PPC
What Is a Go-To-Market Strategy? 9 Steps to Build Your Own (with Examples)

To successfully launch a new product, service, or business, you need a go-to-market strategy. Without a go-to-market strategy, running your business will be like driving in the dark without headlights. You might end up at your destination, but it’ll probably take longer than it should and you’ll be much more likely to run into problems along the way.
What it’s like launching a new product or service without a go-to-market strategy.
And that’s because the success of your business or new product launch requires planning. It’s not just about the product, the story, or even the team behind it all. It’s about how you’ll promote that product and to whom.
Because it won’t matter how great what you offer is if the right people never hear about it.
But what is a go-to-market strategy, who needs one, and how do you get started? We’ll cover everything you need to know about building a successful go-to-market strategy in this post.
Table of contents
- What is a go-to-market strategy?
- Benefits of a go-to-market strategy
- Who needs a go-to-market strategy?
- The components of a go-to-market strategy
- Steps to build a go-to-market strategy
- Go-to-market strategy examples
- Go-to-market strategy template
- Go-to-market strategy FAQs
What is a go-to-market strategy?
A go-to-market strategy is a framework for how you will sell your products or services.
It helps you understand what you need to do in order to make money off of your idea, and it guides you through the process of getting your product into the hands of customers.
It’s essential.
Why? Because when you’re launching something new, there aren’t yet customers with loyalty to your brand or reasons to buy what you’re selling.
A go-to-market strategy is the plan to get people both aware of and excited about your idea, enough that they’ll want to pay for it.
The problem with most companies’ go-to-market strategy is that they often believe that because their product is so great, there’s no way it won’t succeed. They don’t take into account their ideal target audience, their competitors, and their own abilities to deliver at scale.
The result? Either heartbreak and disappointment or a lot of wasted time and money thrown at the wrong things while hoping to get lucky.
Benefits of a go-to-market strategy
The most important benefit of a solid go-to-market plan is that it helps you grow your business. A well-executed go-to-market strategy…
1. Shortens the amount of time it takes to get to market
The sooner you get to market, the sooner you can start making money. Likewise, if you can’t get to market quickly, you may not be able to get there at all.
A go-to-market strategy helps you expedite the time to market by prioritizing the tasks needed to launch your idea.
2. Helps ensure that your product launches are successful
Go-to-market strategies provide a roadmap for the team members involved to follow. This ensures that all parties are working toward the same goal and are on the same page regarding timelines, goals, and resources.
It allows for regular checkpoints where you can evaluate your progress against the plan and make adjustments as needed before it’s too late (e.g., before launch).
You don’t want to announce a new product or feature without a plan and the right resources in place. A good go-to-market strategy is one of the best ways to ensure that you get the most out of your launch.
A well-executed strategy considers how you’ll bring your product to market, including how you’ll price it, who will sell it, and how you’ll advertise it. It helps you understand what comes first, second, and last. Should you spend time building awareness before selling? Or should you focus on getting a few critical people to buy, then worry about building larger awareness later?
Some companies take a linear approach–they start by building awareness and then move on to sales–while others take an iterative approach–selling first and building awareness later. The right way depends on your business model and goals for the product itself.
3. Helps companies adapt to change
In a world where consumers are more likely distracted than engaged, a go-to-market strategy can help companies adapt to inevitable change.
A GTM strategy can help you achieve your goals in a way that’s flexible enough to adapt to trends in the marketplace and disruptions in both the economy and the outside world. It can also help you execute your vision on a day-to-day basis.
If you don’t have an effective GTM strategy, then it will be difficult for you to respond effectively when things happen outside of your control.
For example, if you’re not prepared for a disruption in the economy or for a new competitor entering the marketplace, then it will be difficult for you to respond quickly.
A good go-to-market strategy can give you time to react and adapt when these things happen because you’ve prepared and had a plan for when these types of things would inevitably happen.
4. Reduces the likelihood of expensive product launch failures
In going through the process of preparing your go-to-market strategy, companies have ostensibly planned for everything, including the worst that could happen: failure.
The product launch is the most important part of any business. It’s where you prove to the world that what you’ve been working on is actually worth paying for.
It’s also where some companies fall flat on their faces. It happens all too often: a company spends months or even years developing their product, they finally get it out into the market, and…nothing happens.

Coca-Cola could have used a different go-to-market strategy approach before launching New Coke.
The reasons for this are many but one of the biggest is a poorly planned go-to-market strategy. This can mean anything from not knowing how to reach potential customers to not having enough capital to market the product properly.
In short, if there’s no strategy in place, then there’s no way for people outside your company to know about it–and without that knowledge, they won’t buy it.
Because you’ve prepared for the worst, you’ve likely reduced the likelihood of it happening. And if things do start to turn south, you’ll have a plan for how to pivot and reduce the damage.
5. Makes managing challenges less stressful
Let’s face it, life is filled with challenges. As a business owner, you’re not immune to them. But if you’ve done your homework and prepared for every possible scenario, you’ll be able to adapt quickly no matter what comes your way.
Preparing for every possible challenge involves understanding your customer, your market, and what you’re selling. If you know these things well enough, you’ll be able to anticipate and respond to challenges before they become a problem for your business.
When prepared, challenges simply become pivots you were prepared to make.
Rather than feeling the stress of not knowing what to do, you’ll have a plan B ready to be put into action.
6. Provides a better customer experience
The customer experience has become a top priority for most organizations. Why? Because it’s the only way to achieve long-term success. It’s not enough to have a great product anymore; you have to offer an overall experience that is as positive as possible.

To do this, you need to focus on how your company interacts with its customers–from the moment they start their journey with your brand until they’ve been using it for some time, and even after that.
A go-to-market strategy is designed to ensure that you’re covering all the bases when it comes to providing this kind of experience.
7. Streamlines regulatory compliance
A go-to-market strategy allows businesses to streamline regulatory compliance by ensuring that all aspects of the product or service comply with laws and regulations.
They also help companies protect their intellectual property rights. This can be especially important for software companies that rely on software patents to protect their brand from competitors who try to copy their product designs or functionality.
When do you need a go-to-market strategy?
Anyone who finds themselves in the following situations needs a GTM strategy:
1. Launching a new product in an existing market
Many companies launch a new product in an existing market. But they don’t always have a go-to-market strategy.
When entering an existing market, you’ll need to describe how you will communicate with your target audience and what you will say to persuade them to buy your product or service instead of your competitors.
An example of this would be to create something people already know well while attempting to compete with brands they have known and loved for years.
This gluten-free bakery launched build-your-own gluten-free pizzas.
It’s the equivalent of creating a new brand of tennis shoes or jeans. You’ll be entering an existing market and need to convince buyers why you’re worth taking a chance on.
When creating a go-to-market strategy for your new product, it’s important to consider who your target audience is, what they value, and what motivates them. You should also think about the competition and how they are marketing their products or services.
It’s also important to consider how you can differentiate yourself from other companies that are already in the market with competing products or services.
2. Launching an existing product in a new market
Continuing with the tennis shoes or jeans example: say you’re trying to introduce your tennis shoes or jeans to a country that doesn’t currently wear tennis shoes or jeans. What’s your plan to introduce these to them and convince them they are worth spending their money on?
The most important thing to remember is that your target audience will be different from your home market. You need to understand their needs and how you can meet those needs better than your competitors.
To do this, you need to conduct research and find out what’s working and what’s not working in the new market.
This can be done by using surveys, focus groups, or interviews with potential customers. It’s also important to understand what marketing channels are available for this market (e.g., social media platforms) and how they can be used to reach these customers.
Find out the best customer feedback questions to include when you collect feedback.
3. Testing a new product’s market for growth
You can’t just take your product and throw it out into the world, hoping that people will buy it. You need to have a plan for how you’re going to get it into their hands.
There’s no one way to do this, but here are some things you should consider:
- Who are your target customers? Think about who will use your product or service and what they’re looking for when they buy it.
- What do they need? How will you reach them? Does your product solve their problem? How can you get them excited about what you have to offer? If not, how can you make them realize how much they need it?
- What channels will work best for reaching your target customers? Think about where they get their information from–online blogs and podcasts, TV commercials, social media influencers–and figure out which ones would be most effective for reaching them.
- How much does it cost to reach each channel? Each channel has a different advertising price and audience size, so figure out which are the most cost-effective and valuable to be focusing your efforts on.
This makeup brand launched limited-edition hoodies and partnered with music superstar Kacey Musgraves to get the word out.
In the end, don’t be afraid to admit that you’ve run the numbers, and if it doesn’t make sense, don’t push forward.
The components of a go-to-market strategy
By now you understand exactly what a go-to-market strategy is, what types of businesses need them, and why they are necessary. Now we’re getting into the details of exactly how to build one.
The best way to build your go-to-market strategy will always be a combination of factors including:
- Your product
- Your target customer
- Your market size
- The competition within that market
Now let’s walk through the steps you need to take to build an effective go-to-market strategy.
9 steps to build a go-to-market strategy
As a business owner, you’re probably used to thinking about the product or service you offer. But to be successful, you need to think about how people will buy your product and what they’ll do with it after they purchase.
The “how” is your go-to-market strategy–a plan for how you’ll reach your customers and sell them on your product or service. It’s about understanding who your target customer is and what motivates them to buy from you rather than your competitors.
You don’t inherently need to create a formal document describing every step of your go-to-market strategy; in fact, doing so can be counterproductive because it can make it difficult to adapt as needed.
Instead, you could focus on creating an overall approach that gives everyone involved in your company a shared sense of direction and purpose–and then build out those details over time.
Here are some tips for creating an effective go-to-market strategy:
Step 1: Identify the problem you’re solving
If you want to build a great product and have it succeed, you need to know the problem you are solving.
A great product solves a specific problem.
For example:
- Match.com simplifies dating by providing a database of potential suitors and their information.
- Evernote helps you remember things by allowing you to save notes, photos, and other information in one place.
- Airbnb offers an alternative to staying in hotels, letting users rent out their homes to travelers.
- StitchFix allows customers to order curated clothing subscription boxes and returns what they don’t want.

Each of those products has a unique value proposition. They address the pain points of their customers in different ways. This concept (product-market fit) is the degree to which a product satisfies strong market demand.
If you don’t have product-market fit, it’s as if you’re trying to start a football team with no players, no field, and no coach.
Perhaps most importantly: when those products were launched, there was no competition–the market was not yet saturated.
You don’t want to build something that will help people accomplish what they already do easily. You want to solve a problem that’s hard, annoying, or painful.
Identifying the problem isn’t always easy, but it’s critical to building a successful product launch strategy.
Step 2: Define your target audience
In order to have a successful GTM launch, you must clearly understand your target audience and ask yourself the following three questions:
- Who needs your product enough to pay for a solution?
- What specific frustrations do your customers experience that your product can solve?
- How much is your audience willing to pay to be free of the problem?
You could also consider who might be interested in your product but not yet ready to buy. These are typically prospects that are further along in their buying process than those who will immediately purchase but still need more convincing. You can use this information to create marketing campaigns that target these prospects.
There are two common ways to define a business’ target market: The first is by creating an ideal customer profile (ICP), and the second is by creating buyer personas.
Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
The Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) is a hugely important piece of your go-to-market strategy. It’s how you’ll identify your target customer, understand their needs, and find opportunities to reach them.
The ICP approach helps define your “ideal” customer–someone who is experiencing the frustrations your product solves and is in need of purchasing a solution.
It’s important that the ICP is not only already aware of the problem and looking for a solution, but can also buy your product.
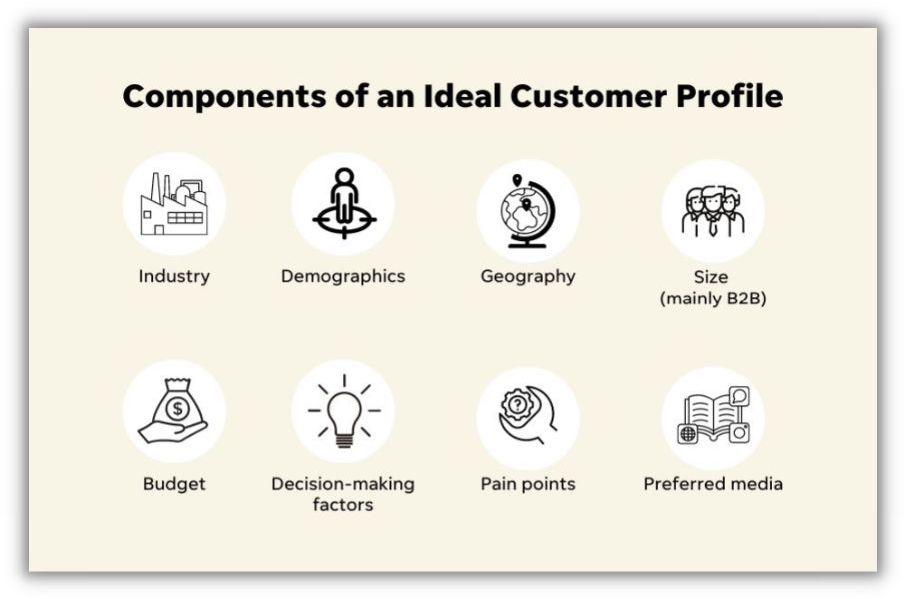
To establish an ideal customer profile, consider the following:
Industry
If you’re selling to businesses, a good way of handling this is to identify the entire industry you’re targeting. For example, if your product is a small business accounting software, it would make sense to target any company that falls under the umbrella of accounting and finance. This could include banks, financial advisors, accountants and bookkeepers, lawyers, and so on.
If you only sell to one branch of an industry (e.g., construction companies), then your ideal customer profile will be quite specific. However, if you want to sell to multiple branches of an industry (e.g., construction and architecture), then your ideal customer profile needs to be more general and flexible.
The most important thing is that your ideal customer profile reflects the reality of who is actually buying your products or services, rather than who you would like them to be!
Demographic
If you’re selling to individuals, define specific demographics your ideal customer falls within.
Demographics are a great way to start building your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP). It’s important to understand that there are many different ways you can define a demographic, but the most popular are gender, age, and income.
For example: If you were selling children’s clothing, your demographic would-be parents with children between the ages of 0-12 months. If you were selling adult clothing, your demographic would be adults between the ages of 25-65 years old.
Demographics are typically used by companies that sell goods or services directly to consumers. However, if you sell to businesses, then some of these same rules will apply.
If you were selling software for businesses; in this case, the demographics might be small business owners with less than 20 employees who operate in an industry that uses computers as part of their daily operations (e.g., retail stores or restaurants).
Geography
Where do your ideal customers live? Your answer will determine where you advertise, how you promote your products, the amount of traffic you should expect to receive, and perhaps even the manner in which you present your business.
If they’re all over the country but most of them reside in New York City or San Francisco, it might be worthwhile to spend more time and money on those cities’ local publications and communities than on national publications.
Geography can also be used as a tool to segment your customer base and identify which groups are most likely to purchase from you. This can be done by analyzing where they live or work (or both).
Size
This is a tactic mostly employed by B2B companies. It’s where you consider the size of the businesses you’re targeting—for example, you may market your product only to businesses with less than 10 employees, or more than 100.
You can also consider how much money these businesses have to spend on your product. This is often referred to as “buying power” and it can be broken down into different areas: revenue, headcount, average revenue per employee (ARPE), etc.
Once you’ve determined what size of the company will be most likely to buy from you, then it’s time to plan how those companies will be found and reachable by potential customers.
Budget
Before you set your price, consider how much your customers have to spend on your product. It influences people’s perception of what you offer and how much they’re willing to pay for it, so it should impact both price and marketing strategy.
A high-end product can command a higher price tag because it implies quality and exclusivity. A low-end product may benefit from being priced lower than competitors or even free so that customers see value in using the service or product over existing alternatives.
When deciding on a pricing strategy, you also need to consider how your product compares with alternatives. If there are no direct competitors, then you can set prices however high or low you want–but if there are similar products available elsewhere at similar prices, then you need to make sure that yours offers something different enough that makes it worth paying extra for.
Decision-making factors
What outside factors influence their purchase decision, and how can you take advantage of them to generate more sales? Do they rely on referrals? Do they need to get approval from a superior before they pull the trigger? Do they read reviews before deciding whether to buy?
When you know what matters most to your customer, you can tailor your marketing strategy accordingly. For example, if you know that people trust recommendations from friends and family members more than anything else, then give them more opportunities to share on social media and leave reviews.
Here are some of the most common factors that influence customer purchasing decisions:
- Price. The price is an obvious consideration for any potential buyer. If you can’t offer something at a competitive price, expect your sales numbers to suffer.
- Features. Features are another important consideration for buyers — especially when buying technology products and services. If you can offer more features than your competitors, then you’ll likely be able to win over more customers.
- Quality. Quality is also very important when it comes to buying products and services — especially when there’s no significant price difference between similar items. Your goal should be to offer quality products at reasonable prices so that people will choose yours over competing alternatives based on quality alone (if possible).
- Ease of use. Most buyers prefer products that are easy to use or have intuitive interfaces because these qualities make the product easier to say yes to.
You need to know these things so that when it comes time to make a sale, you know what works best with your customers. There are many ways to reach out to potential buyers: email, social media, in person, over the phone, etc.
The key is figuring out what makes sense for your business and your customers.
Pain points
The first step in the go-to-market strategy is identifying the pain points of your customer.
The best way to do this is to speak with a few customers and ask them questions about their problems and frustrations.
Here are some examples:
- “What specific frustrations does your ideal customer have when it comes to accounting?”
- “What solutions have they tried that haven’t worked?”
The answers you get will give you insight into what kind of product or service you should develop, who it should be marketed toward and how much they’ll pay for it.
Preferred media
To be successful, you must identify the channels your target audience uses, and then determine how to reach them there.
If your product or service is for consumers, take a moment to look at their daily lives. How do they consume information? What do they like to read? What do they like to watch? What websites do they visit? Are there any blogs or social media channels or online communities that could help you reach them?
If you want to sell in B2B markets, think about how your product can be used by businesses. How does it fit into their workflow? Is there a specific industry or vertical where it makes sense for you to focus first?
The best way to find out is by asking your customers. You can do this in a number of ways:
- Customer interviews
- Surveys
- Focus groups
- Social media analysis
- Customer journey mapping (This is especially helpful if you already have an existing customer base)
You can use this customer journey map template to help.
Buyer personas
Not all members of your audience are the same. Each person has their own unique set of problems, values, and goals. Creating buyer personas is a great way to humanize your customers, so you can better visualize who they are and what they need.
Remember, you’re selling to real people–not just statistics. Creating multiple customer personas helps you understand your target audience on a more personal level.
Here’s an example of a buyer persona for a SaaS company that sells off-the-beaten-path traveling tips to adventurous wanderers:
Persona: “The Sophisticated Traveler”
Description
“This person is a frequent traveler who has been to multiple countries, most of which have been in Europe or Asia. They’ve also visited all 50 states in the United States and know their way around some major cities in America.
They love learning about different cultures and ways of life, but they don’t have time to research every new place they visit. They want to know what’s interesting in each area before they get there, so they can make the most of their time while on vacation.
This person would prefer an app that can be downloaded onto their smartphone or tablet device instead of having to open up a website every time they enter a new location—they’d rather just use their phone as another tool for exploring wherever they happen to be staying at that moment.”
Notice how this example doesn’t treat their buyer like a number? You can (and should) imagine that this is a real human being with values and emotions and things they care about unique to their personality.
Here’s another example of a buyer persona (in a more visual format).

Aim for that level of depth as much as possible and you’ll be rewarded.
Step 3: Evaluate your competitors
Now that you’ve identified the problem you are solving and the target audience that you are solving the problem for, the next step is to evaluate your competition.
The goal here is not to create a long list of competitors, but rather to narrow it down to a handful of players that make up your competitive landscape.
If you’re building an entirely new product or service, then this will be easy (ie. if you’re the only one offering this, you have no competition). However, if you’re trying to improve upon an existing market, then this process can be more complicated.
The key is to think like a buyer and evaluate the product or service from their perspective. Are there any obvious gaps in what they offer? How could they make their solution better?
Once you have your list of competitors, it’s time to do some more digging into each one by answering these questions:
- Who are they?
- What do they do well?
- Where do they have opportunities for improvement?
- What makes them better than me?
- What makes them worse than me?
By answering these questions about your competitors, you are conducting what is called competitive analysis.
A competitive analysis is a process of determining your competitor’s strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. It can be either a formal process or informal, but the point is that it’s designed to help you understand your market and the best way to approach it.

A SWOT analysis is helpful in this scenario.
Note: It’s important to understand how a competitive analysis is different from market research. Whereas market research focuses on what your customers want, a competitive analysis focuses on what your competitors specifically are doing.
In other words, market research provides insights into trends and customer needs, while competitive analysis provides insights into how your competitors are addressing those needs.
Step 4: Evaluate the market
If you’re working on a new product or service, don’t even think about going to market until you have the answer to the question, “is anyone actually going to buy this?”
Most of us start a business because we have a great idea, but that’s not enough to guarantee that you’ll succeed. One of the biggest mistakes entrepreneurs make is to blindly launch a product or service without doing their homework on whether there’s demand for it.
That can mean having an idea and building it, even though no one will buy it. Or it can mean creating a solution to a problem that doesn’t exist in the marketplace.
Before you invest money in bringing your product or service to market, do the research needed to be sure that there’s enough demand for it and that there isn’t too much competition from other solutions or alternatives.
You may find that there isn’t enough demand for your product or service in your region, country, or even the world at large. Perhaps more important than how much demand there is, though, is how much of the market share you could feasibly capture.
Before you invest in bringing your product or service to market, you need to make sure that there is enough demand and not too much competition.
Investigating demand for your products or services requires planning and research, so it could take some time and energy, but it’s worth the extra effort to ensure that there’s a good chance you’ll succeed before investing even more into something that might be at high risk of failure.
Step 5: Decide on messaging
The next step is to determine how you’re going to tell your customers how great your product is. It’s best to use a different message for each buyer persona, so you can address their unique needs, values, and frustrations.
For example, imagine you’re building a new set of kitchen knives.
You could have four personas: home cooks who are trying to cook healthy meals for their families; professional chefs who want to make sure their knives are sharp enough for restaurant-quality cooking; professional chefs who are looking for an edge over other chefs in competitions; and home cooks who love cooking but aren’t as skilled as they’d like to be.
Each persona has different needs–they might all want sharp knives, but some will want them because they’re afraid of cutting themselves while others are concerned about optimal performance.
Once we’ve broken down those needs, we can go further into identifying what pain points each persona experiences around them…and build out our messaging tailored to each.
A message map can help you organize your proof points and best communicate with your audience.
Step 6: Plan out your buyer’s journey
Now that you’ve identified your buyer personas and messaging, you can map the journey customers take from realizing their problem to buying your solution.
Determining the path your buyers take through the buyer’s journey is a crucial part of content marketing because it helps you create messages that are relevant and timely to customers.
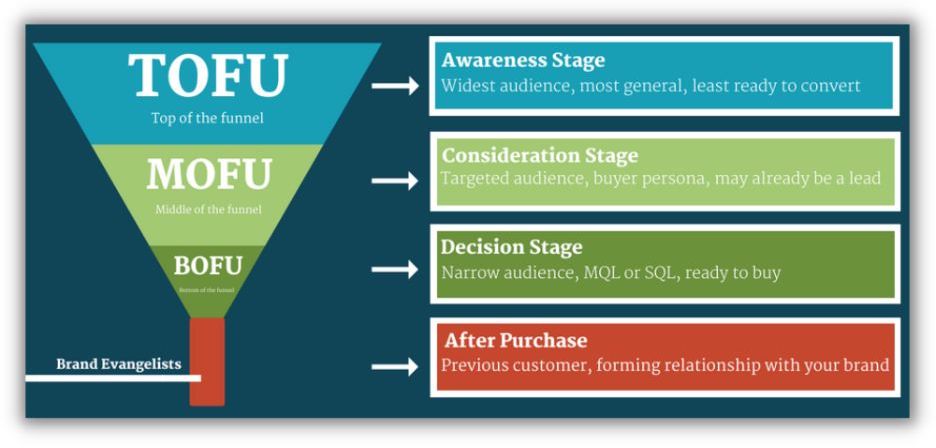
The buyer’s journey is often depicted as a funnel broken into three sections:
- The Top of the Funnel is where you attract prospective customers. This may include advertising on social media or search engines or sending emails to people who have signed up for your newsletter.
- Middle of Funnel refers to things like customer surveys, content upgrades or other ways to warm up potential customers so they’re more likely to buy from you later on down the line. The goal is to get them talking about your brand with others, which will help build your authority as an expert in your field.
- Bottom of Funnel is where you convert those warm leads into paying customers by offering an incentive like a discount code or free shipping if they buy now.
Step 7: Decide your marketing channels
Marketing channels are the different places you post content, like social media, blogs, and email, to create buzz, generate demand, and move customers down your marketing funnel.
The problem is that there is no one-size-fits-all marketing channel.
The best channels for you depend on who you’re trying to reach, what message you want to send, and what type of business you run.
Here are two tips to consider when deciding which marketing channel to use:
- Align your channels to your target audience’s needs and behaviors. You’ll want to make sure the marketing channels you choose to align with how your target audience consumes content.
- Use different channels depending on which part of the funnel your audience is in. Customers in different stages of the marketing funnel can be moved to the next stage by different types of content, found in different areas based on how they use technology.
(This is why knowing your customer is so important!)
Step 8: Create content to get customers interested
Inbound leads are more likely to become customers than outbound leads because inbound leads are already partially educated about your product, aware of its benefits, and interested in buying.
Content marketing is the concept of creating “content” that meets your customers in the appropriate state of the funnel they are in, and then getting it in front of them to begin considering purchasing your products and services.
The name of the game is creating content that targets keywords (aka, what people type into a search engine). That keyword-rich content then ranks on Google and drives traffic to your website, which then allows customers to find you and buy your products and services.
In other words, you’re creating content that addresses not only what your business does but also what it can do for your target audience.
As you come up with ideas for your content strategy, think about what your readers want to know about your company or industry and how you can deliver that information to them in a way that makes their lives easier.
Content marketing works because it’s authentic and relevant to people’s lives. It’s not salesy or pushy–it’s useful. People are more likely to share things they find useful than things they find boring or annoying. This means that when you create good content, people will want to share it with their friends, family members, or colleagues.
If your business solves a problem (which it should), then simply write articles, post social media content or share videos that educate your audience on those problems and why your business is the solution they need.

Continue to create and distribute your work to get it in front of the most amount of people possible to start the process of getting inbound leads to contact you about purchases and business inquiries.
Step 9: Create repeatable processes and optimize as you go
It’s one thing to have a plan, but it’s another to continue to execute it forever onward and show up consistently even when you might not feel like it. For this reason, it’s imperative to have replicable processes that you can not only follow yourself but share with your team and train others to follow as well.
Here are two ways to create content with repeatable processes:
1. Create a content calendar
A calendar can be anything from a simple Google spreadsheet with dates and topics listed down a column to an elaborate Trello board that keeps track of everything in real-time.
The goal is to create a system that allows you to plan out every piece of content you want to publish each month or quarter so that when it comes time for the big day (or days), you and your team know exactly what needs doing and when.

2. Outline your content in advance
Outlining forces you to think through your ideas before writing them down and makes the creation process so much simpler once you get started. It helps to eliminate writer’s block because before you get started, you know exactly what points you need to discuss.
Here’s how to create a simple outline:
- Start with an idea for a topic or theme that you want to write about
- Brainstorm as many related topics as possible (what else can be said about this subject? What other angles can be explored?)
- Think about what points you’ll need to make in order to develop those themes (what is the point of view I want to take on these ideas?)
- Organize those points into an order that makes sense (do they flow naturally?)
Once you’ve completed all of these steps, it’s as “simple” as showing up every day, putting in the work, and continuing to adjust and iterate as much as necessary.
Remember, this is a never-ending process. It’s not something you do once, set it and forget it. Always be on the lookout for opportunities to improve and grow if you want to stay ahead of the curve.
Here are a few examples of how others have done this to get you started…
Go-to-market strategy examples
Up until this point, we’ve mainly covered how to bring a new product or service to market, however, businesses can also go to market with a new feature or components of an already existing product.
That’s what the brand Eight Sleep Mattresses did for one of its newest features.
Eight Sleep’s partnership with IFTTT
To market their latest technology, they opted to partner up with IFTTT, a service that lets users create conditional “if this then that” statements where previously separate technologies are able to work together in unison.
By using IFTTT, users could connect their Eight Sleep mattresses with other smart home systems to turn on/off lights, start their coffee machines, activate bed warming, and much more, all through their smartphones. Eight Sleep leveraged this technology with their go-to-market strategy flawlessly.
Their GTM strategy was surprisingly simple, despite how sophisticated technologically it sounded:
They designed an email announcement to get users excited, a landing page to educate the target audience about the new feature, and promoted it on social media after launch, highlighting the benefits and use cases.
Sounds simple, right?
The result was an outpouring of enthusiasm from customers.
Why Eight Sleep’s go to market strategy worked:
Eight Sleep officials said that the secret to success was to invest heavily in showing practical use cases that potential customers could envision themselves using themselves.
By focusing on creating a story around the benefits that would resonate with consumers, they were able to develop an emotional connection with people and were rewarded by helping people envision themselves being able to achieve everything they might be able to in an Eight Sleep mattress.
Fitbit Smart Coach
In 2019, Fitbit, the activity-tracking wearable, launched Smart Coach, a premium personal training service that integrates with a customer’s FitBit.
Their GTM strategy included objectives such as increasing revenue from subscriptions and getting more out of those who had already committed to their product.
They launched a marketing campaign called “Get More With FitBit” that leveraged both paid and owned channels to reach their target audience of people who already owned their wearable devices and smartphones.
Fitbit’s digital marketing strategy was simple: they used paid retargeting display ads to direct potential customers to a landing page that would encourage them to make an additional purchase.
They also utilized push notifications, social media accounts, and newsletters to reach their existing customer base and let them know about new deals being offered.
Why Fitbit’s go-to-market strategy worked:
Fitbit was smart in targeting people who already owned their products. These were people who had already made the commitment to improving their health and trusted Fitbit enough to have paid money for what they had to offer.
Thus, they required much less convincing of what their problem was and simply needed to be made aware of a quicker, better way of solving it that required only a small investment.
The result? Their annual revenue rose from $1.4B in 2017 to $2.1B in 2019.
Go-to-market plan template
While a go-to-market strategy won’t guarantee your product’s success, it can help you manage expectations and work out any kinks before you invest in bringing your products to market.
To help you in this process, our friends at LocaliQ have created a free go-to-market template that will help you build a strategy that positions your product in front of the right people.
Go-to-market strategy FAQs
Below are some quick responses to some of the most common questions we see about GTM Strategies:
1. Who is responsible for GTM strategy?
The person responsible for creating a go-to-market strategy will vary from company to company, but it’s typically someone who has experience in marketing or sales. In some companies, like startups, the founder usually takes responsibility for this task and then passes it off once the business becomes larger and more profitable.
In larger corporations with dedicated marketing departments, often there are specialists who focus on developing these strategies; however, even here it’s still important that everyone understands how their work fits into the bigger picture of generating revenue and growing market share.
2. What is the difference between product-based and customer-based go-to-market strategy?
A product-based go-to-market strategy is the most common and easiest way for a company to get started. It’s based on the idea of creating a core product and then selling it to a large audience. A customer-based go-to-market strategy is more complicated and requires more planning.
A customer-based go-to-market strategy is based on the idea that you should identify your best customers, study their needs and wants, then tailor your products to those needs and wants.
If you’re just starting out, you probably don’t have enough data or experience yet to develop a truly customer-focused approach. However, even if you’re a veteran at this point, it’s still useful to think about how your customers use your product or service and what they need from it.
3. What is the difference between a go-to-market strategy and a marketing strategy?
The go-to-market strategy is the plan for how you will bring your product or service to market and get it sold. It encompasses all aspects of the marketing mix–product, price, promotion, place, and people.
A marketing strategy is an overall plan for how you will communicate with your customers and prospects. It may include aspects of your go-to-market strategy, but it also includes many other aspects of your business that are not part of an overall go-to-market plan.
Next steps: Create a GTM strategy for your next big thing
Before launching a new product or service, it is critical to have a go-to-market strategy in place.
By following the steps and examples in this guide (and using the provided template), you’ll be well on your way to creating a profitable venture that solves customer problems and gets ahead of the competition as quickly as possible.










