John Mueller Answers What to Do About Link Building
Google’s John Mueller answered a question about link building practices in an Office Hours hangout. Mueller outlined Google’s passive and proactive actions against certain links and offered suggestions for a better way to acquire links.
Is it Necessary to Spend Thousands of Dollars for Links?
The person asking the question noted that he watched many link building YouTube videos and read case studies that demonstrated that link building is necessary for best rankings.
The question asked:
“…The question is on link building practices. So we …approached many… companies… they say they will charge thousands of dollars or ten thousands of dollars to get the link… from the home page or the news sites and…
They also talk a lot… about …we should get a high authority …link and stuff like that.”
Next he explained how companies he approached showed him examples of sites that were high ranking because of their link building.
The person continued:
“…they also showcase that okay, see this is a site which is ranking high on …Google and …they have taken our service and they have paid us.
So if you pay us then your site will also rank because we are going to put …your site backlink with the good article on the home page…”
Are “Such Practices” Necessary to Rank in Google?
Next he questioned the wisdom of spending money on what he perceived as low quality link building, what he called, “such practices,” implying manipulative practices.
He seemed troubled that according to the link building claims, Google’s search rankings reward manipulative practices that cost thousands of dollars.
He continued the question:
“I don’t think that it is wise to put money in such practices or not. Like what are your opinion, like what are your final wordings?
And one more thing. …There are a lot of people over at YouTube and they’re writing a lot of blogs also like these are the best link building practices, you do this… and you do like that and they are charging a lot of money but we don’t want to engage in such stuff like that.”
The person asking the question ended by asking:
“We just want to know… what we should do now?“
Screenshot of John Mueller in the Office Hours Hangout

How Google Treats Manipulative Link Building
John Mueller related how Google treats artificial links:
“What should you do now…
I think that’s a super complicated question because there’s no one answer for everyone.
So I think first of all, like you probably recognized, artificially building links, dropping links on other sites, buying links, all of that is against the webmaster guidelines.
And we take action on that algorithmically, we take action on that manually.
And the actions that we take include demoting the site that is buying the links, demoting the site that is selling the links.
Sometimes we also take more subtle action in that we just ignore all of those links.”
Screenshot of John Mueller Explaining How Google Handles Paid Links

Google: Paid Links Have No Effect
Google’s John Mueller says paid links have no effect:
“For example if we recognize that a site is regularly selling links but they also have other things around that, then we often go in and say okay, we will ignore all links on this website.
That basically means …a lot of these sites are things where people still sell links because it’s like they can sell it and they find a seller then of course they’ll try to do that.
But those links have absolutely no effect.
So that seems like a big waste of time from my point of view.”
Mueller Describes Non-Black Hat Links
Mueller ends his answer by suggesting Google-friendly link building tactics.
His first suggestion is the classic create content and tell others about it approach. It’s an oldie but a goodie but it can work.
Mueller suggests to build it and tell others about it:
“That said, I do think that there are ways that you can approach the topic of links in a way that is less black hat where you’re buying links from other sites.
But where you’re actually kind of actively creating content that you know will attract links and then going out and reaching out to other sites and saying hey, we have this interesting content, don’t you want to take a look at it.
And …kind of encouraging them to link to your site but without this kind of exchange of value, exchange of money, all of that.
And that’s something where some people are very experienced in doing that and they can really kind of guide you to find those topic areas that are interesting for other people.”
Building Links to Product Pages is Hard
Creating content and telling others about it isn’t always an appropriate strategy for an ecommerce website. An ecommerce website offers products, not articles.
Attracting links to product pages is one of the toughest kinds of links to acquire because people generally don’t feel enthusiastic about certain products and when they do feel enthusiastic the typical ecommerce store is one store of out thousands selling the same product.
The problem with attracting links to product pages is that it’s extremely difficult to make the case that one store out of thousands is more deserving of a link than the other stores selling identical products.
The tactic of building content to help rank a product page rarely works because the links acquired for that content boosts the content and not the products.
One can internally link from the content pages to the product pages and that might help.
But I’ve rarely seen that happen, even for content pages that went viral.
There is simply no replacement for a direct link to a products page.
Here’s what John Mueller said about acquiring links:
“Where if you’re selling refrigerators then obviously a category page of refrigerators is not going to be very interesting for other people.
But if you can create a survey around refrigerators that is somehow fascinating to others that’s something that’s a lot more interesting for people where they say, oh… here’s this really cool survey about refrigerators.
Did you know that they were like this or they were invented like this or whatever.
That’s the kind of thing where you’re creating something that other people find interesting that other people want to link to.
From my point of view that’s the kind of link building that I have less of an issue with because you’re creating something that other people are linking to it because of what you’ve created.
But it’s not that other people are linking to your content because you’re giving them money to do that or because you have kind of these back door relationships with the other site.
So that’s kind of the direction I would take there.”
Mueller Warns Against Link Building Shortcuts
Next Mueller turns away from offering constructive suggestions for building links and returns to discouraging short term solutions because they can get you banned, don’t go for short term rewards at the expense of long term success. That’s pretty much what he advised (you can watch the video below if you’re interested).
Links More Important than Popularity?
Some sites have built-in advantages that help them acquire links.
For example, a wildly popular store cannot rank for their key terms, forcing them to pay to rank for those terms. Their popularity is driven through social media.
A keyword phrase that the popular store should rank has a search result that has in fourth place a regional brick and mortar with stores in a handful of rural states.
Site A is the wildly popular store and Site B is the regional store.
Google Trends Showing Search Popularity of Two Online Stores
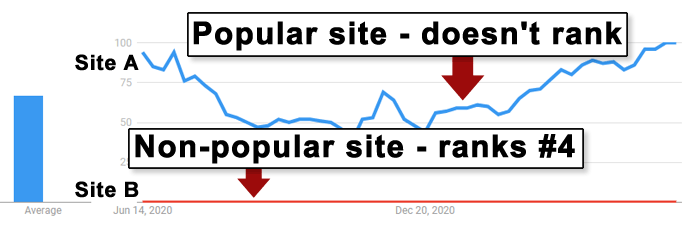
Site A is wildly popular online with tens of millions of followers on social media.
Site B has social media followers in the low six figures.
The Google Trends graph makes it clear that there is enormous search traffic for Site A’s brand name but Google ranks a relatively unpopular website as #4 for a highly coveted two word keyword phrase.
The relatively unpopular Site B is a regional site that acquires many links from regional news media sites. They also have live links (with coupon codes) from “influencers” which seems to indicate an active promotional campaign.
How Popular is Site A?
Here is a Google Trends graph showing how Site A is nearly as popular as McDonald’s:
Google Trends Graph Comparison with McDonald’s
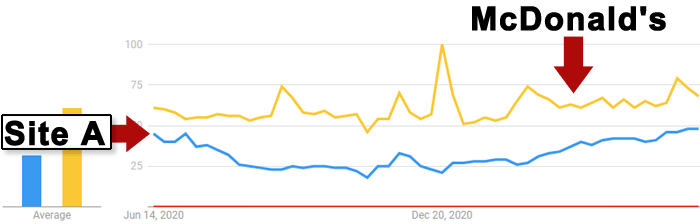
As you can see, site A is nearly as popular as McDonald’s but it can’t outrank a regional store that happens to have decent links…
Circling back to the person who asked John Mueller the question, one can understand the frustration that is inherent in the question that was asked:
“We just want to know… what we should do now?“
Citation
Watch John Mueller answer discuss link building at 1 minute mark:



![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-400x240.png)
![How AEO Will Impact Your Business's Google Visibility in 2026 Why Your Small Business’s Google Visibility in 2026 Depends on AEO [Webinar]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/How-AEO-Will-Impact-Your-Businesss-Google-Visibility-in-2026-80x80.png)













