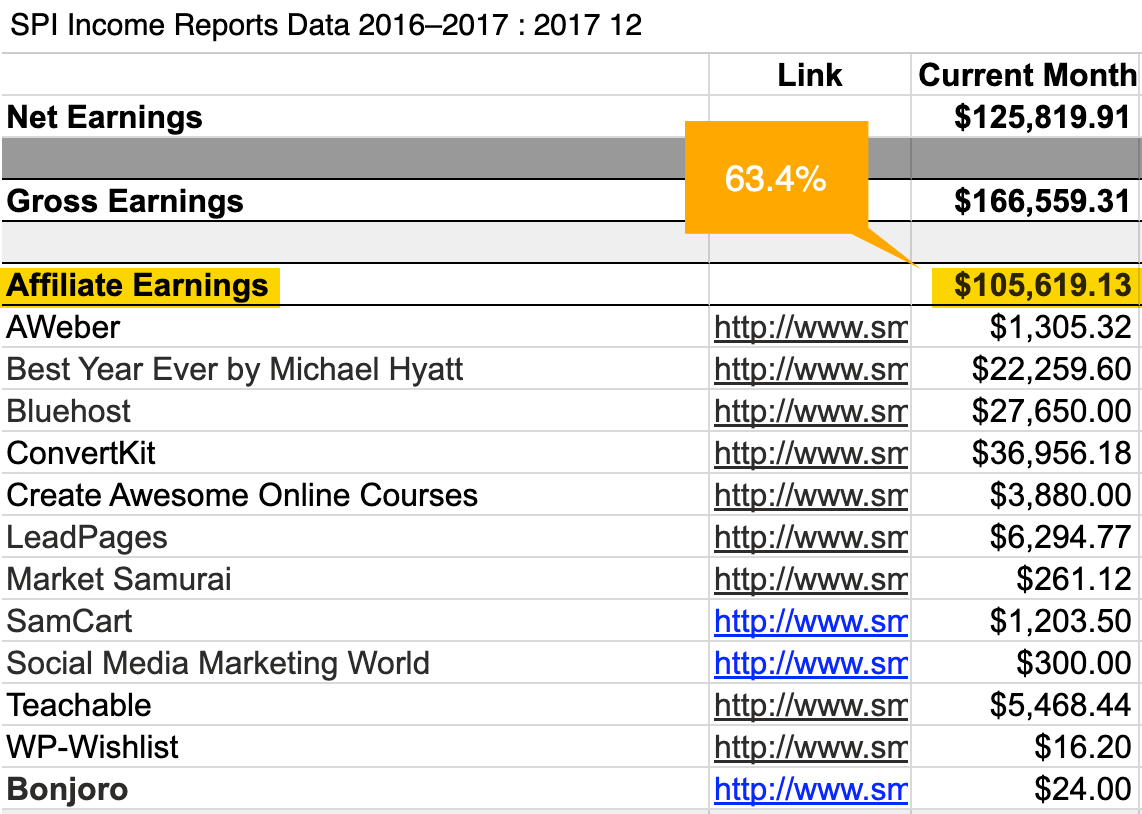
Secondly, affiliate programs are typically a substantial part of a blogger’s earnings. For example, the Smart Passive Income blog generated approximately 63.4% (over $100K) of its income from affiliate deals.
Some blogs review all kinds of products that offer commission, while others focus on a particular niche such as tech gadgets or parenting products. As long as there’s an affiliate program for the product or the merchant (seller) can offer you a deal, any product niche can be profitable.
If you’re curious about the ingredients of success for this type of blog, check out our case studies:
Tip
Starting a personal blog is probably the easiest thing. You can write just about anything—it’s your blog. But a personal blog designed to make money is something a bit different.
Of course, it has that unique, personal tone. It’s written from a personal point of view, but it does need to have a strategy to monetize “something.”
That something can be:
Or it can be something no one has ever done before. I mean, before I discovered Gala Darling’s blog, I wouldn’t dare to think you could monetize EFT tapping sessions (a real thing, look it up).
In terms of topics and content formats, there are no rules for personal topics. They can talk about everything and anything. What’s typical for these blogs, though, is that they offer some kind of content upgrade or a product, such as a book or a course.

Personal brand blogs are blogs with the sole purpose of making one’s name in the business. What sets them apart from personal blogs is that their content is a lot more focused on the industry the brand is set in.
Here are some typical content formats you will find on such blogs:
- How-to guides
- Tutorials and courses
- Definition posts
- Original research
- Feature release notes
- Opinion pieces
- Case studies
- Listicles
- Product reviews
- Podcasts
- Videos
- Products and/or services
- Free resources: tools, cheat sheets, checklists, templates, etc
An example of such a blog is Charli Marie. It’s run by a designer whose personal mission is “to help anyone else who falls in love with design to succeed in their careers.” Charli uses various educational content (articles, videos, podcasts) to cater to an audience of over 250K people.
As you can imagine, that kind of audience helps Charli grow her brand in the design business. But on top of that, she monetizes her recognition by offering paid speaking engagements, mentoring, site audits, and an original hand-made font.

The purpose of business and corporate blogs is to promote products, services, and brands owned by the business.
This is usually achieved by creating educational content around the product or service in order to attract and retain customers. Typical content formats you will find on such blogs include these:
- How-to guides
- Definition posts
- Original research
- Interviews
- Feature release notes
- Opinion pieces
- Case studies
- Listicles
- Company news
- Free resources: cheat sheets, checklists, templates, etc
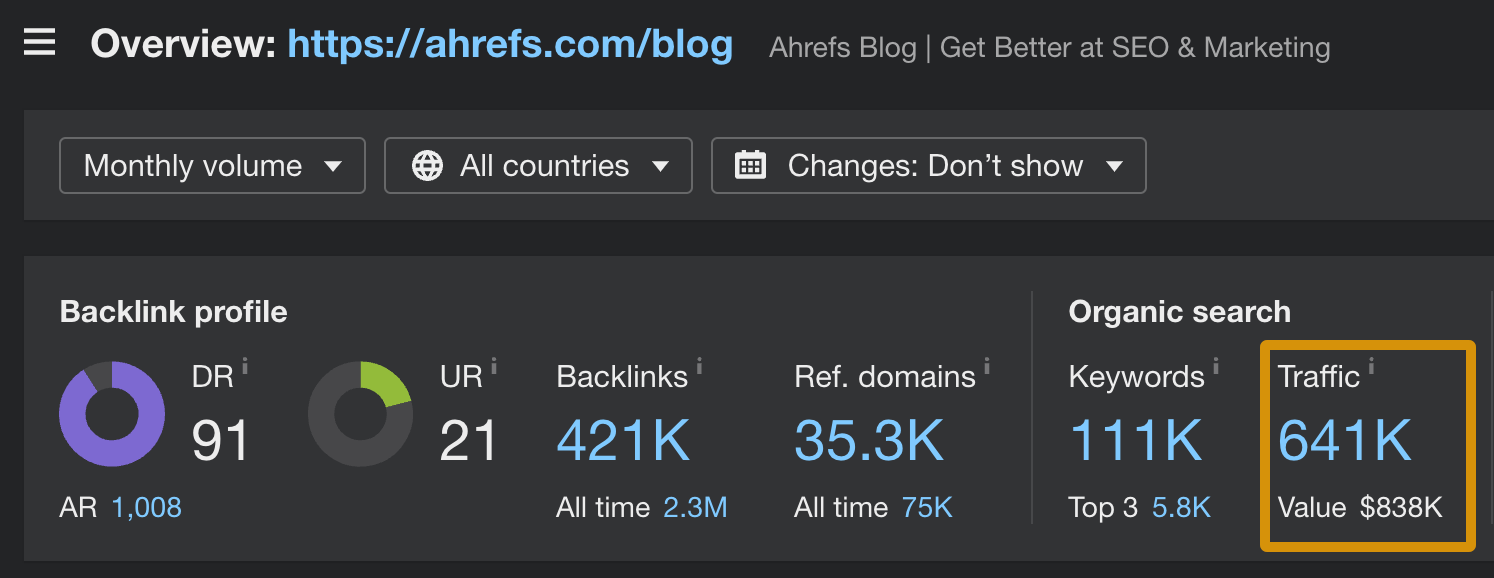
The blog you’re reading right now is an example of this type. By regularly publishing and updating SEO content, we generate an estimated 641K visits from search engines each month. We’d need to spend about $838K each month to get similar traffic from ads.
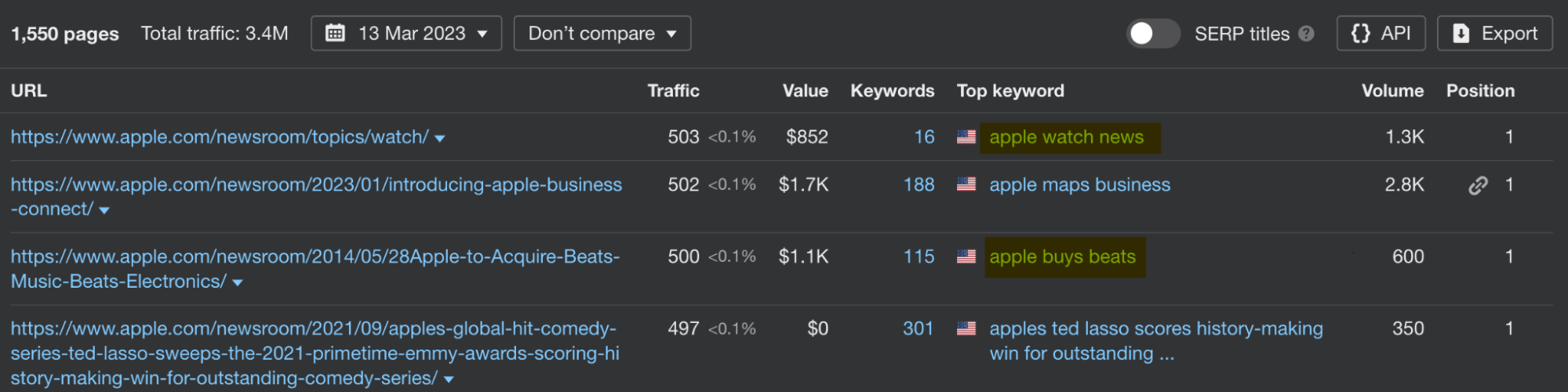
Blogs owned by big corporations tend to be less about acquiring customers and more about providing an outlet for the company to communicate with the audience. For instance, Apple calls its blog the Newsroom. The type of stuff it writes about is releasing a new iPhone color or a story about how the company supports sustainable farming.
By the way, a corporate blog like that can be a good idea for catching branded keywords that are hard to cover anywhere else.
Writing what you want and how you want can be very satisfying. It’s one of the best things about having a blog. But if you want your blog to make money, a good portion of your content should be based on existing demand for information, products, and services.
One of the best ways to gauge that demand is to learn what people search for online. And the best part about it is that once you rank for relevant search queries, you can get a free, passive, and compounding source of traffic.
Here are three basic methods. They can give you topic ideas even if you’re not an expert in the topic or niche.
1. Do keyword research
Keyword research is the process of discovering valuable search queries that your target customers type into search engines like Google to look for products, services, and information.
There are many techniques to do keyword research, so I’ll link to some at the end of this section. The basic process goes like this:
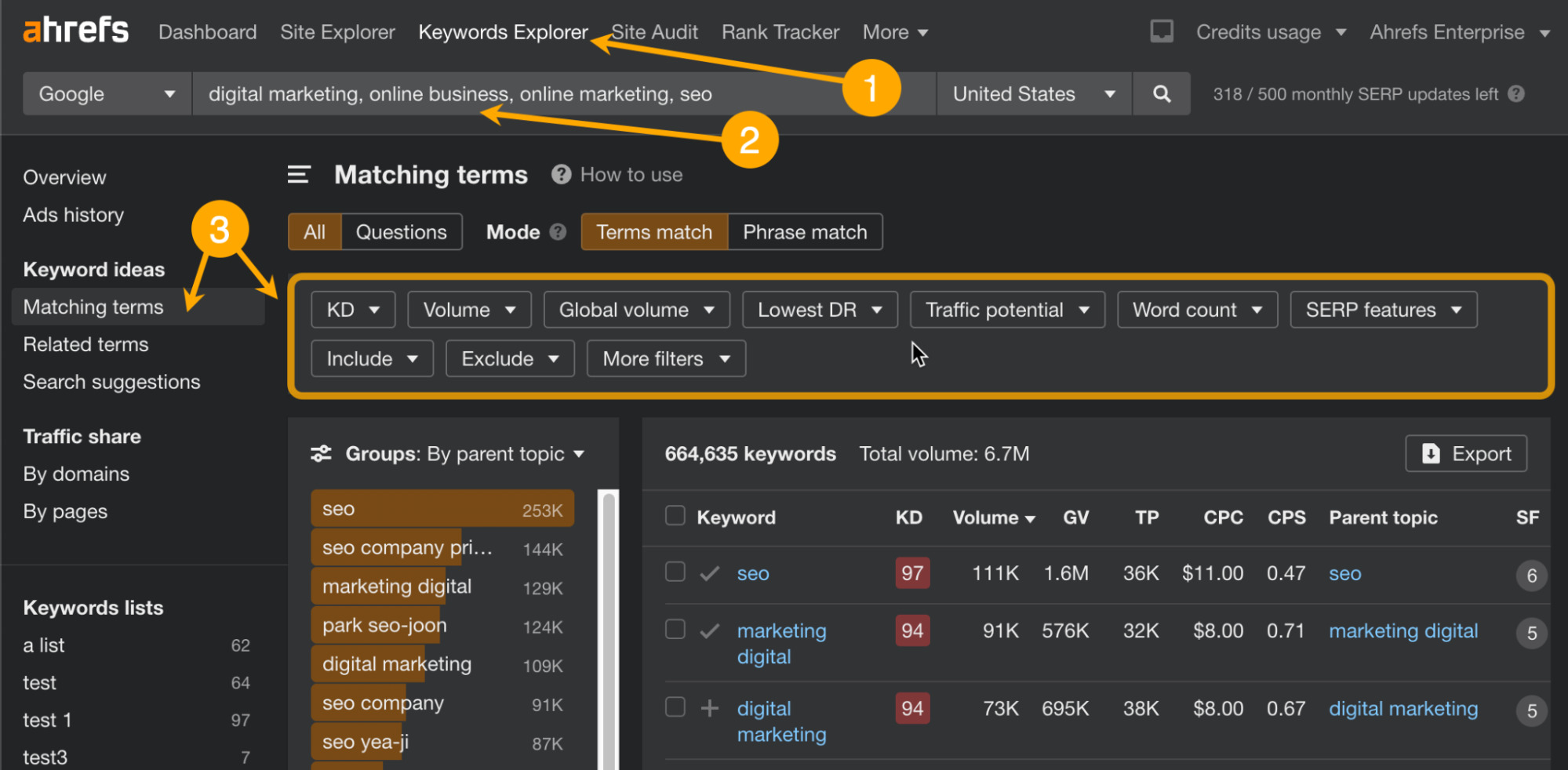
- Get a tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter seed keywords related to your niche, e.g., seo, digital marketing, online marketing, online business
- Use filters to refine the results and find the best keywords for your website
How do you know which keywords will be the best for your website?
- Your keywords should have traffic potential.
- You can match the search intent behind your keywords.
- Your keywords can bring valuable traffic (i.e., traffic you can monetize).
- You can rank for those keywords.
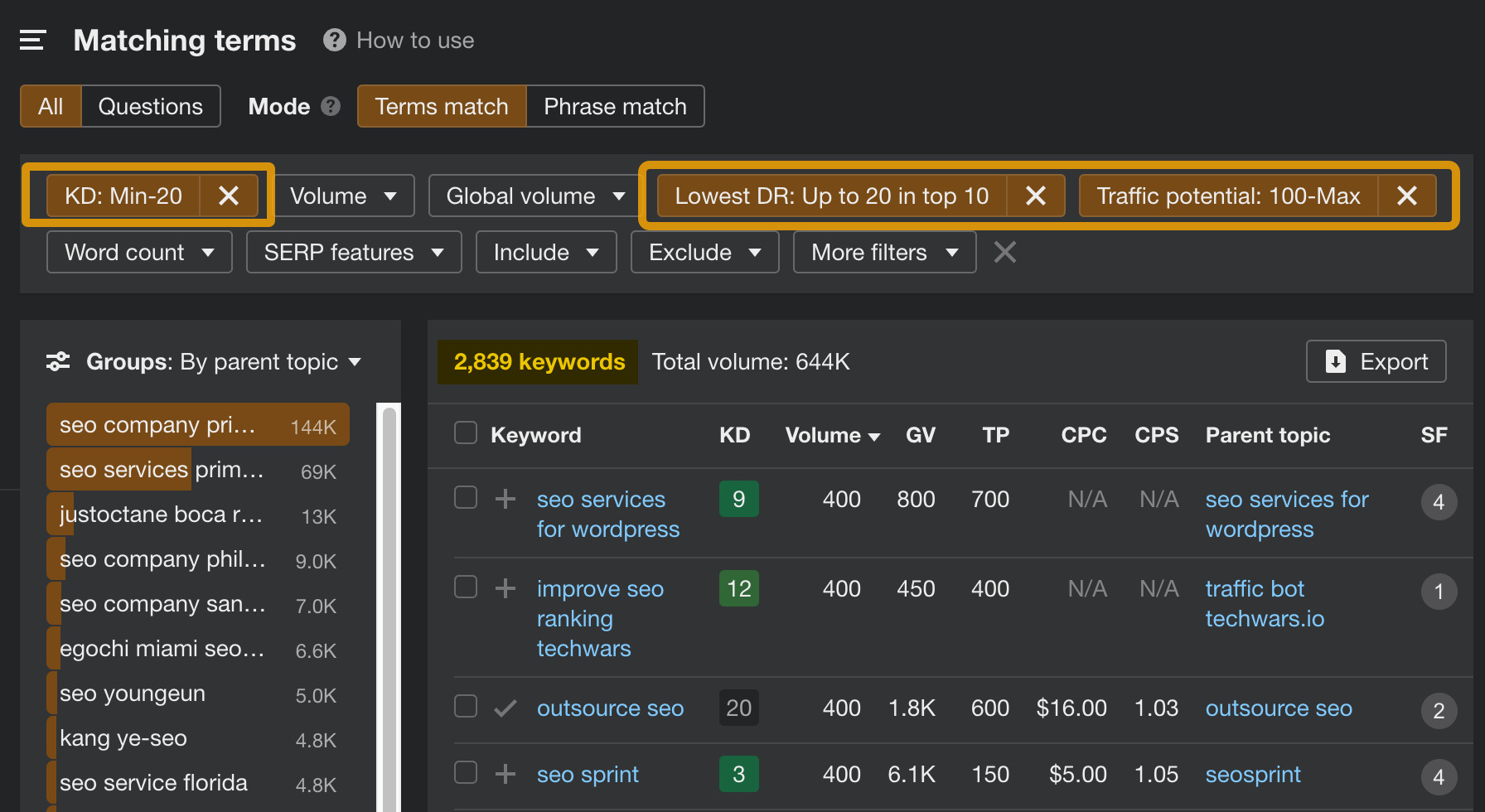
For instance, you can look for low-competition keywords that could get your blog ranking relatively fast. For this, you can use the Keyword Difficulty filter (KD), Lowest DR filter, and Traffic Potential minimum of 100. In this case, you’ll get nearly 3K potential keyword ideas.
2. Analyze other blogs in the niche
Having organic competitors has its good sides. You can get keyword ideas from someone else’s website.
In Ahrefs, there are two handy tools you can use for that.
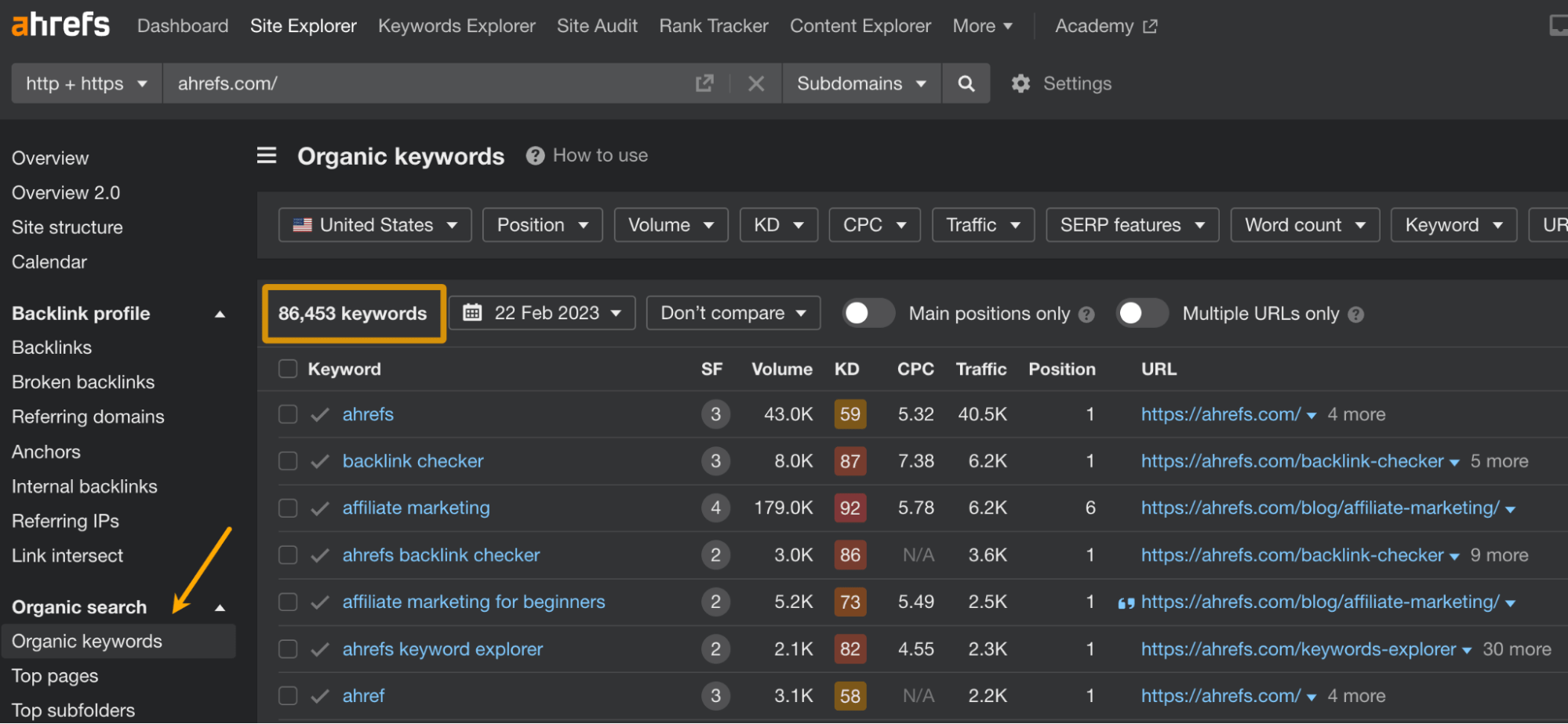
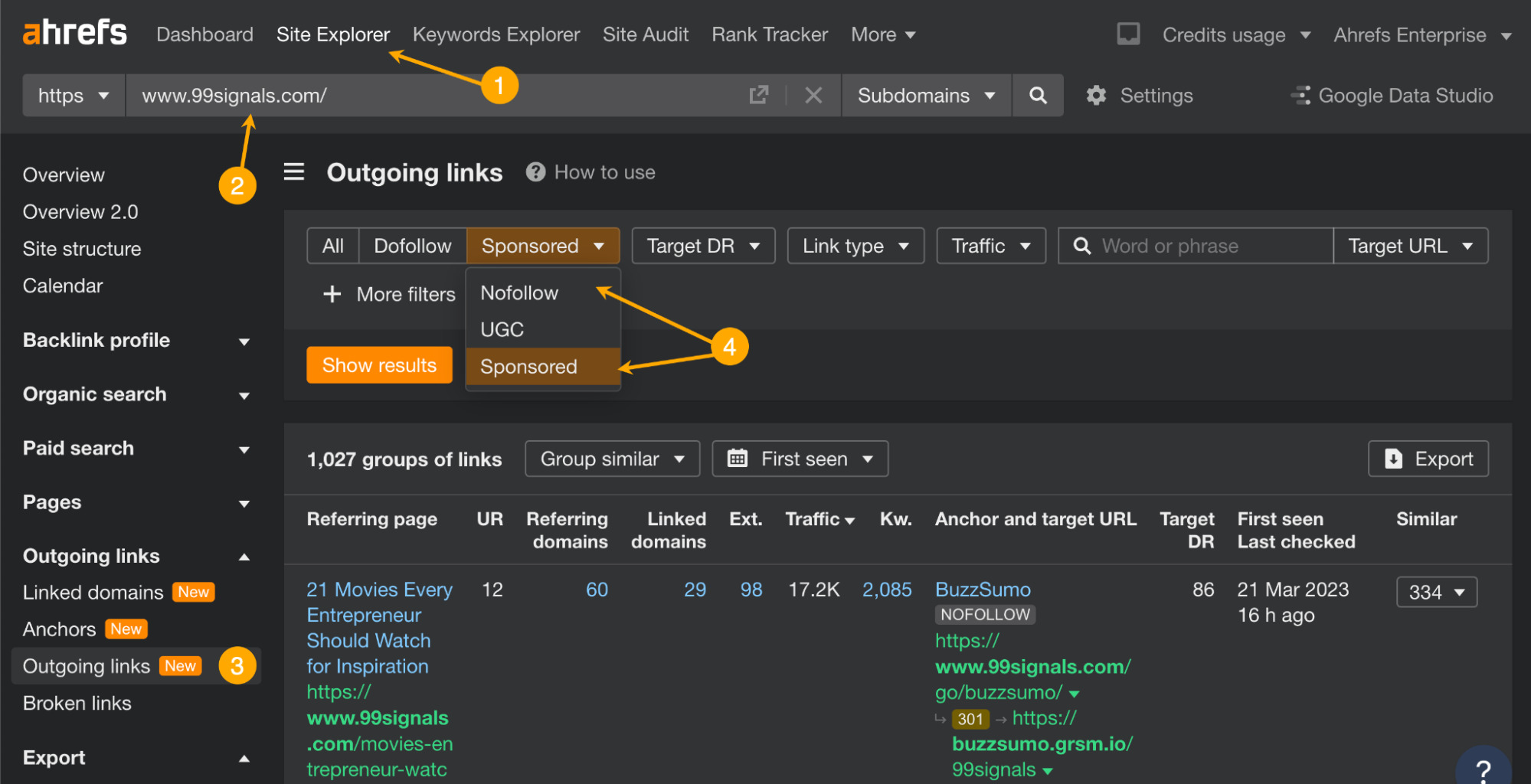
The first is Site Explorer. You can paste any URL and discover organic (and paid) keywords that the URL is ranking for.
The second is our Content Gap tool. It shows you keywords that your competitors rank for, but you don’t. It’s a shortcut to discovering good keyword ideas that you haven’t targeted already.
3. Discover high-performing content in your niche
You can also come up with good topics by researching already existing content instead of keywords. You can do that using Content Explorer.
The first technique is to look for pages that get high organic traffic without many backlinks (a key ranking factor, but they’re hard to get).
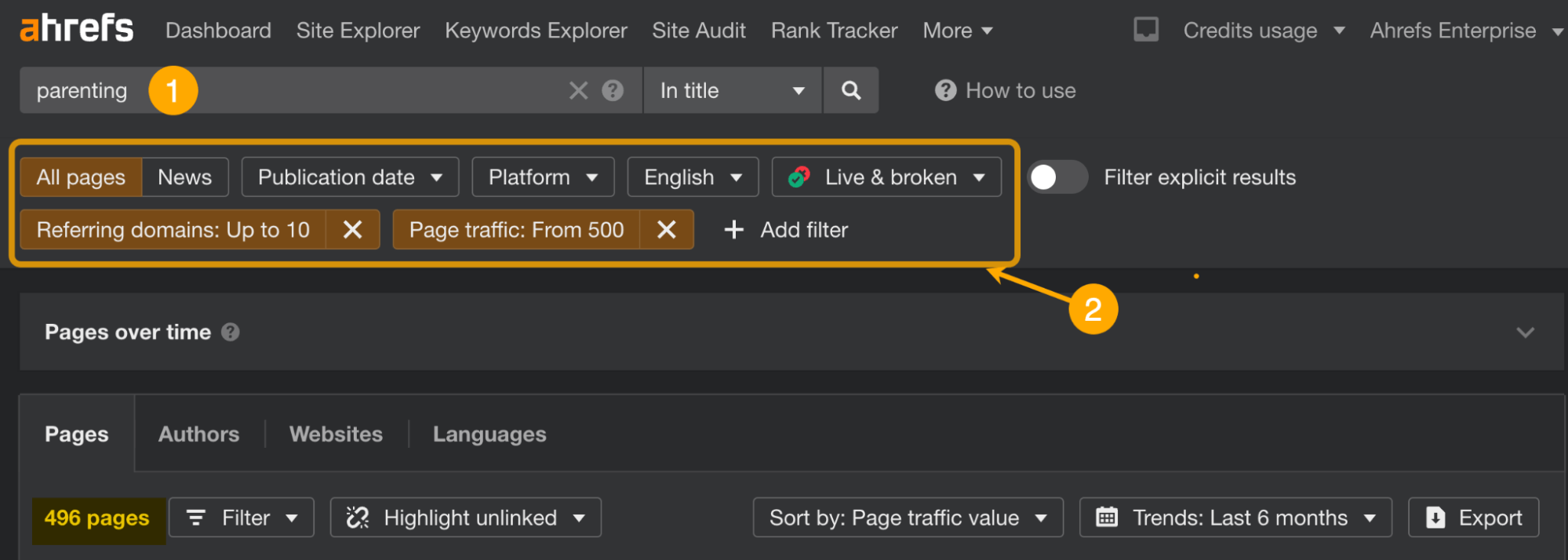
- Enter a topic and set the mode to “In title”
- Set the filters: Referring domains up to 10, Page traffic min. 500, and set the language you want the results in
The second technique is to look for content ideas that generate links. They won’t necessarily bring you a lot of traffic, but the links they can generate can boost your overall SEO.
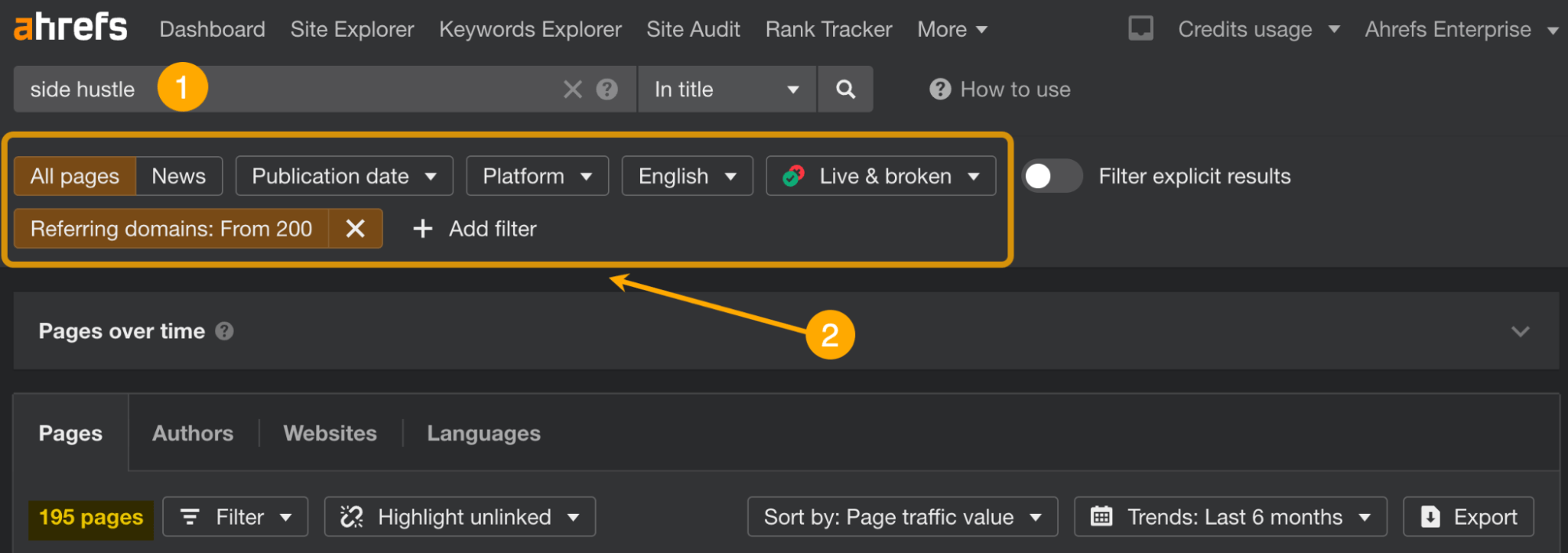
- Enter a topic and set the mode to “In title”
- Set filters: Referring domains from 200, the language of the page
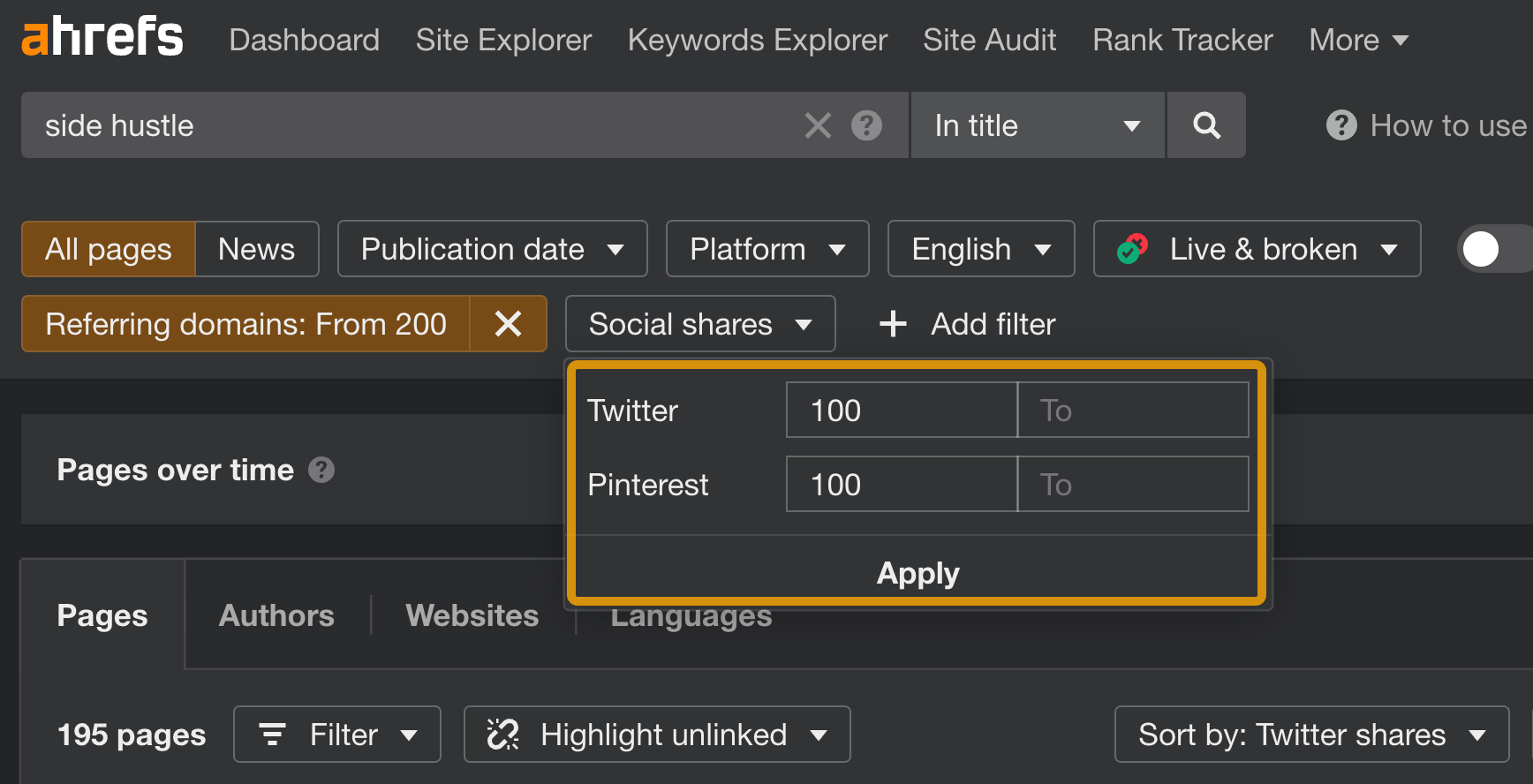
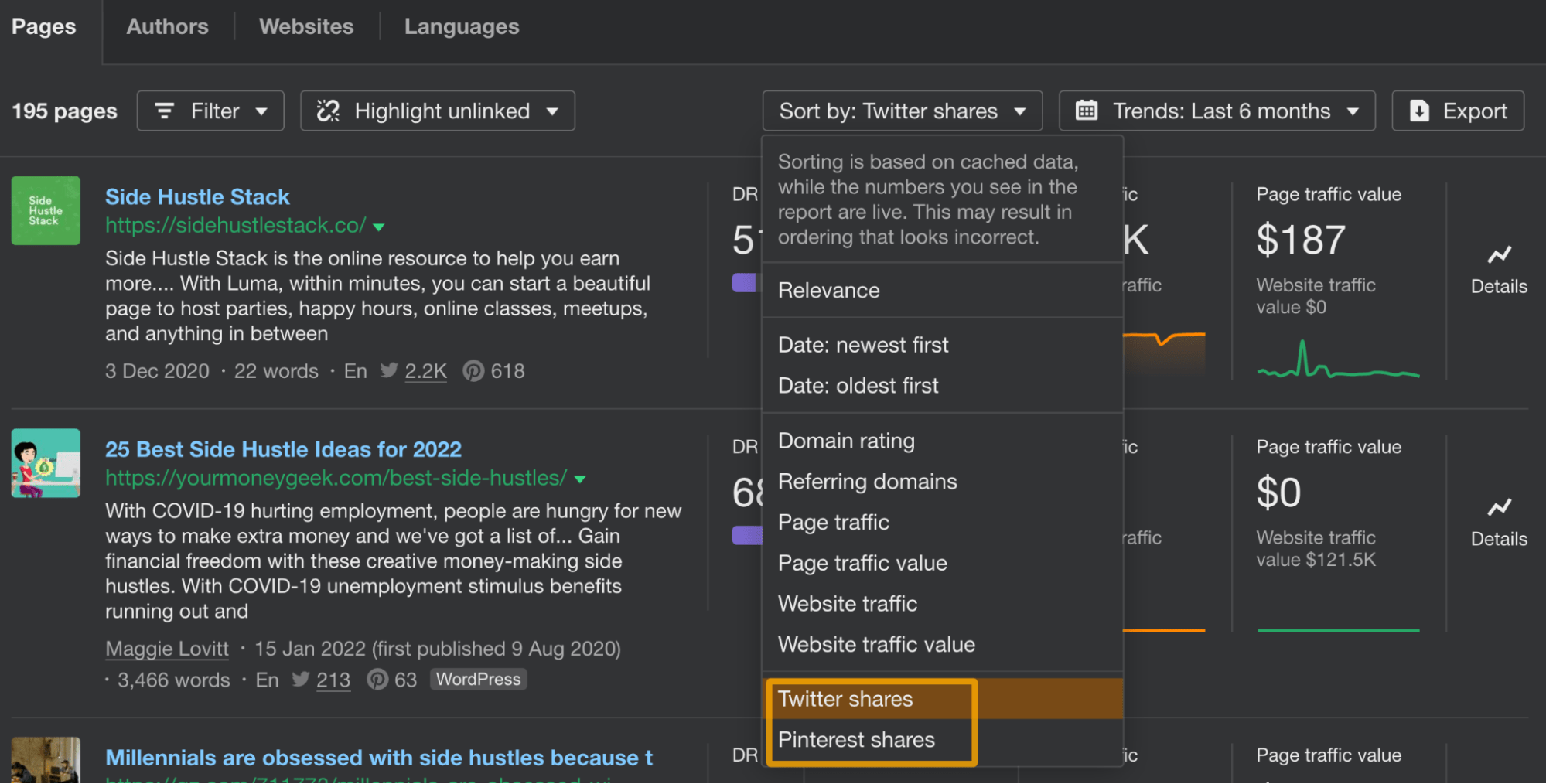
If you’re looking for content that did well on Twitter and Pinterest, there are filters for that too.
You can opt to show only pages with a minimum share number or sort the results by shares.
So how is money made in the blogging industry, actually? There are at least nine ways, and you can use most of them simultaneously.
1. Advertising
Advertising monetizes your traffic directly in the simplest way possible. The more traffic, the more you earn.
On average, bloggers make $0.1 to $0.5 per pageview from ad networks (source).
You can sign up with an ad network like Google AdSense directly or use an ad management platform (which seems to be the common solution). Some of the popular ad management platforms are AdThrive, Mediavine, and Ezoic.
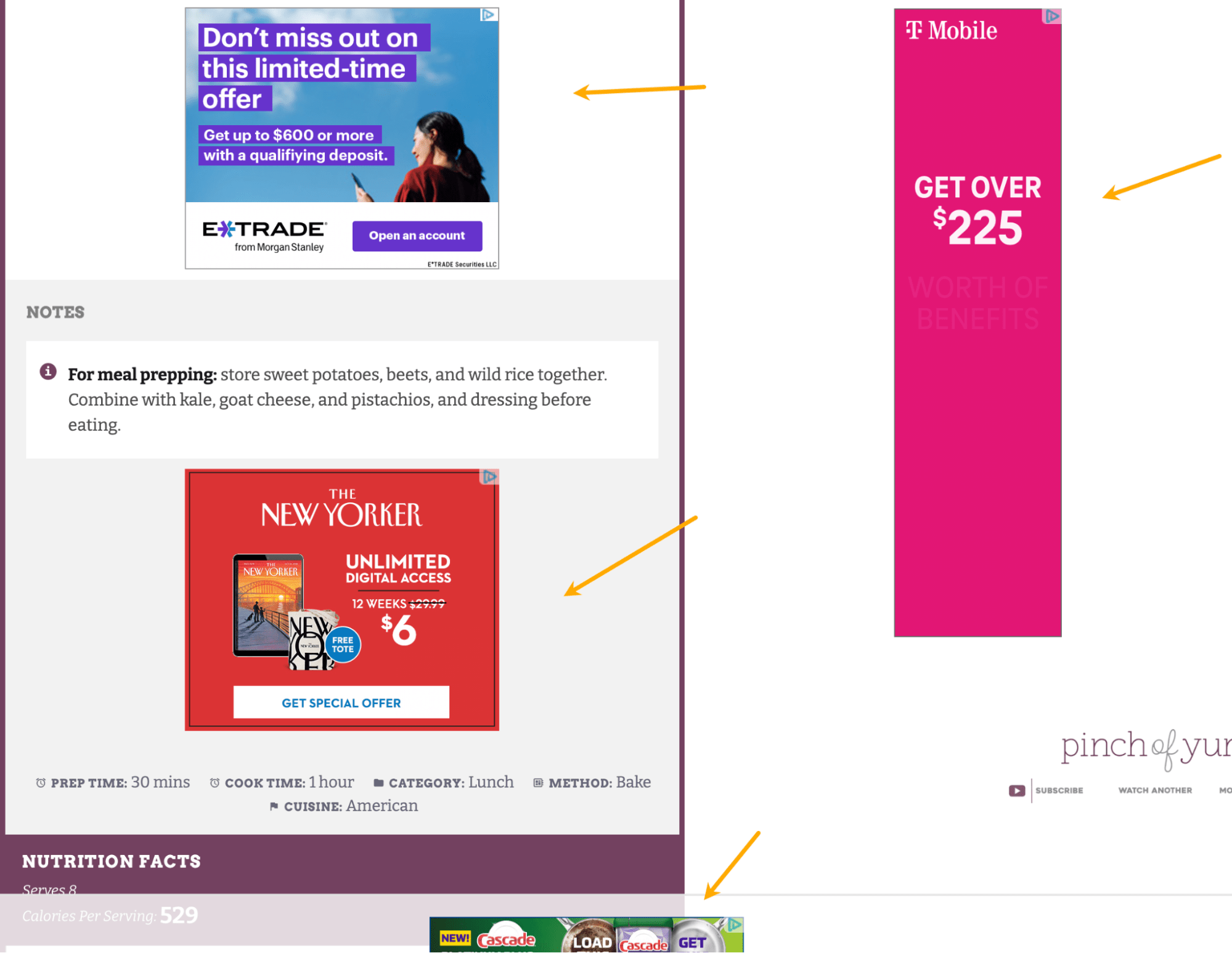
To illustrate, Pinch of Yum generated around 55% ($52,313.13) of its income from ads in November 2017. You can’t miss the ads on the website.
2. Affiliate programs
Affiliate programs allow bloggers to earn a commission whenever their visitors buy a product after clicking on an affiliate link. It’s earning money by recommending things.
With ads, you get paid based on the number of people that visited the page with the ad. But the bar is higher with affiliate programs—your content has to entice somebody to make a purchase decision. But you can potentially earn more through affiliates.
Plus, this method doesn’t clutter your blog with ads. Of course, you can use both methods.
Here’s an example. We visit Jennifer Maker where we see a guide on how to make a heart-shaped explosion box. Everything looks great, so we want to make that decoration. Here’s a shopping list with links to Amazon.
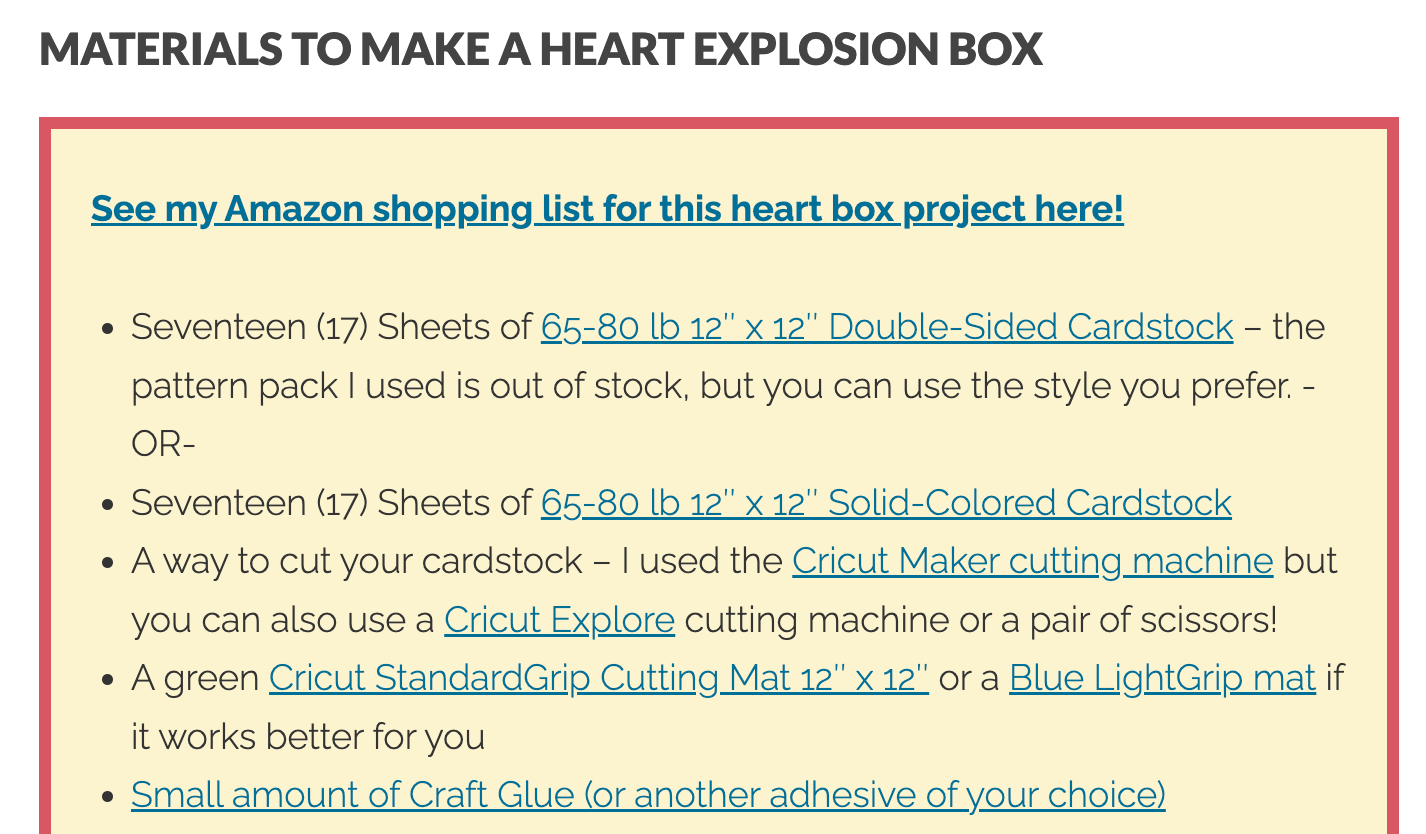
Each one has an affiliate program tag. So if we buy, Jennifer earns a percentage of that (which she discloses on her blog). Everyone’s happy.
Jennifer earned only 1.73% ($261.91) from affiliate programs in her last income report. But as we’ve seen earlier with the Smart Passive Income blog, affiliate programs can earn you a hefty sum and become the pillar of your income.
There are quite a few affiliate programs out there. Some pay as little as 3%, some 50%, and you can get up to 90% commission on rare occasions. A few popular affiliate platforms are Amazon Affiliate Program, ShareASale, and ClickBank.
Tip
3. Sponsored content
In this monetization method, you create one or a series of content pieces (articles, social media posts, newsletters, etc.) dedicated to promoting a single brand. It usually comes in the form of a product review, guide on using the product, or product placement.

It’s a deal based on participation. The visitor doesn’t need to buy the product, and you get rewarded per published content (and not views like with ads).
For example, Hot Beauty Health reported earning 39.37% ($3.8K) of her monthly income by doing six sponsored post campaigns (articles + social media).
Furthermore, she didn’t even need to reach out to the sponsors. They reached her through brand networks she signed up for.
Indeed, there are services where content creators can sign up and wait for the sponsored post opportunity to come or choose a partnership they qualify for and negotiate a deal. A few examples are IZEA, Impact Radius, or Captiv8.
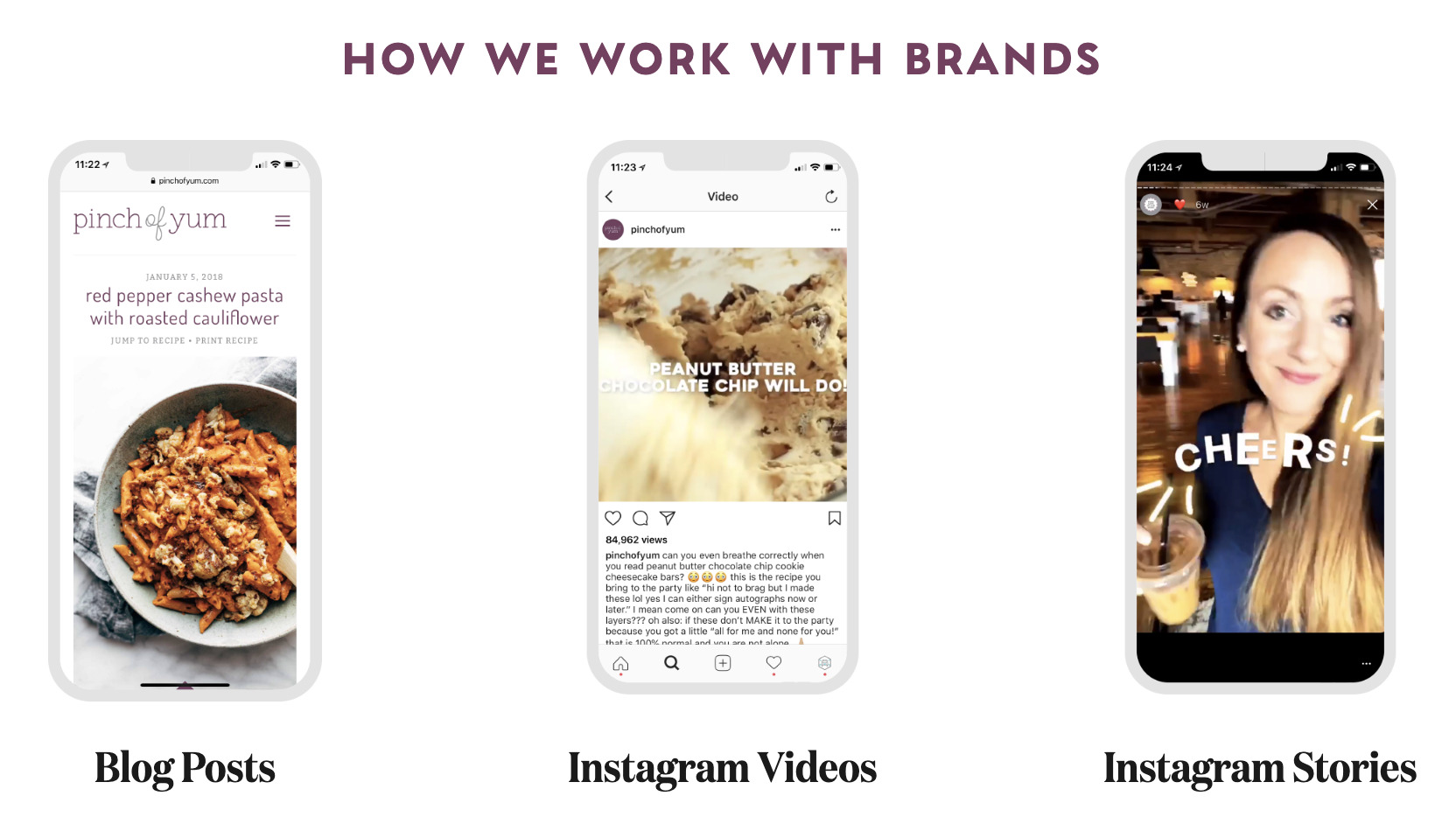
Of the monetization methods covered so far, this is the most “exclusive” one. How much you earn depends on your reputation in a particular niche, the quality of your content, and the size of your regular audience.
Once you get Pinch-of-Yum-famous (or even slightly less famous), you practically become an online magazine and can act like one:

4. Selling products
Your blog can be an e-commerce platform too. You can use it to sell others’ products or even your own products.
Well, “e-commerce” may be an overstatement here. Most bloggers don’t actually store products or even do dropshipping. They just make it look like a shop.
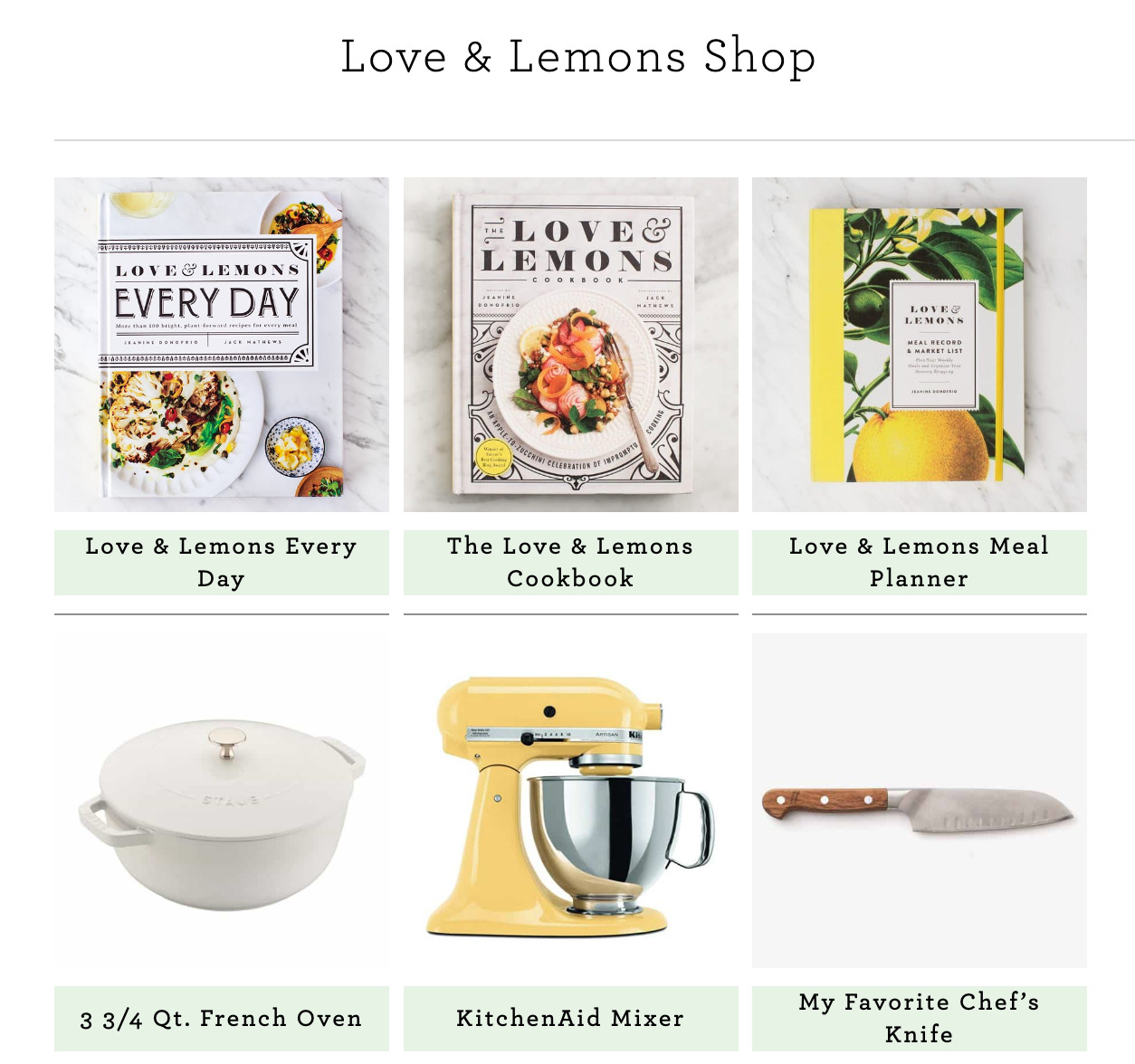
For example, at Love & Lemons Shop, all the links lead to Amazon. The first three products are original; the rest are third-party products with affiliate links.
Here’s another example. The Financial Samurai used the blog to create and promote his best-selling book “Buy This Not That.”

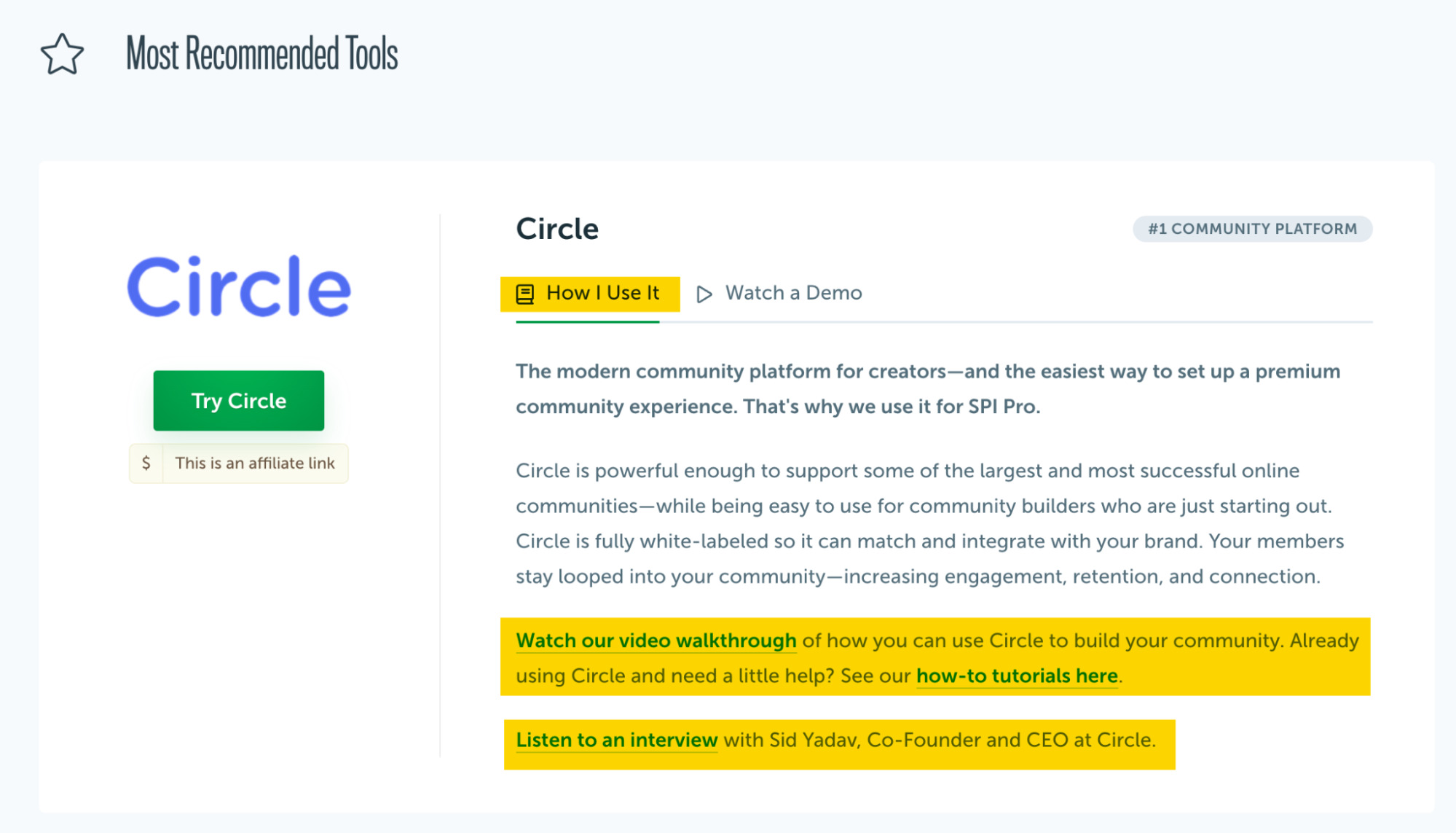
Here’s an interesting example from Smart Passive Income. What is essentially a directory of affiliate links feels like the best shopping experience for tools for online entrepreneurs. All thanks to SPIs’ original content and reputation.
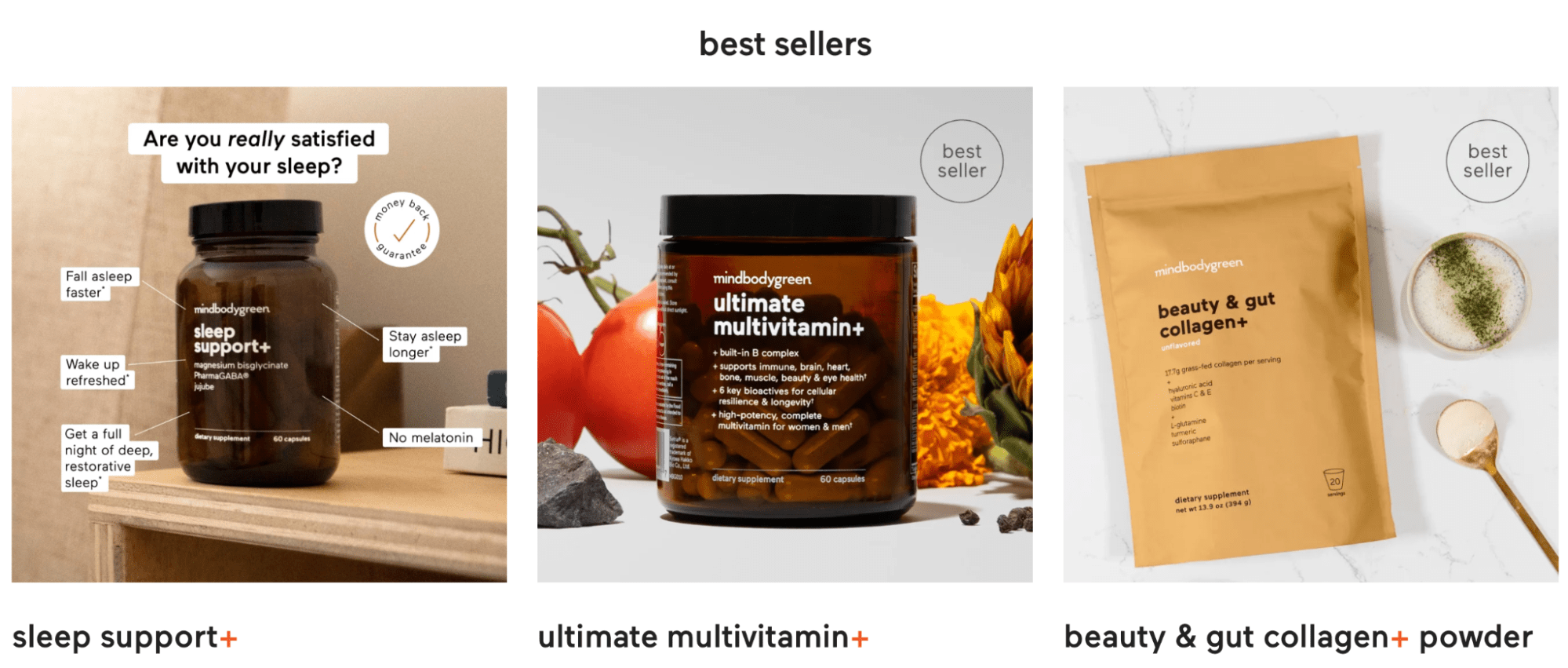
Can blogs sell their own physical products through their own stores? Sure, mindbodygreen supplements are a good example.
5. Online courses
A very popular option among bloggers.
Interestingly enough, one of the most popular types of courses I’ve seen so far is online entrepreneurship courses, such as making money by blogging.
Online courses, like any other original products, are in the sky-is-the-limit category when it comes to income. To illustrate, Melyssa Griffin earned “only” $25,572 from affiliate programs while a staggering $258,108 from an online course. In one month.
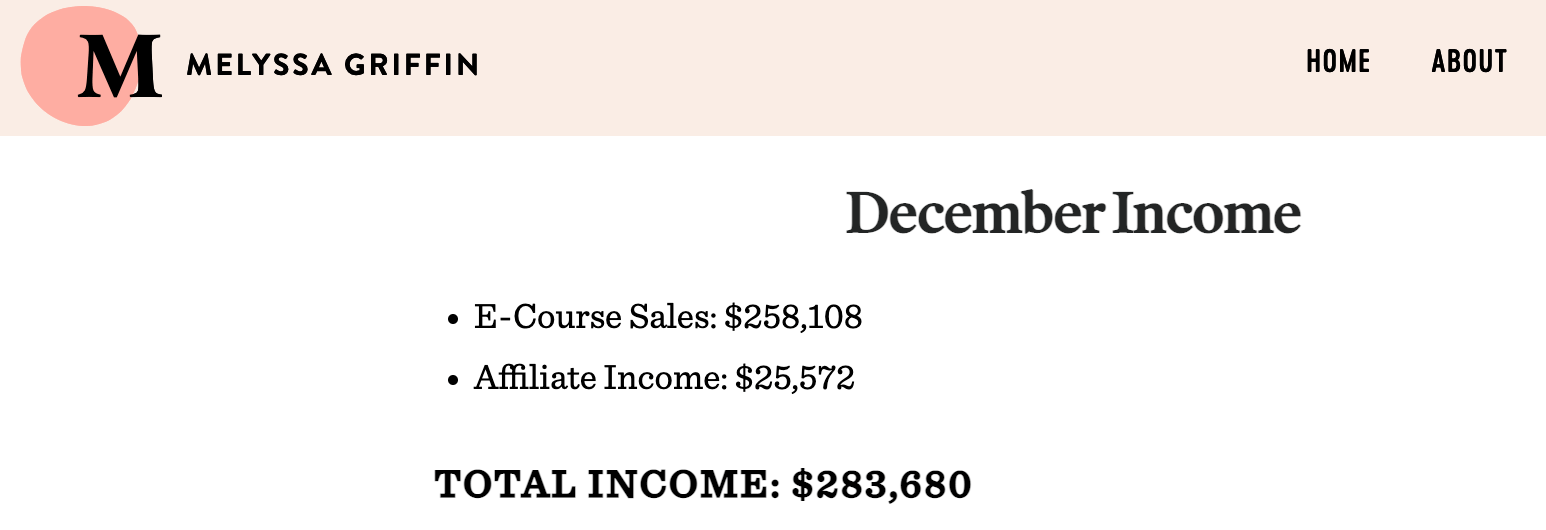
All you need to create an online course is your original content. There are affordable tools that will cover the tech side and payments for you, such as Teachable, Thinkific, Kajabi.
6. Subscription-based membership
With this method, you’re offering access to special content or a community gathered around the blog on a recurring payment plan.
To illustrate such a business model, let’s go back to Gala Darling. On the blog, Gala shares her life philosophy and teaches personal development techniques, self-love, and empowerment.
She also offers two subscription packages priced at $44/mo and $99/mo. Subscribers get access to exclusive content and a community for group EFT tapping (an actual self-healing method, despite the appearance).
There is an entire blogging platform based on this monetization method: Substack. This is one of your options for monetizing a blog too.
The benefits of using Substack are it is a turnkey publishing platform with built-in payments and support; you can also get subscribers within the Substack network. However, you won’t be able to run ads or add affiliate links.

Just like with ecourses, the tools for paid communities are already there. Try Patreon, Memberstack, Slack, or even Facebook.
7. Events and speaking
Some people who run personal or personal brand blogs offer others the ability to hire them for events and speaking.
But this is a monetization method with a high entry barrier. You need to be a recognizable figure in your niche. But once you’re there…
… you could be like Tom Bilyeu of Impact Theory and earn up to $100K in speaking fees (source).

8. Coaching and mentoring
Unlike public speaking, you don’t need to be famous to offer paid coaching. You just have to be really good at what you do—and your blog can prove it.
Actually, your blog can prove that you’re good at blogging, and that is the value you can monetize. That’s exactly what Practical Wanderlust does:

Coaching and mentoring can be the perfect monetization option if your blog is about solving professional challenges: marketing, web design, management, SEO, and so on.
9. Selling the blog
Last but not least, you can make money by selling the blogs you own.
Selling the blog can be your goal from day one. Or if after some time you decide that blogging is not for you, you don’t need to bury everything. Someone may be interested in buying the blog, even if it’s for the domain and links that you earned.
To illustrate: On Flippa, at the time of writing, there are 1,134 blogs for sale selling for as high as $4.7M.

You don’t even have to start a blog from scratch to sell with profit. You can “flip” a blog: buy a blog that already makes some revenue, improve it, and then sell. Repeatedly.
Before we wrap this section up, there may be even more ways to monetize than the mentioned nine (depending on the niche). For example, according to Pinch of Yum’s ebook, there are as many as 16 ways you can monetize a food blog. Did you know that you could make money by developing recipes and licensing them?
Final thoughts
So now you know what types of blogs can generate an income, how to find traffic-generating topics even if you don’t know anything about the niche, and nine ways to monetize your blog (or blogs).
But how about actually writing a blog post? We’ve got you covered—check out our guide to writing blog posts that people will actually want to read.
What’s next? Learn how to promote your blog through various marketing channels and a number of tried and tested tactics:
Got questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter or Mastodon.



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













