MARKETING
How to Know When You Need a Dedicated Paid Landing Page
The author’s views are entirely his or her own (excluding the unlikely event of hypnosis) and may not always reflect the views of Moz.
The average SEO-focused product page converts at only 2.9 percent, which is among the reasons many companies pursue paid advertising traffic to achieve their goals and KPIs.
But creating custom, campaign-specific landing pages is resource-intensive, and not every team has the necessary tools, expertise, or personnel to build the content. So, how do you know if you need a custom page or if you can safely send paid traffic to an organic page and still achieve your KPIs? This three-step, data-driven evaluation helps answer this question.
Paid vs. SEO landing pages — why have both?
Before diving into the evaluation process, you need to understand why having paid and organic pages is crucial and some of the drawbacks when you send paid traffic to your organic pages without analyzing them beforehand.
First, search intentions often differ between paid and organic users, and each group will have different content needs. We can classify these users into two groups based on whether they use high-intent or low-intent keywords.
Per WordStream’s definition, people who use high intent keywords like “best” want to conduct a transaction or perform an action, such as inquiring about a service, which can lead to an eventual conversion. This behavior aligns with the motivations of paid users, 75% of whom engage with ads because they believe landing pages make it easier to find their desired information.
In comparison, WordStream defines low intent keywords as navigational or informational in nature instead of transactional.
For example, somebody who wants to learn about a specific topic is more likely to use a longtail keyword and less likely to commit to a purchase because they’re gathering information rather than making a decision. Organic results are better suited for longtail terms, so the user will more likely engage with the organic SERP result rather than an ad.
These behavioral differences create a challenging situation for users and content creators.
Because organic content must play by Google’s rules, paid users are forced to sift through irrelevant information, which can increase bounce and exit rates and decrease conversion rates. And sadly, you can’t simply remove the extra information from the page because organic users and search algorithms need it.
Second, mixing paid and organic traffic on the same page makes it difficult to separate and track audience-specific user behavior, content performance, and conversion rationale. Without data clarity like closed-loop analytics, you can quickly get a misleading picture of content performance and miss crucial KPIs because of your clouded judgment.
Consequently, in most cases, directing the paid traffic to a custom-built, campaign-specific landing page produces higher quality conversions. You can ignore all SEO rules, which empowers you to accommodate user intentions and elicit specific user behaviors.
With the forewarning out of the way, let’s break down how organic page performance can determine if you need custom landing pages to achieve your goals.
Step 1: Gather and analyze performance baselines from multiple data sources
The first task is to gather and analyze a lot of data — from multiple sources — that shows you exactly how well your organic page is performing. Ideally, you want to scrounge up analytics data, user behavior insights, and keyword rankings. Even if you wind up making a custom paid page, this effort still pays dividends by highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of your organic content.
Analytics data
You’ll start by collecting a smattering of classic analytics data points from your preferred analytics platform to gain insights about page performance over time.
If your content is old enough, gather the following data in three-month, six-month, and one-year intervals. The breadth of data makes it easier to spot recurring themes and create a more educated guess about what will happen if you send paid traffic to the page.
Remember to filter the metrics so you’re only getting data from organic traffic sources.
Pageviews and unique pageviews
Imagine you have a well-optimized product page that converts with organic visitors at an even three percent. However, you need the equivalent of a five percent monthly conversion rate to reach the year’s KPIs and maintain a healthy company.
You can use pageview data to calculate how much missing traffic you need to conjure, either targeting new keywords or starting a paid campaign. For example, suppose you currently get 100 pageviews every month and three conversions. In that case, you’ll roughly need an additional 67 pageviews per month to get five conversions at the three percent conversion rate.
If that traffic growth is not feasible with new or improved keyword rankings, then paid traffic is a solution to consider.
Should you decide to send paid traffic to that page, you can also calculate the difference between pageviews and unique pageviews to estimate how many returning users you can effectively target in a PPC retargeting campaign.
Time on page and bounce rate
Paid landing pages are designed to be simple, straightforward, and action-oriented. The following image is an excellent example of this concept:
Lengthy or complex paid pages generally suffer from high bounce rates and low conversions. If people are spending more than one or two minutes on the page without converting, it’s a sign the content isn’t convincing enough to convert, and it needs alterations.
On the contrary, organic pages can thrive with relevant content, internal links, and other information to capture rankings and keep people interested.
You want a high time on page because that means people care about the content you provide, which sends positive ranking signals to search engines.
If you’re seeing an average time on page three minutes or more from your organic page, it’s likely not a good fit for paid users. You can always redesign or reorganize the page to accommodate paid traffic, but you risk isolating your organic users by being pushy with conversion-focused information so early.
Previous page path and conversions
Among the most challenging aspects of organic conversions is understanding what stage of the buyer’s journey somebody is in.

Are you converting with high-funnel users? Or do your users first view a case study or blog post and then visit the product page, only to leave and return later? Knowing the answer lets you see what type of content matters most from a conversion standpoint and helps determine if your content is reaching the right people at the correct time.
If your organic conversions rely heavily on return visits or high page depth, sending paid traffic to the page likely will not improve your conversions. Paid users will lack the previous knowledge and feel overwhelmed or dissatisfied, with many bouncing from the page.
Event and goal tracking data
Event and goal tracking are two types of user behavior insights you can use to determine what content users care about the most. This process also illuminates what content users often disregard, which can then be removed from the page. Knowing this information helps you determine if time-starved paid users will be interested in your existing content.
Set up the following metrics as events or goals in your analytics tool to lay the groundwork.
Hyperlinks
Do you know how many clicks each hyperlink on your page gets? If not, how do you know users find them helpful?
Traditionally, paid pages don’t have any engagement options that take people away from a conversion point. However, most organic pages do.
So, if you’re going to use an organic page for paid traffic, you’ll need to only provide internal links that add significant value and actively engage users. Otherwise, if paid users stick around, they may get lost down the rabbit hole and then abandon the site without converting.
Videos and completion rates
If you have video content, particularly content that explains your product or service, it’s crucial to know how well that video performs and how often people complete it.

If the video has high engagement and completion rates, it’s useful to include it high up on organic and paid pages. However, if most users only watch 25 percent or less of the video, then pushing it further down the organic page and omitting it from a paid page is a smarter choice.
Forms
Forms are often a high-friction page element that can easily frustrate users, especially when visiting a page with conversion intentions. Your forms need to be flawless.

If you’re noticing that users get stuck on a form or abandon it, you need to rework the form. Paid users expect forms to be simple, only require absolutely necessary information, and take very little effort. If your organic forms can’t do that, either replace the form or build a custom paid page with a bare-bones version.
CTAs
CTA location, text, and purpose dictate a lot of your page’s conversion potential. If your organic page has multiple CTAs, you need to accurately track which one gets the most engagement. If you choose to send paid traffic to the page, then the highest-engagement CTA should be the first CTA option shown.
Additionally, every CTA should be:
-
Visually distinct
-
Above the fold (in most instances)
-
Actionable with precise copy
-
Avoiding generic statements like “learn more,” “buy now,” or “subscribe”
-
Giving users an idea of what happens after interacting with the CTA
If you have too many competing CTAs, or for whatever reason, your organic page can’t meet these requirements, then you need to create a custom paid page instead.
Navigation interaction
Most paid pages include a link back to the main website but not full navigation options. Organic content doesn’t have this luxury. Knowing how many of your users interact with the navigation after landing on the organic page in question is crucial to predicting what a paid user may do.

For example, suppose your page gets 2,500 organic visitors per month and 1,963 of them leave the page via navigation options. In that case, that’s a great sign that the page is either lacking conversion intent or doesn’t have enough information to convince users to convert. Either way, it’s not the behavior you want to see from paid traffic.
Heat mapping and click-tracking data
Once you’ve gathered your analytics data and set up event tracking, the next step is to collect and analyze data from a heat mapping tool like Hotjar or Mouseflow. The goal is to discover how users interact with the existing page, notice troublesome areas, and determine if those behaviors align with paid landing page best practices.
Let’s break down the types of information you’ll want to collect and how to evaluate it.
Heat mapping and scroll depth
Do you know how much of your organic page is seen by the average user before they leave the page or convert? Heat maps will tell you.

Paid pages are purposefully short so users don’t have opportunities to get distracted or disappointed by the content. If your scroll depth is deep enough that more than 75 percent of users see the most important content on the page, then the page layout and content priority may be okay for a paid user. However, if you’re seeing 30-plus percent of users leaving after scrolling just past the hero region, then paid users will most likely follow suit and you’ll either need to design a new page or alter the existing one.
Click tracking
Click tracking is a great way to visualize and confirm the event tracking data you set up previously. The maps can also pinpoint engagement issues or opportunities you may have overlooked.

The goal of click tracking is to figure out what content users care about the most. If you can naturally surface that information at the top of the page, then your paid users will be more likely to stick around. If that’s not possible, then you can design a paid page using the most popular organic page elements as inspiration.
Mouse flow
Mouse flow lets you observe the mouse movement of your users. Sometimes users hit friction points that we can’t detect by monitoring scroll depth, clicks, or other common engagement factors. These scenarios are where mouse flow reigns supreme.
While a mouse flow report is often an erratic mess of multi-colored blobs and squiggly lines, you can use it to understand what content your users may spend more time looking at or read more carefully based on where the mouse moves.
For example, in the following image, the mouse flow shows that more users hover their cursor in the “Inner Circle Guide to Next-Generation Customer Contact” section than any other content block.

Although the CTA associated with this section isn’t showing a high click density, the mouse flow report determines that users have some level of interest in the topic. If this example was on your website, you could shuffle the content order to prioritize the popular content or run A/B tests to determine if the language or information needs to be changed or simplified for a paid user’s short attention span.
Session recording
Watching actual users interact with your organic page is by far the most valuable way to determine what does and doesn’t work about your content. Most heat mapping tools let you set up recordings based on triggered events, such as clicking into a form.
You can observe the user’s entire interaction with your page and determine if the behavior is consistent among converting customers. If the behavior is consistent, it’s feasible that paid users may act the same way. However, if the recording behavior is erratic (and it likely will be), then you’ll want to build a custom page to provide a more “hand-held” experience.
Step 2: Map user behavior data to your KPIs
Now that you’ve collected and analyzed all of your data, it’s time to start looking for patterns and mapping the desired user behavior to the actual user behavior your data shows. If the two align, you’re in a great position to send paid traffic to your organic page and hopefully reap more conversions.
However, suppose there is a discrepancy between the desired and actual behaviors. In that case, you’ll need to map user behavior with specific stages of the customer journey and sales funnel, and then build a paid page that amplifies the desired behavior based on how you see users interacting with your organic page.
Let’s break down an example.
Recently, one of Portent’s clients chose to design a PPC version of an organic product page because the page wasn’t converting at their desired rate — despite already funneling paid traffic to it.
Before the client could design the new campaign content, they needed to determine what conversion-focused information users engage with most on the organic page. Otherwise, they risk supplying users with unnecessary information and wasting ad spend.
I analyzed three months of event tracking data from Google Analytics and Hotjar to determine exactly how users interacted with the product page. To narrow the results, I only focused on page elements with a call to action or internal link to pages that may lead to a conversion, such as the client’s demo page or case study archive.
Once I established which page elements get the most attention, I then isolated the users’ behaviors by using Hotjar’s filters to watch session recordings that contain the chosen events.

I watched 20 recorded user sessions to see what information people interacted with first and which they ignored, how long they took to digest the content, friction-causing UX elements, and what additional pages or resources they viewed. I then took these learnings and built a PPC campaign page that told the client’s story in the order converting users demonstrated.
The client is still building the page, so I can’t report on how well it performed. However, in theory, they should earn higher conversion rates on the paid campaign page because I isolated the content that converting users interacted with, which eliminated any non-esstial information.
Step 3: Make your choice
Now that you understand how your users interact with your organic page and some of the restrictions and considerations that come when sending paid traffic to organic content, you can choose. Invest the time and resources into building a custom paid campaign, or modify your organic content to try and target two user groups in one fell swoop?
Creating the paid page will likely give you better and more consistent results, but there is also little harm in trying your organic page first if you think it’s good enough. Run a small test, say 20 percent of your advertising budget for this project, and see if the page performance improves. If it doesn’t, then you have a definitive answer and you’re prepared with the resources you need to build a stellar paid landing page.
MARKETING
Streamlining Processes for Increased Efficiency and Results

How can businesses succeed nowadays when technology rules? With competition getting tougher and customers changing their preferences often, it’s a challenge. But using marketing automation can help make things easier and get better results. And in the future, it’s going to be even more important for all kinds of businesses.
So, let’s discuss how businesses can leverage marketing automation to stay ahead and thrive.
Benefits of automation marketing automation to boost your efforts
First, let’s explore the benefits of marketing automation to supercharge your efforts:
Marketing automation simplifies repetitive tasks, saving time and effort.
With automated workflows, processes become more efficient, leading to better productivity. For instance, automation not only streamlines tasks like email campaigns but also optimizes website speed, ensuring a seamless user experience. A faster website not only enhances customer satisfaction but also positively impacts search engine rankings, driving more organic traffic and ultimately boosting conversions.
Automation allows for precise targeting, reaching the right audience with personalized messages.
With automated workflows, processes become more efficient, leading to better productivity. A great example of automated workflow is Pipedrive & WhatsApp Integration in which an automated welcome message pops up on their WhatsApp
within seconds once a potential customer expresses interest in your business.
Increases ROI
By optimizing campaigns and reducing manual labor, automation can significantly improve return on investment.
Leveraging automation enables businesses to scale their marketing efforts effectively, driving growth and success. Additionally, incorporating lead scoring into automated marketing processes can streamline the identification of high-potential prospects, further optimizing resource allocation and maximizing conversion rates.
Harnessing the power of marketing automation can revolutionize your marketing strategy, leading to increased efficiency, higher returns, and sustainable growth in today’s competitive market. So, why wait? Start automating your marketing efforts today and propel your business to new heights, moreover if you have just learned ways on how to create an online business
How marketing automation can simplify operations and increase efficiency
Understanding the Change
Marketing automation has evolved significantly over time, from basic email marketing campaigns to sophisticated platforms that can manage entire marketing strategies. This progress has been fueled by advances in technology, particularly artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, making automation smarter and more adaptable.
One of the main reasons for this shift is the vast amount of data available to marketers today. From understanding customer demographics to analyzing behavior, the sheer volume of data is staggering. Marketing automation platforms use this data to create highly personalized and targeted campaigns, allowing businesses to connect with their audience on a deeper level.
The Emergence of AI-Powered Automation
In the future, AI-powered automation will play an even bigger role in marketing strategies. AI algorithms can analyze huge amounts of data in real-time, helping marketers identify trends, predict consumer behavior, and optimize campaigns as they go. This agility and responsiveness are crucial in today’s fast-moving digital world, where opportunities come and go in the blink of an eye. For example, we’re witnessing the rise of AI-based tools from AI website builders, to AI logo generators and even more, showing that we’re competing with time and efficiency.
Combining AI-powered automation with WordPress management services streamlines marketing efforts, enabling quick adaptation to changing trends and efficient management of online presence.
Moreover, AI can take care of routine tasks like content creation, scheduling, and testing, giving marketers more time to focus on strategic activities. By automating these repetitive tasks, businesses can work more efficiently, leading to better outcomes. AI can create social media ads tailored to specific demographics and preferences, ensuring that the content resonates with the target audience. With the help of an AI ad maker tool, businesses can efficiently produce high-quality advertisements that drive engagement and conversions across various social media platforms.
Personalization on a Large Scale
Personalization has always been important in marketing, and automation is making it possible on a larger scale. By using AI and machine learning, marketers can create tailored experiences for each customer based on their preferences, behaviors, and past interactions with the brand.
This level of personalization not only boosts customer satisfaction but also increases engagement and loyalty. When consumers feel understood and valued, they are more likely to become loyal customers and brand advocates. As automation technology continues to evolve, we can expect personalization to become even more advanced, enabling businesses to forge deeper connections with their audience. As your company has tiny homes for sale California, personalized experiences will ensure each customer finds their perfect fit, fostering lasting connections.
Integration Across Channels
Another trend shaping the future of marketing automation is the integration of multiple channels into a cohesive strategy. Today’s consumers interact with brands across various touchpoints, from social media and email to websites and mobile apps. Marketing automation platforms that can seamlessly integrate these channels and deliver consistent messaging will have a competitive edge. When creating a comparison website it’s important to ensure that the platform effectively aggregates data from diverse sources and presents it in a user-friendly manner, empowering consumers to make informed decisions.
Omni-channel integration not only betters the customer experience but also provides marketers with a comprehensive view of the customer journey. By tracking interactions across channels, businesses can gain valuable insights into how consumers engage with their brand, allowing them to refine their marketing strategies for maximum impact. Lastly, integrating SEO services into omni-channel strategies boosts visibility and helps businesses better understand and engage with their customers across different platforms.
The Human Element
While automation offers many benefits, it’s crucial not to overlook the human aspect of marketing. Despite advances in AI and machine learning, there are still elements of marketing that require human creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking.
Successful marketing automation strikes a balance between technology and human expertise. By using automation to handle routine tasks and data analysis, marketers can focus on what they do best – storytelling, building relationships, and driving innovation.
Conclusion
The future of marketing automation looks promising, offering improved efficiency and results for businesses of all sizes.
As AI continues to advance and consumer expectations change, automation will play an increasingly vital role in keeping businesses competitive.
By embracing automation technologies, marketers can simplify processes, deliver more personalized experiences, and ultimately, achieve their business goals more effectively than ever before.
MARKETING
Will Google Buy HubSpot? | Content Marketing Institute

Google + HubSpot. Is it a thing?
This week, a flurry of news came down about Google’s consideration of purchasing HubSpot.
The prospect dismayed some. It delighted others.
But is it likely? Is it even possible? What would it mean for marketers? What does the consideration even mean for marketers?
Well, we asked CMI’s chief strategy advisor, Robert Rose, for his take. Watch this video or read on:
Why Alphabet may want HubSpot
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, apparently is contemplating the acquisition of inbound marketing giant HubSpot.
The potential price could be in the range of $30 billion to $40 billion. That would make Alphabet’s largest acquisition by far. The current deal holding that title happened in 2011 when it acquired Motorola Mobility for more than $12 billion. It later sold it to Lenovo for less than $3 billion.
If the HubSpot deal happens, it would not be in character with what the classic evil villain has been doing for the past 20 years.
At first glance, you might think the deal would make no sense. Why would Google want to spend three times as much as it’s ever spent to get into the inbound marketing — the CRM and marketing automation business?
At a second glance, it makes a ton of sense.
I don’t know if you’ve noticed, but I and others at CMI spend a lot of time discussing privacy, owned media, and the deprecation of the third-party cookie. I just talked about it two weeks ago. It’s really happening.
All that oxygen being sucked out of the ad tech space presents a compelling case that Alphabet should diversify from third-party data and classic surveillance-based marketing.
Yes, this potential acquisition is about data. HubSpot would give Alphabet the keys to the kingdom of 205,000 business customers — and their customers’ data that almost certainly numbers in the tens of millions. Alphabet would also gain access to the content, marketing, and sales information those customers consumed.
Conversely, the deal would provide an immediate tip of the spear for HubSpot clients to create more targeted programs in the Alphabet ecosystem and upload their data to drive even more personalized experiences on their own properties and connect them to the Google Workspace infrastructure.
When you add in the idea of Gemini, you can start to see how Google might monetize its generative AI tool beyond figuring out how to use it on ads on search results pages.
What acquisition could mean for HubSpot customers
I may be stretching here but imagine this world. As a Hubspoogle customer, you can access an interface that prioritizes your owned media data (e.g., your website, your e-commerce catalog, blog) when Google’s Gemini answers a question).
Recent reports also say Google may put up a paywall around the new premium features of its artificial intelligence-powered Search Generative Experience. Imagine this as the new gating for marketing. In other words, users can subscribe to Google’s AI for free, but Hubspoogle customers can access that data and use it to create targeted offers.
The acquisition of HubSpot would immediately make Google Workspace a more robust competitor to Microsoft 365 Office for small- and medium-sized businesses as they would receive the ADDED capability of inbound marketing.
But in the world of rented land where Google is the landlord, the government will take notice of the acquisition. But — and it’s a big but, I cannot lie (yes, I just did that). The big but is whether this acquisition dance can happen without going afoul of regulatory issues.
Some analysts say it should be no problem. Others say, “Yeah, it wouldn’t go.” Either way, would anybody touch it in an election year? That’s a whole other story.
What marketers should realize
So, what’s my takeaway?
It’s a remote chance that Google will jump on this hard, but stranger things have happened. It would be an exciting disruption in the market.
The sure bet is this. The acquisition conversation — as if you needed more data points — says getting good at owned media to attract and build audiences and using that first-party data to provide better communication and collaboration with your customers are a must.
It’s just a matter of time until Google makes a move. They might just be testing the waters now, but they will move here. But no matter what they do, if you have your customer data house in order, you’ll be primed for success.
HANDPICKED RELATED CONTENT:
Cover image by Joseph Kalinowski/Content Marketing Institute
MARKETING
5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails

Welcome to Creator Columns, where we bring expert HubSpot Creator voices to the Blogs that inspire and help you grow better.
I’ve tested 100s of psychological tactics on my email subscribers. In this blog, I reveal the five tactics that actually work.
You’ll learn about the email tactic that got one marketer a job at the White House.
You’ll learn how I doubled my 5 star reviews with one email, and why one strange email from Barack Obama broke all records for donations.
5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails
Imagine writing an email that’s so effective it lands you a job at the White House.
Well, that’s what happened to Maya Shankar, a PhD cognitive neuroscientist. In 2014, the Department of Veterans Affairs asked her to help increase signups in their veteran benefit scheme.
Maya had a plan. She was well aware of a cognitive bias that affects us all—the endowment effect. This bias suggests that people value items higher if they own them. So, she changed the subject line in the Veterans’ enrollment email.
Previously it read:
- Veterans, you’re eligible for the benefit program. Sign up today.
She tweaked one word, changing it to:
- Veterans, you’ve earned the benefits program. Sign up today.
This tiny tweak had a big impact. The amount of veterans enrolling in the program went up by 9%. And Maya landed a job working at the White House

Inspired by these psychological tweaks to emails, I started to run my own tests.
Alongside my podcast Nudge, I’ve run 100s of email tests on my 1,000s of newsletter subscribers.
Here are the five best tactics I’ve uncovered.
1. Show readers what they’re missing.
Nobel prize winning behavioral scientists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky uncovered a principle called loss aversion.
Loss aversion means that losses feel more painful than equivalent gains. In real-world terms, losing $10 feels worse than how gaining $10 feels good. And I wondered if this simple nudge could help increase the number of my podcast listeners.
For my test, I tweaked the subject line of the email announcing an episode. The control read:
“Listen to this one”
In the loss aversion variant it read:
“Don’t miss this one”
It is very subtle loss aversion. Rather than asking someone to listen, I’m saying they shouldn’t miss out. And it worked. It increased the open rate by 13.3% and the click rate by 12.5%. Plus, it was a small change that cost me nothing at all.
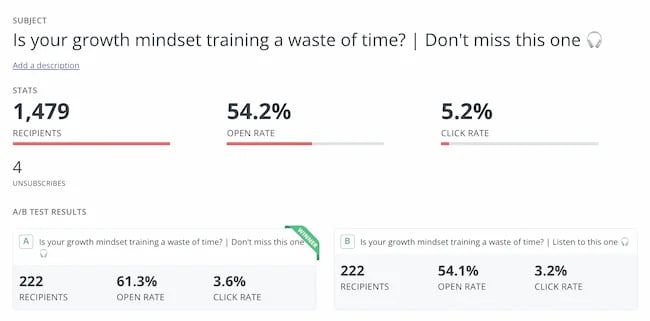
2. People follow the crowd.
In general, humans like to follow the masses. When picking a dish, we’ll often opt for the most popular. When choosing a movie to watch, we tend to pick the box office hit. It’s a well-known psychological bias called social proof.
I’ve always wondered if it works for emails. So, I set up an A/B experiment with two subject lines. Both promoted my show, but one contained social proof.
The control read: New Nudge: Why Brands Should Flaunt Their Flaws
The social proof variant read: New Nudge: Why Brands Should Flaunt Their Flaws (100,000 Downloads)
I hoped that by highlighting the episode’s high number of downloads, I’d encourage more people to listen. Fortunately, it worked.
The open rate went from 22% to 28% for the social proof version, and the click rate, (the number of people actually listening to the episode), doubled.
3. Praise loyal subscribers.
The consistency principle suggests that people are likely to stick to behaviours they’ve previously taken. A retired taxi driver won’t swap his car for a bike. A hairdresser won’t change to a cheap shampoo. We like to stay consistent with our past behaviors.
I decided to test this in an email.
For my test, I attempted to encourage my subscribers to leave a review for my podcast. I sent emails to 400 subscribers who had been following the show for a year.
The control read: “Could you leave a review for Nudge?”
The consistency variant read: “You’ve been following Nudge for 12 months, could you leave a review?”
My hypothesis was simple. If I remind people that they’ve consistently supported the show they’ll be more likely to leave a review.
It worked.
The open rate on the consistency version of the email was 7% higher.
But more importantly, the click rate, (the number of people who actually left a review), was almost 2x higher for the consistency version. Merely telling people they’d been a fan for a while doubled my reviews.
4. Showcase scarcity.
We prefer scarce resources. Taylor Swift gigs sell out in seconds not just because she’s popular, but because her tickets are hard to come by.
Swifties aren’t the first to experience this. Back in 1975, three researchers proved how powerful scarcity is. For the study, the researchers occupied a cafe. On alternating weeks they’d make one small change in the cafe.
On some weeks they’d ensure the cookie jar was full.
On other weeks they’d ensure the cookie jar only contained two cookies (never more or less).
In other words, sometimes the cookies looked abundantly available. Sometimes they looked like they were almost out.
This changed behaviour. Customers who saw the two cookie jar bought 43% more cookies than those who saw the full jar.
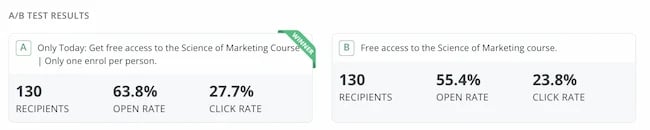
It sounds too good to be true, so I tested it for myself.
I sent an email to 260 subscribers offering free access to my Science of Marketing course for one day only.
In the control, the subject line read: “Free access to the Science of Marketing course”
For the scarcity variant it read: “Only Today: Get free access to the Science of Marketing Course | Only one enrol per person.”
130 people received the first email, 130 received the second. And the result was almost as good as the cookie finding. The scarcity version had a 15.1% higher open rate.
5. Spark curiosity.
All of the email tips I’ve shared have only been tested on my relatively small audience. So, I thought I’d end with a tip that was tested on the masses.
Back in 2012, Barack Obama and his campaign team sent hundreds of emails to raise funds for his campaign.
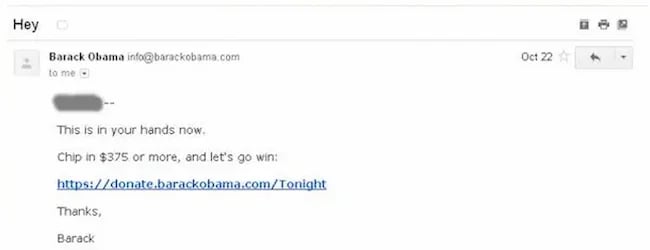
Of the $690 million he raised, most came from direct email appeals. But there was one email, according to ABC news, that was far more effective than the rest. And it was an odd one.
The email that drew in the most cash, had a strange subject line. It simply said “Hey.”
The actual email asked the reader to donate, sharing all the expected reasons, but the subject line was different.
It sparked curiosity, it got people wondering, is Obama saying Hey just to me?
Readers were curious and couldn’t help but open the email. According to ABC it was “the most effective pitch of all.”
Because more people opened, it raised more money than any other email. The bias Obama used here is the curiosity gap. We’re more likely to act on something when our curiosity is piqued.
Loss aversion, social proof, consistency, scarcity and curiosity—all these nudges have helped me improve my emails. And I reckon they’ll work for you.
It’s not guaranteed of course. Many might fail. But running some simple a/b tests for your emails is cost free, so why not try it out?
This blog is part of Phill Agnew’s Marketing Cheat Sheet series where he reveals the scientifically proven tips to help you improve your marketing. To learn more, listen to his podcast Nudge, a proud member of the Hubspot Podcast Network.
-

 WORDPRESS7 days ago
WORDPRESS7 days agoTurkish startup ikas attracts $20M for its e-commerce platform designed for small businesses
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoRoundel Media Studio: What to Expect From Target’s New Self-Service Platform
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Limits News Links In California Over Proposed ‘Link Tax’ Law
-
SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
Daily Search Forum Recap: April 12, 2024
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Search Results Can Be Harmful & Dangerous In Some Cases
-

 SEO5 days ago
SEO5 days ago10 Paid Search & PPC Planning Best Practices
-

 SEARCHENGINES5 days ago
SEARCHENGINES5 days agoGoogle Core Update Volatility, Helpful Content Update Gone, Dangerous Google Search Results & Google Ads Confusion
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoGoogle Unplugs “Notes on Search” Experiment











![5 Psychological Tactics to Write Better Emails → Download Now: The Beginner's Guide to Email Marketing [Free Ebook]](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/11-Free-Email-Hacks-to-Step-Up-Your-Productivity.png)



You must be logged in to post a comment Login