SEO
Navigating The SEO Career Landscape: Degrees, Myths, And Realities

In the dynamic realm of search engine optimization (SEO), my career spans nearly two decades, starting in 2004 when I started working for an agency and just two years later moved to in-house SEO for a large company.
Since then, I’ve held various in-house SEO roles at esteemed organizations, including Classmates.com, Concur, Smartsheet, ADP (usedcars.com), Nordstrom, Groupon, GitHub, and my most recent role at RingCentral – experiences which have deepened my understanding of the field and allowed me to shape SEO within different business contexts.
I began my career as an SEO specialist at the agency; my role involved understanding website optimization, keyword research, and refining on-page and off-page strategies.
When I moved to management, I had to understand how to lead a team properly.
As my journey progressed, transitioning to roles like SEO manager involved overseeing SEO strategies, developing comprehensive plans, educating and leading teams, and ensuring alignment with overarching business goals.
These roles collectively form the backbone of SEO, showcasing its dynamism and emphasizing each position’s indispensable role in driving effective digital marketing strategies.
My journey isn’t that much different from that of many SEO professionals, aside from the fact that some SEO pros may decide to stay with an agency or focus on consulting rather than working for another company.
There are so many avenues one could go down when choosing their career path for SEO, so let me help break it down.
SEO Roles
As someone immersed in the SEO field for many years, I fully understand today’s many diverse SEO roles.
Let’s explore these roles, the average salaries in the US, and advice I have for anyone looking to move into these roles, considering both their nuances and the path ahead for aspiring SEO professionals:
SEO Specialist
Embarking on the SEO journey often starts as a specialist. In this entry-level role, one will dig into the complexities of optimizing websites to boost rankings.
As a specialist, my early days involved conducting keyword research, analyzing website performance, and implementing strategies that enhanced organic visibility for clients.
This foundational role serves as a stepping stone to grasp the fundamentals of digital marketing in both the agency and in-house environments.
- Salary*: $63,699 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Focus on entry-level content optimization, conducting keyword research, and honing on-page and off-page strategies.
- Advice: This is a great role to grasp the fundamentals, immerse yourself in various facets of digital marketing, and adapt to evolving trends.
SEO Content Strategist
Transitioning to a content strategist role within SEO reveals the creative side of drafting engaging, search-engine-friendly content.
Most SEO pros in this position are expected to sharpen their writing skills and plan and optimize content calendars based on comprehensive keyword research.
As an SEO content strategist, creating informative and captivating content is paramount to retaining readers and adhering to evolving SEO best practices.
Technical SEO Manager
My background in engineering has allowed me to focus heavily on the technical aspects of SEO. The position as a technical SEO manager requires a solid knowledge of coding, engineering processes, and database management.
The role of a technical SEO professional involves handling site structure, indexing, and resolving intricate technical issues that impact search performance.
Responsibilities extend to collaborating with engineering teams, ensuring effective communication, and mitigating risks associated with technical SEO.
This role requires a unique blend of technical acumen and collaborative skills.
- Salary*: $99,548 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Tackle technical aspects impacting search performance, focusing on site structure, indexing, and technical troubleshooting.
- Advice: Understand what goes into the development of a website, including the various coding languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Java, Python, React, Angular, etc.), database connectivity, and server administration, followed by the specifics of what Google expects and recommends for the benefits of SEO. In addition, SEO pros are expected to cultivate collaboration skills and have a solid understanding of using tools like Botify to aid in effective communication with engineers, which is pivotal for project success and seamless cooperation.
Link Building Specialist
As a link building specialist, the focus shifts to acquiring high-quality backlinks to enhance website authority and rankings.
This role demands persistence in building relationships, performing strategic outreach, and executing link-building strategies.
SEO pros interested in pursuing a career focused on off-site SEO must demonstrate the meticulous effort and specialization required in acquiring valuable links, making this role a dynamic and rewarding part of the SEO landscape.
- Salary*: $63,699 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Acquire high-quality backlinks from relevant sites to enhance website authority, involving relationship-building and strategic outreach.
- Advice: Develop persistence and relationship-building skills; the role demands time and specialization in acquiring valuable links while avoiding what could be considered spammy links. It would be very detrimental to a link building specialist’s career if they were to get a website banned by Google for using bad practices.
Local SEO Specialist
Optimizing websites for local searches can be a specialized avenue in any SEO journey.
Local SEO specialists manage local citations and Google My Business profiles and ensure consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) data for region-specific platforms.
This role highlights the importance of attention to detail and local nuances for businesses aiming to attract nearby customers.
- Salary*: $62,852 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Optimize websites for local searches, manage local citations and Google My Business profiles, and ensure NAP data consistency.
- Advice: Understand the nuances of local SEO; attention to detail and consistency are key for localized online visibility. Learn the various tools available to help manage these listings, such as RenderSEO and Yext.
Ecommerce SEO Product Manager
Working at ecommerce companies brings a unique challenge of its own.
SEO product manager roles require an SEO pro to specialize in optimizing online stores; the focus shifts to product optimization, category pages, site structure, and enhancing user experience.
Balancing SEO knowledge with product management skills becomes essential in navigating this niche, offering both challenges and lucrative opportunities.
- Salary*: $117,277 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Specialize in optimizing online stores, focusing on product optimization, category pages, and user experience.
- Advice: Combine SEO knowledge with product management skills; leveling up enhances prospects in this unique and lucrative niche.
SEO Consultant
My role as an SEO consultant involved advising businesses on enhancing online visibility. Analyzing websites, developing customized strategies, and offering guidance on effective SEO became integral.
The SEO consultant role offers relief when I find myself out of work in my in-house roles due to a layoff or if the company culture isn’t a good fit.
While my consulting is a second and infrequent role, many SEO pros decide that consulting is what they prefer to do full-time.
Either way, providing optimization services to companies neglecting SEO is a great way to make a substantial income.
- Salary*: $63,298 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Advise businesses on improving online visibility, analyzing websites, developing strategies, and offering SEO guidance.
- Advice: Gain diverse optimization experience; providing services to companies neglecting SEO can yield rapid improvement.
SEO Account Manager
Anyone interested in an SEO account manager role will experience the dynamic facet of serving as a bridge between clients and staff.
Meeting clients to understand their needs and relaying information for improved optimization efforts is the cornerstone of this position.
Performance-driven account managers could earn additional commissions, adding an incentive-driven layer to the role.
- Salary*: $68,314 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Serve as a company’s point of contact, meeting clients and relaying information for improved optimization efforts.
- Advice: Understand industry standards; performance-driven account managers can earn additional commissions, boosting income.
SEO Data Analyst
An SEO data analyst role involves collecting and interpreting website performance and search rankings data.
Using tools like Google Analytics, Semrush, and Botify while obtaining knowledge of running SQL queries provides insights to inform strategic decisions.
This role underlines the significance of data analysis, specifically focusing on SEO-related metrics and their implications.
- Salary*: $76,575 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Collect and interpret website performance and search rankings data, offering insights for strategic decisions.
- Advice: Know how to run SQL queries and manipulate data in Excel. Focus on SEO-related data analysis and understanding traffic from various search engines to improve decision-making.
SEO Manager
The majority of my roles in my career have been under the SEO manager title.
Those roles involved overseeing entire SEO strategies, developing comprehensive plans, managing teams, and ensuring alignment with overarching business goals. This mid-to-senior-level management position requires a diverse skill set.
- Salary*: $74,494 per year (Indeed).
- Duties: Oversee entire SEO strategy, develop comprehensive plans, manage teams, and ensure alignment with business goals.
- Advice: Understand what it takes to be a team leader. Nurture your team, build relationships in the organization, and articulate the benefits of what you’re asking to accomplish SEO growth. Management books like StrengthsFinder 2.0: Gallup by Don Clifton and Radical Candor by Kim Scott are great resources for becoming a good leader. If an SEO manager can tap into effective communication and leadership, the senior positions can lead to higher earnings of up to $210,000.
Notes:
The salary for the link building and local specialist roles are the same as that of an SEO specialist, since they tend to be at the same level.
In addition, the SEO product manager’s salary is taken from what a standard product manager makes since the roles are very similar.
Also, note that consultants can make upwards of $200,000 per year or more as they decide what to charge clients and how many clients they choose to take on.
*US National average salary reported by Indeed.com as of January 2024
Is SEO A Good Career Choice? Debunking Myths And Realities
Having navigated the dynamic landscape of SEO for over two decades, I have found that, while choosing a career in SEO has been rewarding, there are many things I would have done differently if I had the chance to do it all over again.
The good part about the SEO career path is that it unfolds across various roles, each offering unique challenges and opportunities for growth.
Starting from entry-level positions to assuming leadership roles like SEO manager, professionals gain a diverse skill set and invaluable experience.
However, it’s crucial to understand that the journey rarely leads to executive positions like director of SEO in larger companies and even more rarely to vice president positions.
The salaries of roles that SEO pros work with (i.e., product managers, engineers, growth managers, etc.) are much higher than what SEO pros usually make. So if it’s money you’re after in an SEO career, then you may be on the wrong path.
Agencies often embrace SEO professionals in executive roles, highlighting the need for a blended approach to SEO strategy involving in-house and agency collaboration. Still, the salaries tend to be less than for in-house roles.
Most SEO professionals should begin their journey as specialists and envision their desired position in 5 to 10 years.
If aspirations lean towards engineering, take the initiative to learn to code and acquire the necessary skills expected of an engineer. Collaborate closely with engineering teams, expressing a keen interest in contributing to their projects to transition to an engineering role.
For those eyeing executive roles in large corporations, strategically plan a career trajectory that navigates beyond SEO and aligns with roles leading to executive positions.
Typically, chief marketing officers (CMOs) have backgrounds in product marketing or growth marketing, progressing from directors to VPs in those domains before making the leap to CMO.
While SEO expertise enhances marketability, transitioning from SEO to these roles can be challenging. Therefore, be prepared to undertake the necessary steps to facilitate a smooth transition when the time comes.
For those contemplating an SEO career, embrace the diverse roles within SEO, each contributing to a robust skill set.
Junior roles provide foundational knowledge, strategists refine creativity and analytical abilities, and managers oversee comprehensive SEO plans.
It’s essential to evaluate personal preferences – whether one aspires to be a specialist excelling in a specific area or climb the ladder to managerial roles.
Be aware that large companies might not offer executive SEO positions, leading to the importance of understanding the industry’s dynamics and considering agency opportunities.
Education In SEO: Unveiling The Reality of Degrees
After spending over two decades submerged in SEO, a formal degree is not a prerequisite for a successful career in SEO.
My journey began with college, where I majored in English and Art History. However, realizing the potential in web design and development, I dropped out to focus on freelance work.
The SEO industry thrives on practical skills and hands-on experience, making degrees less significant.
Numerous online resources and guides offer a wealth of information to aid in mastering SEO techniques. It’s a field where continuous learning is integral, and personal initiative often surpasses the value of formal education.
The insights shared by others resonate with my own experiences. SEO is a realm where proven expertise often outshines academic credentials.
The industry includes individuals with diverse educational backgrounds, from MBAs to those without formal education. What matters most is the ability to adapt, learn, and implement effective strategies.
For aspiring SEO professionals, the key lies in taking the initiative, exploring online resources, and gaining practical experience.
Whether starting a business or pursuing a career, hands-on learning and staying updated with industry trends are the real benchmarks of success. While a degree might be a plus, it’s not mandatory for carving a rewarding path in SEO.
The Diverse Paths Of SEO
The potential routes within the SEO career landscape are numerous, starting with opportunities at agencies that provide an excellent learning ground, exposing individuals to various aspects of digital marketing.
Alternatively, one could enter an in-house position at a company where guidance from an experienced SEO professional is crucial.
Freelancing or working as an independent consultant presents another viable option, offering flexibility in the work environment and schedule.
The SEO career path encompasses a spectrum of roles, from entry-level to junior roles, strategists, managers, and senior managers, each with distinctive responsibilities and salary ranges.
Agency
One significant route involves commencing the journey at agencies, which serve as excellent learning grounds.
Working at an agency exposes individuals to various facets of digital marketing, offering a dynamic environment where skills are honed through hands-on experience.
This path allows for a comprehensive understanding of SEO within the broader context of marketing strategies.
In-House
On the other hand, individuals may choose to embark on an in-house position within a company.
The crucial guidance characterizes this path experienced SEO professionals provide in the corporate setting.
The in-house route often entails a deeper integration with the company’s goals and strategies, requiring a specialized skill set tailored to the organization’s needs.
Freelancing
For those inclined towards independence and flexibility, freelancing or working as an independent consultant represents a viable option within the SEO career landscape.
This path allows individuals to shape their work environment and schedules according to personal preferences.
Freelancers have the opportunity to work with a variety of clients, gaining diverse experiences that contribute to their professional growth.
Conclusion
In this exploration of the SEO career landscape, I am reminded of the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of SEO.
From my humble beginnings as a freelance developer optimizing websites to my most recent work as a consultant, each step has presented unique challenges and learning opportunities, adding to my comprehensive grasp of SEO.
These experiences have enriched my understanding of various business environments.
I hope this article helps readers interested in a career in SEO carve out a path for themselves.
More resources:
Featured Image: New Africa/Shutterstock
SEO
Big Update To Google’s Ranking Drop Documentation

Google updated their guidance with five changes on how to debug ranking drops. The new version contains over 400 more words that address small and large ranking drops. There’s room to quibble about some of the changes but overall the revised version is a step up from what it replaced.
Change# 1: Downplays Fixing Traffic Drops
The opening sentence was changed so that it offers less hope for bouncing back from an algorithmic traffic drop. Google also joined two sentences into one sentence in the revised version of the documentation.
The documentation previously said that most traffic drops can be reversed and that identifying the reasons for a drop aren’t straightforward. The part about most of them can be reversed was completely removed.
Here is the original two sentences:
“A drop in organic Search traffic can happen for several reasons, and most of them can be reversed. It may not be straightforward to understand what exactly happened to your site”
Now there’s no hope offered for “most of them can be reversed” and more emphasis on understanding what happened is not straightforward.
This is the new guidance
“A drop in organic Search traffic can happen for several reasons, and it may not be straightforward to understand what exactly happened to your site.”
Change #2 Security Or Spam Issues
Google updated the traffic graph illustrations so that they precisely align with the causes for each kind of traffic decline.
The previous version of the graph was labeled:
“Site-level technical issue (Manual Action, strong algorithmic changes)”
The problem with the previous label is that manual actions and strong algorithmic changes are not technical issues and the new version fixes that issue.
The updated version now reads:
“Large drop from an algorithmic update, site-wide security or spam issue”
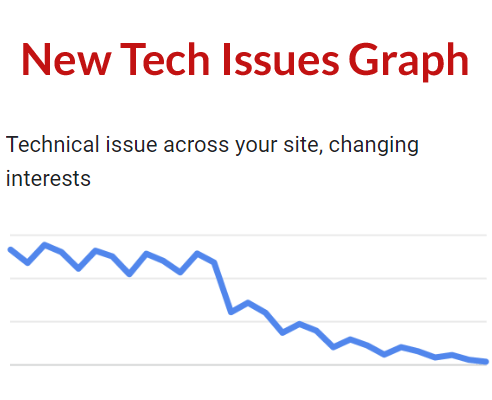
Change #3 Technical Issues
There’s one more change to a graph label, also to make it more accurate.
This is how the previous graph was labeled:
“Page-level technical issue (algorithmic changes, market disruption)”
The updated graph is now labeled:
“Technical issue across your site, changing interests”
Now the graph and label are more specific as a sitewide change and “changing interests” is more general and covers a wider range of changes than market disruption. Changing interests includes market disruption (where a new product makes a previous one obsolete or less desirable) but it also includes products that go out of style or loses their trendiness.
Change #4 Google Adds New Guidance For Algorithmic Changes
The biggest change by far is their brand new section for algorithmic changes which replaces two smaller sections, one about policy violations and manual actions and a second one about algorithm changes.
The old version of this one section had 108 words. The updated version contains 443 words.
A section that’s particularly helpful is where the guidance splits algorithmic update damage into two categories.
Two New Categories:
- Small drop in position? For example, dropping from position 2 to 4.
- Large drop in position? For example, dropping from position 4 to 29.
The two new categories are perfect and align with what I’ve seen in the search results for sites that have lost rankings. The reasons for dropping up and down within the top ten are different from the reasons why a site drops completely out of the top ten.
I don’t agree with the guidance for large drops. They recommend reviewing your site for large drops, which is good advice for some sites that have lost rankings. But in other cases there’s nothing wrong with the site and this is where less experienced SEOs tend to be unable to fix the problems because there’s nothing wrong with the site. Recommendations for improving EEAT, adding author bios or filing link disavows do not solve what’s going on because there’s nothing wrong with the site. The problem is something else in some of the cases.
Here is the new guidance for debugging search position drops:
“Algorithmic update
Google is always improving how it assesses content and updating its search ranking and serving algorithms accordingly; core updates and other smaller updates may change how some pages perform in Google Search results. We post about notable improvements to our systems on our list of ranking updates page; check it to see if there’s anything that’s applicable to your site.If you suspect a drop in traffic is due to an algorithmic update, it’s important to understand that there might not be anything fundamentally wrong with your content. To determine whether you need to make a change, review your top pages in Search Console and assess how they were ranking:
Small drop in position? For example, dropping from position 2 to 4.
Large drop in position? For example, dropping from position 4 to 29.Keep in mind that positions aren’t static or fixed in place. Google’s search results are dynamic in nature because the open web itself is constantly changing with new and updated content. This constant change can cause both gains and drops in organic Search traffic.
Small drop in position
A small drop in position is when there’s a small shift in position in the top results (for example, dropping from position 2 to 4 for a search query). In Search Console, you might see a noticeable drop in traffic without a big change in impressions.Small fluctuations in position can happen at any time (including moving back up in position, without you needing to do anything). In fact, we recommend avoiding making radical changes if your page is already performing well.
Large drop in position
A large drop in position is when you see a notable drop out of the top results for a wide range of terms (for example, dropping from the top 10 results to position 29).In cases like this, self-assess your whole website overall (not just individual pages) to make sure it’s helpful, reliable and people-first. If you’ve made changes to your site, it may take time to see an effect: some changes can take effect in a few days, while others could take several months. For example, it may take months before our systems determine that a site is now producing helpful content in the long term. In general, you’ll likely want to wait a few weeks to analyze your site in Search Console again to see if your efforts had a beneficial effect on ranking position.
Keep in mind that there’s no guarantee that changes you make to your website will result in noticeable impact in search results. If there’s more deserving content, it will continue to rank well with our systems.”
Change #5 Trivial Changes
The rest of the changes are relatively trivial but nonetheless makes the documentation more precise.
For example, one of the headings was changed from this:
You recently moved your site
To this new heading:
Site moves and migrations
Google’s Updated Ranking Drops Documentation
Google’s updated documentation is a well thought out but I think that the recommendations for large algorithmic drops are helpful for some cases and not helpful for other cases. I have 25 years of SEO experience and have experienced every single Google algorithm update. There are certain updates where the problem is not solved by trying to fix things and Google’s guidance used to be that sometimes there’s nothing to fix. The documentation is better but in my opinion it can be improved even further.
Read the new documentation here:
Debugging drops in Google Search traffic
Review the previous documentation:
Internet Archive Wayback Machine: Debugging drops in Google Search traffic
Featured Image by Shutterstock/Tomacco
SEO
Google March 2024 Core Update Officially Completed A Week Ago

Google has officially completed its March 2024 Core Update, ending over a month of ranking volatility across the web.
However, Google didn’t confirm the rollout’s conclusion on its data anomaly page until April 26—a whole week after the update was completed on April 19.
Many in the SEO community had been speculating for days about whether the turbulent update had wrapped up.
The delayed transparency exemplifies Google’s communication issues with publishers and the need for clarity during core updates
Google March 2024 Core Update Timeline & Status
First announced on March 5, the core algorithm update is complete as of April 19. It took 45 days to complete.
Unlike more routine core refreshes, Google warned this one was more complex.
Google’s documentation reads:
“As this is a complex update, the rollout may take up to a month. It’s likely there will be more fluctuations in rankings than with a regular core update, as different systems get fully updated and reinforce each other.”
The aftershocks were tangible, with some websites reporting losses of over 60% of their organic search traffic, according to data from industry observers.
The ripple effects also led to the deindexing of hundreds of sites that were allegedly violating Google’s guidelines.
Addressing Manipulation Attempts
In its official guidance, Google highlighted the criteria it looks for when targeting link spam and manipulation attempts:
- Creating “low-value content” purely to garner manipulative links and inflate rankings.
- Links intended to boost sites’ rankings artificially, including manipulative outgoing links.
- The “repurposing” of expired domains with radically different content to game search visibility.
The updated guidelines warn:
“Any links that are intended to manipulate rankings in Google Search results may be considered link spam. This includes any behavior that manipulates links to your site or outgoing links from your site.”
John Mueller, a Search Advocate at Google, responded to the turbulence by advising publishers not to make rash changes while the core update was ongoing.
However, he suggested sites could proactively fix issues like unnatural paid links.
“If you have noticed things that are worth improving on your site, I’d go ahead and get things done. The idea is not to make changes just for search engines, right? Your users will be happy if you can make things better even if search engines haven’t updated their view of your site yet.”
Emphasizing Quality Over Links
The core update made notable changes to how Google ranks websites.
Most significantly, Google reduced the importance of links in determining a website’s ranking.
In contrast to the description of links as “an important factor in determining relevancy,” Google’s updated spam policies stripped away the “important” designation, simply calling links “a factor.”
This change aligns with Google’s Gary Illyes’ statements that links aren’t among the top three most influential ranking signals.
Instead, Google is giving more weight to quality, credibility, and substantive content.
Consequently, long-running campaigns favoring low-quality link acquisition and keyword optimizations have been demoted.
With the update complete, SEOs and publishers are left to audit their strategies and websites to ensure alignment with Google’s new perspective on ranking.
Core Update Feedback
Google has opened a ranking feedback form related to this core update.
You can use this form until May 31 to provide feedback to Google’s Search team about any issues noticed after the core update.
While the feedback provided won’t be used to make changes for specific queries or websites, Google says it may help inform general improvements to its search ranking systems for future updates.
Google also updated its help documentation on “Debugging drops in Google Search traffic” to help people understand ranking changes after a core update.
Featured Image: Rohit-Tripathi/Shutterstock
FAQ
After the update, what steps should websites take to align with Google’s new ranking criteria?
After Google’s March 2024 Core Update, websites should:
- Improve the quality, trustworthiness, and depth of their website content.
- Stop heavily focusing on getting as many links as possible and prioritize relevant, high-quality links instead.
- Fix any shady or spam-like SEO tactics on their sites.
- Carefully review their SEO strategies to ensure they follow Google’s new guidelines.
SEO
Google Declares It The “Gemini Era” As Revenue Grows 15%

Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, announced its first quarter 2024 financial results today.
While Google reported double-digit growth in key revenue areas, the focus was on its AI developments, dubbed the “Gemini era” by CEO Sundar Pichai.
The Numbers: 15% Revenue Growth, Operating Margins Expand
Alphabet reported Q1 revenues of $80.5 billion, a 15% increase year-over-year, exceeding Wall Street’s projections.
Net income was $23.7 billion, with diluted earnings per share of $1.89. Operating margins expanded to 32%, up from 25% in the prior year.
Ruth Porat, Alphabet’s President and CFO, stated:
“Our strong financial results reflect revenue strength across the company and ongoing efforts to durably reengineer our cost base.”
Google’s core advertising units, such as Search and YouTube, drove growth. Google advertising revenues hit $61.7 billion for the quarter.
The Cloud division also maintained momentum, with revenues of $9.6 billion, up 28% year-over-year.
Pichai highlighted that YouTube and Cloud are expected to exit 2024 at a combined $100 billion annual revenue run rate.
Generative AI Integration in Search
Google experimented with AI-powered features in Search Labs before recently introducing AI overviews into the main search results page.
Regarding the gradual rollout, Pichai states:
“We are being measured in how we do this, focusing on areas where gen AI can improve the Search experience, while also prioritizing traffic to websites and merchants.”
Pichai reports that Google’s generative AI features have answered over a billion queries already:
“We’ve already served billions of queries with our generative AI features. It’s enabling people to access new information, to ask questions in new ways, and to ask more complex questions.”
Google reports increased Search usage and user satisfaction among those interacting with the new AI overview results.
The company also highlighted its “Circle to Search” feature on Android, which allows users to circle objects on their screen or in videos to get instant AI-powered answers via Google Lens.
Reorganizing For The “Gemini Era”
As part of the AI roadmap, Alphabet is consolidating all teams building AI models under the Google DeepMind umbrella.
Pichai revealed that, through hardware and software improvements, the company has reduced machine costs associated with its generative AI search results by 80% over the past year.
He states:
“Our data centers are some of the most high-performing, secure, reliable and efficient in the world. We’ve developed new AI models and algorithms that are more than one hundred times more efficient than they were 18 months ago.
How Will Google Make Money With AI?
Alphabet sees opportunities to monetize AI through its advertising products, Cloud offerings, and subscription services.
Google is integrating Gemini into ad products like Performance Max. The company’s Cloud division is bringing “the best of Google AI” to enterprise customers worldwide.
Google One, the company’s subscription service, surpassed 100 million paid subscribers in Q1 and introduced a new premium plan featuring advanced generative AI capabilities powered by Gemini models.
Future Outlook
Pichai outlined six key advantages positioning Alphabet to lead the “next wave of AI innovation”:
- Research leadership in AI breakthroughs like the multimodal Gemini model
- Robust AI infrastructure and custom TPU chips
- Integrating generative AI into Search to enhance the user experience
- A global product footprint reaching billions
- Streamlined teams and improved execution velocity
- Multiple revenue streams to monetize AI through advertising and cloud
With upcoming events like Google I/O and Google Marketing Live, the company is expected to share further updates on its AI initiatives and product roadmap.
Featured Image: Sergei Elagin/Shutterstock
-

 MARKETING7 days ago
MARKETING7 days agoAdvertising in local markets: A playbook for success
-

 SEARCHENGINES7 days ago
SEARCHENGINES7 days agoGoogle Core Update Flux, AdSense Ad Intent, California Link Tax & More
-

 SEARCHENGINES6 days ago
SEARCHENGINES6 days agoGoogle Needs Very Few Links To Rank Pages; Links Are Less Important
-

 SEO6 days ago
SEO6 days agoHow to Become an SEO Lead (10 Tips That Advanced My Career)
-

 MARKETING6 days ago
MARKETING6 days agoHow to Use AI For a More Effective Social Media Strategy, According to Ross Simmonds
-

 PPC5 days ago
PPC5 days ago10 Most Effective Franchise Marketing Strategies
-

 PPC6 days ago
PPC6 days agoBiggest Trends, Challenges, & Strategies for Success
-

 SEARCHENGINES4 days ago
SEARCHENGINES4 days agoGoogle Won’t Change The 301 Signals For Ranking & SEO










![The Current State of Google’s Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] person typing on laptop with](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It.webp-400x240.webp)
![The Current State of Google’s Search Generative Experience [What It Means for SEO in 2024] person typing on laptop with](https://articles.entireweb.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/The-Current-State-of-Googles-Search-Generative-Experience-What-It.webp-80x80.webp)



