SEO
Parasite SEO Explained (It’s Not Always Evil!)

Parasite SEO can help you rank for more competitive keywords, rank faster, and get more traffic to your content.
But do these benefits come at the risk of a Google penalty?
It depends…
Parasite SEO is where you leverage the authority of an established website to rank for competitive keywords. You do this by publishing content on the high-authority website instead of your own.
There are obviously pros and cons to this approach:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Not always. But often, yes.
Most SEOs doing parasite SEO opt for a “churn and burn” approach. This is where they pay for a sponsored post on one site, reap the rewards while they last, and then move on to publishing on another site when Google penalizes the first one.
If you’re wondering why Google might penalize sites for publishing this content, it’s because of something called site reputation abuse:
Site reputation abuse is when third-party pages are published with little or no first-party oversight or involvement, where the purpose is to manipulate search rankings by taking advantage of the first-party site’s ranking signals. Such third-party pages include sponsored, advertising, partner, or other third-party pages that are typically independent of a host site’s main purpose or produced without close oversight or involvement of the host site, and provide little to no value to users.
Put simply, it’s when established sites publish junk content from parasite SEOs en masse. You see it happen a lot with local newspapers as they try desperately to compensate for declining advertising revenue with other revenue sources.
It “works” for a while, but eventually, these sites get caught by a Google update.
This is exactly what happened to Outlook India (don’t worry, it’s not a site anyone knows about outside the black-hat community!). In 2023, it was a parasite SEO’s dream, seemingly able to rank high for pretty much any topic. It published content about everything from “best mushroom coffee” to “best dating sites” to “best nootropics.”
But the party was short-lived. It got penalized in September 2023 and traffic fell off a cliff:
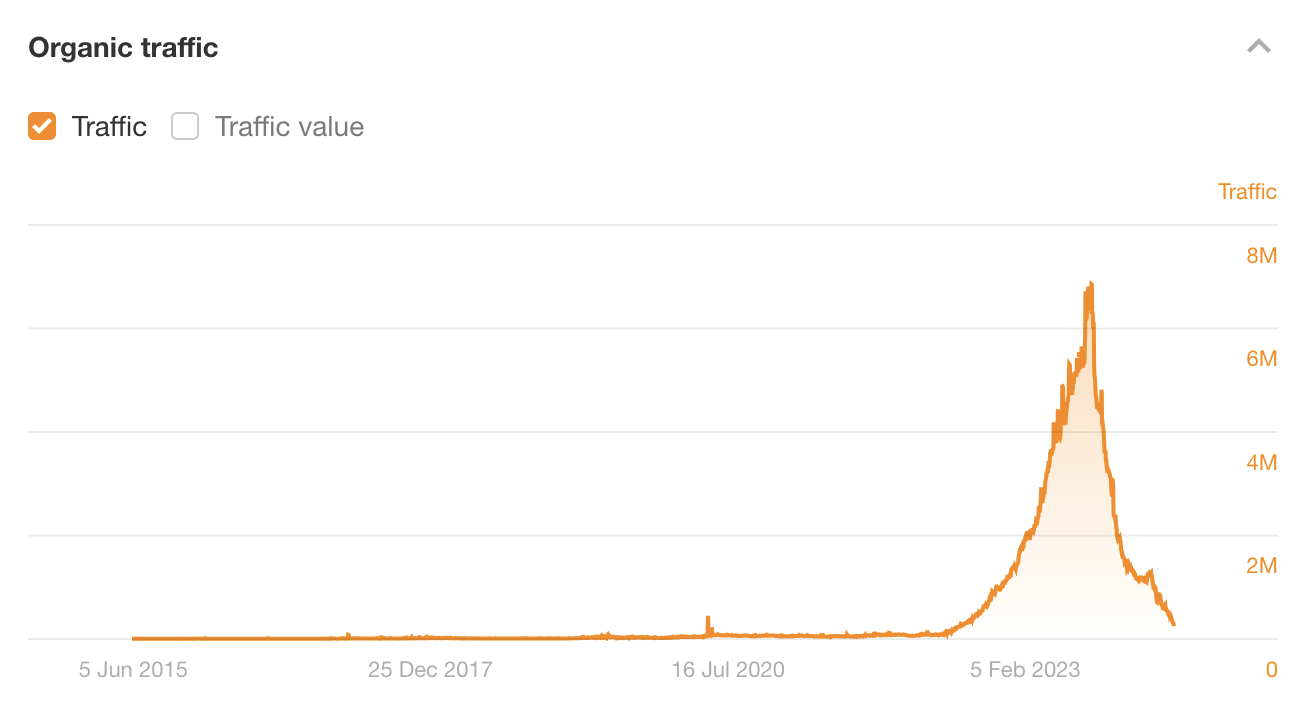

This is just one of countless similar examples over the years, and it’s why black-hat parasite SEO is risky. Unless you know what you’re getting yourself into and are happy to play the “churn and burn” game, I wouldn’t touch news sites like these with a barge pole.
But there is a white-hat alternative: writing guest posts about competitive topics for well-known blogs in your industry. There’s nothing wrong with doing this. I’ve done it before and had great success with it (more on that later).
Sidenote.
People often refer to the white-hat version of parasite SEO as barnacle SEO. Makes sense… but also I think SEOs need to stop coming up with silly names for every slight variation of tactics 😉
Let’s take a look at a few examples of parasite SEO. Specifically, a black-hat, grey-hat, and white-hat example. I want to show you that the tactic itself isn’t unethical but rather the way it often gets used.
Black-hat: Outlook India’s page on the best free movie streaming sites


Between July and December 2023, this page on Outlook India attracted between an estimated ~25K and ~377K search visits per month!
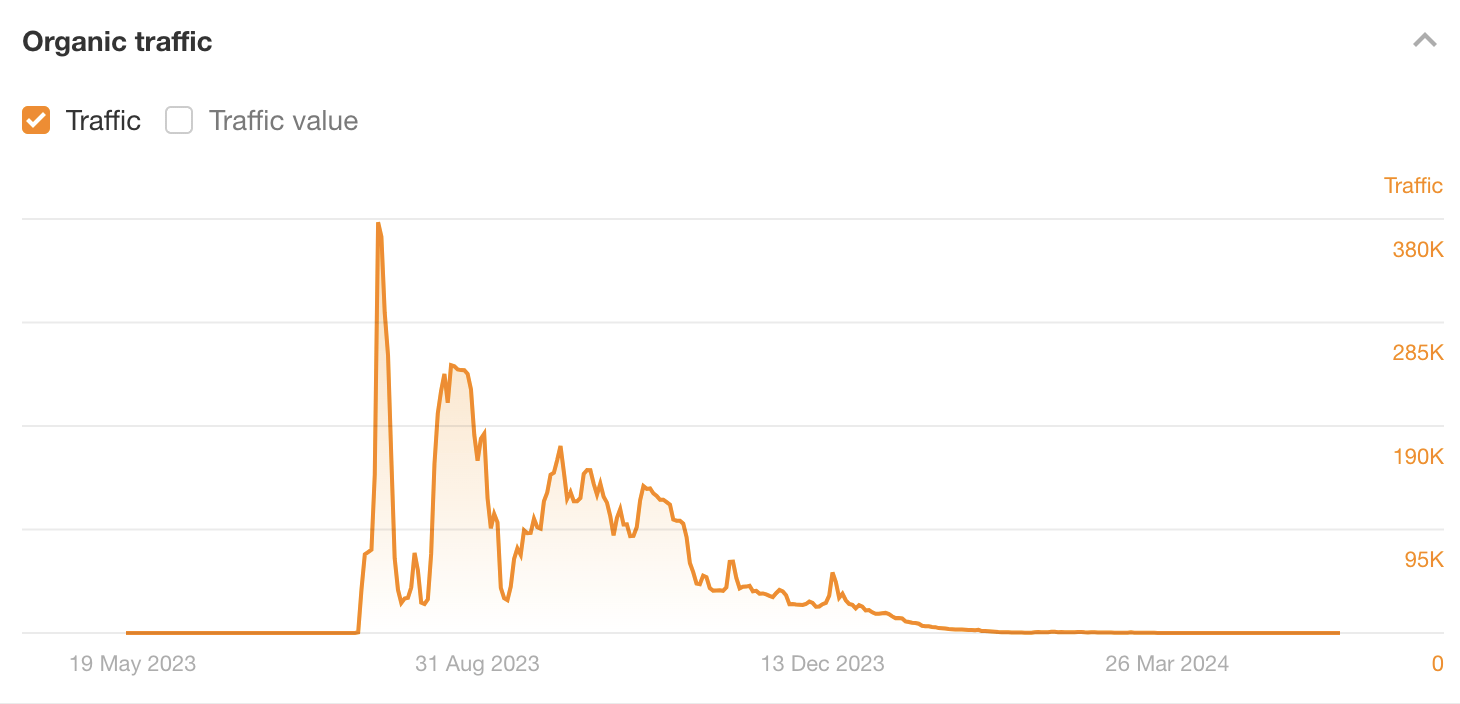

Although the page did not declare sponsored content, it was clearly that, as the piece contained multiple very dodgy links to a movie-streaming service. It was trying to turn traffic into users.


The content was also absolute trash. ChatGPT could write better.
Sidenote.
The site these links went to isn’t even indexed by Google anymore, so I assume it was pretty sketchy!
Grey-hat: Washington City Paper’s post on the best essay writing services
A marketing agency used parasite SEO to rank for “top essay writing service”—a highly competitive keyword with a Keyword Difficulty (KD) score of 87 and only high-authority websites ranking in the top 10.
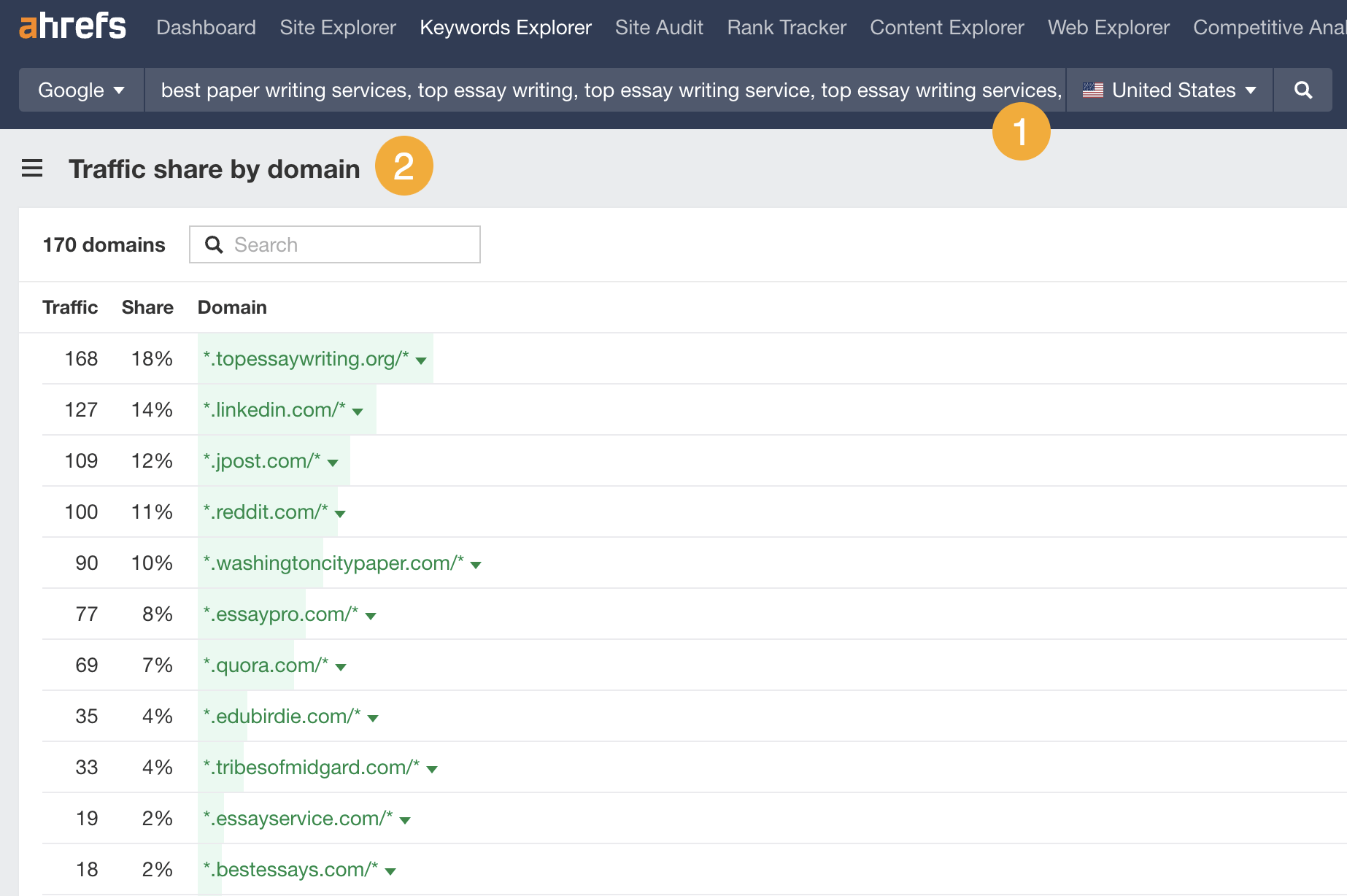

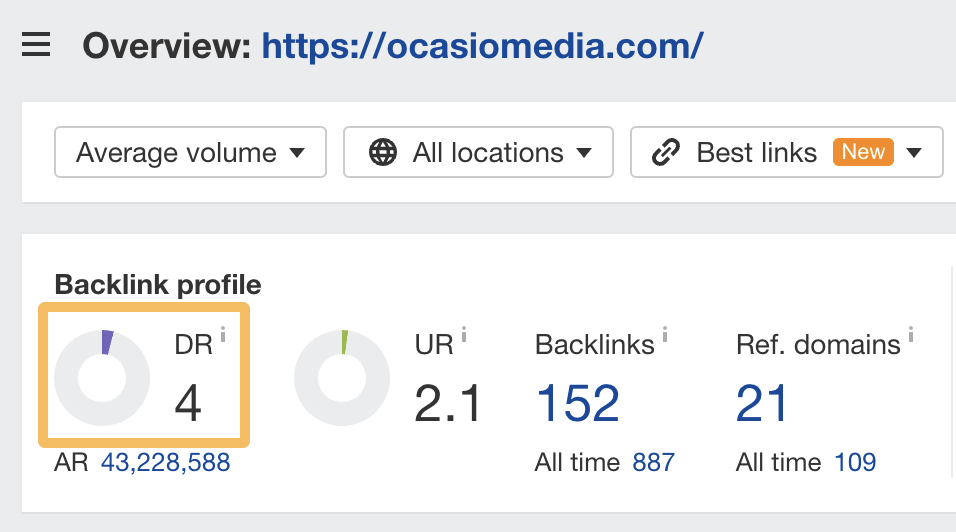
They did this by publishing a sponsored post on a strong DR 80 site: washingtoncitypaper.com.

It’s likely that this helped them to rank faster and more easily compared to publishing on their low-authority DR 4 website:

How did this benefit them?
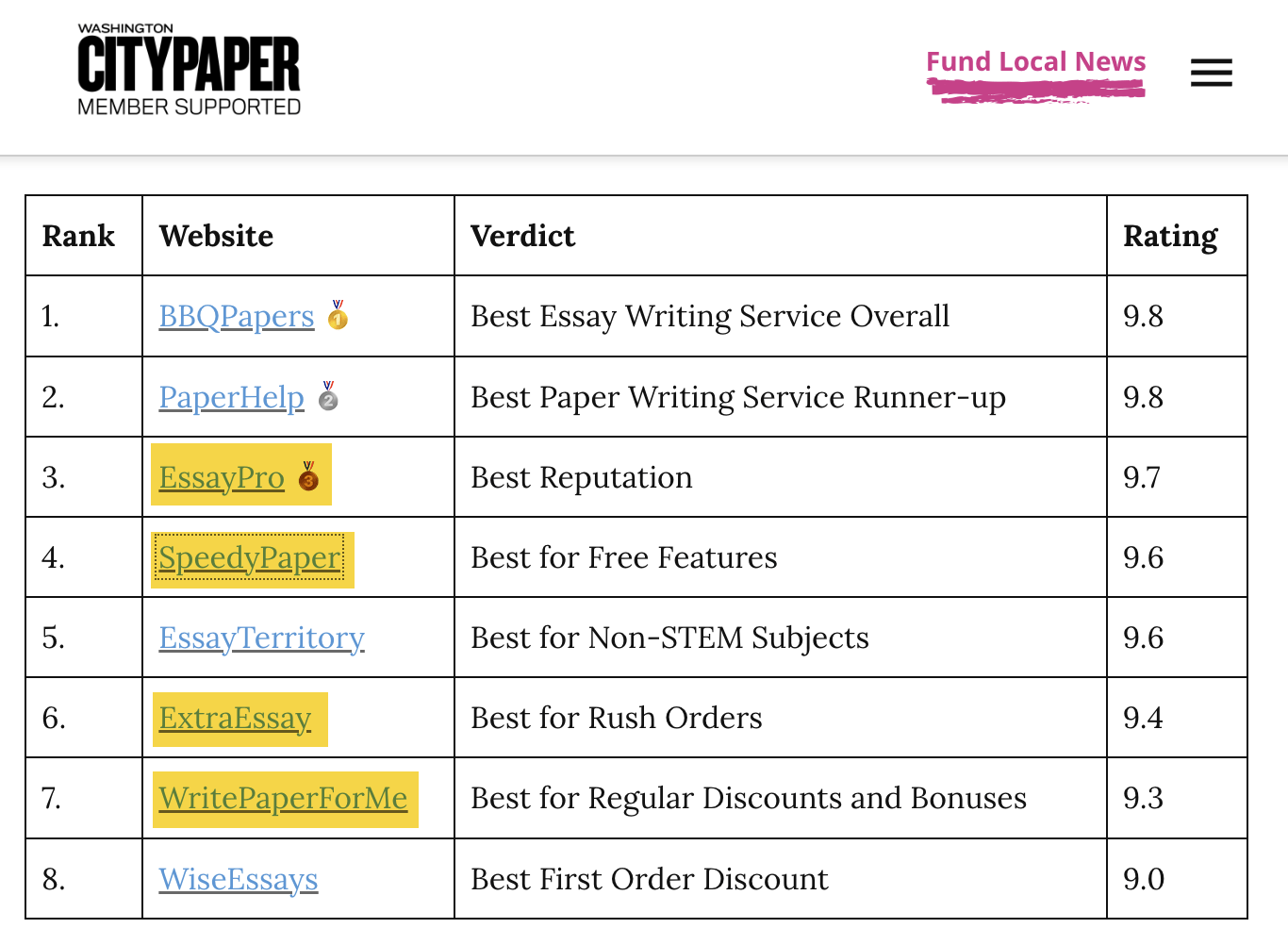
Their post features a list of links to top essay writing services—half of which are monetized with affiliate links (see the highlighted ones below):

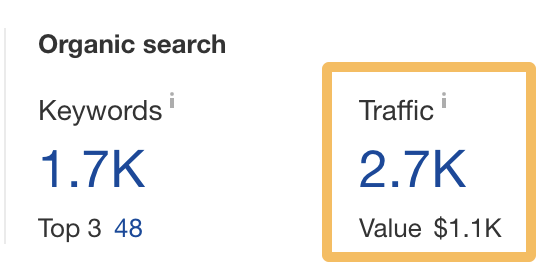
According to Ahrefs, this page gets an estimated 2.7K monthly visits from organic search…

… and one of the affiliate programs has a 60% commission on first orders over $60:


Even if we assume that only 1% of those 2.7K visits result in an affiliate conversion of $60, that’s potentially ~$1K/month in affiliate revenue for the agency.
White-hat: Moz’s blog post on SEO services
In 2015, Ryan Stewart published a post on the Moz blog about why he stopped selling SEO services.

This ranked for the keyword “SEO services” (as well as many others) for years—getting thousands of monthly organic visits as a result.
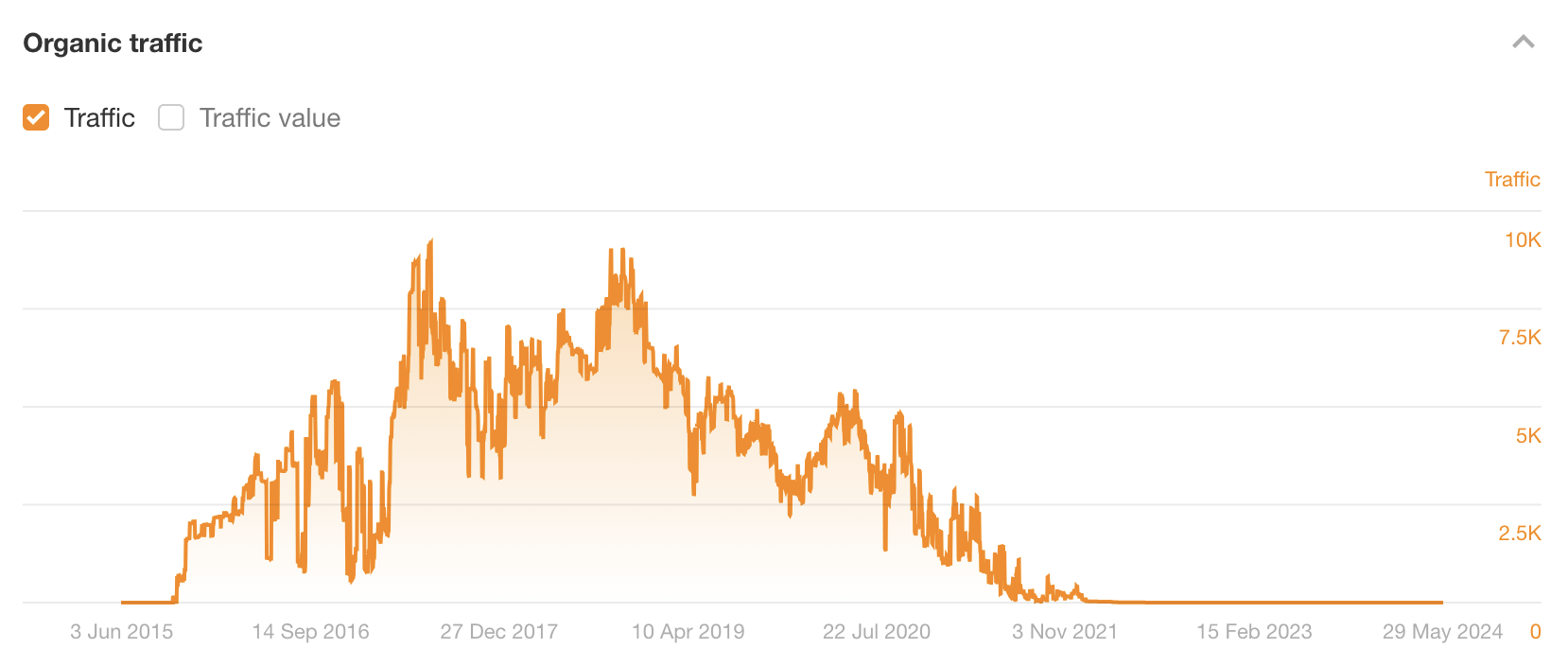

The estimated organic traffic graph above shows that the post’s traffic only dropped off in 2021. It ranked pretty well for almost six years before that.
At the time of publishing, Ryan ran WEBRIS…
Here’s the difference in WEBRIS and Moz’s Domain Rating (DR) at the time of publishing:
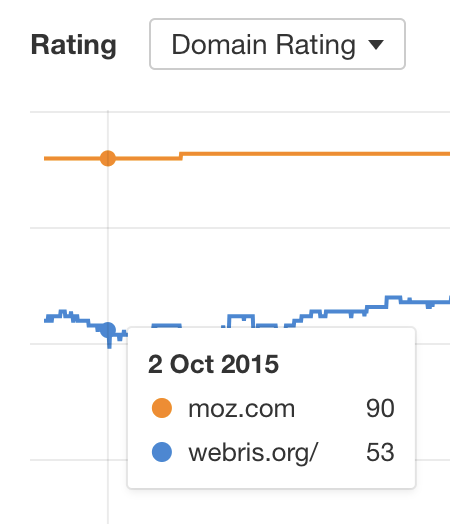

Given that DR is logarithmic, DR 90 is massively more authoritative than DR 53. This is likely part of the reason Ryan’s post ranked so quickly and for so long. It probably wouldn’t have done quite as well if he had published it on his own website.
What did Ryan get out of this? Unlike black-and-grey hat parasite SEO, the game here wasn’t to directly monetize the content. It was to build Ryan’s personal brand and establish thought leadership in the space. After all, Moz has a lot of readers.
Parasite SEO works for a mix of three reasons:
You benefit from the site’s ‘authority’
Google representatives have said many times that website authority isn’t a ranking factor. But what is a ranking factor is PageRank (PR). Despite being decades old, Google still uses this to help rank websites—and high-authority sites have more of it than low-authority ones.
For this reason, the average page on a high-authority website has more ‘authority’ than the average page on a low-authority website. This is because internal links to the page send it more PageRank.
You benefit from the site’s ‘topical authority’
If you’re posting on a site with lots of content about a particular topic (as big sites often have), your post will likely have internal links with relevant anchor text from lots of similar content. This helps build “topical authority” because Google uses anchor text to help rank web pages.
Google employs a number of techniques to improve search quality including page rank, anchor text, and proximity information.
You (might) benefit from the site’s ‘brand equity’
People want to see results from websites they know and trust, right? This likely means that big, credible sites will have an easier time ranking in search because searchers trust them more than small unknown sites. (Or maybe it’s just because Google favors big sites these days?)
If you’re sold on parasite SEO and want to try it, there are only four steps to the process.
1. Find high-authority websites ranking well in your niche
The best contenders for parasite SEO are websites already ranking well for the types of keywords you want to rank for. Here’s a quick way to find these sites in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer:
- Enter a handful of similar keywords to what you want to rank for (10-20 is plenty)
- Go to the Traffic Share by Domain report


This report shows you the sites getting the most combined traffic from the keywords you entered. For example, the sites above all rank well for keywords related to the best essay writing services.
2. Pull out the best opportunities for parasite SEO
For a website to be a potential candidate for parasite SEO, it needs to be open to publishing guest posts, sponsored content, or be somewhere you can self-publish like Reddit or LinkedIn Pulse.
It’s easy to spot the websites that allow self-publishing; there are a few on our list:
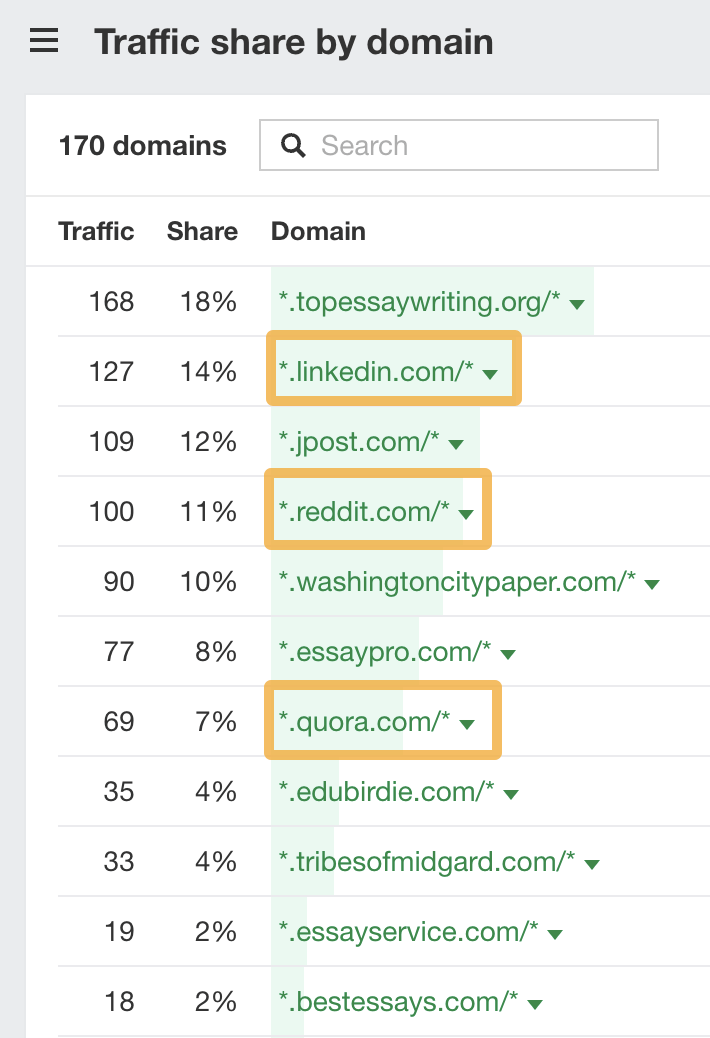

The rest of the sites will typically fall into one of three buckets:
- Competitors
- Niche blogs
- Newspapers/magazines
Competitors are bad candidates for parasite SEO because they’re unlikely to publish your content—even if you’re willing to pay them. There’s no incentive for them to do this because they’d just be helping a competitor.
Niche blogs are good candidates if they’re likely to be open to guest posts (like the one from Ryan Stewart in the previous section). This is probably the case if there are numerous authors with just one or two posts in the last few months.
Here’s an easy way to check for this using Ahrefs’ Content Explorer:
- Search for
site:theirwebsite.com - Filter for pages published in the last 90 days
- Go to the Authors tab
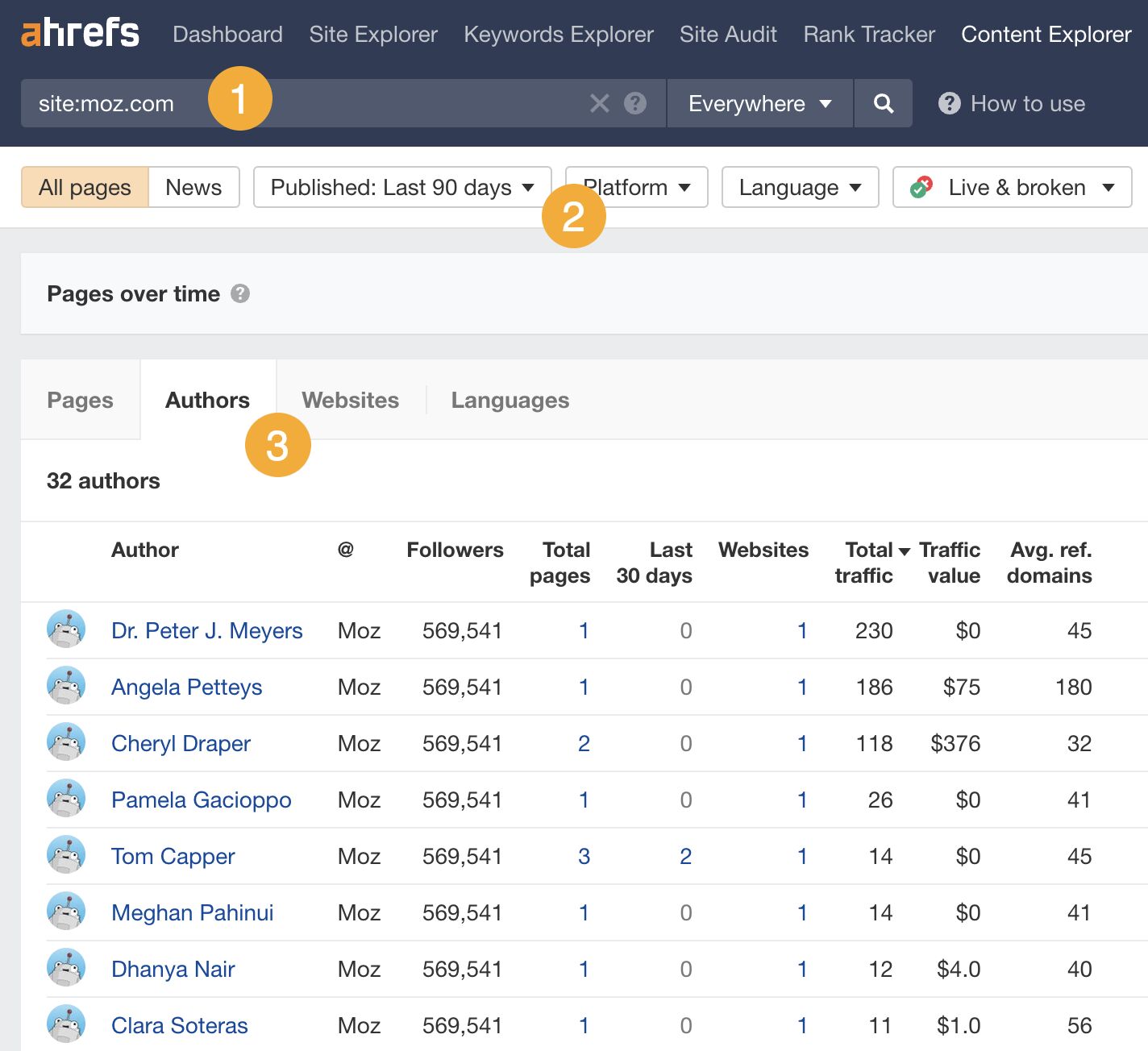

In the example above, Moz has published posts from 32 different authors in the last 90 days—each of whom has only published 1-2 posts. This is a strong sign that they accept guest posts.
Newspapers and magazines are good candidates if you’re happy to pay for sponsored content and understand that the website will probably get penalized by Google at some point. (More on this in the section on black-hat vs white-hat SEO).
Want to find easy parasite SEO opportunities on Reddit?
Instead of starting new Reddit threads and hoping they rank, look for threads that already rank and leave a useful comment. Here’s how to find such threads in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer:
- Enter reddit.com
- Go to the Organic Keywords report
- Filter for
- URL contains comments (this excludes subreddit homepages)
- Top 5 rankings
- Keywords you want (e.g., ones containing “essay”)
- View “Main positions” only (this removes the discussion and forum results)
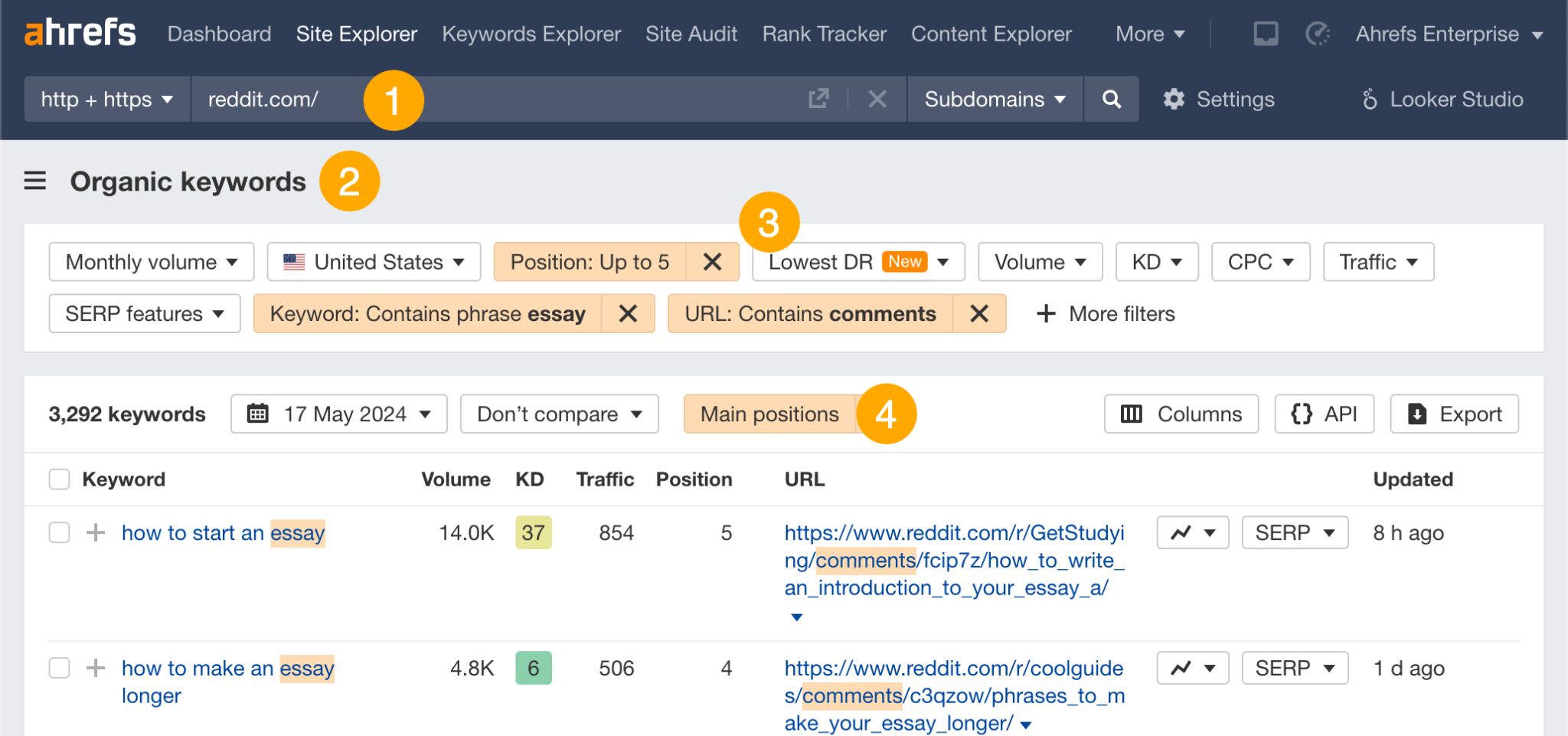

Click through to the Reddit threads in the results and leave comments where it makes sense.
3. Publish optimized content on the site
It’s now time to get some content onto the sites you found.
With places like Reddit and LinkedIn Pulse, this is pretty straightforward. You simply publish content there with little to no gatekeeping.
For newspapers and magazines (i.e., the black/grey-hat route), you need to reach out and ask if they’re open to a sponsored post. In other words, you’ll have to pay to get your content live in such places.
If you’re going after niche blogs, reach out and pitch a guest post (don’t offer money). Remember to choose a competitive topic with search volume as the whole point of parasite SEO is to take advantage of “strong” sites to rank for keywords you’d otherwise struggle to rank for.
This is exactly what I did back in 2013 (yes, over a decade ago!) when I ran a very small video production company with my brother. Because our site was brand new and weak, there was a slim chance of us ranking for a competitive term like “video SEO”—so I wrote a guest post for Kissmetrics instead:

This post ranked for years, and attracted significant search traffic until June 2018 (that’s over 5 years after I wrote it!)
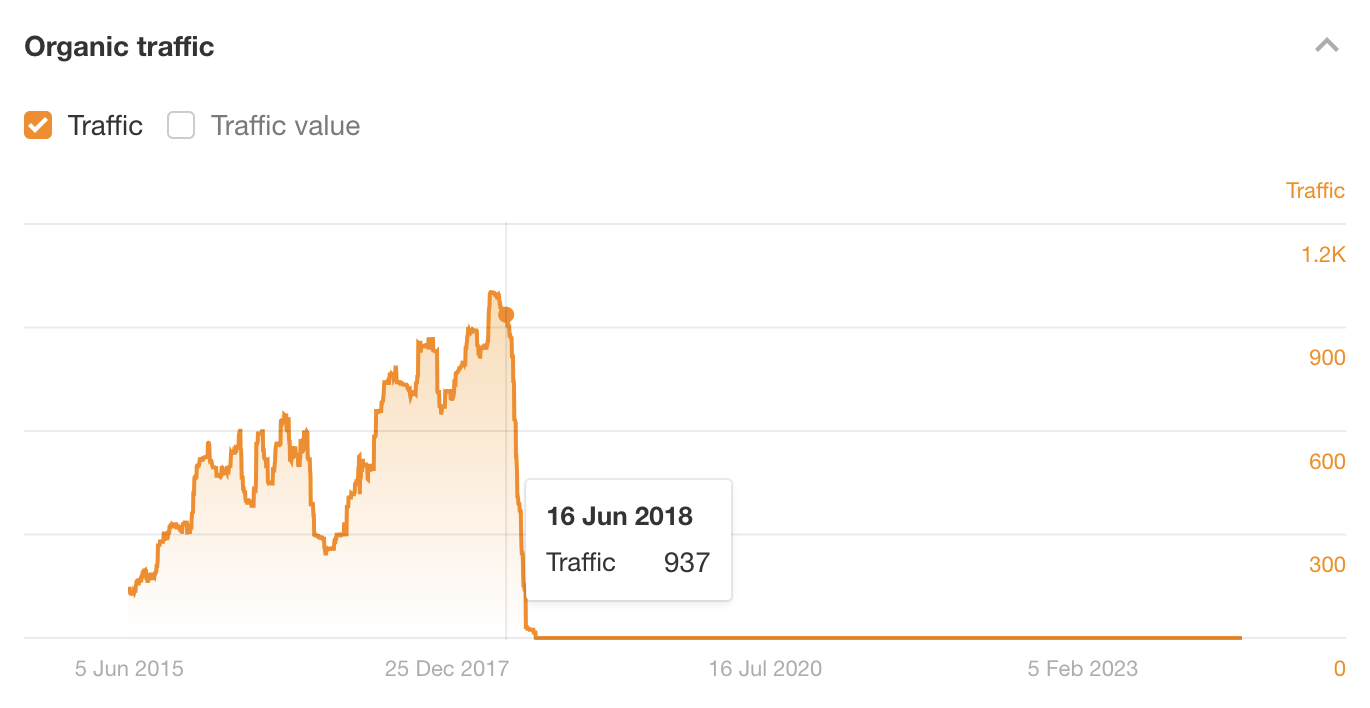

In fact, the only reason traffic appears to fall off a cliff in 2018 is because Neil Patel bought Kissmetrics and moved the content to NeilPatel.com. My post is actually still ranking there to this day!
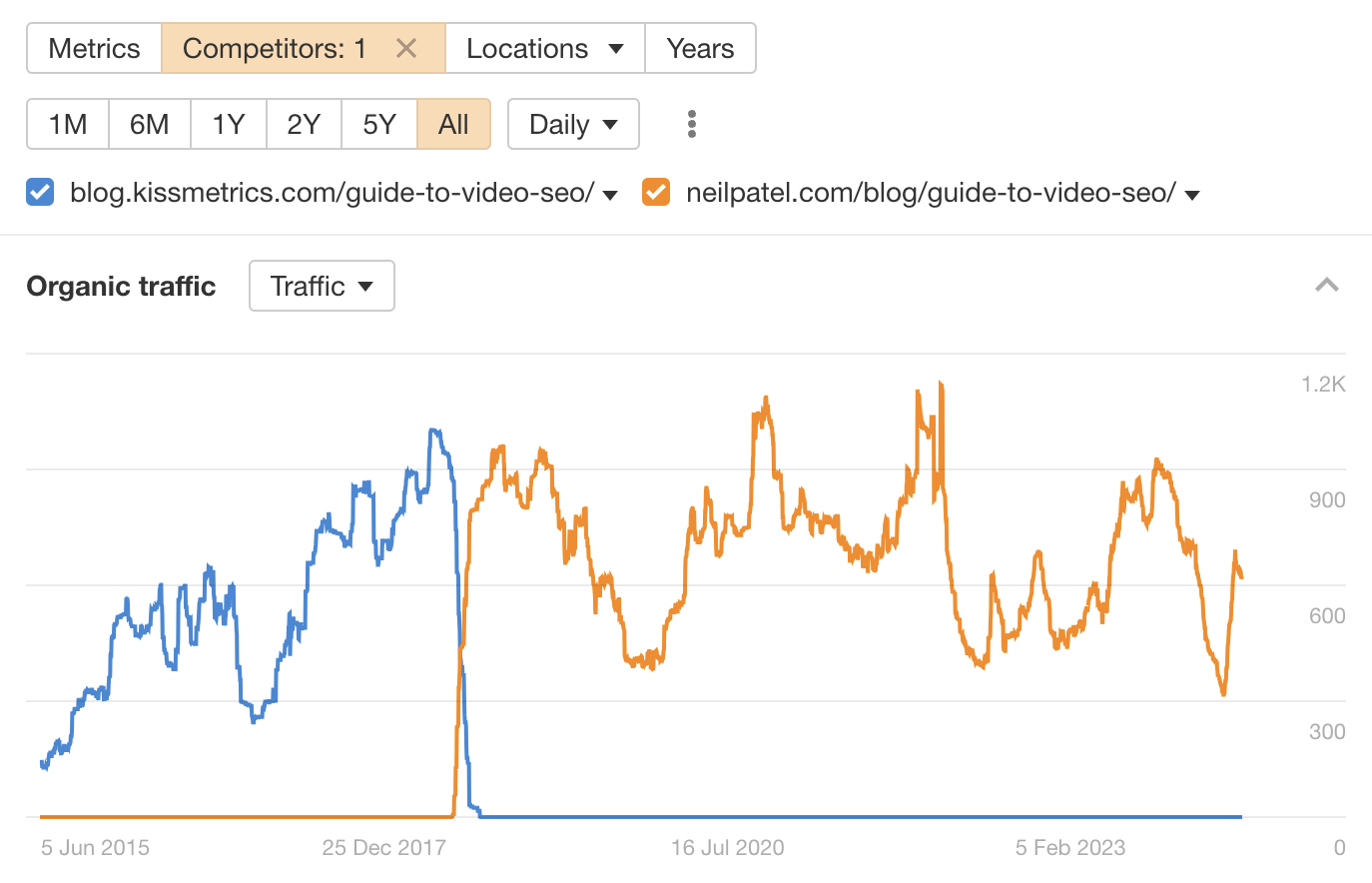

This wasn’t entirely a fluke, though. It stood the test of time largely because I wrote an optimized post that matched search intent and followed SEO best practices.
Check out the resources below to learn more about creating optimized content.
4. Build links to your content (optional)
Posts published on “strong” websites will often rank well without links, but not always. In this case, building a few links to your post can sometimes make sense to give it a nudge in the right direction.
Why only sometimes? Two reasons:
- Link building is a lot of work. Unless you’re buying links or building bad links (don’t do this!), link building is hard. If you’re going to go to that effort, it’s probably better to publish content on your own website and build links to there.
- It might be a waste of time (and money). If you’re doing parasite SEO on news websites, they’ll probably get penalized at some point. If this happens, all that hard work building links will be for nothing.
If you still want to build some links to your parasite post, check out the resources below.
Final thoughts
Parasite SEO (or barnacle SEO, or whatever you want to call it) isn’t always bad.
Sure, it’s most commonly used by black-hat SEOs opting for a “churn and burn” approach—but there’s no reason you can’t use it for good. It’s perfectly possible to take advantage of a site’s authority to rank truly great content quickly and more easily.



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













