SEO
How to Do an SEO Competitor Analysis

Your competitors are a goldmine of information you can use to improve your SEO strategy.
In this post, you’ll learn how to find that information with an SEO competitor analysis.
An SEO competitor analysis is where you dig into the SEO strategies of your competitors. The aim is to find their strengths and weaknesses so you can outrank them.
Performing an SEO competitor analysis allows you to:
- Learn what works and what doesn’t in your industry and avoid mistakes.
- Capitalize on your competitors’ weaknesses.
- Replicate your competitors’ strengths.
- Understand what SEO tasks to prioritize going forward.
- Understand how difficult outperforming competitors is likely to be.
You should perform an SEO competitor analysis when:
- You have a new website.
- You’re planning your SEO strategy.
- Competitors are outranking you or when your rankings have dropped.
For this process, let’s pretend we’re a new infographic design tool. This is how your hypothetical SEO competitor analysis will look like:
1. Identify your SEO competitors
Your SEO competitors are the websites competing for your desired keywords in organic search. These may not be the same as your direct business competitors.
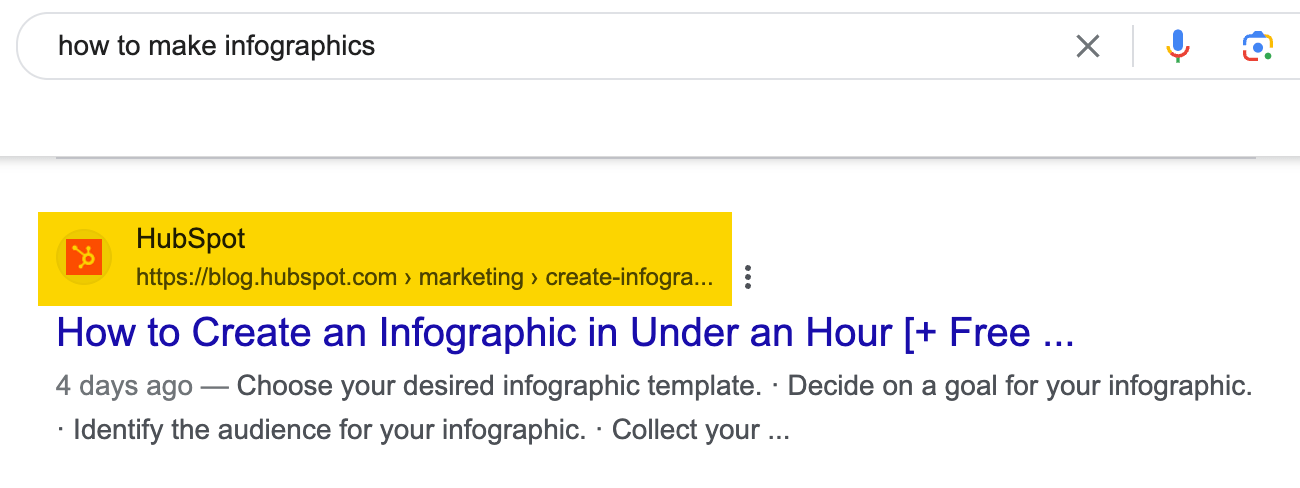
For example, HubSpot ranks for “how to make infographics” even though it’s not a direct business competitor of any infographic design tool:
Here’s how you can identify SEO competitors fast:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your domain
- Go to the Organic competitors report
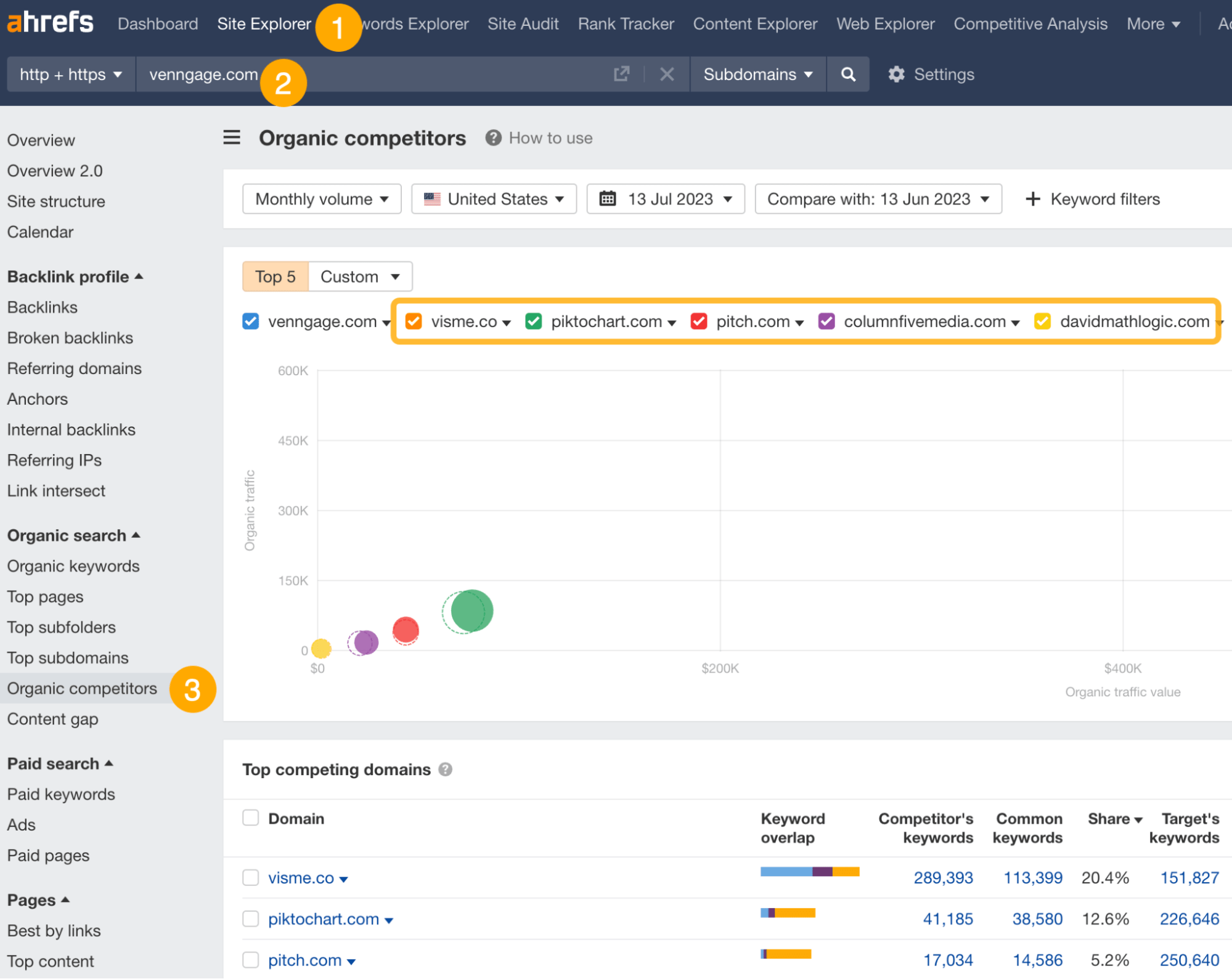
This report shows you competing websites that rank in the top 10 for the same keywords as your website.
These are likely your SEO competitors.
If your site is new, this may not give you great results. So here’s what you can do instead:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
- Enter some keywords potential customers may use to search for your product or service
- Go to Traffic share by domain
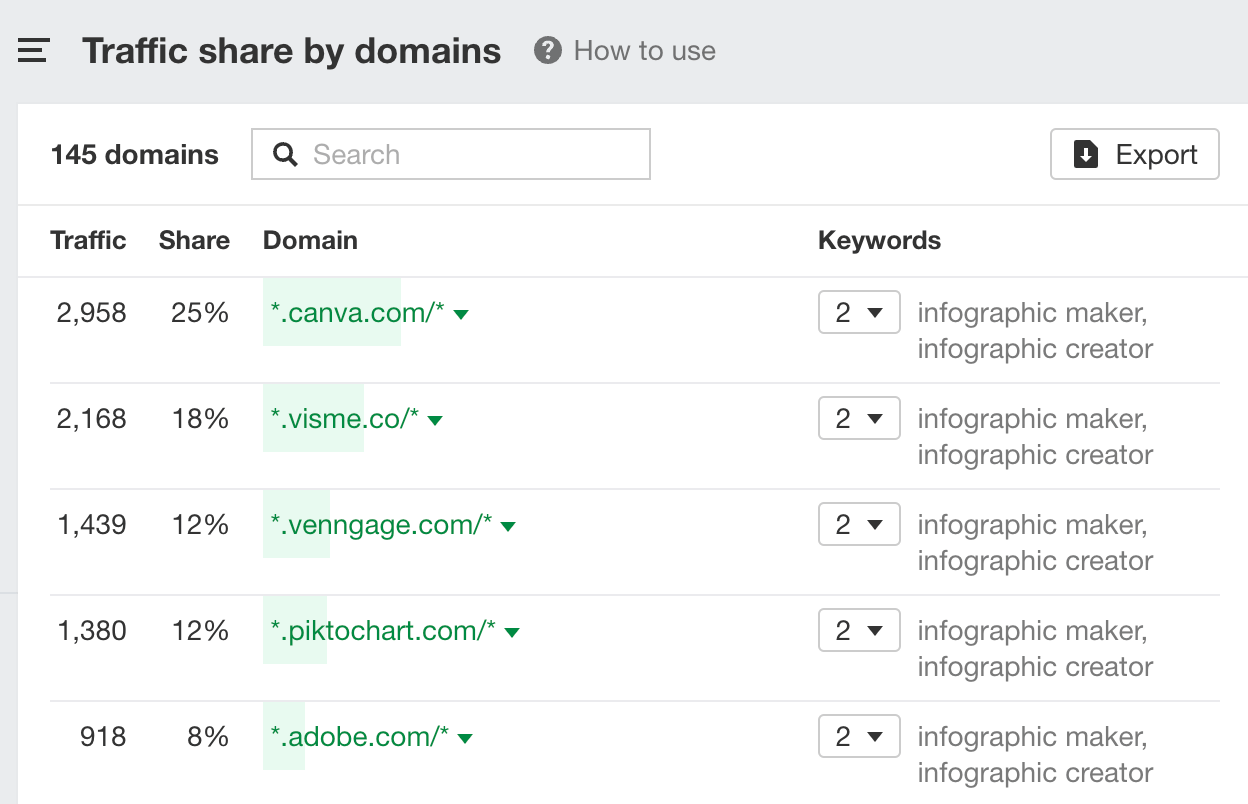
For this example, we can see that our potential top five competitors are sites like Canva, Visme, Venngage, Piktochart, and Adobe.
Pro Tip
You can check a site’s DR by plugging each competing domain into Site Explorer individually or pasting all of them into our Batch Analysis tool:
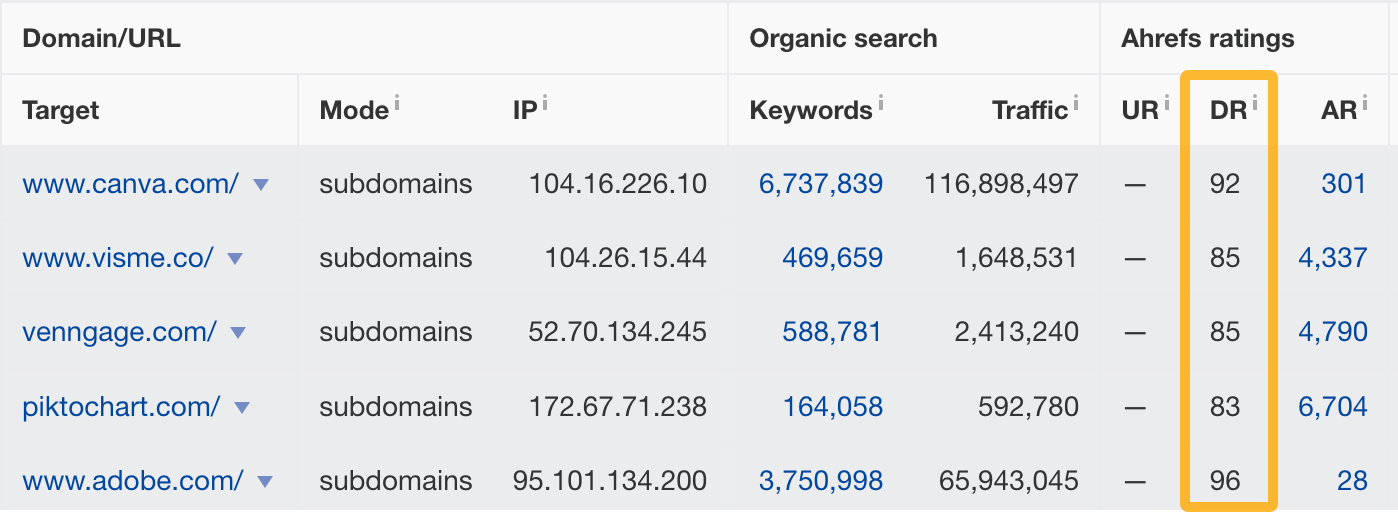
So if you’re a DR 50 site, you probably can compete with sites like Visme, Venngage, and Piktochart, as opposed to Adobe and Canva.
2. Investigate how they’re getting traffic
You can look at your competitor’s website architecture to understand where most of their search traffic is going.
Here’s how to see your competitor’s website structure:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Site structure report
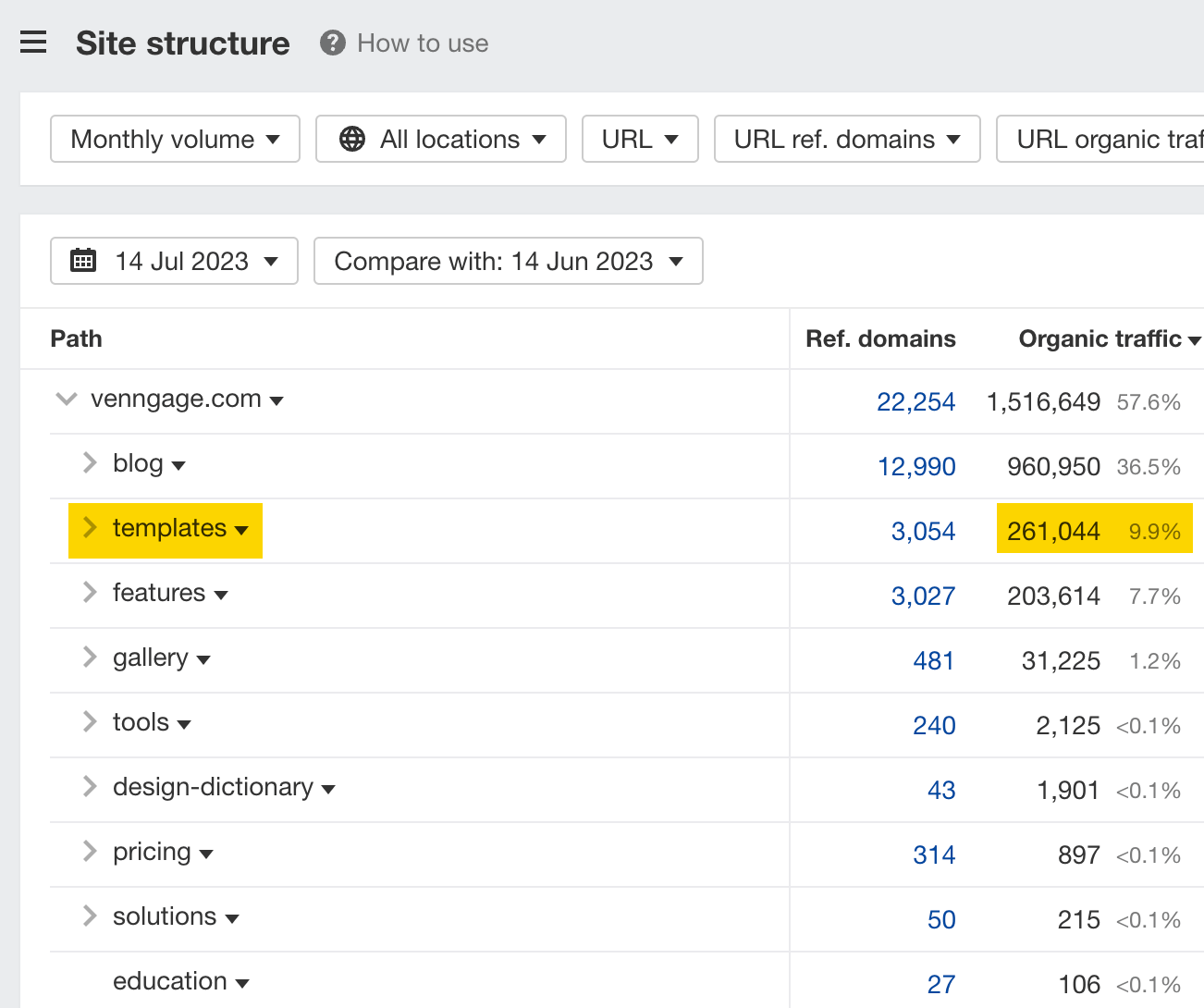
For example, we can see that Venngage gets 260,000 estimated monthly search visits to its template subfolder, which is 9.9% of its total organic traffic.
If we click one level deeper, we can see the types of templates that send it the most traffic.
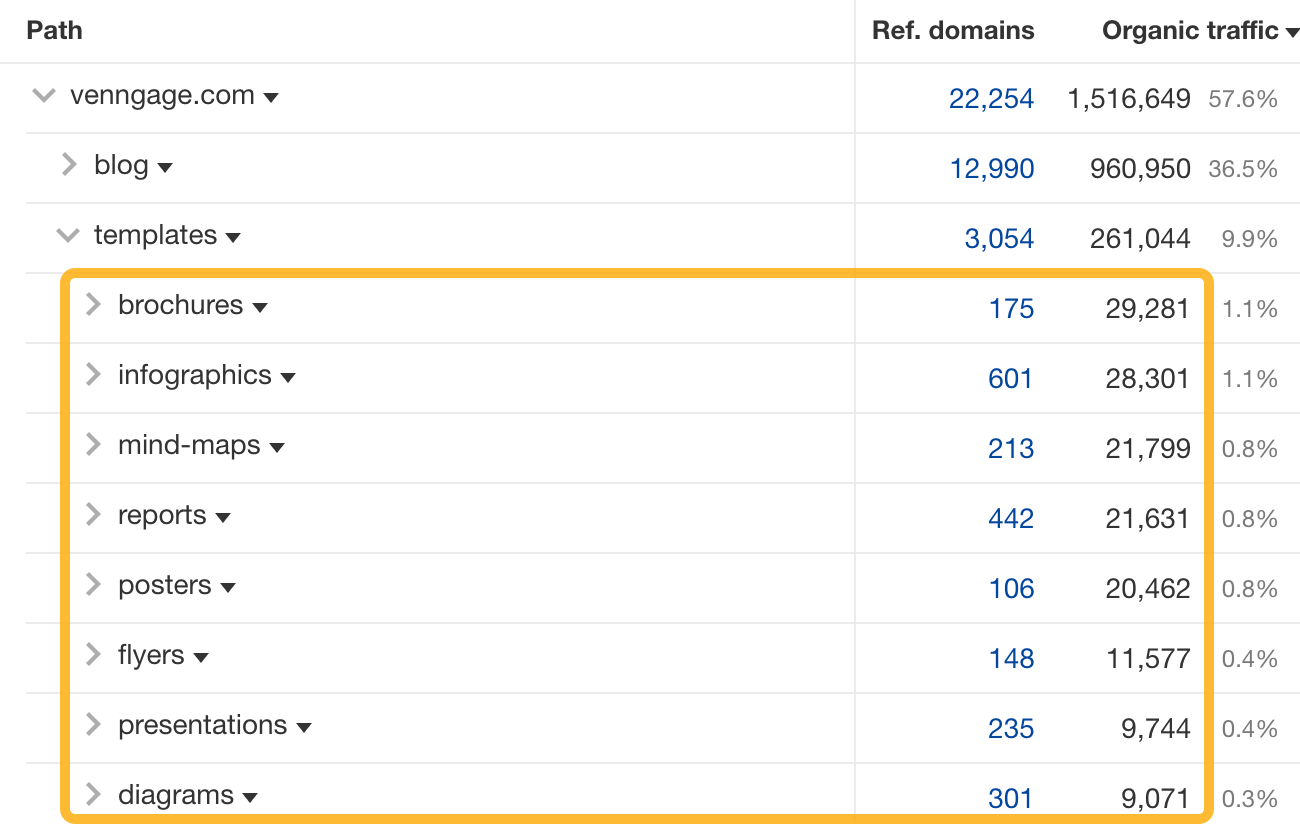
From this, it looks like creating brochure and infographic templates is a perfect SEO opportunity for a competing tool.
3. Find and cover content gaps
Content gaps are keywords that your competitors rank for, but you don’t.
Here’s how to find content gaps for your site:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Competitive Analysis tool
- Enter your domain in the Target section
- Enter your competitors’ domains in the Competitors section
- Hit “Compare”
- Click the Content Gap report
Hit the Main positions only toggle to exclude your competitors’ rankings in SERP features like “Top stories” and “Image packs.”
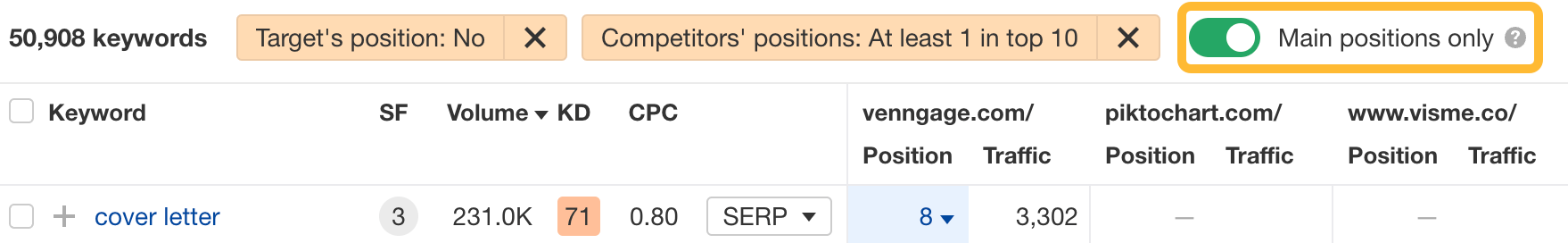
Look through the report and identify keywords that are relevant for your site.
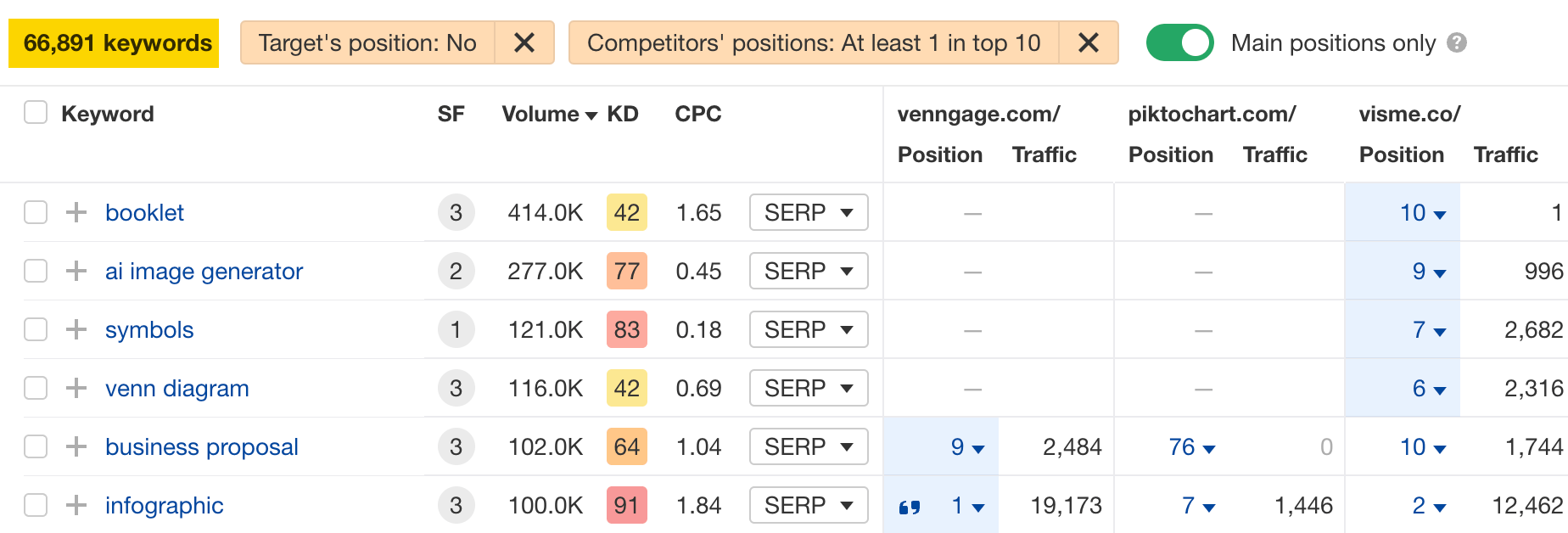
For example, “infographic examples” looks like a good keyword to target:

Pro Tip
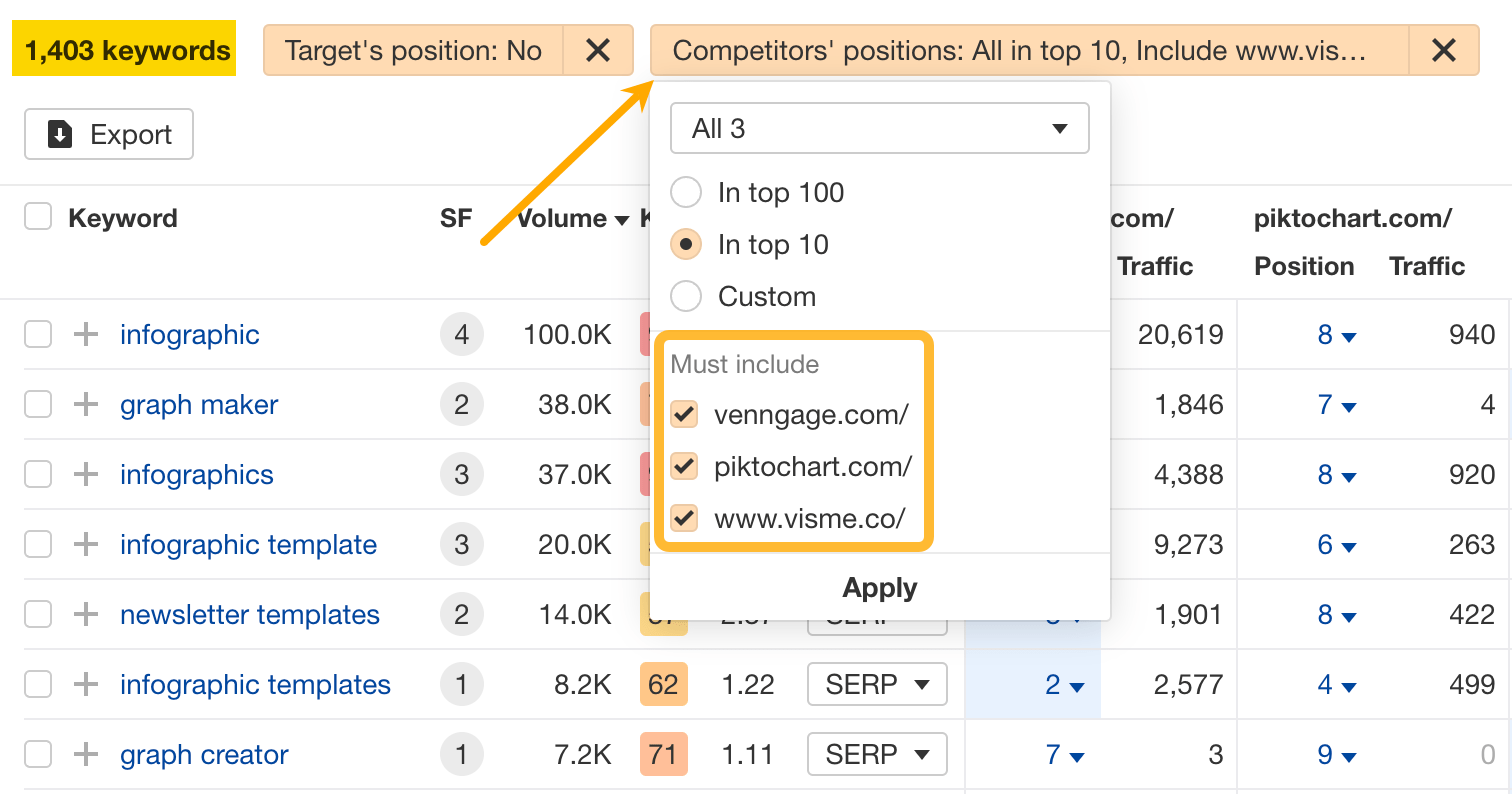
4. Spy on your competitors’ featured snippets
Featured snippets are quick answers in search results that Google pulls from a page ranking in the top 10.
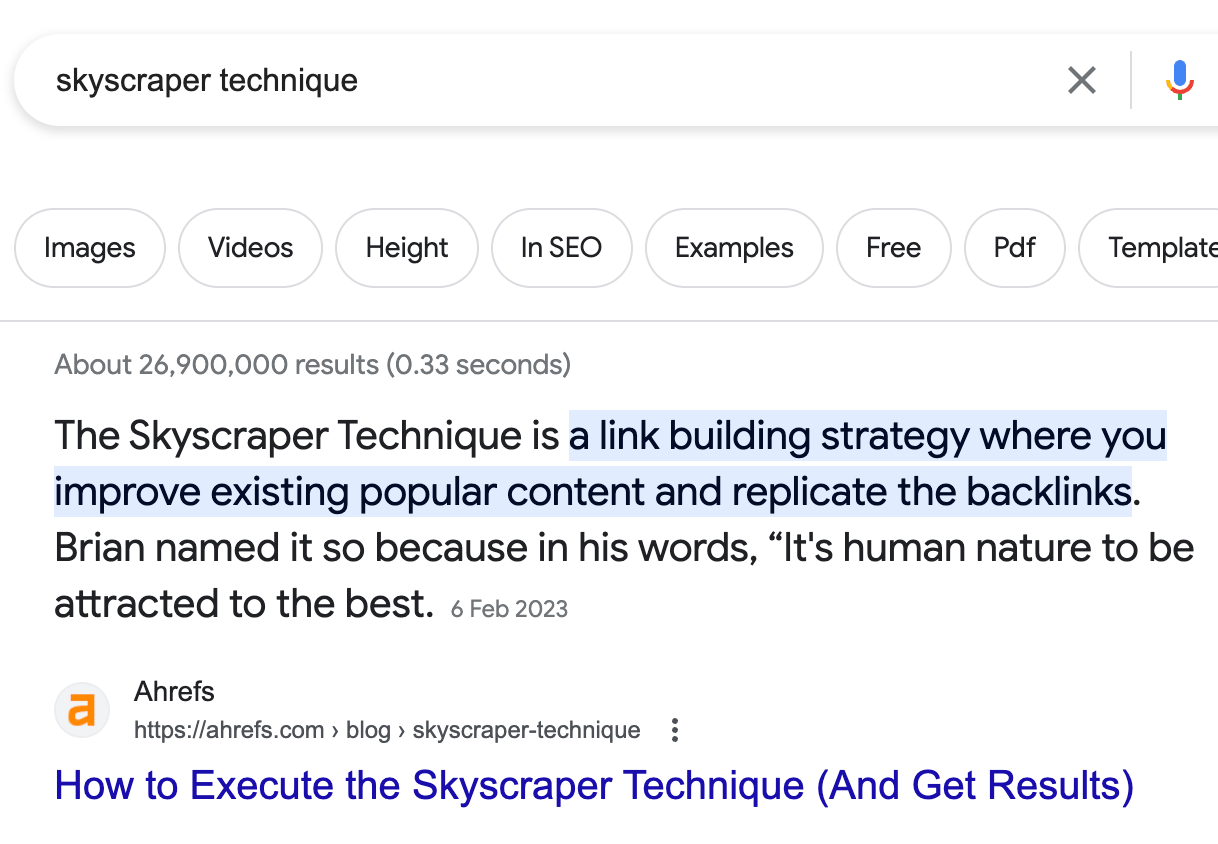
If you can find featured snippets your competitors own where you rank in the top 10, you can potentially “steal” these featured snippets.
Here’s how you can see these opportunities:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Competitive Analysis tool
- Enter a competitor’s domain in the Target section
- Enter your domain in the Competitors section
- Hit “Compare”
- Click the Content Gap report
- Set the SERP features filter to “Where target ranks” and check “Featured snippet”
- Set Target’s position from “No” to “Any”
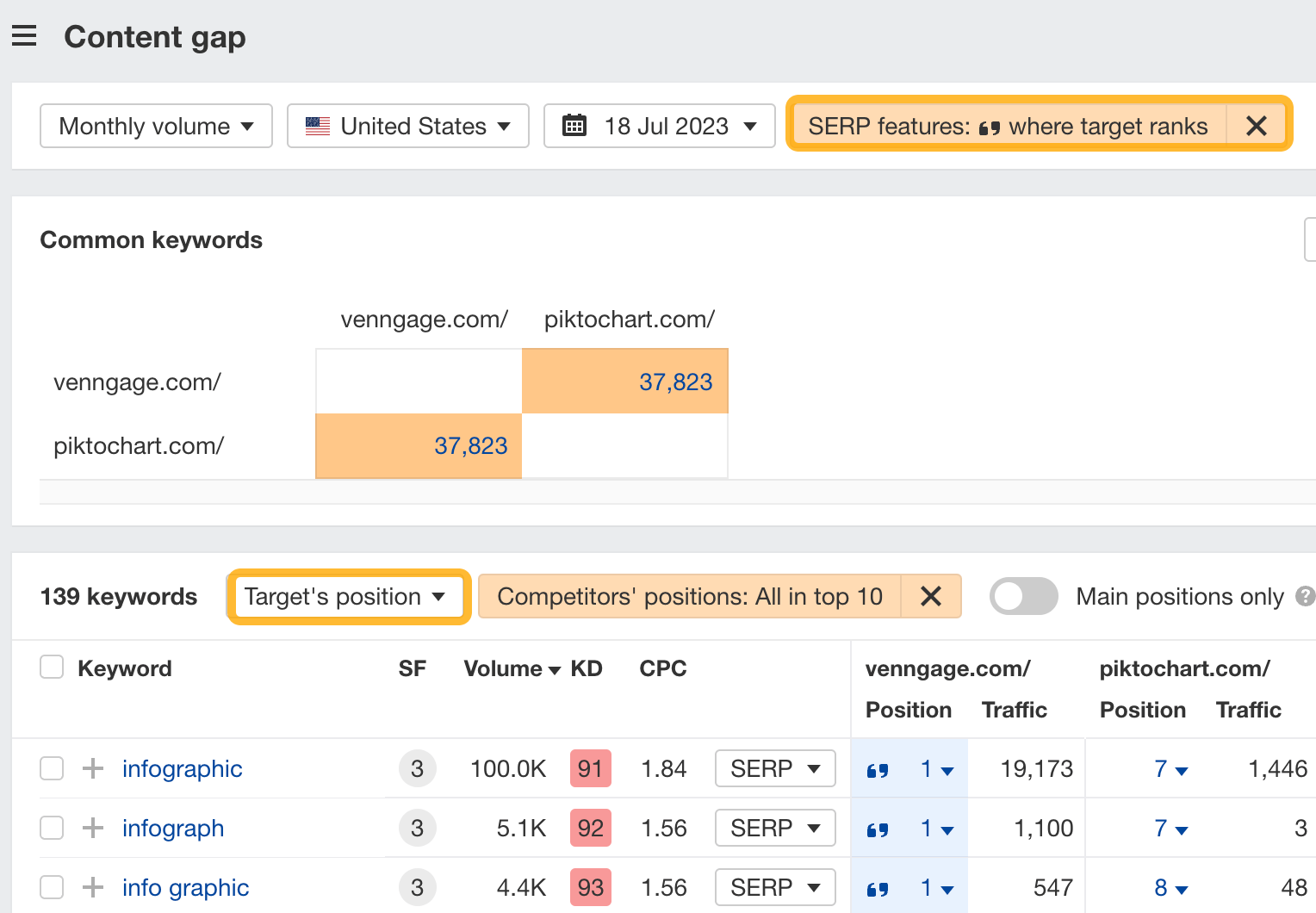
Look through the report to see if there are any keywords where you could optimize an existing page to grab the featured snippet.
For example, Venngage owns the featured snippet for “how to make posters,” which is a list of steps:

If you’re targeting this keyword, you’ll want to re-optimize your page and add clear steps in H3s.
5. See where your competitors’ traffic is coming from
Knowing which countries your competitors get the bulk of their organic traffic from helps you understand whether you can get more traffic by translating or creating your content in other languages.
Here’s how to see this:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Look at the Traffic by country section
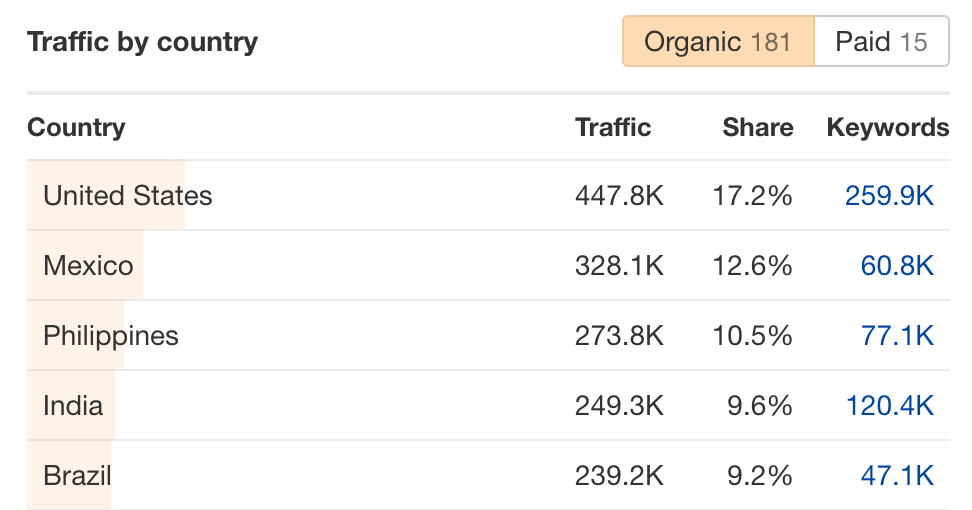
We can see that the U.S. is where Venngage gets the bulk of its traffic. So as a competitor, you’ll naturally want to focus on English-language content.
However, there are opportunities for countries like Mexico, Philippines, Brazil, and India too. You could potentially translate your homepage and landing pages into Spanish, Portuguese, Tagalog, and Hindi. You could even launch a multilingual blog to maximize traffic from these countries.
In fact, Venngage has done that for a number of languages, like Spanish:
6. Find backlink gaps
Links are an important Google ranking factor. Generally speaking, the more links you have, the higher you’ll likely rank on Google.

If you can figure out how your competitors have been acquiring links, you can potentially replicate the same strategies.
Here’s how to do it:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your domain
- Go to the Link Intersect report
- Enter your competitors’ domains in the top section
- Enter your domain in the bottom section
- Hit “Show link opportunities”
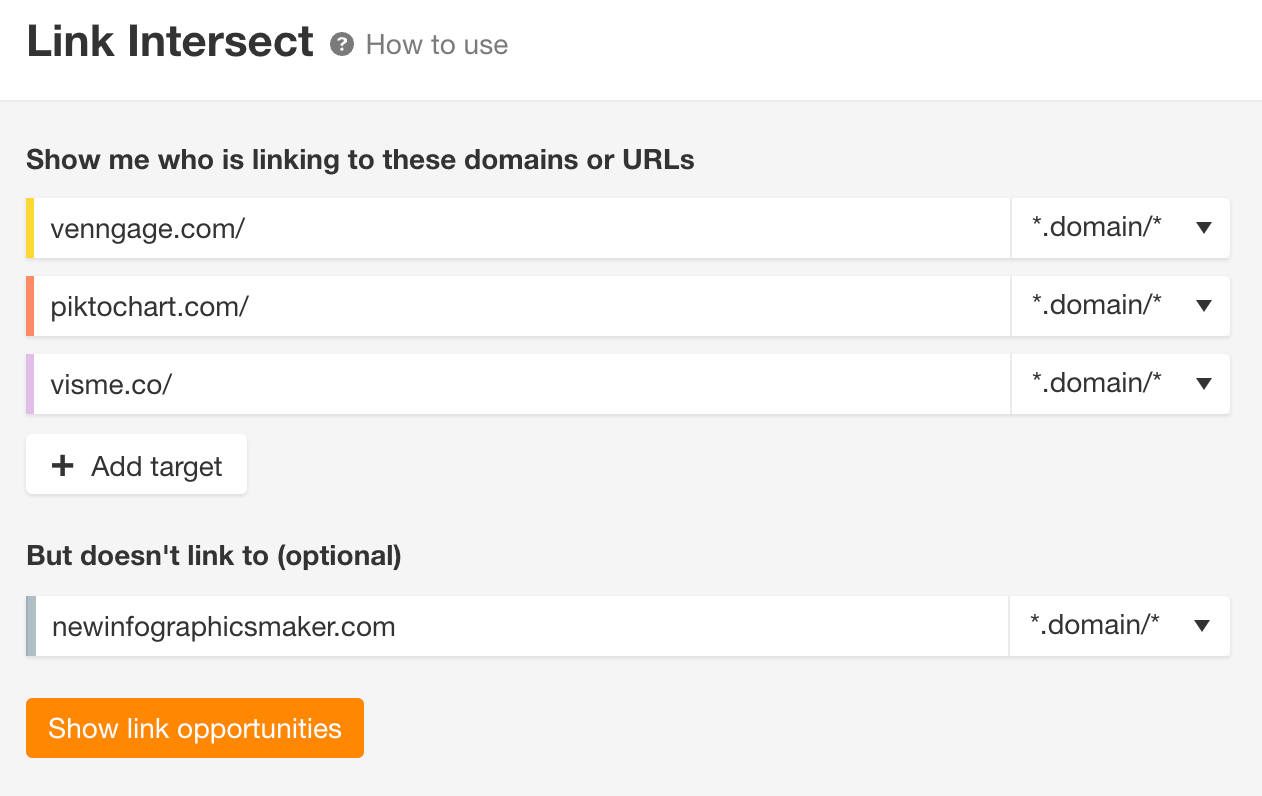
This report will show you the websites that are linking to your competitors, but not you.
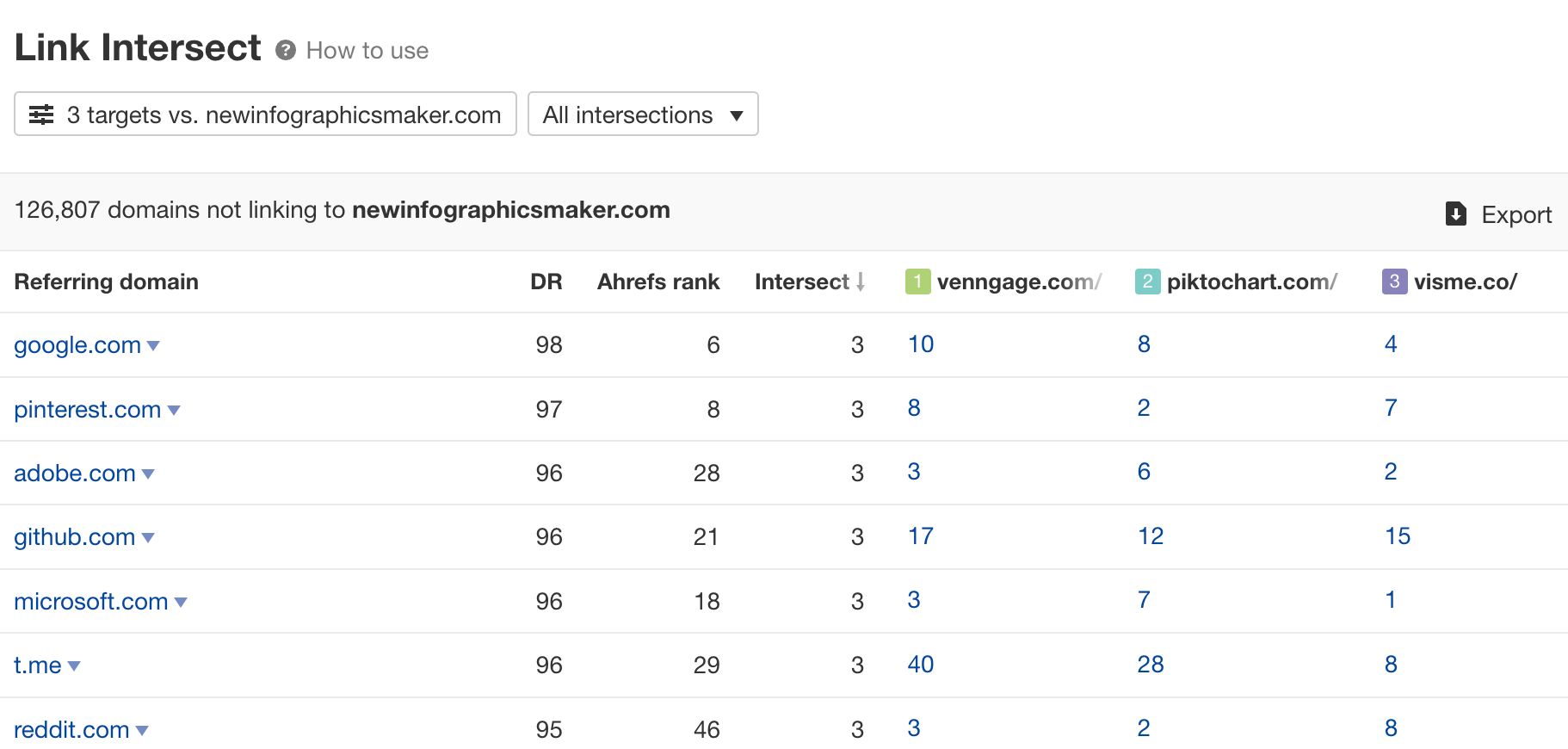
You’d want to look for easily replicable links that might have value for you.
For example, clicking on the number for cnet.com reveals that your competitors are listed as to-try tools:
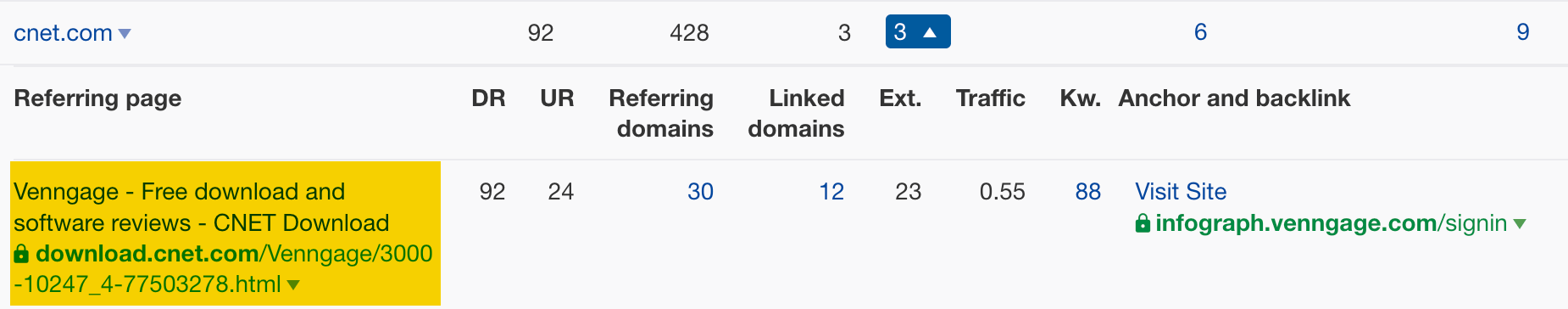
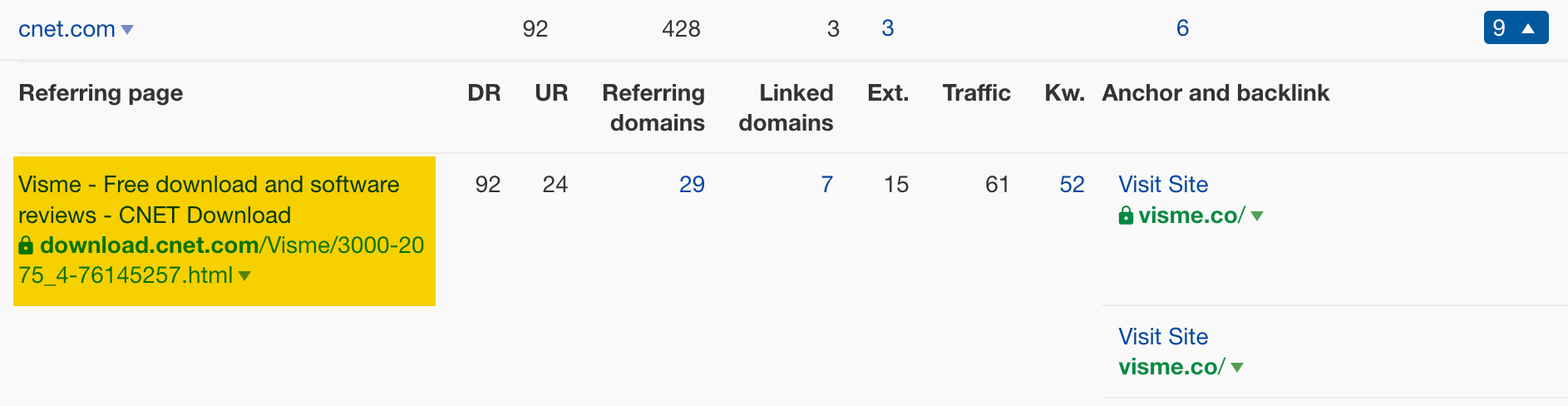
If you’re competing with these sites, you’ll want to be added to CNET too.
7. Spot link bait opportunities
Links are important if you want to rank higher on Google. But it can be difficult to get people to link to your “money pages,” as they provide no value.
You can solve this by creating link bait and then redistributing the “authority” your link bait attracts to your most important pages. This can help boost their rankings.
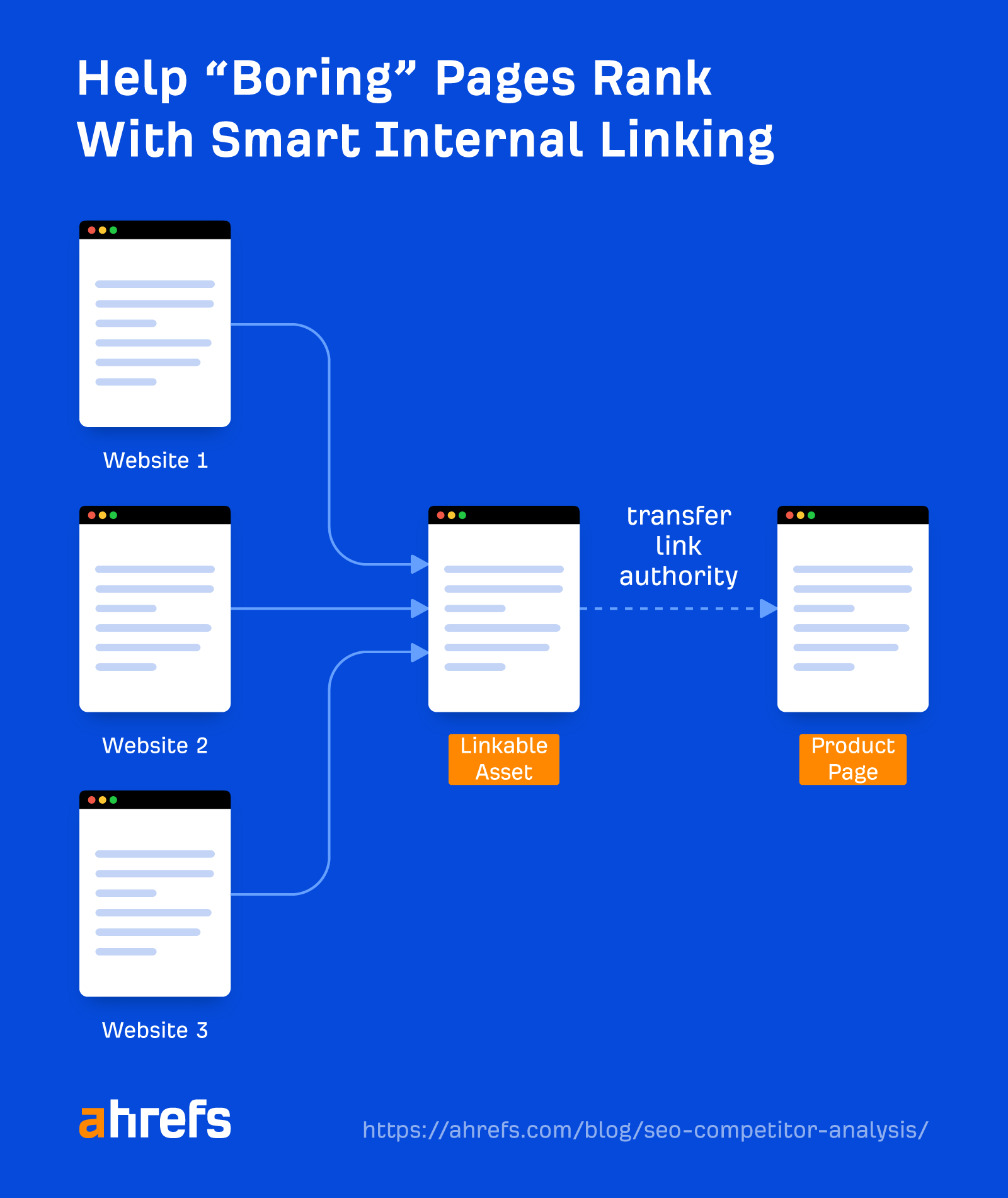
To find great link bait ideas, you can piggyback off what’s working for your competitors.
Here’s how to find them:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Best by links report
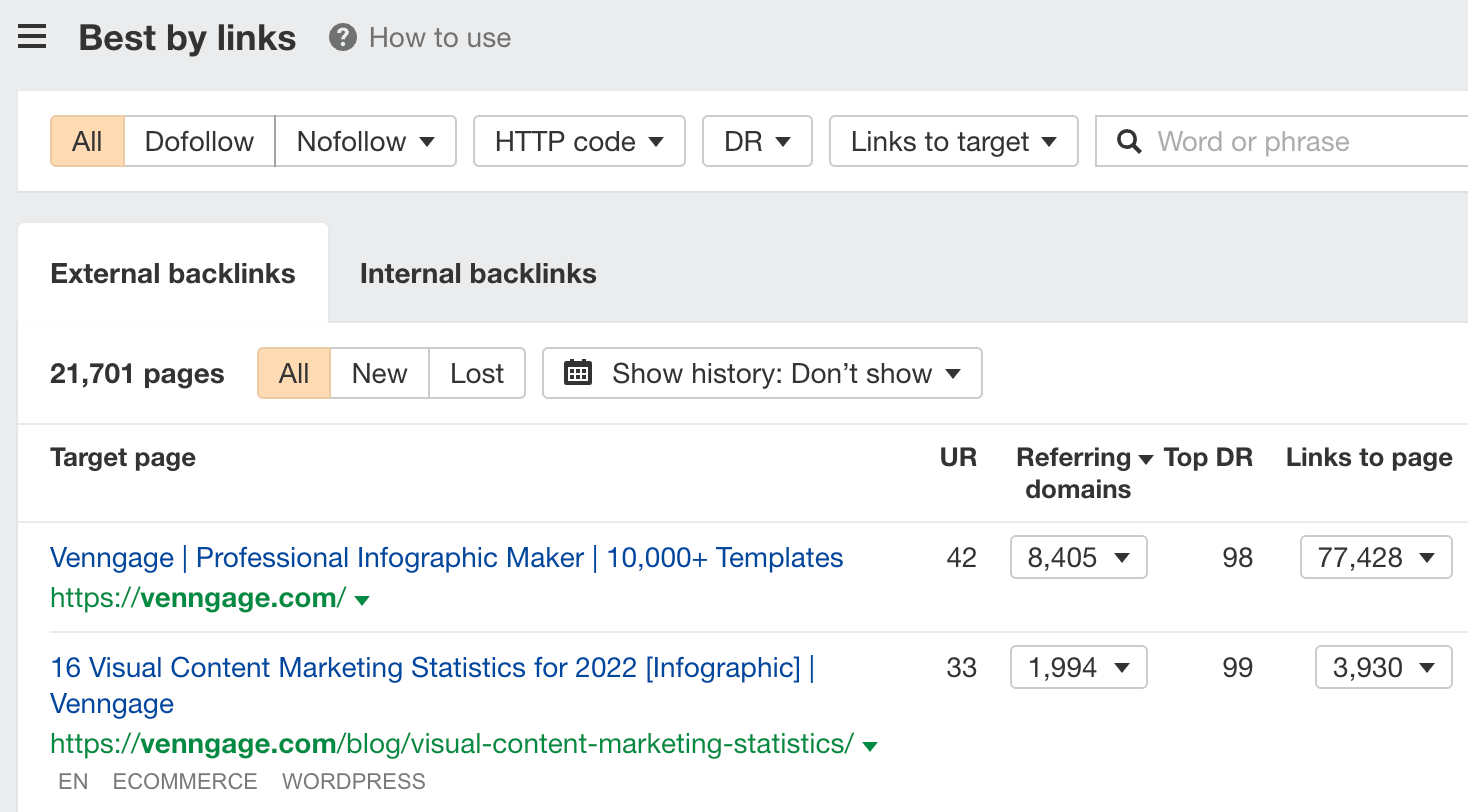
This report shows you the pages that have the most backlinks pointing at them. Eyeball the list to see what kind of formats and topics resonate with your niche.
For example, we can see that statistics posts work well for Venngage:
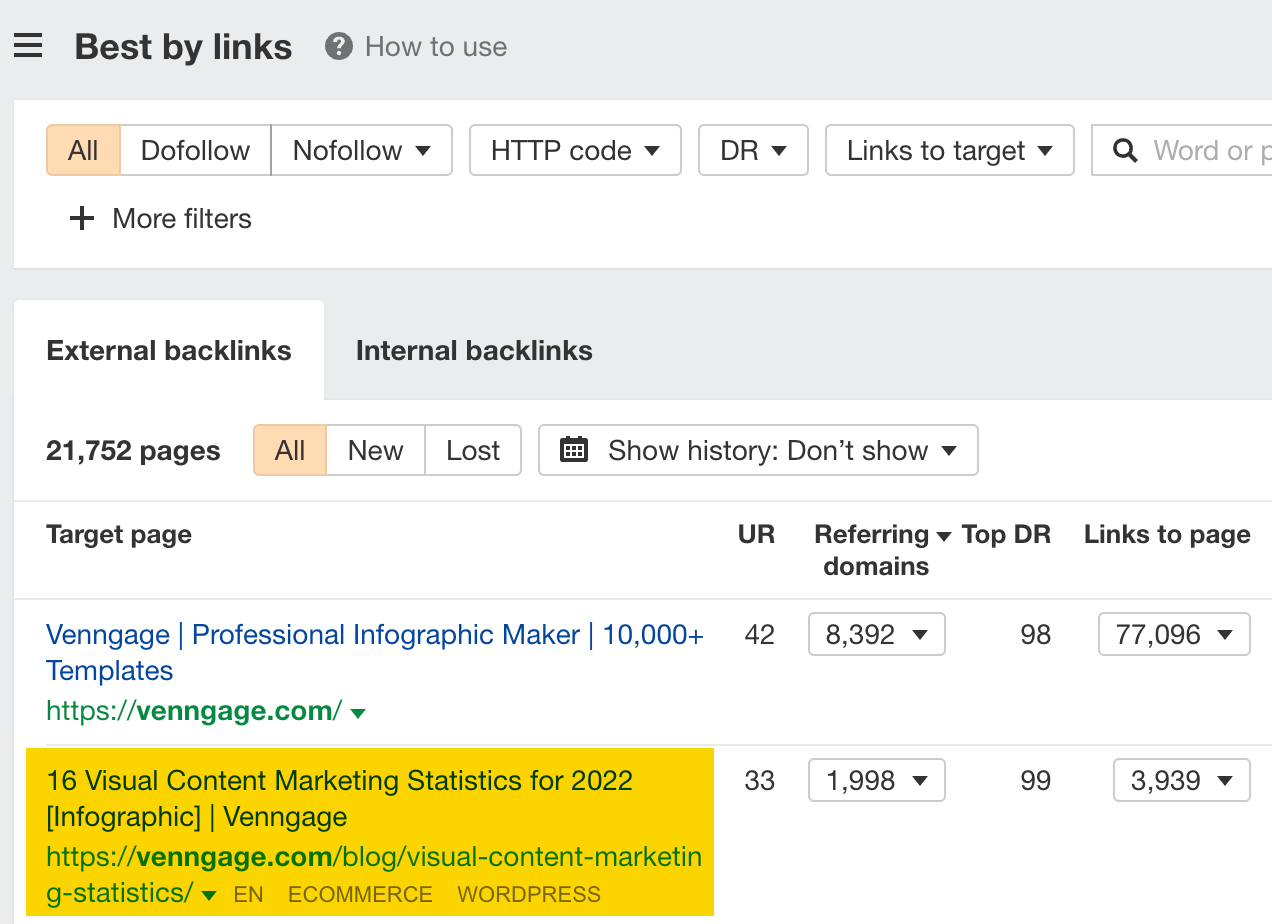
8. Find your competitors’ broken pages
If our competitors have broken pages with backlinks, we can:
- Publish working replacements.
- Ask everyone linking to the dead pages to link to us instead.
Here’s how to find these broken pages:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Best by links report
- Set the HTTP code filter to 404 not found
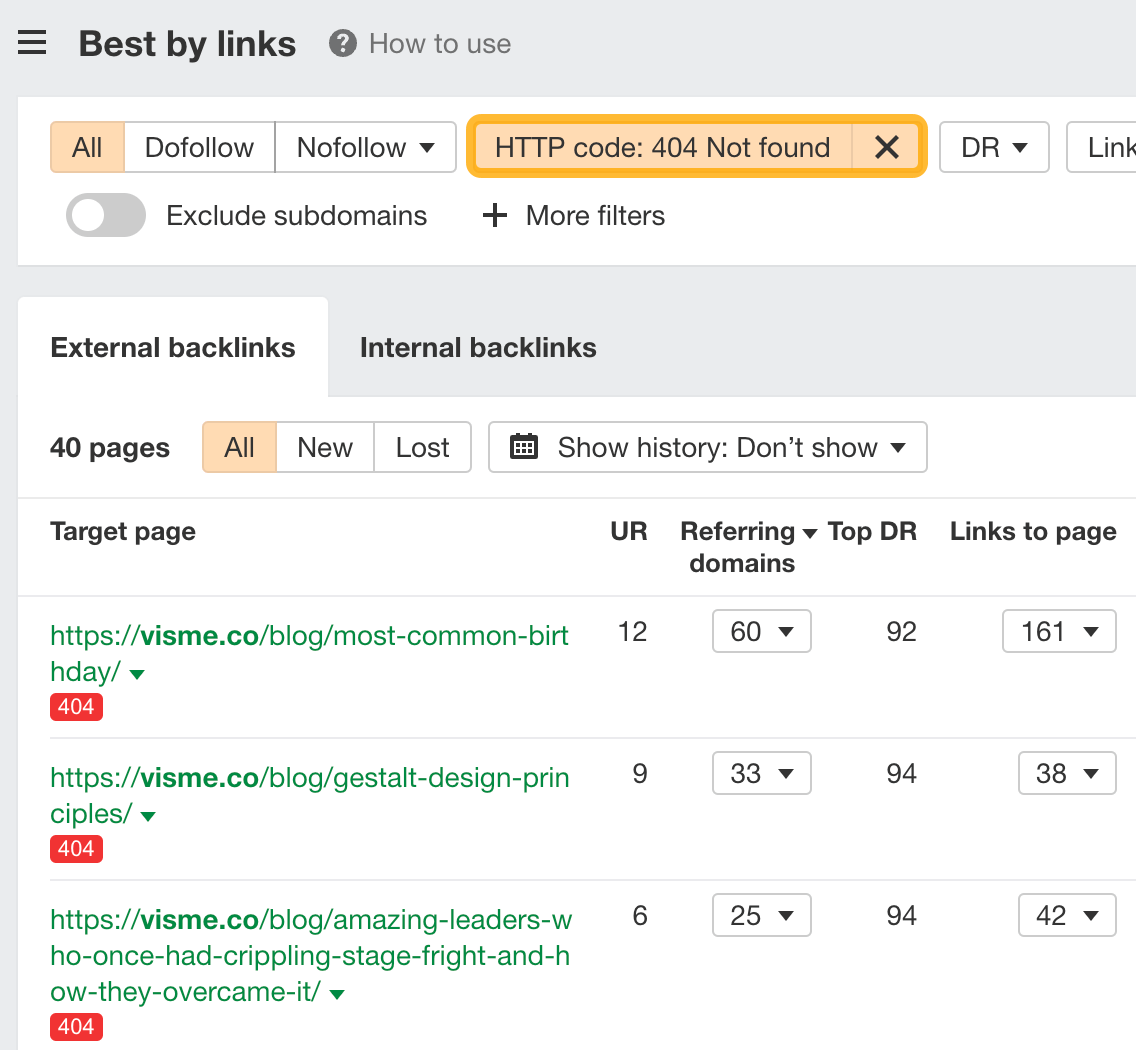
This will show you all the broken pages with links on your competitor’s site. Go through the report and see if there are any relevant pages you can potentially replicate.
For example, this post on Gestalt design principles seems decent and has 33 sites linking to it:
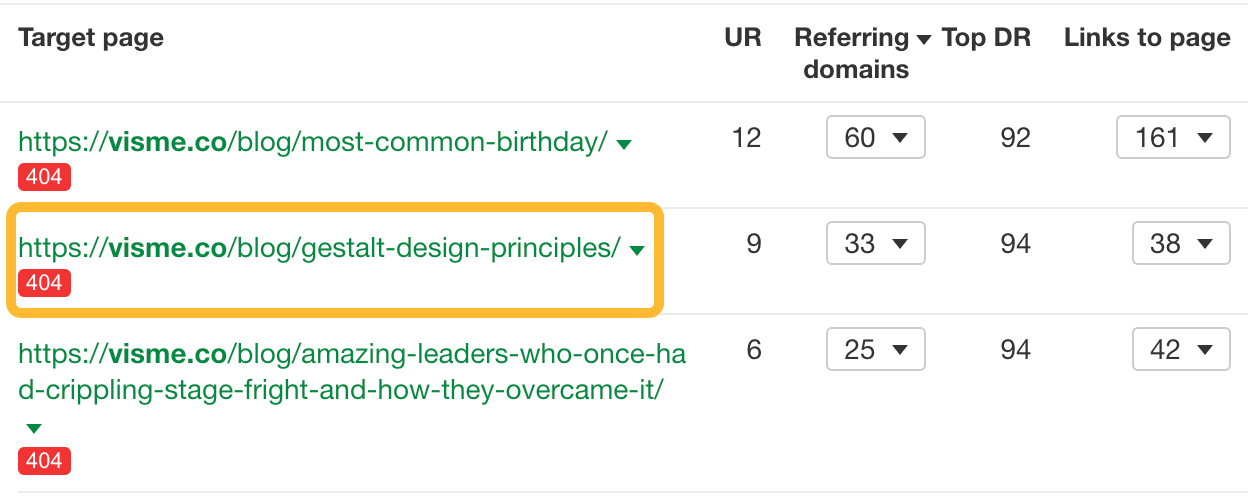
Click on the caret and click on View on Archive.org.
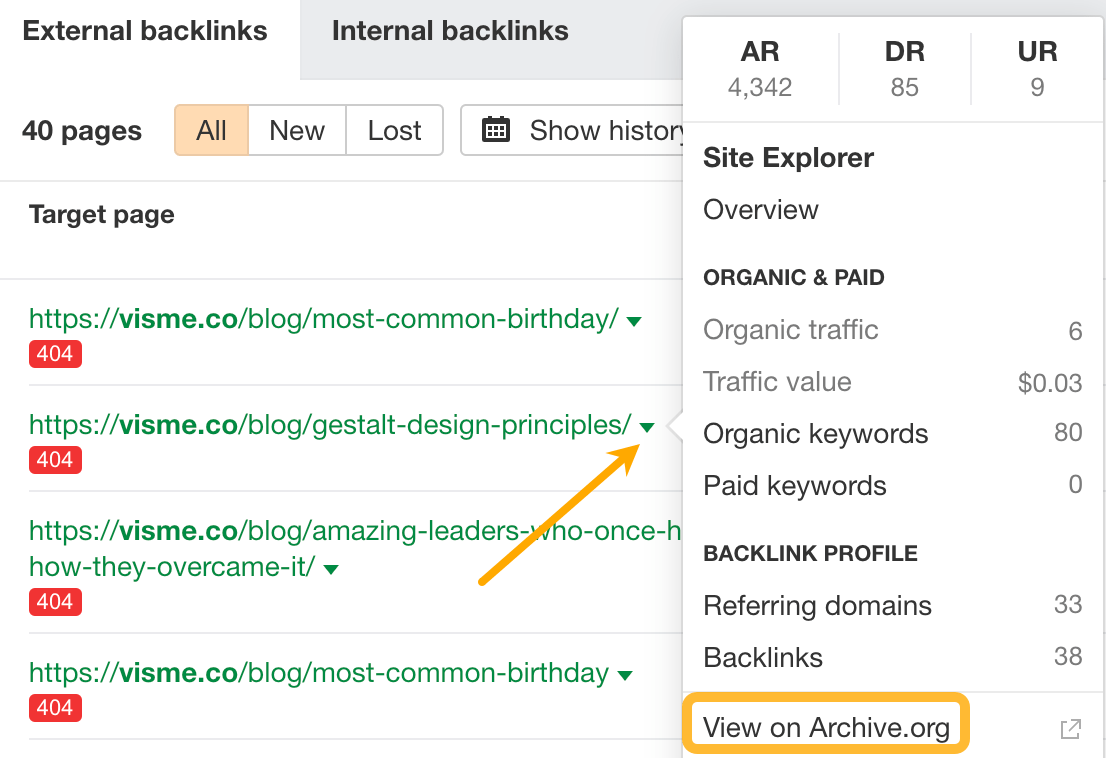
This will open up the page in Wayback Machine so you can check how it looked in the past.
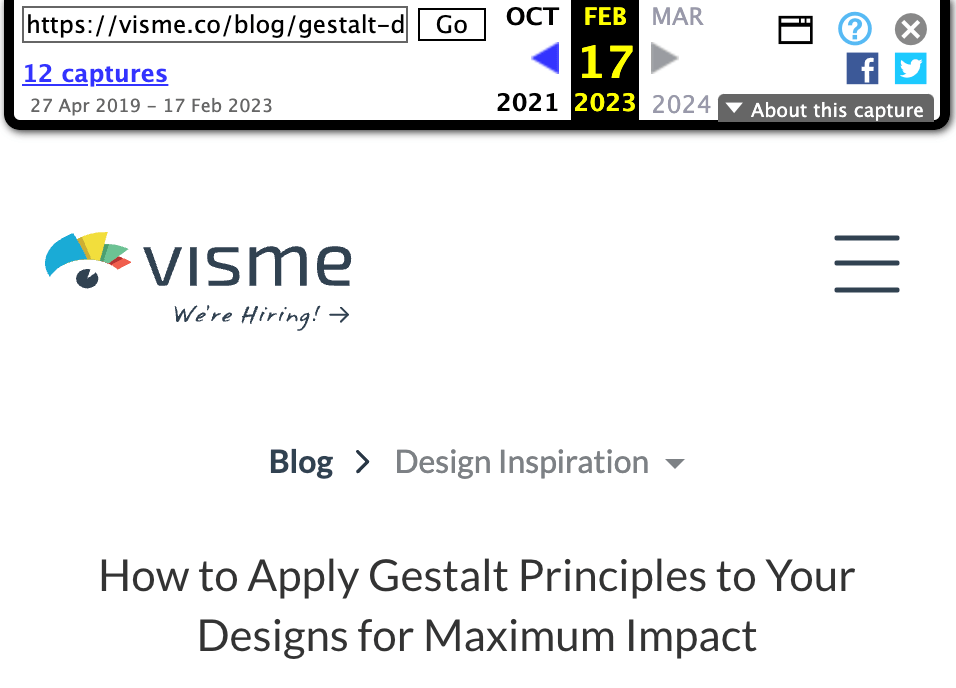
You can potentially improve it and get people to link to you instead. Follow the guide below to learn how to do this.
9. Check your competitors’ Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are part of Google’s Page Experience signals used to measure user experience. They’re Google ranking factors.
So you’d want to see their Core Web Vitals—alongside their overall technical health—and compare them to yours.
You can do this analysis by entering your competitor’s pages one by one into PageSpeed Insights.
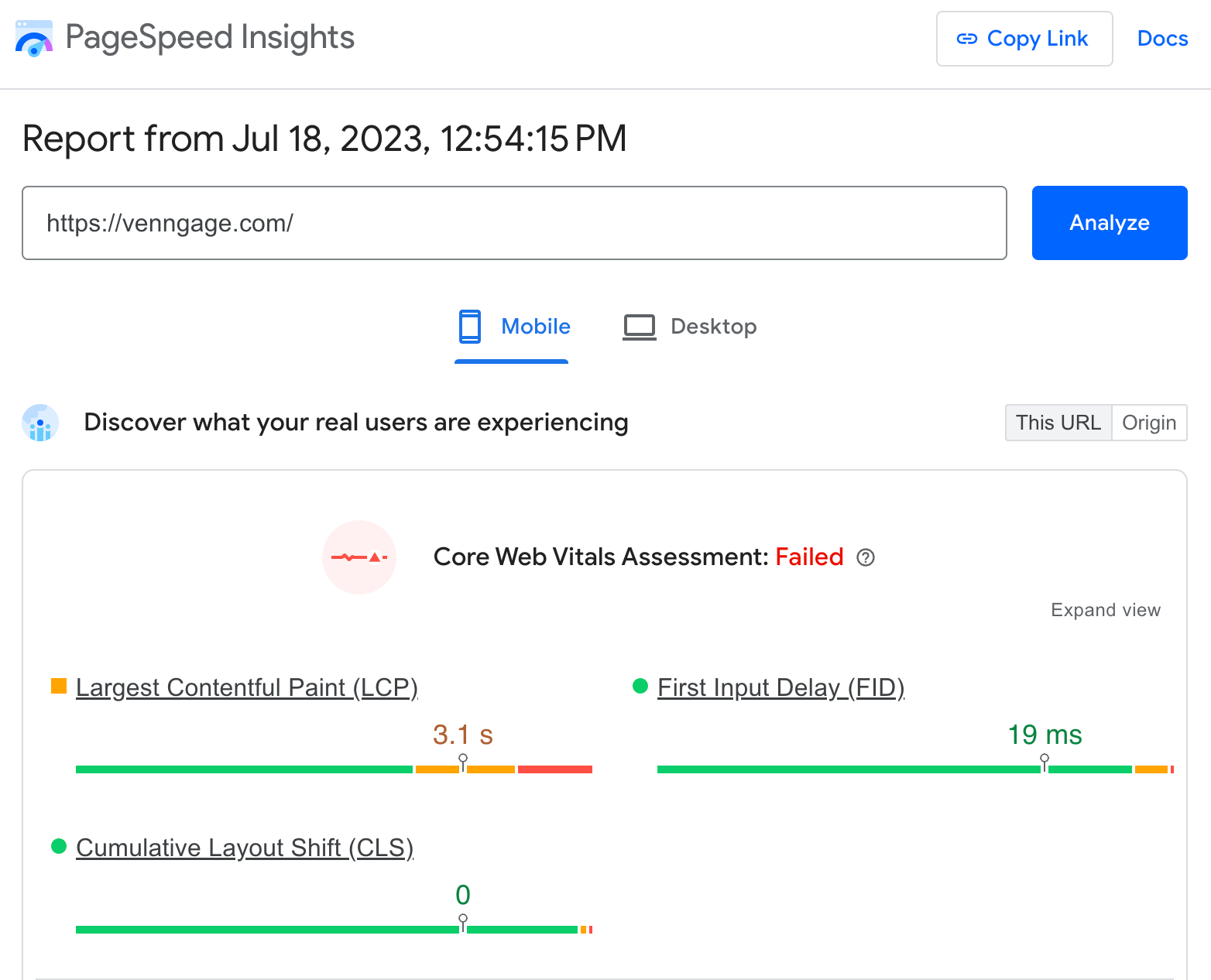
Doing that can be tiresome. So a better way is to run a crawl of your competitor’s domain using Ahrefs’ Site Audit, connect PageSpeed Insights’ API, and see your competitor’s Core Web Vitals together with other technical SEO issues.
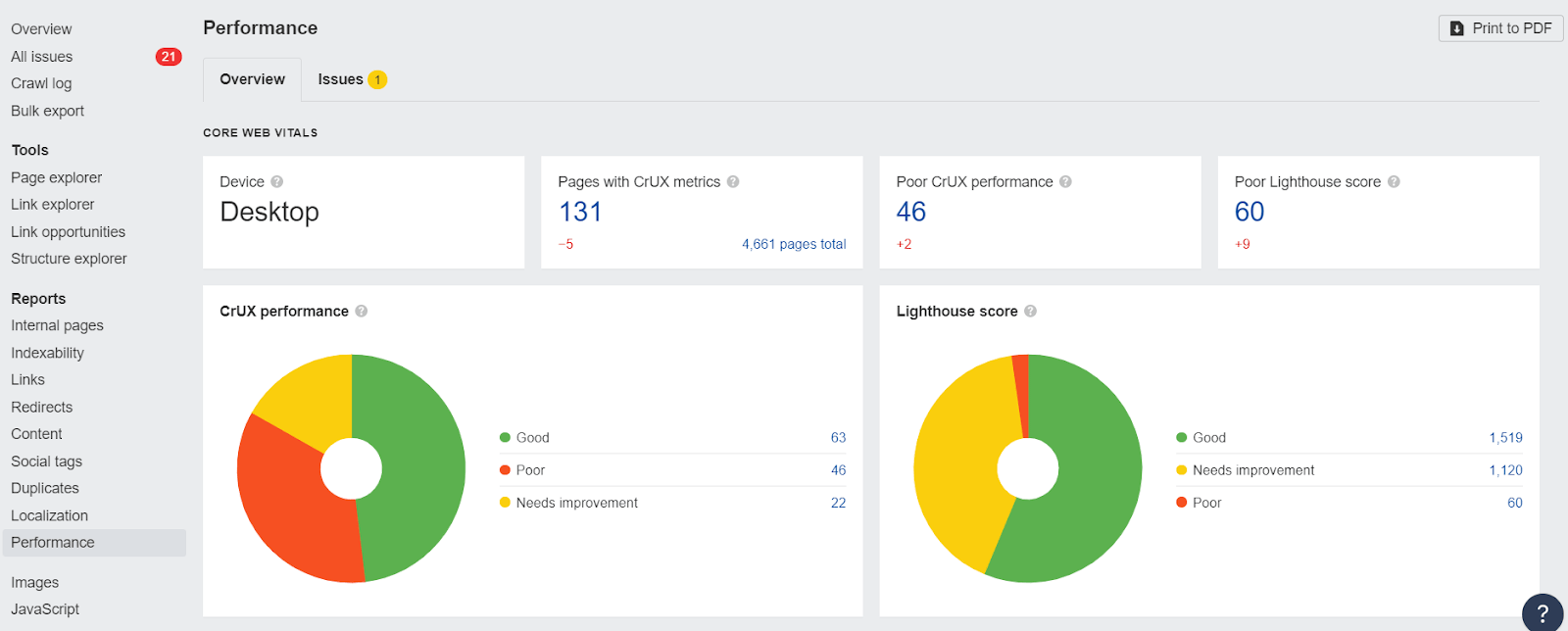
10. See what keywords your competitors are bidding on in paid search
If your competitors are bidding on certain keywords, then it’s likely those keywords are profitable.
Here’s how to see the keywords they’re bidding on:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report
- In the Keywords filter, add “Doesn’t include [brand]” to filter out branded keywords
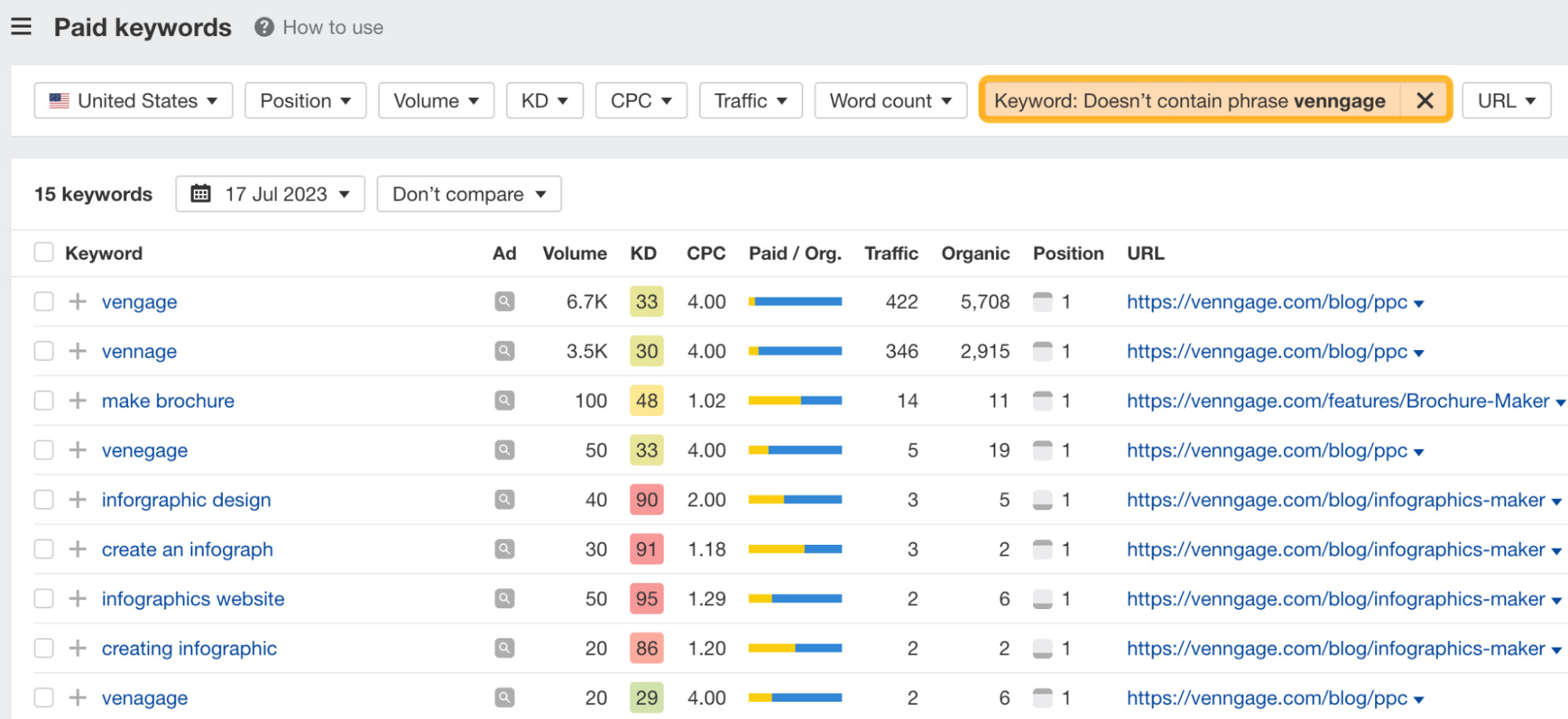
Looking through this report can help unearth low-volume, high-converting keywords that you may have missed during keyword research.
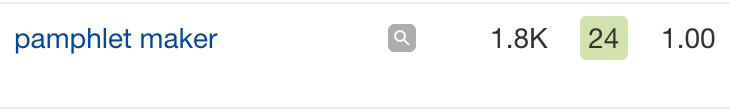
For example, this seems like a good keyword to target:
11. Learn from your competitors’ PPC ads
Google rewards more relevant ads with a lower cost per click (CPC). So it’s in your competitors’ interest to make sure their ads win the click.
Typically, that means better headlines and descriptions. We can use them as inspiration to write title tags and meta descriptions that increase click-throughs.
Here’s how to see your competitors’ ad copy:
- Go to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Paid keywords report
- Hover over the magnifying glass icon beside the keyword you wish to target
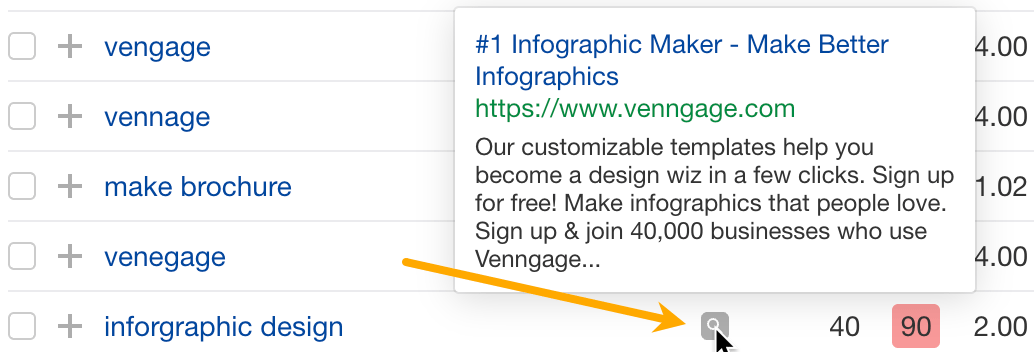
This is the current ad Venngage is using to target the keyword “infographic design.” Looks like it’s using words like “customizable,” “few clicks,” and “design wiz” to attract clicks.
They could be useful additions to our own title tags or meta descriptions.
Final thoughts
When it comes to competitor analysis for SEO, everything above is merely the tip of the iceberg. There’s more you can do, but it’s good enough for you to get started.
Our advice is to run through the process above and start applying the insights to your SEO strategy. Execution is important, after all.
Any questions or comments? Let me know on Twitter or Threads.










