SEO
How to Use Ahrefs to Improve SEO

Whether you’re new or old to Ahrefs, you’re in the right place.
This tutorial will walk you through the most practical, repeatable, and actionable Ahrefs use cases from our six core tools that will help improve your SEO.
Site Explorer is our competitive research tool. With Site Explorer, you can see a website’s:
- Backlinks
- Keywords it ranks for in Google
- Site structure in a tree format
- Pages that are responsible for generating the most search traffic
- Google ads campaigns
And more.
Because there are so many things you can do in Site Explorer, we won’t be able to go through every use case. Instead, we’ll cover a few low-hanging fruits:
1. Restore lost link equity from broken backlinks
If there are broken pages with backlinks on your website, that link equity is wasted.
You can reclaim the value of the link equity by either restoring those pages or redirecting the broken URLs to relevant live pages.
Here’s how to find broken pages with backlinks on your website:
- Enter your domain
- Go to the Best by links report
- Set the HTTP code filter to 404
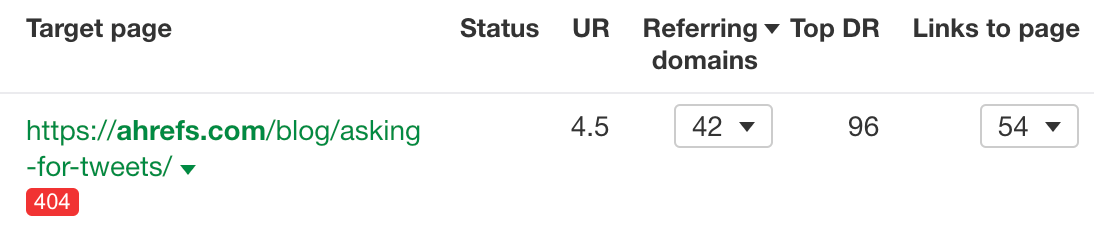
For example, we could redirect this blog post about asking for tweets to this one on blogger outreach to reclaim around 42 referring domains:

2. Find featured snippet opportunities
Featured snippets are full or partial answers to a query directly on the SERPs.
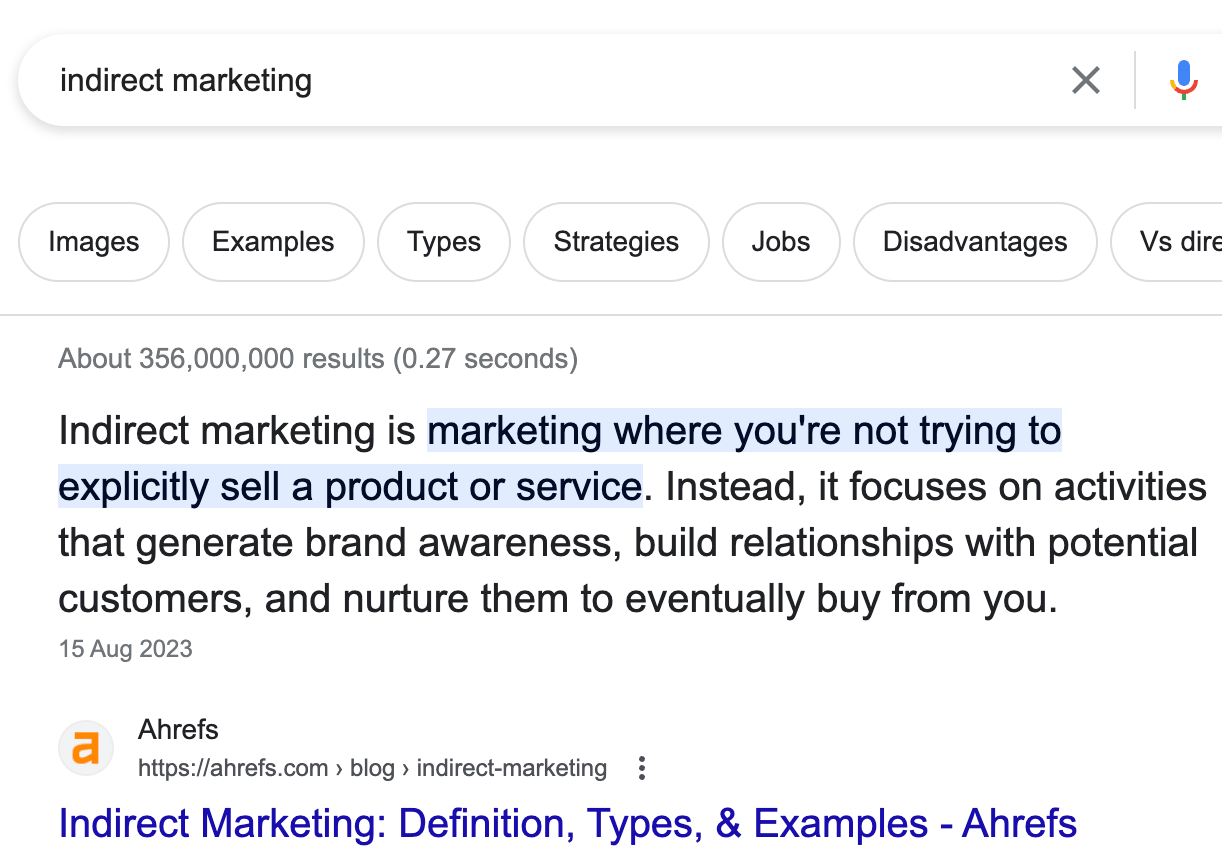

If you can grab the snippet, you can jump ahead of everyone else. That means more search traffic to your site.
Here’s how to find low-hanging featured snippet opportunities:
- Enter your domain
- Go to the Organic keywords report
- Set a Positions filter from 1 – 10 (you need to be on the first page to win it)
- Set a SERP features filter to “where target doesn’t rank” and check featured snippet
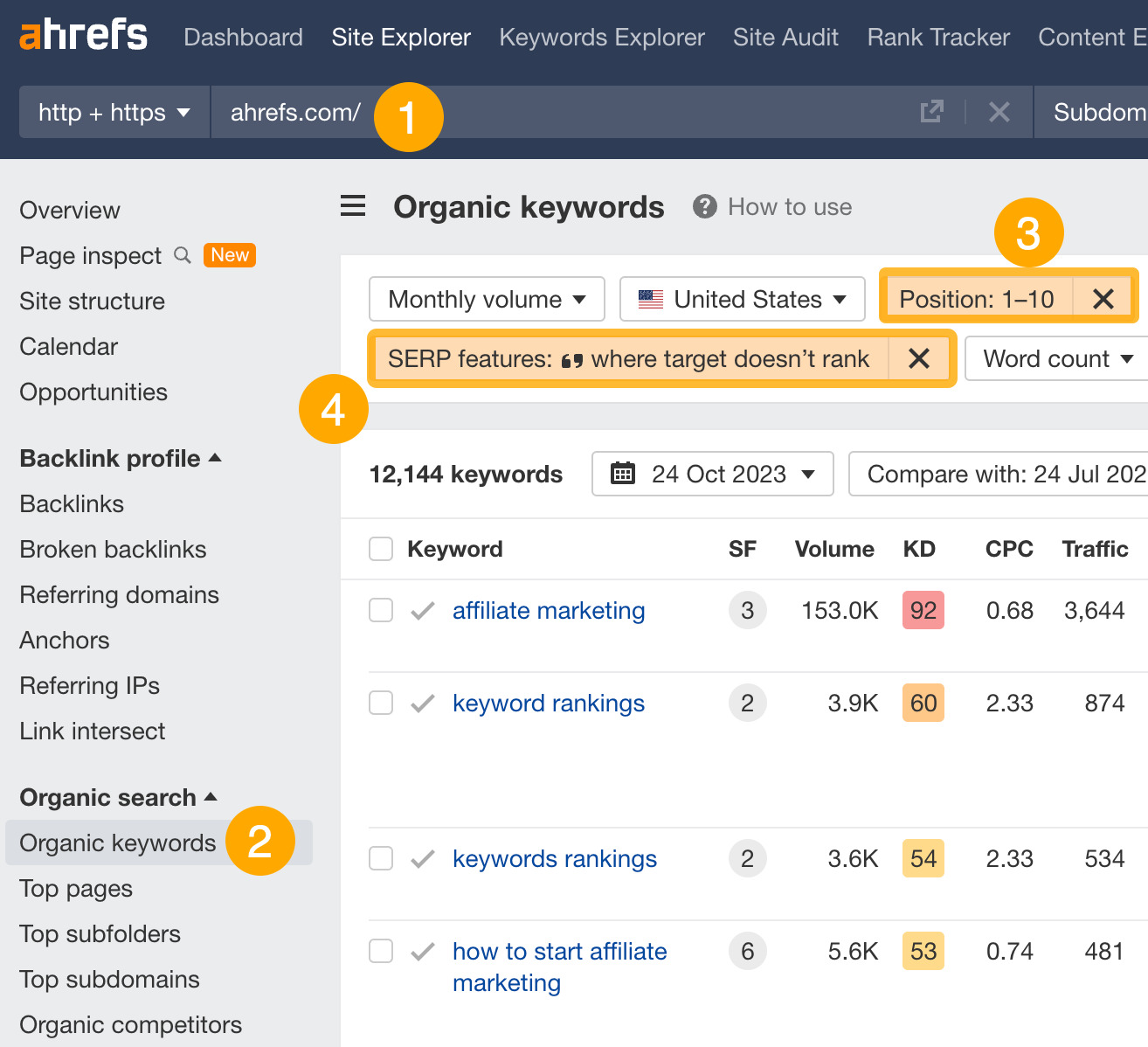

You can now see thousands of keywords where you can try and optimize your pages to win the featured snippet.
Follow the tutorial below to learn how to capture featured snippets.
3. Reverse engineer a site’s structure
Investigating a site’s structure shows you which parts of the site attract the most search traffic.
Here’s how to see a high-level overview of a website’s structure:
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Site structure report
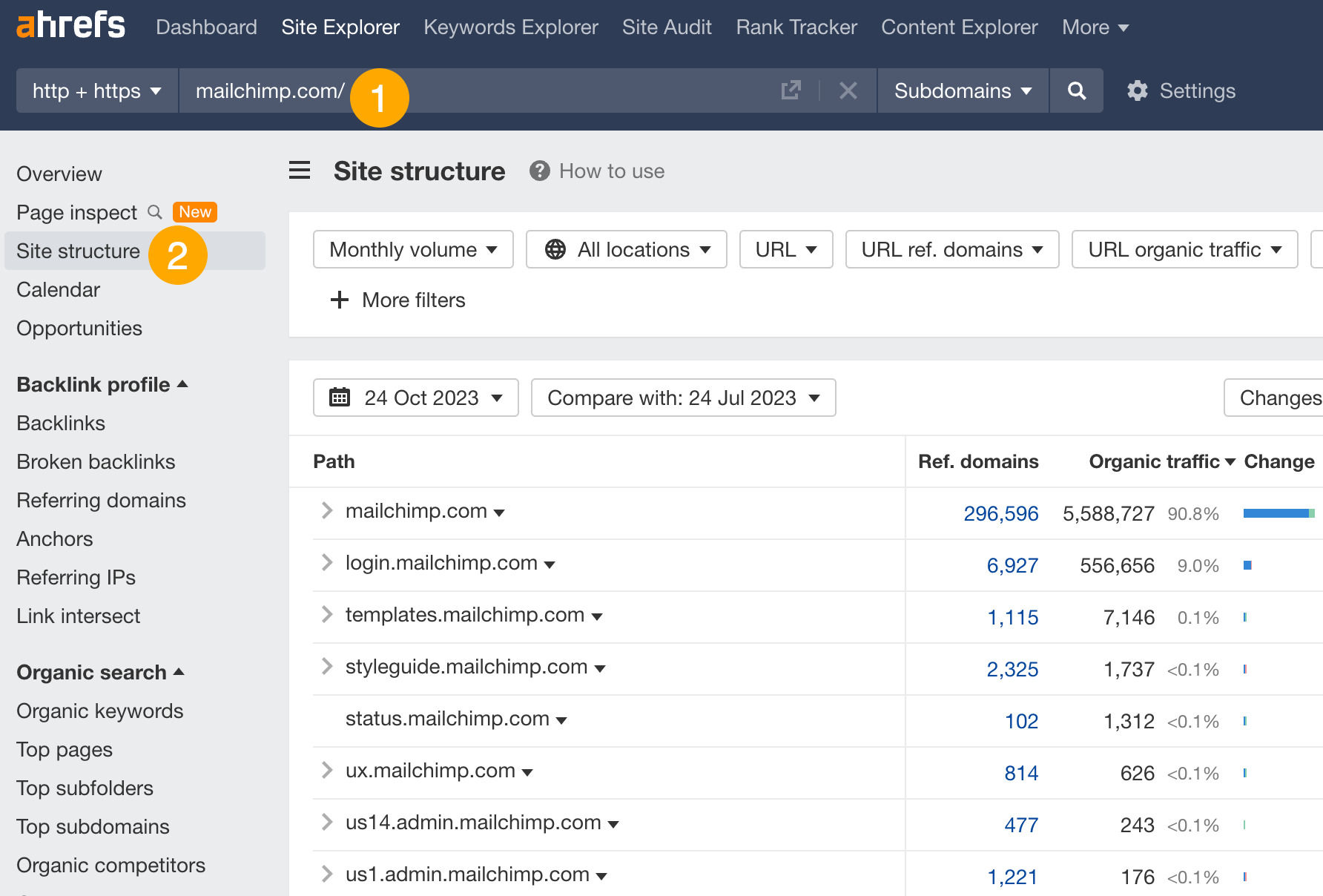

For example, we can see that most of Mailchimp’s search traffic goes to its root domain. We can also click on the arrow to see a more detailed breakdown.
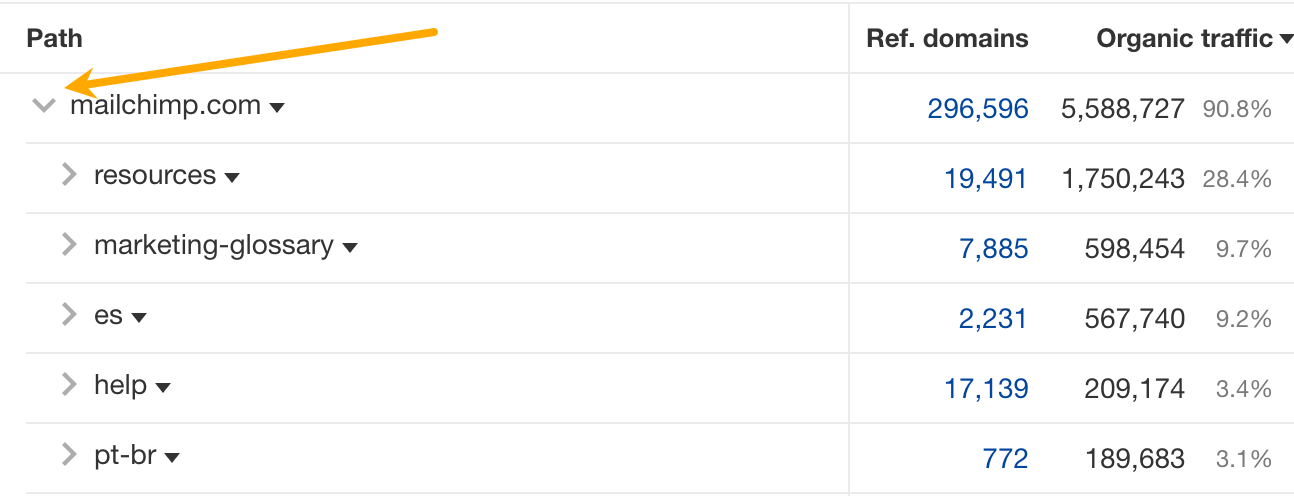

From here, we learn that Mailchimp has a subfolder called “marketing-glossary” that gets an estimated 600K monthly search visits.
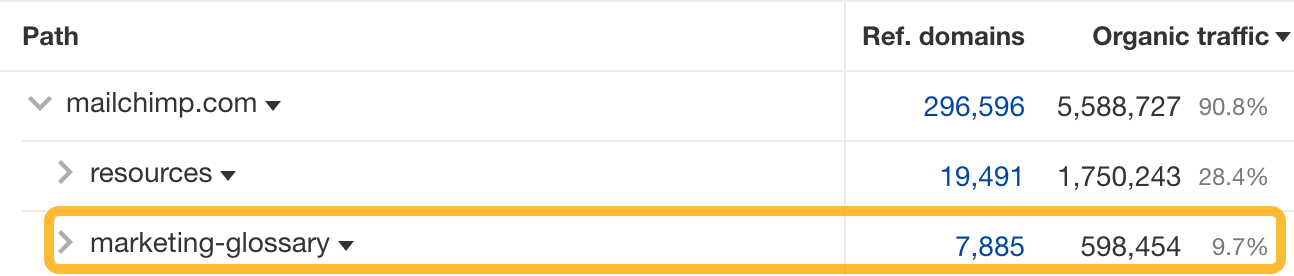

If you’re a competitor, creating a glossary could be a potential strategy you might want to replicate.
4. Replicate your competitors’ top pages
If competitors get lots of traffic to pages about certain topics, you probably can, too.
Here’s how to find your competitors’ top pages:
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Top pages report
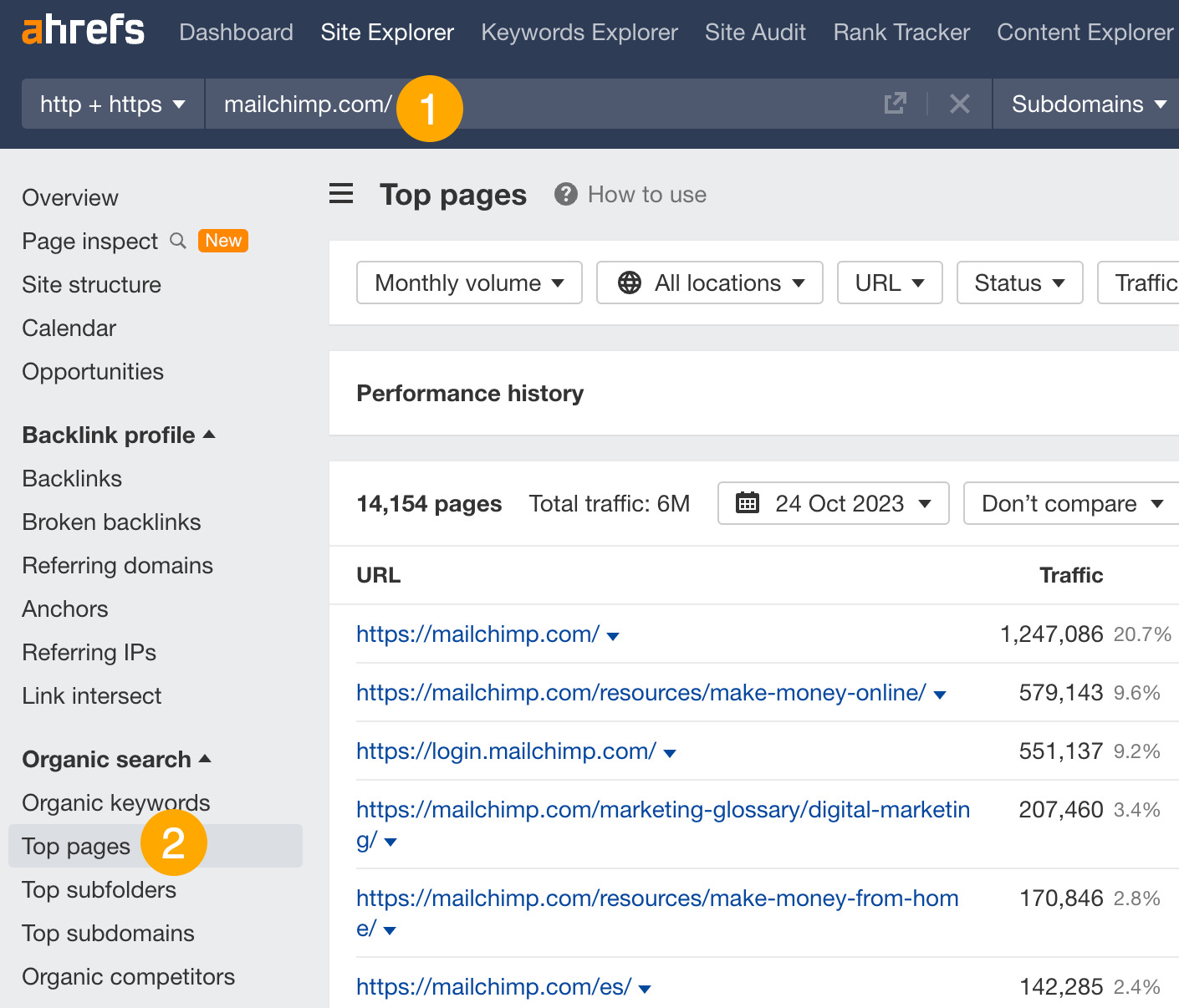

This report shows you the pages that attract the most search traffic for your competitor.
For example, Mailchimp’s email marketing guide gets an estimated 53,000 monthly search visits. The keyword that sends them the most traffic is “email marketing,” which they rank #1 for in the US.


If you’re a competitor, this might be a topic worth targeting.
5. Analyze your competitors’ backlinks for link-building opportunities
If you want to rank for anything remotely competitive, merely publishing content isn’t enough. You need backlinks.
One way to do this is to analyze your competitor’s backlink profile to see how they’ve been acquiring theirs.
Here’s how to see your competitor’s backlinks:
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Backlinks report
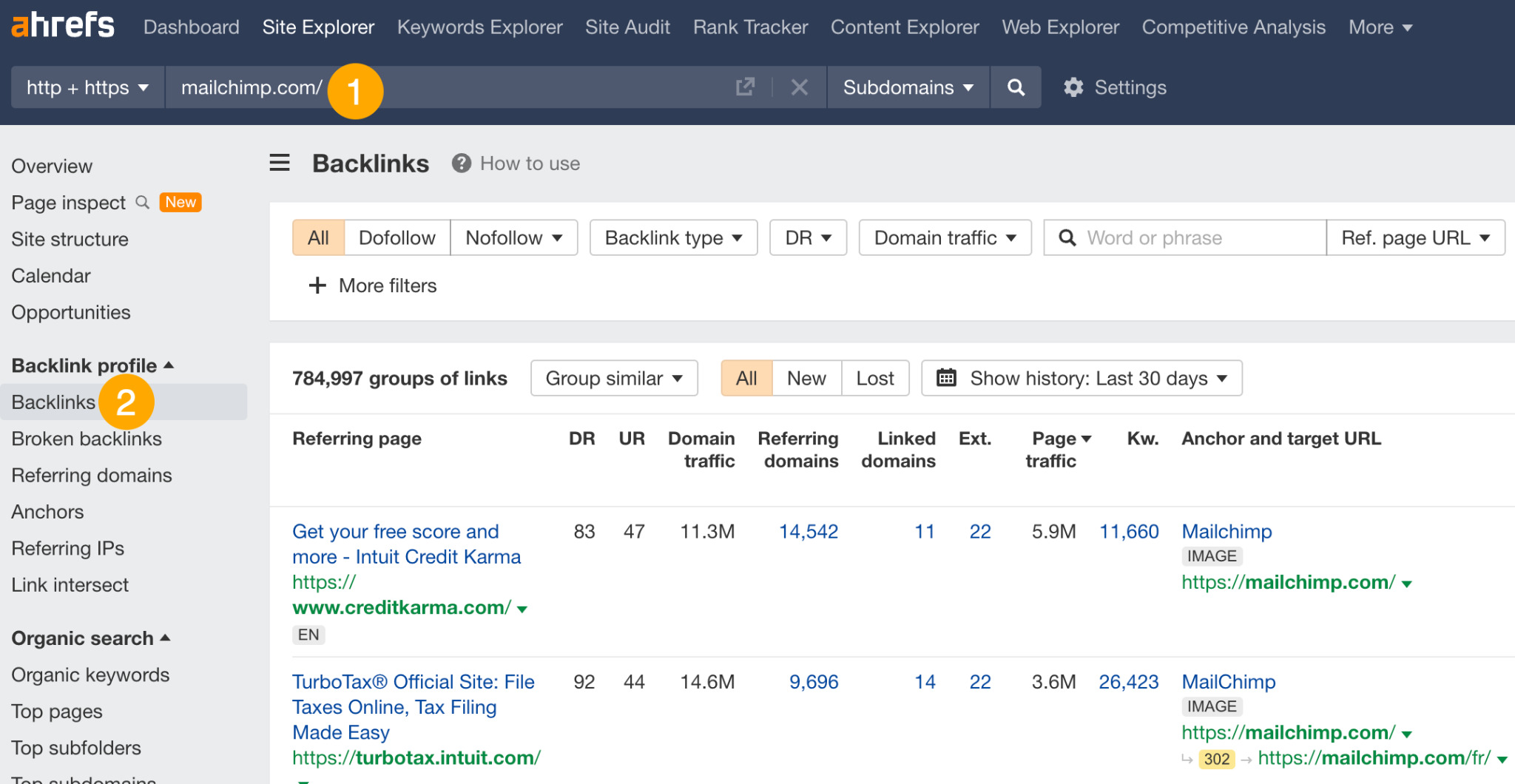

You can see that Mailchimp has close to 800K backlinks.
Here’s the thing: Your chances of finding anything useful by manually sifting through all 800K is slim. But if you know what you’re looking for, you can add the right filters and find the right link prospects.
For example, if you’re looking for resource page opportunities, you can add a “Ref. page URL” filter to search for terms like resources.html, resources.php, resources.asp, links.html, links.php, and links.asp.
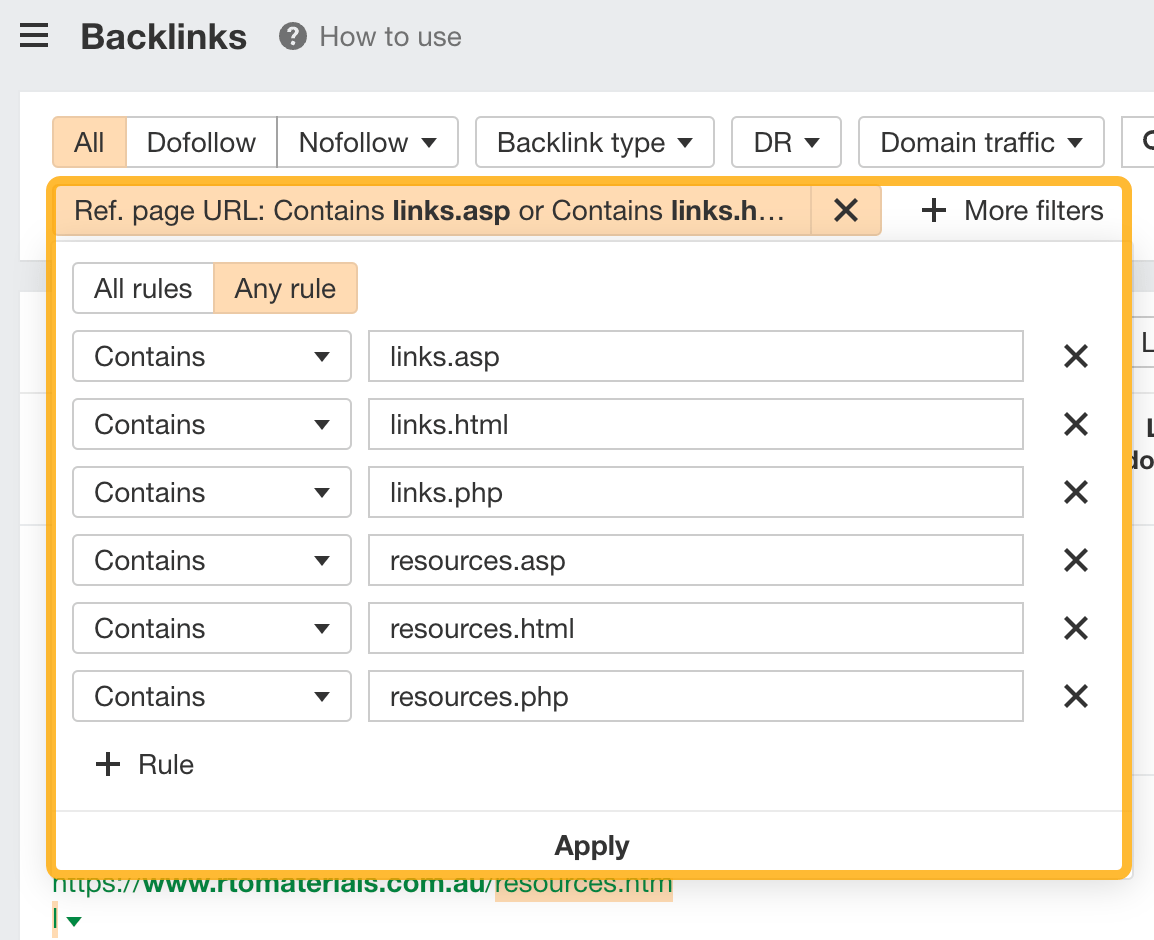

Apply the filters and hit show results, and you now have over 700 potential opportunities for resource page link building.
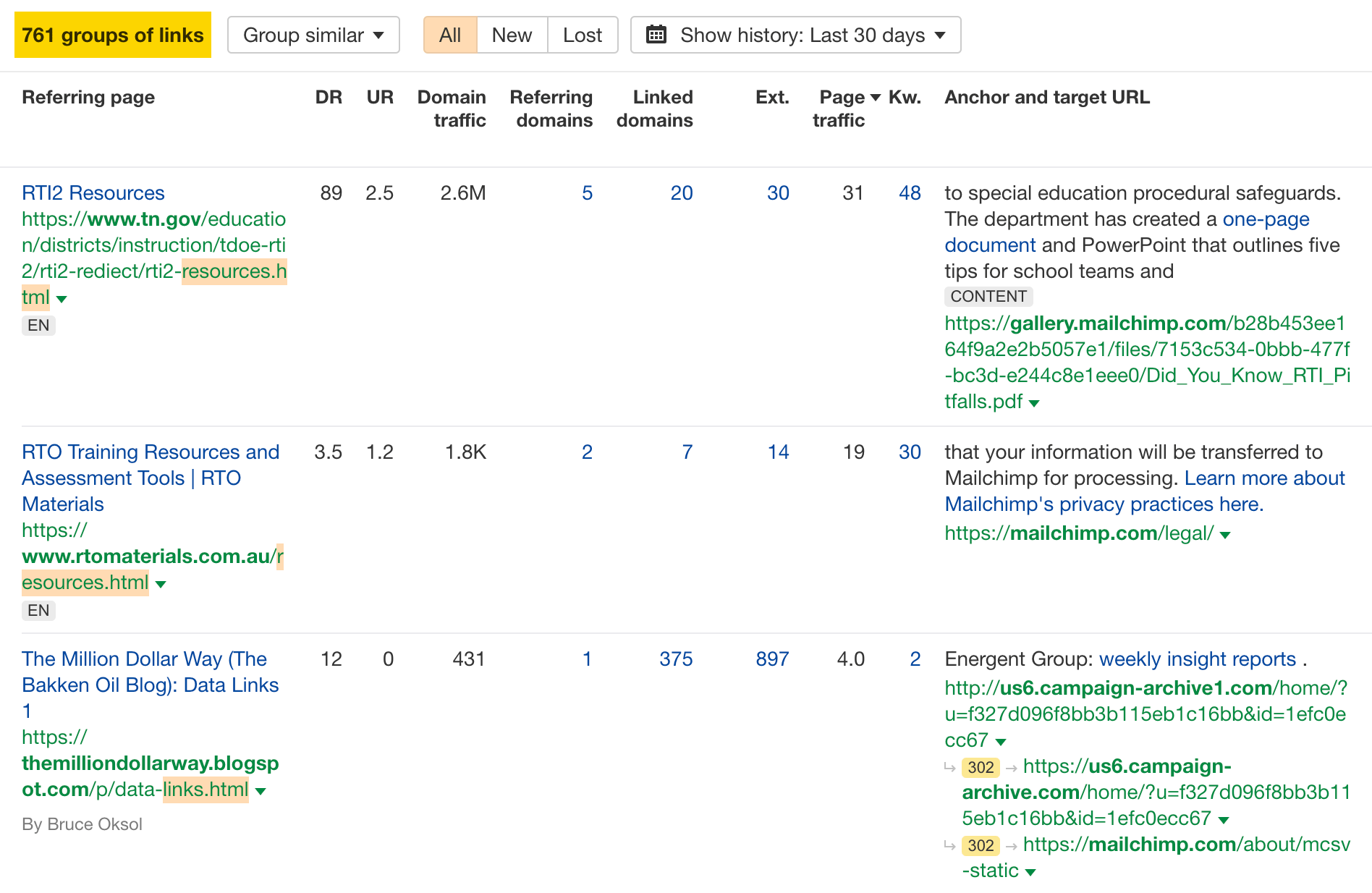

6. Analyze competing pages’ backlink profiles for link opportunities
You can also do the same backlink analysis as above but on a page level.
For example, say we want to analyze the backlink profile of HubSpot’s blog post on email marketing statistics. We want to create a competing page targeting that topic, so we want to know how HubSpot got so many links to their page.
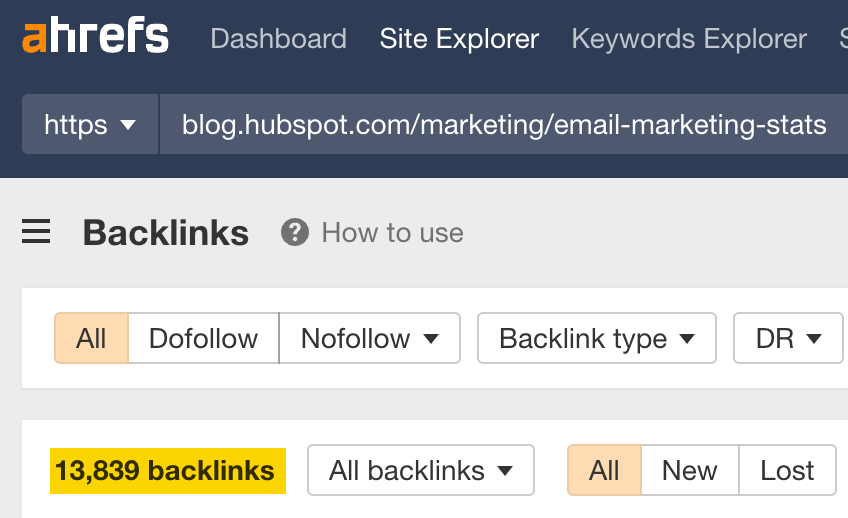

Manually sifting through 14K backlinks is a huge waste of time, so we’ll go to the Anchors report to see all anchor texts of backlinks pointing at HubSpot’s article.
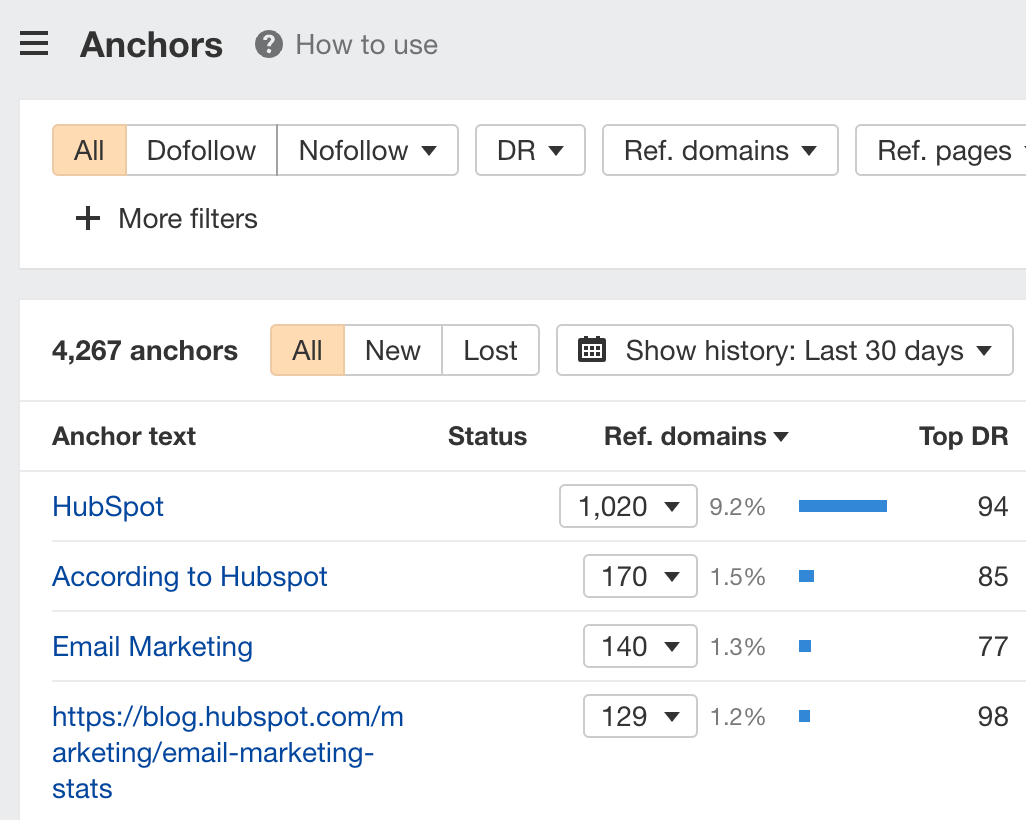

Eyeballing the report tells us that most people are linking to HubSpot’s page because of some specific stats:
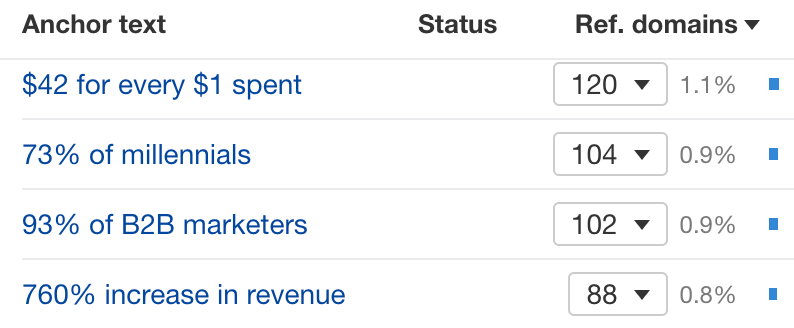

There are two actionable takeaways:
- We should include similar stats on our page, as these earn links.
- We should replace outdated stats so we can use them in our outreach campaign.
FYI, that’s exactly what we did for our SEO statistics post. Since then, we’ve earned thousands of backlinks and ranked #1 consistently.


Learn how we did that in our video series below.
7. Find broken link building opportunities
Broken link building is where you:
- Find a broken page that has backlinks
- Create your own page on the topic
- Reach out to those linking to the broken page to link to you instead
Here’s how you can find broken link building opportunities:
- Enter your competitor’s domain
- Go to the Best by links report
- Set a HTTP code filter to 404 not found
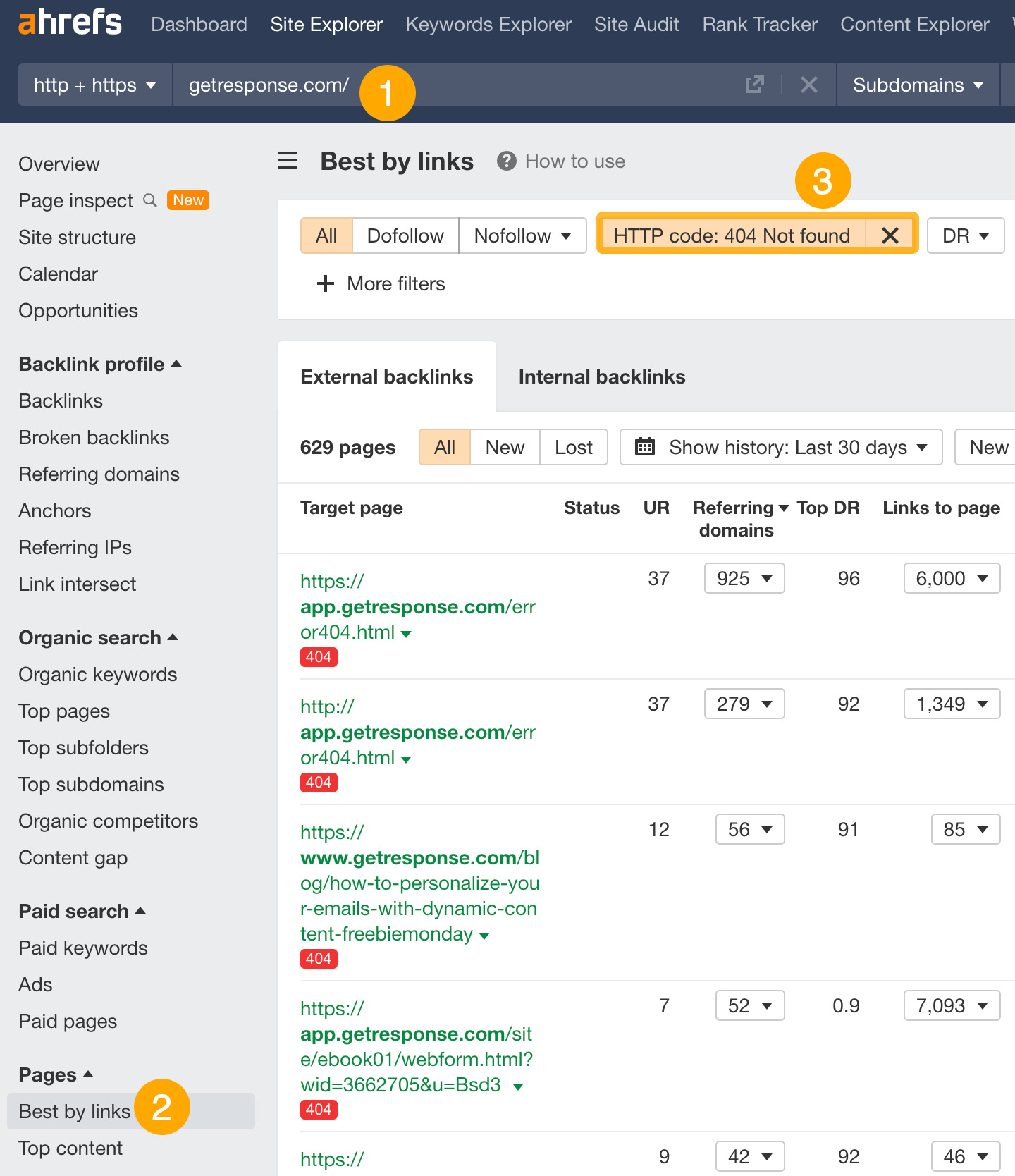

For example, if you’re a competitor to GetResponse, this topic on “what are popups” might make sense for you to cover because 21 websites are linking to it.


To see who’s linking to these pages, click on a caret beside the URL and go to the Backlinks report.
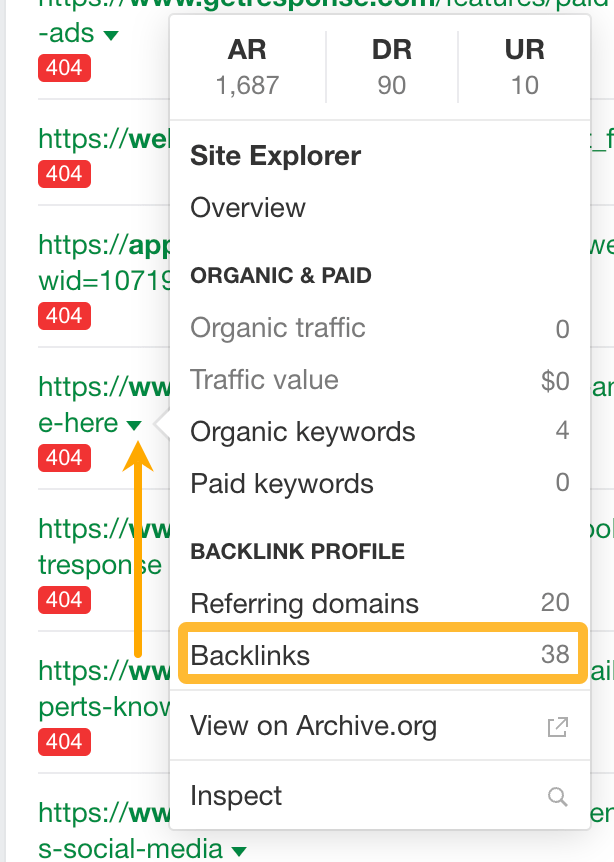

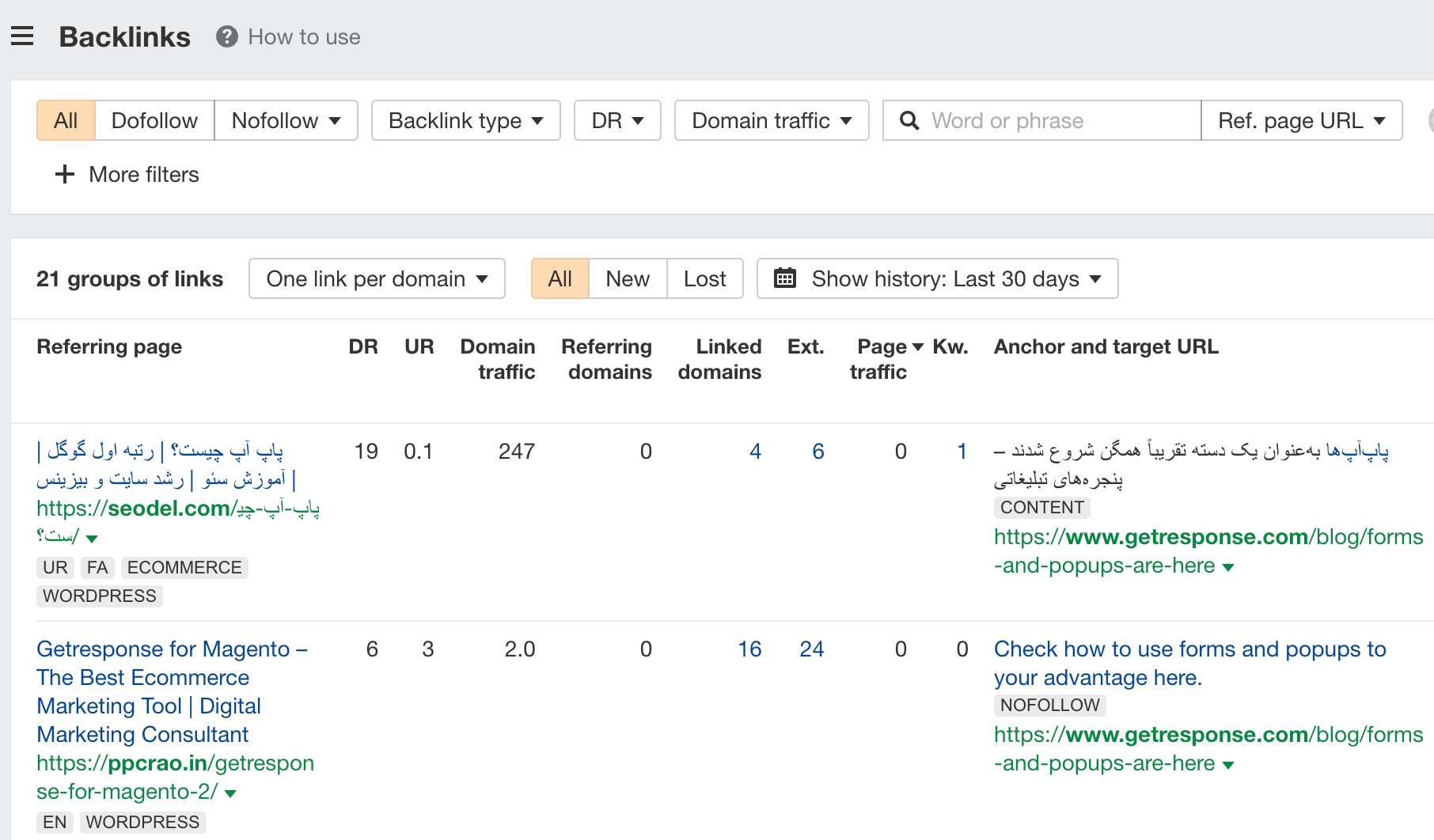

From here, you can reach out to the people linking to these broken pages and ask them to link to your new guide on the topic.
Keywords Explorer is our keyword research tool.
Let’s look at a few ways to find good keywords to target, fast.
1. Find keywords by search intent
Search intent is the reason behind a searcher’s query. To rank high on Google, you’ll need to match search intent.
But, analyzing the SERPs for thousands of keywords manually can be incredibly time-consuming. So, a quick way is to use keyword modifiers like “best,” “how,” and “buy.”
So, let’s say we have an ecommerce store that sells camping equipment. Here’s how we would find keywords by search intent:
- Enter a few broad seed keywords (e.g., camping, tent, sleeping bag, campfire)
- Go to the Matching terms report
- Add an Include filter for these modifiers (how, what, when, where, why, tutorial, tips)
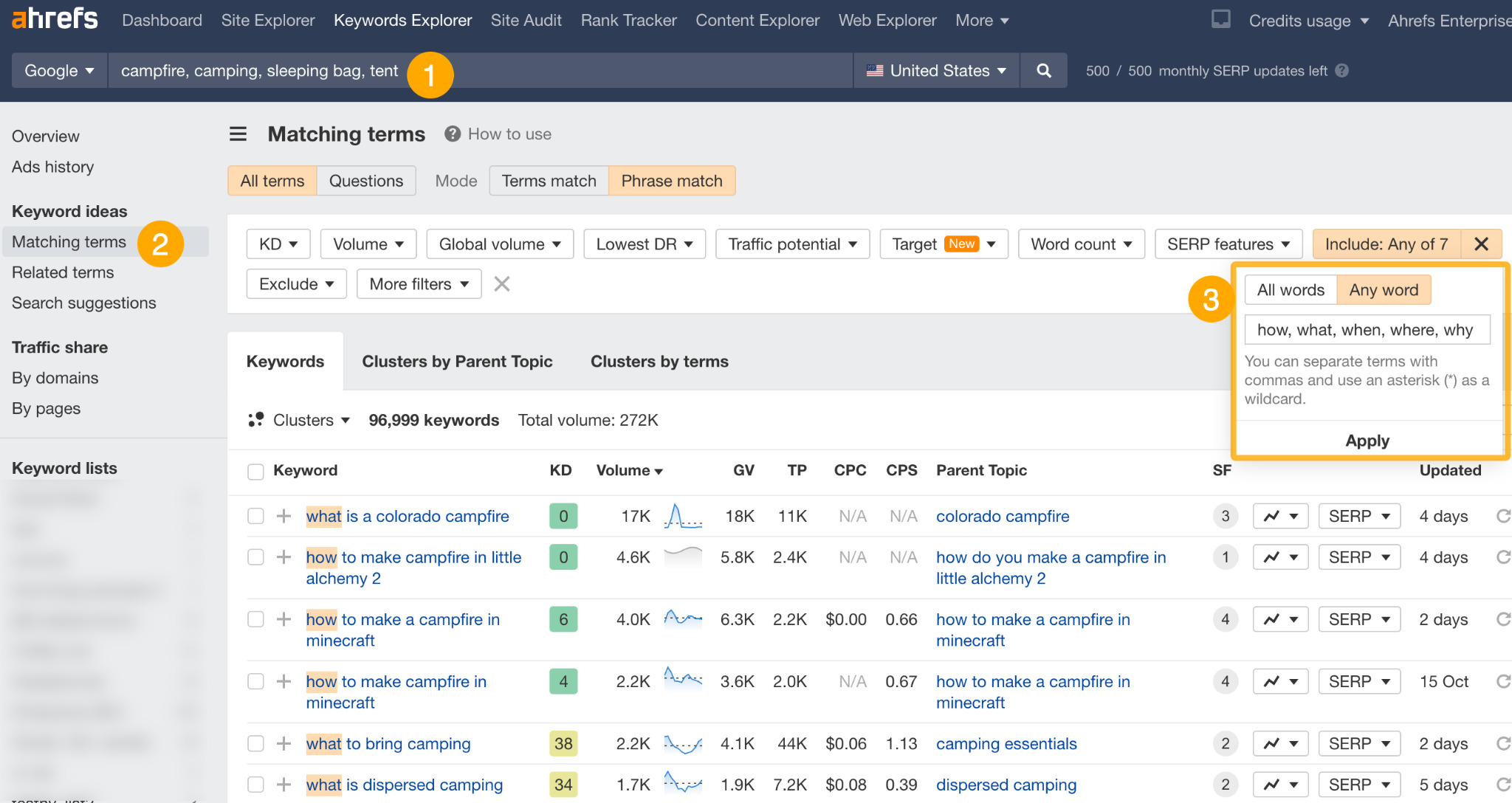

This will show us a list of informational keywords we can create content for on our blog.
If we want to find commercial investigation keywords, we can simply add an Include filter for words like “best,” “vs,” and “review.”
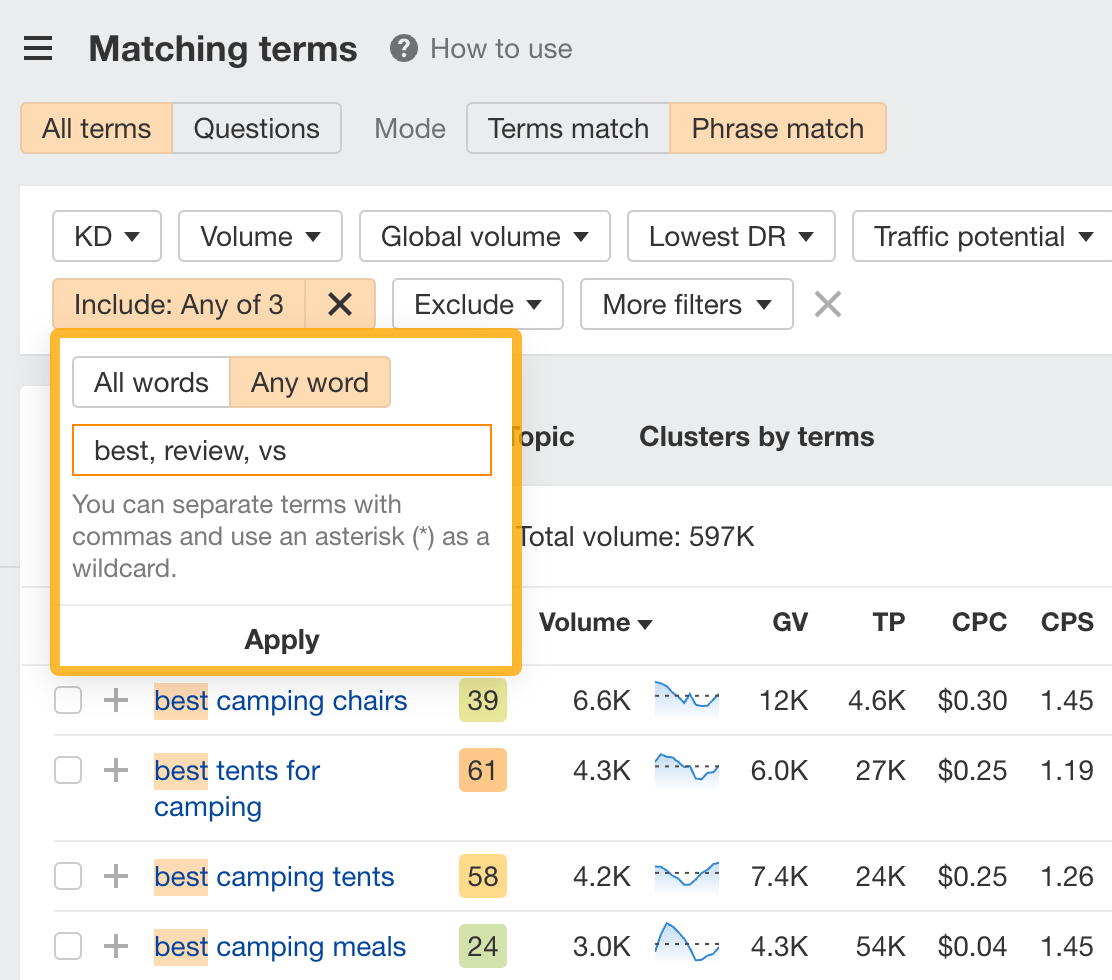

9. Find low-competition keywords
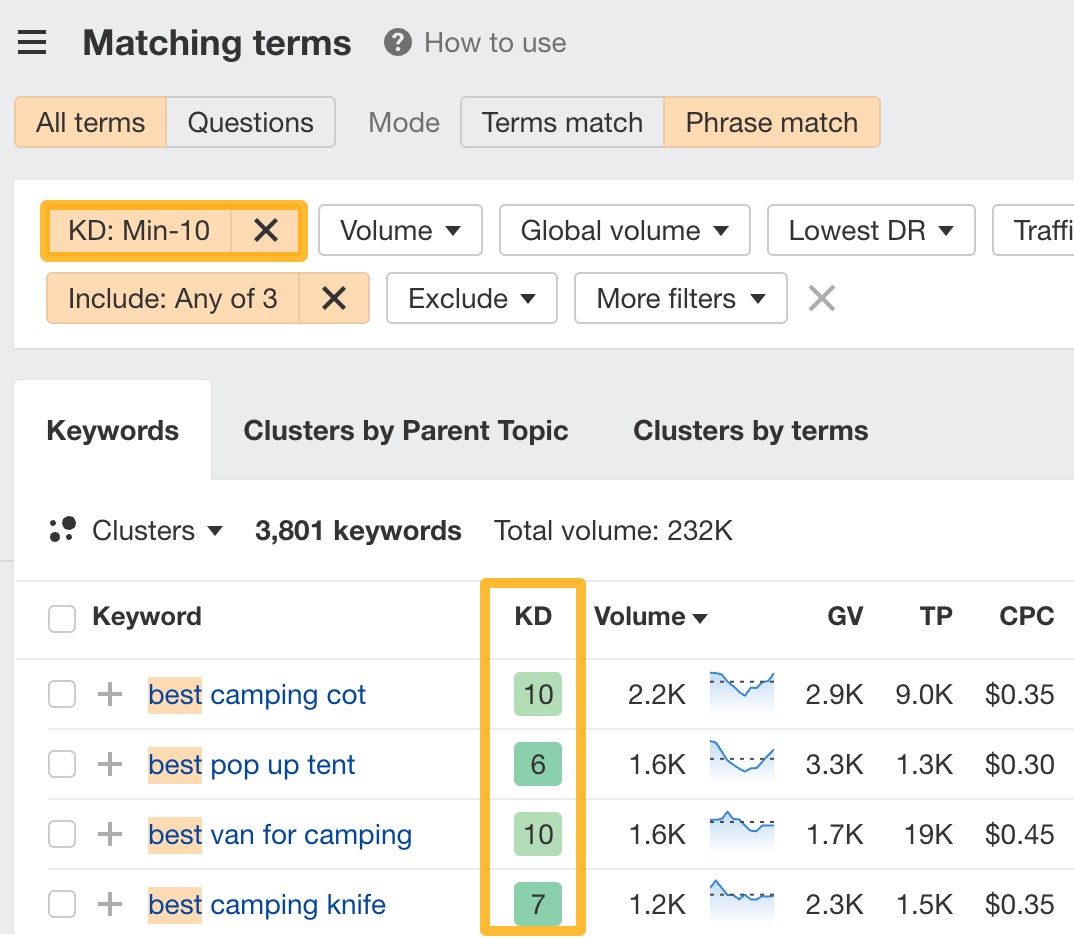
There are two ways to find low-competition keywords in Keywords Explorer.
The first way is to set a Keyword difficulty (KD) filter. Set it to a low number, like 10, and you’ll see low-difficulty keywords you can target:

The second way is to set a Domain Rating (DR) filter. DR is widely used in the SEO community to estimate a website’s authority. So, setting a DR filter can help you find keywords where non-authoritative sites rank high in the SERPs.
So, let’s set it to a low value like 30. This will show us keywords that have at least one website with a DR up to 30 in the top 5.
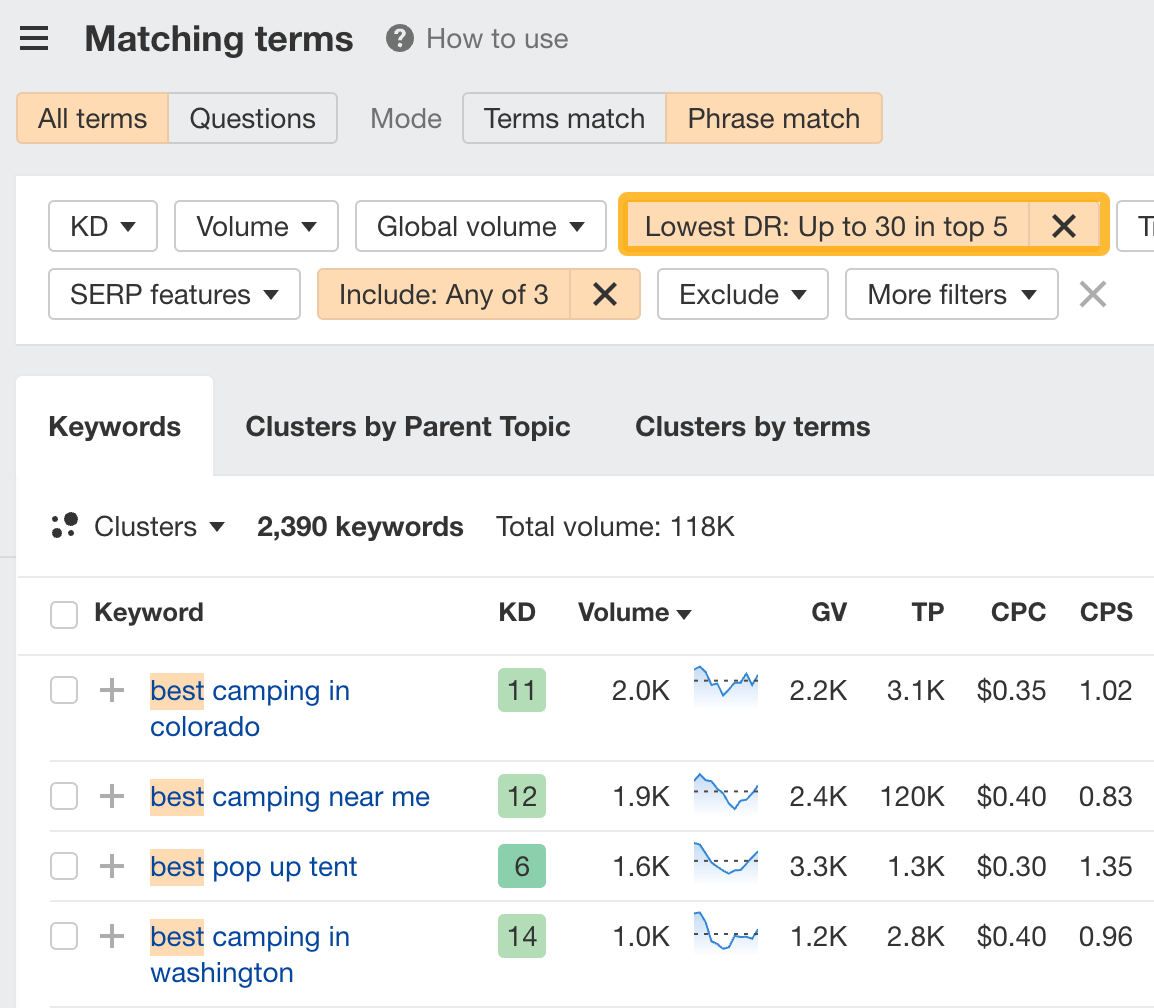

If we expand one of the SERPs, we see a result with <DR30 and 0 backlinks!
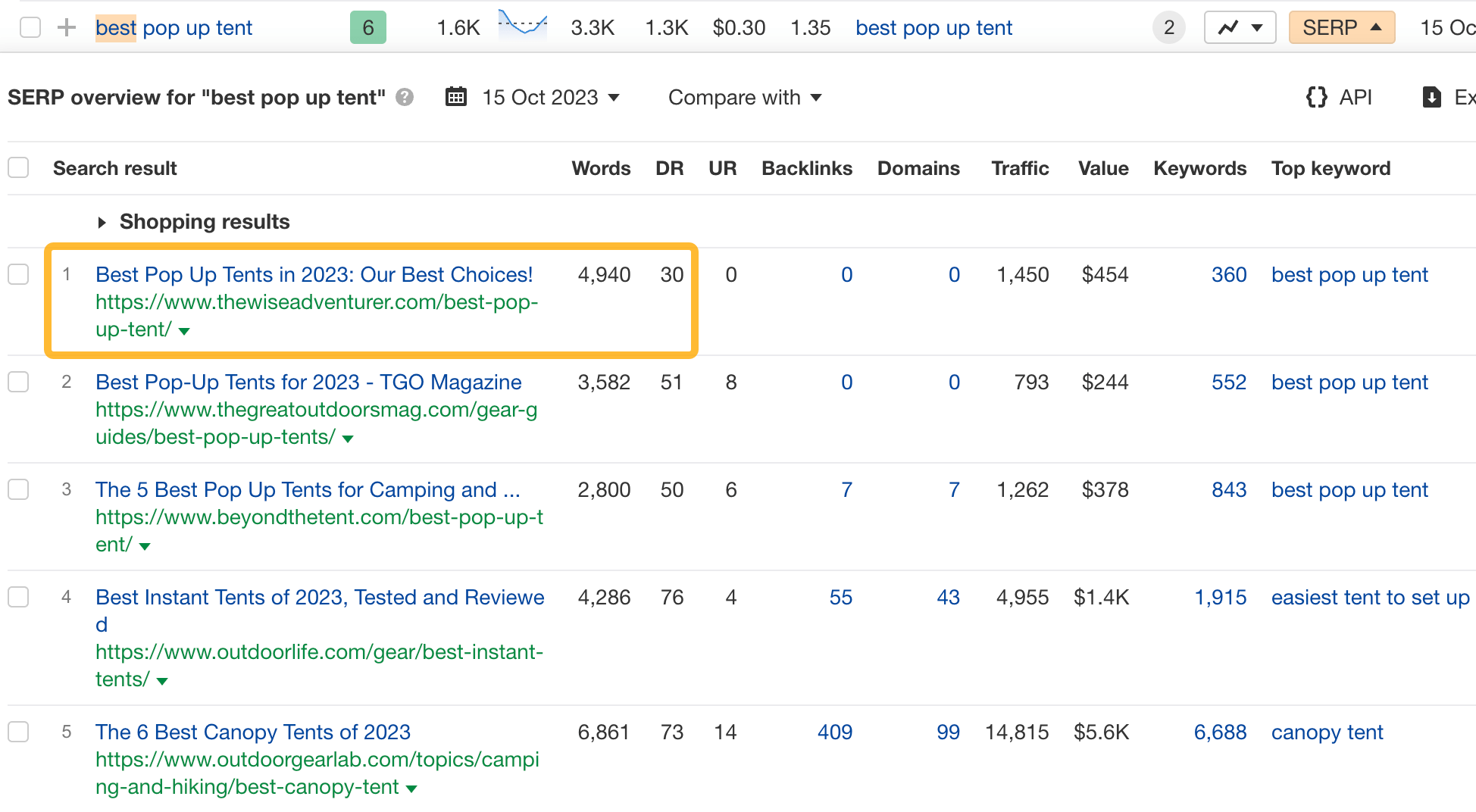

This certainly seems like an easy topic to rank for.
10. Bulk analyze a list of keywords
You can enter up to 10,000 keywords at a time in Keywords Explorer, which allows you to analyze any custom list of keywords.
Once you’ve pasted your list, you’ll be able to view all their metrics.
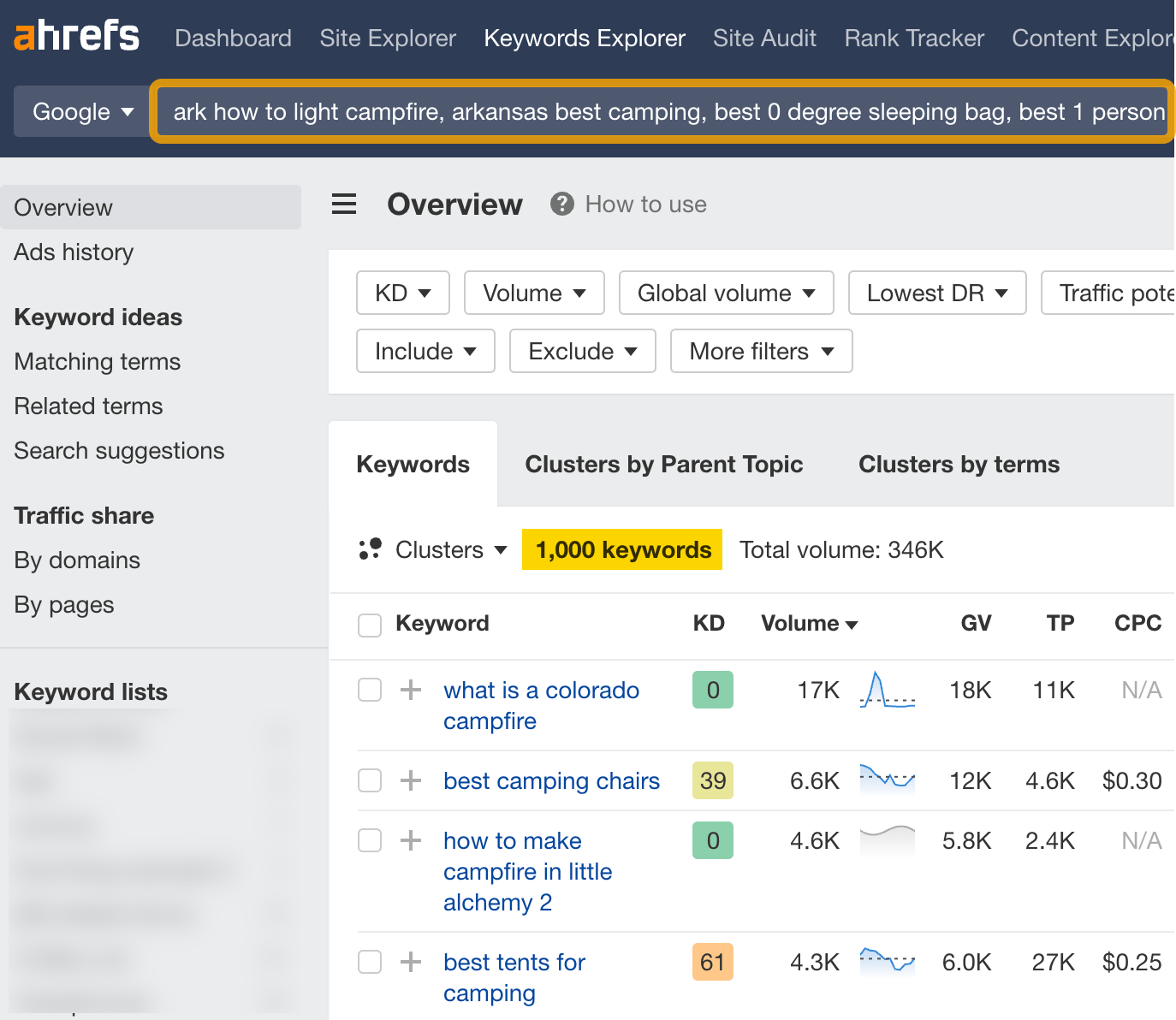

You can also cluster them by terms or Parent Topics.
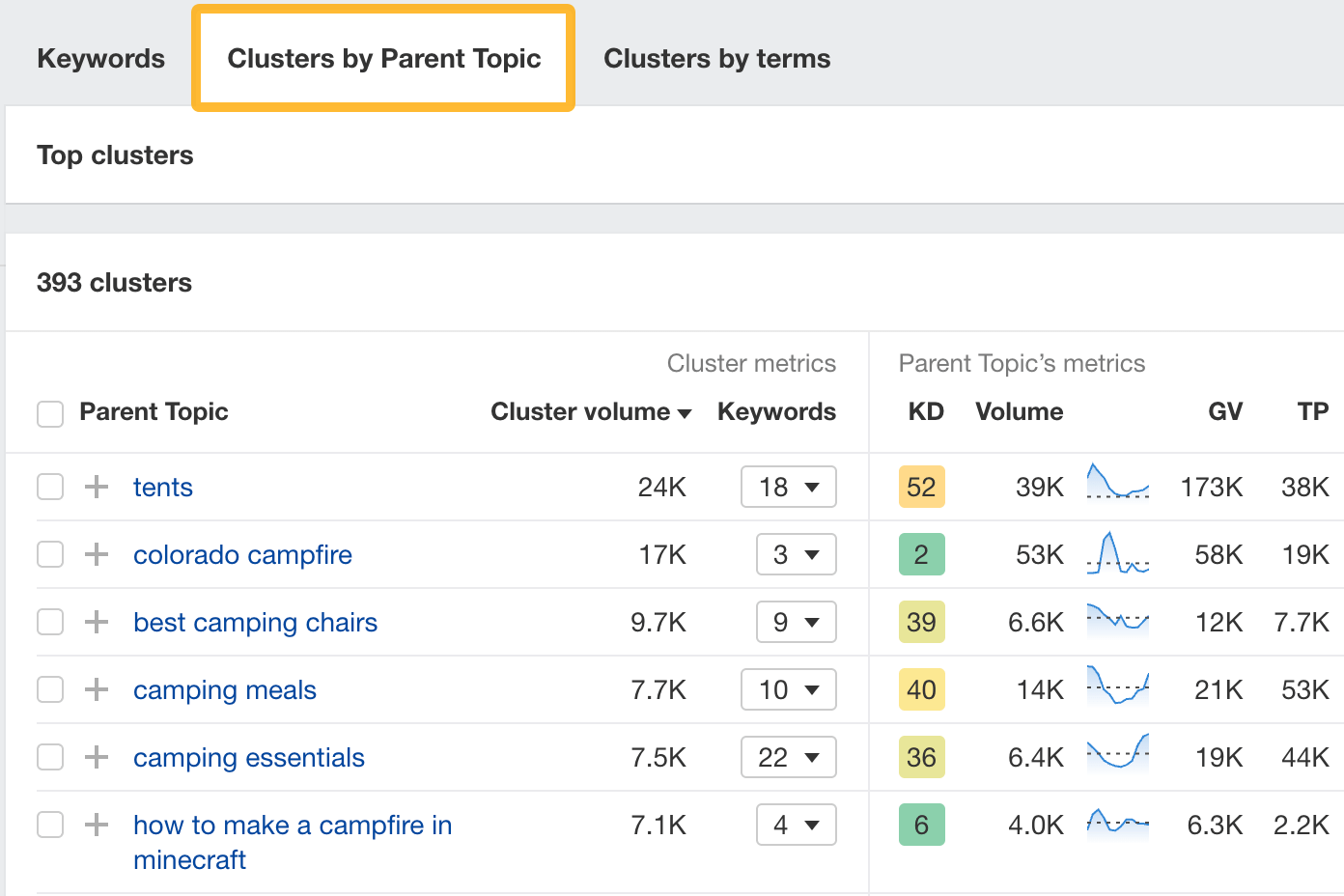

11. See organic share of voice for your competitors
If you’ve entered your own list of keywords, you can go to the Traffic share by domains report to see sites that rank for your list of keywords, along with the traffic share they own.
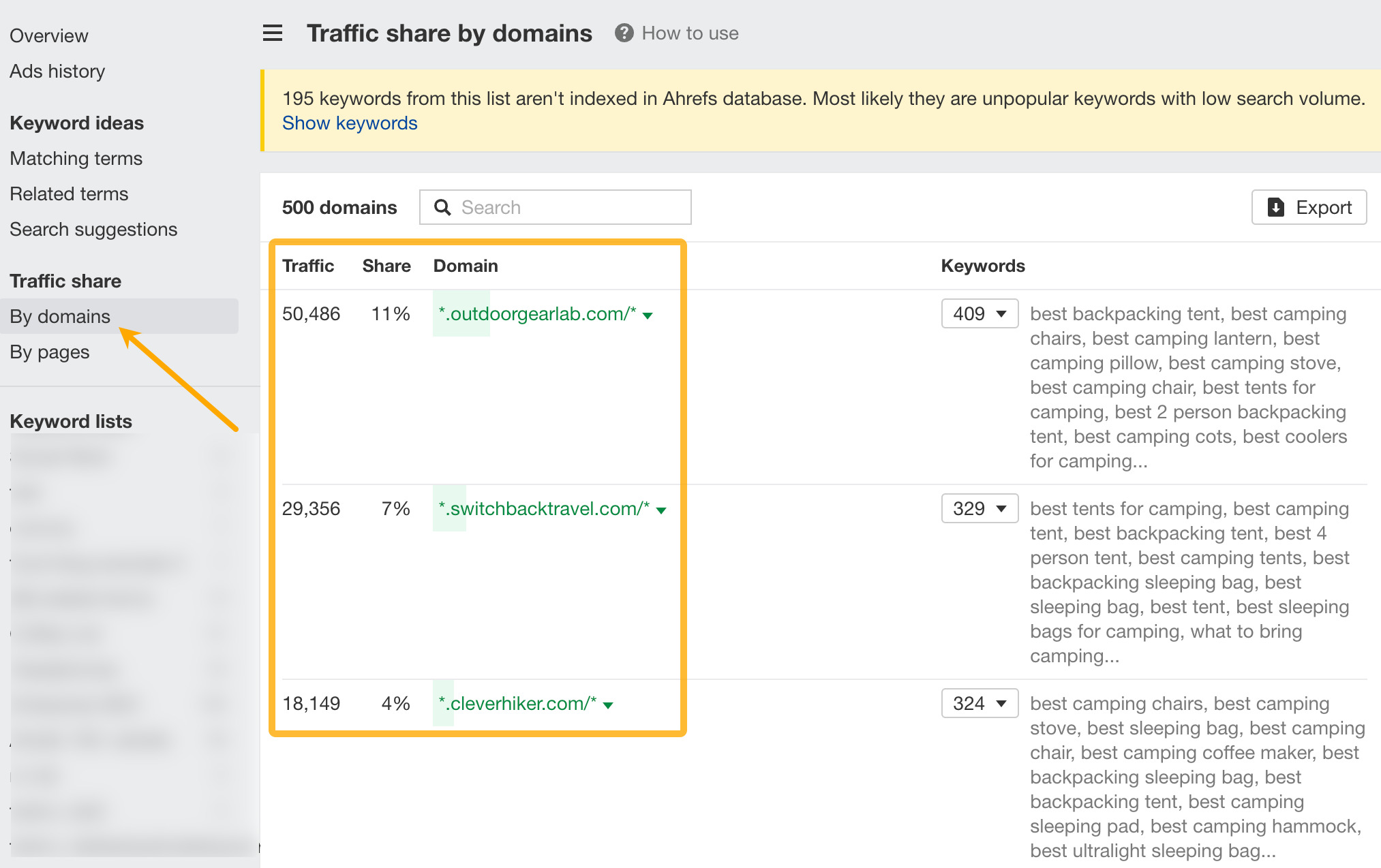

This tactic is great for keyword research.
For example, we can click on the caret for any of the websites, choose Top pages, and we can see all the topics that are sending them the most search traffic.

Site Audit lets you crawl your website to find and monitor for 100+ technical and on-page SEO issues.
To run a crawl, create a new project and either import your websites from Google Search Console (GSC) or add them manually.

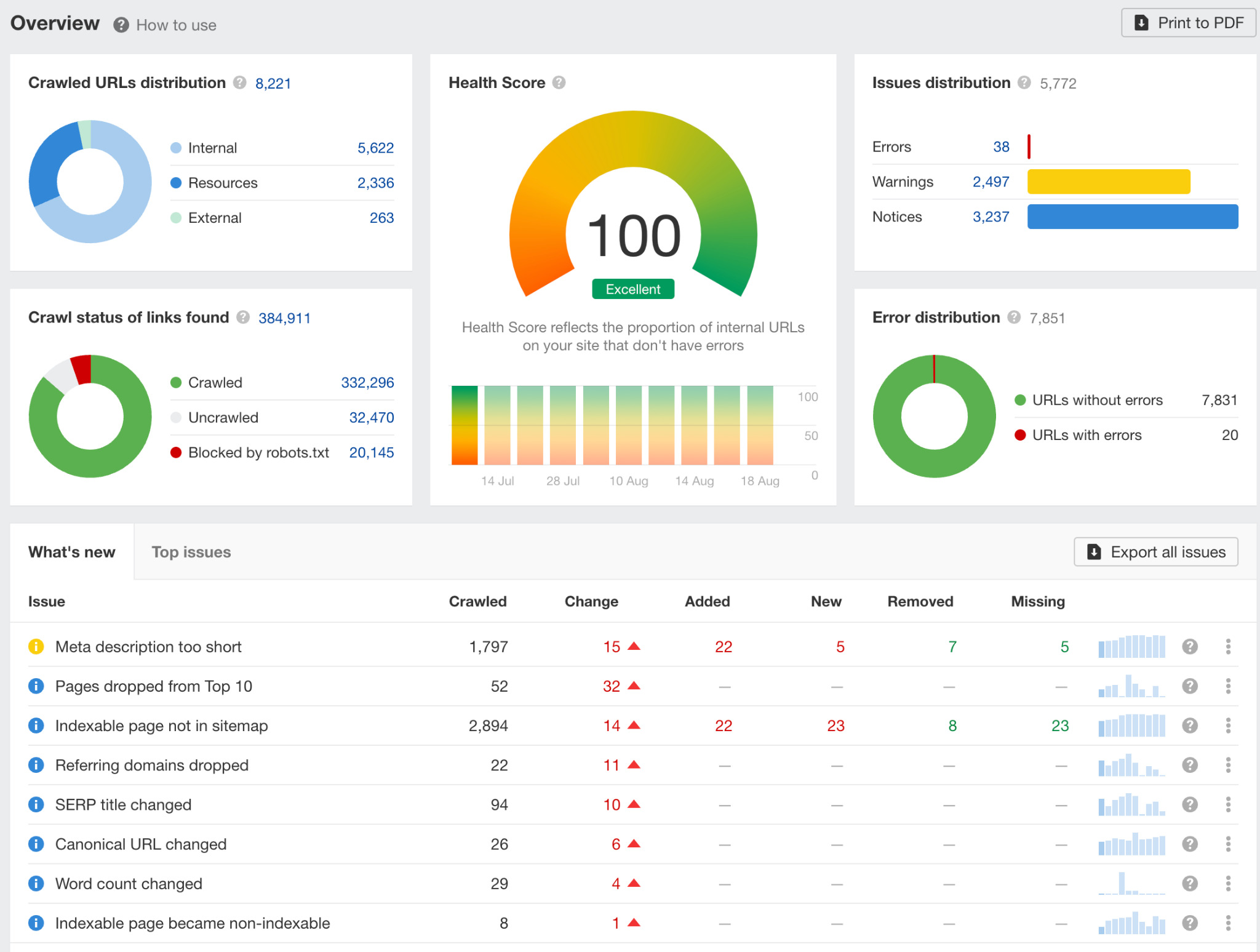
When your crawl is complete, you’ll see the Overview report, which will show you a high-level overview of all technical and on-page issues Ahrefs found on your site.

If your main goal is to keep your site in good technical health, then all you need to do is work on fixing the issues we found when crawling your site.
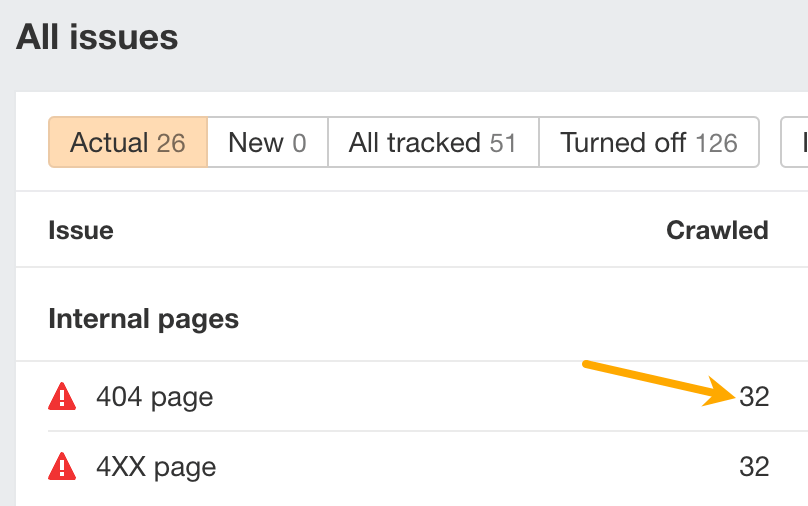
To do that, head to the All issues report.
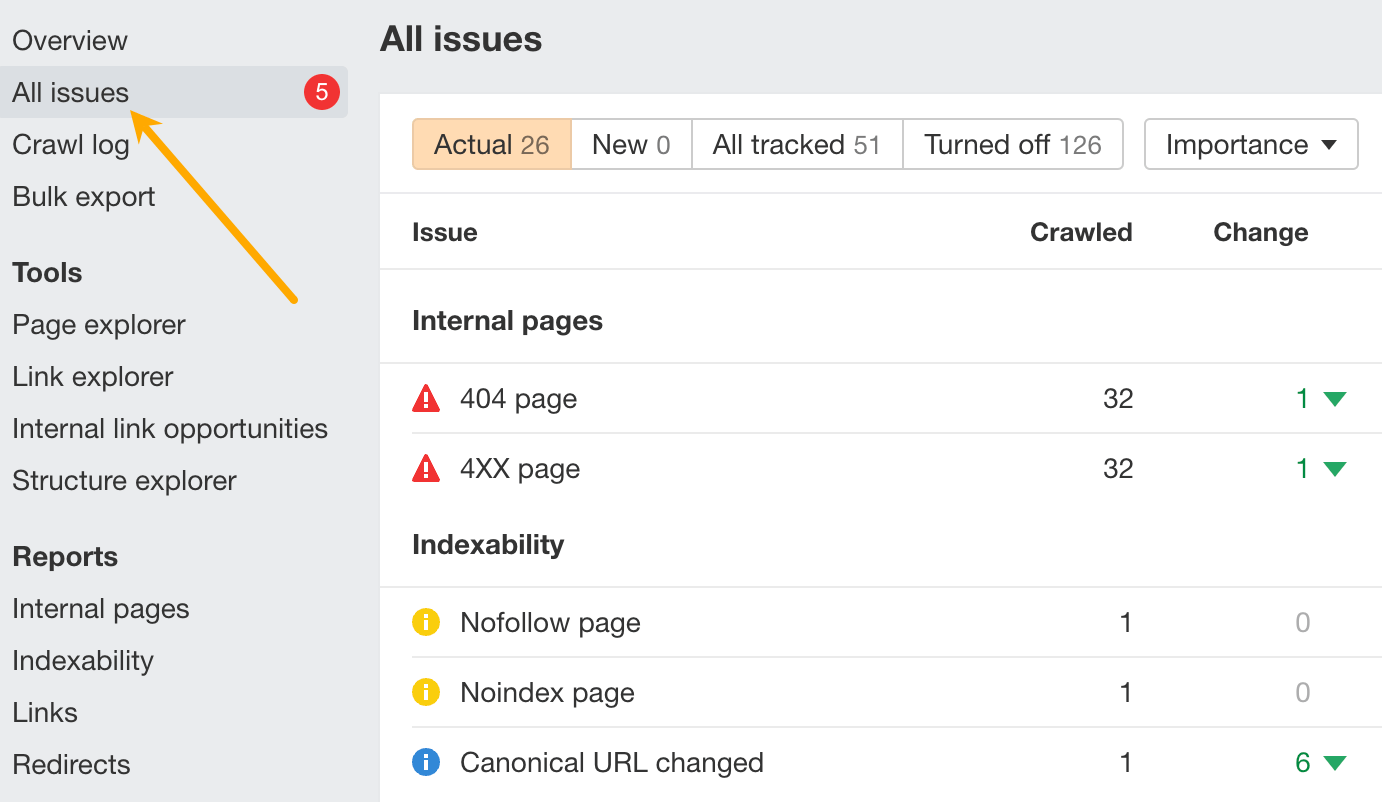

You can prioritize by working on the red ones first, which represent errors. Then, work on the yellow ones (warnings) and the blue ones (notices).
To see the affected URLs, click on the number in the corresponding row:

There’s more to Site Audit than maintaining your site’s technical health, though. Here are some more use cases (that are not technical SEO):
12. Find all affiliate links on a website
Let’s say you own a recipe blog that mostly makes money from Amazon affiliate links. However, you recently joined a new affiliate program with higher payouts than Amazon. Now, you need to swap out the Amazon links for your new affiliate ones.
But rather than doing a sitewide change, you want to test the new affiliate links on a few pages to get a sample size for conversion rates.
Here’s how you can do this with Site Audit (after running a crawl):
- Go to Page Explorer
- Hit Advanced filter
- Create a rule to find URLs that have an external link containing amzn.to (Amazon’s short link).
- Set an Organic traffic filter to show pages that get at least 1,000 monthly organic visits
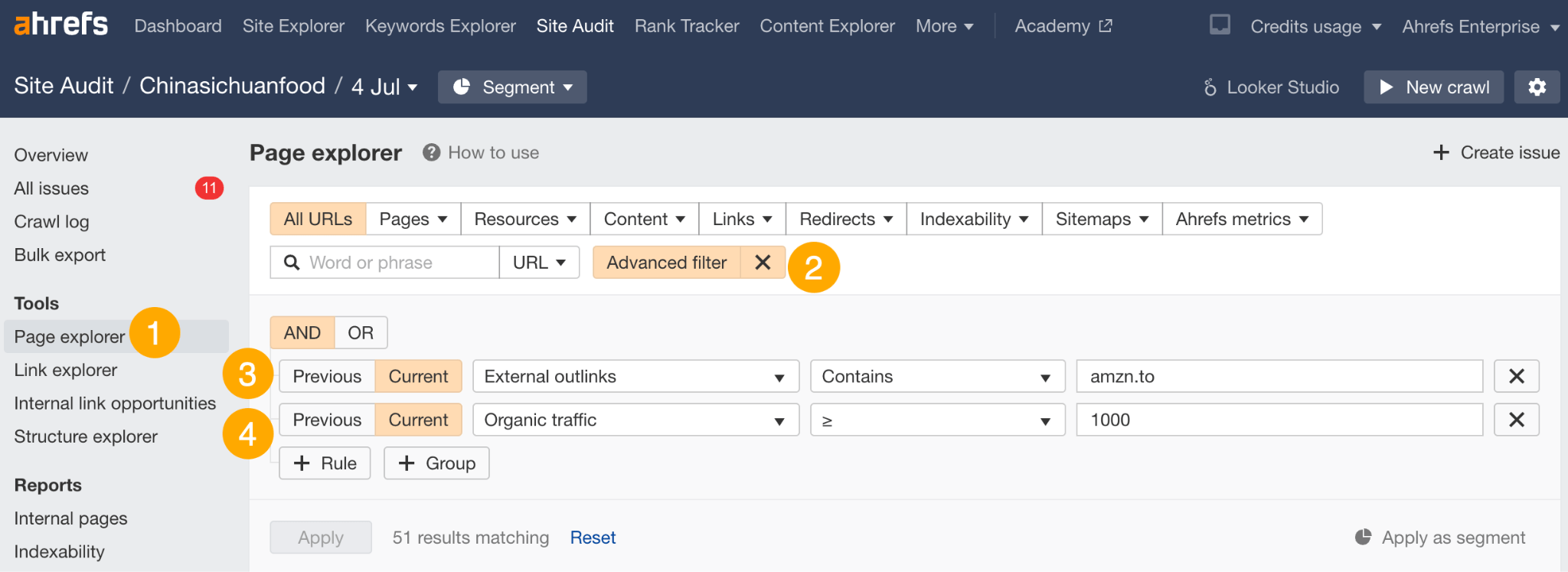

Hit ‘Apply,’ and you’ll see 51 pages that match these filters:
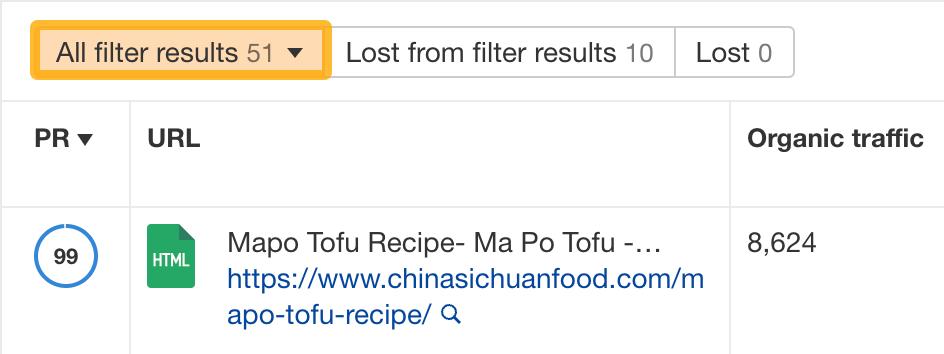

You can pick from these pages to replace the Amazon links.
13. Find internal linking opportunities
The Internal Link Opportunities report shows you internal linking opportunities based on keywords your pages rank for.
Specifically, it shows:
- The page we recommend you link from
- The keyword that’s mentioned on the source page (also the keyword that the target page ranks for)
- The page we recommend you link to
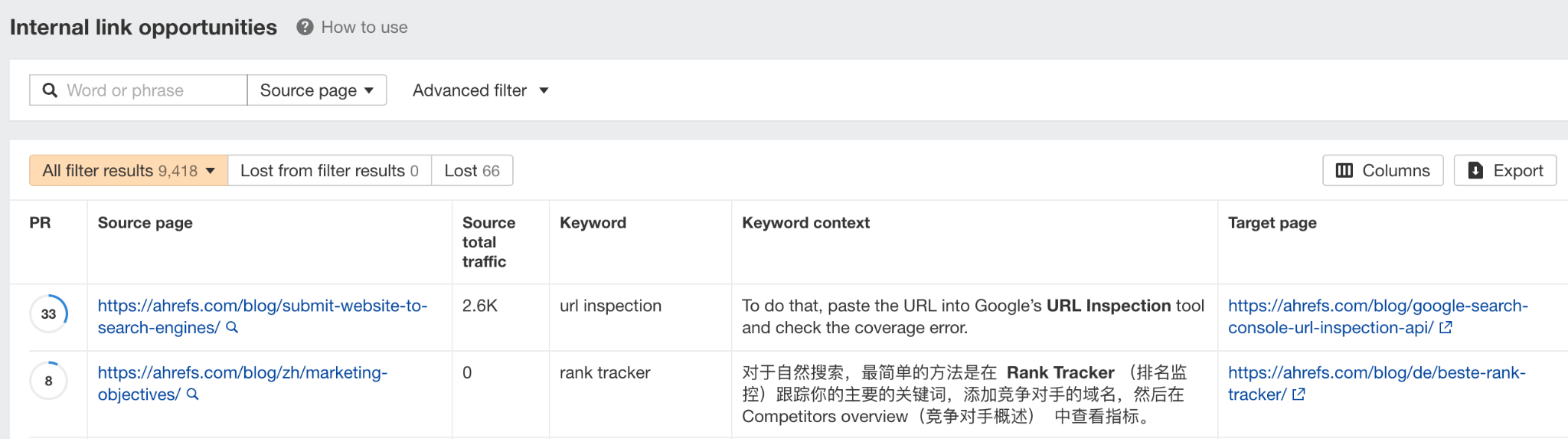

For example, let’s say we want to add internal links to our blog post on keyword research. In the report, we can set a Target page filter and paste the URL to our keyword research guide.
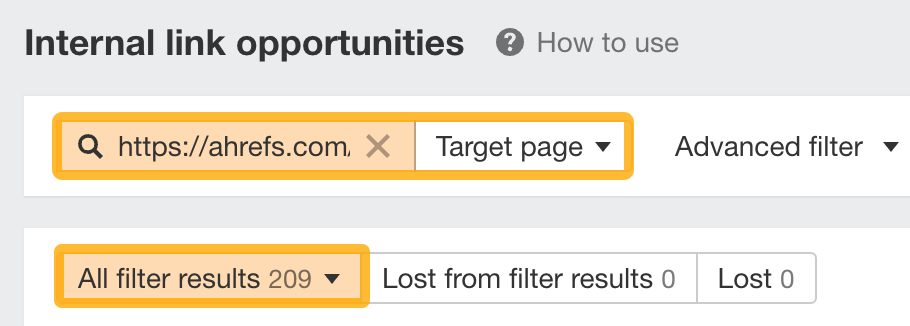

We now have over 200 potential pages we can link from.
Rank Tracker lets you monitor your Google rankings over time. You can track rankings from any country, city, zip, or postal code. On top of that, you can segment your keywords using tags and track your performance against your competitors.
In the Rank Tracker Overview, you can see charts that give you a nice visualization of various categories like share of voice, average position, traffic, SERP features, and positions. And these graphs are affected by the filters you set.
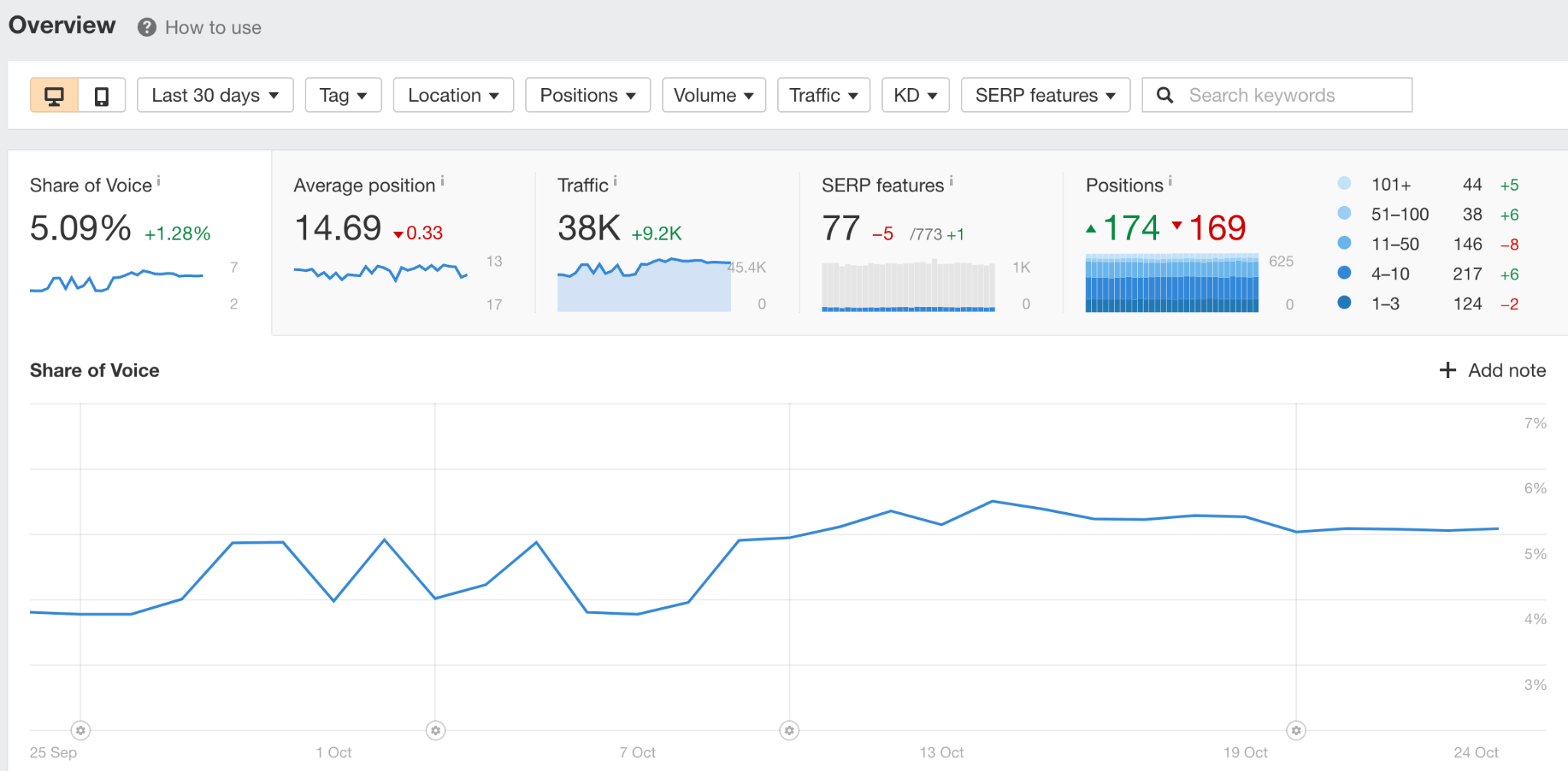

Below these groups is the data table where you’ll see ranking, keyword, and traffic data for each tracked keyword.

A cool feature in Rank Tracker is that we keep track of your competitors too:
14. Automatically track your competitors’ rankings
Go to the Competitors overview report and you’ll see the same data, plus how your competitors are performing for every keyword.
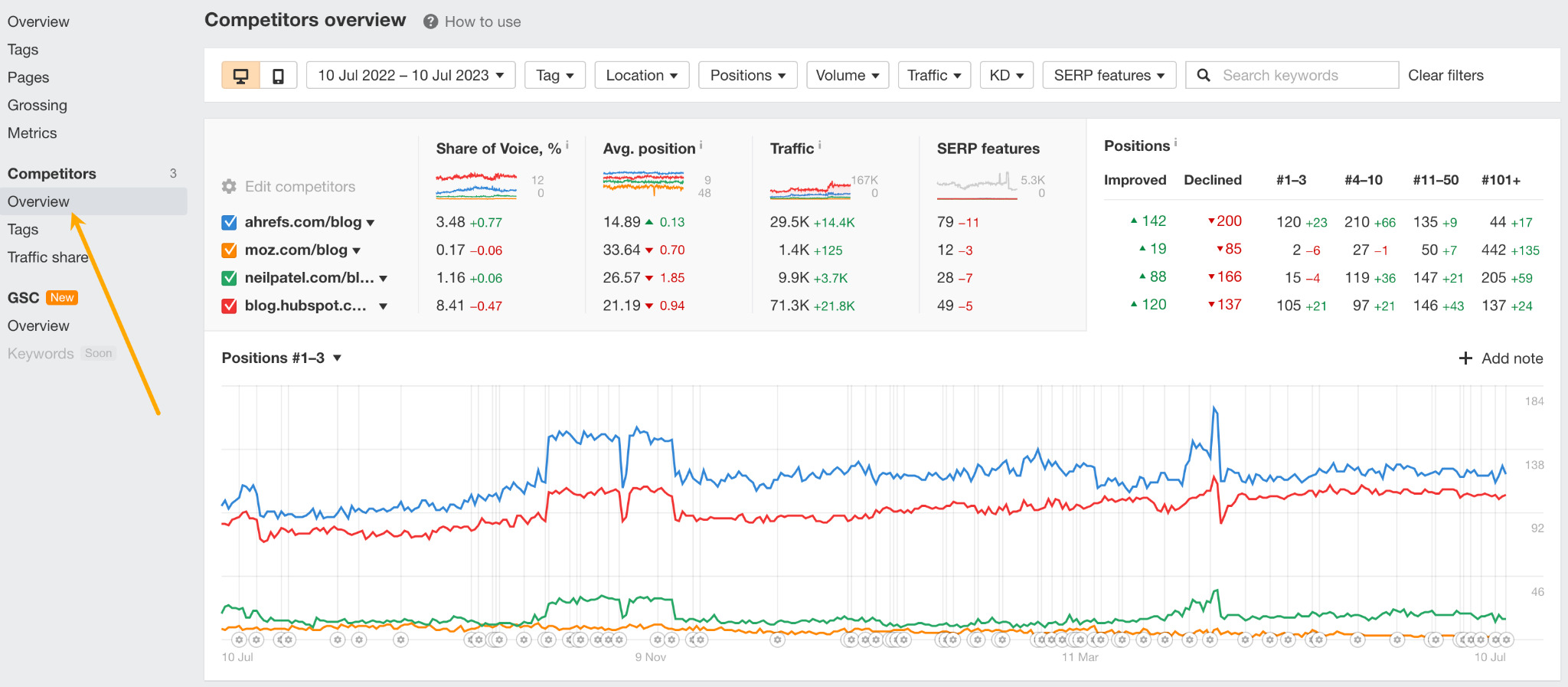

Even if you didn’t add any tracked competitors to your project, you can still get competitor insights by going to the Competitors traffic share report.
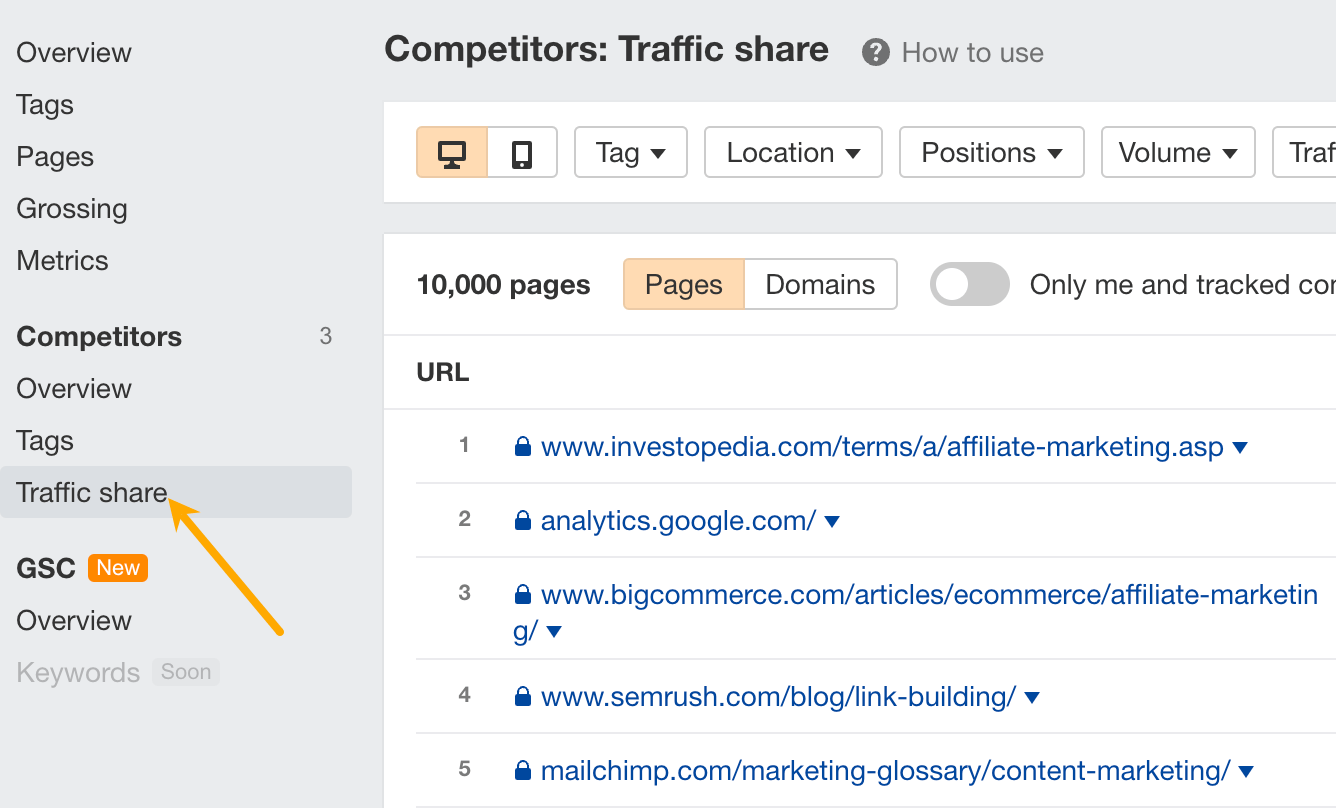

This report shows you all your organic search competitors for your tracked keywords. If you look at the Pages tab, you can see the exact pages you’re competing with in organic search. If you go to the Domains tab, you’ll see all websites ranking for your tracked keywords.
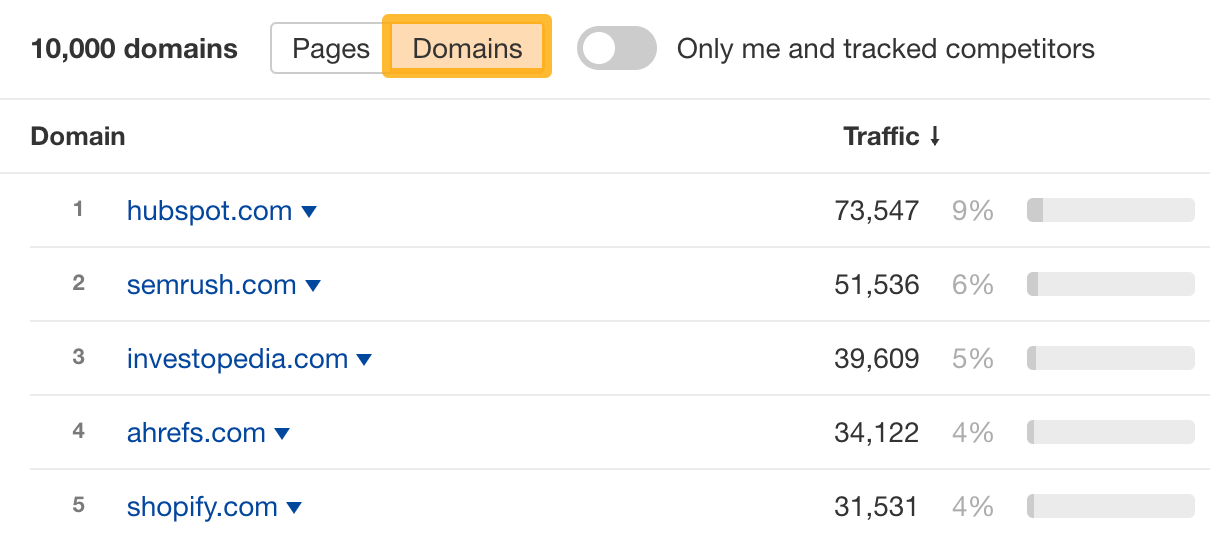

For example, both HubSpot and Shopify own a lot of traffic for our tracked keywords. So, they likely rank for a ton of topics that might be interesting for our own blog, which means we could dig deeper into them in Site Explorer.
Content Explorer is a search engine for marketers with billions of pages in its index. Search for any topic, and you’ll see all pages that match your query, along with their SEO and social metrics.
The best part: You can apply any combination of filters to dig into the data.
Here are some use cases for Content Explorer:
15. Find low-competition topics with high search traffic potential
Here’s how:
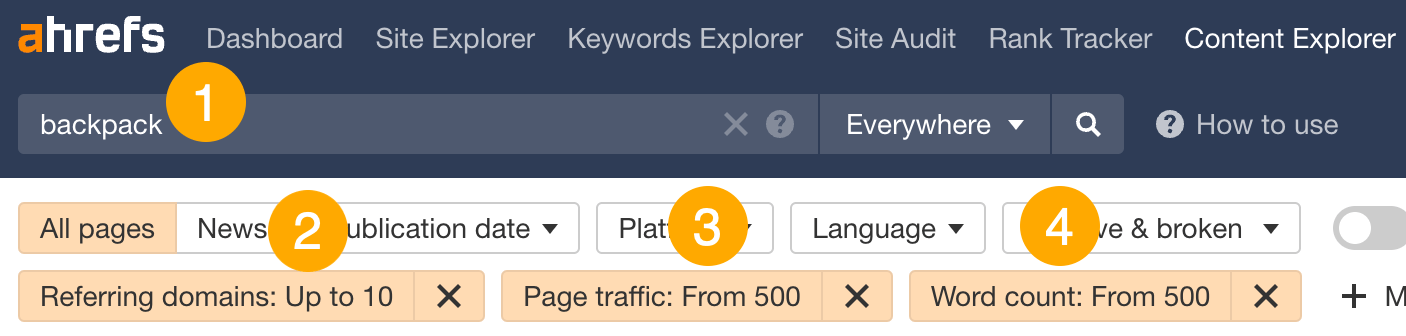
- Enter a broad query (e.g., backpack)
- Set a Referring domains filter <10 (to find low-competition topics)
- Set a Page traffic filter >500 (to find topics with high traffic potential)
- Set a Word count filter >500 (to find blog content)

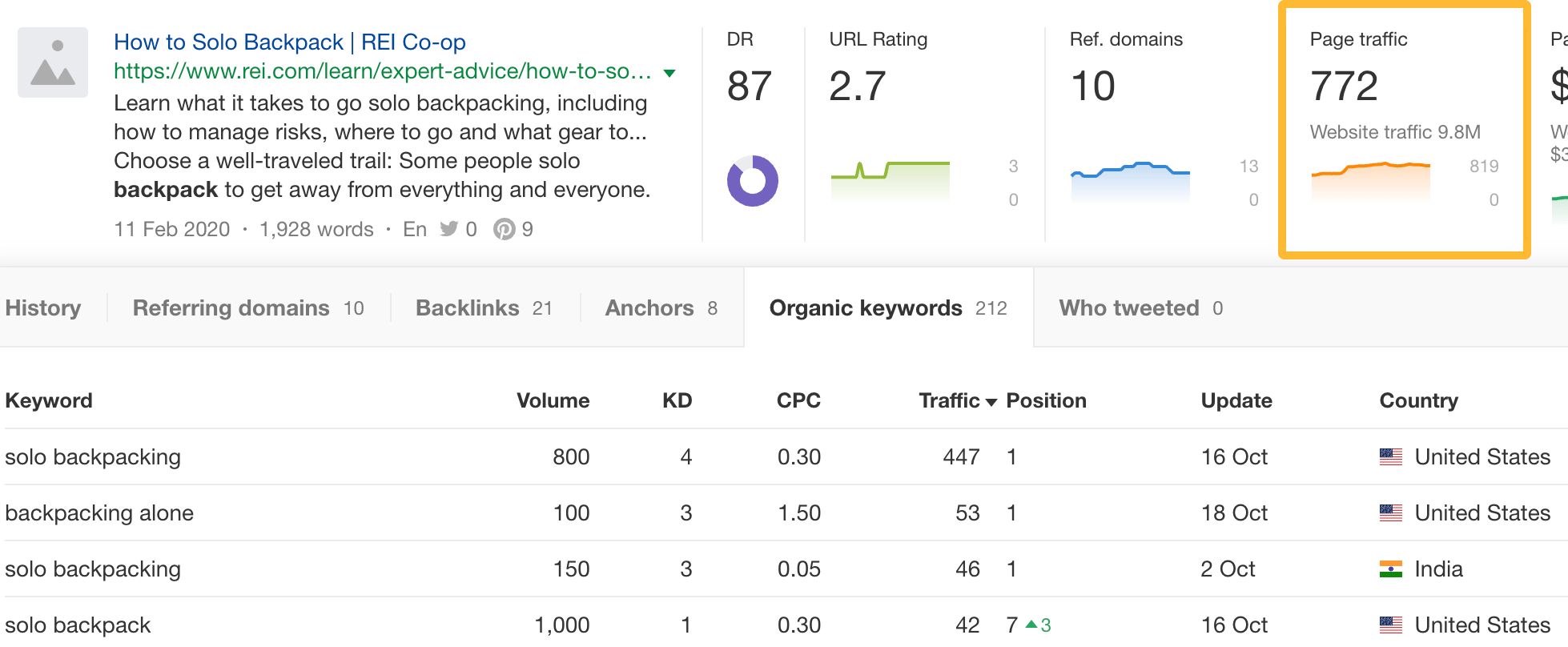
For example, this seems like a great topic to cover for a website that sells backpacks:
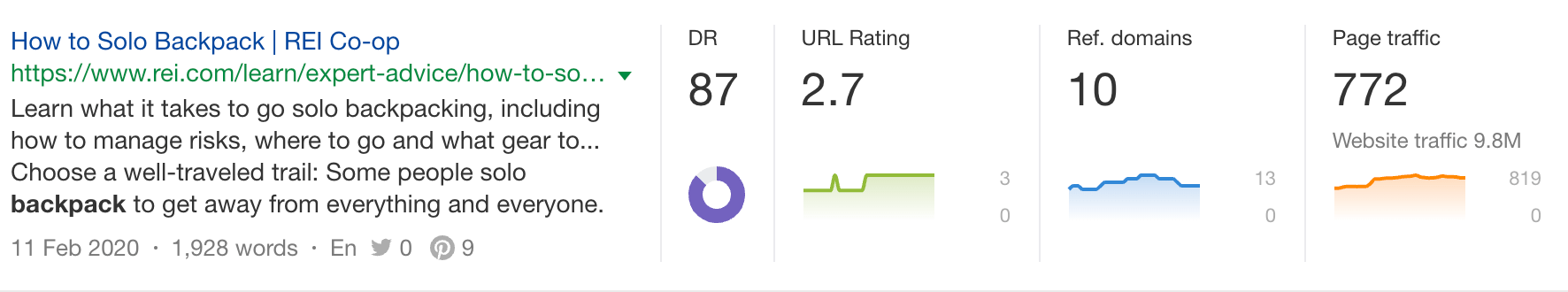

Click the Page traffic box and you’ll see the exact keywords it ranks for, its ranking positions, and more:

16. Find guest post opportunities
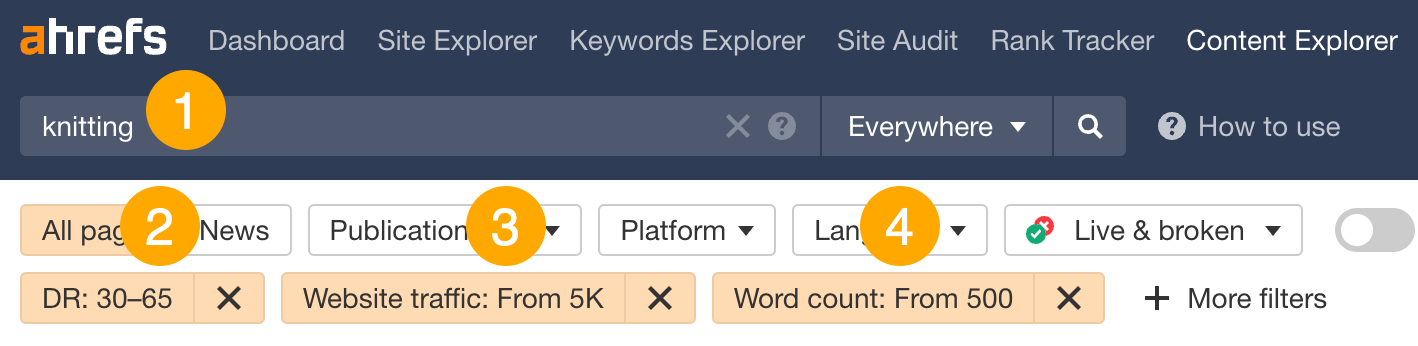
Here’s how:
- Enter a niche-related query (e.g., knitting)
- Set a DR filter of 30-65 (to find low- to mid-authority websites)
- Set a Website traffic filter of >5,000 (to find sites that get a good amount of search traffic)
- Set a Word count filter of >500 (to narrow results to blog content)

Head to the Websites tab to see sites that match our filters:
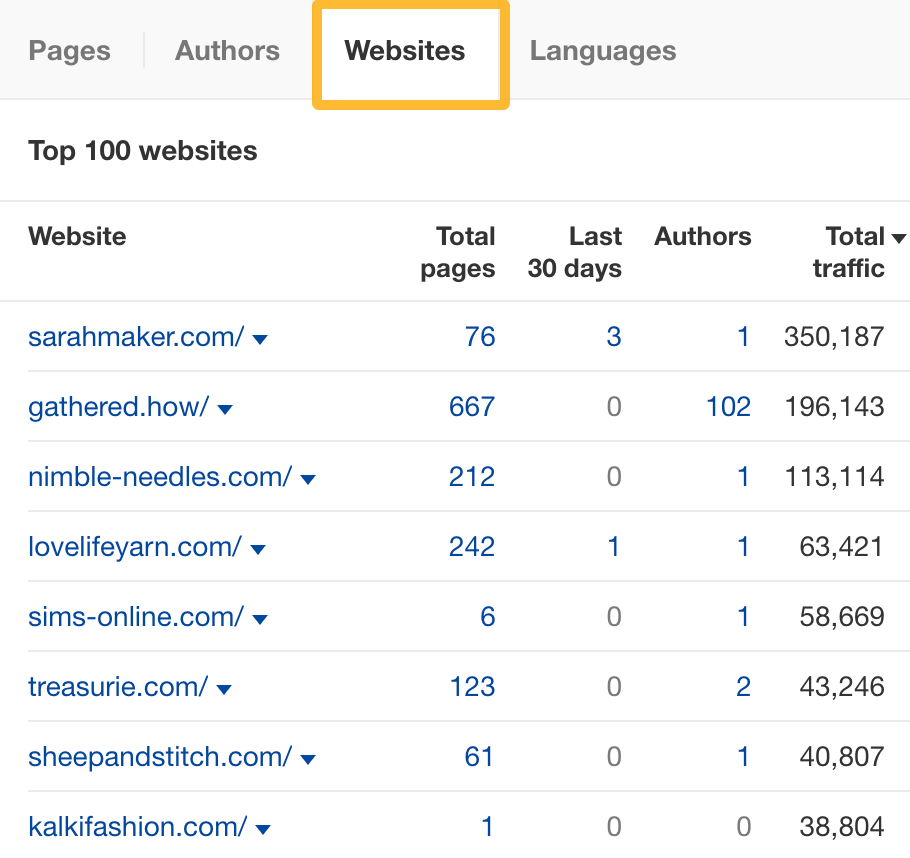

Eyeball the report to find potential sites to pitch. For example, a site like Nimble Needles would make a good guest post target.
Web Explorer allows you to search through all pages, domains, and links that are indexed by Yep, which is our search engine. This index is around 500 billion pages, ~36 times larger than Content Explorer’s index.
Basically, you can search through almost anything and filter them down by SEO metrics.
Here are some use cases:
17. Find unlinked brand mentions
Unlinked mention link building is when you:
- Find pages that mention your brand but don’t link to you
- Reach out and ask them to link to you
The reason why this tactic works well is because the battle is halfway won. They know who you are and probably like you, but they may have just forgotten to link to you.
To find unlinked mentions, search for [your brand] -outlinkdomain:[yourwebsite].com -site:[yourwebsite].com.
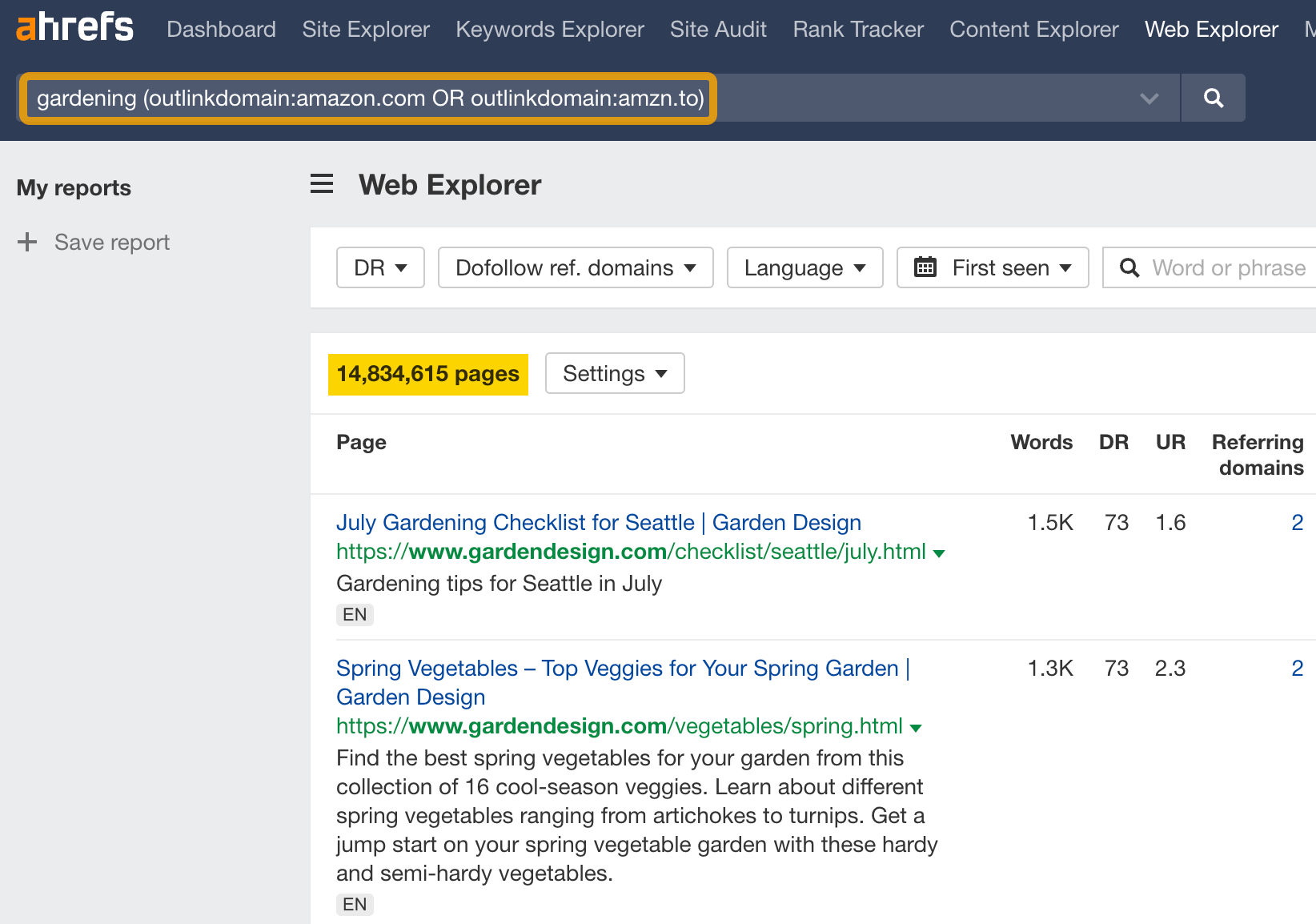

You’ll see over 61 million pages that mention Ahrefs but don’t link to us.
18. Search niche-relevant pages that link out to Amazon affiliate URLs
For example, let’s say you want to find pages on gardening that link out to Amazon affiliate URLs. The reason you might search this is to find potential acquisition targets, find websites that might be interested in joining your affiliate program, or find affiliate content ideas for your own gardening website.
To find these pages, run this search: “gardening” (outlinkdomain:amazon.com OR outlinkdomain:amzn.to)
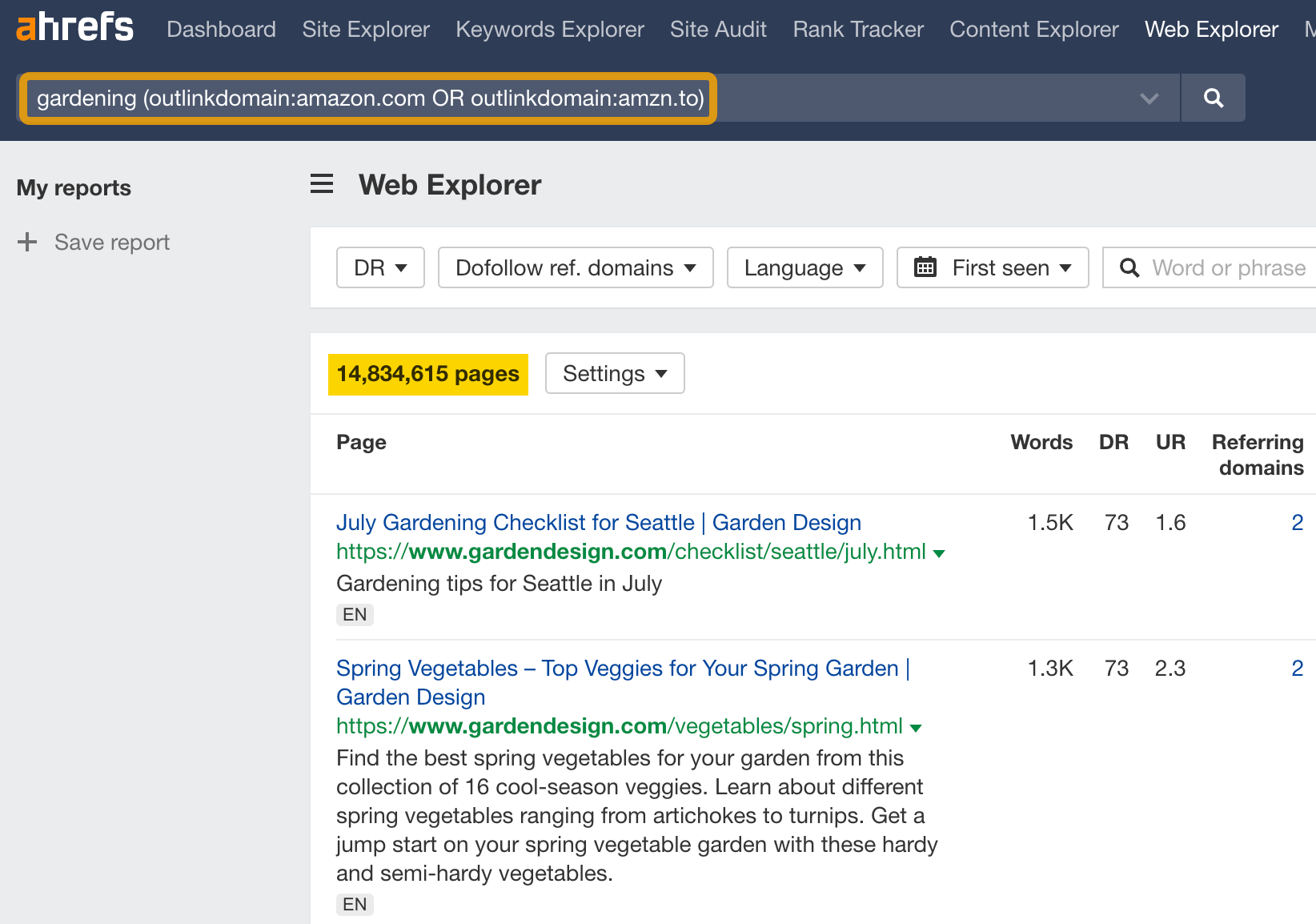

You’ll see 14 million pages that match this query.
FYI, if you want to explore more use cases in Web Explorer, simply hit the Examples tab.


Final thoughts
We’ve barely scratched the surface with all available use cases in Ahrefs. That’s why we’ve also created a 7-hour certification course that digs deep into how Ahrefs works. I highly recommend checking it out.
Even though we’ve covered our core tools, we have some other tools as well.
Check out Competitive Analysis, which includes tools like Content Gap and Link Intersect.
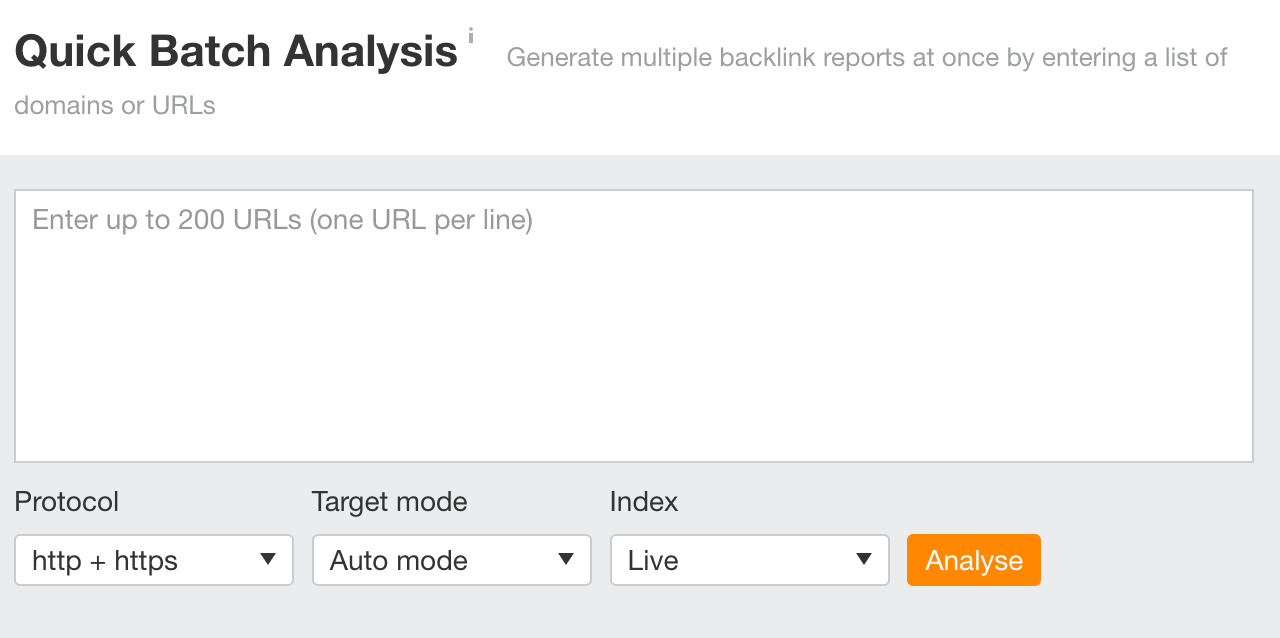

Our Batch Analysis tool lets you get SEO metrics on up to 200 targets in seconds:


And don’t forget to install our free SEO toolbar where you can get Ahrefs metrics laid over your SERPs and web pages.

Any questions or comments? Let me know on X (Twitter).










